This section describes on how to install Xdebug.
How you install Xdebug depends on your system. There are the following possibilities:
- Linux with a package manager such
asapt,yum, or something else. - Linux without an Xdebug package with PECL.
- macOSX with homebrew, through PECL.
- Windows, with help from a wizard.
- Unix-like operating systems, from source.
Installing on Linux #
Installing Xdebug with a package manager is often the fastest way. Depending on your distribution, run the following command:
- Alpinelinux:
sudo apk add php7-pecl-xdebug, or
sudo apk add php8-pecl-xdebug - Arch Linux:
sudo pacman -S xdebug - CentOS:
sudo yum install php-xdebug - CentOS (Remi Repo):
sudo yum install php74-php-xdebug3, or
sudo yum install php80-php-xdebug3, or
sudo yum install php81-php-xdebug3 - Debian (9/stretch, testing/buster/bullseye/sid):
sudo apt-get install php-xdebug - Fedora (32):
sudo yum install php-xdebug - Fedora (Remi Repo):
sudo yum install php74-php-xdebug3 - Gentoo:
emerge dev-php/xdebug - Manjaro (20.1/Mikah):
sudo pacman -S xdebug - RHEL:
sudo yum install php-xdebug - RHEL (Remi Repo):
sudo yum install php74-php-xdebug3 - SUSE (openSUSE, Enterprise):
sudo zypper in php7-xdebug, or
sudo zypper in php8-xdebug - Ubuntu (18.04 LTS/Bionic, 20.04 LTS/Focal):
sudo apt-get install php-xdebug - Ubuntu (Ondřej Surý’s PPA):
sudo apt-get install php7.4-xdebug, or
sudo apt-get install php8.0-xdebug, or
sudo apt-get install php8.1-xdebug
Xdebug’s latest version is 3.4.2.
For packages that have the PHP version in the package name, such as in
php81-php-xdebug3, you can substitute the PHP
version with the one that matches the PHP version that you are running.
Linux distributions might be providing an old and/or outdated version.
If the package manager
installs a version that is no longer supported (see Supported Versions), please install
Xdebug with PECL, or from source
instead.
Installing with PECL #
You can install Xdebug through PECL on Linux & macOS with Homebrew.
Prerequisites:
- macOS:
- Xcode’s command line tools (run:
xcode-select).
--install - PHP installed through Homebrew.
- Xcode’s command line tools (run:
- Linux:
- GCC and associated libraries.
- PHP development headers (see Compile below).
Run:
pecl install xdebug
You should ignore any prompts to add
"extension=xdebug.so" to
php.ini — this will cause problems.
In some cases pecl will change the php.ini file to
add a configuration line to load Xdebug. You can check whether it did by
running php -v. If Xdebug shows up with a version number, than
you’re all set and you can configure Xdebug’s other functions, such as
Step Debugging, or Profiling.
If it is there, you can skip to the What’s Next?
section.
If pecl did not add the right line, skip to the Configure PHP section.
Issues on macOS #
On Apple M1 hardware, programs can either be compiled for the native M1/ARM64
architecture, or for the emulated x86_64 architecure. Sometimes there is a
mismatch with the default and PECL will fail, or Xdebug won’t load with a
message such as:
PHP Warning: Failed loading Zend extension 'xdebug.so' (tried: /opt/homebrew/lib/php/pecl/20190902/xdebug.so (dlopen(/opt/homebrew/lib/php/pecl/20190902/xdebug.so, 9): no suitable image found. Did find:
/opt/homebrew/lib/php/pecl/20190902/xdebug.so: mach-o, but wrong architecture
/opt/homebrew/lib/php/pecl/20190902/xdebug.so: stat() failed with errno=22), /opt/homebrew/lib/php/pecl/20190902/xdebug.so.so (dlopen(/opt/homebrew/lib/php/pecl/20190902/xdebug.so.so, 9): image not found)) in Unknown on line 0
You can verify what your PHP’s architecture is with:
file `which php`
If that says arm64e, then you need to run:
arch -arm64 sudo pecl install xdebug
And if it’s x86_64, then you need to run:
arch -x86_64 sudo pecl install xdebug
1 On macOS, you should have PHP installed with Homebrew.
Installing on Windows #
There are a few precompiled modules for Windows, they are all for the non-debug
version of PHP. You can get those at the download
page. Follow these instructions to get Xdebug
installed.
Installation From Source #
Obtain #
You can download the source of the latest stable release 3.4.2.
Alternatively you can obtain Xdebug from GIT:
git clone git://github.com/xdebug/xdebug.git
This will checkout the latest development version which is currently
3.5.0dev. This development branch might not always work as
expected, and may have bugs.
You can also browse the source on GitHub at https://github.com/xdebug/xdebug.
Compile #
There is a wizard available that provides you
with the correct file to download, and which paths to use.
You compile Xdebug separately from the rest of PHP. You need access to the
scripts phpize and php-config. If your system
does not have phpize and php-config, you will
need to install the PHP development headers.
Debian users can do that with:
apt-get install php-dev
And RedHat and Fedora users with:
yum install php-devel
It is important that the source version matches the installed version as there
are slight, but important, differences between PHP versions. Once you have
access to phpize and php-config, take the
following steps:
-
If you downloaded a tarball, unpack it:
tar -xzf xdebug-3.4.2.tgzYou should not
unpack the tarball inside the PHP source code tree.
Xdebug is compiled separately, all by itself, as stated above. -
Change into the source directory:
- tarball:
cd xdebug-3.4.2 - GIT clone:
cd xdebug
- tarball:
-
phpizeIf phpize is not in your path, please make sure
that it is, by expanding thePATHenvironment variable. Make sure
you use the phpize that belongs to the PHP version that you want to use Xdebug
with. See this FAQ entry if you’re having some
issues with finding which phpize to use. -
./configure --enable-xdebug -
make -
make install
Configure PHP #
-
Find out which PHP ini file to modify.
Run a script with the following to find all configuration files that PHP has
loaded:<?php var_dump(php_ini_loaded_file(), php_ini_scanned_files());
Alternatively, you can run
php --inion the command line.If there is a file with
xdebugin the name, such as
/etc/php/7.4/cli/conf.d/99-xdebug.ini, then this is the
file to use.If that file does not exist, but there are other files in a
conf.dor similar directory, you can create a new file there too.
Please name it99-xdebug.iniin that case.Otherwise, modify the
php.inifile that is displayed through
the script, orphp --inicommand.There could be more than one
php.inifile. In many set-ups there is a different one for the
command line (oftencli/php.ini) and the web server (often
fpm/php.ini).If you want to use Xdebug and
OPCache together, you must have thezend_extensionline for Xdebug
below the line for OPCache, or in a file starting with a higher number (ie.
99-xdebug.inivs20-opcache.ini), otherwise they
won’t work properly together. -
Add the following line to this PHP ini file:
zend_extension=xdebug -
Restart your webserver, or PHP-FPM, depending on what you are
using. -
Verify that Xdebug is now loaded.
Create a PHP page that calls xdebug_info(). If you request the
page through the browser, it should show you an overview of Xdebug’s settings
and log messages.On the command line, you can also run
php -v. Xdebug and its
version number should be present as in:PHP 7.4.10 (cli) (built: Aug 18 2020 09:37:14) ( NTS DEBUG ) Copyright (c) The PHP Group Zend Engine v3.4.0, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies with Zend OPcache v7.4.10-dev, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies with Xdebug v3.0.0-dev, Copyright (c) 2002-2020, by Derick Rethans
If Xdebug does not show up, or you get a warning from PHP that an
xdebug.sofile or similar was not found, you might need to use the
full path instead of justzend_extension=xdebug, such as
zend_extension=/usr/lib/php/20190902/xdebug.so.On Windows, you should place the
php_xdebug.dllin the
ext/directory, which is a child directory in your PHP
installation tree.
If you have trouble with this, please refer to the installation wizard to help you guide through this
process.
What’s Next? #
With Xdebug loaded, you can now enable individual features, such as
Step Debugging, or Profiling. Information on what these featers are,
how they work, and how to configure them is available on each feature’s
documentation page:
- Step Debugging — Analyse PHP code while it runs
- Profiling — Check your application for performance issues
- Function Trace — Show every function call, assignment, and return value
- Code Coverage Analysis — Analyse whether your tests cover your whole code base
Related Content #
- Activation and Triggers
This video explains how to activate, through triggers and other method’s Xdebug’s step debugger, profiler, and tracer.
- Xdebug 3: Diagnostics
This video teaches you how to troubleshoot your Xdebug setup. It explains how to find out how Xdebug is configured, which settings have been made, and what it is attempting to do regarding its different features.
- Xdebug 3: Modes
This video introduces Xdebug 3’s modes — the new way to configure which parts of Xdebug you have enabled.
Related Settings and Functions #
- string xdebug.log =
- integer xdebug.log_level = 7
- string xdebug.mode = develop
- xdebug_info() : mixed
Settings #
string xdebug.log = #
Configures Xdebug’s log file.
Xdebug will log to this file all file creations issues, Step Debugging
connection attempts, failures, and debug communication.
Enable this functionality by setting the value to a absolute path. Make sure
that the system user that PHP runs at (such as www-data if you are
running with Apache) can create and write to the file.
The file is opened in append-mode,
and will therefore not be overwritten by default. There is no concurrency
protection available.
The log file will include any attempt that Xdebug
makes to connect to an IDE:
[2693358] Log opened at 2020-09-02 07:19:09.616195 [2693358] [Step Debug] INFO: Connecting to configured address/port: localhost:9003. [2693358] [Step Debug] ERR: Could not connect to debugging client. Tried: localhost:9003 (through xdebug.client_host/xdebug.client_port). [2693358] [Profiler] ERR: File '/foo/cachegrind.out.2693358' could not be opened. [2693358] [Profiler] WARN: /foo: No such file or directory [2693358] [Tracing] ERR: File '/foo/trace.1485761369' could not be opened. [2693358] [Tracing] WARN: /foo: No such file or directory [2693358] Log closed at 2020-09-02 07:19:09.617510
It includes the opening time (2020-09-02 07:19:09.616195), the
IP/Hostname and port Xdebug is trying to connect to
(localhost:9003), and whether it succeeded (Connected to). The number in brackets (
client[2693358]) is the
Process ID.
It includes:
[2693358]- process ID in brackets
2020-09-02 07:19:09.616195- opening time
For Step Debugging:
INFO: Connecting to configured address/port: localhost:9003. ERR: Could not connect to debugging client. Tried: localhost:9003 (through xdebug.client_host/xdebug.client_port).
For Profiling:
ERR: File '/foo/cachegrind.out.2693358' could not be opened. WARN: /foo: No such file or directory
For Function Trace:
ERR: File '/foo/trace.1485761369' could not be opened. WARN: /foo: No such file or directory
All warnings and errors are described on the Description of errors page, with
detailed instructions on how to resolve the problem, if possible. All errors are always logged through
PHP’s internal logging mechanism (configured with error_log
in php.ini). All warnings and errors also show up in the
diagnostics log that you can view by calling xdebug_info().
Step Debugger Communication
The debugging log can also log the communication between Xdebug and an IDE.
This communication is in XML, and starts with the <init XML
element:
<init
xmlns="urn:debugger_protocol_v1" xmlns:xdebug="https://xdebug.org/dbgp/xdebug"
