Safe Mode is a simpler version of Windows that helps you sort out computer problems. It starts your computer with just the basics needed to run, which is great for fixing issues with software, drivers, viruses, or other glitches. Imagine it like stripping down a car to its frame to figure out what’s wrong. In this guide, we’ll show you how to jump into Safe Mode using just command lines through the Command Prompt in Windows 11 or 10.
Also see: Enter Safe Mode in Windows 11/10 when PC isn’t booting
What is Safe Mode in Windows?
Safe Mode is the bare-bones version of Windows, running only the must-have drivers and services. It’s perfect for diagnosing and fixing problems from software clashes, driver mishaps, to malware mess-ups. It’s your go-to tool for when your computer is acting up or when you need to get rid of troublesome software.
Windows has three Safe Mode flavors:
- Safe Mode: The standard mode with just the essential drivers and services.
- Safe Mode with Networking: Just like regular Safe Mode, but you can still get online. Handy for downloading updates or drivers.
- Safe Mode with Command Prompt: This is Safe Mode, but instead of the usual Windows look, you get a Command Prompt. Great for those who love typing commands to fix problems.
We’ll cover how to get into each of these Safe Modes using the Command Prompt in Windows 11/10.
Recommended resource: How to Startup Repair Windows 10/11 using Command Prompt
Steps to enter Safe Mode using Command Prompt
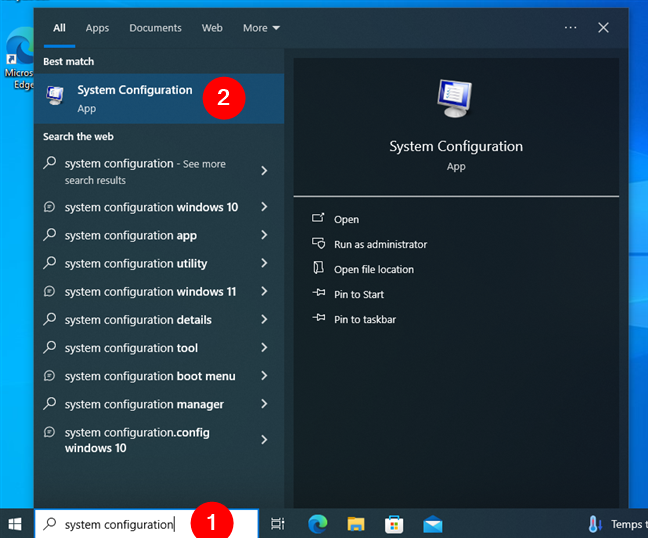
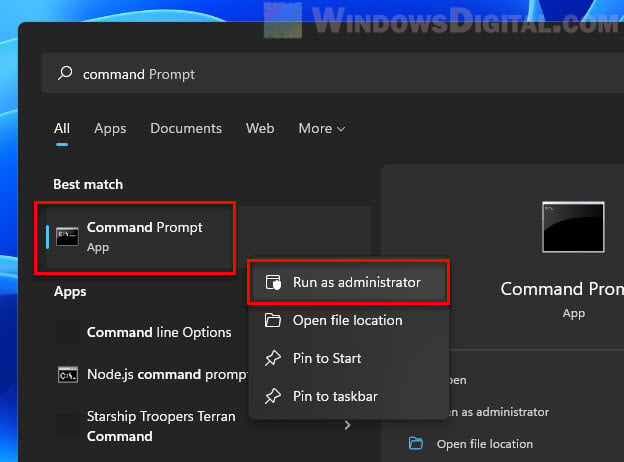
Step 1: Open Command Prompt as administrator
- Hit the Start button or press the Win key to bring up the Start menu.
- Search for “cmd” or “command prompt”.
- Right-click on Command Prompt in the search results and pick Run as administrator. If asked, click Yes to give it the thumbs up.
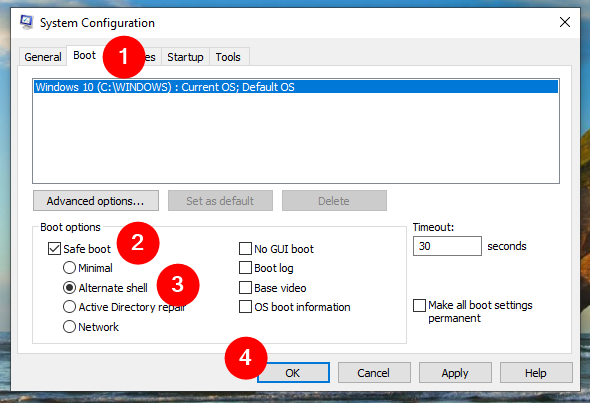
Step 2: Configure Windows to start in Safe Mode
To get into the Safe Mode you want, follow these steps:
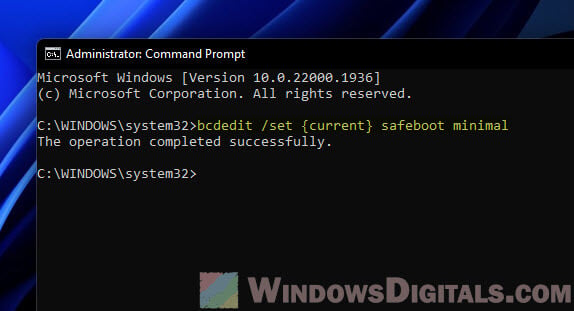
Safe Mode (Basic)
In the Command Prompt window, type this command and hit Enter to kick off Windows in basic Safe Mode:
bcdedit /set {current} safeboot minimal
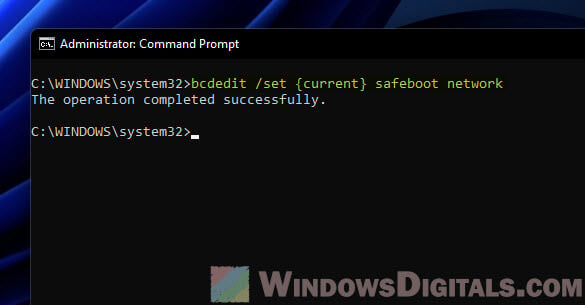
Safe Mode with Networking
Or, type this command and hit Enter for Safe Mode with network smarts, letting you go online:
bcdedit /set {current} safeboot network
Safe Mode with Command Prompt
For Safe Mode with Command Prompt, do this:
First, turn on basic Safe Mode with this command and pressing Enter:
bcdedit /set {current} safeboot minimal
Then, switch to command mode with this command and Enter:
bcdedit /set {current} safebootalternateshell yes
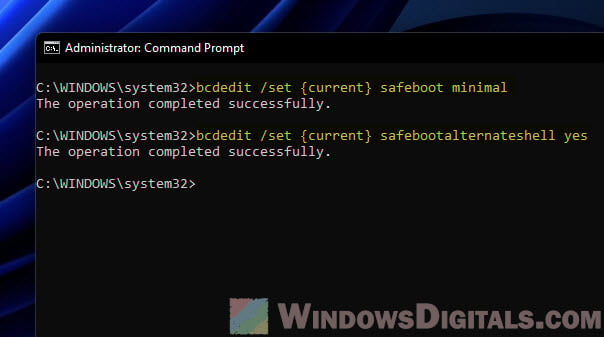
After these commands, you should get a message that you’re all set. Your computer is now ready to start in your chosen Safe Mode next time you restart it.
