Для управления обновлениями Windows можно использовать PowerShell модуль PSWindowsUpdate. Модуль PSWindowsUpdate доступен для загрузки из PowerShell Gallery и позволяет администратору просканировать, скачать, установить, удалить или скрыть обновления на локальном или удаленных рабочих станциях и серверах Windows.
Содержание:
- Установка модуля управления обновлениями PSWindowsUpdate
- Сканировать и загрузить обновления Windows с помощью PowerShell
- Установка обновлений Windows с помощью команды Install-WindowsUpdate
- >Просмотр истории установленных обновлений в Windows
- Удаление обновлений в Windows с помощью PowerShell
- Скрыть ненужные обновления Windows с помощью PowerShell
- Управление обновлениями Windows на удаленных компьютерах через PowerShell
Установка модуля управления обновлениями PSWindowsUpdate
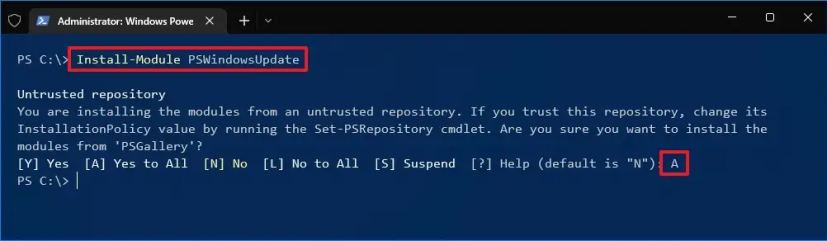
В современных версиях Windows 10/11 и Windows Server 2022/2019/2016 модуль PSWindowsUpdate можно установить из онлайн репозитория PowerShell Gallery с помощью команды:
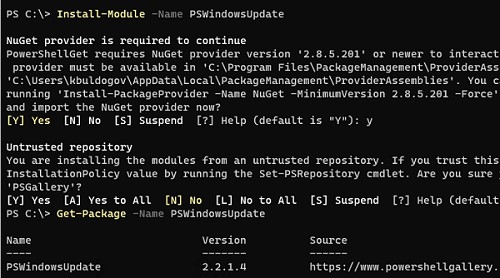
Install-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate
Подтвердите добавление репозитариев, нажав Y. Проверьте, что модуль управлениям обновлениями установлен в Windows:
Get-Package -Name PSWindowsUpdate
- В изолированной среде модуль PSWindowsUpdate можно установить в офлайн режиме;
- В старых версиях Windows для использования модуля нужно предварительно обновить версию PowerShell.
Можно удаленно установить PSWindowsUpdate на другие компьютеры в сети. Следующая команда скопирует файлы модуля на указанные компьютеры (для доступа к удаленным компьютерам используется WinRM).
$Targets = "srv1.winitpro.loc", "srv2.winitpro.loc"
Update-WUModule -ComputerName $Targets -local
Политика выполнения PowerShell скриптов в Windows по умолчанию блокирует запуск командлетов из сторонних модулей, в том числе PSWindowsUpdate. Чтобы разрешить запуск любых локальных скриптов, выполните команду:
Set-ExecutionPolicy –ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -force
Либо вы можете разрешить запускать команды модуля в текущей сессии PowerShell:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope Process
Импортируйте модуль в сессию PowerShell:
Import-Module PSWindowsUpdate
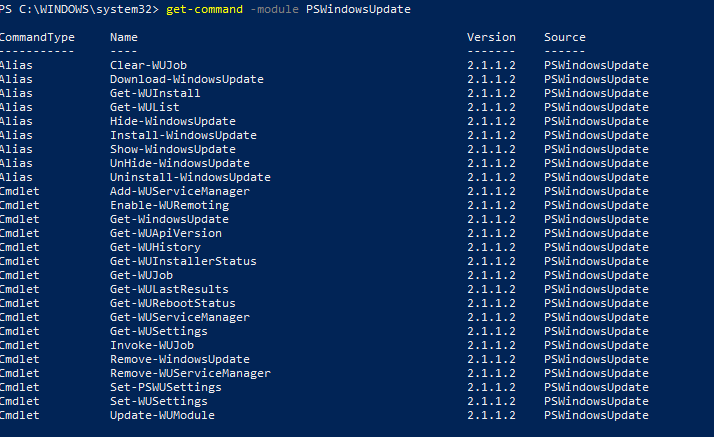
Выведите список доступных командлетов:
Get-command -module PSWindowsUpdate
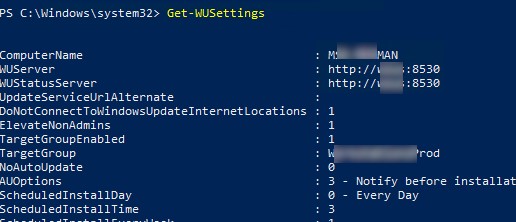
Проверить текущие настройки клиента Windows Update:
Get-WUSettings
ComputerName : WKS22122 WUServer : http://MS-WSUS:8530 WUStatusServer : http://MS-WSUS:8530 AcceptTrustedPublisherCerts : 1 ElevateNonAdmins : 1 DoNotConnectToWindowsUpdateInternetLocations : 1 TargetGroupEnabled : 1 TargetGroup : WorkstationsProd NoAutoUpdate : 0 AUOptions : 3 - Notify before installation ScheduledInstallDay : 0 - Every Day ScheduledInstallTime : 3 UseWUServer : 1 AutoInstallMinorUpdates : 0 AlwaysAutoRebootAtScheduledTime : 0 DetectionFrequencyEnabled : 1 DetectionFrequency : 4
В данном примере клиент Windows Update на компьютере настроен с помощью GPO на получение обновлений с локального сервера обновлений WSUS.
