If you have ever looked at the Task Manager in Windows 10, you might have noticed a process called taskhostw.exe running in the background. What is this process and is it safe or malicious? In this blog post, we will answer these questions and give you some tips on how to deal with taskhostw.exe.

What is taskhostw.exe?
Taskhostw.exe is a system file that belongs to the Windows operating system. The name stands for “Task’s Host for Windows”. The main function of taskhostw.exe is to start the Windows services based on DLLs (Dynamic Link Libraries) whenever the computer boots up. A DLL is a file that contains executable code and resources that can be shared by multiple programs. Taskhostw.exe acts as a host for processes that execute as part of a DLL file rather than through an EXE (Executable) file.
The legitimate taskhostw.exe file is located in the C:\Windows\System32 folder. If you see it located in any other path, it could be malware disguised as taskhostw.exe. You can check the location of the file by right-clicking on it in the Task Manager and selecting “Open file location”.
Is taskhostw.exe malware?
Taskhostw.exe is not malware by itself, but it can be used by malware to hide their activities. Some malware may create a fake taskhostw.exe file and place it in a different folder than the original one. They may also inject malicious code into the legitimate taskhostw.exe process and use it to perform malicious actions.
To determine if taskhostw.exe is malware or not, you can use some of the following methods:
- Check the digital signature of the taskhostw.exe file. A digital signature is a way of verifying the authenticity and integrity of a file. You can check the digital signature by right-clicking on the file and selecting “Properties”. Then go to the “Digital Signatures” tab and click on “Details”. You should see that the file is signed by Microsoft Corporation. If the file is not signed or signed by an unknown or suspicious entity, it could be malware.
- Check the CPU and memory usage of the taskhostw.exe process. Normally, taskhostw.exe should not consume a lot of CPU or memory resources. If you notice that taskhostw.exe is using a high amount of CPU or memory, it could indicate that it is running faulty or malicious DLLs. You can try to identify which DLLs are causing the problem by using the command prompt. Open a command prompt window as an administrator and type the following command:
tasklist /M /FI "IMAGENAME eq taskhostw.exe". This will show you all the DLLs that have been loaded by taskhostw.exe. You can then research each DLL online and see if they are legitimate or not. - Uninstall or repair any recently installed programs that may have affected taskhostw.exe. Some programs may install or modify DLLs that are used by taskhostw.exe. This may cause taskhostw.exe to malfunction or behave suspiciously. You can try to uninstall or repair any programs that you have installed recently and see if that fixes the problem.
If you suspect that Taskhostw.exe is infected with malware, you can follow the below free malware removal guide to clean up your device.
Remove malware from your Windows device
The below malware removal instructions are for Windows users, however, we also have an Android Guide and a Mac Guide which should help clean up your device.
This malware removal guide may appear overwhelming due to the number of steps and numerous programs that are being used. We have only written it this way to provide clear, detailed, and easy-to-understand instructions that anyone can use to remove malware for free.
Please perform all the steps in the correct order. If you have any questions or doubts at any point, stop and ask for our assistance.
To remove the Taskhostw.exe Trojan and other malware from your computer, follow these steps:
- STEP 1: Use Rkill to terminate malicious processes
- STEP 2: Uninstall malicious programs from Windows
- STEP 3: Reset browsers back to default settings
- STEP 4: Use Malwarebytes to remove for Trojans and Unwanted Programs
- STEP 5: Use HitmanPro to remove Rootkits and other Malware
- STEP 6: Use AdwCleaner to remove Malicious Browser Policies and Adware
- STEP 7: Perform a final check with ESET Online Scanner
- STEP 8: Run the System File Checker (SFC) tool
- STEP 9: Run the Disk Check tool
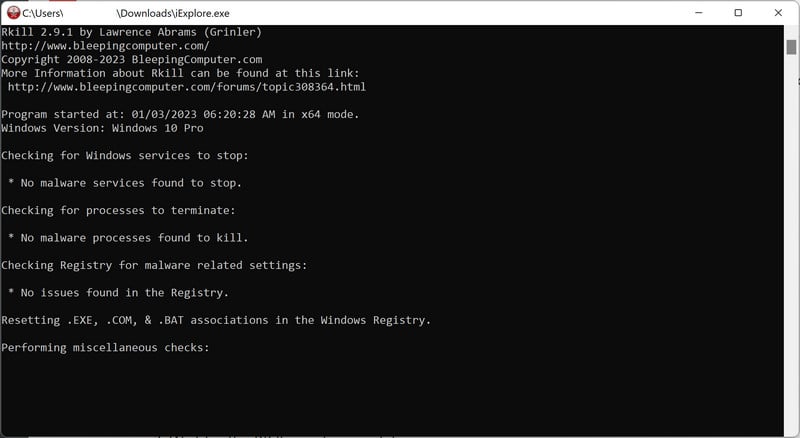
STEP 1: Use Rkill to terminate malicious processes
In this first step, we will download and run Rkill to terminate malicious processes that may be running on your computer.
RKill is a program that was developed at BleepingComputer.com that attempts to terminate known malware processes so that your normal security software can then run and clean your computer of infections. When RKill runs it will kill malware processes and then removes incorrect executable associations and fixes policies that stop us from using certain tools.
-
Download Rkill.
You can download RKill to your computer from the below link. When at the download page, click on the Download Now button labeled iExplore.exe. We are downloading a renamed version of Rkill (iExplore.exe) because some malware will not allow processes to run unless they have a certain filename.
-
Run RKill.
After downloading, double-click the iExplore.exe icon to kill malicious processes. In most cases, downloaded files are saved to the Downloads folder.
The program may take some time to search for and end various malware programs.When it is finished, the black window will close automatically and a log file will open. Do not restart your computer. Proceed to the next step in this guide.
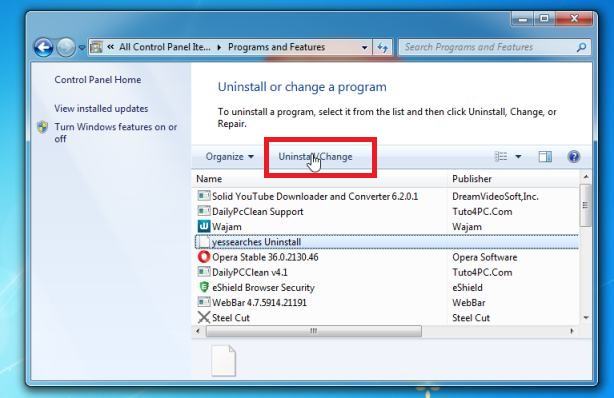
STEP 2: Uninstall malicious programs from Windows
In this second step, we will manually check if any unknown or malicious programs are installed on the computer. Sometimes adware and browser hijackers can have a usable Uninstall entry that can be used to remove them.
Windows 11Windows 10Windows 8Windows 7
-
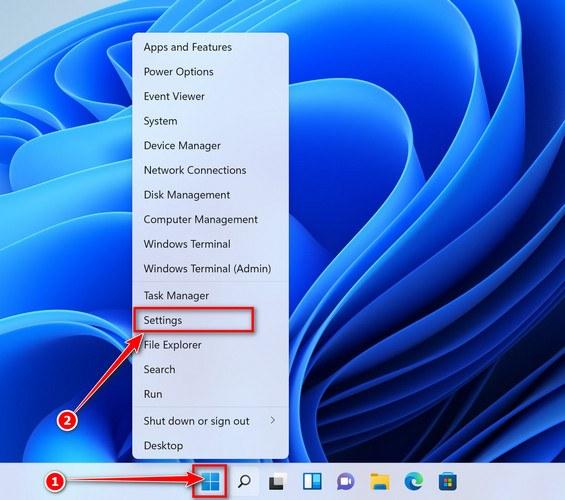
Press the Windows key + I on your keyboard to open the Settings app.
First, open Windows Settings by pressing Windows+I on your keyboard. You can also right-click your Start button and select “Settings” from the list.
-
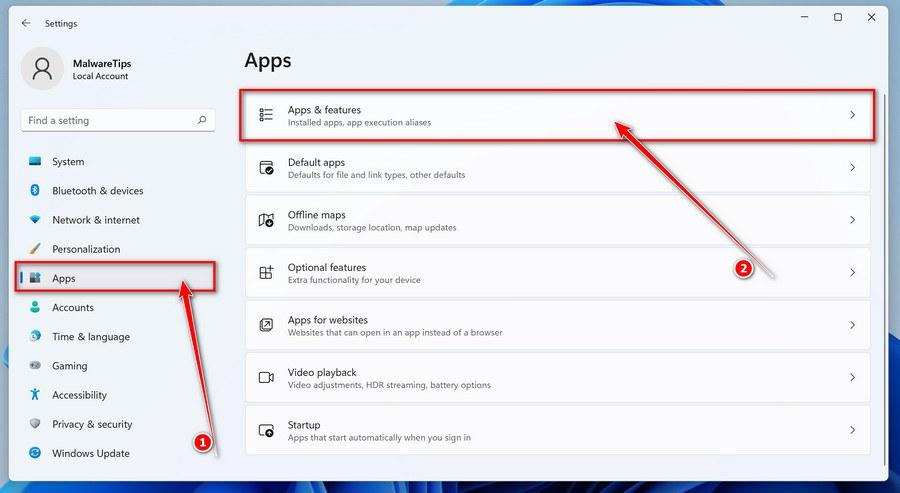
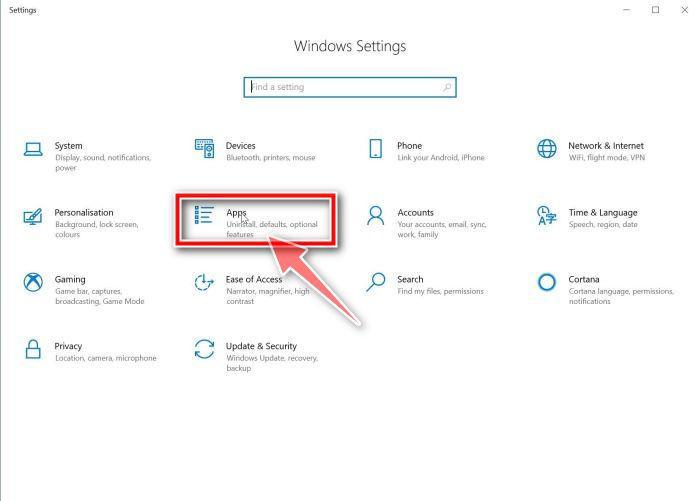
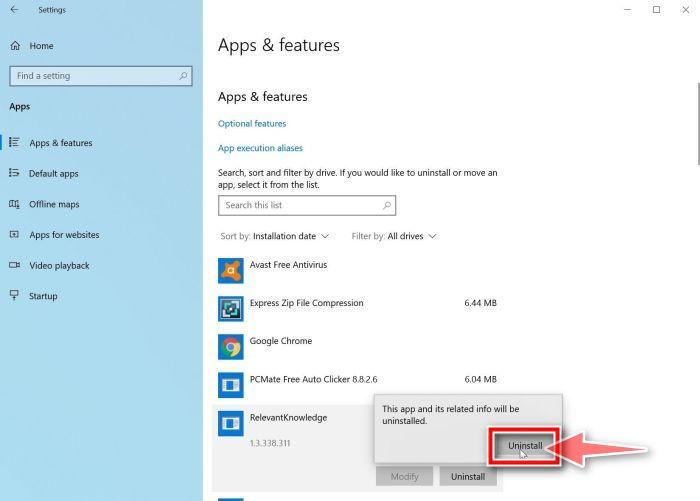
In the Settings app, click on “Apps” and then “Apps & features”.
When Settings opens, click “Apps” in the sidebar, then select “Apps & Features”.
-
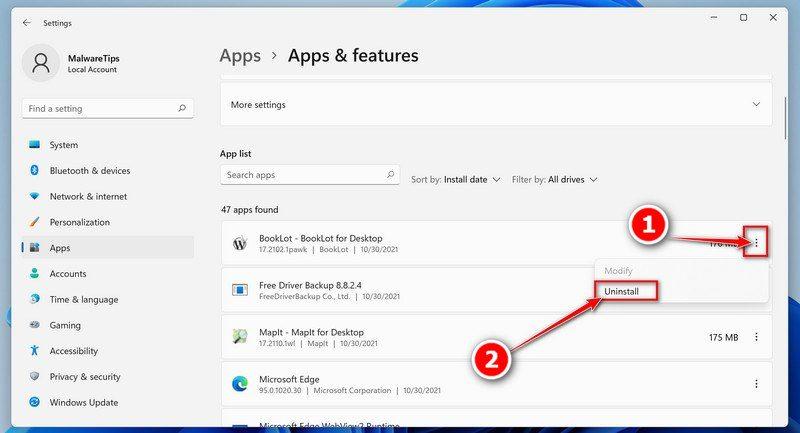
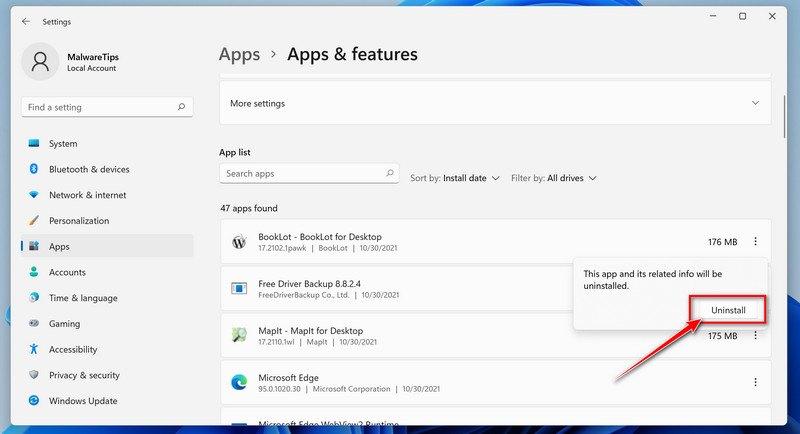
Find the malicious program in the list of installed apps and uninstall it.
In Apps & Features settings, scroll down to the app list and search for unknown or suspicious programs. To make things easier, you can sort all installed programs by their installation date. To do this, click “Sort by” and select “Install date”.
Look out for any suspicious program that could be behind all the drama – anything you don’t remember downloading or that doesn’t sound like a genuine program. When you find a malicious program, click the three dots button beside it and select “Uninstall” in the menu that appears.If you have checked your computer for malicious programs and did not find any, you can proceed with the next step in this guide.
-
Follow the prompts to uninstall the program.
In the next message box, confirm the uninstall process by clicking on Uninstall, then follow the prompts to uninstall the malicious program.
Make sure to read all of the prompts carefully, because some malicious programs try to sneak things in hoping that you won’t read them closely.
-
Press the Windows key + I on your keyboard to open the Settings app.
Press the Windows key + I on your keyboard to open the Settings app. You can also ope the Settings app by clicking the Start button on the taskbar, then select “Settings” (gear icon).
-
In the Settings app, click on “Apps”.
When the “Windows Settings” window opens, click on “Apps“. By default, it should open “Apps and Features” but if it doesn’t, select it from the list on the left.
