If you are a beginner, then this article is for you. As a beginner, you might face problems in setting a proper path for python. In today’s tutorial, we will learn how to set a default path for python whenever we install python into our system.
Introduction
Unlike most operating systems such as Unix, Windows does not include a system-supported installation of Python. To run Python conveniently from a command prompt, you might consider changing some default environment variables in Windows. To temporarily set environment variables, open Command Prompt and use the set command:
C:\>set PATH=C:\Program Files\Python 3.6; %PATH%
Why to set up a path for python?
If you’ve installed Python in Windows using the default installation options, then the path to Python will not be added to the Windows Path variable. The Path variable lists the directories that will be searched for executing when you type a command in the command prompt. By adding the path to the Python executable, you will be able to access python.exe just by typing the python keyword in your command prompt. You will not need to specify the full path to the program.
Let us see what happens if we enter the python command in the command prompt and the path to that executable is not added to the Path variable:
C:\>python 'python' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file.
As you can see from the above output, the command was not found. Therefore, to run python.exe, you will need to specify the full path to the executable.
How to select default path while installing python?
There is an easy way to set up the default path during installing the Python. Every python installer comes with an option to add a python path into environmental variables. This will ensure that you can run python from your terminal. To do this –
- Get Python Installer from python.org.
- Get the installer and an installation window will appear.
- Press the “Add Python X.X to your PATH” option and install the python.
This way you can set up a default path without any headache. If you already have python installed and do not want to reinstall it, then move on to the next methods.
To permanently modify the default environment variables : My Computer > Properties > Advanced System Settings > Environment Variables > Edit
Steps to follow in detail.
- Right-click on ‘My Computer’ or ‘This PC.’ :-To navigate to the Windows Environment Variables screen, where you can add/edit your paths, right-click on the ‘This PC‘ icon. Then, select ‘Properties.’
- Select ‘Properties’ at the bottom of the Context Menu.: – After selecting the properties, the settings pop up.
- Next, select ‘Advanced system settings.’
- Check ‘Environment Variables...’ in the Advanced Tab.: After pressing on the advance settings, another window comes up which shows the Environment Variable option.
- Under ‘System Variables, ‘ Check on the New button in the top half of the dialog to make a new user variable.

- A new user dialog box pop ups which contain Variable name and variable value.

Before you type any values, you’ll need to locate the relevant Python paths. The paths that you’ll need to get are:
- copy the python path as show in the image below
Now let’s fill the New User Variable box that you saw earlier:
For the Variable name, type ‘Path.‘ For the Variable value, copy the full Python application path, then use a semicolon.
Now select OK
Using python from Command Prompt
- Press on the start menu.
- Type Command Prompt and open it
- Type “python.”
- A response from the python interpreter comes, i.e., it will show the python version currently installed in your system else.
- You will get an error message that will be written as “python is not recognized as an internal or external command.” This means that there is something wrong with the path variable setting.
Checking of python path
- Press on the start menu.
- Type Command Prompt and open it
- Type “python.”
- Now type the following code.
import os os.environ['PYTHONPATH']
OUTPUT:- 'C:\Program Files\Python 3.6'
How to handle multiple paths in python?
You may have two versions of python installed in windows in your system, let’s say 2.7 and 3.9. You want to run one of your projects in the python 2.7 version and another project in the 3.9 version. So the problem that lands up here is how you can specify which version you want to use for a specific python project?
So, to check all the versions of python installed in your windows environment , just type
py -0p in command prompt

So, today I will show you 2 methods of how to manage multiple python paths in windows?
Method 1: By defining the path of the versions
Whenever you try to run Python in the command prompt, it searches the %PATH% environment variable and checks for an executable file which can either be a batch file (.bat), command file (.exe), or any other executable file (.exe) that matches the name given. Once the correct file is found, it executes the program using that file. Now, if you have two versions of Python installed on your system (Python 2.7 and 3.9), then the path variable will contain the location of both the directories. But, there is a problem. The problem is once Windows finds the first match, it will stop examining any other path.
To overcome this problem, you have to call one or both applications using their path explicitly. For example, as you can see below, I have two versions of Python installed on my system.
- To execute python 2.7 you must call C:\Python27\python.exe

- To execute python 3.9 we had to type python3.9.exe

This method is one of the simplest method for managing multiple paths of python.
Method 2: Creating a shortcut
If you want to avoid using the entire path, create a shortcut for each python.exe file and rename it as python27 and python39.
In order to create the shortcuts, follow the given steps:
- Navigate to the folder containing the Python version you want to create a shortcut for.