Сканировать и загрузить обновления Windows с помощью PowerShell
Чтобы просканировать компьютер на сервере обновлений и вывести список обновлений, которые ему требуется, выполните команду:
Get-WindowsUpdate
или
Get-WUList
Команда должна вывести список обновлений, которые нужно установить на вашем компьютере.
Команда Get-WindowsUpdate при первом запуске может вернуть ошибку:
Value does not fall within the expected range.
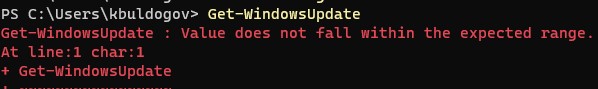
Для исправления ошибки нужно сбросить настройки агента Windows Update, перерегистрировать библиотеки и восстановить исходное состояние службы wususerv с помощью команды:
Reset-WUComponents -Verbose
Чтобы проверить, откуда получает ли Windows обновлений с серверов Windows Update в Интернете или локального WSUS, выполните команду:
Get-WUServiceManager
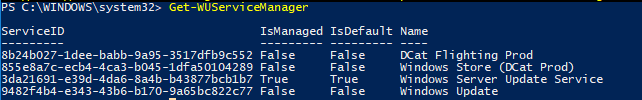
В этом примере вы видите, компьютер настроен на получение обновлений с локального сервера WSUS (Windows Server Update Service = True). В этом случае вы должны увидеть список обновлений, одобренных для вашего компьютера на WSUS.
Если вы хотите просканировать ваш компьютер на серверах Microsoft Update в Интернете (кроме обновлений Windows на этих серверах содержатся обновления Office и других продуктов), выполните команду:
Get-WUlist -MicrosoftUpdate
Вы получаете предупреждение:
Get-WUlist : Service Windows Update was not found on computer
Чтобы разрешить сканирование на Microsoft Update, выполните команду:
Add-WUServiceManager -ServiceID "7971f918-a847-4430-9279-4a52d1efe18d" -AddServiceFlag 7
Чтобы убрать определенные продукты или конкретные KB из списка обновлений, которые получает ваш компьютер, вы их можете исключить по:
- Категории (-NotCategory);
- Названию (-NotTitle);
- Номеру обновления (-NotKBArticleID).
Например, чтобы исключить из списка обновления драйверов, OneDrive, и одну конкретную KB:
Get-WUlist -NotCategory "Drivers" -NotTitle OneDrive -NotKBArticleID KB4533002
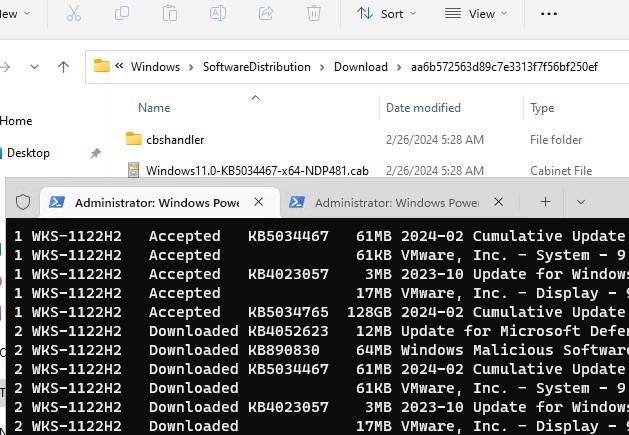
Скачать все доступные обновления на компьютер (обновления загружаются в локальный кэш обновлений в каталоге
C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution\Download
).
Get-WindowsUpdate -Download -AcceptAll
Windows загрузит все доступные патчи сервера обновлений (MSU и CAB файлы) в локальный каталог обновлений, но не запустит их автоматическую установку.