-
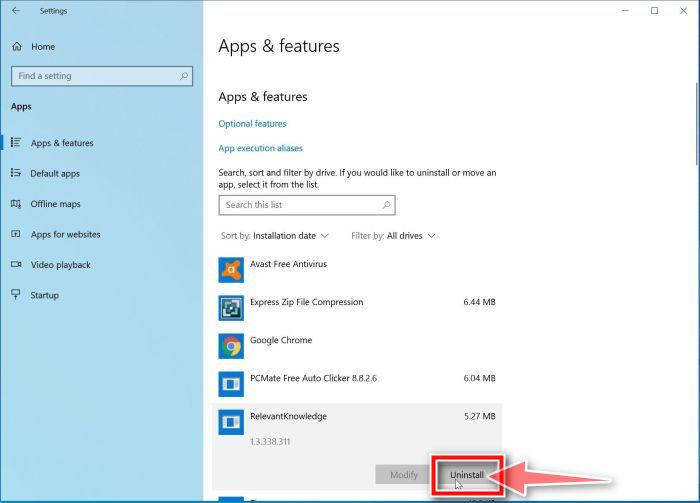
Find the malicious program in the list of installed apps and uninstall it.
In Apps & Features settings, scroll down to the app list and search for unknown or suspicious programs. To make things easier, you can sort all installed programs by their installation date. To do this, click “Sort by” and select “Install date”.
Look out for any suspicious program that could be behind all the drama – anything you don’t remember downloading or that doesn’t sound like a genuine program. When you find a malicious program, click on it and select “Uninstall” in the menu that appears.If you have checked your computer for malicious programs and did not find any, you can proceed with the next step in this guide.
-
Follow the prompts to uninstall the program.
In the next message box, confirm the uninstall process by clicking on Uninstall, then follow the prompts to uninstall the malicious program.
Make sure to read all of the prompts carefully, because some malicious programs try to sneak things in hoping that you won’t read closely.
-
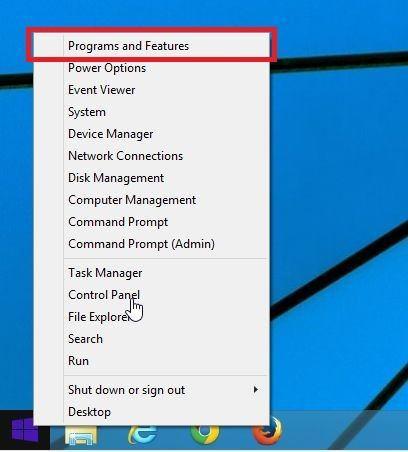
Go to “Program and Features”.
Right-click on the Start button in the taskbar, then select “Programs and Features”. This will take you directly to your list of installed programs.
-
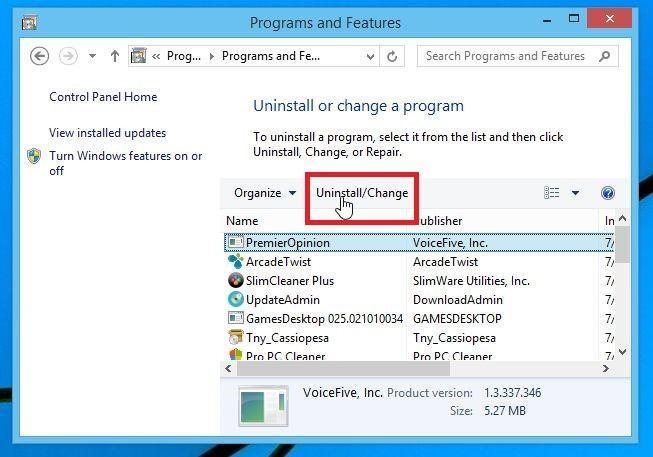
Search for malicious program and uninstall it.
The “Programs and Features” screen will be displayed with a list of all the programs installed on your computer. Scroll through the list until you find any unknown or suspicious program, then click to highlight it, then click the “Uninstall” button.
Look out for any suspicious program that could be behind all the drama – anything you don’t remember downloading or that doesn’t sound like a genuine program.
If you have checked your computer for malicious programs and did not find any, you can proceed with the next step in this guide.
-
Follow the on-screen prompts to uninstall malicious program.
In the next message box, confirm the uninstall process by clicking on Yes, then follow the prompts to uninstall malicious program. Make sure to read all of the prompts carefully, because some malicious programs try to sneak things in hoping that you won’t read closely.
-
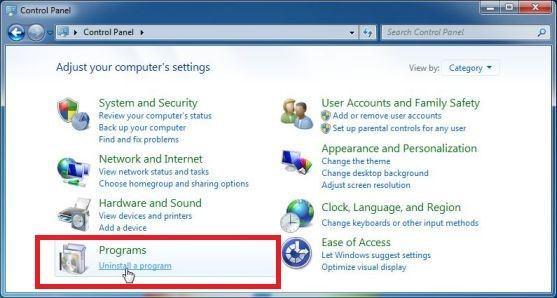
Open the “Control Panel”.
Click on the “Start” button, then click on “Control Panel“.
-
Click on “Uninstall a Program”.
When the “Control Panel” appears, click on “Uninstall a Program” from the Programs category.
-
Search for malicious programs and uninstall them.
The “Programs and Features” screen will be displayed with a list of all the programs installed on your computer. Scroll through the list until you find any suspicious or unknown program, then click to highlight it, then click the “Uninstall” button.
Look out for any suspicious program that could be behind all the drama – anything you don’t remember downloading or that doesn’t sound like a genuine program.If you have checked your computer for malicious programs and did not find any, you can proceed with the next step in this guide.
-
Follow the on-screen prompts to uninstall malicious program.
In the next message box, confirm the uninstall process by clicking on Yes, then follow the prompts to uninstall malicious program. Make sure to read all of the prompts carefully, because some malicious programs try to sneak things in hoping that you won’t read closely.
If you are experiencing difficulty while attempting to uninstall a program, you can use Revo Uninstaller to completely remove the unwanted program from your computer.
Now that the malicious programs have been removed from your computer, we can proceed with the next step in this guide.
STEP 3: Reset browsers back to default settings
In this step, we will remove spam notifications, malicious extensions, and change to default any settings that might have been changed by malware.
Please note that this method will remove all extensions, toolbars, and other customizations but will leave your bookmarks and favorites intact. For each browser that you have installed on your computer, please click on the browsers tab below and follow the displayed steps to reset that browser.
ChromeFirefoxMicrosoft EdgeInternet Explorer
Reset Chrome for Windows to default settings
We will now reset your Chrome browser settings to their original defaults. This will reset your startup page, new tab page, search engine, and pinned tabs. It will also disable all extensions and clear temporary data like cookies. Your favorites, history, and saved passwords will not be cleared.
-
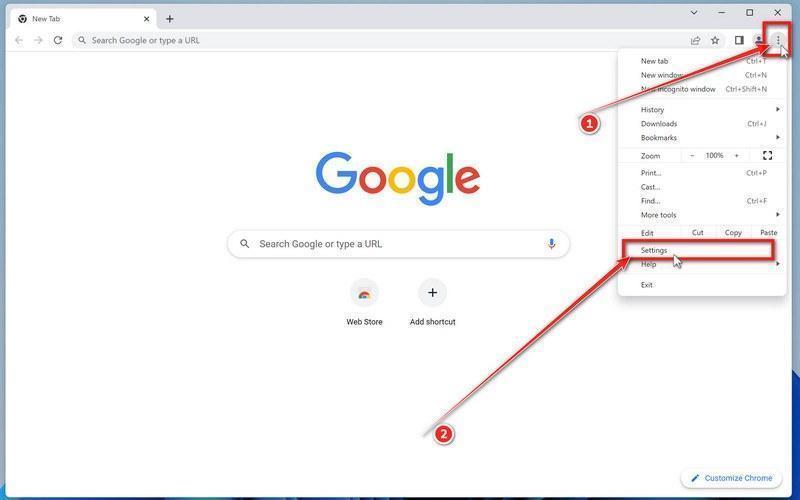
Click the three dots in the top-right corner and then click on “Settings”.
Open Chrome and click on the menu button (represented by three vertical dots) in the top right corner of the window. In the dropdown menu that opens, click “Settings“.
-
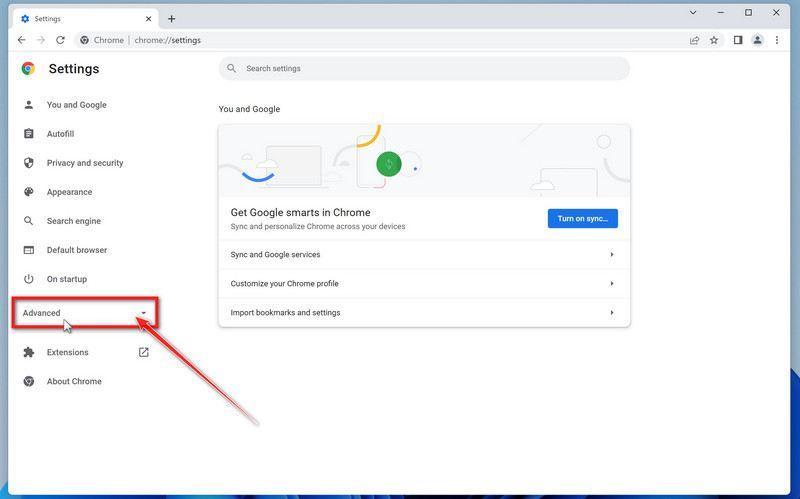
Click “Advanced”.
Chrome’s “Settings” should now be displayed in a new tab or window, depending on your configuration. In the left sidebar, click on the “Advanced” link.
-
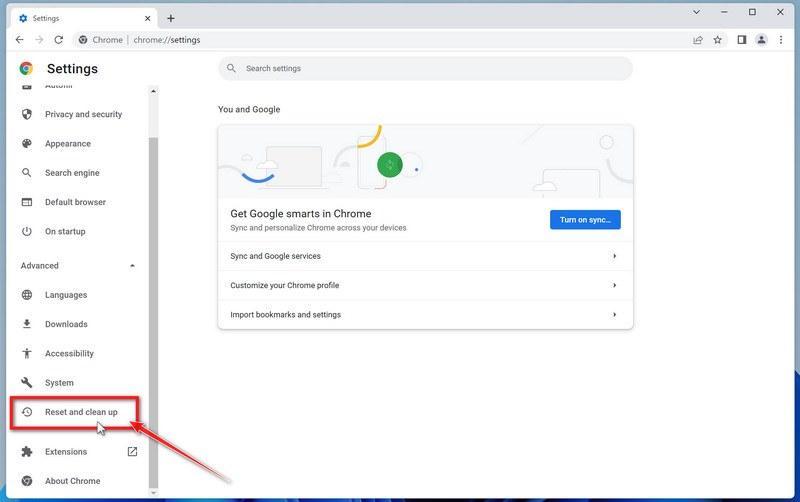
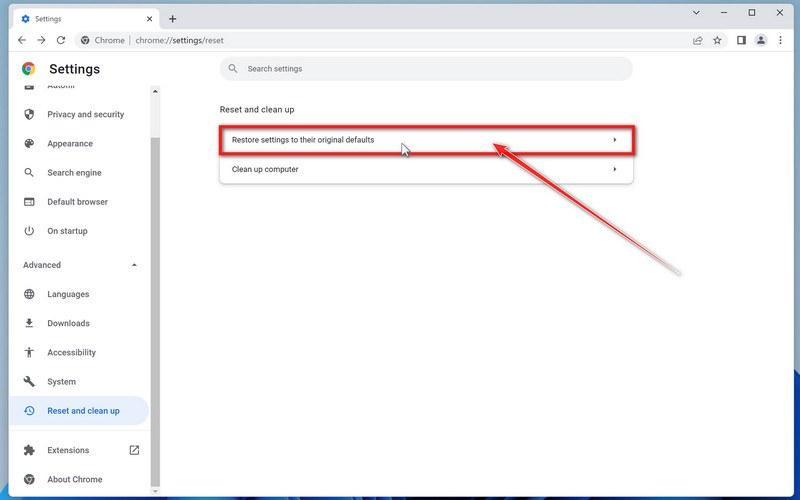
Click “Reset and clean up”.
In the left sidebar, under the “Advanced” section, click on “Reset and clean up“.
-
Click “Reset settings to their original defaults”.
In the main window, the “Reset and clean up” section is visible, as shown in the screenshot below. Click on “Reset settings to their original defaults“.
-
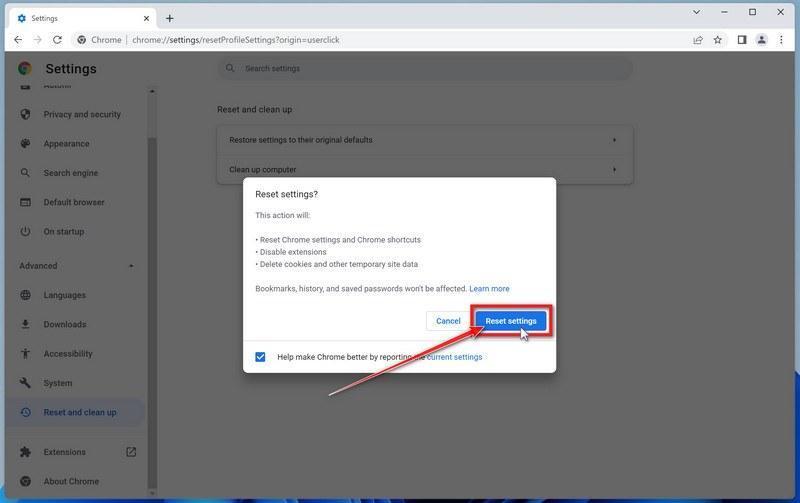
Click “Reset settings”.
A confirmation dialog will now be displayed, detailing the components that will be restored to their default state should you continue with the reset process. To complete the restoration process, click on the “Reset settings” button.
-
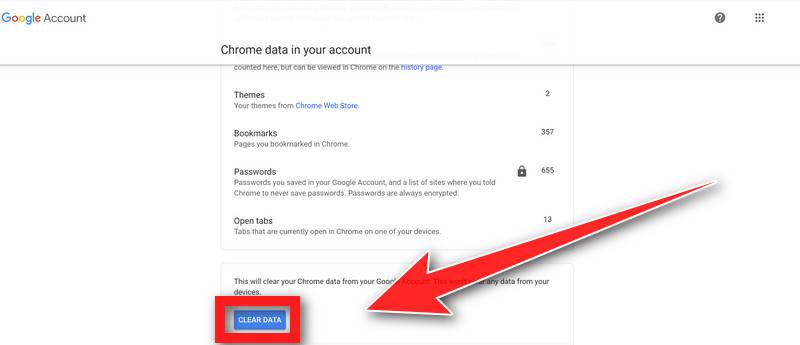
(Optional) Reset Chrome Data Sync.
In case a malicious extension reinstalls itself even after performing a browser reset, you have an additional option to reset the data sync for your browser. To do this, navigate to chrome.google.com/sync and click on the Clear Data button.
Reset Firefox for Windows to default settings
We will now reset your Firefox browser settings to their default. The reset feature fixes many issues by restoring Firefox to its factory default state while saving your essential information like bookmarks, passwords, web form auto-fill information, browsing history, and open tabs.
