|
Wine — (своеобразный акроним для «Wine Is Not an Emulator», т.е. «Wine не эмулятор») это слой совместимости, который может запускать приложения Windows на некоторых POSIX-совместимых операционных систем, например Linux, Mac OSX, или BSD. Вместо имитации внутренней логики Windows, как это делают виртуальные машины или эмуляторы, Wine переводит на лету вызовы Windows API в POSIX, избегая проблемы с производительностью и памятью при использовании других методах, и позволяет вам лучше интегрировать приложения Windows в ваш десктоп. |
Contents
- Доступные версии
-
Установка
-
Debian Jessie и новее
- Приготовления: включение мультиархитектуры (multiarch)
- Установка
- Установка из jessie-backports
- Зависимости Wine
- Debian Wheezy и старше
-
Debian Jessie и новее
- Конфигурация
- Установка и удаление программ
- Winetricks
- Дополнительные программы для Wine
- Альтернативы
- Ссылки
Доступные версии
С версии Debian Jessie вы можете выбрать между двумя пакетами Wine: wine и wine-development.
wine tracks the stable releases from winehq.org (e.g. version 1.6.2), and wine-development the development releases (e.g. version 1.7.29).
Несмотря на свое название wine-development этот пакет также подходит для использования обычными пользователями. Не надо путать с *-dev пакетами, которые содержат заголовочные файлы и библиотеки для разработки.
Вы можете установить оба пакета одновременно, или только один из них.
Чтобы использовать wine-development вы должны добавлять суффикс «-development» к каждой команде (например, «wine-development foo.exe» или «winecfg-development»).
Установка
Debian Jessie и новее
Приготовления: включение мультиархитектуры (multiarch)
Если ваша система имеет 64-битную архитектуру, то вы должны включить multiarch. Вы можете определить вашу архитектуру с помощью следующей команды:
$ dpkg --print-architecture
Пример для amd64 (у большинства пользователей), а нам надо добавить i386:
# dpkg --add-architecture i386 && sudo apt update
Установка
Устанавливаем wine:
# apt install wine
и/или wine-development:
# apt install wine-development
Установка из jessie-backports
Для Debian Jessie также доступны версии из Backports. Для включения jessie-backports на вашей системе добавьте строчку в ваш файл sources.list (или добавьте новый файл, с расширение «.list» в директорию /etc/apt/sources.list.d/):
deb http://httpredir.debian.org/debian jessie-backports main
и запустите
# apt update
Пакеты из Backports не устанавливаются/обновляются автоматически. Но после установки пакетов из jessie-backports, они будут (в будущем) автоматически обновляться. В примерах ниже, пакеты будут установлены из jessie-backports, а не из jessie.
Instead of the following examples you might simply use «apt install -t jessie-backports wine» (or «apt install -t jessie-backports wine-development»). But then you will end up with many packages installed unnecessarily from jessie-backports!
Установим пакет wine из jessie-backports на 64-битную архитектуру (с дополнительными компонентами из i386):
# apt install \
wine/jessie-backports \
wine32/jessie-backports \
wine64/jessie-backports \
libwine/jessie-backports \
libwine:i386/jessie-backports \
fonts-wine/jessie-backports
Установим пакет wine из jessie-backports на 32-битную архитектуру:
# apt install \
wine/jessie-backports \
wine32/jessie-backports \
libwine/jessie-backports \
fonts-wine/jessie-backports
Установим пакет wine-development из jessie-backports на 64-битную архитектуру (с дополнительными компонентами из i386):
# apt install \
wine-development/jessie-backports \
wine32-development/jessie-backports \
wine64-development/jessie-backports \
libwine-development/jessie-backports \
libwine-development:i386/jessie-backports \
fonts-wine/jessie-backports
Установим пакет wine-development из jessie-backports на 32-битную архитектуру:
# apt install \
wine-development/jessie-backports \
wine32-development/jessie-backports \
libwine-development/jessie-backports \
fonts-wine/jessie-backports
Зависимости Wine
Пакеты wine и wine-development имеют в зависимостях некоторые пакеты wine*. Некоторые пакеты необязательные и могут быть не установлены автоматически.
Прользователя 64-битной архитектуры следует убедиться, что установлены оба пакета — wine32 и wine64 (или wine32-development и wine64-development) (although not strictly required, this is what most people want).
Пакет wine поставляется с:
-
wine-binfmt provides support for launching windows executables directly.
-
wine32 provides the binary loader for 32-bit Windows applications.
-
wine64 provides the binary loader for 64-bit Windows applications.
-
wine32-tools provides wine’s 32-bit developer tools.
-
wine64-tools provides wine’s 64-bit developer tools.
-
libwine provides the wine library (one separate package for each the 32-bit and the 64-bit arch, e.g. libwine:i386 and libwine:amd64).
-
libwine-dev provides wine’s C header files and development libraries.
-
fonts-wine provides the fonts used by both wine and wine-development (since stretch/jessie-backports).
Пакет wine-development поставляется с:
-
wine32-development provides the binary loader for 32-bit Windows applications.
-
wine64-development provides the binary loader for 64-bit Windows applications.
-
wine32-development-preloader provides the prelinked loader for 32-bit Windows applications.
-
wine64-development-preloader provides the prelinked loader for 64-bit Windows applications.
-
wine32-development-tools provides wine’s 32-bit developer tools.
-
wine64-development-tools provides wine’s 64-bit developer tools.
-
libwine-development provides the wine library (one separate package for each the 32-bit and the 64-bit arch, e.g. libwine-development:i386 and libwine-development:amd64)
-
libwine-development-dev provides wine’s C header files and development libraries.
Debian Wheezy и старше
В Debian Wheezy, для удобства, Wine разбит на несколько пакетов, чтобы вы могли использовать только те возможности Wine, которые вам нужны.
Полный стандартный комплект можно получить, установив wine. Это фиктивный пакет, зависящий от стандартных компонент Wine.
# apt-get install wine
Минимальный комплект можно получить, установив wine-bin. Данный пакет предоставляет двоичный загрузчик для запуска исполняемых файлов Windows.
# apt-get install wine-bin
После установки пакета wine-bin, если необходимо, добавьте дополнительные модули:
-
libwine — Этот пакет содержит библиотеку wine.
-
libwine-alsa — Звуковой модуль ALSA; пакет содержит драйвер для звука, ALSA.
-
libwine-capi — Модуль ISDN; пакет содержит интерфейс CAPI, который позволяет приложениям Windows взаимодействовать с картами ISDN, поддерживаемыми capi4linux.
-
libwine-cms — Модуль управления цветом; пакет содержит реализацию Системы Управления Цветом (Color Management System), которая позволяет приложениям Windows калибровать цвета, используемые для дисплея и печати
-
libwine-dbg — Символы для отладки (debugging symbols); пакет предоставляет символы для отладки.
-
libwine-dev — Файлы для разработки; пакет предоставляет заголовочные файлы на ‘C header files’.
-
libwine-gl — Модуль OpenGL; пакет содержит модули OpenGL и Direct3D, которые позволяют приложениям Windows использовать 3D ускорение.
-
libwine-gphoto2 — Модуль камеры; пакет содержит интерфейс TWAIN, который позволяет приложениям Windows взаимодействовать с камерами, поддерживаемыми gphoto2.
-
libwine-ldap — Модуль LDAP; пакет содержит модуль, который позволяет приложениям Windows доступ к службам каталогов LDAP.
-
libwine-oss — Звуковой модуль OSS; пакет содержит драйвер для звука, OSS.
-
libwine-print — Модуль печати; пакет содержит спулер, поддерживающий CUPS, и драйвер PostScript, предоставляя возможность печати из приложений Windows.
-
libwine-sane — Модуль сканера; пакет содержит интерфейс TWAIN, который позволяет приложениям Windows взаимодействовать со сканерами, поддерживаемыми SANE .
Конфигурация
wine 1.6.2-20 packages in Debian Jessie
To use the wine-wrapper scripts such as winecfg, wineboot or regedit you have to set them as an option to the command «wine». See Debian bug #784280. wine-development and later wine versions are are not affected.
E.g. typing only «winecfg» will cause an error if no wineprefix exists yet, while «wine winecfg» works as expected.
Чтобы открыть окно настроек Wine, введите следующую команду (в зависимости от используемой версии Wine):
$ wine winecfg $ winecfg-development
Чтобы открыть редактор реестра, введите следующую команду (в зависимости от используемой версии Wine):
$ wine regedit $ regedit-development
Установка и удаление программ
Для установки программы, запустите установочный файл Windows (.exe/.msi), используя следующую команду (в зависимости от используемой версии Wine):
$ wine ~/file.exe $ wine-development ~/file.exe
Для удаления программ, запустите в «wine uninstaller», используя следующую команду (в зависимости от используемой версии Wine):
$ wine ~/file.exe $ wine-development ~/file.exe
«Wine uninstaller» не удаляет кнопки меню и иконки установленных программ, поэтому вам придётся сделать это вручную, для этого удалите всё лишнее из папок /home/имя_пользователя/.local/applications/wine и /home/имя_пользователя/.local/icons или удалите их (в этом случае все кнопки созданные Wine исчезнут)
Winetricks
winetricks — это вспомогательный скрипт для загрузки и установки различных необходимых компонентов (например, библиотеки), для запуска программ в Wine. Некоторые компоненты могут включать в себе библиотеки с закрытым кодом.