Linked issue: Windows 11 Keeps Booting in Safe Mode (Fix)
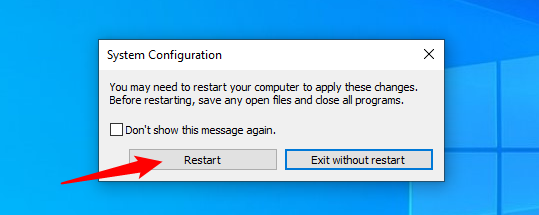
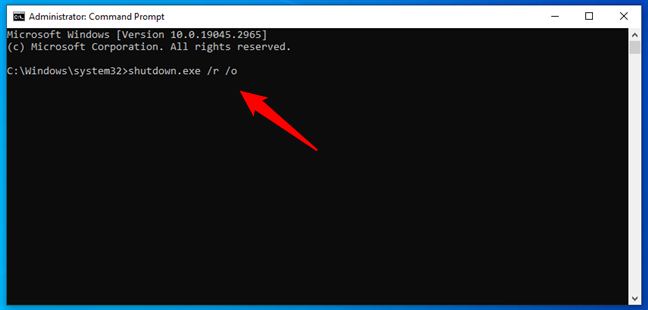
Step 3: Restart your computer
- Restart your computer with this command:
shutdown /r /t 0
- Now, your computer will restart and head straight into the Safe Mode you picked.
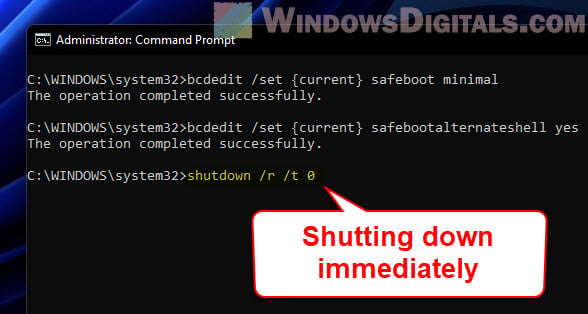
Exiting Safe Mode and returning to normal mode
If you’re done in Safe Mode and want to get back to regular Windows, follow these steps:
- Open Command Prompt in safe mode.
- Run this command and press Enter:
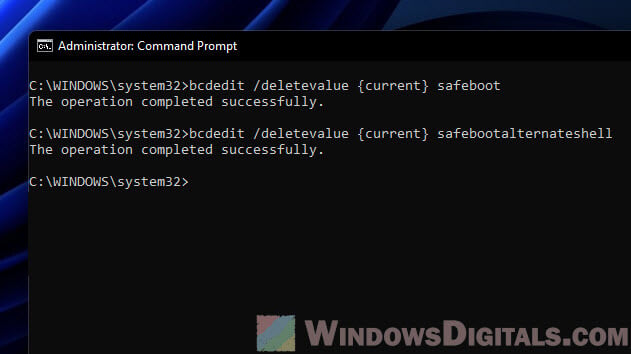
bcdedit /deletevalue {current} safeboot - If you were in Safe Mode with Command Prompt, turn off the command-only mode with this command:
bcdedit /deletevalue {current} safebootalternateshell - You’ll see a message that everything went smoothly. Your computer is now set to start normally next time you boot up.
- To restart and go back to normal Windows, type this and press Enter:
shutdown /r /t 0
- And that’s it, you’ll boot up as usual.
What we’ve learned
Using the Command Prompt to start Safe Mode gives you more power and options if you like using command-line tools. Here’s why you might want to use this approach to get into Safe Mode:
- It lets you easily choose between different Safe Mode options (like the basic one, one with networking, or one with Command Prompt). This is super useful when you need to figure out tricky problems that need checking in different settings.
- If you’re someone who knows their way around computers really well or if you’re an IT pro who often needs to start Safe Mode on lots of computers, or as part of fixing bigger issues, using Command Prompt can save you a lot of time. You can make scripts or set things up to happen automatically.
- Sometimes, you can’t use the usual way of doing things because of computer bugs, nasty viruses, or problems with drivers. In these situations, Command Prompt is a lifesaver because it doesn’t need the normal graphical stuff to work.
To wrap it up, although there are other ways to get into Safe Mode, going through the Command Prompt is a great choice for those who need that extra level of control and precision for solving complicated Windows problems.
Download Article
Plus, which type of safe mode to use to diagnose your computer problems
Download Article
If Windows 10 isn’t behaving properly, you can boot into Safe Mode to run scans, uninstall software, and access the Command Prompt. Whether you’re trying to get to the Command Prompt in Safe Mode or you want to learn how to boot into Safe Mode using CMD commands, we can help! This wikiHow article will teach you different ways to get to a safe Command Prompt window, and how to use Command Prompt to start Safe Mode.
What is the command prompt for Windows 10 Safe Mode?
Restart your computer and select Enable Safe Code with Command Prompt (f6) on the Startup Settings screen. Open the command prompt window, then enter the code bcdedit /set {default} safeboot minimal to reboot in Safe Mode.