Установка обновлений Windows с помощью команды Install-WindowsUpdate
Чтобы автоматически скачать и установить все доступные обновления для вашей версии Windows с серверов Windows Update (вместо локального WSUS), выполните:
Install-WindowsUpdate -MicrosoftUpdate -AcceptAll -AutoReboot
Ключ AcceptAll включает одобрение установки для всех пакетов, а AutoReboot разрешает автоматическую перезагрузку Windows после завершения установки обновлений.
Также можно использовать следующе параметры:
- IgnoreReboot – запретить автоматическую перезагрузку;
- ScheduleReboot – задать точное время перезагрузки компьютера.
Можете сохранить историю установки обновлений в лог файл (можно использовать вместо WindowsUpdate.log).
Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll -Install -AutoReboot | Out-File "c:\$(get-date -f yyyy-MM-dd)-WindowsUpdate.log" -force
Можно установить только конкретные обновления по номерам KB:
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB2267602, KB4533002 -Install
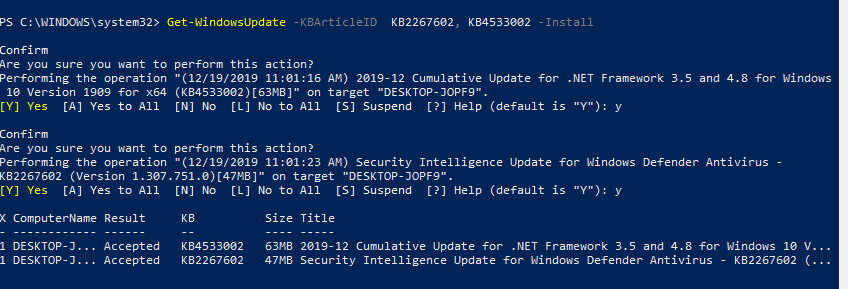
Если вы хотите пропустить некоторые обновления при установке, выполните:
Install-WindowsUpdate -NotCategory "Drivers" -NotTitle OneDrive -NotKBArticleID KB4011670 -AcceptAll -IgnoreReboot
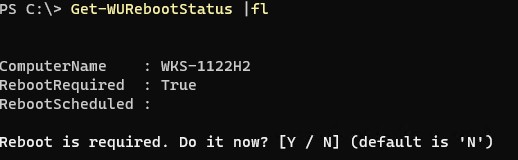
Проверить, нужна ли перезагрузка компьютеру после установки обновления (атрибуты RebootRequired и RebootScheduled):
Get-WURebootStatus
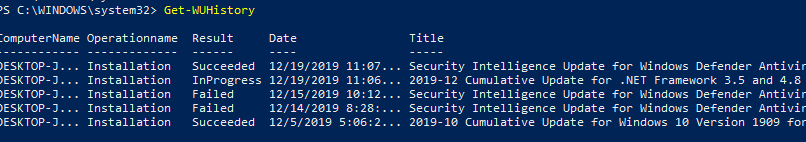
>Просмотр истории установленных обновлений в Windows
С помощью команды Get-WUHistory вы можете получить список обновлений, установленных на компьютере ранее автоматически или вручную.
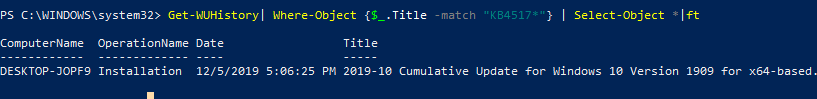
Можно получить информацию о дате установки конкретного обновления:
Get-WUHistory| Where-Object {$_.Title -match "KB4517389"} | Select-Object *|ft
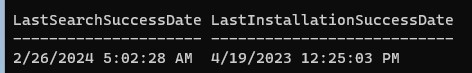
Вывести даты последнего сканирования и установки обновлении на компьютере:
Get-WULastResults |select LastSearchSuccessDate, LastInstallationSuccessDate
Удаление обновлений в Windows с помощью PowerShell
Для корректного удаления обновления Windows используется командлет Remove-WindowsUpdate. Вам достаточно указать номер KB в качестве аргумента параметра KBArticleID.
