Для завершения процессов в Windows можно использовать команду (программу) taskkill, через командирую строку CMD, используя ключи f im. Команда taskkill позволяет закрывать одно или несколько программ как по имени образа, так и по идентификатору процесса (PID) в Windows системах.
На обычных рабочих станциях данная команда не особо востребована, так как можно завершить процесс через диспетчер задач. Хотя, не всегда это получается и в данной ситуации команда Taskkill пригодится, но, это скорее исключение из правил.
В каких ситуациях пригодится программа Taskkill?
В основном, данная команда используется системными администраторами и лично я сталкивался со следующими ситуациями:
- Обновление программ на терминальном сервере – при администрировании терминального сервера большое количество людей может запустить одно и тоже приложение. Но, в большинстве случаев, при обновлении программы её необходимо сначала закрыть, т.е. завершить её процесс. Если клиентов не много, то, можно воспользоваться диспетчером задач, а если их порядка 100, то это уже проблематично. А команда Taskkill позволяет убить все процессы для определенного приложения.
- Автоматический перезапуск программы – как вы знаете не все программы работают идеально и бывает, что они подвисают. А если данная программа должна работать 24 часа в сутки и 7 дней в неделю, то приходится периодически проверять её работоспособность.
Лично я сталкивался со следующей ситуацией: есть интернет магазин, в который данные о товарах выгружаются из 1С-ки. Но, обработчик написан как-то криво, в результате чего обмен подвисает раз в сутки, а то и через каждые 2-3 часа. По этому, появилась необходимость каждый час принудительно перезапускать обработчик, не зависимо от того, подвисла программа или нет.
И так, перейдем к практике.
Синтаксис команды Taskkill
Запустим браузер Google Chrome и попробуем завершить его процесс (Пуск \ Стандартные \ Выполнить \ cmd \ taskkill /? — чтобы посмотреть синтаксис команды)
- /s КОМПЬЮТЕР, где КОМПЬЮТЕР — это IP или адрес удаленного компьютера. По умолчанию, операция выполняется в локальной системе. Если именно это вас и интересует, данную опцию можно не использовать.
- /u ДОМЕН\ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЬ, где ДОМЕН — это имя домена, а ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЬ — имя пользователя, для которого нужно выполнить команду. Данная опция позволяет запускать taskkill с правами определенной учетной записи или домена.
- /p — обязательно используется в сочетании с опцией /u для указания пароля к учетной записи пользователя.
- /fi — позволяет выполнять команду taskkill с определенными фильтрами.
- /f — принудительно завершает выполнение команды.
- /IM — позволяет использовать имя приложения вместо идентификатора процесса.
- /T — завершение дерева процессов.

Теперь нам нужно узнать имя приложения, которое использует данный процесс. Это можно сделать через диспетчер задач (Ctrl+Alt+Del \ Запустить диспетчер задач \ Процессы \ chrome.exe).
Если у вас нет возможности запустить диспетчер задач, допустим, вы подключились к компьютеру удаленно через командную строку, то можно воспользоваться командой tasklist, она так же отображает все процессы.
Завершение процесса через Taskkill /f /im
Taskkill /f /im chrome.exe – принудительно завершить приложение с именем chrome.exe

Chrome завершил работу, однако, возможно появление ошибки «Не удалось завершить процесс, ни один из экземпляров задания не запущен». Данное сообщение появляется из-за того, что эти процессы были связанными и когда завершил работу основной, остальные автоматически завершились.
Теперь запустим Chrome под разными пользователями, чтобы сымитировать работу терминального сервера, для этого запустим под обычным пользователем и под пользователем XP (Chrome \ Shift \ ПКМ \ Запустить от имени другого пользователя \ ОК). Теперь мы видим, что одно и тоже приложение запущено под разными пользователями, повторим команду Taskkill /f /im chrome.exe, чтобы проверить, для всех ли пользователей будет завершен процесс.