-
Safe Mode is the standard diagnostic startup mode for Windows. When you boot into Safe Mode, only the basic device drivers will load—you won’t have internet access, and no third-party apps or drivers will launch at boot time. You can uninstall software, remove files, run your antivirus scanner, and perform tasks in the Command Prompt in regular Safe Mode.
-
This version of Safe Mode is the same as the original Safe Mode, except Windows will also load your network card drivers so you can connect to the internet.[1]
Use this version of Safe Mode if you want to download files, run updates, or do anything else that requires network access.Advertisement
-
All versions of Safe Mode have access to the Command Prompt, but this version will only give you the Command Prompt. You won’t have your typical Start menu or icons to click—just a simple admin-level Command Prompt window, making this mode useful only to IT professionals and system administrators.
Advertisement
-
This method is essentially a workaround to getting an administrator-level command prompt when you can’t boot into Windows. Even if your screen is blank or you can’t get to the login screen, you’ll be able to get a Command Prompt in Windows 10 thanks to the built-in recovery environment WinRE.
- You will still need your administrator password to sign in. If you don’t have the administrator password, you can still use this method to boot into Safe Mode.
- If you deleted the recovery partition, WinRE won’t work without a bootable Windows 10 DVD or flash drive, but we’ll get to that soon.
-
- Reboot your PC to the sign-in screen.
- Hold down the Shift key as you click the Power icon and choose Restart.
- Now skip to Step 4.
-
If you are unable to get to the sign-in screen, you can still get to a Command Prompt for troubleshooting using the power button your PC to enter a special diagnostic mode.[2]
Warning: this involves a lot of turning your PC off and back on again:- Start with your PC on.
- Hold down the power button on your computer for 10 seconds—your PC will turn off.
- Press the power button again to turn the PC back on.
- As soon as the computer turns back on (you’ll usually see the manufacturer’s logo), press and hold the power button for 10 seconds to turn it off again.
- Press the power button again to turn the PC back on.
- Again, as soon as the computer turns back on, press and hold the power button for 10 seconds to turn it off.
- Press the Power button again and allow your PC to boot into WinRE.
- If this doesn’t work, you may have deleted the recovery partition. You can boot your PC from a bootable Windows 10 DVD or USB drive. Once you boot from that media, continue to the next step.
-
This is a blue screen with several icons.
-
It’s at the bottom of the screen.
-
Choose this option if all you want is a Command Prompt. This option gives you a safe administrator prompt that you can use to diagnose problems with your PC. What it won’t give you is a Windows desktop or Start menu.
- If you’d rather start your PC in Safe Mode so you can use your typical menus and icons as well as have the option to launch the Command Prompt, choose Startup Settings, click Restart, and then press 4 or F4 to start Safe Mode (with no internet/network support) or 5 or F5 to start Safe Mode with Networking. You can launch the Command Prompt from either of these two modes.
Advertisement
-
If you want to access the Command Prompt while you’re in Safe Mode to run commands, it’s easy. To restart your computer in Safe Mode from the Windows desktop:[3]
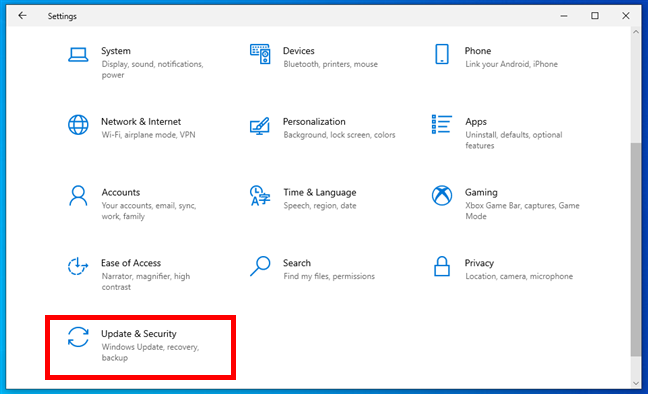
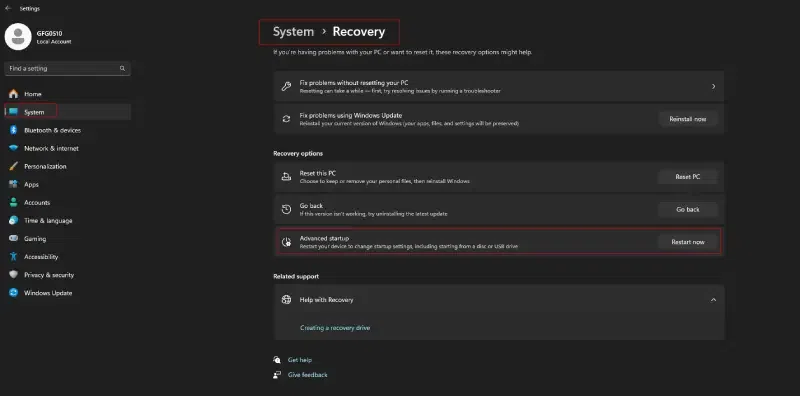
- Open the Start menu and click Settings.
- Click Update & Security.
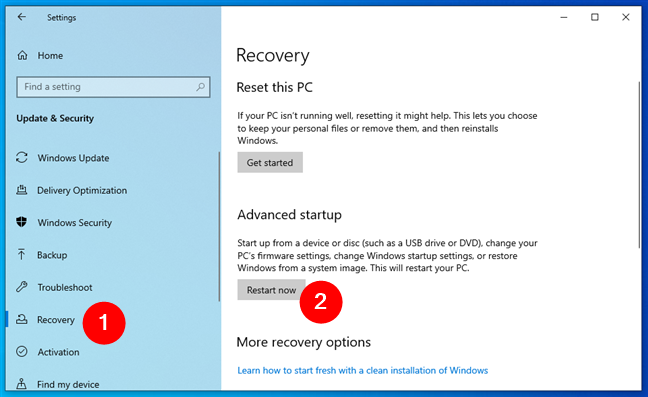
- Click Recovery.
- Click Restart now under «Advanced startup.»
- When the computer reboots, click Troubleshoot and select Advanced options.
- Click Startup Settings.
- Click Restart.
- When the Safe Mode menu appears, press 5 or F5 to start Safe Mode with Networking, or press 4 or F4 to start Safe Mode without internet support.
-
A list of matching results will appear.
-
If you don’t need to perform administrative tasks, you can open a regular Command Prompt window just by left-clicking Command Prompt in the search results.