Для установки, введите следующие:
# apt install winetricks
Если у вас установлен одновременно wine и wine-development, то для того, чтобы использовать wine-development, вы должны выполнить следующие команды, перед запуском winetricks:
$ export WINE=/usr/bin/wine-development $ export WINESERVER=/usr/bin/wineserver-development
Если вы используете wine-development из Jessie (не из jessie-backports) используете следующие команды (make sure to replace the * in the WINESERVER line with the appropriate directory based on your system’s architecture):
$ export WINE=/usr/bin/wine-development $ export WINESERVER=/usr/lib/*/wine-development/wineserver
-
PlayOnLinux — Оболочка для Wine, облегчающая установку Windows-игр и приложений в Linux.
-
q4wine — Помогает управлять префиксами Wine и устанавливать приложения.
-
winegame — Это программа для легкой установки игр и приложений Windows в Linux.
Альтернативы
-
Crossover — CrossOver is developed by CodeWeavers and based on Wine, an open-source Windows compatibility layer. CrossOver lets you run thousands of Windows apps on your favorite Linux distros like Ubuntu, Mint, Fedora, Debian, RHEL and more.
-
Wine Staging Wine Staging (formerly wine-compholio) is a special wine version containing bug fixes and features, which are not yet available in regular wine versions. The idea of Wine Staging is to provide new features faster to end users and to give developers the possibility to discuss and improve their patches before they are sent upstream.
Ссылки
-
Официальный сайт Wine
-
README.debian
CategoryGame | CategoryNotNative | CategorySoftware
Using Wine 8.0 on Debian Linux unlocks a range of functionalities, allowing you to run Windows applications seamlessly. Here’s a quick overview of Wine’s features and benefits with the release of Wine 8.0:
- PE Modules: All modules are now converted to PE format, enabling better copy protection and support for 32-bit applications on 64-bit hosts.
- WoW64: Enhanced support allows 32-bit PE modules to call 64-bit Unix libraries, with an experimental mode miming Windows WoW64.
- Graphics: A new “Light” theme, implementation of the Print Processor architecture, and added support for effects in Direct2D enhance the visual and functional aspects.
- Direct3D: Performance boosts through optimizations, streaming map acceleration, and a new WINE_D3D_CONFIG environment variable.
- Audio/Video: Improved content type resolution and rate control, alongside support for Enhanced Video Renderer, ensures better media handling.
- Media Foundation: Further enhancements in content type resolution and rate control.
- Input Devices: Better controller hotplug support, force feedback effects, and enhanced compatibility with various controllers.
- Internationalization: Introduction of a proper locale database and support for high Unicode plane characters.
- Text and Fonts: Font linking enabled for most system fonts, improving text rendering.
- Kernel: Implementation of the ApiSetSchema database reduces disk space and address space usage.
These enhancements make Wine 8.0 a robust solution for integrating Windows applications into your Debian environment. With this groundwork laid, let’s dive into the technical steps to install and configure Wine on your Debian system.
Wine 8.0 Pre-installation Steps
Updating Your Debian Before Wine 8.0 Installation
Update your system to ensure a smooth and successful installation. Use the following command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeThe command sudo apt update refreshes your system’s local repository database to get the latest metadata from the Debian repositories. The command sudo apt upgrade then upgrades the currently installed packages to their newest versions.
Install Initial Required Packages For Wine 8.0
Make sure to install a few essential packages that aid the installation process:
sudo apt install software-properties-common apt-transport-https curl -yThis command installs software-properties-common (for adding and removing PPAs) and apt-transport-https (allowing apt to retrieve data using HTTPS).
Enabling 32-bit Support (Optional)
A lot of Windows applications, especially games, use a 32-bit architecture. To maximize compatibility with these applications, enable 32-bit support on your system:
sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386This command lets your system recognize i386 packages, allowing you to install 32-bit software. Regardless of whether you have a low-end system wanting to play classic 32-bit games or a high-end setup, this feature broadens your software compatibility.
Import WineHQ GPG Key & Repository
Prepare to install Wine by importing a GPG key, which verifies that the software you install is genuine and untouched, and by adding the WineHQ repository containing the installation packages.
First, import the GPG key with this command:
curl -fSsL https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/winehq.key | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/winehq.gpg > /dev/nullThen, add the WineHQ APT repository:
echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/winehq.gpg] http://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/debian/ $(lsb_release -cs) main | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/winehq.listThis command creates a file named winehq.list in the /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ directory. This file tells our system where to locate the Wine packages. The echo command displays the text line, and the tee command saves this display to the file.
After you add the repository, update your local package database again:
sudo apt updateSelect Wine 8.0 Version to Install
Now that our system is primed and ready, let’s focus on our main goal: installing Wine. We have three options, each catering to different user needs.
Option 1: Installing Wine 8.0 Stable Release
The stable release of Wine balances recent updates and reliable functionality, making it a safe choice for most users. To install this version, enter the following command:
sudo apt install winehq-stable --install-recommends This command downloads and installs the winehq-stable and recommended packages for optimal performance.
To verify the installation and see the version you’ve installed, type:
wine --versionIf you prefer a time-tested version of Wine, you can only install the default repository’s 64-bit version:
sudo apt install wine64If you enabled 32-bit support in the earlier steps, you could install both the 64-bit and 32-bit versions with the following:
sudo apt install wine64 wine32Option 2: Install Wine Staging Release
If you like staying on the cutting edge of software developments, the WineHQ Staging Release is for you. This version gives you features almost ready for broad use, placing it a step ahead of the stable release.
To install the Wine-Staging Release, type:
sudo apt install --install-recommends winehq-stagingAfter you install, verify the version and ensure successful installation with:
wine --versionOption 3: Install Wine Development Release
The WineHQ Development Release provides a glimpse into upcoming features and improvements. However, remember that this version may have bugs or be less stable. We mainly recommend it for seasoned users or developers.
To install the Wine Development Release, input:
sudo apt install --install-recommends winehq-devel -yTo confirm your installation and view the installed version, type:
wine --versionFinalize Wine 8.0 Installation
Congratulations! You’ve installed WineHQ on your Debian system. Now, let’s ensure everything is set up correctly. Run the winecfg command in the terminal. This command sets up essential environments for Wine, including Mono, which allows .NET applications to run on Linux.