-
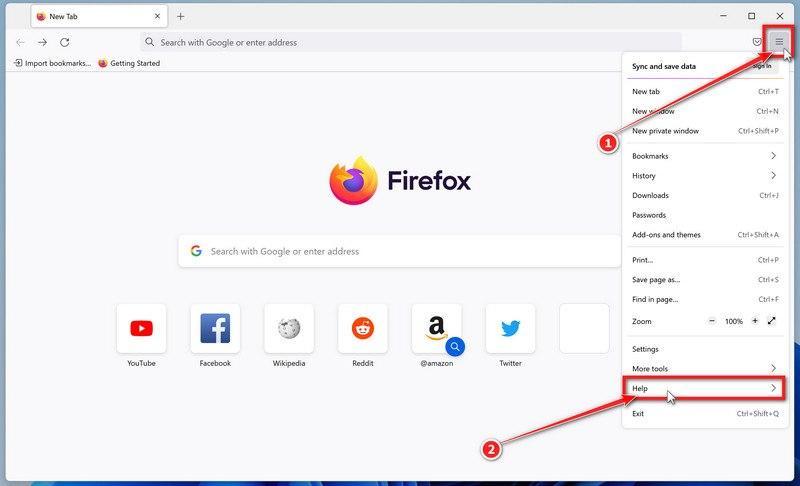
Click the three horizontal lines in the top-right corner and then click on “Help”.
Click on Firefox’s main menu button, represented by three horizontal lines. When the drop-down menu appears, select the option labeled “Help“.
-
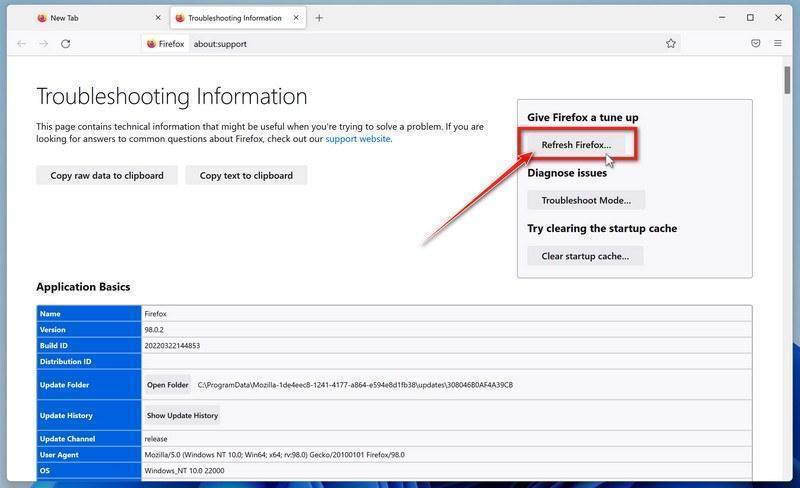
Click “More troubleshooting information”.
From the Help menu, click on “More troubleshooting information“.
-
Click on “Refresh Firefox”
When the “Troubleshooting Information” page opens, click on the “Refresh Firefox” button.
-
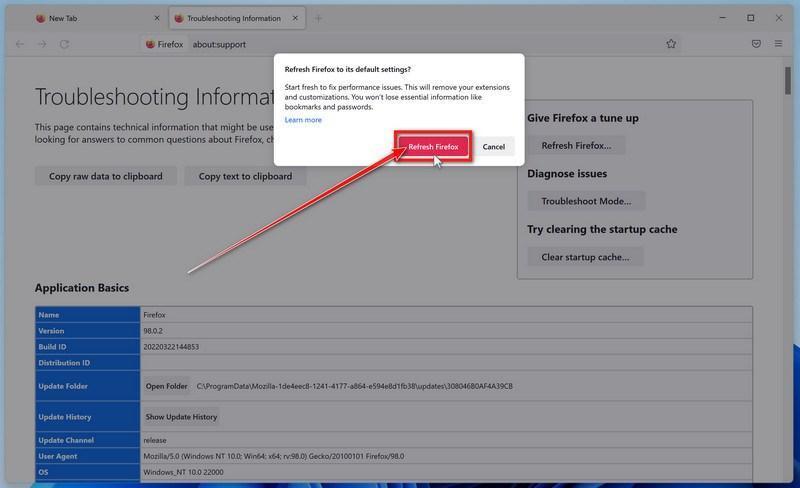
Confirm that you want to reset your browser settings.
To finish the reset process, click on the “Refresh Firefox” button in the new confirmation window that opens.
-
Click “Finish”.
Firefox will now close itself and will revert to its default settings. When it’s done, a window will list the information that was imported. Click on “Finish“.
Your old Firefox profile will be placed on your desktop in a folder named “Old Firefox Data“. If the reset didn’t fix your problem you can restore some of the information not saved by copying files to the new profile that was created. If you don’t need this folder any longer, you should delete it as it contains sensitive information.
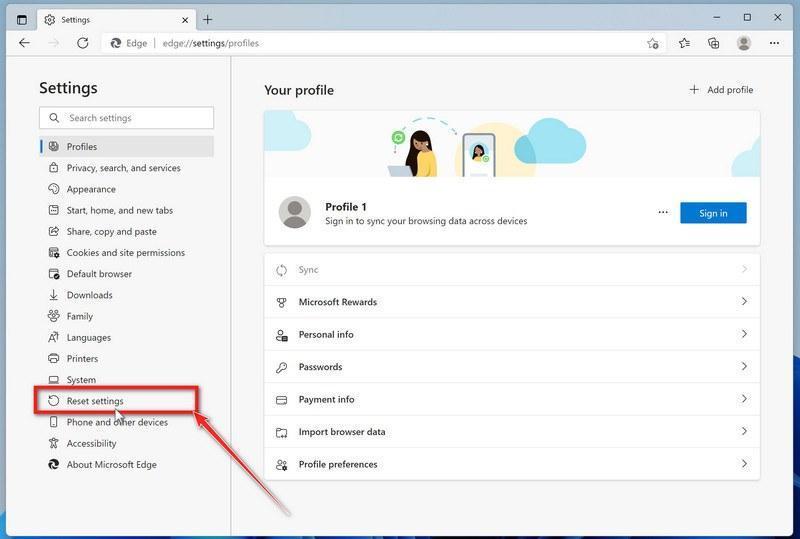
Reset Microsoft Edge to default settings
We will now reset your Microsoft Edge browser settings to their default. This will reset your startup page, new tab page, search engine, and pinned tabs. It will also disable all extensions and clear temporary data like cookies. Your favorites, history, and saved passwords will not be cleared.
-
Click the three dots in the top-right corner and then click on “Settings”.
In the top right corner, click on Microsoft Edge’s main menu button, represented by three horizontal dots. When the drop-down menu appears, click on “Settings“.
-
Click on “Reset Settings”.
On the left side of the window, click on “Reset Settings“.
-
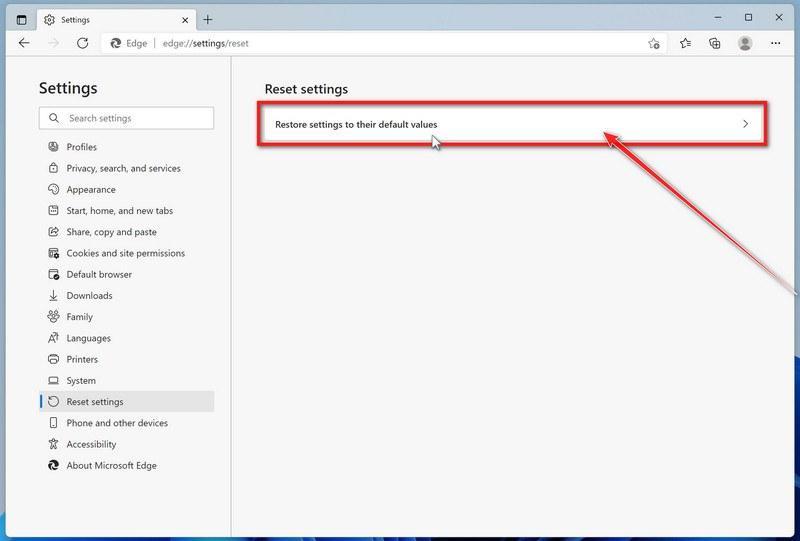
Click on “Restore settings to their default values”.
In the main window, click on “Restore settings to their default values“.
-
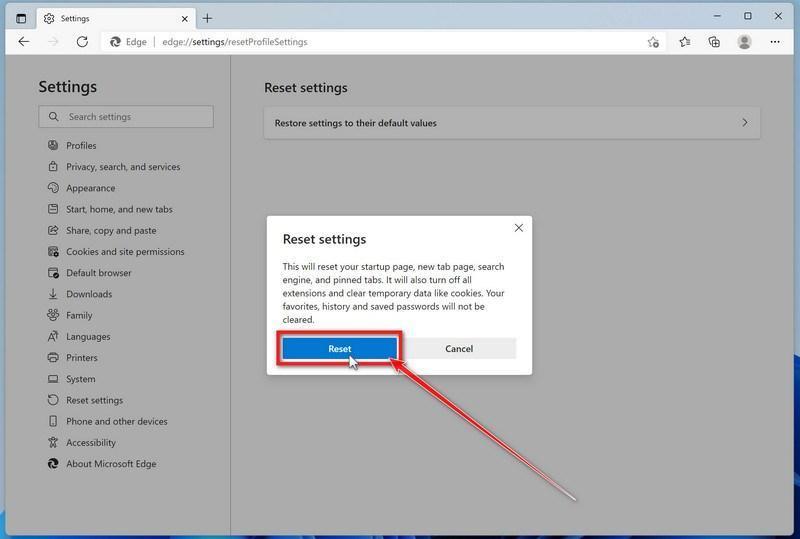
Click “Reset”.
A confirmation dialog should now be displayed, detailing the components that will be restored to their default state should you continue with the reset process. To complete the restoration process, click on the “Reset” button.
Microsoft Edge will now erase all your personal data, browsing history, and disable all installed extensions. Your bookmarks, though, will remain intact and still be accessible.
Reset Internet Explorer to default settings
We will now reset your Internet Explorer browser settings to their default. You can reset Internet Explorer settings to return them to the state they were in when Internet Explorer was first installed on your computer.
-
Go to “Internet Options”.
Open Internet Explorer, click on the gear icon in the upper-right part of your browser, then select “Internet Options“.
-
Select the “Advanced” tab, then click “Reset”
In the “Internet Options” dialog box, select the “Advanced” tab, then click on the “Reset” button.
-
Click on “Reset”.
In the “Reset Internet Explorer settings” section, select the “Delete personal settings” checkbox, then click on the “Reset” button.
-
Click on “Close”.
When Internet Explorer has completed its task, click on the “Close” button in the confirmation dialogue box.
Close your browser and then you can open Internet Explorer again.
STEP 4: Use Malwarebytes to remove for Trojans and Unwanted Programs
In this next step, we will we will install Malwarebytes to scan and remove any infections, adware, or potentially unwanted programs that may be present on your computer.
Malwarebytes stands out as one of the leading and widely-used anti-malware solutions for Windows, and for good reason. It effectively eradicates various types of malware that other programs often overlook, all at no cost to you. When it comes to disinfecting an infected device, Malwarebytes has consistently been a free and indispensable tool in the battle against malware. We highly recommend it for maintaining a clean and secure system.
-
Download Malwarebytes for Windows
You can download Malwarebytes by clicking the link below.
-
Install Malwarebytes
After the download is complete, locate the MBSetup file, typically found in your Downloads folder. Double-click on the MBSetup file to begin the installation of Malwarebytes on your computer. If a User Account Control pop-up appears, click “Yes” to continue the Malwarebytes installation.
-
Follow the On-Screen Prompts to Install Malwarebytes
When the Malwarebytes installation begins, the setup wizard will guide you through the process.
-
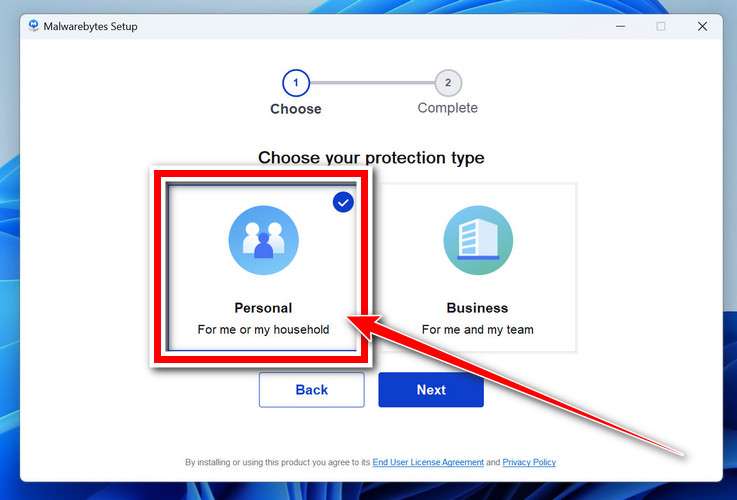
You’ll first be prompted to choose the type of computer you’re installing the program on—select either “Personal Computer” or “Work Computer” as appropriate, then click on Next.
-
Malwarebytes will now begin the installation process on your device.
-
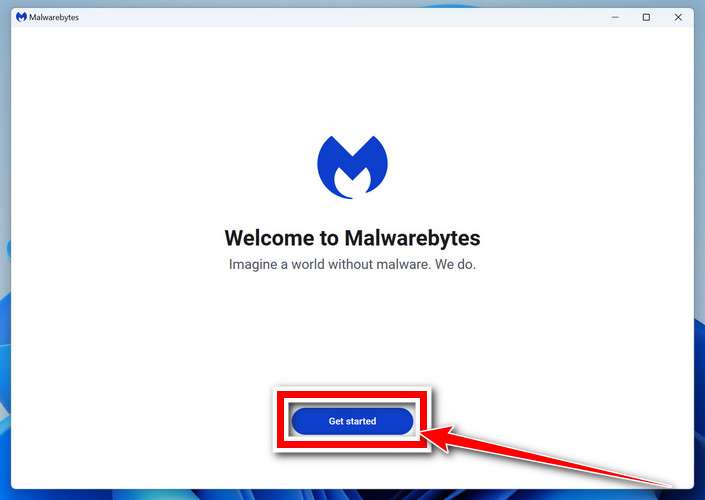
When the Malwarebytes installation is complete, the program will automatically open to the “Welcome to Malwarebytes” screen.
-
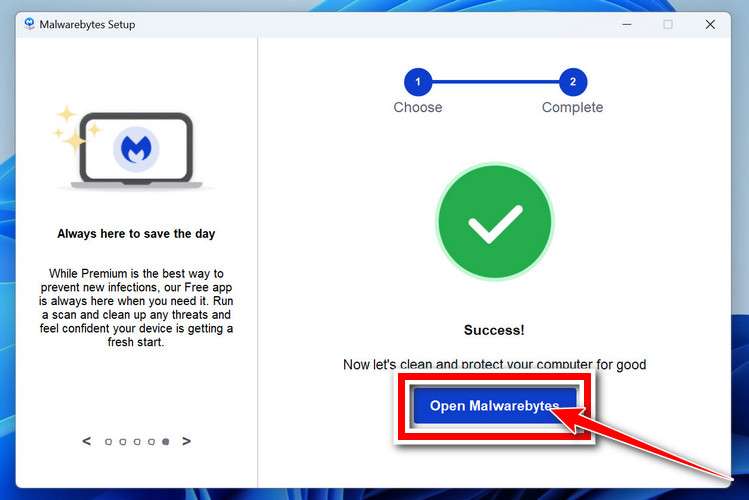
On the final screen, simply click on the Open Malwarebytes option to start the program.