Advertisement
-
Getting into Safe Mode from the Command Prompt is a lot more complicated than any other way you could access Safe Mode. This is because you’ll need to run commands that edit your PC’s boot configuration, making it so your PC only boots in Safe Mode until you change it back. If possible, use the steps in the «Get a Command Prompt in Safe Mode» method to get to Safe Mode instead—if that doesn’t work, you can continue with this method.[4]
-
If you want to be able to reboot Windows into Safe Mode using the command line, you can do so by modifying the boot record, and then changing it back after you’re finished in Safe Mode. To get started:
- Press Windows key + S to activate the Search bar.
- Type cmd.
- Right-click Command Prompt and select Run as administrator.
-
You can start three types of safe mode from the command line—regular Safe Mode (with no network support), Safe Mode with Networking, and Safe Mode with Command Prompt.[5]
Type the command for the type of Safe Mode you want to use, and then press Enter. This will force the computer to reboot into that version of safe mode immediately after rebooting.- Safe Mode: bcdedit /set {current} safeboot minimal
- Safe Mode with Networking: bcdedit /set {current} safeboot network
-
Safe Mode with Command Prompt: Most people won’t need to use this, as you can access the Command Prompt from both other Safe Modes. But if you prefer just a Command Prompt window without icons or menus, you’ll need to enter two commands:
- Type bcdedit /set {current} safeboot minimal and press Enter.
- Type bcdedit /set {current} safebootalternateshell yes and press Enter.
-
If you’re unable to restart normally for any reason, you can restart from the command line by typing shutdown /r and pressing Enter. When the computer restarts, it’ll boot into Safe Mode.
-
Now that you’re in Safe Mode, you can perform diagnostics, remove viruses and malware, uninstall software and drivers, or any other business you need to attend to.
-
Before you get out of Safe Mode, you will need to undo the command you did earlier so Windows can boot normally. Just open Windows Search, type cmd, right-click Command Prompt, and then choose Run as administrator as you did earlier to get started.
-
When you type this command and press Enter, you’ll remove the «safeboot» value from the boot configuration, which allows Windows to boot normally next time: bcdedit /deletevalue {current} safeboot.[6]
-
This time, your Windows PC will reboot into your normal login screen and desktop.
Advertisement
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
About This Article
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 113,392 times.
Is this article up to date?
One way to troubleshoot Windows 10 problems or fix boot failures is to start the system in Safe Mode. Safe Mode only loads the essential components, which helps you isolate and solve the issues. However, some problems are so severe that they interfere with the graphical user interface, making Safe Mode with Command Prompt a better option, as it doesn’t run the Explorer shell. In this guide, I will show you eight different ways to boot Windows 10 in Safe Mode with Command Prompt. Let’s begin:
NOTE: This guide explains how to start Windows 10 in Safe Mode with Command Prompt. As you probably know, Safe Mode is a diagnostic mode that lets you troubleshoot problems on your PC. If you’d rather boot your computer in standard Safe Mode or in Safe Mode with Networking, follow the instructions in these tutorials: How to boot Windows 10 in Safe Mode and How to start Windows 10 in Safe Mode with Networking.
Understanding Safe Mode with Command Prompt. What’s different from standard Safe Mode in Windows 10?
Safe Mode with Command Prompt is a special startup mode that allows you to access Windows 10 with an extremely minimal set of drivers and services. In this mode, you can use a Command Prompt window to perform various tasks for troubleshooting, repairing, or restoring your system. The Safe Mode with Command Prompt is designed for IT professionals and administrators who need to perform advanced operations like managing disk partitions or repairing boot problems.
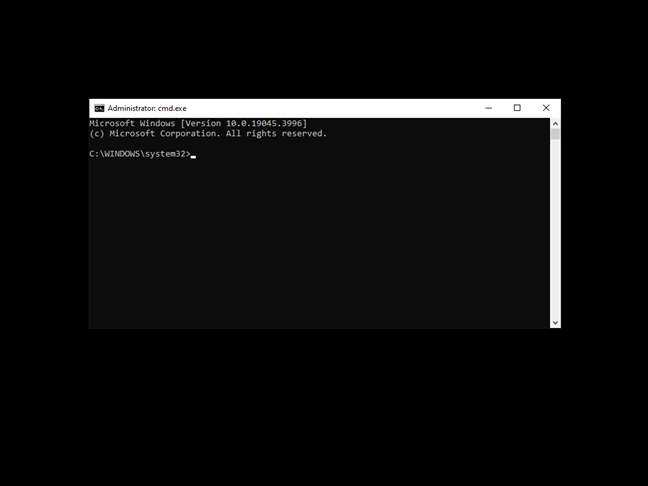
Safe Mode with Command Prompt differs from standard Safe Mode in that it doesn’t load the Explorer shell, which is the main component of the Windows 10 graphical user interface. Instead, all you get is a black screen with a Command Prompt window, like in the screenshot below. However, it’s worth noting that you can still use keyboard shortcuts to switch between applications (Alt + Tab, for example), access the Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc), or shut down your computer (Alt + F4).
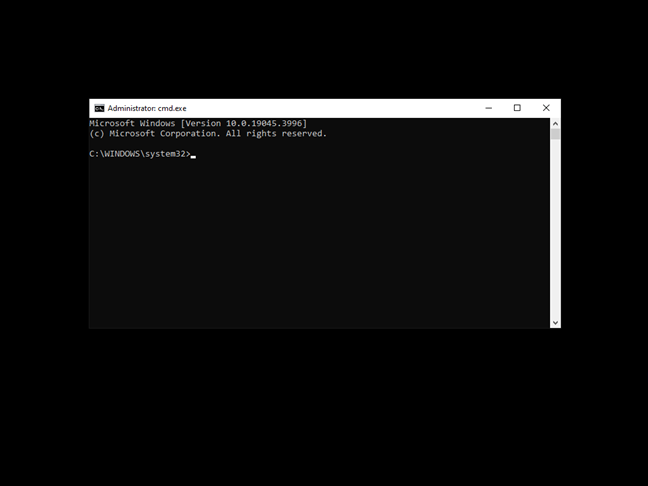
Windows 10 in Safe Mode with Command Prompt
There are many ways to access Safe Mode with Command Prompt, and I’ll cover all of them in the next chapters of this guide. I’m going to start with the methods that allow you to restart in Safe Mode with Command Prompt when you can’t log in to Windows 10, and I’ll continue with the ones available when you can sign in.