Автоматическое завершение процесса через Taskkill
Теперь попробуем сделать автоматический перезапуск приложения, в этом нам поможет планировщик задач (Пуск \ Все программы \ Стандартные \ Служебные \ Планировщик заданий \ Библиотека планировщика \ ПКМ \ Создать папку \ Перезапуск Chrome – в зависимости от вашей цели)
Создаем задачу на запуск (Создать новую задачу \ Запуск \ Выполнять с наивысшими правами \ Триггер: по расписанию, ежедневно, начиная с 11:00, повторять каждый час бесконечно, включено \ Действия: запуск программы, chrome \ ОК)
Создадим задачу на завершение процесса (Создать новую задачу \ Завершение \ Выполнять с наивысшими правами \ Триггер: по расписанию, ежедневно, начиная с 10:59:50, повторять каждый час бесконечно, включено \ Действия: запуск программы, Taskkill, дополнительные аргументы: /f /im chrome.exe \ ОК)

Теперь запустим Chrome и подведем часы к более близкому времени, чтобы увидеть, как Хром завершит работу, а потом запустится заново.
Однако, порой требуется запретить только процесс запущенный под определенным пользователем. Именно такая ситуация у меня возникла с обработчиком 1С, который выгружал данные о товарах на сайт.
Дело в том, что, можно каждый час перезапускать зависшую 1С-ку, но, если завершать все процессы 1С, то все удаленные пользователи будут из неё вылетать, а этого нельзя допустить. По этому, нужно завершать процесс, запущенный из под определенной учетной записи.
Завершение процесса для определенного пользователя
Для этого в дополнительные аргументы добавим следующую строчку /fi “username eq station-4-7” данная команда фильтрует по имени пользователя и завершает процесс только того, чье имя совпадает с указанным в фильтре.
Запустим Chrome под другим пользователем и посмотрим, сработал ли фильтр.
We can kill a process from GUI using Task manager. If you want to do the same from command line., then taskkill is the command you are looking for. This command has got options to kill a task/process either by using the process id or by the image file name.
Kill a process using image name:
We can kill all the processes running a specific executable using the below command.
taskkill /IM executablename
Example:
Kill all processes running mspaint.exe:
c:\>taskkill /IM mspaint.exe SUCCESS: Sent termination signal to the process "mspaint.exe" with PID 1972.
Kill a process forcibly
In some cases, we need to forcibly kill applications. For example, if we try to to kill Internet explorer with multiple tabs open, tasklist command would ask the user for confirmation. We would need to add /F flag to kill IE without asking for any user confirmation.
taskkill /F /IM iexplore.exe
/F : to forcibly kill the process. If not used, in the above case it will prompt the user if the opened pages in tabs need to be saved.
To kill Windows explorer, the following command would work
C:\>taskkill /F /IM explorer.exe SUCCESS: The process "explorer.exe" with PID 2432 has been terminated.
The above command would make all GUI windows disappear. You can restart explorer by running ‘explorer’ from cmd.
C:\>explorer
Not using /F option, would send a terminate signal. In Windows 7, this throws up a shutdown dialog to the user.
C:\>taskkill /IM explorer.exe SUCCESS: Sent termination signal to the process "explorer.exe" with PID 2432. C:\>
Kill a process with process id:
We can use below command to kill a process using process id(pid).
taskkill /PID processId
Example:
Kill a process with pid 1234.
taskkill /PID 1234
Kill processes consuming high amount of memory
taskkill /FI "memusage gt value"
For example, to kill processes consuming more than 100 MB memory, we can run the below command
taskkill /FI "memusage gt 102400"
More examples
Sometimes applications get into hung state when they are overloaded or if the system is running with low available memory. When we can’t get the application to usable state, and closing the application does not work, what we usually tend to do is kill the task/process. This can be simply done using taskkill command.