Remove-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB4011634
Скрыть ненужные обновления Windows с помощью PowerShell
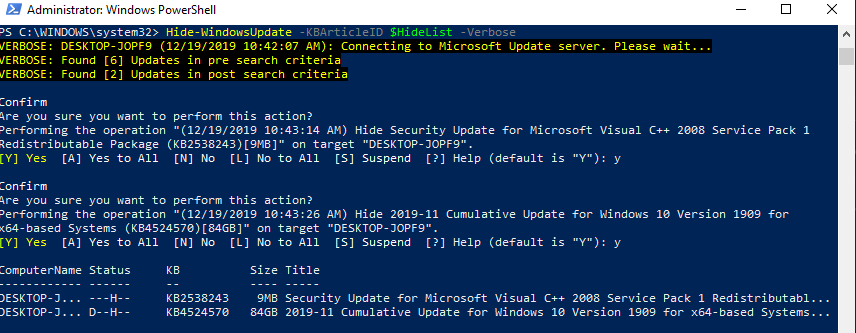
Вы можете скрыть определенные обновления, чтобы они никогда не устанавливались службой обновлений Windows Update на вашем компьютер (чаще всего скрывают обновления драйверов). Например, чтобы скрыть обновления KB2538243 и KB4524570, выполните такие команды:
$HideList = "KB2538243", "KB4524570"
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList -Hide
или используйте alias:
Hide-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList -Verbose
Теперь при следующем сканировании обновлений с помощью команды Get-WindowsUpdate скрытые обновления не будут отображаться в списке доступных для установки.
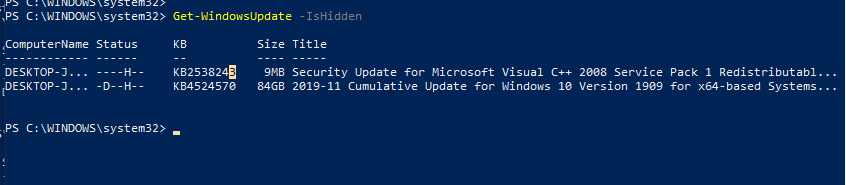
Вывести список скрытых обновлений:
Get-WindowsUpdate –IsHidden
Обратите внимание, что в колонке Status у скрытых обновлений появился атрибут H (Hidden).
Отменить скрытие обновлений можно так:
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList -WithHidden -Hide:$false
или так:
Show-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList
Управление обновлениями Windows на удаленных компьютерах через PowerShell
Практически все командлеты модуля PSWindowsUpdate позволяют управлять обновлеями на удаленных компьютерах. Для этого используется атрибут
-Computername Host1, Host2, Host3
. На удаленных компьютерах должен быть включен и настроен WinRM (вручную или через GPO). Модуль PSWindowsUpdate можно использовать для удаленного управлений обновлениями Windows как на компьютерах в домене AD, так и в рабочей группе (потребует определенной настройки PowerShell Remoting).
Для удаленного управления обновлениями компьютерах, нужно добавить имена компьютеров доверенных хостов winrm, или настроить удаленное управление PSRemoting через WinRM HTTPS:
winrm set winrm/config/client ‘@{TrustedHosts="HOST1,HOST2,…"}’
Или с помощью PowerShell:
Set-Item wsman:\localhost\client\TrustedHosts -Value wsk-w10BO1 -Force
С помощью Invoke-Command можно разрешить использовать модуль PSWindowsUpdate на удаленных компьютерах и открыть необходимые порты в Windows Defender Firewall (команда
Enable-WURemoting
):
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $computer -ScriptBlock {Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -force }
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $computer -ScriptBlock {Import-Module PSWindowsUpdate; Enable-WURemoting}
Проверить список доступных обновлений на удаленном компьютере:
Get-WUList –ComputerName server2
Скачать и установить все доступные обновлений на нескольких удаленных серверах:
$ServerNames = “server1, server2, server3”
Invoke-WUJob -ComputerName $ServerNames -Script {ipmo PSWindowsUpdate; Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll | Out-File C:\Windows\PSWindowsUpdate.log } -RunNow -Confirm:$false -Verbose -ErrorAction Ignore
Командлет Invoke-WUJob (ранее командлет назывался Invoke-WUInstall) создаст на удаленном компьютере задание планировщика, запускаемое от SYSTEM. Можно указать точное время для установки обновлений Windows:
Invoke-WUJob -ComputerName $ServerNames -Script {ipmo PSWindowsUpdate; Install-WindowsUpdate –AcceptAll -AutoReboot | Out-File C:\Windows\PSWindowsUpdate.log } -Confirm:$false -TriggerDate (Get-Date -Hour 20 -Minute 0 -Second 0)
Проверить статус задания установки обновлений:
Get-WUJob -ComputerName $ServerNames
Если команда вернет пустой список, значит задача установки на всех компьютерах выполнена.