How to boot in Safe Mode with Command Prompt when unable to log in to Windows 10
If you have to boot a Windows 10 device in Safe Mode with Command Prompt but can’t log in, here are the methods you have on hand:
1. How to reboot to Safe Mode with Command Prompt using Shift + Restart
Power on your Windows 10 PC and let it boot normally. When you reach the sign-in screen, press and hold the Shift key while clicking the Power button, and then Restart.

How to boot Windows 10 in Safe Mode with Command Prompt without login
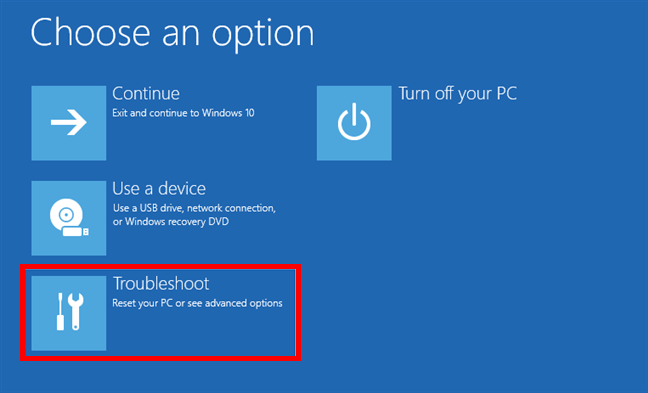
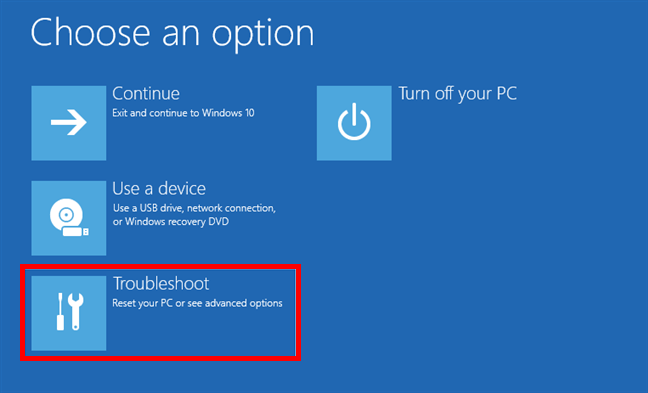
After a short while, you’ll see a blue screen with multiple choices. Click or tap Troubleshoot.
Click Troubleshoot (Reset your PC or see advanced options)
On the Troubleshoot screen, click or tap Advanced options.
Accessing the advanced troubleshooting options
Next, select the Startup Settings from the list of Advanced options.
Click the Startup Settings option
This loads the Startup Settings screen, where you get to see what options will become available once you reboot your Windows 10 device. Click tap the Restart button.

Startup Settings: Choose Restart for Windows 10 Safe Mode options
After your PC restarts, you’ll see all the boot options you can use. To start Safe Mode with Command Prompt, select the sixth option: “6) Enable Safe Mode with Command Prompt.” You can do this by pressing 6 or F6 on your keyboard.
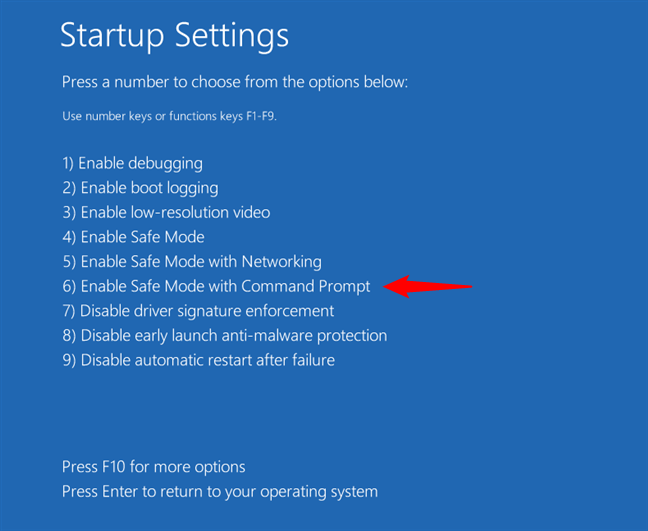
Press 6 or F6 to start Safe Mode with Command Prompt
Windows 10 will restart again, but this time, your computer will boot straight into Safe Mode with Command Prompt.
2. How to reboot into Safe Mode with Command Prompt when Windows 10 shows only a black screen
If your Windows 10 device doesn’t display anything on the screen after you start it, you can try to force restart it to Safe Mode with Command Prompt in order to troubleshoot and fix problems using commands. To force restart, you must interrupt the normal boot process by pressing the Reset or the Power button on your computer while it’s starting. Moreover, you need to do this three times in a row. The fourth time it attempts to boot, Windows 10 will automatically launch Automatic Repair. You can tell that you have successfully interrupted the boot process when you see the “Preparing Automatic Repair” message on the screen.
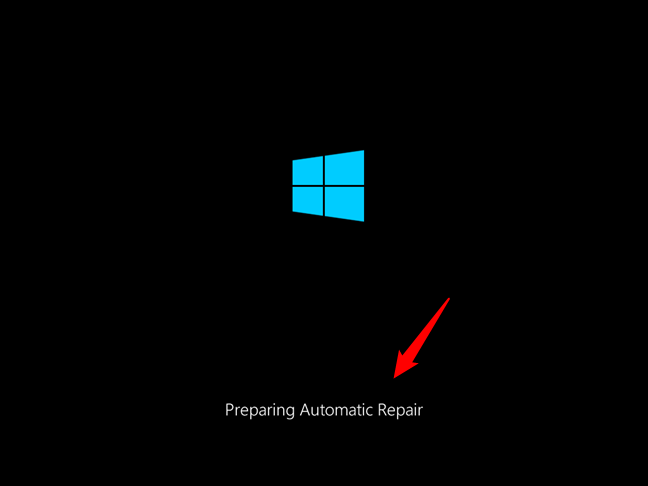
How to boot into Safe Mode with Command Prompt from a black screen
After some time, the message will change to “Diagnosing your PC.” You need to wait for the operating system to do that.