fileuri="file:///home/httpd/www.xdebug.org/html/router.php"
language="PHP" xdebug:language_version="7.4.11-dev"
protocol_version="1.0" appid="2693358" idekey="XDEBUG_ECLIPSE">
<engine version="3.0.0-dev"><![CDATA[Xdebug]]></engine>
<author><![CDATA[Derick Rethans]]></author>
<url><![CDATA[https://xdebug.org]]></url>
<copyright><![CDATA[Copyright (c) 2002-2020 by Derick Rethans]]></copyright>
</init>
The fileuri attribute lists the entry point of your
application, which can be useful to compare to breakpoint_set
commands to see if path mappings are set-up correctly.
Beyond the <init element, you will find the configuration of
features:
<- feature_set -i 4 -n extended_properties -v 1
-> <response
xmlns="urn:debugger_protocol_v1" xmlns:xdebug="https://xdebug.org/dbgp/xdebug"
command="feature_set" transaction_id="4" feature="extended_properties" success="1">
</response>
And continuation commands:
<- step_into -i 9
-> <response
xmlns="urn:debugger_protocol_v1" xmlns:xdebug="https://xdebug.org/dbgp/xdebug"
command="step_into" transaction_id="9"
status="break" reason="ok">
<xdebug:message filename="file:///home/httpd/www.xdebug.org/html/router.php" lineno="3">
</xdebug:message>
</response>
You can read about DBGP — A common debugger protocol specification at its dedicated documation page.
The xdebug.log_level setting controls how much information is
logged.
Many Linux distributions now use systemd, which
implements private tmp directories. This means that when PHP
is run through a web server or as PHP-FPM, the /tmp directory is
prefixed with something akin to:
/tmp/systemd-private-ea3cfa882b4e478993e1994033fc5feb-apache.service-FfWZRg
This setting can additionally be configured through the
XDEBUG_CONFIG
environment variable.
integer xdebug.log_level = 7 #
Configures which logging messages should be added to the log file.
The log file is configured with the xdebug.log setting.
The following levels are supported:
| Level | Name | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Criticals | Errors in the configuration |
| 1 | Errors | Connection errors |
| 3 | Warnings | Connection warnings |
| 5 | Communication | Protocol messages |
| 7 | Information | Information while connecting |
| 10 | Debug | Breakpoint resolving information |
Criticals, errors, and warnings always show up in the
diagnostics log that you can view by calling xdebug_info().
Criticals and errors are additionally logged through
PHP’s internal logging mechanism (configured with error_log
in php.ini).
This setting can additionally be configured through the
XDEBUG_CONFIG
environment variable.
string xdebug.mode = develop #
This setting controls which Xdebug features are enabled.
This setting can only be set in php.ini or
files like 99-xdebug.ini that are read when a PHP process starts
(directly, or through php-fpm). You can not set this value in
.htaccess and .user.ini files, which are read
per-request, nor through php_admin_value as used in Apache VHOSTs
and PHP-FPM pools.
The following values are accepted:
off- Nothing is enabled. Xdebug does no work besides checking whether
functionality is enabled. Use this setting if you want close to 0
overhead. develop- Enables Development Helpers including the overloaded var_dump().
coverage- Enables Code Coverage Analysis to generate code coverage reports, mainly in
combination with
PHPUnit. debug- Enables Step Debugging. This can be used to step through your code while it
is running, and analyse values of variables. gcstats- Enables Garbage Collection Statistics to collect statistics about PHP’s Garbage
Collection Mechanism. profile- Enables Profiling, with which you can analyse performance bottlenecks
with tools like KCacheGrind. trace- Enables the Function Trace feature, which allows you record every function
call, including arguments, variable assignment, and return value that is made
during a request to a file.
You can enable multiple modes at the same time by comma separating their
identifiers as value to xdebug.mode: xdebug.mode=develop,trace.
XDEBUG_MODE environment variable
You can also set Xdebug’s mode by setting the XDEBUG_MODE
environment variable on the command-line; this will take precedence over the
xdebug.mode setting, but will not change the value of the xdebug.mode
setting.
Some web servers have a configuration option to
prevent environment variables from being propagated to PHP and Xdebug.
For example, PHP-FPM has a clear_env
configuration setting that is on by default, which you will
need to turn off if you want to use XDEBUG_MODE.
Make sure that your web server does not clean the environment, or specifically
allows the XDEBUG_MODE environment variable to be passed on.
Functions #
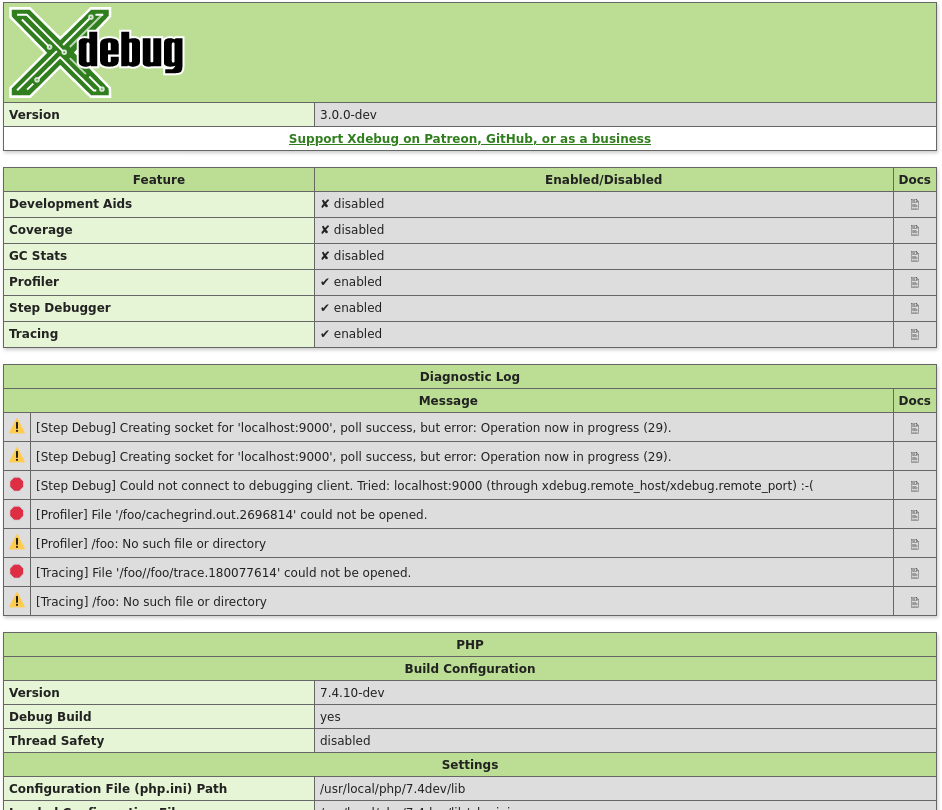
xdebug_info( string $category = null )
: mixed
#
Show and retrieve diagnostic information
This function presents APIs to retrieve information about Xdebug itself. Which
information gets returned, or displayed, depends on which arguments, or none at
all, are given.
$category =
Without arguments, this function returns an HTML page which shows diagnostic
information. It is analogous to PHP’s phpinfo() function.
The HTML output includes which mode is active, what the settings are, and
diagnostic information in case there are problems with debugging connections,
opening of files, etc.
Each warning and error in the diagnostics log also links through to the
Description of errors documentation page.
$category = 'mode' (New in Xdebug 3.1)
The function returns an array of all the
enabled modes, whether through xdebug.mode or the
XDEBUG_MODE environment variable.
Example:
<?php
var_dump( xdebug_info( 'mode' ) );
?>
Returns:
array(3) { [0] => string(5) "debug" [1] => string(7) "develop" [2] => string(5) "trace" }
$category = 'extension-flags' (New in Xdebug 3.1)
The function returns an array of all the compile flags that were enabled when
running ./configure as part of Xdebug’s compilation process.
The only flag that is available, is the compression flag. If this
flag is enabled, then the xdebug.use_compression setting is available, and enabled by default.
Profiling and Function Trace will create GZip compressed files if the
xdebug.use_compression setting is turned on (the default).
Example:
<?php
var_dump( xdebug_info( 'extension-flags' ) );
?>
Returns:
array(1) { [0] => string(11) "compression" }
For Windows[edit]
Starting with version 1.7, XAMPP includes the XDebug PHP debugger, but it needs to be configured for use. To do that, we will edit the php.ini file to configure XDebug. The Loaded Configuration File tells you which php.ini file is being used. For Windows, this is normally c:\xampp\apache\bin\php.ini.
Important note for Windows 7 & Vista users: As of August 2013 (XAMPP version 1.8.2), the file php_xdebug.dll that is included with XAMPP now works with Windows 7 & Vista. In some earlier versions of XAMPP, the distributed version of XDebug did not work correctly. The symptom of this earlier problem was that the Apache server would stop if this version of XDebug is loaded. To check that you are running the correct version of XDebug on your system, follow these instructions on the XDebug site.
We need to edit this file to configure XDebug as follows:
- Find the line implicit_flush and set it as follows:
- Find the section called [Zend] and comment out all of the lines by putting a semicolon (;) at the start of each line.
- Find the line: zend_extension = «c:\xampp\php\ext\php_xdebug.dll» and uncomment it.
- Find the [XDebug] section and uncomment all of the lines (except for the first comment line). For Windows, it should look like the example below:
[XDebug] ; Only Zend OR (!) XDebug zend_extension_ts="C:\xampp\php\ext\php_xdebug.dll" xdebug.remote_enable=true xdebug.remote_host=localhost xdebug.remote_port=10000 xdebug.remote_handler=dbgp
You do not need to enable XDebug profiling to use XDebug to debug Joomla code. Profiling allows you to find performance bottlenecks in your PHP code. However, enabling profiling with XDebug can slow down your system substantially, so it is not recommended unless you need it. To enable XDebug profiling, add these entries to your php.ini file.
xdebug.profiler_enable=1 xdebug.profiler_output_dir="C:\xampp\tmp"
For Windows 7 & Vista, you will use the file downloaded from the XDebug site. So the first line will be
zend_extension_ts="C:\xampp\php\ext\php_xdebug-2.0.0-5.2.2.dll"
For PHP version 5.3 and later, the _ts has been dropped, so the first line will read:
zend_extension="C:\xampp\php\ext\php_xdebug.dll"
In XAMPP 1.7.3 on Windows 7, XDebug may not work correctly if the path to the DLL file is in quotes. In this case, the line should be
zend_extension = C:\xampp\php\ext\php_xdebug-2.1.0-5.3-vc6.dll
For Linux[edit]
We will edit the php.ini file to configure XDebug. The Loaded Configuration File in your phpinfo display tells you what php.ini file is being used. For Linux, it will be something like /etc/php/7.2/apache2/php.ini. (The PHP configuration is available in the Administrator of your website: Administrator → System → System Information → PHP Information tab.)
Edit this file to configure XDebug as follows:
- Find the line implicit_flush and set it as follows:
- Add the following lines at the end:
;xDebug Configuration starts zend_extension = /opt/lampp/lib/php/extensions/no-debug-non-zts-20090626/xdebug.so xdebug.profiler_output_dir = "/tmp/xdebug/" xdebug.profiler_enable = On xdebug.remote_enable=On xdebug.remote_host="localhost" xdebug.remote_port=10000 xdebug.remote_handler="dbgp" ;xDebug Configuration ends
If Using php5-xdebug on Ubuntu[edit]
The xDebug Configuration detailed above can be appended to:
/etc/php5/apache2/conf.d/xdebug.ini
It should already contain the zend_extension variable and only needs the following variables added:
xdebug.profiler_enable = On xdebug.remote_enable=On xdebug.remote_host="localhost" xdebug.remote_port=10000 xdebug.remote_handler="dbgp"
Tip for Users with LAN or Remote Servers[edit]
xdebug.remote_host="localhost"
Should be set to the IP address of your Eclipse workstation [LAN users] or your public IP. For example:
xdebug.remote_host=192.168.0.199
For Mac OS X[edit]
XAMPP for Mac OS X includes the XDebug PHP debugger, but it needs to be added to the php.ini file so that XDebug runs when Apache is started. To do this, open up the php.ini file, located at /Applications/XAMPP/xamppfiles/etc/php.ini.
Edit this file to configure XDebug:
- Find the line implicit_flush and set it as follows:
- Add the following lines at the end:
;xDebug Configuration starts zend_extension="/Applications/XAMPP/xamppfiles/lib/php/php-5.3.1/extensions/no-debug-non-zts-20090626/xdebug.so" xdebug.profiler_output_dir = "/tmp/xdebug/" xdebug.profiler_enable = On xdebug.remote_enable=On xdebug.remote_host="localhost" xdebug.remote_port=10000 xdebug.remote_handler="dbgp" ;xDebug Configuration ends
Be sure to navigate to the directory where you targeted the extension and verify that the file path is correct. The folders in your XAMPP installation may be named differently.
The current (as of Sept 2010) version of the XAMPP binary for OS X contains the 2.0.4 version of XDebug which will not let you see the variable data from included files when running XDebug. You can download a newer version from the ActiveState website. Unzip and copy one of the xdebug.so files to /Applications/XAMPP/xamppfiles/lib/php/php-5.3.1/extensions/no-debug-non-zts-20090626.
Test the XDebug Installation[edit]
Now we need to verify that XDebug is installed correctly. Restart XAMPP. In Windows, we can just browse to the c:\xampp folder in Windows Explorer and double-click the program xampp-control.exe to open the application shown below.