Start the Wine configuration with this command:
winecfg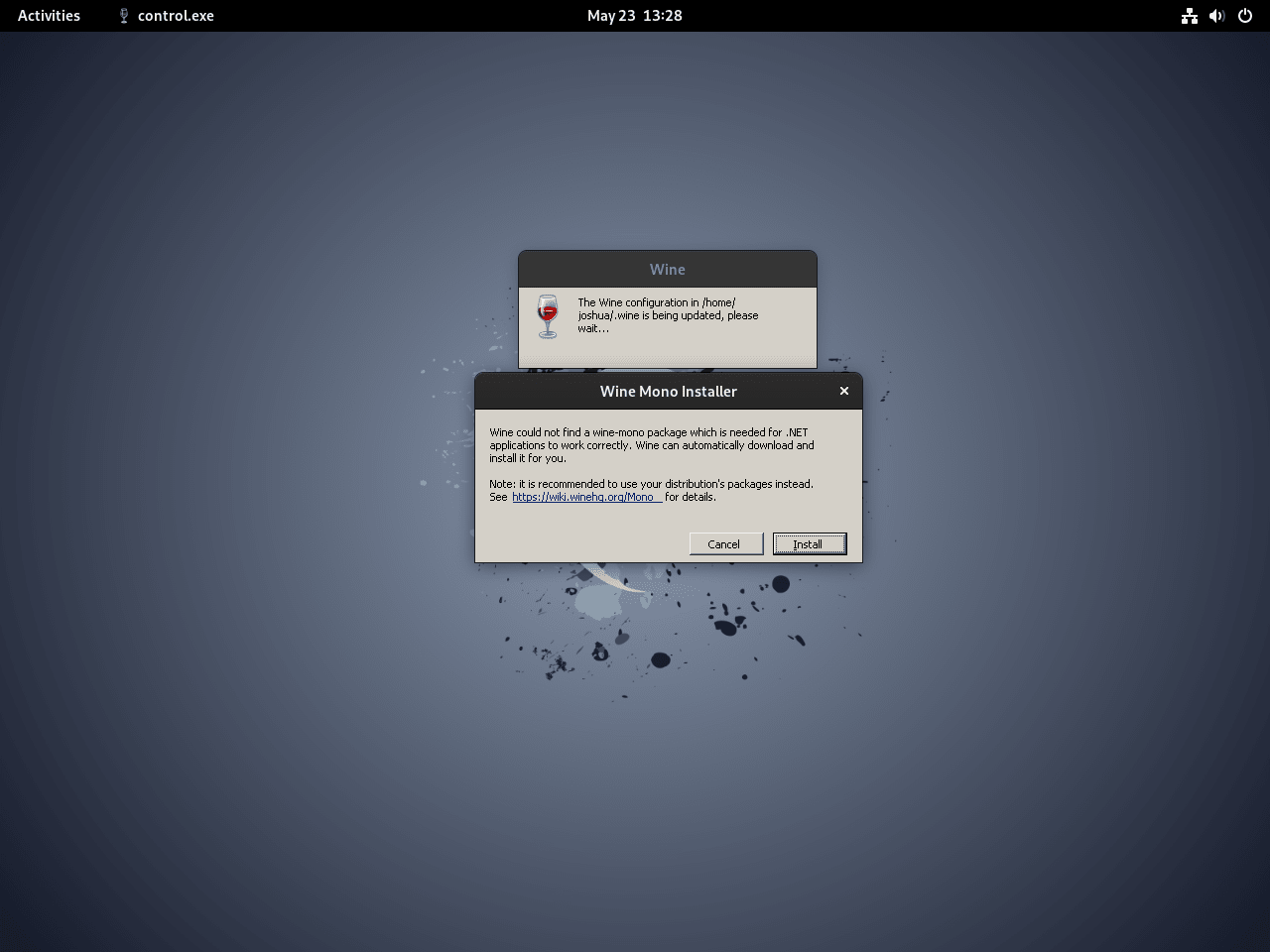
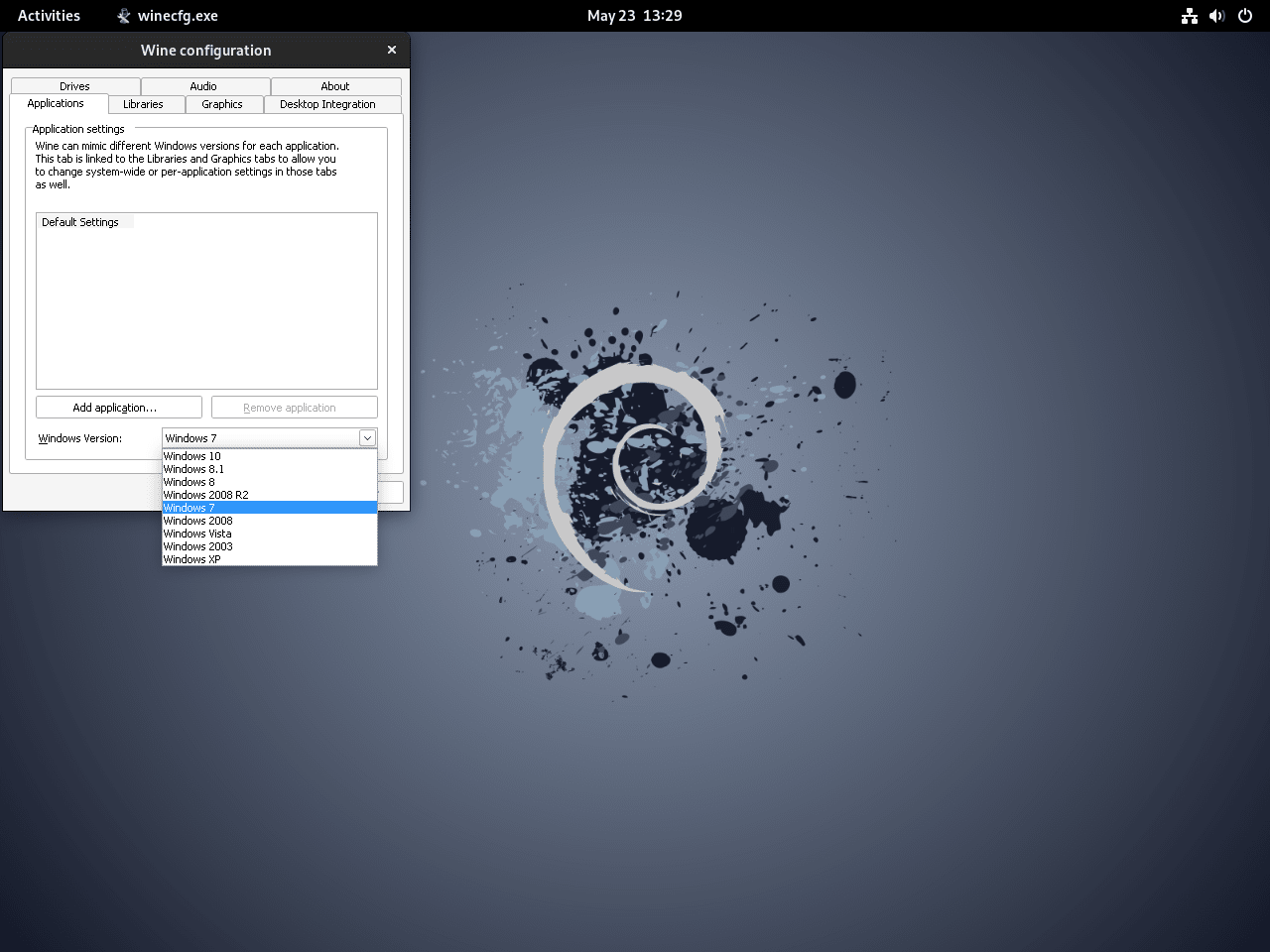
A prompt will ask for your permission to install the necessary components. Click “Install.” After the installation, the Wine configuration dialogue box will open. Here, you can adjust Wine’s settings.
Most users will find the default settings adequate. By default, Wine mimics the Windows 7 environment. You can change this to a different version, like Windows 10. However, as of this writing, Wine doesn’t support Windows 11.
After adjusting the settings, close the dialogue box to save them.
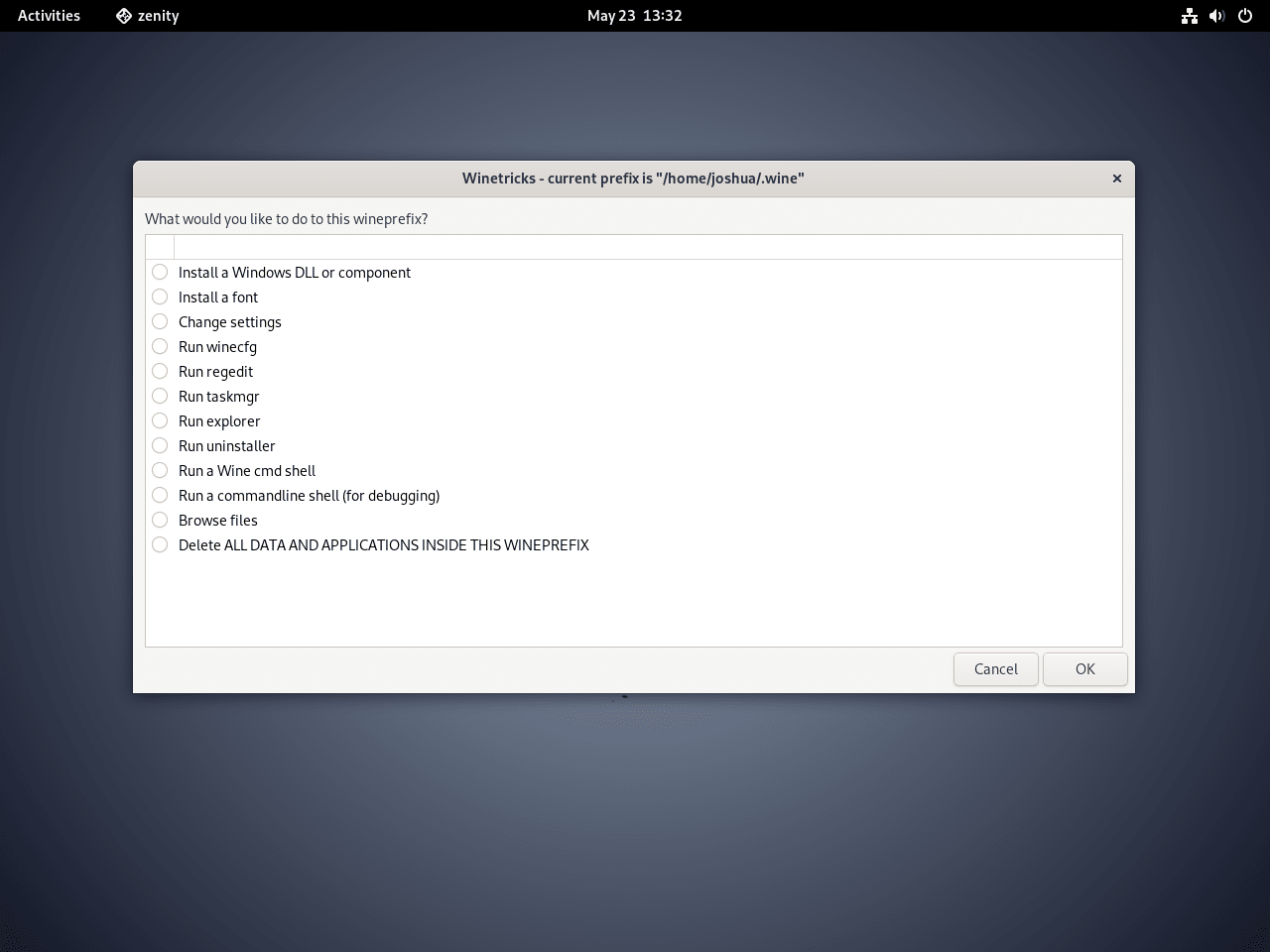
Optional: Install Optional Wine Enhancements
With your Wine installation in place, you might want to explore optional enhancements to optimize the experience. One such tool is winetricks, designed to streamline the installation of specific libraries and applications for better compatibility with Windows software.