To kill Chrome browser from CMD
Taskkill /F /IM Chrome.exe
Kill Chromedirver from command line
Taskkill /F /IM Chromedriver.exe
To kill firefox browser application
taskkill /F /IM firefox.exe
To kill MS Word application(Don’t do this if you haven’t saved your work)
taskkill /F /IM WinWord.exe
Sometimes, the command window itself might not be responding. You can open a new command window and kill all the command windows
taskkill /F /IM cmd.exe
This even kills the current command window from which you have triggered the command.
We use the taskkill command to terminate applications and processes in the Windows command prompt. Running taskkill is the same as using the End task button in the Windows Task Manager.
With taskkill, we kill one or more processes based on the process ID (PID) or name (image name). The syntax of this command is as follows:
taskkill /pid PID
taskkill /im nameYou can use the tasklist command to find the PID or image name of a Windows process.
The /F option tells Windows to force kill the process:
taskkill /f /im notepad.exeKill a Process by PID
In the following example, we run the taskkill command to terminate a process with a PID of 1000:
taskkill /f /pid 3688The multiple processes can be terminated at once, as shown in the following example:
taskkill /pid 3688 /pid 4248 /pid 4258Kill a Process by Name
To kill a process by its name, we use the /IM option. In the following example, we run the taskkill command to terminate the notepad.exe process:
taskkill /im notepad.exeThe /t option tells Windows to terminate the specified process and all child processes. In the following example, we force kill Microsoft Edge and its child processes:
taskkill /f /t /im msedge.exeCommand Options
| /S | Specifies the IP Address or name of the remote system to connect to. |
| /U | Specifies the name of the Windows user under which the command should execute. |
| /P | Password for the user. Prompts for input if omitted. |
| /FI | This option is to apply filters (see examples below). |
| /PID | Specifies the PID of the process to be terminated. |
| /IM | Specifies the image name of the process to be terminated. |
| /T | Terminates the specified process and its child processes (end all tasks). |