Press the Stop button for Apache. The button with then read Start. Press Start for Apache and wait a few seconds and the green Running message will again display. Then press Exit to close the application.
In Windows, if you get ERROR: MySQL service not started [-1], you may be able to correct this by going to c:\xampp\mysql and running mysql_uninstallservice.bat followed by mysql_installservice.bat.
In Linux, to restart LAMPP execute the command:
sudo /opt/lampp/lampp restart
In Mac, open the XAMPP Control application, stop, and then start the Apache service.
Once XAMPP has been restarted, open a browser and navigate to http://localhost to display the XAMPP welcome message. (If you set XAMPP to listen to another port, you must append the port to the URL. For example: http://localhost:8080/). Press the phpinfo() link again to display the PHP information screen. Scroll down to the lower part of the screen. You should see a section for XDebug as shown below.

Look at the settings you entered in the php.ini file above. You should see these same settings in the XDebug display, as shown below.
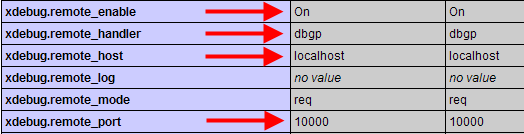
At this point, XDebug is set up correctly.

Xdebug 3 is an extremely powerful debugging tool for PHP. Although print_r(), var_dump() and dd() have their uses,
Xdebug gives more powerful debugging options: step debugging allows the ability to
view execution of each line of code, including the ability to view all variables and their
values. Code coverage is useful to identify untested code, or code which is
never executed (dead code). Development helpers improve the built-in var_dump()
function, providing stack traces etc. VS Code can also change the variable, which is useful when testing manually
particular functions while stepping through your code.
Xdebug’s step debugger allows you to interactively walk through your code to debug control flow and examine data
structuresCode coverage tells you which lines of script (or set of scripts) have been executed during a request. With this
information you can for example find out how good your unit tests are.Xdebug’s development helpers allow you to get better error messages and obtain more information from PHP’s built-in
functions. The helpers include an upgraded var_dump() function; location, stack, and argument information upon
Notices,
Warnings and Exceptions; and numerous functions and settings to tweak PHP’s behaviour.
This is how I set up VS Code to use PHP with Xdebug on
Windows using Laragon.
Install Laragon for Windows #
Laragon is a portable, isolated, fast & powerful universal development environment for PHP, Node.js, Python, Java, Go,
Ruby. It is fast, lightweight, easy-to-use and easy-to-extend.Laragon is great for building and managing modern web applications. It is focused on performance — designed around
stability, simplicity, flexibility and freedom.
Download and Install, the Laragon Full (64-bit) version. Run the
installation, next>, next>, next>. You now have a fully working WAMP stack, plus Node/NPM, git, Composer and many more
tools.
Once installed Add Laragon to Path: Menu > Tools > Path > Add Laragon to Path
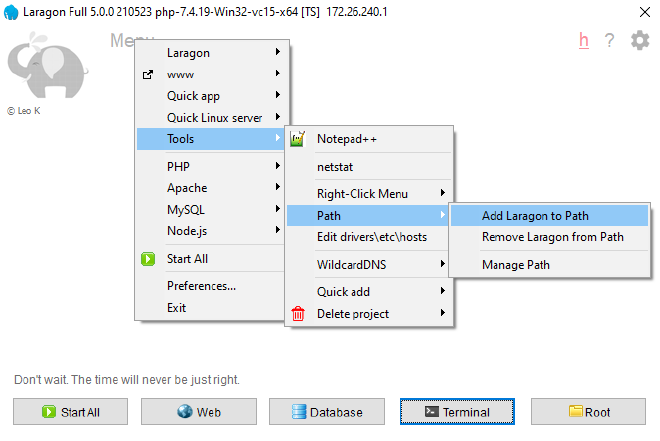
You then need to Sign out and back in for the path to be added to your user profile for all terminals and
programs (CMD / PowerShell / Terminal / VS Code etc.)
Add Xdebug to PHP #
Xdebug can be downloaded from xdebug.org, there are currently 16 versions to choose!
PHP has 4 versions, from PHP 7.2 to PHP 8.0, each version can be 32-bit (x86) or 64-bit (x64), Thread Safe (TS) or Non
Thread Safe (NTS). For Laragon v5 you would use 64 bit. Apache requires the Thread Safe (TS) version, Internet
Information Services (IIS) requires the Non-Thread Safe version (NTS). The version of Xdebug needs to match the version
of PHP. Look at the version installed to match the version required.
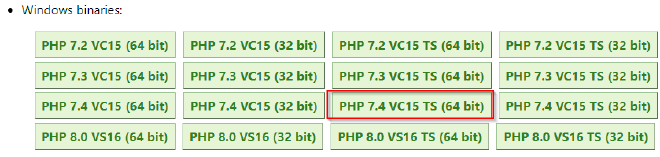
- Laragon ships with: php-7.4.19-Win32-vc15-x64 [TS] -> download PHP 7.4 VC15 TS 64 bit
- If you install: php-8.0.8-Win32-vs16-x64 [TS] -> download PHP 8.0 VS16 TS 64 bit
Once the correct dll is downloaded (e.g. ) copy it from your download folder to the php ext folder. Tip: Use
Laragon to open this folder using: Menu > PHP > dir:ext
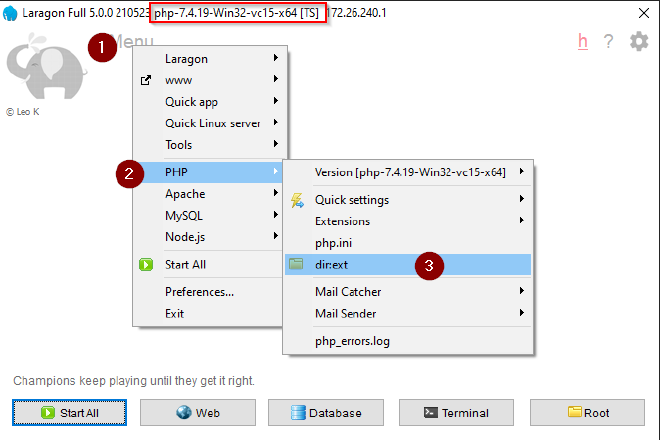
Back in Laragon enable the Xdebug extension:
Menu > PHP > Quick settings > ☑ xdebug
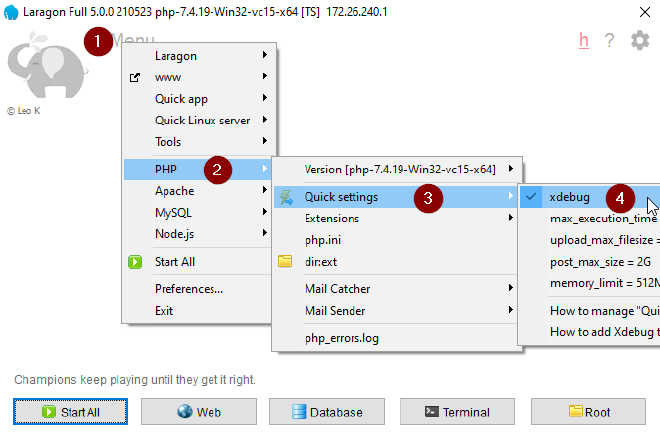
Next add Xdebug configuration to php.ini
Laragon Menu > PHP > php.ini
Wait for php.ini to open with Notepad++, scroll to the bottom of the file and add:
[xdebug]
xdebug.mode = coverage,debug,develop
Save and close the php.ini file.
This is the minimum required for debugging and code coverage, Xdebug default setting for xdebug.client_port is now **
9003** and xdebug.client_host localhost, these no longer need to be specified in the php.ini.
Check Xdebug using Laragon Web #
- Click the start button (it changes to Stop when running)
- Click Web
- Check the information on the Laragon webpage and next to the PHP version click info
The phpinfo() page will display, check Xdebug is displayed
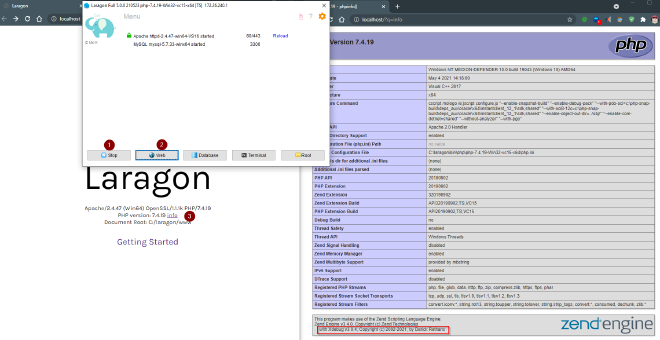
Scroll down and see the section on Xdebug, check coverage, debug and develop features are ticked.
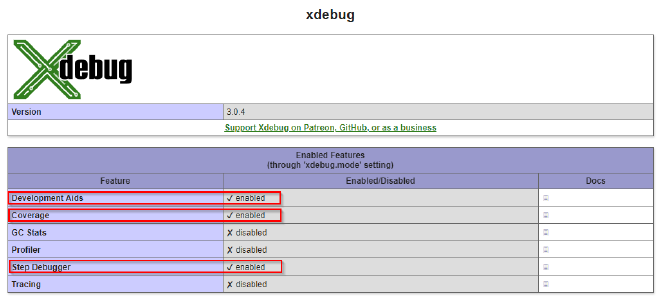
Install VS Code #
Code editing. Redefined. Free. Built on open source. Runs everywhere.
Download for Windows
The installer is straightforward, run, next, next finish.
Add Xdebug extension for VS Code #
Open VS Code and install the extension: Press F1, press Backspace to delete the > and
type ext install php-debug
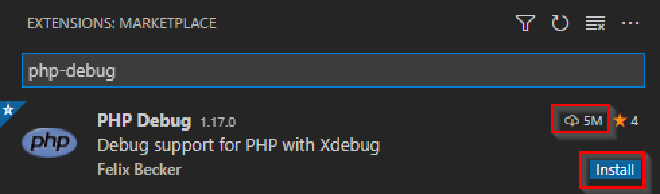
There are several extensions with the same name, install the one with 5M downloads.
Configure VS Code #
Next VS Code needs to have a launch script created, select Run from the menu and click Add Configuration…
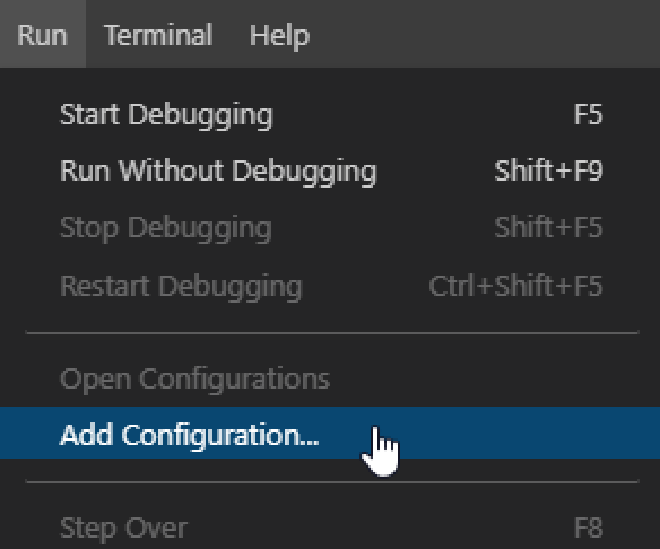
This will auto generate a launch.json file. If you are prompted for a language select PHP. The file can be
closed.
Run test code from CLI #