To get winetricks, enter:
sudo apt install winetricksUse winetricks to add Windows components that are not included in Wine. For example, to get a complete set of 32-bit Microsoft fonts, use:
winetricks allfontsOr locate the application user interface and launch it: Activities > Show Applications > Winetricks
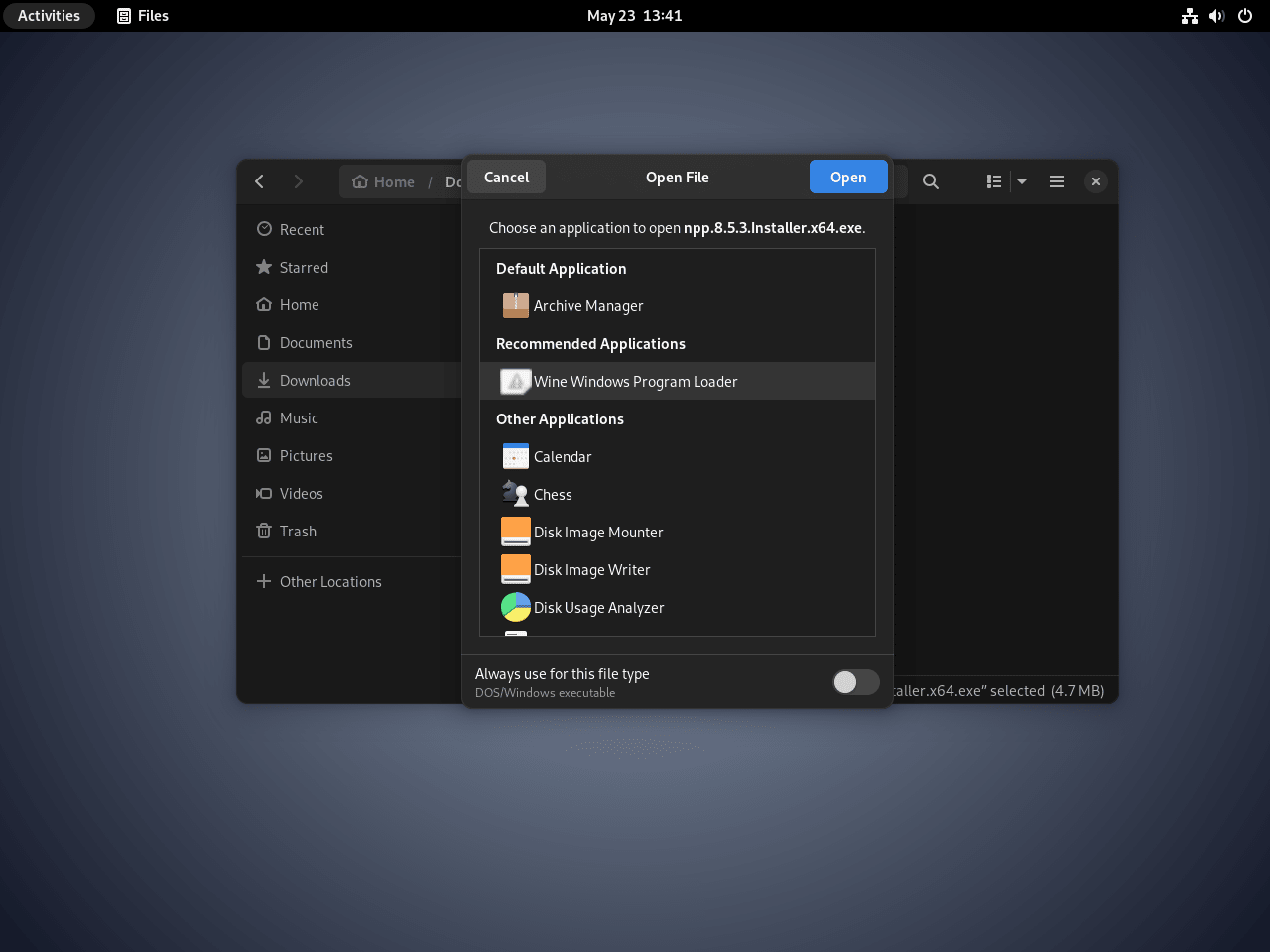
Example: Install NotePAD++ on Debian with Wine 8.0
Wine makes it simple if you’re looking to run Windows applications on your Debian system. One popular example is Notepad++, a widely used free source code editor and a solid alternative to the native Notepad in Windows. Here’s how you can install and run Notepad++ using Wine:
- Download the Notepad++ Installer: Go to the official website and download the Notepad++ installation executable file (.exe).
- Install with Wine: Find the .exe file in your directory after downloading. Right-click the file, choose “Open With” or “Open With Other Application,” and then pick Wine. This action tells your Linux system to use Wine to run the .exe file, allowing you to install Notepad++ as if you were on a Windows machine.
Click the Notepad++ application icon. It will open like on a Windows system, showcasing Wine’s capability.
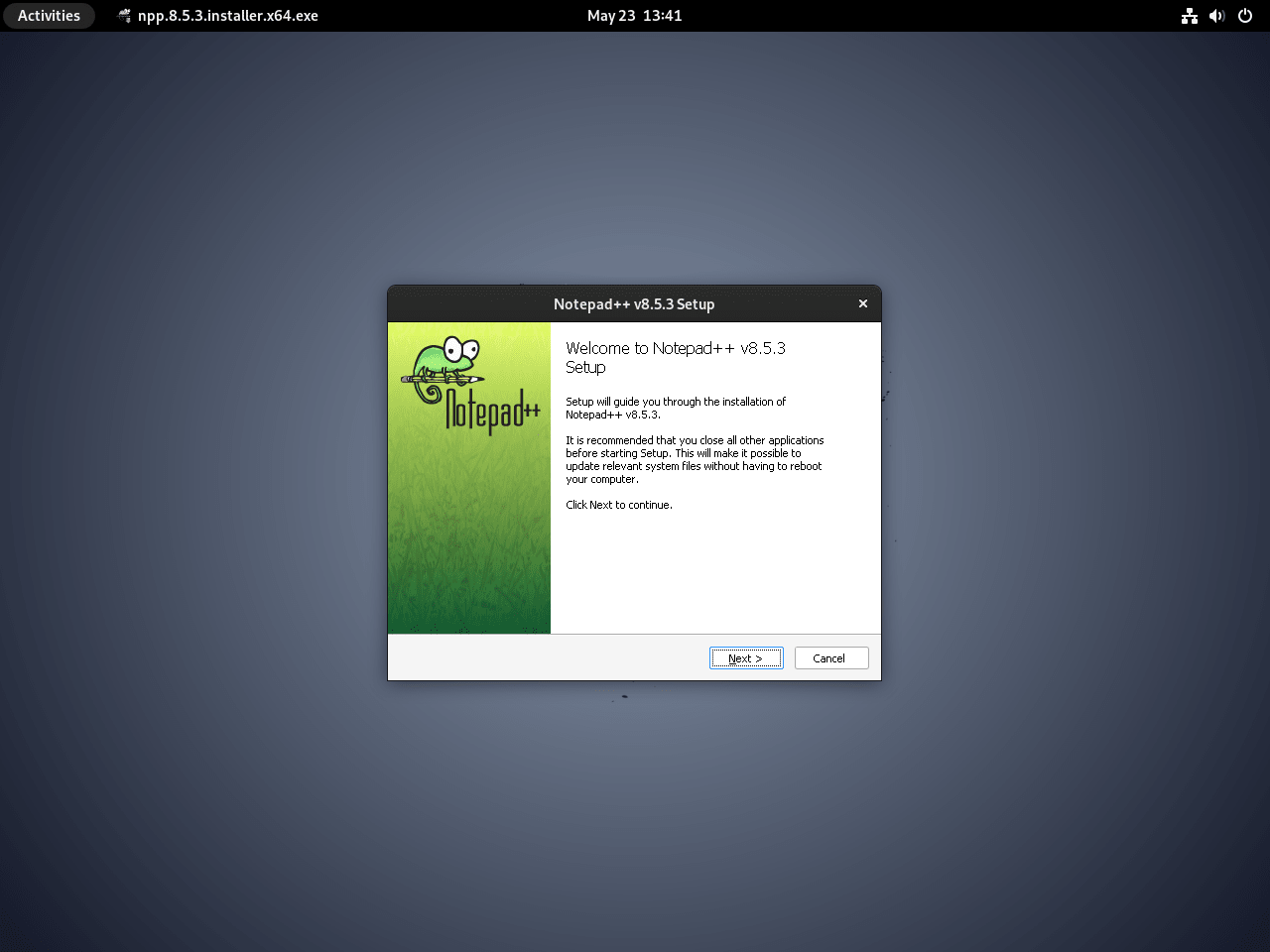
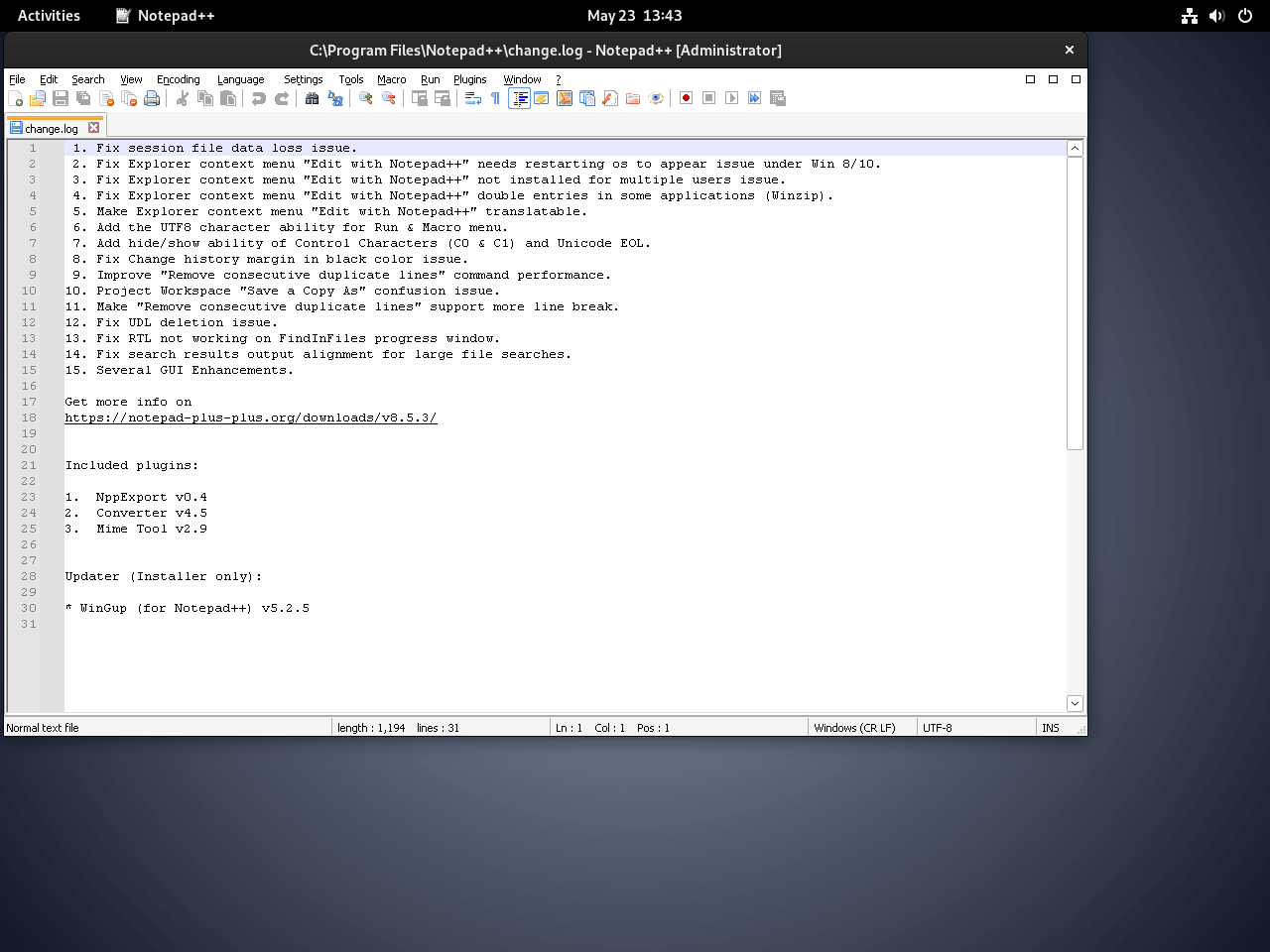
Remember, this installation method using Wine isn’t exclusive to Notepad++. You can use it for many other Windows applications. With Wine, you bridge the gap between Linux and Windows, broadening your software options.
Additional Wine Commands
Configure Wine for 32-bit Applications
Wine can run both 64-bit and 32-bit Windows applications. However, you must adjust Wine to run older 32-bit software.
To configure Wine for 32-bit, change two environment variables: WINEARCH and WINEPREFIX. Set WINEARCH to “win32” to indicate Wine will run 32-bit apps. Set WINEPREFIX to a directory other than the default ~/.wine.
As explained above, set WINEARCH with this command:
export WINEARCH=win32Create a separate directory for 32-bit with this command:
export WINEPREFIX=~/.wine32Now, initialize the new 32-bit Wine setup:
winecfgThis command opens the Wine configuration, where you can adjust settings for 32-bit apps.
Operating Wine From Terminal
Operating Wine from the terminal is advantageous, offering you greater control over the software you’re running. Here, I’ll walk you through some of the most commonly used Wine commands and how to use them.
The most elementary Wine command is, simply, wine. This command allows you to run Windows applications directly from the terminal. All you need to do is type wine followed by the path to the .exe file you wish to run.
For example:
wine /path/to/program.exeThe winecfg command opens the Wine configuration dialogue box where you can modify settings such as the Windows version, audio, and graphics.
Example:
winecfgThe regedit command lets you access the Wine registry editor, which stores configuration settings for Wine and the Windows applications you’re running.
Example:
wine regeditThe winetricks command is a valuable tool for installing additional components and libraries not included initially with Wine.
Example:
winetricks allfontsThe winepath command assists in converting Windows-style paths to Unix-style paths and vice versa.
Example:
winepath -w /unix/pathThe wineserver command, while rarely used, can come in handy for debugging or troubleshooting.
Example:
wineserver -kUpdate Wine 8.0
To keep Wine updated with the latest version, you’ll need to use the sudo apt upgrade and sudo apt update commands:
sudo apt upgrade && sudo apt updateRemove Wine 8.0
If the need arises to uninstall Wine from your system, you have to use specific commands based on the version you have installed. Here are the commands for removing each version:
For WineHQ Stable Release:
sudo apt remove winehq-stableStaging Release:
sudo apt remove winehq-stagingFor WineHQ Development Release:
sudo apt remove winehq-develOnce the specific version of Wine has been removed from your system, you can then proceed to delete the repository file:
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/winehq.listFor those who have removed the WineHQ repository, it is also advisable to remove the associated GPG key:
sudo rm /usr/share/keyrings/winehq.gpgIf Wine was installed from the default Debian repository, a different command is required for its removal:
sudo apt remove wine32 wine64Closing Thoughts
The path to successfully installing and utilizing Wine 8.0 with the WineHQ repository on a Debian Linux system can seem intricate and overwhelming at first glance. Yet, through the process we’ve walked through, we’ve seen that it’s not as daunting as it might initially appear. Each command, each step in the process, has a purpose and contributes to creating an environment where Windows applications can run smoothly on your Linux system. From configuring Wine to handle 32-bit applications to running applications using Wine from the terminal to updating and managing Wine installations – each action you’ve learned to perform plays an integral part in creating an efficient, flexible workspace for your cross-platform needs.
When it comes to installing Windows applications on Linux, there’s no application that does it better than Wine. Wine is a compatibility layer that enables users to run Windows applications on POSIX compliant operating systems such as Linux and UNIX derivatives such as BSD, FreeBSD, and macOS.
Not all Windows applications are supported, and to get a comprehensive list of all supported applications, head over to the Wine application database – AppDB.
[ You might also like: How to Install Wine in Ubuntu Desktop ]
At the time of publishing this guide, the latest version of Wine is Wine 7.2, which is a development release. The latest stable release is Wine 7.0 Without further ado, let’s switch gears and install Wine on Debian desktops.
Installing Wine in Debian Linux
Straight off the bat, log into your system and update the package index as a sudo user.
$ sudo apt update
A few dependencies are required for the installation of Wine to go through smoothly.
$ sudo apt install software-properties-common gnupg2
With your system up to date and prerequisites installed, proceed to the next step.
Next, you need to enable 32-bit architecture on the Debian system to seamlessly run 32-bit applications with Wine.
$ sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386
There are two approaches to installing Wine. You can install Wine from the Debian repository using the APT package manager, which is simple and straightforward and all you need is to run the command:
$ sudo apt install wine
However, this will give you an older version of Wine than the one in the WineHQ repository. Therefore, to install the latest Wine version, it’s recommended to install it from the WineHQ repository.
$ wget -nc https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/winehq.key $ sudo apt-key add winehq.key
Once you have successfully added the GPG keys, proceed and add the WineHQ repository to your system.
$ sudo add-apt-repository 'deb https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/debian/ bullseye main'
Then update the package lists to notify Debian about the newly added Wine repository and start using it.
$ sudo apt update
To install the latest stable version of Wine, run the command
$ sudo apt install --install-recommends winehq-stable
This will give you Wine 7.0.
Alternatively, you can install the development branch which provides the most recent version – Wine 7.2.
$ sudo apt install --install-recommends winehq-devel
The installation is quite heavy as it involves the installation of hundreds of packages and dependencies. In my case, this came to about 1.7GB and took roughly 15min. At this point, you can take a much-needed break as the installation of Wine goes on.

Once installed, verify the Wine version as follows.
$ wine --version wine-7.2
Configuring Wine on Debian Linux
So far, we have successfully installed Wine on Debian. However, some post-installation steps are required before Wine is ready to install Windows Apps.
To configure Wine, run the command:
$ winecfg
This creates a hidden directory in the home directory called .wine that contains a “virtual” drive C that contains directories that you would find on a Windows system such as Program Files, Program Files, Program Files (x86), users, and Windows.
On the next pop-up, click ‘Install‘ to install the wine-mono package which is a prerequisite for .NET applications.
The installation will get underway. This takes a minute or two.
Finally, you will see the Wine configuration window as shown. You should be good to go with the default settings, but feel free to adjust the settings to your own preference.

Installing Windows Application with Wine in Debian
Now, let us see how you can install a Windows App using Wine. To demonstrate this, we will install a VLC media player which is a free and open-source cross-platform media player.
So, head over to the official VLC download page and download the executable file. Once downloaded, right-click on select ‘Open with other application’.

On the pop-up that appears, select ‘Wine Windows Program Loader‘.

Once again, right-click on the installer and select ‘Open with Wine Windows Program Loader‘. The VLC media installation wizard will open. Click ‘Ok’ to start the installation and follow along right till the end.

Inside the .wine folder, navigate to the ‘Virtual’ drive_c folder and then the ‘Program Files’ folder. Here you will see a directory for the just installed VLC multimedia application.

This wraps up this guide. In this tutorial, we have demonstrated how to install Wine on Debian Linux. We went a step further and showed you how you can run and install a Windows application with Wine in Debian.
Last Updated :
05 Jun, 2024
Wine is a free program that lets you run Windows apps on your Linux computer. The Wine team released the new stable version 8.0 in January 24 2023. You can get the Wine 8 from the official website or using the package manager on your Linux system.
This guide will show you how to install the Wine 8 version on Debian 11 and Debian 10 using the PPA (Personal Package archive). Wine is made by volunteers and companies who want to help Linux users run Windows programs.
Table of Content
- What is Wine and why install it on Debian 11 ?
- Installation of Wine version 8
- Step 1: Configure PPA
- Step 2: Install Wine on Debian
- Step 3: Verify Installation
- Step 4: Run Windows Application
- Conclusion
- FAQs — How to Install Wine 8 on Debian 11
- What if I do not have the 64 bit computer Can I still install Wine?
- Why do I need to add a special key for the Wine repository?
- How do I know which Windows programs will work with Wine?
- What if the Wine program opens but doesn’t work right?
- Can I install Windows programs from a CD/DVD using Wine?
What is Wine and why install it on Debian 11?
Wine is a program that allows running Windows software on the Linux computers like Debian 11. Windows programs normally only work on Windows, but Wine makes them work on Linux. Installing Wine 8 on Debian 11 is useful if you need the Windows programs but do not want to install the full Windows operating system. With the Wine, these Windows programs run directly on the Debian 11.
People install Wine 8 because it is the newest version with the latest improvements for smoothly running Windows programs without any issues.
Installation of Wine version 8
Step 1: Configure PPA
First, check if your computer has 64-bit. Mostly the newer computers are 64-bit. If the computer is 64-bit then you need to make it able to use the 32-bit programs too. Do this by running the below command. This command will tell your 64-bit computer that it can also use 32-bit programs.
Command :
sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386
Output :
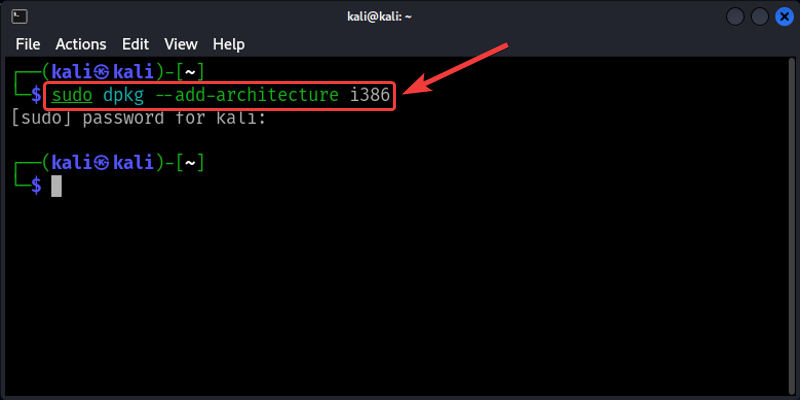
Next we need to get a special key file. This key file lets your computer trust that the Wine software is safe to install. Without this key your computer might think Wine is unsafe. Run the below command This command gets the key file from the Wine website. It then adds this key to your computers list of trusted keys.
Command :
wget -qO - https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/winehq.key | sudo apt-key add -
Output :

Now tell your Debian computer where to find the Wine software. Use the below command to do that. This command adds the Wine software address to your computer’s list of places to look for programs.
Command :
sudo apt-add-repository https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/debian/
Output :

After doing these three steps, your computer knows it can trust and install Wine 8 from the official Wine place. Your computer is now ready for the actual Wine 8 installation command.
Step 2: Install Wine on Debian
Now we are ready to actually install Wine on your Debian computer. Use the below command. This command updates the list of available software on your computer.
Command :
sudo apt update
The following command installs the Wine software along with any other recommended programs that Wine needs to work properly. The —install-recommends part tells your computer to install those recommended programs too.
Command :
sudo apt install --install-recommends winehq-stable
Output :

In some cases Wine might get installed in a special directory called `/opt/wine-stable`. If that happens you need an extra step to let your whole computer system access and use the Wine programs. The below command updates a setting called `PATH` that tells your computer where to look for programs. By adding `/opt/wine-stable/bin` to the `PATH` your computer can now find and run the Wine programs from anywhere.
Command :
export PATH=$PATH:/opt/wine-stable/bin
Output :

After running these commands, Wine 8.0 should be successfully installed on your Debian system! You can now try running Windows programs using Wine.
Step 3: Verify Installation
To make sure Wine was installed correctly, you can check which version is now on your computer. Use the below command this command asks the Wine program to tell you its current version number.
Command :
wine --version
Output :

Step 4: Run Windows Application
Now that Wine is installed you can use it to run the Windows programs right onto your Debian desktop. Next download the Windows program file with a .exe extension. For this example we use the popular PuTTY program. Save the putty.exe file in your Downloads folder. Open a terminal window and run the below command.
Command :
wine ~/Downloads/putty.exe
Output :

Conclusion
Wine allows to run the Windows programs directly to the your Debian Linux computer. By following the steps of enabling the 32 bit support adding the Wine repository and installing the Wine package and running the .exe file with the Wine you can easily use your favorite Windows software with your regular Linux programs.
Wine makes your Debian system more versatile by giving the access to Windows applications without needing a full Windows operating system installed.
Всё больше людей переходят на операционные системы, семейства Linux. И каждый из них хочет проводить время за привычными Windows играми на новой платформе. На данный момент вопрос игр на Linux стоит довольно остро , но эта отрасль активно развивается. Не менее востребованы и некоторые приложения Windows.
Wine — свободное программное обеспечение, которое позволяет запускать Windows программы в системах семейства Linux и MacOS. В данной статье мы рассмотрим, как установить Wine на Debian 10.
Содержание статьи
- Установка Wine в Debian 10
- Удаление Wine из Debian
- Выводы
Перед установкой вам необходимо определиться, какая версия Wine вам нужна. При установке программ на Linux почти всегда есть выбор между стабильной версией и самой свежей. Если вы не уверены, какая версия необходима, и программа не входит в список официально поддерживаемых, то следует сперва попробовать последнюю стабильную версию Wine и только если программа не работает, пытаться запустить её с самой свежей версией. Установить Wine можно несколькими способами.