- Right-click and create a shortcut.

- Rename the shortcut.
To run a file in python 2.7

Also, Check Out Editors Choice:
Conclusion
I hope this article helps you in setting a proper path for python in Windows operating system. As a beginner, you might face difficulties, but no worries, keep reading our tutorials on python and being a pro. Drop a comment if you have doubts. We are just one reply away. Till then, keep reading.
Happy Pythoning Geeks!!
Python is a versatile and widely used programming language, known for its simplicity and easy-to-understand syntax. When you’re setting up a Python development environment, one of the first tasks is locating where Python is installed on your machine. This information is crucial for configuring different tools and managing libraries and environments.
Python is normally installed in the system’s default program files directory. On Windows, it’s typically found in the “C:\PythonXX” folder. On Linux or Mac, it’s often in “/usr/local/bin/pythonX.X”. You can check your Python installation path by running “python –version” or “which python” in the command line.

This article will help you understand how to find the Python installation location on your system, focusing on different methods and operating systems. This knowledge will assist you in setting up your programming environment correctly and provide a better understanding of how Python interacts with your machine.

Let’s get into it!
Python Installation Locations
On various operating systems like Windows, macOS, or Linux, Python’s installation location can vary due to user preferences or installation packages from different sources.

In this section, we’ll look at the installation location of Python for different operating systems. Specifically, we’ll look at the following:
- Python Installation location on Windows
- Python Installation location on MacOS
- Python Installation location on Linux
1. Python Installation Location on Windows
By default, Python installations on Windows are located in the C:\ directory or C:\Users\<User>\AppData\Local\Programs.
The common installation paths for both 32-bit and 64-bit versions may reside in the C:\PythonXX folder, where XX stands for the Python version (e.g., C:\Python27 for Python 2.7).
In newer installations, the 64-bit version is often located in the C:\Program Files\PythonXX folder, while the 32-bit version is in the C:\Program Files (x86)\PythonXX folder.

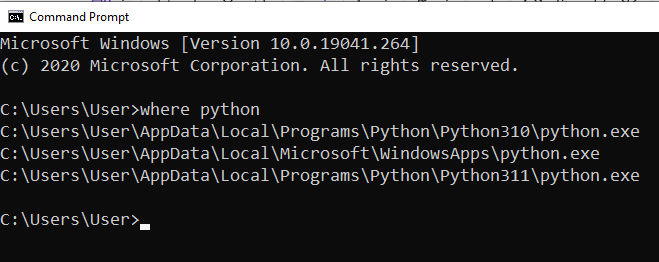
To find the exact location of your Python installation on Windows, you can use the command prompt by typing where python and press Enter. This command will display the file paths of any installed Python versions on your system.
The following image demonstrates this prompt:
2. Python Installation Location on MacOS
On macOS, Python is typically installed in the /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions directory, with different versions contained in their respective subfolders (e.g., /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.9 for Python 3.9).
Alternatively, Python installations managed by Homebrew are located in /usr/local/Cellar/python.
To check the exact path of your Python installation, you can open the terminal and type which python or which python3. Pressing “Enter” will display the file path of the active Python version on your system.
3. Python Installation Location on Linux
In most Linux distributions, Python is installed by default and can be found in the /usr/bin/ directory. The installed versions usually include both Python 2 and Python 3.
For Python 2.x, the executable is named python, while for Python 3.x, it’s named python3.
For systems with multiple Python installations or custom installation paths, you can find the location by typing which python or which python3 in the terminal and pressing Enter.
The command will show the file path of the active Python version on your system.
In the next section, we’ll go over how you can use built-in Python modules to locate the Python folder in your system.
How to Use Python’s os and sys Modules to Locate Python Folder
Python’s os and sys modules are built-in modules that allow you to interact with the operating system.