-
-
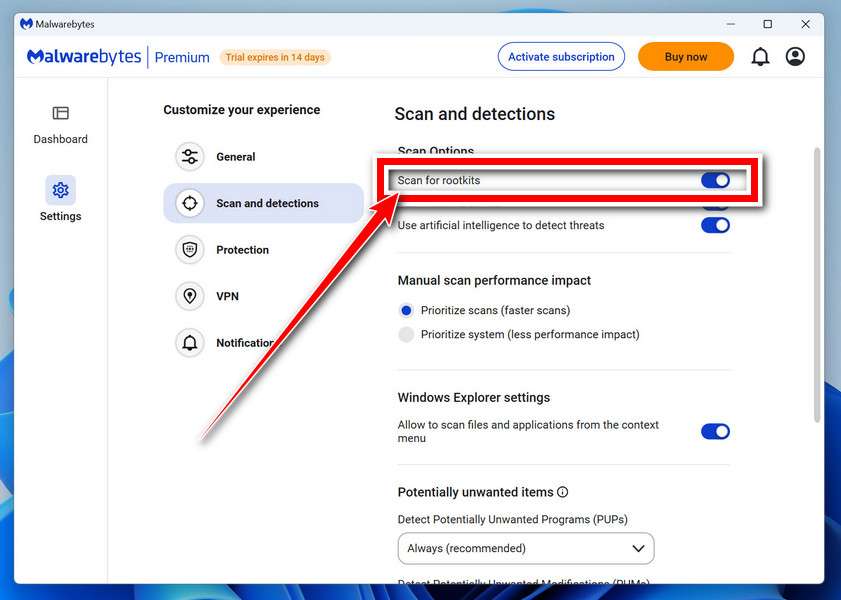
Enable “Rootkit scanning”.
Malwarebytes Anti-Malware will now start, and you will see the main screen as shown below. To maximize Malwarebytes’ ability to detect malware and unwanted programs, we need to enable rootkit scanning. Click on the “Settings” gear icon located on the left of the screen to access the general settings section.
In the settings menu, enable the “Scan for rootkits” option by clicking the toggle switch until it turns blue.
Now that you have enabled rootkit scanning, click on the “Dashboard” button in the left pane to get back to the main screen.
-
Perform a Scan with Malwarebytes.
To start a scan, click the Scan button. Malwarebytes will automatically update its antivirus database and begin scanning your computer for malicious programs.
-
Wait for the Malwarebytes scan to complete.
Malwarebytes will now scan your computer for browser hijackers and other malicious programs. This process can take a few minutes, so we suggest you do something else and periodically check the status of the scan to see when it is finished.
-
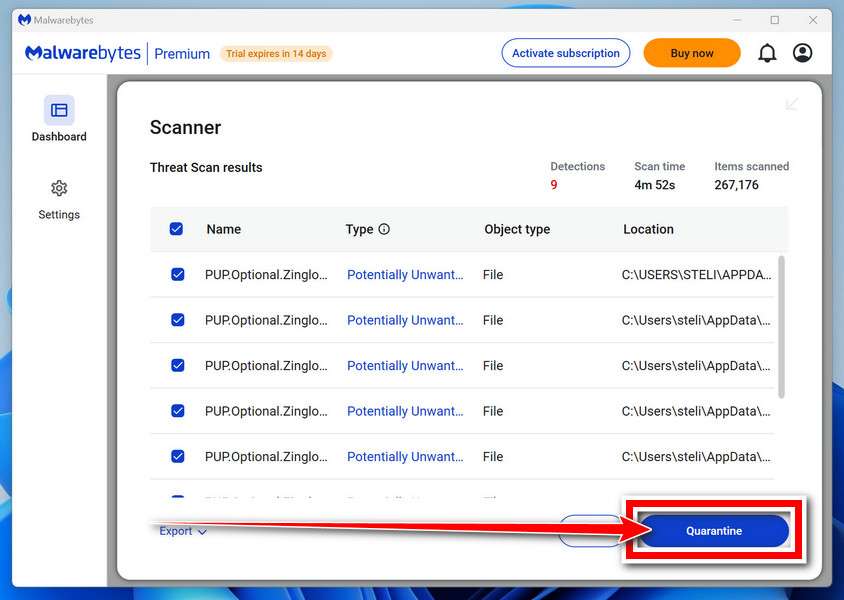
Quarantine detected malware
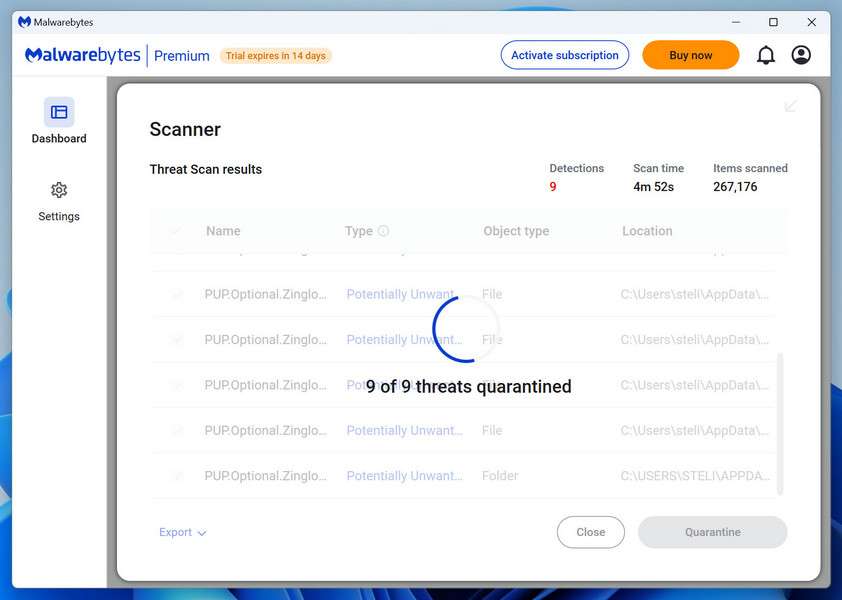
Once the Malwarebytes scan is complete, it will display a list of detected malware, adware, and potentially unwanted programs. To effectively remove these threats, click the “Quarantine” button.
Malwarebytes will now delete all of the files and registry keys and add them to the program’s quarantine.
-
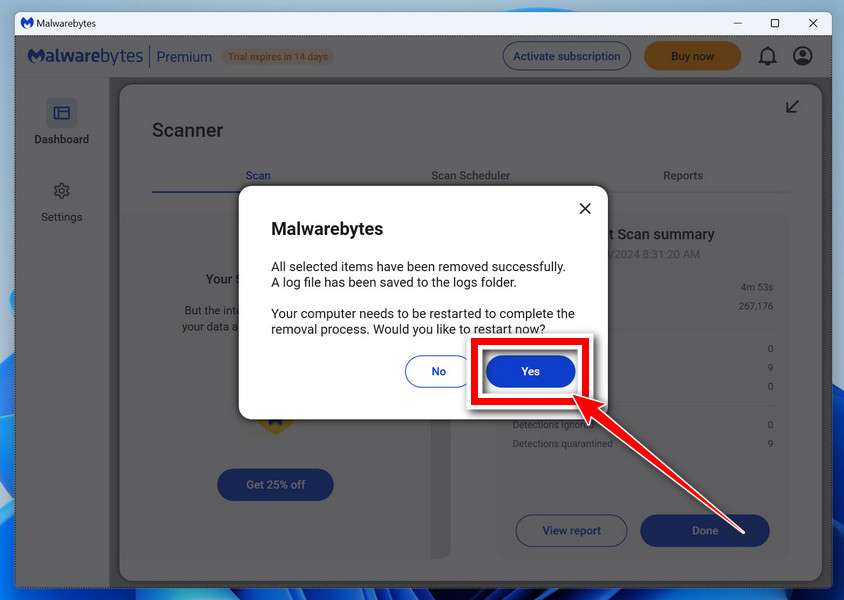
Restart your computer.
When removing files, Malwarebytes may require a reboot to fully eliminate some threats. If you see a message indicating that a reboot is needed, please allow it. Once your computer has restarted and you are logged back in, you can continue with the remaining steps.
STEP 5: Use HitmanPro to remove Rootkits and other Malware
In this fifth step, while the computer is in normal back, we will download and run a scan with HitmanPro to remove Trojans, rootkits, and other malicious programs.
HitmanPro is a second-opinion scanner that takes a unique cloud-based approach to malware scanning. HitmanPro scans the behavior of active files and also files in locations where malware normally resides for suspicious activity. If it finds a suspicious file that’s not already known, HitmanPro sends it to its clouds to be scanned by two of the best antivirus engines today, which are Bitdefender and Kaspersky.
Although HitmanPro is shareware and costs $24.95 for 1 year on 1 PC, there is no limit on scanning. The limitation only kicks in when there is a need to remove or quarantine detected malware by HitmanPro on your system and by then, you can activate the one-time 30-days trial to enable the cleanup.
-
Download HitmanPro.
You can download HitmanPro by clicking the link below.
HITMANPRO DOWNLOAD LINK
(The above link will open a new web page from where you can download HitmanPro) -
Install HitmanPro.
When HitmanPro has finished downloading, double-click on “hitmanpro.exe” (for 32-bit versions of Windows) or “hitmanpro_x64.exe” (for 64-bit versions of Windows) to install this program on your computer. In most cases, downloaded files are saved to the Downloads folder.
You may be presented with a User Account Control pop-up asking if you want to allow HitmanPro to make changes to your device. If this happens, you should click “Yes” to continue with the installation.
-
Follow the on-screen prompts.
When HitmanPro starts you will be presented with the start screen as shown below. Click on the “Next” button to perform a system scan.
-
Wait for the HitmanPro scan to complete.
HitmanPro will now begin to scan your computer for malicious programs.
-
Click on “Next”.
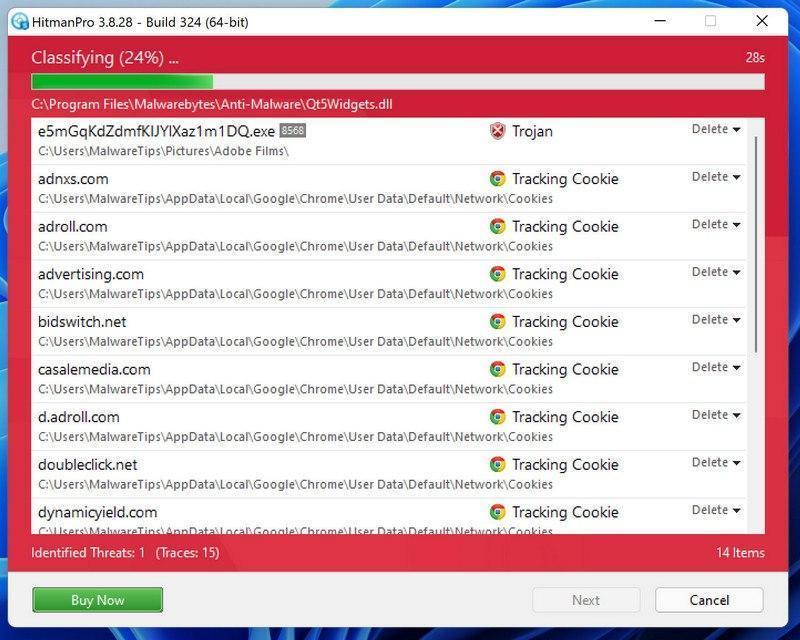
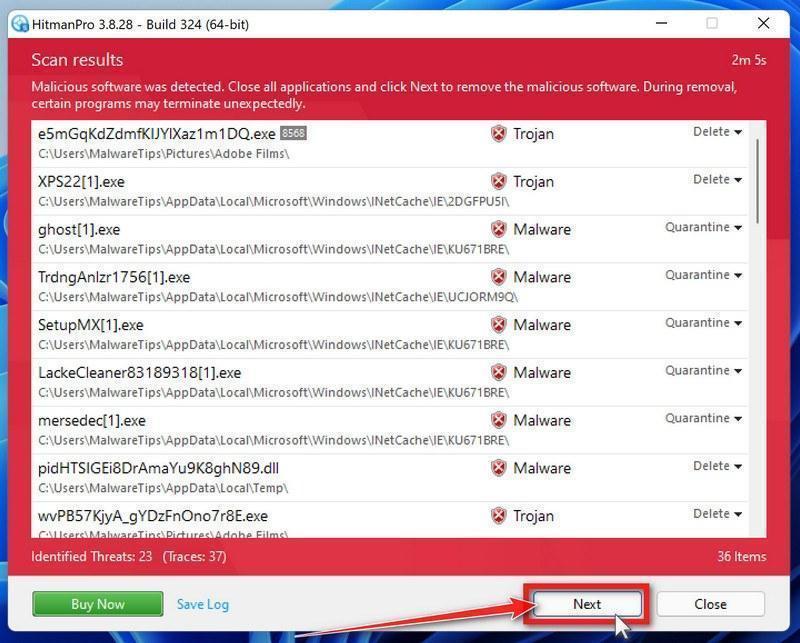
When HitmanPro has finished the scan, it will display a list of all the malware that it has found. Click on the “Next” button to have HitmanPro remove the detected items.
-
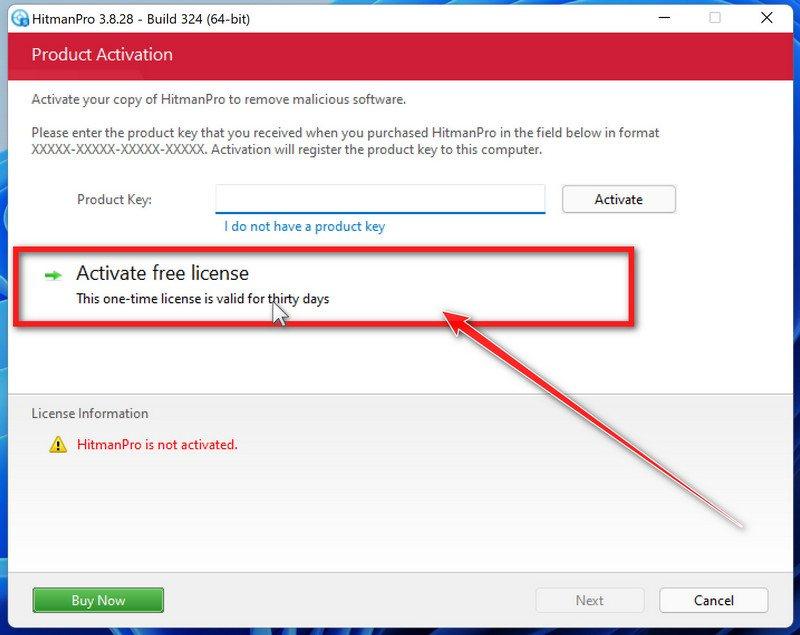
Click on “Activate free license”.
HitmanPro may now require to activate the free 30-days trial to remove the malicious files. To do this, click on the “Activate free license” button to begin the free 30 days trial and remove all the malicious files from your computer.
When the malware removal process is complete, it will display a screen that shows the status of the various programs that were removed. At this screen, you should click on the Next button and then if prompted you should click on the Reboot button. If HitmanPro does not prompt you to reboot, please just click on the Close button.
STEP 6: Use AdwCleaner to remove Malicious Browser Policies and Adware
In this next step, we will use AdwCleaner to remove malicious browser policies and unwanted browser extensions from your computer.