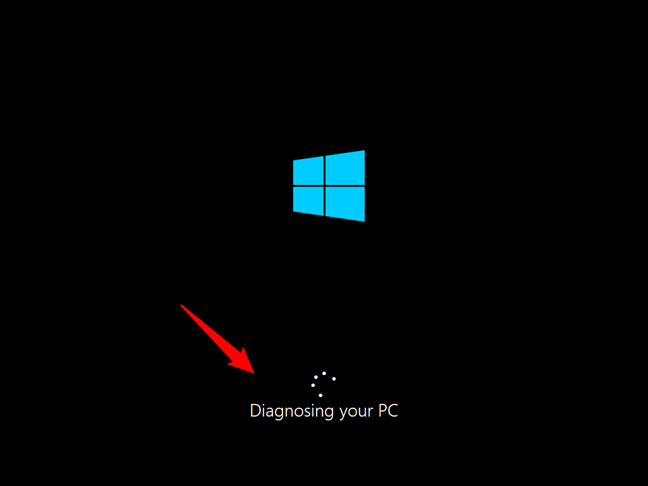
Diagnosing your Windows 10 PC
When it’s done, Windows 10 will display the Automatic Repair screen, which looks like the following screenshot. On it, click or tap on Advanced options.
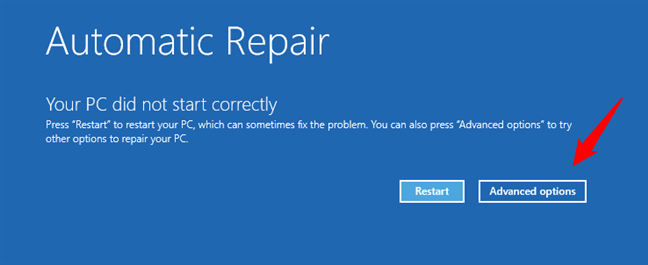
Accessing the advanced troubleshooting options
Then, click or tap Troubleshoot on the Choose an option screen.
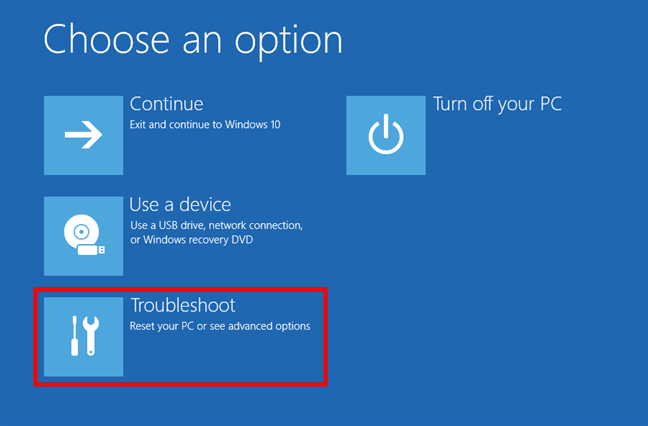
Click or tap on Troubleshoot
Next, take the same steps shown in the first method of this guide, which is to go to Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart > Enable Safe Mode with Command Prompt (press the 6 or the F6 key).
Go to Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart > Enable Safe Mode with Command Prompt
TIP: If you need help exiting Safe Mode with Command Prompt, here are the ways to do that: How to exit Safe Mode in Windows.
3. How to start Windows 10 in Safe Mode with Command Prompt using CMD and a Windows 10 installation disc or USB drive
This is another way to access Safe Mode with Command Prompt when Windows 10 fails to start. Use another computer and a blank DVD or USB drive to create your own Windows 10 installation media. Then, insert the DVD or USB drive into the broken PC and boot from it. When you see the Windows 10 setup screen, choose your language and keyboard layout. Click or tap Next to proceed.
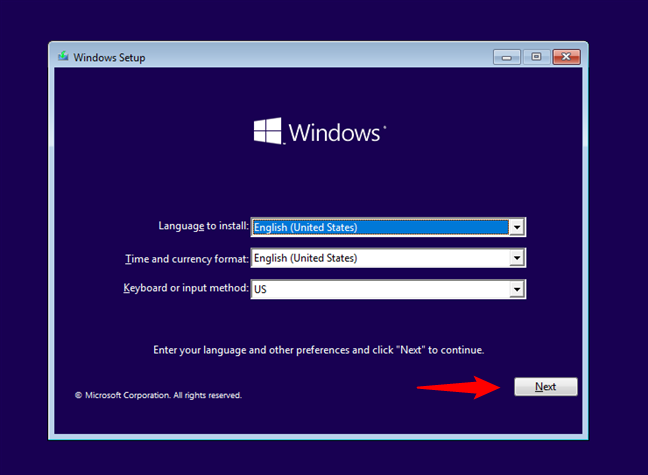
The Windows 10 Setup
Once you see the Windows Setup wizard, click or tap the Repair your computer link in the bottom-left corner.
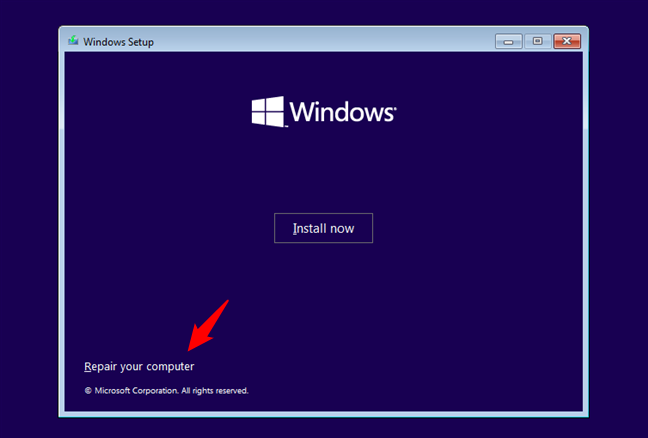
Click on Repair your computer
The Windows 10 setup wizard will then load the Choose an option screen. On it, click or tap Troubleshoot.