Create a basic script to test the setup. Create a directory in the Laragon www directory, i.e. C:\laragon\www\ **
xdebug-test**, call the file example.php
<?php
$message = "<h1>Hello, world</h1>";
$xdebugBreak = xdebug_break();
echo $message;
?>
- Click the Run and Debug menu
- Change the drop-down options to Launch currently open script
- Click the Run icon
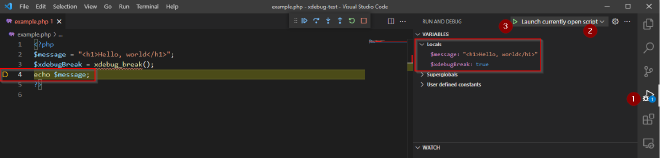
Notice although no debug point was created the script has triggered debugging after the xdebug_break() line. You can
also see the local variables.
The xdebug_break() function is useful when setting up Xdebug, if Xdebug isn’t loaded an exception will be thrown
instead! If you get this error re-check Xdebug has been enabled and the php.ini has xdebug.mode line as above.
It is also possible to set a different version of PHP to run from the command line. See troubleshooting below.
Fatal error: Uncaught Error: Call to undefined function xdebug_break() in
C:\laragon\www\xdebug-test\index.php:3 Stack trace: #0 {main} thrown in
C:\laragon\www\xdebug-test\example.php on line 3
Install Xdebug helper on Chrome #
For debugging on a web page a helper extension can be installed for Google Chrome browser (it is also available on other
browsers).
- Xdebug helper Offered by: Wrep
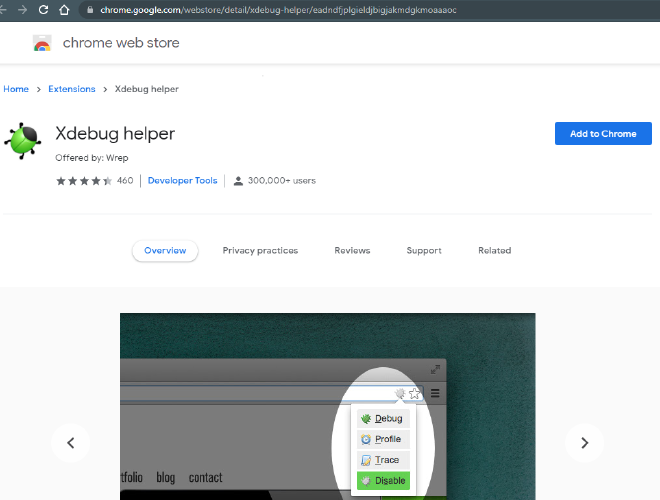
Click Add to Chrome (if you get a notification to add to Chrome click that too). Then find the grey xdebug helper
icon in your list of icons (it maybe under the jigsaw icon), click it and select debug, I find it is useful to click the
pin too, which will display the icon in the main icon it will turn green.
Debug code in a browser #
In VS Code:
- Click the Run and Debug menu
- Change the drop-down options to Listen for Xdebug
- Click the Run icon
The bar on the bottom of VS Code will display orange with the text Listen for Xdebug (xdebug-test)
Rename the file index.php
In Laragon:
- Click Menu
- Click www
- Select the xdebug-test folder
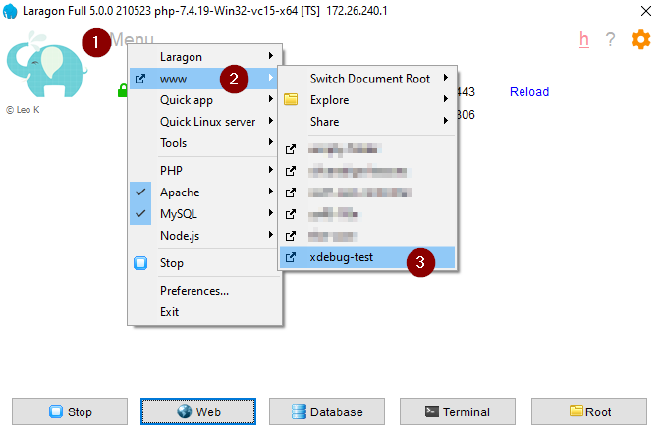
Your web browser will launch, switch to VS Code and you will see the debug session has stopped as before.
If it doesn’t automatically stop check the debug icon is green, if it is grey click it and select debug, then refresh
the page.
The xdebug_break() function has now served its purpose, you can continue to use that function, however when the Xdebug
is disabled the code will throw an exception. Delete the line with the Xdebug function, press F9 to toggle a breakpoint,
a red dot will display to the right of the selected line.
If you are still debugging press F5 to continue. Refresh the webpage page and debugging will trigger at the breakpoint.
Refresh the webpage and the debugging will stop at the breakpoint.
Debug actions #
Once a debug session starts, the Debug toolbar will appear on the top of the editor.

- Continue / Pause
F5 - Step Over
F10 - Step Into
F11 - Step Out
Shift+F11 - Restart
Ctrl+Shift+F5 - Stop
Shift+F5
For more information on how to use debug see the links in Further information, which link to official documentation and
official YouTube video.
Troubleshooting #
Port 9003 is in use #
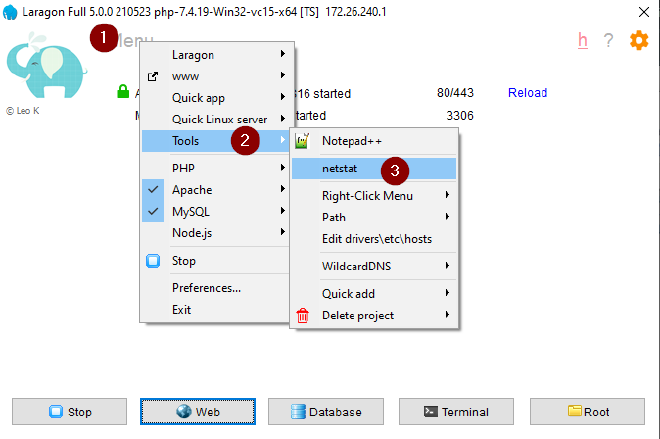
If there are any problems with port 9003 being used by another application run netstat
From Laragon:
- Menu
- Tools
- netstat
Wait a few seconds and Notepad++ will open with the stats.
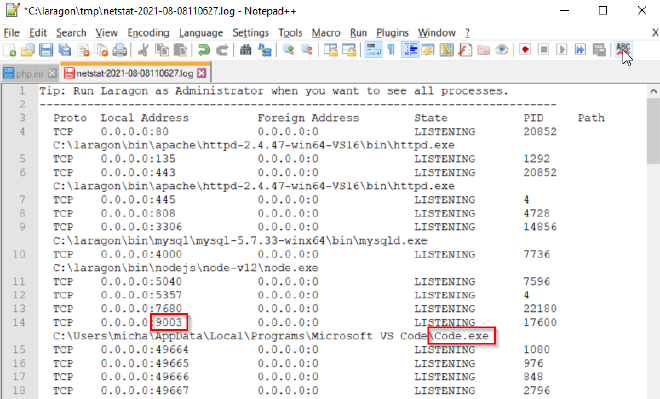
The important line is for port 9003, this is required for Xdebug to work, this example is correct, I have set VS
Code to listen for Xdebug. If another program is using this port then change the port Xdebug uses and VS Code listens
on:
- php.ini, e.g. add the line for Xdebug to use port 9004
[xdebug]
xdebug.mode = coverage,debug,develop
xdebug.client_port = 9004
- VS Code open launch.json (in the .vscode directory), change the two locations from “port”: 9003 to »
port»: 9004
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Listen for Xdebug",
"type": "php",
"request": "launch",
"port": 9004
},
{
"name": "Launch currently open script",
"type": "php",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${file}",
"cwd": "${fileDirname}",
"port": 0,
"runtimeArgs": [
"-dxdebug.start_with_request=yes"
],
"env": {
"XDEBUG_MODE": "debug,develop",
"XDEBUG_CONFIG": "client_port=${port}"
}
},
{
"name": "Launch Built-in web server",
"type": "php",
"request": "launch",
"runtimeArgs": [
"-dxdebug.mode=debug",
"-dxdebug.start_with_request=yes",
"-S",
"localhost:0"
],
"program": "",
"cwd": "${workspaceRoot}",
"port": 9004,
"serverReadyAction": {
"pattern": "Development Server \\(http://localhost:([0-9]+)\\) started",
"uriFormat": "http://localhost:%s",
"action": "openExternally"
}
}
]
}
In Laragon, next to Apache click Reload. Click web button and info, as previously, scroll down to Xdebug and
look for xdebug.client_port:
| Directive | Local Value |
|---|---|
| …. | …. |
| xdebug.client_port | 9004 |
| …. | …. |
Refresh the webpage created earlier and Xdebug will now work on port 9004.
Check the Xdebug helper icon is green, if it was grey click it and select Debug, wait for it to turn green and refresh
the page once more.
PHP CLI is different from the PHP used by Apache #
Laragon makes is easy to switch versions of PHP, this can lead to the version used by Apache being different from the
one used by VS Code or the command line.
PHP 7.4.19 (cli) (built: May 4 2021 14:24:38) ( ZTS Visual C++ 2017 x64 )
Copyright (c) The PHP Group
Zend Engine v3.4.0, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies
with Xdebug v3.0.4, Copyright (c) 2002-2021, by Derick Rethans
The output for PHP is slightly different, the important lines are PHP 7.4.19 should be the same as used by Apache
and with Xdebug v3…, if the PHP version is different see Add Laragon to all terminals below. If they are the same
PHP version, but Xdebug doesn’t display check the php.ini and Xdebug is enabled, see Add Xdebug to PHP above.
Add Laragon to all terminals #
Just click Menu > Tools > PATH environment variable > Add Laragon to Path