| /F | Forcefully kill a process. |
Examples
Terminate a process with a PID of 4000:
taskkill /pid 4000Terminate spoolsv.exe (which is the Print Spooler service on Windows):
taskkill /im spoolsv.exeUsing /f and /t options to forcefully terminate the entire process tree of the Microsoft Edge browser:
taskkill /f /t /im msedge.exe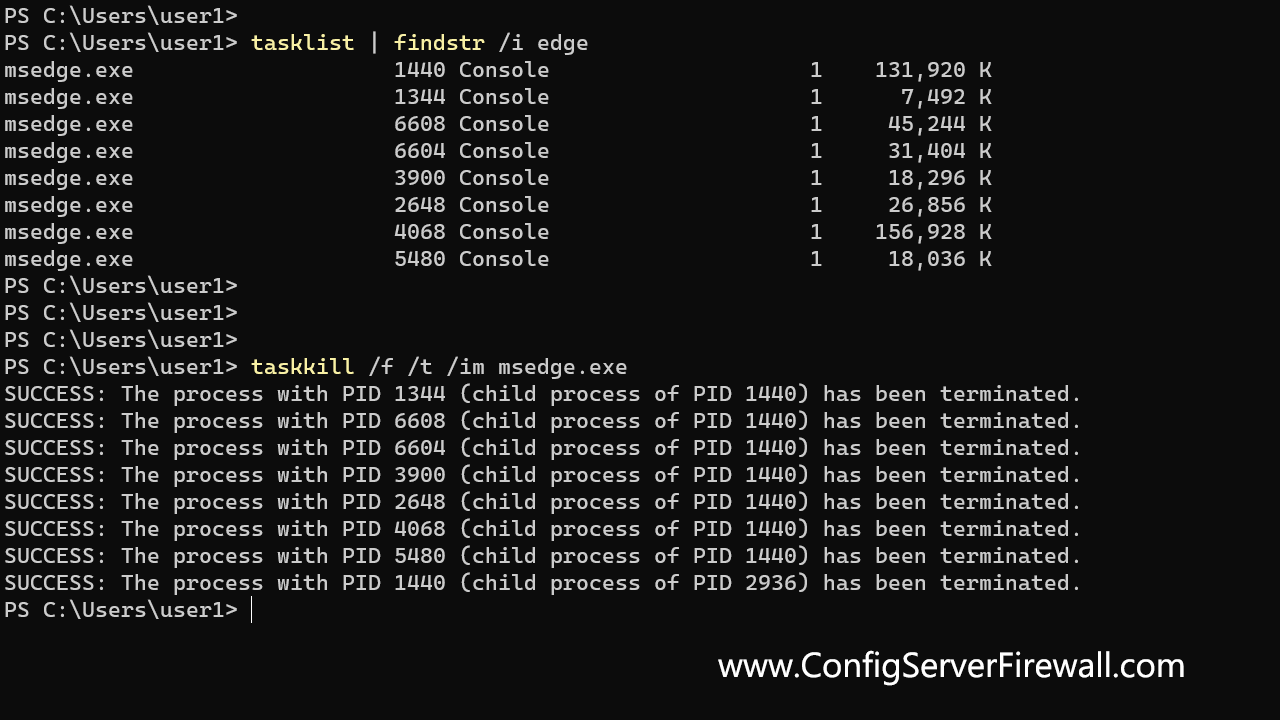
Force kill any process that starts with the name note:
taskkill /f /t /im note*In the following example, we terminate all processes that are not responding by using a filter:
taskkill /f /fi "status eq not responding"In the above example, eq stands for equal. You can use the following filters with the /fi option.
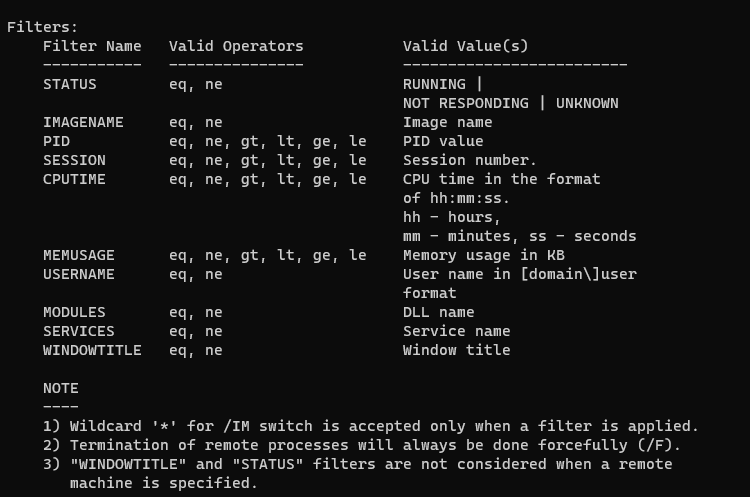
Run taskkill command on a remote computer:
taskkill /s 192.168.1.100 /u robst /pid 5936In the above example, the process with PID 5936 will be terminated on a remote computer with an IP address of 192.168.1.100.
Note that the Windows Firewall must be configured on the remote computer to allow the taskkill command. Click the link below for instructions on how to do it.
How to allow tasklist and taskkill commands from Windows Firewall
All right, here’s the end of this tutorial. While working on the CMD, you can run taskkill /? to display the help page, command options, and filters of the tasklist command.
The PowerShell equivalent to the taskkill is the Stop-Process cmdlet. But you can always use taskkill in PowerShell as well.
Multitasking with many apps and programs in the background can become difficult to manage and kill the processes running in the background using just the Task Manager or even with tools like Microsoft Process Explorer. However, another way to kill tasks and processes is from the command line in Windows.
However, you can open the Task Manager, right-click the process, and then click “End Task” to kill off the process. You can also terminate a specific process from the Details tab in the Task Manager. Sometimes you encounter issues with the Task Manager itself. For times like these, you may need to kill a process using the command line, which includes both the Command Prompt and Windows PowerShell.