1. Установка из официальных репозиториев
Для того, чтобы установить wine стабильной версии из официального репозитория, введите в терминале команду:
sudo apt install wine
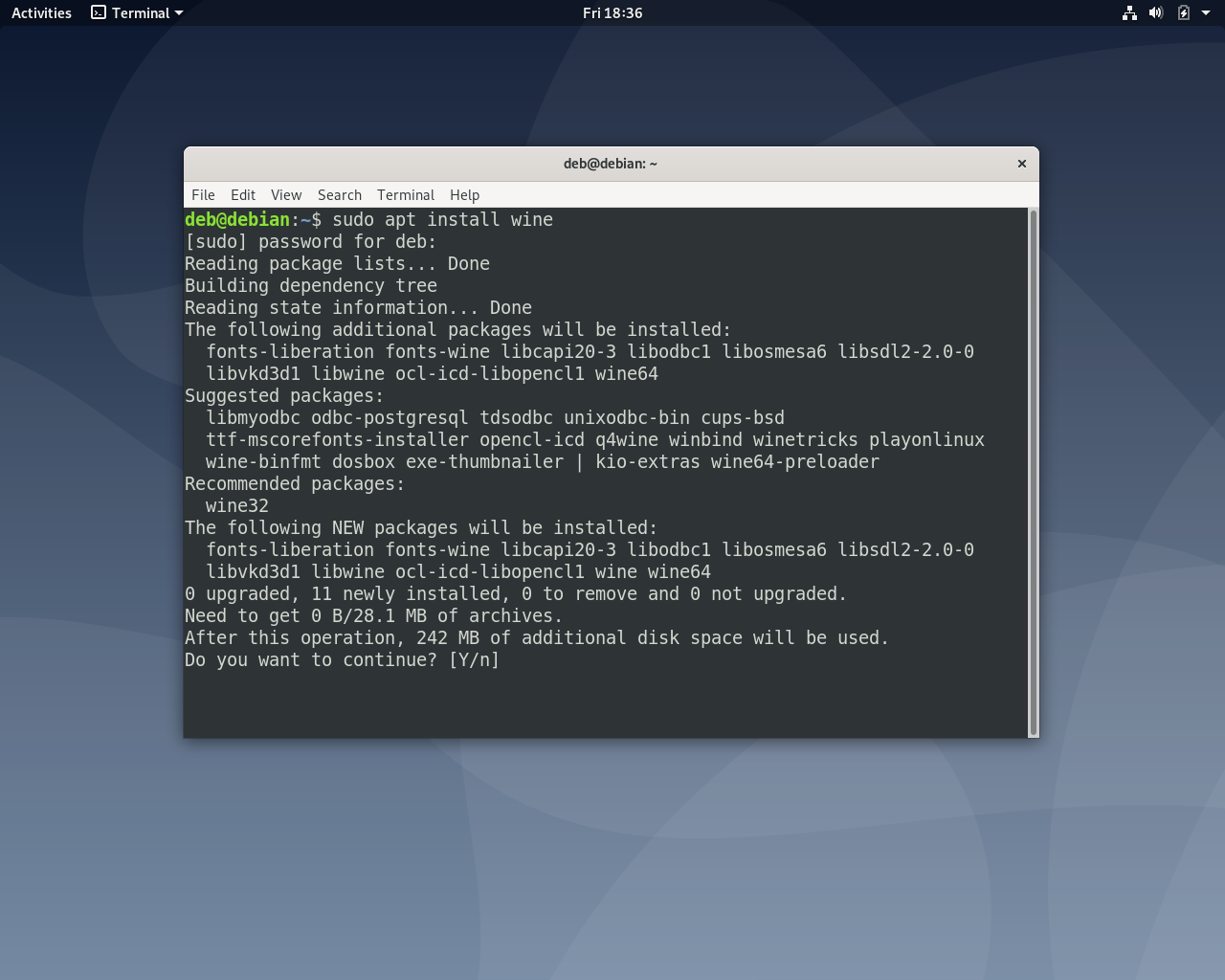
После установки, версию установленной программы можно проверить командой:
wine --version
Программное обеспечение в репозиториях Debian обновляется раз в несколько лет, поэтому ждать что там будет свежая стабильная версия не стоит. Скорее всего программа будет уже устаревшей. Если вы хотите более свежую версию с добавлением поддержки новых программ — надо использовать PPA репозитории.
2. Установка из PPA репозиториев
Сначала необходимо включить поддержку 32-битной архитектуры пакетов:
sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386
Затем необходимо добавить PPA репозиторий разработчиков. Для этого сначала импортируйте его ключ в систему:
wget -nc https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/winehq.key
sudo apt-key add winehq.key
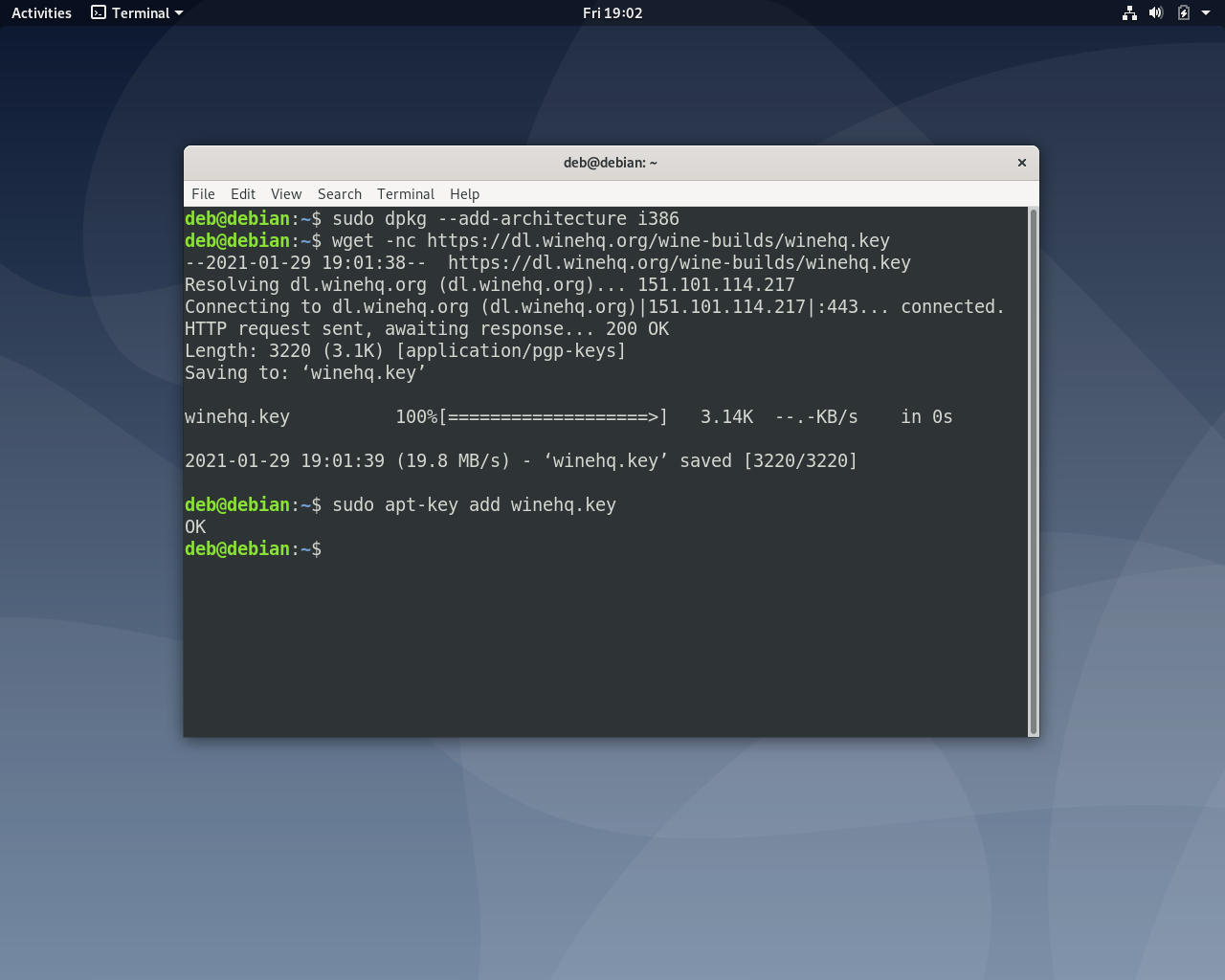
Затем добавьте сам репозиторий в файл /etc/apt/sources.list
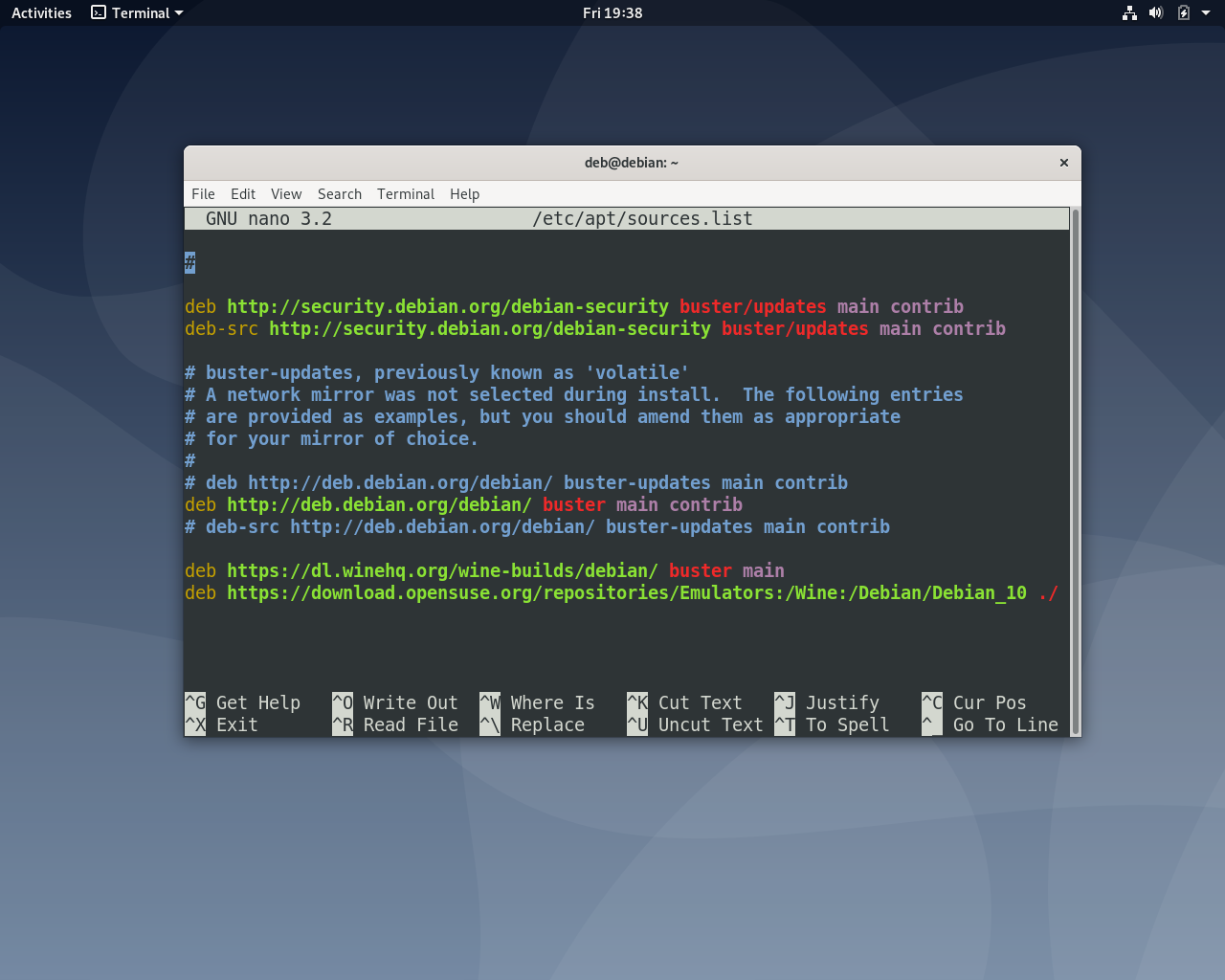
sudo vi /etc/apt/sources.list
deb https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/debian/ buster main
Кроме репозитория разработчиков, вам понадобится ещё один репозиторий, потому что в отличие от Ubuntu, для которой создан этот PPA репозиторий, в Debian не поставляются библиотеки libaudio, которые нужны для полноценной работы Wine. Эти библиотеки можно установить из специального репозитория подготовленного в рамках проекта OBS. Загрузите и добавьте его ключ:
wget -nc https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/Emulators:/Wine:/Debian/Debian_10/Release.key
sudo apt-key add Release.key
Затем добавьте сам репозиторий в файл /etc/apt/sources.list:
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list
deb https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/Emulators:/Wine:/Debian/Debian_10 ./
Обновите список доступных в системе пакетов с помощью команды:
sudo apt update
Из репозитория разработчиков можно установить стабильную (stable), экспериментальную (staging) или версию для разработчиков (devel). Для установки стабильной версии выполните:
sudo apt install --install-recommends winehq-stable
Экспериментальная версия:
sudo apt install --install-recommends winehq-staging
Версия для разработчиков:
sudo apt install --install-recommends winehq-devel
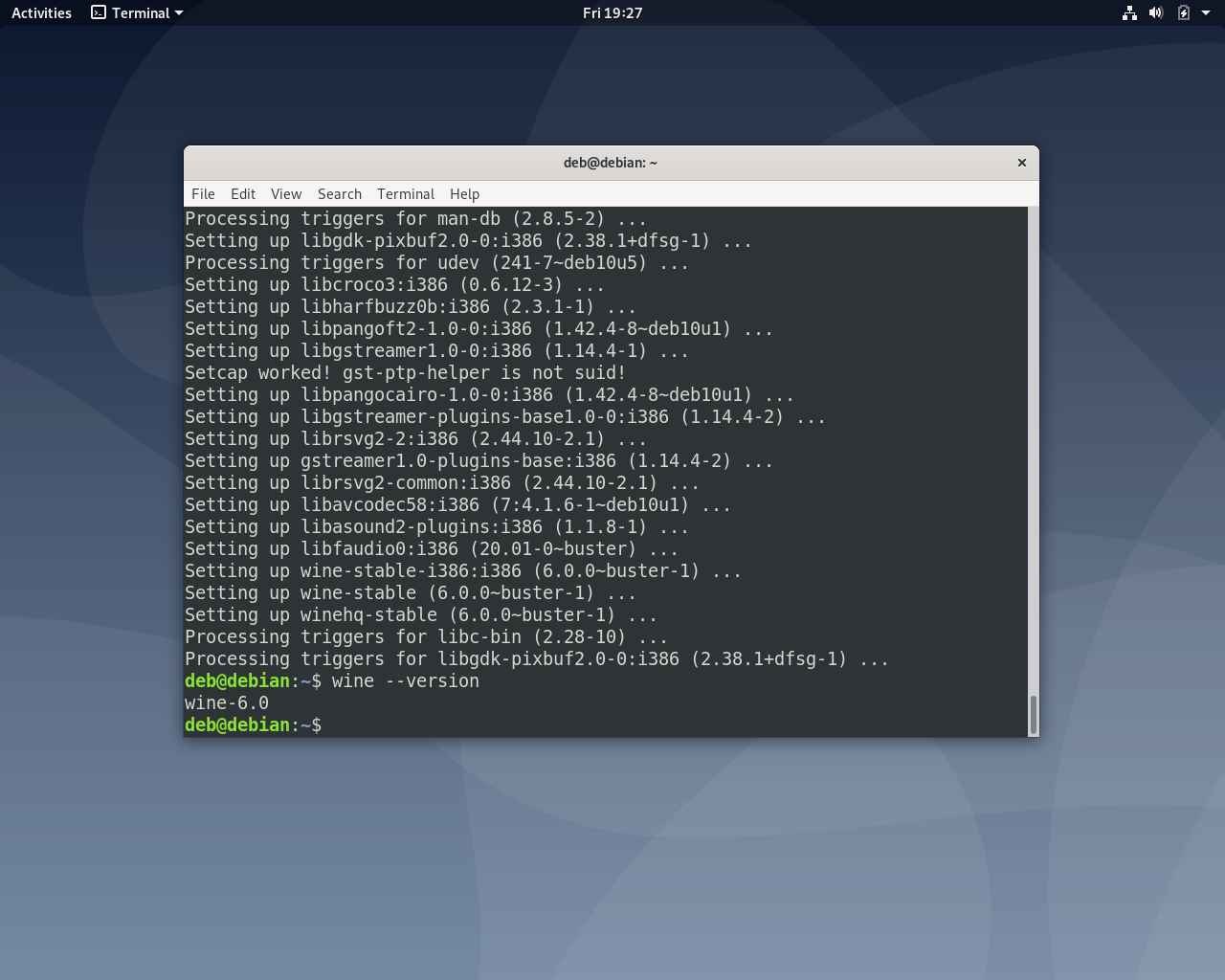
Удаление Wine из Debian
Для удаления программы необходимо выполнить в терминале команду с указанием установленного пакета. Для стабильной версии это команда:
sudo apt purge winehq-stable
Выводы
Итак, мы рассмотрели как установить wine на Debian 10. Программа активно развивается и в неё постоянно добавляется поддержка новых Windows приложений. Уже сейчас Wine справляется с запуском тысяч игр и приложений, которые могут не работать даже в режиме совместимости Windows. Это и делает программу уникальной в своем роде. Какие игры или приложения вы запускаете с помощью Wine? Делитесь в комментариях!
Статья распространяется под лицензией Creative Commons ShareAlike 4.0 при копировании материала ссылка на источник обязательна.