You then need to Sign out and back in for the path to be added to your user profile for all terminals and
programs (CMD / PowerShell / Terminal / VS Code etc.)
One point to note: if you change PHP version, you need to run Remove Laragon from Path, log off and back on. Then **
Add Laragon to Path** log off and back on to update the path set in user profile!
PHP and all the other Laragon applications will then be available in all terminals and applications, including VS Code.
Known problems #
Port 9003 conflicts with Nginx #
- Port conflict when using xdebug with nginx #374
Laragon configures Nginx using laragon/etc/nginx/php_upstream.conf, which has the conflicting post 9003 with
xDebug.
upstream php_upstream {
server 127.0.0.1:9003 weight=1 max_fails=1 fail_timeout=1;
server 127.0.0.1:9004 weight=1 max_fails=1 fail_timeout=1;
}
The workaround is to change the port used by xDebug in php.ini
[xdebug]
zend_extension = xdebug-3.2.0-8.2-vs16-nts-x86_64
xdebug.mode = coverage,debug,develop
debug.client_port = 9000
Xdebug changed the default port from 9000 to 9003 a few years ago. This will conflict with Nginx using the same
port 9003, the work-around is to use the original post 9000.
netstat #
To check which posts are in run netstat:
- Laragon Start all
- Run Laragon menu > Tools > netstat
- Notepad++ will open with the results
- Look for port 9000 and 9003
Xdebug can not be automatically enabled #
- Xdebug can not be automatically enabled #332
When Xdebug is downloaded and copied to the ext directory, when switching to Lagaon and try to enable in Extensions
or Quick settings, Laragon does not automatically add the Xdebug extension.
It is listed in the list of Extensions, when clicked the menu closes. If Apache is running it is restarted. However,
the extension isn’t added to php.ini.
The workaround is to manually add the extension to php.ini:
[xdebug]
zend_extension = xdebug-3.2.0-8.2-vs16-nts-x86_64
xdebug.mode = coverage,debug,develop
Laragon will happily toggle the Xdebug extension on and off via Extensions or Quick settings.
Further information #
- Xdebug 3 — Documentation — full documentation for Xdebug 3
- YouTube Xdebug 3 Documentation — by Derick
Rethans — A series of videos to explain how Xdebug 3 and all of its features work. - Debugging in VS Code — official VS Code documentation.
- Laragon’s discussions — useful GitHub discussions for anything
Laragon related, you may see some answers from me too 😃
Unless specifically mentioned, each setting can be set in
php.ini, files like 99-xdebug.ini, but also in
Apache’s .htaccess and PHP-FPM’s .user.ini files.
A select set of settings can be set through an XDEBUG_CONFIG
environment variable. In this situation, the xdebug. part should
be dropped from the setting name. An example of this is:
The documentation for each setting below will indicate if it can be set through
XDEBUG_CONFIG.
integer xdebug.cli_color = 0 #
If this setting is 1, Xdebug will color var_dumps and stack traces
output when in CLI mode and when the output is a tty. On Windows, the ANSICON tool needs to be
installed.
If the setting is 2, then Xdebug will always color var_dumps and stack
trace, no matter whether it’s connected to a tty or whether ANSICON is
installed. In this case, you might end up seeing escape codes.
See this article for
some more information.
This setting can additionally be configured through the
XDEBUG_CONFIG
environment variable.
string xdebug.client_discovery_header = «HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR,REMOTE_ADDR» #
If xdebug.client_discovery_header is configured to be a non-empty string, then the
value is used as key in the $_SERVER superglobal array to determine
which header to use to find the IP address or hostname to use for ‘connecting
back to’. This setting is only used in combination with
xdebug.discover_client_host and is otherwise ignored.
For example, if xdebug.client_discovery_header is set to
HTTP_FORWARD_HOST, then Xdebug will check
$_SERVER['HTTP_FORWARD_HOST'] to obtain the IP address to use for
‘connecting back’.
It is possible to configure multiple fallbacks by using a comma separated
list of values. For example if you want to use HTTP_FORWARD_HOST
first, and then also want to check REMOTE_ADDR, then you set
xdebug.client_discovery_header to
HTTP_FORWARD_HOST,REMOTE_ADDR.
PHP automatically prepends HTTP_, and converts
- to _, for received HTTP header names. The
THIS-IS-MY-HOST HTTP header is converted into
$_SERVER['HTTP_THIS_IS_MY_HOST']. Therefore, the
xdebug.client_discovery_header needs to be set to
HTTP_THIS_IS_MY_HOST to match this.
If you have logging enabled, and set the xdebug.log_level setting to
10, then Xdebug will list every header, the header value, and the
used header (if any) when attempting to find the IP address to connect back
to.
Xdebug 3.2 and later no longer fall back to the
$_SERVER['HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR'] and
$_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR'] header values by default. If you want
these headers to be used as well, you specifically need to add these to the
list of headers, by setting xdebug.client_discovery_header to
YOUR_OWN_HEADER,HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR,REMOTE_ADDR.
string xdebug.client_host = localhost #
Configures the IP address or hostname where Xdebug will attempt to connect to when initiating a
debugging connection. This address should be the address of the machine where your IDE or debugging
client is listening for incoming debugging connections.
On non-Windows platforms, it is also possible to configure a Unix domain socket which is supported by
only a select view debugging clients. In that case, instead of the hostname or IP address, use
unix:///path/to/sock.
If xdebug.discover_client_host is enabled then Xdebug will only use the value of this setting in
case Xdebug can not connect to an IDE using the information it obtained from HTTP headers. In that
case, the value of this setting acts as a fallback only.
This setting can additionally be configured through the
XDEBUG_CONFIG
environment variable.
integer xdebug.client_port = 9003 #
The port to which Xdebug tries to connect on the remote host. Port
9003 is the default for both Xdebug and the Command Line Debug Client.
As many clients use this port number, it is best to leave this setting
unchanged.
This setting can additionally be configured through the
XDEBUG_CONFIG
environment variable.
string xdebug.cloud_id = #
With this setting you configure Xdebug for use with Xdebug Cloud. It needs to match one of the
tokens from your profile
page.
Your IDE needs to be configured with the same token for Xdebug and your IDE to
communicate through Xdebug Cloud.
In PhpStorm you can find this setting under:
File | Settings | PHP | Debug | Xdebug Cloud for Windows and Linux
PhpStorm | Preferences | PHP | Debug | Xdebug Cloud for macOS
boolean xdebug.collect_assignments = false #
This setting, defaulting to 0, controls whether Xdebug should add
variable assignments to function traces. Assign-by-var (=&)
assignments are included too.
boolean xdebug.collect_params = true #
Introduced in Xdebug >= 3.3
If enabled (default), files created with the Function Trace feature will
include all arguments to functions and methods.
When disabled, the argument to each function and method will not be present
in the trace files.
boolean xdebug.collect_return = false #
This setting, defaulting to 0, controls whether Xdebug should write the
return value of function calls to the trace files.
integer xdebug.connect_timeout_ms = 200 #
The amount of time in milliseconds that Xdebug will wait for on an
IDE to acknowledge an incoming debugging connection. The default value of 200
ms should in most cases be enough. In case you often get dropped debugging
requests, perhaps because you have a high latency network, or a development box
far away from your IDE, or have a slow firewall, then you can should increase
this value.
Please note that increasing this value might mean that your requests seem to
‘hang’ in case Xdebug tries to establish a connection, but your IDE is not
listening.
boolean xdebug.discover_client_host = false #
If enabled, Xdebug will first try to connect to the client that made the
HTTP request. It checks the $_SERVER['HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR'] and
$_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR'] variables to find out which hostname or IP
address to use.
If xdebug.client_discovery_header is configured, then the $_SERVER
variable with that configured name will be checked instead of the default variables.
If Xdebug can not connect to a debugging client as found in one of the HTTP
headers, it will fall back to the hostname or IP address as configured by the
xdebug.client_host setting.
This setting does not apply for debugging through the CLI, as the
$_SERVER header variables are not available there.
This setting can additionally be configured through the
XDEBUG_CONFIG
environment variable.
Please note that there is no filter
available, and anybody who can connect to the webserver will then be able to
start a debugging session, even if their address does not match
xdebug.client_host.
string xdebug.dump.* = Empty #
* can be any of COOKIE, FILES, GET, POST, REQUEST, SERVER, SESSION.
These seven settings control which data from the superglobals is shown when an
error situation occurs.
Each of those php.ini setting can consist of a comma separated list of
variables from this superglobal to dump, or * for all of them.
Make sure you do not add spaces in this setting.
In order to dump the REMOTE_ADDR and the REQUEST_METHOD when an error
occurs, and all GET parameters, add these settings:
xdebug.dump.SERVER = REMOTE_ADDR,REQUEST_METHOD xdebug.dump.GET = *
boolean xdebug.dump_globals = true #
When this setting is set to true, Xdebug adds the values
of the super globals as configured through the xdebug.dump.* to on-screen stack
traces and the error log (if enabled).
boolean xdebug.dump_once = true #
Controls whether the values of the superglobals should be dumped on all
error situations (set to 0) or only on the first (set to 1).
boolean xdebug.dump_undefined = false #
If you want to dump undefined values from the superglobals you should set
this setting to 1, otherwise leave it set to 0.
string xdebug.file_link_format = #
This setting determines the format of the links that are made in
the display of stack traces where file names are used. This allows IDEs to set
up a link-protocol that makes it possible to go directly to a line and file by
clicking on the filenames that Xdebug shows in stack traces. An example format might look like:
myide://%f@%l
The possible format specifiers are:
| Specifier | Meaning |
|---|---|
| %f | the filename |
| %l | the line number |
For various IDEs/OSses there are some instructions listed on how to make this work:
PhpStorm
In the configuration file, add the following line, including the single
quotes. This uses PhpStorm’s REST API.
xdebug.file_link_format='javascript: var r = new XMLHttpRequest; r.open("get", "https://localhost:63342/api/file/%f:%l");r.send()'
Firefox on Linux
- Open about:config
- Add a new boolean setting «network.protocol-handler.expose.xdebug» and set it to «false»
- Add the following into a shell script
~/bin/ff-xdebug.sh:#! /bin/sh f=`echo $1 | cut -d @ -f 1 | sed 's/xdebug:\/\///'` l=`echo $1 | cut -d @ -f 2`
Add to that one of (depending whether you have komodo, gvim or netbeans):
komodo $f -l $lgvim --remote-tab +$l $fnetbeans "$f:$l"
- Make the script executable with
chmod +x ~/bin/ff-xdebug.sh - Set the xdebug.file_link_format setting to
xdebug://%f@%l
Windows and Netbeans
- Create the file
netbeans.batand save it in your path (C:\Windowswill work):@echo off setlocal enableextensions enabledelayedexpansion set NETBEANS=%1 set FILE=%~2 set FILE=!FILE:%%5C=\! %NETBEANS% --nosplash --console suppress --open "%FILE:~19%" nircmd win activate process netbeans.exe
Note: Remove the last line if you don’t have
nircmd. - Save the following code as