AdwCleaner is a free popular on-demand scanner that can detect and remove malware that even the most well-known anti-virus and anti-malware applications fail to find. This on-demand scanner includes a lot of tools that can be used to fix the side effects of adware. browser hijackers and other malware.
-
Download AdwCleaner.
You can download AdwCleaner by clicking the link below.
-
Double-click on the setup file.
Double-click on the file named “adwcleaner_x.x.x.exe” to start AdwCleaner. In most cases, downloaded files are saved to the Downloads folder.
AdwCleaner program will now open and you will be presented with the program’s license agreement. After you read it, click on the I agree button if you wish to continue. If Windows prompts you as to whether or not you wish to run AdwCleaner, please allow it to run.
-
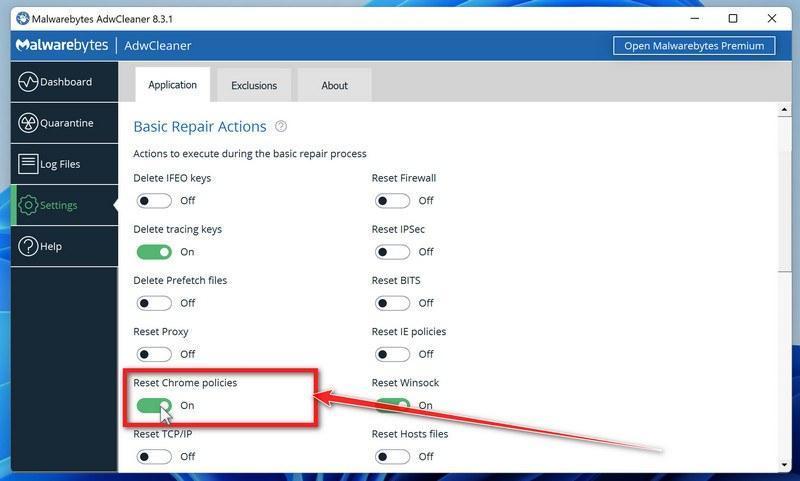
Enable “Reset Chrome policies” to remove malicious browser policies.
When AdwCleaner starts, on the left side of the window, click on “Settings” and then enable “Reset Chrome policies“.
-
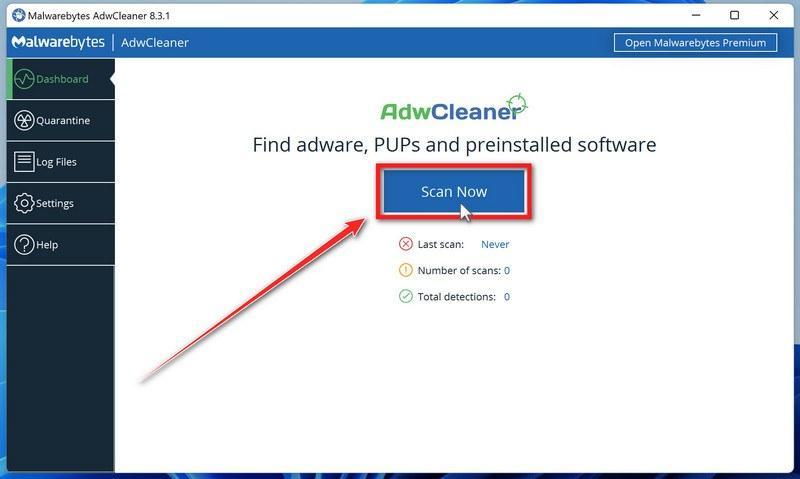
Click on the “Scan” button.
On the left side of the AdwCleaner window, click on “Dashboard” and then click “Scan” to perform a computer scan.
-
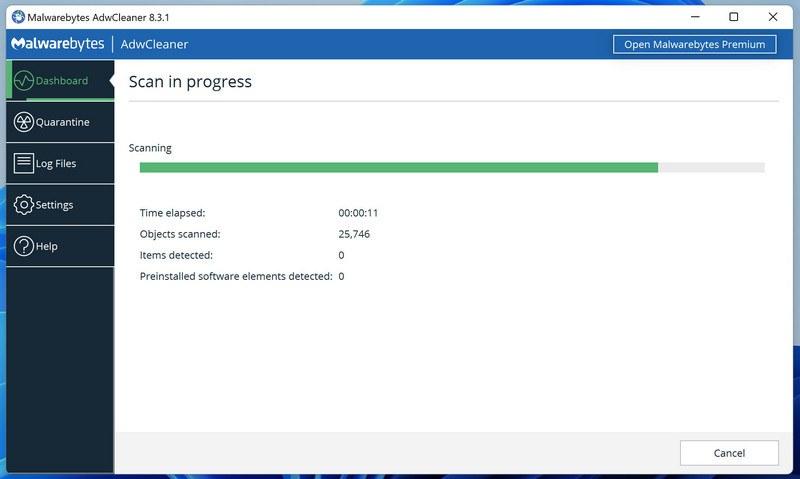
Wait for the AdwCleaner scan to finish.
AdwCleaner will now scan your computer for malware. This process can take a few minutes.
-
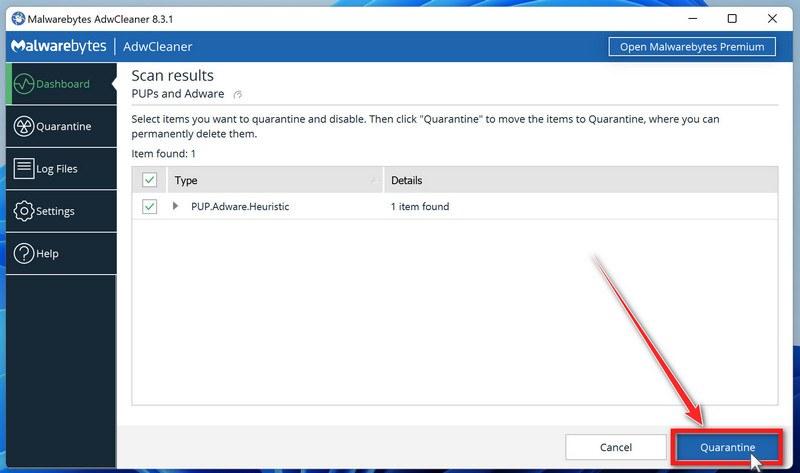
Click on “Quarantine” to remove malware.
When the AdwCleaner scan is completed it will display all of the items it has found. Click on the “Quarantine” button to remove the malicious programs from your computer.
-
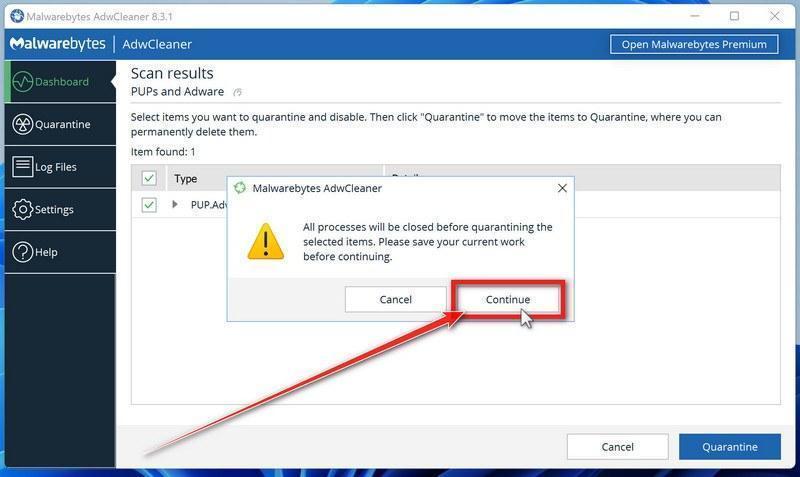
Click on “Continue” to remove the malicious programs.
AdwCleaner will now prompt you to save any open files or data as the program will need to close any open programs before it starts to clean. Click on the “Continue” button to finish the removal process.
AdwCleaner will now delete all detected malware from your computer. When the malware removal process is complete, you may be asked to restart your computer.
STEP 7: Perform a final check with ESET Online Scanner
This step involves installing and running a scan with ESET Online Scanner to check for any additional malicious programs that may be installed on the computer..
ESET Online Scanner is a free second-opinion scanner, designed to rescue your computer from malware (viruses, trojans, rootkits, etc.) that have infected your computer despite all the security measures you have taken (such as anti-virus software, firewalls, etc.).
-
Download ESET Online Scanner.
You can download ESET Online Scanner by clicking the link below.
-
Double-click on esetonlinescanner.exe to run the installer.
When ESET Online Scanner has finished downloading, double-click on “esetonlinescanner.exe” to install it program on your computer. In most cases, downloaded files are saved to the Downloads folder.
-
Install ESET Online Scanner.
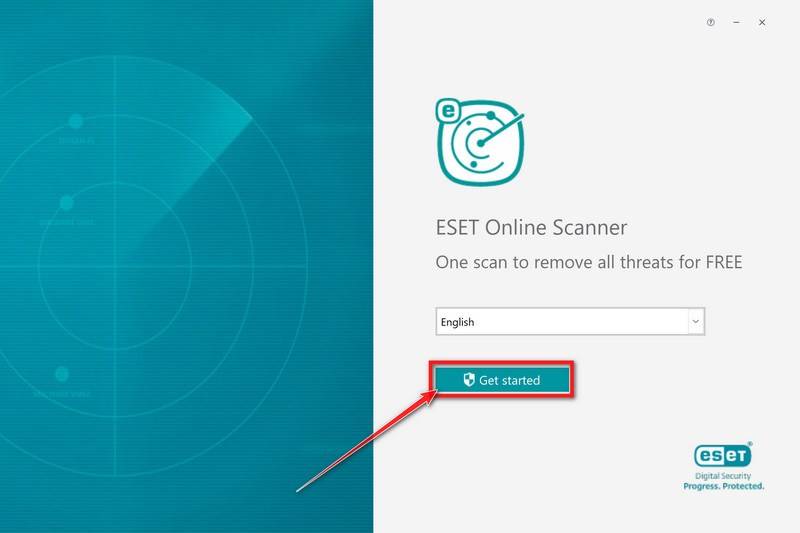
When ESET Online Scanner starts you will be presented with the start screen as shown below. Select your desired language from the drop-down menu and click Get started.
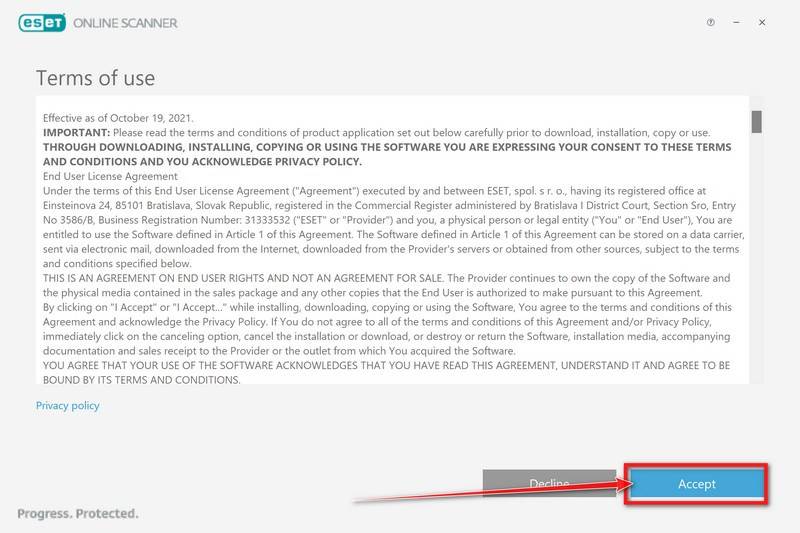
In the Terms of use screen, click Accept.
Select your preference for the Customer Experience Improvement Program and the Detection feedback system and click Continue.
-
Start a Full Scan with ESET Online Scanner
Click on Full Scan to perform an in-depth inspection of the entire computer.
Select Enable for Detection of Potentially Unwanted Applications, then click Start scan.
-
Wait for the ESET Online Scanner scan to finish.
ESET Online Scanner will now begin to scan your computer for malware. This process can take quite a while, so we suggest you do something else and periodically check on the status of the scan to see when it is finished.
-
ESET Online Scanner will automatically remove the malicious files.
At the end of the scan, the Found and resolved detections screen will be displayed. You can click View detailed results to view specific information. Detected threats are automatically cleaned and quarantined.
STEP 8: Run the System File Checker (SFC) tool
In this step, we will use System File Checker (SFC) tool to detect and repair files that may have been corrupted by malware.
The SFC tool scans all protected system files on your computer and replaces any files that are corrupt or damaged with a cached copy that is stored in a compressed folder at %WinDir%\System32\dllcache. By running the SFC tool, you can help ensure that your system is functioning properly and fix any issues.
-
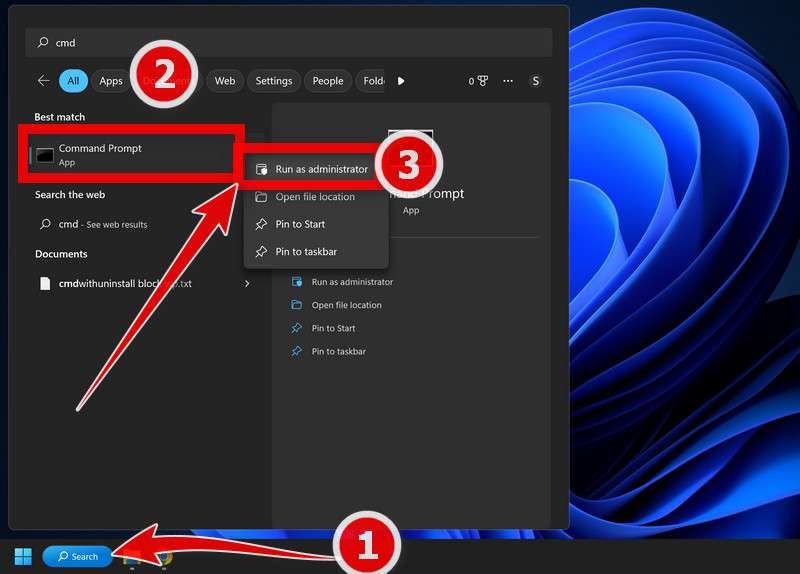
Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
To open the Command Prompt as an administrator in Windows, type “cmd” in the search bar and then right-click on the Command Prompt result and select “Run as administrator” as shown in the image below.
A User Account Control (UAC) prompt will appear asking for permission to allow the program to run. Click “Yes”.
-
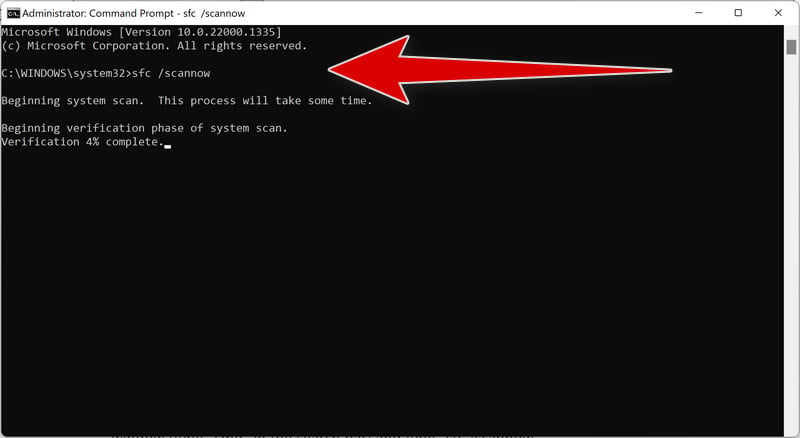
Type “sfc /scannow”.