Проверьте наличие обновления на нескольких удаленных компьютерах:
"server1","server2" | Get-WUHistory| Where-Object {$_.Title -match "KB4011634"} | Select-Object *|ft
Получить дату последней установки обновлений на всех компьютерах в домене можно с помощью командлета Get-ADComputer из модуля AD PowerShell:
$Computers=Get-ADComputer -Filter {enabled -eq "true" -and OperatingSystem -Like '*Windows*' }
Foreach ($Computer in $Computers)
{
Get-WULastResults -ComputerName $Computer.Name|select ComputerName, LastSearchSuccessDate, LastInstallationSuccessDate
}
PowerShell модуль PSWindowsUpdate удобно использовать для загрузки и установки обновлений Windows из командной строки (единственный доступны вариант в случае установки обновлений на хосты без графического интерфейса: Windows Server Core и Hyper-V Server). Также этот модуль незаменим, когда нужно одновременно запустить и проконтролировать установку обновлений сразу на множестве серверов/рабочих станциях Windows.
- To install updates on Windows 10 from PowerShell, open “PowerShell (admin),” run the “Install-Module PSWindowsUpdate” command to install the module, “Get-WindowsUpdate” to view available updates, and “Install-WindowsUpdate” to install all the cumulative updates.
- To download, install, and reboot Windows 10, open “PowerShell (admin)” and run the “Get-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll -Install -AutoReboot” command.
- The “Get-WindowsUpdate -Install -KBArticleID ‘KB5031445′” command allows you to install a specific Windows 10 update.
UPDATED 11/8/2023: Windows 10 updates happen automatically or manually through the Windows Update settings. However, if you try to patch a new installation or create a custom script to automate the process, you can use commands to download and install missing patches with the “PSWindowsUpdate” module on PowerShell.
Michal Gajda has created the PSWindowsUpdate module, and it’s available through the PowerShell Gallery. It includes the components to make it easy to check, download, and install updates on Windows 10.
In this guide, I will teach you the steps to check and install updates for Windows 10 using PowerShell.
- Update Windows 10 from PowerShell
- Manage updates with PowerShell
To check and install updates with PowerShell, use these steps:
-
Open Start on Windows 10.
-
Search for PowerShell, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
-
Type the following command to install the module to run Windows Update and press Enter:
Install-Module PSWindowsUpdate
Quick note: After installing the module, you no longer need to repeat step No. 3 to use the module and manage updates.
-
Type A and press Enter to confirm.
-
Type the following command to check for updates with PowerShell and press Enter:
Get-WindowsUpdate
-
Type the following command to install the available Windows 10 updates and press Enter:
Install-WindowsUpdate
-
Type A and press Enter to confirm.
Once you complete the steps, the latest cumulative updates will be downloaded and installed on your computer.
Manage updates with PowerShell
The PSWindowsUpdate module includes many options to manage updates. You can always use the Get-Command –Module PSWindowsUpdate command to query a list of the available commands.
1. Auto reboot system after update command
To download, install, and then reboot the computer to complete the update process, use these steps:
-
Open Start.
-
Search for PowerShell, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
-
Type the following command to download and install all the available updates, reboot the system, and press Enter:
Get-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll -Install -AutoReboot
After completing the steps, Windows 10 will download and install all the available updates, rebooting the computer to apply the changes automatically.
2. Download a specific update command
To download and install a specific update on Windows 10 from PowerShell, use these steps:
-
Open Start.
-
Search for PowerShell, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
-
Type the following command to list the available updates along with their KB numbers with PowerShell and press Enter:
Get-WindowsUpdate
-
Type the following command to download, install a specific update, reboot the system, and press Enter:
Get-WindowsUpdate -Install -KBArticleID 'KB5031445'
In the command, replace “KB5031445” with the KB name of the update you want to install.
Once you complete the steps, in this case, Windows 10 will download and install update KB5031445 on your device.
Windows 10 comes with the Windows Update Provider but has limited options compared to the PSWindowsUpdate module and is more complicated to use.
Update November 8, 2023: This guide has been updated to ensure accuracy and reflect changes.
Why You Can Trust Pureinfotech
The author combines expert insights with user-centric guidance, rigorously researching and testing to ensure you receive trustworthy, easy-to-follow tech guides. Review the publishing process.
Начиная с версии Windows 10 1709, PowerShell обзавелся несколькими командлетами позволяющими выполнить установку обновлений.

Содержание
- Проверка Наличия Обновлений
- Установка Доступных Обновлений
- Дополнительные Командлеты
- Итог
Проверка Наличия Обновлений
Прежде чем выполнить обновление, нужно убедиться в их наличии. Дальнейшие действия предполагают, что командная оболочка PowerShell была запущена от имени администратора (Win+X, выбрать в открывшемся меню пункт Windows PowerShell (администратор)).

Выполняем проверку наличия новых обновлений.
Start-WUScan
Если выполнение команды завершилось выводом списка обновлений, то значит данные обновления в системе отсутствуют. В противном случае обновлений необходимых для установки нет.