In this article, we show you multiple ways to kill a process in Windows using Command Line.
Table of Contents
Why use the command line to terminate a process?
Although a normal user will not require killing processes using the command line, there are several use cases where command line tools are much better than their visual counterparts like the task manager. The following command line tools can be used in the following scenarios:
- Troubleshooting: Some processes are simply stubborn. They just stop responding and refuse to die. In such a condition, killing them forcefully using the command line is an easier and safer option.
- System administration: If you are a sysadmin, you should be a fan of command line utilities. These tools save a lot of work and time. You can run these commands remotely throughout your network to troubleshoot systems remotely.
- Script Automation: If you are a developer and need to start or stop processes in Windows, you will need these command line tools for automation.
- Virus prevention: If your system gets infected with viruses, it will simply not let you kill the compromised processes, as they will respawn upon kill. In this case, you can automate a monitoring process where the process is killed as soon as it starts.
There are several other use cases, but these are the most common ones.
How to Kill a Process from Command Prompt
You can kill the process in cmd using the taskkill command. However, you must either know its Process Identifier (PID) or the name of the process before you can end it.
To view and list the tasks and processes currently running on your computer, run the following command in an elevated Command Prompt:
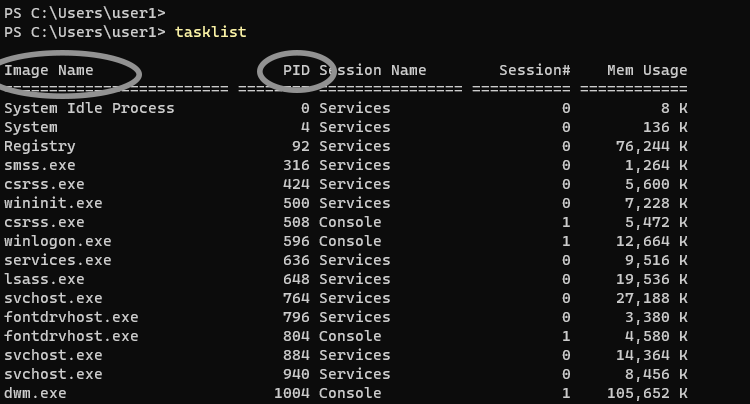
Tasklist
Note either the name under the Image name column or the PID number of the task you want to kill. These will be used in the cmdlets to kill the respective process.
Once you have either the name or the PID of the task, use either of the following cmdlets to kill the process:
-
Kill task using process name in Command Prompt:
Replace [ProcessName] with the name of the process.
taskkill /IM "[ProcessName]" /FKill process from Command Prompt using process name -
Kill task using PID in Command Prompt:
Replace [PID] with the Process ID.
taskkill /F /PID [PID]Kill process from Command Prompt using a process ID
If you are using earlier versions of Windows, like Windows 7, Windows Vista or even Windows XP, you can use tskill command, which is similar to taskkill but limited in functionality. You just need to provide the process ID to kill a task using tskill command:
tskill process-idReplace process-id with the actual process ID. For example,
tskill 1234How to Kill a Process from Windows PowerShell
Similar to the Command Prompt, you can also kill processes using PowerShell. But first, we must get the name or the process ID for the process to kill.
To obtain a list of the running processes in PowerShell, run the following command in PowerShell with elevated privileges:
Get-Process
From here, note down the process name or the PID (in the ID column) of the process that you want to kill, and then use it in the following commands:
Note: Unlike the Command Prompt, Windows PowerShell shows no output once a process is killed.
-
Kill task using process name in PowerShell:
Replace [ProcessName] with the name of the process.
Stop-Process -Name "[ProcessName]" -ForceKill process from PowerShell using process name -
Kill task using PID in PowerShell:
Replace [PID] with the Process ID.