You will now be presented with a black screen called the ‘Administrator: Command Prompt’. On this screen, type “sfc /scannow” to scan for and repair any corrupt system files.
-
Restart your computer.
Restart your computer if sfc /scannow repaired files. System File Checker may or may not prompt you to restart but even if it doesn’t, you should restart anyway.
-
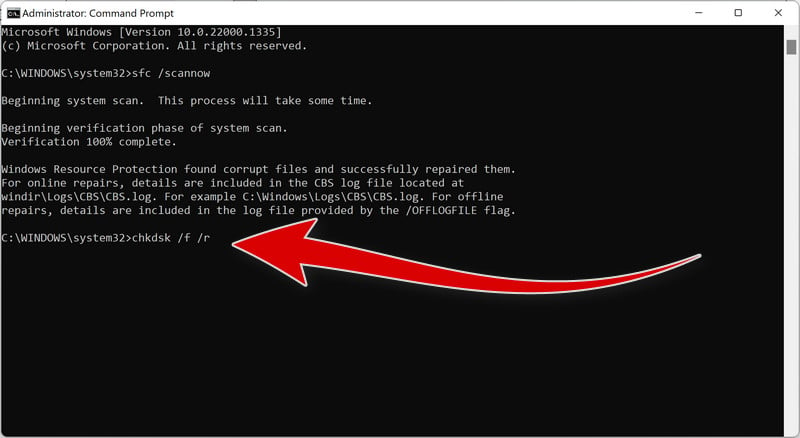
Run again sfc /scannow.
Run again sfc /scannow to check if the files were repaired.
STEP 9: Run the Disk Check tool
As a final step, we will utilize the Disk Check tool, commonly referred to as “chkdsk,” to identify and resolve any issues that were caused by malware.
This tool checks your hard disk for errors and can fix any issues it finds. To use the Disk Check tool, you will need to open the command prompt and enter the “chkdsk” command followed by the drive letter (e.g., “chkdsk C:”). You can also add the “/f” flag to the command to instruct the tool to fix any errors it finds. By running the Disk Check tool, you can help ensure that your hard disk is functioning properly and fix any issues that may be causing high disk usage.”
-
Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
To open the Command Prompt as an administrator in Windows, type “cmd” in the search bar and then right-click on the Command Prompt result and select “Run as administrator” as shown in the image below.
A User Account Control (UAC) prompt will appear asking for permission to allow the program to run. Click “Yes”.
-
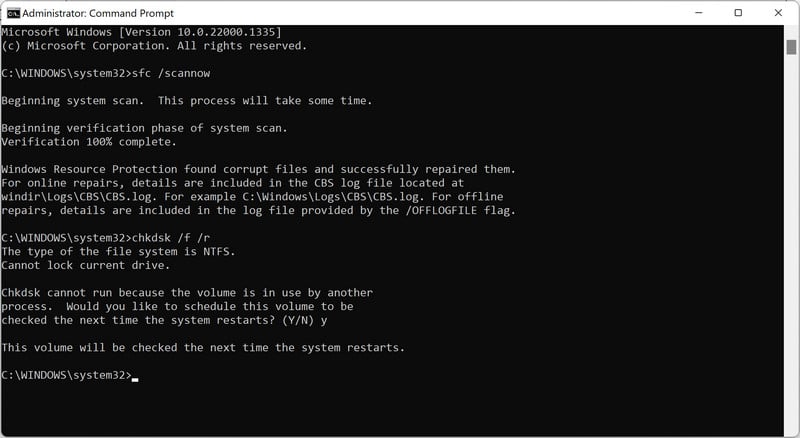
Type “chkdsk /f /r”
You will now be presented with a black screen called the ‘Administrator: Command Prompt’. On this screen, type “chkdsk /f /r” to repair any errors on your hard drive.
-
Restart your computer
The Disk Check tool may require you to restart your computer in order to complete the scan and repair process. Type “Y” and click on Enter, then restart the computer.
A CHKDSK command can take a long time, especially when performed on larger drives. Once it’s done, however, it will present a summary of results including total disk space, byte allocation, and, most importantly, any errors that were found and corrected.
Your computer should now be free of the Taskhostw.exe Trojan and other malware.
If your current antivirus allowed this malicious program on your computer, you may want to consider purchasing Malwarebytes Premium to protect against these types of threats in the future.
If you are still having problems with your computer after completing these instructions, then please follow one of the steps:
- Run a computer scan with ESET Online Scanner
- Ask for help in our Windows Malware Removal Help & Support forum.
Conclusion
Taskhostw.exe is a system file that starts the Windows services based on DLLs whenever the computer boots up. It is not malware by itself, but it can be used by malware to hide their activities. You can use various methods to check if taskhostw.exe is safe or malicious, such as scanning your computer with security software, checking the digital signature of the file, checking the CPU and memory usage of the process, uninstalling or repairing any recently installed programs, or performing a system restore or a clean boot.
Here are 10 basic security tips to help you avoid malware and protect your device:
To avoid potential dangers on the internet, it’s important to follow these 10 basic safety rules. By doing so, you can protect yourself from many of the unpleasant surprises that can arise when using the web.
Уровень сложностиПростой
Время на прочтение12 мин
Количество просмотров30K
В этой статье моей целью будет быстро и понятно внести памятку о легитимных процессах Windows. Немного расскажу, какой процесс за что отвечает, какие нормальные свойства имеют процессы, и приправлю это все небольшим количеством краткой, но полезной информации.
Я искренне приношу извинения за возможные неточности в изложении материала, информация в этой статье является «сборной солянкой» из моих слов и тысячи и тысячи источников!
По мере возможности я постараюсь обновлять материал, исправляя неточности, делая его более детализированным и актуальным.
System
Путь: Процесс не создается за счет исполняемого файла
Родительский процесс: Нет
Количество экземпляров: Один
Время запуска: Запуск системы
Здесь многословить не стоит: этот процесс отвечает за выполнение ядра операционной системы, других процессов и драйверов устройств, поэтому в основном под ним запускаются файлы .sys и некоторые важные для системы библиотеки. В обязанности System входит контроль за управлением оперативной и виртуальной памятью, объектами файловой системы.
smss.exe
Путь: %SystemRoot%\System32\smss.exe
Родительский процесс: System
Количество экземпляров: Один и дочерний, который запускается после создания сеанса
Время запуска: Через несколько секунд после запуска первого экземпляра
Session Manager Subsystem — диспетчер, отвечающий за создание новых сеансов, запуск процессов csrss.exe и winlogon.exe, отвечающих за графический интерфейс и вход в систему, а также за инициализацию переменных окружения. Первый экземпляр создает сеанс нуля и дочерний экземпляр, и как только дочерний экземпляр инициализирует новый сеанс, запуская csrss.exe и wininit.exe для сеанса 0 или winlogon.exe для сеанса 1, дочерний экземпляр завершается.
Если обнаружены проблемы с файловой системой, первостепенной функцией smss.exe является запуск системной утилиты для проверки диска — autochk.
После выполнения этих задач smss.exe переходит в пассивный режим.
Немного о сеансе 0 и сеансе 1
Сеанс 0 и сеанс 1 — это разные типы сеансов Windows, которые используются для запуска процессов.
Сеанс 0 создается при запуске системы, и в нем в фоновом режиме работают службы и процессы Windows.
Сеанс 1 создается для пользовательских процессов.Chkdsk и autochk — что это вообще, и зачем? А разница в чем?
На самом деле, autochk — это версия chkdsk, которая запускается автоматически smss.exe при обнаруженных проблемах с диском. А разница их в том, что chkdsk можно запустить в среде Windows напрямую из командной строки, а autochk — нет.
Да и autochk работает только с NTFS, что не скажешь про chkdsk — он, в дополнение к NTFS, поддерживает FAT и exFAT.Кстати!
По сути, chkdsk тоже может запускаться smss.exe, но это зависит от того, что указано в ключе реестраHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM \CurrentControlSet\Control\SessionManager(здесь хранится информация, предназначенная для Диспетчеpa сеансов ) в параметреBootExecute). При запуске chkdsk Диспетчер сеансов использует параметр/r, что позволяет утилите производить поиск повреждённых секторов (наряду с ошибками файловой системы).
csrss.exe
Путь: %SystemRoot%\System32\csrss.exe
Родительский процесс: smss.exe, который, запустив csrss.exe, завершает работу
Количество экземпляров: Два или больше
Время запуска: Через несколько секунд после запуска первых двух экземпляров — для сеанса 0 и сеанса 1
Client/Server Run-Time Subsystem — подсистема выполнения «клиент/сервер» обеспечивает пользовательский режим подсистемы Windows. Csrss.exe отвечает за импорт многих DLL-библиотек, которые предоставляют WinAPI (kernel32.dll, user32.dll, ws_2_32.dll и другие), а также за обработку графического интерфейса завершения работы системы.
Процесс запускается для каждого сеанса, а именно 0 и 1, дополнительные сеансы создаются при помощи удаленного рабочего стола или за счет быстрого переключения между пользователями.
Что интересно для Windows Server
Можно проверить количество активных сеансов, введя
query SESSIONв командной строке. Так можно проверить, соответствует ли количество сеансов количеству запущенных csrss.exe.И еще..
До Windows 7 csrss.exe обеспечивал старт окна консоли, но теперь этим занимается conhost.exe.
wininit.exe
Путь: %SystemRoot%\System32\wininit.exe
Родительский процесс: smss.exe, который завершает работу перед запуском wininit.exe
Количество экземпляров: Один
Время запуска: Через несколько секунд после запуска системы
После получения управления от процесса smss.exe, wininit.exe помечает себя как критический, что позволяет ему избегать нежелательного отключения при аварийном завершении сеанса или входа систему в гибернацию. Целью Windows Initialisation (wininit.exe) является запуск ключевых фоновых процессов в рамках сеанса нуля. Он запускает:
-
services.exe — Диспетчер управления службами
-
lsass.exe — Сервер проверки подлинности локальной системы безопасности
-
lsaiso.exe — для систем с включенной Credential Guard.
Дополнительно на протяжении всего сеанса работы системы wininit.exe отвечает за создание и наполнение папки TEMP. Перед выключением wininit.exe снова «активизируется» — теперь уже для корректного завершения запущенных процессов. .
Кстати!
До Windows 10 lsm.exe (Диспетчер локальных сеансов) также запускался с помощью wininit.exe. Начиная с Windows 10, эта функция перенесена в lsm.dll, которая размещена в svchost.exe.
services.exe
Путь: %SystemRoot%\System32\services.exe
Родительский процесс: wininit.exe
Количество экземпляров: Один
Время запуска: Через несколько секунд после запуска системы
В функции services.exe входит реализация Унифицированного диспетчера фоновых процессов (UBPM), который отвечает за фоновую работу таких компонентов, как Диспетчер управления службами (SCM) и Планировщик задач (Task Sheduler). Словом, services.exe отвечает за управление службами, а также за контроль за взаимодействием служб, обеспечивая их безопасную и эффективную работу.
UBPM: немного для тех, кто видит первый раз
Унифицированный диспетчер фоновых процессов (UBPM) — компонент системы, который автоматически управляет фоновыми процессами, такими как службы и запланированные задачи. Словом, он помогает оптимизировать запущенные в фоновом режиме службы, приостанавливать или завершать фоновые процессы, что позволяет экономить ресурсы системы.
Кстати!
До Windows 10, как только пользователь успешно вошел в систему в интерактивном режиме, services.exe считал загрузку успешной и устанавливал для последнего удачного набора элементов управления
HKLM\SYSTEM\Select\LastKnownGoodзначениеCurrentControlSet.А LastKnownGood — что это вообще?
LastKnownGood являлся опцией восстановления, благодаря которой можно запустить систему с последней рабочей конфигурацией, если система не может загрузиться из-за каких-либо причин. LastKnownGood сохранял резервную копию части реестра, в которой хранится информация о системе, драйверах и настройках.
Когда это могло пригодиться? Например, если загрузка нового ПО или изменение параметров системы не привело ни к чему хорошему. Тогда можно было бы использовать эту опцию, чтобы отменить изменения и откатиться к прошлому состоянию.
svchost.exe
Путь: %SystemRoot%\system32\svchost.exe
Родительский процесс: services.exe (чаще всего)
Количество экземпляров: Несколько (обычно не менее 10)
Время запуска: В течение нескольких секунд после загрузки, однако службы могут запускаться в течение работы системы, что приводит к появлению новых экземпляров svchost.exe.
svchost.exe (в Диспетчере задач прописывается как Служба узла) — универсальный хост-процесс для служб Windows, использующийся для запуска служебных DLL. В системе запускается несколько экземпляров svchost.exe, и каждая служба работает в своем собственном процессе svchost, что позволяет изолировать ошибки в работе одной службы от других, хотя в системах с ОЗУ менее 3,5 ГБ службы приходится группировать (см. ниже). Ну а в системах с оперативной памятью более 3,5 ГБ можно увидеть даже более 50 экземпляров svchost.exe.
Злоумышленники часто пользуются преимуществом наличия большого количества процессов svchost.exe, и могут воспользоваться этим, чтобы разместить какую-либо вредоносную DLL в качестве службы, либо запустить вредоносный процесс с именем svchost.exe или что-то типа scvhost.exe, svhost.exe и так далее.
Хотя, как известно, так можно сделать с любым процессом, но с svchost.exe это происходит почаще.
Кстати!
До Windows 10 версии 1703 экземпляры svchost.exe по умолчанию запускались в системе с уникальным параметром
-k, благодаря которому была возможна группировка похожих служб. Типичные параметры-kвключают:
DcomLaunch — служба, которая запускает компоненты COM и DCOM, благодаря которым программы взаимодействуют между собой на удаленных компьютерах
RPCSS — служба RPC (удаленный вызов процедур), благодаря которой программы взаимодействуют между собой через сеть.
LocalServiceNetworkRestricted — локальная служба, которая работает в пределах компьютера и имеет доступ к сети только для определенных операций.
LocalServiceNoNetwork — локальная служба, идентичная LocalServiceNetworkRestricted, но не имеющая доступа к сети.
netsvcs — группа служб Windows, благодаря которым выполняются задачи, связанные с сетью.
NetworkService — служба, которая позволяет выполнять задачи на удаленных хостах, и имеет доступ к сети для обмена данными.
Здесь можно почитать о разделении служб SvcHost.
RuntimeBroker.exe
Путь: %SystemRoot%\System32\RuntimeBroker.exe
Родительский процесс: svchost.exe
Количество экземпляров: Один или больше
Время запуска: Может быть разным
Работающий в системах Windows, начиная с Windows 8, RuntimeBroker.exe действует как прокси между ограниченными приложениями универсальной платформы Windows (UWP) и набором функций и процедур Windows API. В целях безопасности приложения UWP должны иметь ограниченные возможности взаимодействия с оборудованием, файловой системой и другими процессами, поэтому процессы-брокеры а-ля RuntimeBroker.exe используются для обеспечения требуемого уровня доступа для таких приложений.
Обычно для каждого приложения UWP существует один файл RuntimeBroker.exe. Например, запуск сalculator.exe приведет к запуску соответствующего процесса RuntimeBroker.exe.