Установка Доступных Обновлений
Установка ранне найденных обновлений выполняется командлетом Install-WUUpdates. Но простой запуск данного командлета ничего не даст. Так же как и подстановка UpdateID в качестве аргумента.

В качестве аргумента командлет Install-WUUpdates ожидает массив объектов типа Microsoft.Management.Infrastructure.CimInstance[], или же любой другой объект который можно привести к данному типу.
Получить подходящий объект можно из вывода командлета Start-WUScan.
$wu = Start-WUScan
Переменная $wu в данном случае будет содержать массив объектов CimInstance. Как раз то, что необходимо командлету Install-WUUpdates.
Install-WUUpdates $wuУчитывая все вышесказанное составим итоговую команду выполнения установки обновлений.
$wu = Start-WUScan; if ($wu) {$wu; Install-WUUpdates $wu} else {echo "Обновлений пока нет! :)"}

Данная команда запускает процесс получения списка обновлений в переменную $wu, и если список не пуст, то запускается командлет Install-WUUpdates с переданным списком ей списком $wu в качестве аргумента.
Запуск данной команды, при отсутствии доступных обновлений завершится соответствующим сообщением.

Выполнение процедуры по отдельности будет выглядеть следующим образом.
# Выпоолняем получение списка обновлений в переменную $wu
$wu = Start-WUScan
# Выводим содержимое переменной $wu чтобы убедиться в наличии в ней данных (обновлений)
$wu
# Выполняем установку обновлений при условии что переменная $wu не пуста
Install-WUUpdates $wuДополнительные Командлеты
Get-WUIsPendingReboot — проверяет, необходимо ли выполнять перезагрузку операционной системы после выполнения процедуры обновления. Возможные варианты вывода True (перезагрузка необходима) или False (перезагружать не нужно).

Get-WULastScanSuccessDate — выводит дату последнего сканирования обновлений выполненного через Центр обновления Windows.

Get-WULastInstallationDate — выводит дату последней установки обновлений выполненных через Центр обновления Windows.

Install-WUUpdates -DownloadOnly … — выполняет загрузку указанного списка обновлений без установки.
Итог
Темы освещенные в данной статье: Как выполнить обновление Windows 10 последних редакций штатными средствами через PowerShell. Как выполнить проверку наличия обновлений Windows 10 в PowerShell. Как выполнить установку обновлений командлетом Install-WUUpdates.
Ways to Get Windows Update With PowerShell on Windows 10. – PowerShell options have occupied locations on the Win+X menu replacing Command prompt. Microsoft is emphasizing the use of this Command line shell on Windows 10. So let’s learn to use PowerShell to receive the Windows update on Windows 10. See a very interesting guide in this concern How to Create Restore Point on Windows 10 Using PowerShell.
PowerShell, however, was misunderstood to be the replacement for Command Prompt. This is why users did not use PowerShell as much as they use command prompt. There is nothing to be feared of while using the PowerShell. It has a completely different purpose except the inclusion and execution using commands thing in the former.You can update and upgrade your Windows version easily by using the PowerShell.
Launched in 2006, this tool has established itself to be the first choice for network administrators and advanced users altogether. Not just this, it has even extended its functionality by coming with the Linux versions as well. The Powershell, being a framework, targets to achieve configuration management and task automation. It consists of a command shell and a language based on the NET framework.
This article will tell you that how you can get Windows Update With PowerShell. So without wasting more time, let’s get started.
Ways to Get Windows Update With PowerShell in Windows 10
Section 1 – Installation of PowerShell Windows Update Module
Read the steps given below carefully to install this module on your system.
Step 1 – Go to Microsoft TechNet and download the zip file named PSWindowsupdate.zip from there.
Step 2 – Right click on the downloaded file and choose Extract all. This will make a separate folder for its components (file’s).
Step 3 – Select a destination or extract the Zip content (archive) to C: > Windows > System32 > WindowsPowerShell > v1.0 > Modules
Step 4 – After clicking extract, click on Continue on the Destination Folder Access Denied pop up.
Step 5 – Open elevated PowerShell (as an admin) and change the policy from Restricted to RemoteSigned. Just type in the following cmdlet:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
Enter Y to accept the above-mentioned command. This will allow you to run scripts of PowerShell from any unknown publisher as well.
Step 6 - Import the PSWindowsUpdate module with the following command:
Import-Module PSWindowsUpdate
Step 7 – You can also get a complete list of all cmdlets for PSWindowsUpdate through the following command:
Get-Command-Module PSWindowsUpdate
Section 2 – Add Support for other products (Optional)
Step 1 – Go to the Settings app > update & Security > Windows Update > Advanced Options to change your preferences if you wish to receive updates to other Microsoft products while updating your Windows.