Stop-Process -ID [PID] -ForceKill process from PowerShell using a process ID
How to Kill a Process using WMIC
Windows Management Instrumentation Command-Line (WMIC) is a useful command line tool to perform administrative tasks especially for sysadmins and power users. You can terminate the process using wmic command.
Please note all the below mentioned commands will only work if you open Command Prompt, PowerShell or Terminal as an administrator.
wmic process where "ProcessId='process-id'" deleteReplace process-id with the actual process ID. For example,
wmic process where "ProcessId='1234'" deleteYou can also terminate the process using its name:
wmic process where "name='process-name'" deleteReplace process-name with the actual process name. For example,
wmic process where "name='Skype.exe'" deleteIf there are multiple processes by the same name, this command will kill all of them. For example, the above mentioned command will delete all instances with the name Skype.exe.

How to Kill a Process using SysInternals PsKills
PsKill is a tiny tool that comes with the PsTools Suite by SysInternals. This is a command-line tool used to kill processes, both locally and remotely on other computers on the network.
Although it was designed for WindowsNT and Windows 2000 that did not include the other command-line tools (Killtask and Stop-Process), PsKill can still be used to end processes.
Learn how to manage processes and services on remote computers.
Use the following steps to download and use PsKill to kill tasks using the command line on a Windows computer:
-
Start by downloading PsTools.
Download PSTools -
Extract the contents of the PsTool file.
Extract PsTools -
Launch an elevated Command Prompt and then use the
CDcmdlet to change your directory to the extracted PsTools folder.CD [PathToPsTools]Change directory to PsTools folder -
Run the following command to list all the running processes:
PsListList all running processes using PsList Note down the name of the process that you want to kill.
-
Now use the following command to kill a process using its name:
PsKill.exe [ProcessName]Kill process using PsKill
As you can see from the image above, the respective process will be killed, and the associated service or program will be terminated.
Ending Thoughts
Even without the use of the Task Manager, there are multiple ways of killing a task or a process directly from the command line. You can even use these commands in scripts to end a Windows process.
On top of that, you can choose whether to kill a process using its name or its PID. Either way, Command Prompt and Windows PowerShell can be used with both native and external commands for this purpose. Not only that, but you can also use these commands in Windows Terminal for the same purpose.
If you are a sysadmin who wants quick and convenient methods to kill running processes, the given command line methods just might be the most convenient way of accomplishing it.
The «cmd kill» command is typically associated with terminating processes in Windows using the Taskkill command.
Here’s a concise code snippet to illustrate this:
taskkill /IM notepad.exe /F
This command forcefully terminates all instances of Notepad running on the system.
Understanding CMD and Processes
What is CMD?
The Command Prompt (CMD) is a command-line interface in Windows operating systems that allows users to execute commands and perform various administrative tasks. CMD is a powerful tool for users who prefer efficiency over navigating through graphical user interface (GUI) menus. This command-line interface can be utilized for tasks ranging from file management to network troubleshooting.
Key Features of CMD:
- Scripting: Users can automate tasks with batch files.
- System Management: CMD provides access to various system utilities.
- Process Control: CMD allows users to view and manage running processes.
The Concept of Processes
In computer terminology, a process is an instance of a program that is being executed. Processes can range from applications like Notepad to background services that keep your system running smoothly. Each process consumes system resources, and managing these processes effectively is crucial for maintaining optimal performance.
Why You May Need to Kill a Process:
- To free up system resources when an application becomes unresponsive.
- To close malicious processes that could compromise security.
- To stop background processes that are consuming excessive memory or CPU power.

Cmd Kill Service: A Simple Guide to Command Mastery
The CMD Kill Command
What is the ‘kill’ Command?
The term «kill» in the context of computing refers to terminating a running process. Although there isn’t a command explicitly named `kill` in CMD, the functionality is implemented through the `taskkill` command. The `taskkill` command provides a robust way to manage processes from the command line, enabling you to efficiently terminate any unresponsive or unnecessary programs.