И такое было: об утечках памяти, связанных с RuntimeBroker
Когда процесс RuntimeBroker еще был в новинку, пользователи во время работы с системой начали замечать, что RuntimeBroker.exe нещадно занимает аж более 500 МБ памяти, что несвойственно для него.
Оказывается, ошибка заключалась в следующем: каждый вызов методаTileUpdater.GetScheduledTileNotificationsприводила к тому, что RuntimeBroker выделял память без ее дальнейшего высвобождения. Чаще всего с этим сталкивались пользователи, у которых было установлено приложение «The Time» для измерения времени — оно постоянно обновляло информацию на плитке.Об этом казусе в Windows 8 можно почитать тут.
Про метод TileUpdater.GetScheduledTileNotifications
Если кратко, это метод, позволяющий получать запланированные уведомления от плиток в универсальных приложениях Windows (UWP). Он позволяет приложениям отображать информацию на стартовом экране пользователя в виде динамически обновляемых плиток.

taskhostw.exe
Путь: %SystemRoot%\System32\taskhostw.exe
Родительский процесс: svchost.exe
Количество экземпляров: Один или больше
Время запуска: Может быть разным
Процесс Task Host Window отвечает за выполнение различных задач Windows.
С началом работы, taskhostw.exe начинает выполнять задачи, которые были назначены ему системой, а в течение работы системы выполняет непрерывный цикл прослушивания триггерных событий. Примеры триггерных событий, которые могут инициировать задачу, могут включать в себя:
-
Определенное расписание задач
-
Вход пользователя в систему
-
Запуск системы
-
Событие журнала Windows
-
Блокировка/ разблокировка рабочей станции и т.д.
Двое из ларца: В чем разница между Task Host Window и Task Scheduler?
Task Host Window отвечает за выполнение различных системных задач, например, запуск служб и выполнение запросов на исполнение программ. Taskhostw.exe может использоваться для запуска службы обновления Windows, перехода компьютера в режим сна или ожидания после определенного времени и так далее.
Task Sheduler, он же Планировщик задач, — инструмент, благодаря которому пользователь имеет возможность создавать задачи и запускать их по расписанию или при определенных событиях. Планировщик задач может быть использован для запуска программ, скриптов и автоматизации задач.
lsass.exe
Путь: %SystemRoot%\System32\lsass.exe
Родительский процесс: wininit.exe
Количество экземпляров: Один
Время запуска: В течение нескольких секунд после загрузки
Local Security Authentication Subsystem Service (Служба проверки подлинности локальной системы безопасности) отвечает за аутентификацию пользователей путем вызова соответствующего пакета аутентификации, указанного в HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa. Обычно это Kerberos для учетных записей домена или MSV1_0 для локальных учетных записей. Помимо аутентификации пользователей, lsass.exe также отвечает за реализацию локальной политики безопасности (например, политики паролей и политики аудита), а также за запись событий в журнал событий безопасности.
Что любят котята: Mimikatz и LSASS
Многим известно, что злоумышленники могут использовать Mimikatz, зачастую для перехвата учетных данных в операционной системе, и делают они это за счет перехвата данных процесса lsass.exe.
Все просто: работает Mimikatz на уровне ядра и внедряется в процесс LSASS или использует метод DLL-injection. Кража учетных данных происходит либо за счет получения доступа к памяти процесса, в котором лежат заветные креды, либо за счет перехвата вызова функций до шифрования учетных данных.
Также Mimikatz не пренебрегает использованием стандартных функций Win32 LsaProtectMemory и LsaUnprotectMemory, которые используются для шифрования и расшифровки некоторых участков памяти с чувствительной информацией.Чуть больше об lsass.exe можно прочитать тут.
И о любви котят к LSASS — тут.
winlogon.exe
Путь: %SystemRoot%\System32\winlogon.exe
Родительский процесс: smss.exe, который, запустив winlogon.exe, завершает работу
Количество экземпляров: Один или больше
Время запуска: В течение нескольких секунд после загрузки первого экземпляра, дополнительные экземпляры запускаются по мере создания новых сеансов (подключение с удаленного рабочего стола и быстрое переключение пользователей)
Winlogon обрабатывает интерактивный вход и выход пользователей из системы. Он запускает LogonUI.exe, который использует поставщика учетных данных для сбора учетных данных пользователя, а затем передает учетные данные lsass.exe для проверки.
После аутентификации пользователя Winlogon загружает NTUSER.DAT пользователя в HKCU, настраивает окружение пользователя, включая его рабочий стол, настройки реестра и т.д., и запускает оболочку пользователя explorer.exe через userinit.exe.
Совсем чуть-чуть об logonUI.exe
Да, название говорит само за себя: logonUI.exe отвечает за отображение экрана входа пользователя и за взаимодействие с пользователем при входе в систему. Если просто, то вывод того самого экрана входа и поля для ввода учетных данных — старания logonUI.exe.
..И об userinit.exe
Основная функция userinit.exe заключается в подготовке среды пользователя для работы в операционной системе.
Когда пользователь входит в систему, userinit.exe инициирует загрузку профиля пользователя, настройки оболочки (шаблоны рабочего стола, запуск программ и т.д.). После выполнения сих действий, userinit.exe запускает оболочку пользователя explorer.exe, которая отображает рабочий стол и другие элементы интерфейса, после чего завершает работу.Кстати!
Обработка команд из
CTRL+ALT+DEL, между прочим, тоже входит в обязанности winlogon.exe.
А тут можно почитать о Winlogon еще и узнать чуть больше — и про его состояния, и про GINA, и про все-все.
explorer.exe
Путь: %SystemRoot%\explorer.exe
Родительский процесс: userinit.exe, который завершает работу
Количество экземпляров: Один или больше, если включена опция Запускать окна с папками в отдельном процессе
Время запуска: Интерактивный вход пользователя
По своей сути, explorer.exe предоставляет пользователям доступ к файлам, хотя одновременно это файловый браузер через проводник Windows (тот самый Диспетчер файлов) и пользовательский интерфейс, предоставляющий такие функции, как:
-
Рабочий стол пользователя
-
Меню «Пуск»
-
Панель задач
-
Панель управления
-
Запуск приложений через ассоциации расширений файлов и файлы ярлыков
Словом, процесс отвечает за отображение действий пользователя: открытие и закрытие окон, перемещение и копирование файлов и тому подобное.
Запуск приложений через ассоциации расширений файлов
По сути, это процесс, при котором система использует информацию о расширении имени файла (например,
.txt) для определения программы, которая будет запущена, чтобы обработать этот файл. Например, файл расширения.txtассоциируется в системе с текстовым редактором, потому она запустит его при двойном щелчке мышью. Словом, ассоциации расширений файлов определяют, какие программы открываются по умолчанию для определенных типов файлов.Также и с ярлыками — при щелчке запускается связанные с ними ресурсы.
Explorer.exe — это пользовательский интерфейс по умолчанию, указанный в значении реестра HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\Shell, хотя Windows может работать и с другим интерфейсом, например, с cmd.exe.
Следует заметить, что легитимный explorer.exe находится в каталоге %SystemRoot%, а не %SystemRoot%\System32.
Explorer — это же браузер, нет?
В старые добрые времена, когда на системах еще стоял Internet Explorer, запуск этого браузера инициировал процесс iexplore.exe, и с каждой новой вкладкой создавался новый экземпляр этого процесса. Сейчас остался только explorer.exe, который ни в коем случае не связан с браузером.
Вместо Internet Explorer на наших системах стоит MS Edge, который имеет процесс msedge.exe, исполняемый файл которого лежит в\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft\Edge\Application\.
ctfmon.exe
Путь: %SystemRoot%\System32\ctfmon.exe
Родительский процесс: Зависит от того, какой процесс запустил ctfmon.exe
Количество экземпляров: Один
Время запуска: При входе в систему
Процесс ctfmon.exe или, как привыкли его видеть, CTF-загрузчик, управляет функциями рукописного и сенсорного ввода, распознавания голоса и переключения языка на панели задач. Также процесс отслеживает активные программы и настраивает языковые параметры для обеспечения поддержки многоязычного ввода.
Ctfmon.exe может быть запущен разными процессами, и это напрямую зависит от того, какие функции ввода или языка используются в системе. Примеры родительских процессов и причины запуска:
-
svchost.exe — использование рукописного ввода или распознавания речи
-
winword.exe, excel.exe и т.д. — использование программ пакета Microsoft Office
-
searchUI.exe — использование поиска на панели задач или приложения из магазина Windows 10
Конечно, это не исчерпывающий список легитимных процессов, но, как минимум, основной. Хочется верить, что этот материал был полезен тем, кто пугается страшных букв в Диспетчере задач и тем, кто просто хочет узнать немного больше.
Спасибо за прочтение!
*7-day Free Trial w/Credit card, no charge upfront or if you cancel up to 2 days before expiration; Subscription price varies per region w/ auto renewal unless you timely cancel; notification before you are billed; 30-day money-back guarantee; Read full terms and more information about free remover.
Taskhostw.exe is an integral component of the Windows operating system, serving as the host for tasks within Windows. Its primary role is to initiate Windows services that rely on DLLs (Dynamic Link Libraries) during the system’s startup phase. DLLs are files filled with code and resources that various applications can utilize concurrently. Taskhostw.exe provides a platform for processes running as part of a DLL rather than as standalone executable (EXE) files. The authentic version of taskhostw.exe is found in the C:\Windows\System32 directory. If discovered in a different location, it might indicate the presence of malware posing as taskhostw.exe. To verify the file’s location, you can navigate to it via the Task Manager by right-clicking the file and selecting “Open file location”.

Taskhostw.exe, in its genuine form, is not malicious software. However, it can be exploited by malware to conceal nefarious activities. Malicious programs might forge a counterfeit taskhostw.exe file and locate it outside its standard directory. Additionally, they could embed harmful code into the authentic taskhostw.exe process, leveraging it to execute malevolent deeds.
Any computer, that has been attacked by a malware from the Trojan horse family, could have really serious damage to its system as well as its data. Your PC is not an exception if it has been compromised by a Trojan like Taskhostw.exe Virus, Pinaview, StopAbit or Taskbarify. Once inside the PC, this virus can cause issues, which you would better never experience. Usually, it is very difficult to detect the infection without proper security software because it uses various camouflaging techniques to trick you and remain as long as possible on the computer. That’s why the researchers from our “How to remove” team would advise you to be very careful when trying to deal with Taskhostw.exe Virus. Below, you will find more information about the possible damage that this Trojan may cause and a helpful removal tool along with a manual Removal Guide for proper detection and elimination of all the related malicious scripts.
Whаt is Taskhostw.exe?
Ttaskhostw.exe file is a secure system process of Microsoft Windows 10 operating system Often, malware writers, such as viruses, worms, and trojans, intentionally give their processes Taskhostw.exe a filename to avoid detection.
Taskhostw.exe is a new Trojan horse threat, which has many malicious abilities. A number of online users have already been infected with this malware and have reported different issues. According to the latest security analysis, Taskhostw.exe is a sophisticated virus, which can silently infect any computer, without particular symptoms. The moment it gets inside the system, it can initiate various harmful processes, most of which are unlikely to be detected without a proper antivirus software. The Trojan usually hides its traces and camouflages its malicious activities under guise of regular system processes till the moment when some major damage is caused to the infected computer. Only then the victim is actually likely to find out about the presence of the infection. This method of operation based on stealth and disguise is what makes Taskhostw.exe Virus such a dreadful infection which can cause damage when and where you least expect it.
To prevent such dreadful malicious consequences, our “How to remove” team would highly recommend you remove Taskhostw.exe Virus immediately. The quickest way to do that is to scan your PC with the professional Taskhostw.exe Virus removal tool form this article’s page. You can also use the instructions in the Removal Guide below or contact a professional of your choice for additional assistance.
How can you get infected with Taskhostw.exe Virus?
Usually, in order to enter your system, Taskhostw.exe Virus needs to mislead you about its real nature and purpose. Normally, the infection pretends to be an attractive offer, a seemingly harmless link, file or a file which could be delivered as an email, attachment, social share link or a pop-up message on your screen. The aim of this is to trigger your curiosity and make you click on the malicious transmitter without taking a moment to think about whether or not it’s safe. At that very moment, the Trojan activates and exploits your system through a vulnerability or an exploit kit. If your antivirus program is updated, it may detect the threat and inform you on time. However, if you have not updated your virus definitions, it may not provide you with protection against a new Trojan such as Taskhostw.exe Virus.
What issues may Taskhostw.exe Virus cause once in your system?
Trojans are a multipurpose type of malware. They can be programmed to perform specific criminal tasks and serve the purpose of their criminal creators. What exactly the hackers may decide to use a threat like Taskhostw.exe for is very difficult to predict. Still, here we have listed some of the most common and possible malicious activities, which the Trojans could generally be programmed to perform. Take a look at them and know that Taskhostw.exe may be related to them or even some other forms of fraud or theft.
- System crashing, corruption and destruction of data: Partial or total corruption of the infected computer could be one of the goals of the hackers. They may also want to delete certain files from your system or to wipe off the entire data from the computer’s hard drives and with a Trojan like Taskhostw.exe, this could happen very easily.
- Unauthorized access to the computer and exploitation of its resources: With the help of a Trojan like Taskhostw.exe, your PC may be turned into a bot, which the hackers can control remotely and manipulate as they please. They may exploit it for a number of other criminal purposes without your knowledge and indirectly relate you to them.
- Spreading viruses and Ransomware: A Trojan horse can infect any system by using stealth and disguise. With the same ease, it can also provide a backdoor for other infections such as Ransomware, Spyware, other Trojans or some other form of insidious malware programs.
- Theft of banking credentials, passwords, and data: Any information that you keep on your PC could easily be transmitted to the hackers’ remote servers when a Trojan horse is secretly working on your system. This means that everything you type and you do on the machine might be getting monitored and used for further fraud, theft, blackmailing or some other form of abuse.
Should you believe that Taskhostw.exe is compromised by malware, you may adhere to the following complimentary guide for malware eradication to purify your device.
SUMMARY:
Remove Taskhostw.exe
To try and remove Taskhostw.exe quickly you can try this:
- Go to your browser’s settings and select More Tools (or Add-ons, depending on your browser).
- Then click on the Extensions tab.
- Look for the Taskhostw.exe extension (as well as any other unfamiliar ones).
- Remove Taskhostw.exe by clicking on the Trash Bin icon next to its name.
- Confirm and get rid of Taskhostw.exe and any other suspicious items.
If this does not work as described please follow our more detailed Taskhostw.exe removal guide below.
If you have a Windows virus, continue with the guide below.
If you have a Mac virus, please use our How to remove Ads on Mac guide.
If you have an Android virus, please use our Android Malware Removal guide.
If you have an iPhone virus, please use our iPhone Virus Removal guide.
Some of the steps may require you to exit the page. Bookmark it for later reference.
Next, Reboot in Safe Mode (use this guide if you don’t know how to do it).
Uninstall the Taskhostw.exe app and kill its processes
The first thing you must try to do is look for any sketchy installs on your computer and uninstall anything you think may come from Taskhostw.exe. After that, you’ll also need to get rid of any processes that may be related to the unwanted app by searching for them in the Task Manager.