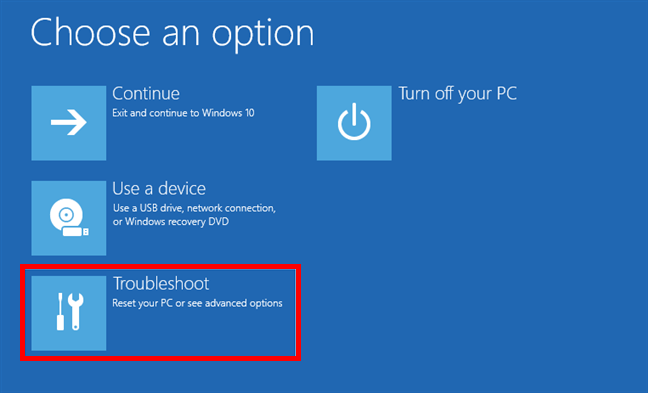
Select Troubleshoot to get to Windows 10 Safe Mode with Command Prompt
The Troubleshoot screen loads. On it, click or tap Advanced options.
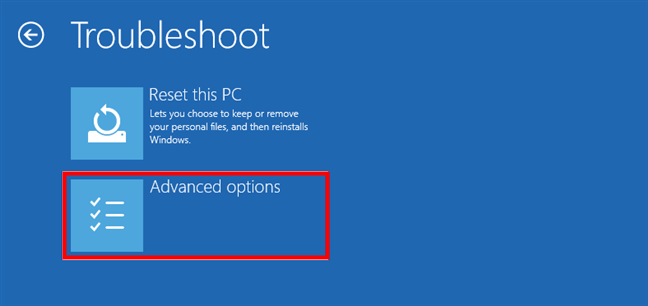
Select Advanced options
Next, on the Advanced options screen, choose “Command Prompt (Use the Command Prompt for advanced troubleshooting).”
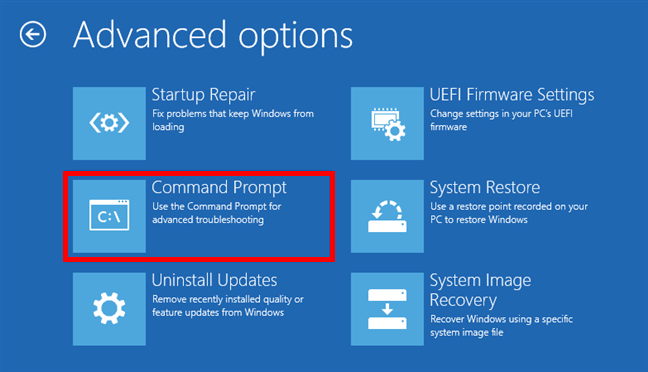
Starting the Command Prompt
For Windows 10 boot into Safe Mode with Command Prompt, you’ll now have to run this commands, one after the other:
bcdedit /set {default} safeboot minimal
bcdedit /set {default} safebootalternateshell yes
Both commands should finish with this message: “The operation completed successfully.”
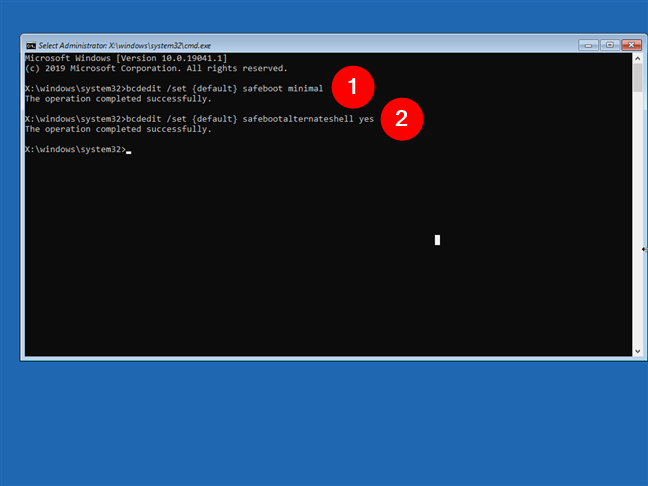
Using CMD to start Safe Mode with Command Prompt
Finally, close the Command Prompt and then click or tap on “Continue (Exit and continue to Windows 10)” to load the Safe Mode with Command Prompt.
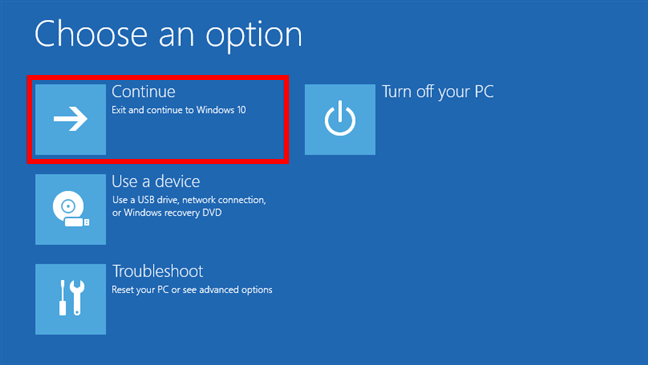
Choose Continue to start Windows 10 in Safe Mode with Command Prompt
IMPORTANT: To get back to normal boot after you’ve finished repairing what’s broken, follow the same steps, but run these commands instead:
bcdedit /deletevalue {default} safeboot
shutdown.exe /r
The first one disables Safe Mode with Command Prompt, and the second one restarts your Windows 10 computer to apply the new setting.
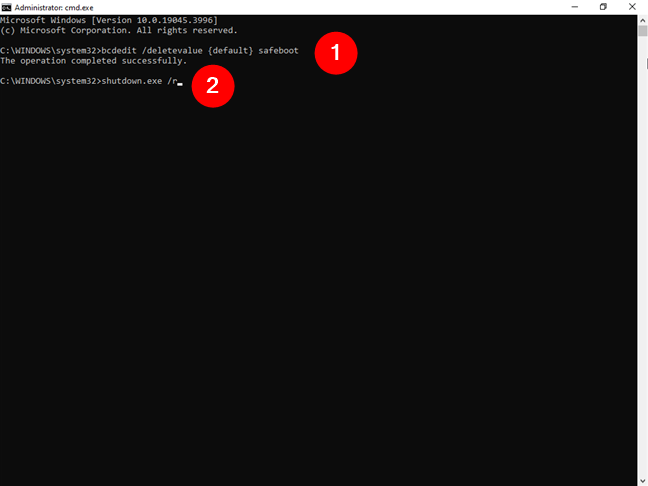
Disable and exit Safe Mode with Command Prompt
TIP: Here are some of the most useful commands you can run in CMD: 20 best Command Prompt (CMD) commands you should know.