Relevant CMD Commands for Killing Processes
taskkill
The `taskkill` command is used to terminate one or more tasks or processes based on various criteria. This command is highly flexible, allowing users to specify the name of the process or its unique Process ID (PID).
Syntax:
taskkill /IM <process_image_name> /F
Key Parameters:
- /IM: This option specifies the image name of the process to be terminated (e.g., `notepad.exe`).
- /F: This flag forces the process to terminate, which can be useful if the process is unresponsive.
Examples of Using taskkill
Killing a Single Process:
To terminate a single application like Notepad, you can use the following command:
taskkill /IM notepad.exe /F
This command abruptly closes all instances of Notepad without warning, making it essential to save your work before executing it.
Killing Multiple Processes:
You can terminate multiple processes in a single command by listing them:
taskkill /IM notepad.exe /IM calculator.exe /F
This command will close both Notepad and Calculator simultaneously.
Using Process ID (PID):
Sometimes, it’s necessary to terminate a process using its PID:
taskkill /PID <pid_number> /F
To find the PID of a running task, you can use the `tasklist` command. For example, if the PID of Notepad is 1234, you would execute:
taskkill /PID 1234 /F
This method is particularly useful for managing services or applications with the same image name.
Alternative Commands
end task
While `taskkill` is the primary command for terminating processes, the `end task` command can also be employed for this purpose. This command is often used in graphical interfaces, such as the Task Manager, but can be accessed in CMD as well. However, `taskkill` is generally more versatile and recommended for command-line use.

Unlocking Cmd Bitlocker: A Quick Guide
Advanced Techniques
Finding Process IDs
To see all currently running processes and their respective PIDs, utilize the `tasklist` command. This command will provide a comprehensive list of active tasks, which is often the first step in process management.
Example command:
tasklist
Upon executing, you’ll see output similar to the following:
Image Name PID Session Name Session# Mem Usage
========================= ======== =============== =========== ============
notepad.exe 1234 Console 1 10,000 K
calculator.exe 5678 Console 1 15,000 K
You can then use the PID from this list in your `taskkill` commands.
Using ‘PowerShell’ to Kill Processes
While CMD provides robust tools for process management, Windows PowerShell offers powerful alternatives for advanced users.
Example command in PowerShell:
Stop-Process -Name "notepad" -Force
Using PowerShell can streamline the process of terminating tasks and is especially useful for users who manage multiple processes or scripts regularly.

Mastering Cmd Filelist: A Quick Guide to File Management
Best Practices
When to Kill Processes
Understanding when it is appropriate to kill a process is crucial. Only terminate processes that you are certain are safe to close. Consider:
- Unresponsive Applications: If an application isn’t responding, it may be time to kill it.
- Malicious Software: When you identify unwanted programs consuming resources.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
You may encounter some challenges when attempting to kill processes. Here are common scenarios:
-
«Access Denied» Errors: This occurs when you lack the necessary permissions. Try running CMD as an administrator by right-clicking and selecting «Run as administrator.»
-
Stubborn Processes: If a process still refuses to terminate, consider using Task Manager or rebooting your computer to clear any residual instances.

Mastering Cmd File Parameters: A Quick Guide
Conclusion
Understanding how to manage processes using CMD commands, particularly the `taskkill` command, empowers users to maintain their system’s performance effectively. Employing these tools responsibly can lead to a more stable and efficient computing experience. As you become more comfortable with CMD, remember to practice caution, especially when terminating processes that may be critical to system operations.

Mastering Cmd File Location: A Quick Guide
Additional Resources
For further learning, consider exploring the official Microsoft documentation on CMD commands and process management. Online forums and communities provide an additional layer of support and knowledge sharing for CMD enthusiasts looking to deepen their understanding.