Note that sometimes an app, especially a rogue one, may ask you to install something else or keep some of its data (such as settings files) on your PC – never agree to that when trying to delete a potentially rogue software. You need to make sure that everything is removed from your PC to get rid of the malware. Also, if you aren’t allowed to go through with the uninstallation, proceed with the guide, and try again after you’ve completed everything else.
-
Uninstalling the rogue app
-
Killing any rogue processes
Type Apps & Features in the Start Menu, open the first result, sort the list of apps by date, and look for suspicious recently installed entries.
Click on anything you think could be linked to Taskhostw.exe, then select uninstall, and follow the prompts to delete the app.

Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc, click More Details (if it’s not already clicked), and look for suspicious entries that may be linked to Taskhostw.exe.
If you come across a questionable process, right-click it, click Open File Location, scan the files with the free online malware scanner shown below, and then delete anything that gets flagged as a threat.
Each file will be scanned with up to 64 antivirus programs to ensure maximum accuracy
This scanner is free and will always remain free for our website’s users.
This file is not matched with any known malware in the database. You can either do a full real-time scan of the file or skip it to upload a new file. Doing a full scan with 64 antivirus programs can take up to 3-4 minutes per file.
Drag and Drop File Here To Scan
Analyzing 0 s
Each file will be scanned with up to 64 antivirus programs to ensure maximum accuracy
This scanner is based on VirusTotal’s API. By submitting data to it, you agree to their Terms of Service and Privacy Policy, and to the sharing of your sample submission with the security community. Please do not submit files with personal information if you do not want them to be shared.

After that, if the rogue process is still visible in the Task Manager, right-click it again and select End Process.
Undo Taskhostw.exe changes made to different system settings
It’s possible that Taskhostw.exe has affected various parts of your system, making changes to their settings. This can enable the malware to stay on the computer or automatically reinstall itself after you’ve seemingly deleted it. Therefore, you need to check the following elements by going to the Start Menu, searching for them, and pressing Enter to open them and to see if anything has been changed there without your approval. Then you must undo any unwanted changes made to these settings in the way shown below:
Type in Start Menu: View network connections
Right-click on your primary network, go to Properties, and do this:

Type in Start Menu: C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts

Type in the Start Menu: Startup apps

Type in the Start Menu: Task Scheduler

Type in the Start Menu: Services

Type in the Start Menu: Registry Editor
Press Ctrl + F to open the search window

Lidia is a web content creator with years of experience in the cyber-security sector. She helps readers with articles on malware removal and online security. Her strive for simplicity and well-researched information provides users with easy-to-follow It-related tips and step-by-step tutorials.
Lidia is a web content creator with years of experience in the cyber-security sector. She helps readers with articles on malware removal and online security. Her strive for simplicity and well-researched information provides users with easy-to-follow It-related tips and step-by-step tutorials.
If you have noticed taskhostw.exe processes in Task Manager, it’s understandable if you’re alarmed, especially during times when your computer is running slow. However, we recommend that you read through this article before you take any drastic action that might end up harming your PC. We’ll explain, in detail, what taskhostw.exe is, what it does, if it’s harmful or not, and how to fix problems related to the file.
What is taskhostw.exe and how to fix it?
Taskhostw.exe is an executable file developed by Microsoft for Windows. This particular file is associated with Windows 10. It is a Windows operating system process and is also identified as a Host Protocol. It also runs on Windows 8 and Windows 7, but with different names, such as “taskhost.exe” for Windows 7. In Windows 10, “takhostw” stands for Task Host for Windows.
The main job of the software is to launch DLL services on your Windows 10 PC when it boots up. It hosts the various processes that carry out the execution of DLL operations on the PC. DLL (Dynamic Link Library) files contain specific instructions that programs on the PC call upon to perform certain actions like locating files in certain directories, using a printer, and looking for space on the hard drive. A DLL file makes it easy for multiple different programs to share and utilize its abilities, even concurrently.
Taskhostw.exe also works to ensure that open applications, programs, and other processes are closed properly during a shut-down. An example that you might be cognizant of is open Microsoft Word files. When Word documents are open and you attempt to shut down your PC without first closing them, a Task Host window will be opened.
Taskhostw.exe can be found in the C:\windows\system32 folder and is a hidden Microsoft-signed Windows file, which means that it isn’t visible but you will be able to see the process in Task Manager. The file, on its own, is safe, but there are issues that can cause it to trigger errors and/or high CPU usage. We’ll explain more of these below.
Is taskhostw.exe a virus?
Most users begin to panic upon seeing the taskhostw.exe process in the task manager because they don’t know what it is. The truth is that the original file itself isn’t a virus and is an important part of Windows. However, it can hog system resources such as RAM and CPU when it is infected or runs into different problems. When this occurs, you can apply certain tweaks to fix the problem.
That said, there have been reports of different malicious programs designed to mimic taskhostw.exe. Hackers and developers of malware programs such as Trojans, worms, and viruses purposely assign the same name to their processes so they can run undetected. While these processes, in this case, are malware that you should get rid of, note that they’re not associated, in any way, to Windows 10 processes and the original taskhostw.exe.
Here are ways that you can detect the true taskhostw.exe and malware masked as the file:
- The original host protocol taskhostw.exe is located in C:\windows\system32.
- The known sizes of the file on Windows 10 are 71,848 bytes, 71,280 bytes, or 71,792 bytes.
Identifying suspicious files:
- Any taskhostw.exe file located in a C:\Program Files subfolder is dangerous. This is a malicious program that has no business being a Windows OS file, and it has no visible window. The malware can record mouse and keyboard inputs, monitor programs, and manipulate other applications. It usually has a file size of 1,113,088 bytes or 1,705,984 bytes.
- If the file is located in your profile subfolder such as a folder in C:\documents and settings\username or C:\Users\username (where “username” is your user account name), then it is a virus. It will have no descriptions, will be able to monitor programs, and can cause serious harm to your computer. The usual size of this file is 1,385,980 bytes or 1,379,328 bytes.
How to fix taskhostw.exe high CPU usage?
With the original taskhostw.exe, there are instances where the process can cause high CPU usage, which will likely result in laggy performance. The process also encounters problems that result in errors such as:
- Taskhostw.exe – Access denied
- Taskhost.exe – Application error
- Taskhost.exe – Error
We’ll explain some of the causes below:
Is your computer running slow or suffering system glitches? If so, it may need maintenance. Try running a dedicated PC optimization tool to check the health of your PC and apply the necessary fixes.
Mistakenly deleted system files
If you delete a system file that is associated with taskhostw.exe or other related files such as DLL files, these errors will pop up when their processes are launched. Also, the files might be mistaken for malware by your antivirus program and deleted as a result.
Partial or improper installation/uninstallation of certain programs
If you’ve recently installed or uninstalled an application and the process is incomplete, this could be the reason you’re facing issues with taskhostw.exe. The program could be one of such applications that use the taskhostw.exe file. When not properly installed or changed, it could leave bad files on your computer, and they will clash with taskhostw.exe because when taskhostw.exe calls these files, there’s no program to respond since the associated program has been removed or has not been installed properly.
Bad DLL files
They are one of the common causes of high CPU usage by taskhostw.exe. Certain applications, upon installation, replace existing DLL files to suit their processes. This usually results in these DLL files malfunctioning. When uninstalling an application, a DLL file can be deleted. What’s more, malware infection can also damage DLL files.
When a DLL file is bad and is called up by taskhostw.exe, errors or high CPU usage occur.
Corrupt registry keys
If registry keys and entries are corrupt, the taskhostw.exe file can run into problems, which will result in error messages and high CPU usage. Malware may infect registry keys that are associated with Windows, or there could be wrong registry entries due to an improper change or uninstallation/installation of certain programs.
Virus attack
Certain malware and viruses can cause damage to the taskhostw.exe file itself. Naturally, this will result in errors.
Device driver problems
Many device drivers, such as printer drivers, are associated with DLL files. If these device drivers are damaged, corrupt or missing, there will be interference with DLL files and, by extension, taskhostw.exe.
Now, without much ado, let’s dive into how the problems can be fixed!
1. Conduct a comprehensive malware scan
Since writers of malware applications disguise their processes as taskhostw.exe, you could well be facing high CPU usage as a result of these programs, and some of the taskhostw.exe processes you’re seeing in Task Manager might be malicious. Running a virus check can save you from future problems such as damage to your PC and theft of sensitive information. Your CPU and RAM will also be freed up.
A good program to use is Auslogics Anti-Malware. It’s a sophisticated tool that can fish out these malicious processes and put an end to them. It is compatible with Windows 10 and can run with or without other system protection software on your computer to give you the protection that you need.
2. Run System File Checker
Certain system files may become corrupt as a result of an improper shutdown or other issues. The System File Checker can be used to scan for such corrupted Windows files and restore them. We’ll put you through a complete step-by-step guide on how to do this:
Since you’re on Windows 10, you’ll first need to run the inbox Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) tool before you scan and restore with the System File Checker:
- Press the Windows and X keys together and select Command Prompt (Admin) from the menu.
- Press Yes in the User Account Control prompt and type the following command into the black window:
DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Restoreheal
Wait for the operation to be completed as it may take several minutes.
Note that the above command works by providing the files required to fix your computer through Windows Update, so your computer has to be online.
- Now, type the command below and hit Enter:
sfc /scannow
This command will scan the protected Windows OS files. If corrupted files are found, they will be replaced with cached copies normally located in a compressed folder at C:\Windows\System32\dllcache.
3. Restore your PC
Another possible solution to the issue is restoring your system to a previously working state. This is effective when you start noticing the high CPU usage or errors after a recent installation or uninstallation of an application. It could also fix Windows registry problems. Follow these steps to restore your PC:
- Go to Cortana search and type “restore point.”
- Select Create a Restore Point from the displayed results.
- The System Properties window will pop up.
- In the System Protection tab, click System Restore.
- When the System Restore window is launched, click Next, select a restore date, and then click Next again.
- Now, click Finish to confirm and allow the tool to do its job. Once your system restarts, check if your CPU usage is still high.
4. Repair corrupted DLL files
Like we stated above, bad DLL files cause taskhostw.exe errors and high CPU usage. In many cases, users experience this when launching or playing games, trying to play certain media files, or when they’re trying to use devices such as printers.
To fix the issue without hassle, it’s best to use Auslogics Driver Updater. The tool will scan for and identify problematic drivers and then download and install them from the right source. You may find it difficult locating the driver in question that’s causing the problem, which is why Auslogics Driver Updater can be a godsend.
5. Reinstall, repair or update problematic software
If you recently installed a program, try reinstalling it. This is because the installation might not be complete and could be causing issues as a result. If there’s a recent update for the software, download and install it.
6. Update your Windows 10
Taskhostw.exe errors can be resolved by installing new Windows updates. The new patches can automatically fix the issue, especially when corrupt system files are involved. To update:
- Click the Start button and go to Settings.
- In the Settings window, click Update & Security.
- Select Check for Updates and allow Windows to download and install the latest patches and software for your computer.
Summing up
We don’t recommend that you delete taskhostw.exe from C:\windows\system32 as it is an important part of Windows. We believe that, at least, one of these solutions will fix the problem you’re facing. If you have any issues or need further clarification, don’t hesitate to let us know in the comments section below and we’ll be happy to help!
Taskhostw.exe, stands for Task’s Host forWindows, is a file that serves as a host for DLL-based processes. In taskmanager, such processes are displayed with the name Host Process for WindowsTasks.
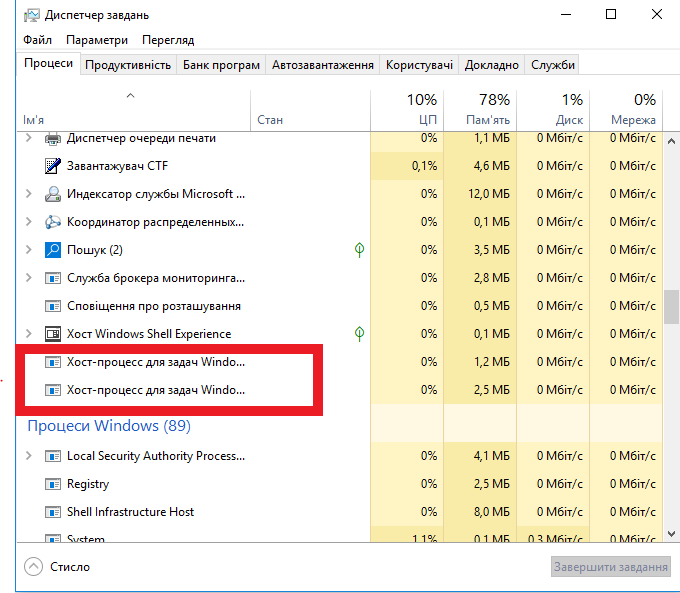
Several processes named Host Process for Windows Tasks can run on the computer at the same time. Windows will create a separate Host Process for Windows Tasks for each service which functions as a part of DLL. On the screenshot above are the examples of two such services working simultaneously.
Windows services types
There are various types of services running in the background in Windows. Some of these services are executed through executable (EXE) files. They are autonomous and are displayed in Task Manager with their own names. Another kind of processes are the tasks which are loaded from Dynamic Link Libraries (DLL). They don’t have their own executable files and cannot be presented as individual tasks of Windows OS in the Task Manager. Thus they need EXE hosts for that. Files named taskhostw.exe do this function for such DLL-based tasks.
How to check which process runs beneath Host Process for Windows Tasks
Unfortunately, Task Manager doesn’t provide you with the information about the service associated with this or that taskhost. But Microsoft has built a tool which allows you to do this. Process Explorer from Microsoft lets you learn which services are encoded inside of the taskhost.
It exists as a portable utility and doesn’t require additional steps such as installation. Once a ZIP archive with the tool is downloaded, you are ready to go.
If you do not have this program, you need to enter command in the cmd window:
C:\> tasklist/M /FI "IMAGENAME eq taskhostw.exe"ImageName PID Modules
================================= ============================================taskhostw.exe 5228 ntdll.dll, KERNEL32.DLL,KERNELBASE.dll,
msvcrt.dll,RPCRT4.dll, combase.dll,
ucrtbase.dll, bcryptPrimitives.dll,
OLEAUT32.dll, msvcp_win.dll, imm32.dll,
USER32.dll,win32u.dll, GDI32.dll,
gdi32full.dll, kernel.appcore.dll,
sechost.dll,uxtheme.dll, dwmapi.dll,
clbcatq.dll,MsCtfMonitor.dll, MSCTF.dll,
MSUTB.dll,WINSTA.dll, PlaySndSrv.dll,
wininet.dll,iertutil.dll, advapi32.dll,
shcore.dll,ESENT.dll, windows.storage.dll,
shlwapi.dll,profapi.dll, powrprof.dll,
FLTLIB.DLL,WINMM.dll, WINMMBASE.dll,
cfgmgr32.dll, CRYPTBASE.DLL, userenv.dll,
profext.dll,ntmarta.dll, MMDevAPI.DLL,
DEVOBJ.dll, PROPSYS.dll,wdmaud.drv,
ksuser.dll,AVRT.dll, AUDIOSES.DLL,
wintypes.dll, msacm32.drv, MSACM32.dll,
midimap.dlltaskhostw.exe 16712 N/A
Mentioned command will call up a list of all DLL files, that are loaded by “tasklistw” process when Windows starts.
In Winx64 system it can known as taskhostw.exe Host Process for Windows Tasks (32-bit)
taskhostw.exe Host Process for Windows Tasks