4. How to boot into Safe Mode with Command Prompt using a Windows 10 recovery drive
If your computer malfunctions and you want to boot into Safe Mode with Command Prompt, you can also use a recovery disk that you already have or that you created on another Windows 10 PC.
Creating a Windows 10 Recovery Drive
Boot your computer using the recovery drive, and select your preferred keyboard layout on the first screen.
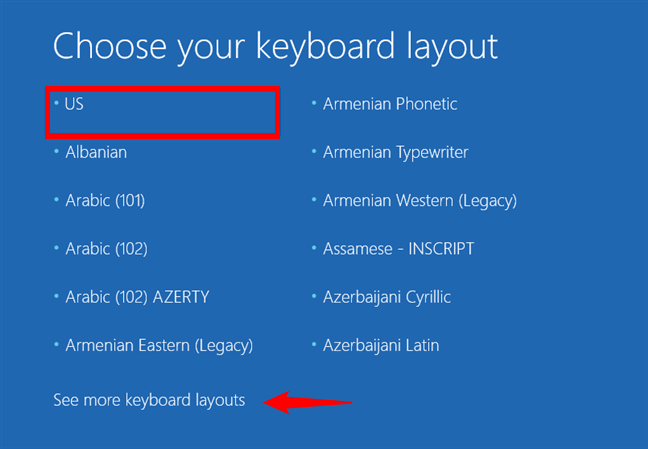
Choose the keyboard layout for the recovery drive
Then, click or tap Troubleshoot on the Choose an option screen.
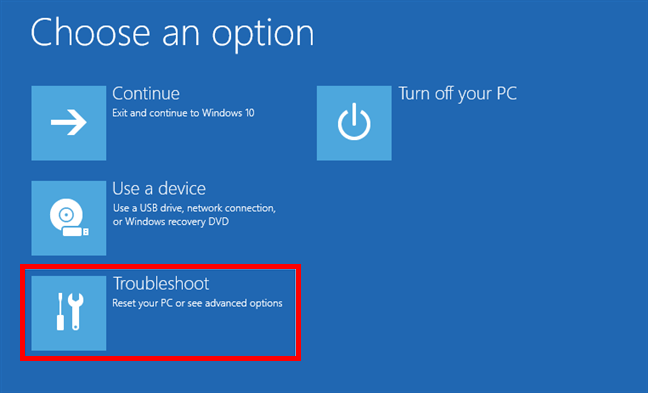
Select Troubleshoot to get to Windows 10 Safe Mode with Command Prompt
Next, follow the same steps presented in this guide’s first method. That means you should navigate the Windows 10 recovery environment to go to Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart > Enable Safe Mode with Command Prompt (press the 6 or the F6 key).
Go to Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart > Enable Safe Mode with Command Prompt
Once you do that, your Windows 10 PC will restart in Safe Mode with Command Prompt.
How to start Safe Mode with Command Prompt when you can sign in to Windows 10
If you require access to the Safe Mode with Command Prompt and Windows 10 still lets you log in, here’s what to do:
5. How to start Windows 10 in Safe Mode with Command Prompt using Shift + Restart
Boot your Windows 10 computer, log in using your account, and open the Start Menu. Then, press and keep the Shift key down, click or tap the Power button, and select Restart from the list of options.
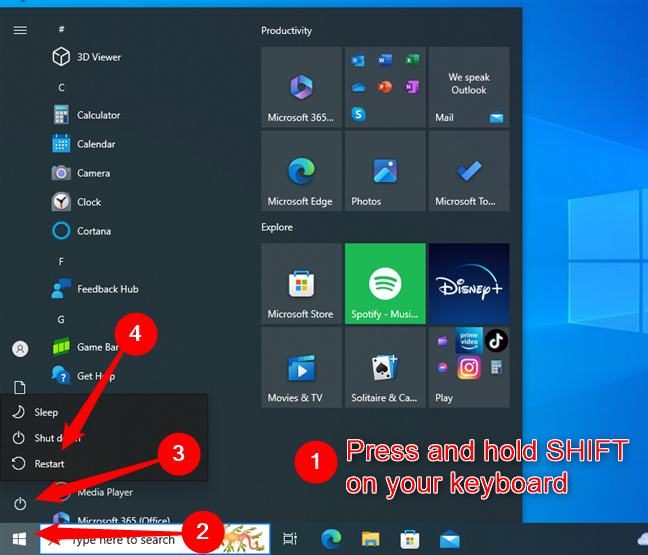
How to start Windows 10 in Safe Mode with Command Prompt from the Start Menu
After a couple of seconds, you will see a blue screen with several options: “Continue (Exit and continue to Windows 10)”, “Use a device (Use a USB drive, network connection, or Windows recovery DVD),” “Troubleshoot (Reset your PC or see advanced options),” and “Turn off your PC.” Click or tap on Troubleshoot.
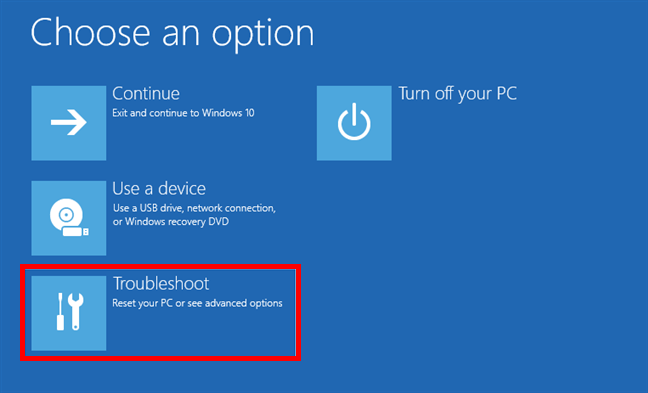
Select Troubleshoot to get to Windows 10 Safe Mode with Command Prompt
Next, perform the same steps shown in this guide’s first method. In short, go to Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart > Enable Safe Mode with Command Prompt (press the 6 or the F6 key).