netbeans_protocol.reg:Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\netbeans] "URL Protocol"="" @="URL:Netbeans Protocol" [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\netbeans\DefaultIcon] @="\"C:\\Program Files\\NetBeans 7.1.1\\bin\\netbeans.exe,1\"" [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\netbeans\shell] [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\netbeans\shell\open] [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\netbeans\shell\open\command] @="\"C:\\Windows\\netbeans.bat\" \"C:\\Program Files\\NetBeans 7.1.1\\bin\\netbeans.exe\" \"%1\""
Note: Make sure to change the path to Netbeans (twice), as well as
thenetbeans.batbatch file if you saved it somewhere else
thanC:\Windows\. - Double click on the
netbeans_protocol.regfile to import it
into the registry. - Set the xdebug.file_link_format setting to
xdebug.file_link_format =
"netbeans://open/?f=%f:%l"
string xdebug.filename_format = …%s%n #
This setting determines the format with which Xdebug renders
filenames in HTML stack traces (default: ...%s%n) and location
information through the overloaded xdebug_var_dump() (default:
%f).
The possible format specifiers are listed in this table. The example output is
rendered according to the full path
/var/www/vendor/mail/transport/mta.php.
| Specifier | Meaning | Example Output |
|---|---|---|
| %a | Ancester: Two directory elements and filename | mail/transport/mta.php |
| %f | Full path | /var/www/vendor/mail/transport/mta.php |
| %n | Name: Only the file name | mta.php |
| %p | Parent: One directory element and the filename | transport/mta.php |
| %s | Directory separator | / on Linux, OSX and other Unix-like systems, \ on Windows |
integer xdebug.force_display_errors = 0 #
If this setting is set to 1 then errors will
always be displayed, no matter what the setting of PHP’s display_errors
is.
integer xdebug.force_error_reporting = 0 #
This setting is a bitmask, like error_reporting.
This bitmask will be logically ORed with the bitmask represented by error_reporting
to dermine which errors should be displayed. This setting can only be
made in php.ini and allows you to force certain errors from being
shown no matter what an application does with ini_set().
string xdebug.gc_stats_output_name = gcstats.%p #
This setting determines the name of the file that is used to dump
garbage collection statistics into. The setting specifies the format with format specifiers, very
similar to sprintf() and strftime(). There are several format specifiers
that can be used to format the file name.
See the xdebug.trace_output_name documentation for the supported
specifiers.
integer xdebug.halt_level = 0 #
This setting allows you to configure a mask that determines
whether, and which, notices and/or warnings get converted to errors. You can
configure notices and warnings that are generated by PHP, and notices and
warnings that you generate yourself (by means of trigger_error()). For example,
to convert the warning of strlen() (without arguments) to an error, you would
do:
ini_set('xdebug.halt_level', E_WARNING);
strlen();
echo "Hi!\n";
Which will then result in the showing of the error message, and the abortion
of the script. echo "Hi!\n"; will not be executed.
The setting is a bit mask, so to convert all notices and warnings into
errors for all applications, you can set this in php.ini:
xdebug.halt_level=E_WARNING|E_NOTICE|E_USER_WARNING|E_USER_NOTICE
The bitmask only supports the four level that are mentioned above.
string xdebug.idekey = *complex* #
Controls which IDE Key Xdebug should pass on to the debugging client or
proxy. The IDE Key is only important for use with the DBGp Proxy Tool,
although some IDEs are incorrectly picky as to what its value is.
The default is based on the DBGP_IDEKEY environment setting. If
it is not present, the default falls back to an empty string.
If this setting is set to a non-empty string, it selects its value over
DBGP_IDEKEY environment variable as default value.
The internal IDE Key also gets updated through debugging session management
and overrides the value of this setting as is explained in the
Step Debugging documentation.
This setting can additionally be configured through the
XDEBUG_CONFIG
environment variable.
string xdebug.log = #
Configures Xdebug’s log file.
Xdebug will log to this file all file creations issues, Step Debugging
connection attempts, failures, and debug communication.
Enable this functionality by setting the value to a absolute path. Make sure
that the system user that PHP runs at (such as www-data if you are
running with Apache) can create and write to the file.
The file is opened in append-mode,
and will therefore not be overwritten by default. There is no concurrency
protection available.
The log file will include any attempt that Xdebug
makes to connect to an IDE:
[2693358] Log opened at 2020-09-02 07:19:09.616195 [2693358] [Step Debug] INFO: Connecting to configured address/port: localhost:9003. [2693358] [Step Debug] ERR: Could not connect to debugging client. Tried: localhost:9003 (through xdebug.client_host/xdebug.client_port). [2693358] [Profiler] ERR: File '/foo/cachegrind.out.2693358' could not be opened. [2693358] [Profiler] WARN: /foo: No such file or directory [2693358] [Tracing] ERR: File '/foo/trace.1485761369' could not be opened. [2693358] [Tracing] WARN: /foo: No such file or directory [2693358] Log closed at 2020-09-02 07:19:09.617510
It includes the opening time (2020-09-02 07:19:09.616195), the
IP/Hostname and port Xdebug is trying to connect to
(localhost:9003), and whether it succeeded (Connected to). The number in brackets (
client[2693358]) is the
Process ID.
It includes:
[2693358]- process ID in brackets
2020-09-02 07:19:09.616195- opening time
For Step Debugging:
INFO: Connecting to configured address/port: localhost:9003. ERR: Could not connect to debugging client. Tried: localhost:9003 (through xdebug.client_host/xdebug.client_port).
For Profiling:
ERR: File '/foo/cachegrind.out.2693358' could not be opened. WARN: /foo: No such file or directory
For Function Trace:
ERR: File '/foo/trace.1485761369' could not be opened. WARN: /foo: No such file or directory
All warnings and errors are described on the Description of errors page, with
detailed instructions on how to resolve the problem, if possible. All errors are always logged through
PHP’s internal logging mechanism (configured with error_log
in php.ini). All warnings and errors also show up in the
diagnostics log that you can view by calling xdebug_info().
Step Debugger Communication
The debugging log can also log the communication between Xdebug and an IDE.
This communication is in XML, and starts with the <init XML
element:
<init
xmlns="urn:debugger_protocol_v1" xmlns:xdebug="https://xdebug.dev/dbgp/xdebug"
fileuri="file:///home/httpd/www.xdebug.dev/html/router.php"
language="PHP" xdebug:language_version="7.4.11-dev"
protocol_version="1.0" appid="2693358" idekey="XDEBUG_ECLIPSE">
<engine version="3.0.0-dev"><![CDATA[Xdebug]]></engine>
<author><![CDATA[Derick Rethans]]></author>
<url><![CDATA[https://xdebug.dev]]></url>
<copyright><![CDATA[Copyright (c) 2002-2020 by Derick Rethans]]></copyright>
</init>
The fileuri attribute lists the entry point of your
application, which can be useful to compare to breakpoint_set
commands to see if path mappings are set-up correctly.
Beyond the <init element, you will find the configuration of
features:
<- feature_set -i 4 -n extended_properties -v 1
-> <response
xmlns="urn:debugger_protocol_v1" xmlns:xdebug="https://xdebug.dev/dbgp/xdebug"
command="feature_set" transaction_id="4" feature="extended_properties" success="1">
</response>
And continuation commands:
<- step_into -i 9
-> <response
xmlns="urn:debugger_protocol_v1" xmlns:xdebug="https://xdebug.dev/dbgp/xdebug"
command="step_into" transaction_id="9"
status="break" reason="ok">
<xdebug:message filename="file:///home/httpd/www.xdebug.dev/html/router.php" lineno="3">
</xdebug:message>
</response>
You can read about DBGP — A common debugger protocol specification at its dedicated documation page.
The xdebug.log_level setting controls how much information is
logged.
Many Linux distributions now use systemd, which
implements private tmp directories. This means that when PHP
is run through a web server or as PHP-FPM, the /tmp directory is
prefixed with something akin to:
/tmp/systemd-private-ea3cfa882b4e478993e1994033fc5feb-apache.service-FfWZRg
This setting can additionally be configured through the
XDEBUG_CONFIG
environment variable.
integer xdebug.log_level = 7 #
Configures which logging messages should be added to the log file.
The log file is configured with the xdebug.log setting.
The following levels are supported:
| Level | Name | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Criticals | Errors in the configuration |
| 1 | Errors | Connection errors |
| 3 | Warnings | Connection warnings |
| 5 | Communication | Protocol messages |
| 7 | Information | Information while connecting |
| 10 | Debug | Breakpoint resolving information |
Criticals, errors, and warnings always show up in the
diagnostics log that you can view by calling xdebug_info().
Criticals and errors are additionally logged through
PHP’s internal logging mechanism (configured with error_log
in php.ini).
This setting can additionally be configured through the
XDEBUG_CONFIG
environment variable.
integer xdebug.max_nesting_level = 512 #
Controls the protection mechanism for infinite recursion protection.
The value of this setting is the maximum level of nested functions that are
allowed before the script will be aborted.
When the maximum nesting level is reached,
an «Error» exception
is thrown.
Before Xdebug 3.3, the default value was 256.
integer xdebug.max_stack_frames = -1 #
Controls how many stack frames are shown in stack traces, both on
the command line during PHP error stack traces, as well as in the
browser for HTML traces.
string xdebug.mode = develop #
This setting controls which Xdebug features are enabled.
This setting can only be set in php.ini or
files like 99-xdebug.ini that are read when a PHP process starts
(directly, or through php-fpm). You can not set this value in
.htaccess and .user.ini files, which are read
per-request, nor through php_admin_value as used in Apache VHOSTs
and PHP-FPM pools.
The following values are accepted:
off- Nothing is enabled. Xdebug does no work besides checking whether
functionality is enabled. Use this setting if you want close to 0
overhead. develop- Enables Development Helpers including the overloaded var_dump().
coverage- Enables Code Coverage Analysis to generate code coverage reports, mainly in
combination with
PHPUnit. debug- Enables Step Debugging. This can be used to step through your code while it
is running, and analyse values of variables. gcstats- Enables Garbage Collection Statistics to collect statistics about PHP’s Garbage
Collection Mechanism. profile- Enables Profiling, with which you can analyse performance bottlenecks
with tools like KCacheGrind. trace- Enables the Function Trace feature, which allows you record every function
call, including arguments, variable assignment, and return value that is made
during a request to a file.
You can enable multiple modes at the same time by comma separating their
identifiers as value to xdebug.mode: xdebug.mode=develop,trace.
XDEBUG_MODE environment variable
You can also set Xdebug’s mode by setting the XDEBUG_MODE
environment variable on the command-line; this will take precedence over the
xdebug.mode setting, but will not change the value of the xdebug.mode
setting.
Some web servers have a configuration option to
prevent environment variables from being propagated to PHP and Xdebug.
For example, PHP-FPM has a clear_env
configuration setting that is on by default, which you will
need to turn off if you want to use XDEBUG_MODE.
Make sure that your web server does not clean the environment, or specifically
allows the XDEBUG_MODE environment variable to be passed on.
string xdebug.output_dir = /tmp #
The directory where Xdebug will write tracing, profiling, and garbage
collection statistics to. This directory needs to be writable for the system
user with which PHP is running.
This setting can be changed in php.ini, .htaccess
(and equivalent files), and within a PHP file with ini_set().
In some cases (when profiling, or when
xdebug.start_with_request=yes with tracing), Xdebug
creates the file before the script runs. In that case, changes made through
ini_set() will not be taken into account.
This setting can additionally be configured through the