Enable the same facility in PSWindowsUpdate using the following command:
Add-WUServiceManager-ServiceID 7971f918-a847-4430-9279-4a52d1efe18d
Type Y to accept the command and entering it for execution
Section 3 – Check, Install or hide Windows Update with PowerShell anytime
Step 1 – To obtain the list of all the updates, type the following cmdlet:
Get-WUInstall-MicrosoftUpdate-ListOnly
Step 2 – To obtain/ check updates and feature upgrades that are available for Windows, type the following cmdlet.
Get-WUInstall-ListOnly
Step 3 – Simply filter the updates with the full or partial title of an update to hide it from the list.
Step 4 – Now type – Hide-WUUpdate-Title “Microsoft*”-Confirm: $ False
This command will hide all the updates having the work Microsoft in their title.
Step 5 – You can even hide any update using KB ID instead of using the title. Use the following command:
Hide-WUUpdate-KBArticleID “”KB4013867” –Confirm: $False
To unhide the updates or feature upgrades:
KB ID or using filters or titles can also unhide an update in the list. Use the following cmdlet for this:
Hide-WUUpdate-Title “Microsoft*”-HideStatus: $False-Confirm: $False
To install all updates with manually handling rejection and acceptance requests from each, use the following cmdlet:
Get-WUInstall
To add additional Microsoft updates, use:
Get-WUInstall-MicrosoftUpdate
Step 8 – Enter Y to accept and N to reject each update manually.
Step 9 – Without accepting manually, switch to the automatic mode by adding the parameter Autoboot or AutoAccept to the command to restart the system.
Get-WUInstall-MicrosoftUpdate-AcceptAll-AutoReboot
Step 10 – You can hide or unhide feature upgrades like Windows installer builds as we did for the case of updates (to hide them).
Section 4 – Uninstalling an Update or to Check the Update History
Step 1 – Enter the following command to check the update history anytime:
Get-WUHistory
Step 2 – Uninstall the updates using the following cmdlet:
Get-WUUninstall-KBArticleID “KB4013867”-Confirm: $False
Section 5 – To obtain Help (the final section)
PowerShell help is also available but you need to type certain cmdlets for that. For example, to get help about Hide-WUUpdate, type the following cmdlet.
Get-Help Hide-WUUpdate
Accept the command by entering Y in the prompt. Get-Help has to be updated while running it for the first time. It is no major concern as it is only a one-time process and need not be done again and again.
That’s it; this is how you can easily Get Windows Update With PowerShell in Windows 10 anytime. Type and execute the commands carefully as failing to this can easily build-up errors in the smooth functioning of the system.
Installing Windows Updates manually can be a drag. Why not automate the entire process with PowerShell? Get started controlling Windows updates with the PSWindowsUpdate module in PowerShell!
In this tutorial, you will learn how to download and install updates on your Windows machine through PowerShell.
A FREE read only tool that scans your AD and generates multiple interactive reports for you to measure the effectiveness of your password policies against a brute-force attack. Download Specops Password Auditor now!
Prerequisites
This tutorial uses Windows 10 Build 19042 for demonstrations throughout this tutorial, but older ones, such as Windows 7 and 8.1, will work.
Installing the PSWindowsUpdate Module
The PSWindowsUpdate module is a third-party module available in PowerShell Gallery that lets you manage Windows updates from the PowerShell console. The PowerShell Gallery is the central repository where you can find and share PowerShell modules.
With the PSWindowsUpdate module, you can remotely check, install, update and remove updates on Windows servers and workstations. But first, you need to install the PSWindowsUpdate module on your machine.
1. Open PowerShell as administrator.
2. Run the Install-Module command to download and install the PSWindowUpdate module from the PowerShell gallery repository. The -Force parameter tells the command to ignore prompt messages and continue installing the module.
Install-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate -ForceIf you’re on an older version of Windows, you can download the PSWindowsUpdate module manually.
3. Next, run the Import-Module command below to import the PSWindowsUpdate module to PowerShell’s current session. Once imported, you can then use the module to manage Windows updates on your machine.
You may run into an error importing the module for the first time saying “The specified module ‘PSWindowsUpdate’ was not loaded”. In that case, you must allow executing scripts on your machine.
Run the command
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSignedto enable execute remote scripts on your computer. Now try importing thePSWindowsUpdatemodule again.
Import-Module PSWindowsUpdate4. Finally, run the command below to see all commands (Get-Command) available for the PSWindowsUpdate module. Some of these commands are what you will use to manage Windows updates on your machine. Get-Command -Module PSWindowsUpdate
Get-Command -Module PSWindowsUpdateChecking for Available Windows Updates
With the PSWindowsUpdate module installed, you can now run a command to list the updates available for your computer before installing them. Checking the list of updates is a good practice to avoid installing an update you don’t need.