XDEBUG_CONFIG
environment variable.
integer xdebug.profiler_append = 0 #
When this setting is set to 1, profiler files will not be overwritten when
a new request would map to the same file (depending on the xdebug.profiler_output_name setting.
Instead the file will be appended to with the new profile.
string xdebug.profiler_output_name = cachegrind.out.%p #
This setting determines the name of the file that is used to dump
traces into. The setting specifies the format with format specifiers, very
similar to sprintf() and strftime(). There are several format specifiers
that can be used to format the file name.
See the xdebug.trace_output_name documentation for the supported
specifiers.
This setting can additionally be configured through the
XDEBUG_CONFIG
environment variable.
boolean xdebug.scream = false #
If this setting is 1, then Xdebug will disable the @ (shut-up)
operator so that notices, warnings and errors are no longer hidden.
integer xdebug.show_error_trace = 0 #
When this setting is set to 1, Xdebug will show a stack trace whenever
an Error is raised — even if this Error is actually caught.
integer xdebug.show_exception_trace = 0 #
When this setting is set to 1, Xdebug will show a stack trace whenever
an Exception or Error is raised — even if this Exception or Error is actually caught.
Error ‘exceptions’ were introduced in PHP 7.
integer xdebug.show_local_vars = 0 #
When this setting is set to something != 0 Xdebug’s generated stack dumps
in error situations will also show all variables in the top-most scope. Beware
that this might generate a lot of information, and is therefore turned off by
default.
string xdebug.start_upon_error = default #
Step Debugging can be activated when a PHP Notice or Warning is emitted, or
when a Throwable
(Exception/Error) is thrown, depending on the value of this setting:
yes-
Initialise a debugging session when a PHP Notice or Warning is emitted, or
when a Throwable is thrown. nodefault-
Do not start a debugging session upon an error situation.
This setting is independent of xdebug.start_with_request, and therefore it is
not necessary to set xdebug.start_with_request=trigger.
string xdebug.start_with_request = default #
A Function Trace, Garbage Collection Statistics, Profiling, or Step Debugging
can be activated at the start of a PHP request. Whether this happens depends on
the value of this setting:
yes-
The functionality starts when the PHP request starts, and before any PHP
code is run.For example xdebug.mode=
traceand
xdebug.start_with_request=yesstarts a Function Trace for the
whole request. no-
The functionality does not get activated when the request starts.
You can still start a Function Trace with xdebug_start_trace(),
or Garbage Collection Statistics with xdebug_start_gcstats().Step Debugging and Profiling will never activate with this value.
trigger-
The functionality only gets activated when a specific trigger is present
when the request starts.The name of the trigger is
XDEBUG_TRIGGER, and Xdebug checks
for its presence in either$_ENV(environment variable),
$_GETor$_POSTvariable, or$_COOKIE
(HTTP cookie name).There is a legacy fallback to a functionality specific trigger name:
XDEBUG_PROFILE(for Profiling),XDEBUG_TRACE
(for a Function Trace), andXDEBUG_SESSION(for
Step Debugging).There is another legacy trigger for Step Debugging only. If you set the
XDEBUG_CONFIGenvironment variable to any value, then the step
debugger will also get activated.Debug session management for Step Debugging is also
available throughXDEBUG_SESSION_START.With xdebug.trigger_value you can control which specific trigger value will
activate the trigger. If xdebug.trigger_value is set to an empty
string, any value will be accepted.In this mode it is also possible to activate Step Debugging with
xdebug_break(). default-
The
defaultvalue depends on xdebug.mode:- debug:
trigger - gcstats:
no - profile:
yes - trace:
trigger
- debug:
integer xdebug.trace_format = 0 #
The format of the trace file.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | shows a human readable indented trace file with: time index, memory usage, memory delta, level, function name, function parameters, filename and line number. |
| 1 | writes a computer readable format which has two different records. There are different records for entering a stack frame, and leaving a stack frame. The table below lists the fields in each type of record. Fields are tab separated. |
| 2 | writes a trace formatted in (simple) HTML. |
Fields for the computerized format:
| Record type | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 — … |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | level | function # | always ‘0’ | time index | memory usage | function name | user-defined (1) or internal function (0) | name of the include or require file | filename | line number | no. of arguments | arguments (as many as specified in field 11) — tab separated |
| Exit | level | function # | always ‘1’ | time index | memory usage | empty | ||||||
| Return | level | function # | always ‘R’ | empty | return value | empty |
See the introduction for Function Trace for a few examples.
integer xdebug.trace_options = 0 #
This settings accepts a bitfield to enable options:
- 1
- Trace file data will be appended to an already existing file with the same name, instead of it being overwritten.
- 2
- Switches the file format to a tab separated format. The format is described in the xdebug.trace_format setting as «format 1».
- 4
- Switches to a file format that shows data as an HTML table
- 8
- With this bit set,
.xtis not added automatically to the end
of trace file names.
To combine multiple flags, you can use bitwise-OR (|).
xdebug.trace_options=2|8 enables both the tab separated format,
and stops the addition of .xt to the end of the file name.
string xdebug.trace_output_name = trace.%c #
This setting determines the name of the file that is used to dump
traces into. The setting specifies the format with format specifiers, very
similar to sprintf() and strftime(). There are several format specifiers
that can be used to format the file name. The ‘.xt’ extension is always added
automatically.
The possible format specifiers are:
| Specifier | Meaning | Example Format | Example Filename |
|---|---|---|---|
| %c | crc32 of the current working directory | trace.%c | trace.1258863198.xt |
| %p | pid | trace.%p | trace.5174.xt |
| %r | random number | trace.%r | trace.072db0.xt |
| %s |
script name 2 |
cachegrind.out.%s | cachegrind.out._home_httpd_html_test_xdebug_test_php |
| %t | timestamp (seconds) | trace.%t | trace.1179434742.xt |
| %u | timestamp (microseconds) | trace.%u | trace.1179434749_642382.xt |
| %H | $_SERVER[‘HTTP_HOST’] | trace.%H | trace.kossu.xt |
| %R | $_SERVER[‘REQUEST_URI’] | trace.%R | trace._test_xdebug_test_php_var=1_var2=2.xt |
| %U | $_SERVER[‘UNIQUE_ID’] 3 | trace.%U | trace.TRX4n38AAAEAAB9gBFkAAAAB.xt |
| %S | session_id (from $_COOKIE if set) | trace.%S | trace.c70c1ec2375af58f74b390bbdd2a679d.xt |
| %% | literal % | trace.%% | trace.%%.xt |
2 This one is only available for trace file names since Xdebug 2.6.
3 New in version 2.2. This one is set by Apache’s mod_unique_id module
string xdebug.trigger_value = «» #
This setting can be used when xdebug.start_with_request is set to
trigger, which is the default for Step Debugging and Function Trace.
In trigger mode, Xdebug will only start its
functionality when the XDEBUG_TRIGGER is set in the environment,
or when the XDEBUG_TRIGGER GET, POST, or COOKIE variable is
set.
The legacy names XDEBUG_SESSION (for Step Debugging),
XDEBUG_PROFILE (for Profiling), and XDEBUG_TRACE
(for Function Trace) can also be used instead of XDEBUG_TRIGGER.
Normally, Xdebug does not look at which value is actually used. If this
setting is set to a non-empty string, then Xdebug will only trigger if the
value matches the value of this setting.
With the following settings:
xdebug.mode=profile xdebug.start_with_request=trigger xdebug.trigger_value=StartProfileForMe
Xdebug’s profiler will only start when either the environment variable
XDEBUG_TRIGGER is set to StartProfileForMe, the GET
or POST variable XDEBUG_TRIGGER is set to
StartProfileForMe, or when the cookie XDEBUG_TRIGGER
has the value StartProfileForMe.
From Xdebug 3.1, it is possible to configure multiple values by using a
comma separated list. In that case, Xdebug will trigger if the supplied value
matches any of the entries that are configured through this setting:
xdebug.trigger_value=StartDebuggerForMe,StartDebuggerForYou
See also:
- xdebug.start_with_request#trigger
- For how the triggering mechanism works, and which environment and server variables Xdebug acts on.
boolean xdebug.use_compression = true #
Introduced in Xdebug >= 3.1
If enabled, the Function Trace and Profiling features will create GZip
compressed files as output. This reduces diskspace.
If GZip compression is not supported by Xdebug, because it was not compiled
in, then Xdebug will add a warning to its log and xdebug_info()
diagnostics section.
It is enabled by default if Xdebug has GZip support, and disable if Xdebug
does not have GZip support.
The QCacheGrind tool that you can use to visualise profiling information
does not support reading GZip compressed profile files, whereas KCacheGrind and
PhpStorm do. If you are a QCacheGrind user, you should set
xdebug.use_compression to false.
integer xdebug.var_display_max_children = 128 #
Controls the amount of array children and object’s properties are shown
when variables are displayed with either xdebug_var_dump(),
xdebug.show_local_vars or when making a Function Trace.
To disable any limitation, use -1 as value.
This setting does not have any influence on the number of children that is
send to the client through the Step Debugging feature.
integer xdebug.var_display_max_data = 512 #
Controls the maximum string length that is shown
when variables are displayed with either xdebug_var_dump(),
xdebug.show_local_vars or when making a Function Trace.
To disable any limitation, use -1 as value.
This setting does not have any influence on the number of children that is
send to the client through the Step Debugging feature.
integer xdebug.var_display_max_depth = 3 #
Controls how many nested levels of array elements and object properties are
when variables are displayed with either xdebug_var_dump(),
xdebug.show_local_vars or when making a Function Trace.
The maximum value you can select is 1023. You can also use -1 as
value to select this maximum number.
This setting does not have any influence on the number of children that is
send to the client through the Step Debugging feature.
Setting the value to a high number could potentially result in
PHP using up all the available memory, so use with caution.
In this tutorial I’ll show my typical procedure when setting up a new development environment on a fresh Windows 10 laptop.
It’s not like I do this every day (as ‘typical’ might suggest) but when I started my current job, I had to do it
several times for me (switched my laptop) as well as for some of my co-workers. I’m going to cover this step-by-step
and will include (hopefully) all necessary information for you to get this setup running as well.
This is the first part of a three-part tutorial, focusing on the development on Windows. In the second part I will
explain how to make the shift to using a virtual machine and in the third we’ll setup a fresh Laravel installation
and put it all together.
- Clipboard cache
- Text expansion
Setup PHP 7
I do almost all of my development in a virtual machine because the final product usually runs on a unix server, but
from time to time I find it helpful to have a local setup available as well.
Installation
We’re almost done, but we should modify the PATH variable in order to make PHP globally available.
The PATH variable
Simply put, the PATH variable defines where Windows looks for executable files when the specified file is not found
in the current directory. So lets say you would like to know the current PHP version on your system, then
stackoverflow will tell you something along the lines of
C:\>php -v
But you will probably get this
php: command not found
or this
‘php’ is not recognized as an internal or external command,
operable program or batch file.

That command would only work if our current working directory (the location from where we executed the php -v command) would
contain the correct php.exe file. In other words: Calling the command is not location-agnostic yet. To make it, though,
we need to modify the PATH environment variable and make it aware of the location PHP is installed at.
To do so, we need to modify the System Properties… and might as well learn some nifty shortcuts to get there along the way 
C:\>php -v
PHP 7.0.7 (cli) (built: May 25 2016 13:08:31) ( NTS )
Copyright (c) 1997-2016 The PHP Group
Zend Engine v3.0.0, Copyright (c) 1998-2016 Zend Technologies
Cool, now on to the IDE.
Installation
That’ll conclude the installation 
Setup for local PHP development
First, let’s create a new PHP file by right-clicking on the project folder and choosing New > PHP File.

Name the file test.php and give it the following content:
<?php
$i = 1;
echo $i."\n";
Now select Run > Run... and choose the test.php with the small PHP icon in the front.
A new window should appear because we did not specify a PHP interpreter yet so PhpStorm doesn’t know how to run the file.

A click on the «Fix» button with the red exclamation mark will open up the PHP interpreter settings. You can get to the
same screen via File > Settings... > Languages & Frameworks > PHP. First, choose 7 (return types,
scalar type hints, etc.) as PHP language level so that scalar type hints won’t get marked as an error, for instance.
Second, hit the ... button to specify an new (local) PHP interpreter and click on the green «+» icon on the top left.
Since we installed PHP 7 before, PhpStorm should automatically provide that as an option. Otherwise choose «Other Local…»
and select the php.exe file from the install location of PHP on your system.

A little warning sign should appear, stating that the
Configuration php.ini file does not exist

Clicking on the «How To Fix» help link reveals, that PHP expects a file called php.ini in either its installation directory
or at C:\Windows. But we’ll come to that in a moment. For now, we can just confirm all dialogs with «OK» and should now
be able to run the PHP file — either by right-click + selecting «Run» or (by default) hitting Shift + F10.
The console window of PhpStorm should open at the bottom and show something like this
"C:\Program Files\php7\php.exe" C:\Users\IEUser\PhpstormProjects\untitled\test.php
1
Process finished with exit code 0

Splendid, PhpStorm is now up and running with PHP7 
Installing Xdebug
Debugging is an invaluable asset during development as it lets you walk step-by-step through the source code, showing
exactly what is happening. var_dump() on freakin’ steroids! Choose Run > Debug 'test.php' (or hit Shift + F9) —
and be greeted by a little error message at the bottom that goes like this:
Connection was no established: debug extension is not installed.

Unfortunately, the help link «Update interpreter info» is not really useful at that point… So what’s actually going on?
In order enable debugging, we need to install the Xdebug extension. To do so, go to the
Xdebug download page and download the appropriate installer for your PHP version…

Just kidding, of course I’m going to explain how to find the right one 
We installed PHP 7 NTS, probably in the 64 bit version, so the link «PHP 7.0 VC14 (64bit)» should be the correct one.
But since I tend forget the exact version I installed, I would like to point to
Xdebug’s fantastic installation wizard which simply requires us to print, copy and
paste some information of our PHP installation. And here’s how we gonna do that:
You could follow those instructions directly, but I would recommend to change the directory of the extension. C:\php\ext is
the default directory for PHP to look for extensions if not specified otherwise in drumroll the php.ini — that we
shall create now. To do so, open you PHP installation directory (just as a reminder: mine was at C:\Program Files\php7), look for the file
php.ini-development copy and rename it to php.ini and open that file. Search for «extension_dir» which should lead
you to a passage that looks like this:
; Directory in which the loadable extensions (modules) reside.
; http://php.net/extension-dir
; extension_dir = "./"
; On windows:
; extension_dir = "ext"
Remove the leading «;» in front of the «extension_dir» directive and set the path to the «ext» folder in your PHP installation
directory as value. For me, the line now looks like this:
extension_dir = "C:\Program Files\php7\ext"
Hint: If you don’t find any «extension_dir» string in your original php.ini file just add it at the end of the file.
Also, don’t forget to save the file.
When re-running the php -i > phpinfo.txt step including the Xdebug wizard, the instructions now look like this:

- Download php_xdebug-2.4.0-7.0-vc14-nts-x86_64.dll
- Move the downloaded file to «C:\Program Files\php7\ext»
- Edit C:\Program Files\php7\php.ini and add the line
zend_extension = "C:\Program Files\php7\ext\php_xdebug-2.4.0-7.0-vc14-nts-x86_64.dll"
You can add the «zend_extension» line simply at the end of the php.ini.
Now we should be good to go — or better to debug. Open up the test.php file in PhpStorm and click on the
little green bug icon on the top right to run the file in debug mode.
The console window pops up again and yields something like this:
"C:\Program Files\php7\php.exe" -dxdebug.remote_enable=1 -dxdebug.remote_mode=req -dxdebug.remote_port=9000 -dxdebug.remote_host=127.0.0.1 C:\Users\IEUser\PhpstormProjects\untitled\test.php
1
Process finished with exit code 0
Please note the -dxdebug parameters following the php.exe call. To actually use the debugger, set a breakpoint in the
second line of the script (that says $i = 1;) by left-clicking on the little margin on the left of said line (you can
unset the breakpoint by simply clicking on it again).
Running the script now (again in debug mode) will stop the execution at that position.
Phew. Glad we got that thing working 
Setup Composer
Next in line: PHP’s beloved dependency manager Composer. I deeply believe that there’s hardly a way around
this wonderful tool when it comes to modern PHP development.
Installation
So let’s quickly take care of this before we continue. (We could also ignore this requirement by checking
the checkbox but I’ll take this opportunity to show you how extensions are enabled for PHP).
Enabling the openssl PHP extension
Open up the php.ini file in your PHP installation directory and search for «php_openssl». You should now see
a line like this:
;extension=php_openssl.dll
The php_openssl.dll file should already come pre-installed in the «ext» directory within your PHP installation
directory. (It’s starting to make sense that we adjusted the «extension_dir», doesn’t id ;)). So you can simply
remove the «;» in front of this line. To verify that the extension is actually loaded, open up a shell and type
php -m to list all enabled modules. The list should contain an item that says openssl.

Cool. Now that that’s working we shall continue with the installation process. Try hitting the «< Back» button
once to get back to the PHP executable selection. Upon clicking «Next >», the openssl warning should be gone.
If not, cancel and restart the setup. You can ignore the Proxy Settings dialog and just hit «Next >» and «Install».
Since we installed Xdebug before, Composer will show a warning that this slows down Composer but that’s nothing
to worry about. Just keep hitting «Next >» and «Finish». Composer will add itself automatically to your PATH
environment variable so you can call it globally. As mentioned before, this will only affect freshly opened shells,
so let’s do a quick WIN + R and a cmd.
Type composer -V to print the Composer version, which should generate something along the lines of
C:\Users\IEUser>composer -V
You are running composer with xdebug enabled. This has a major impact on runtime performance. See https://getcomposer.org/xdebug
Composer version 1.1.1 2016-05-17 12:25:44

Aaaand we’re done.
Phrase Express
This is more of bonus since it’s a somewhat opinionated software but I’ve grown very fond of it over the last
couple of years. Phrase Express is a clipboard manager / text expander for Windows. You can download the
tool for free at the Phrase Express download page (Download Client).
There’s actually not much to tell about the installation process so I’m just gonna outline my major use cases.
Clipboard cache
This one is a biggie: Phrase Express saves everything you copy to the clipboard in a cache that can be accessed
via CRTL + ALT + V (by default). I cannot emphasize how incredibly handy that is.
Text expansion
There’s a couple of things I have to type frequently (or at least from time to time) and it’s just cumbersome
to either write them out in full length or to look them up. Here’s my short list to give you an idea:
| auto text | meaning | |
|---|---|---|
| mee | my email address | |
| myssh | my public ssh key | |
| mytax | my tax id | |
| myserver | ip address of my server | |
| ts | the current timestamp in Y-m-d format | |
| tsf | the current timestamp in Y-m-d H:i:s format | |
| *shrug | ¯\_(ツ)_/¯ | |
| *party | (ツ)_\m/ | |
| cmark | ✓ | |
| killphp | ps aux | grep php | awk '{print $2}' | sudo xargs kill |
Wanna stay in touch?
Since you ended up on this blog, chances are pretty high that you’re into Software Development
(probably PHP, Laravel, Docker or Google Big Query) and I’m a big fan of feedback and networking.
So — if you’d like to stay in touch, feel free to shoot me an email with a couple of words about yourself and/or
connect with me on
LinkedIn or
Twitter
or simply subscribe to my RSS feed
or go the crazy route and subscribe via mail
and don’t forget to leave a comment 
Subscribe to posts via mail