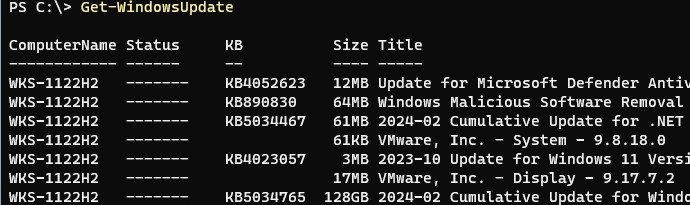
Run the Get-WindowsUpdate command to list all the Windows updates
Below, you can see the list of available Windows updates along with their Knowledge-Base (KB) numbers. Take note of any KB number of a Windows update that you may want to prevent installing later, perhaps one that you deem not important.

Perhaps you also want to check where Windows gets an update from to see if the source is trustworthy. If so, the Get-WUServiceManager command will do the trick.
Run the Get-WUServiceManager to show the list of available update services.
There’s no official documentation about the update the sources, but each is defined below:
- Microsoft Update – the standard update source
- DCat Flighting Prod – an alternative MS supdate ource for specific flighted update items (from previews, etc)
- Windows Store (DCat Prod) – normally just Windows Store, but has Dcat Prod when for insider preview PC
- Windows Update – an older update source for Windows Vista and older Windows OS.

Excluding Windows Updates from Installing
Now you’ve seen the Windows updates available, perhaps you prefer not to install some of them on your computer. In that case, you can choose not to install them by hiding them.
Run the Hide-WindowsUpdate command below to hide a Windows update tagged with the specified KB number (-KBArticleID KB4052623). You can specify the KB number you took note of in the “Checking for Available Windows Updates” section instead.
PowerShell will ask for your confirmation before executing the command. Confirm the command with the “A” key, then press Enter.
Hide-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB4052623

If you change your mind and want to install the update in the future, you can show the update similar to how you hid the update. To show the update, run the
Show-WindowsUpdatecommand along with the update’s KB number, like this:Show-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB4052623
Installing Windows Updates
Now that you can discover and exclude some updates from installing, let’s now check out how to install them.
But before installing updates, checking if updates require a system reboot is a good practice. Why? Knowing whether the Windows updates require a reboot beforehand tells you to save all your work and complete other ongoing installations before diving to the Windows update.
Now run the Get-WURebootStatus command to determine if any of the Windows updates require a reboot. The command returns either True or False value to indicate the reboot status
Below, you can see the command returned a False value, which indicates a reboot is not required. So go nuts and install the updates you deem are necessary.
Downloading and Installing All Available Updates
If you’re not picky when it comes to updates, running the Install-WindowsUpdate command on its own lets you install all available Windows updates. But perhaps, you want to install the updates without having to accept prompts. If so, you need to add the -AcceptAll parameter as shown below.
Run the Install-WindowsUpdate command below to install all available Windows updates. The -AcceptAll parameter tells the command to suppress prompts and continue installing all updates.
If you prefer to reboot your computer once the installation is completed automatically, add the -AutoReboot parameter.
Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll -AutoReboot
If you prefer to install selected updates only, add the
-KBArticleIDparameter in theInstall-WindowsUpdatecommand, followed by the update’s KB number, like this:Install-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB2267602
Checking Windows Update History
Now you have installed windows updates on your computer, but perhaps something has gone wrong during the installation. If so, you can check your update history using the Get-WUHistory command. The Get-WUHistory prints out all the installed updates to the console with their installation result.
Run the Get-WUHistory command below to check Windows update history.
Below, you can see that most of the updates have the Succeeded result status, while some have InProgress status.

Uninstalling Windows Updates
There are times when you install an update you don’t deem important at the moment, or there are updates you suspect of causing an issue on your system. In those times, you can properly uninstall the updates with the Remove-WindowsUpdate command.
Run the Remove-WindowsUpdate command below to uninstall a Windows update tagged with a specific KB number (-KBArticleID KB2267602).
PowerShell will require confirmation before executing the command. Press the “A” key and hit enter to confirm the command.
Remove-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB2267602
Enforce compliance requirements, block over 3 billion compromised passwords, and help users create stronger passwords in Active Directory with dynamic end-user feedback. Contact us today about Specops Password Policy!
Conclusion
Throughout this tutorial, you’ve learned about the PSWindowsUpdate Module. You’ve also gone through selectively installing and uninstalling Windows updates.
You’ve learned that you have full control over the Windows updates with PowerShell. Now, would you prefer installing updates in PowerShell over a GUI method? Perhaps learn more about building a Windows update report?