To locate where Python is installed, follow the steps given below:
- Run Python interpreter by typing python in the terminal or command prompt.
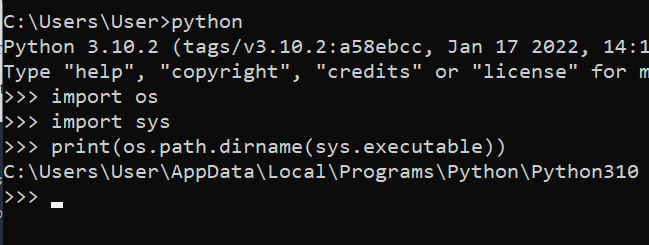
- Execute the following commands:
import os
import sys
print(os.path.dirname(sys.executable))
This Python script is used to print the directory of the Python interpreter being used to execute the script. os.path.dirname(sys.executable) gets the path of the currently running Python interpreter.
The output is given below:
How to Check the Location of Python Executables
When you are working in Python, you’ll want to install libraries from time to time. In most cases, you might want to check the path of a certain library.

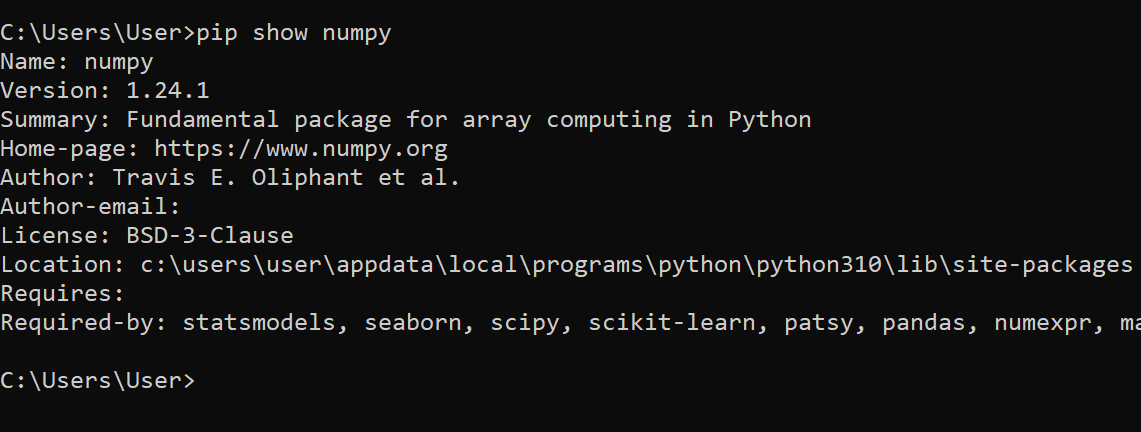
You can check the path of a Python library or executable with the pip package manager. To do this, open up CMD and run the following code:
pip show <package name>Let’s say I want to check the location of NumPy library on my operating system. To do this, I’ll type the following prompt in CMD:
pip show numpyThe output is given below:
How to Configure Python Path
When you first install Python on Windows, it’s important that you configure the path environment variable.
This means you should let your operating system know the path of your installation folder, which will allow the interpreter to refer to this path when running Python files.

We’ve listed a step-by-step guide to setting your environment variable and variables below:
Windows
- Right-click on ‘My Computer’ or ‘This PC,’ and select ‘Properties.’
- Click on ‘Advanced system settings.’
- Go to the ‘Advanced’ tab and click on ‘Environment Variables.’
- In the ‘System variables’ section, locate the ‘Path’ variable, select it, and click on ‘Edit.’
- Add the path to the Python executable (e.g., C:\Python<version>\Scripts;C:\Python<version>), and click ‘OK.’
macOS and Linux
- Open the terminal (Terminal on macOS, and Ctrl + Alt + T on Linux).
- Edit the shell configuration file (~/.bashrc for bash shell, ~/.zshrc for zsh shell).
- Add the following line: export PATH=”/path/to/python-<version>/bin:$PATH”
- Save the file and restart the terminal for the changes to take effect.
How to Verify Python Version and Installation
Before starting any Python project, it’s essential to know the version of Python installed on the system as well as its location.
It’ll help you ensure compatibility between packages, libraries, and other tools.

This section will guide you through verifying your Python version and installation using various Python-related commands and performing cross-platform checks.
1. Python-related Commands
To find the version of Python installed on any platform, you can use the python –version command in the terminal or command prompt.
It returns the Python 2 version installed on your system. To check for the Python 3 version, you can use the python3 –version command instead. These commands help you determine which Python interpreter you are currently using.
In case you are using both Python 2 and Python 3 versions, you can verify the compatibility of a specific module by importing it into the Python interpreter.
For example, to check if the re module is compatible, you can try running the following command:
import re
print(re.__version__)When you run the above command, you’ll get an output similar to the following:
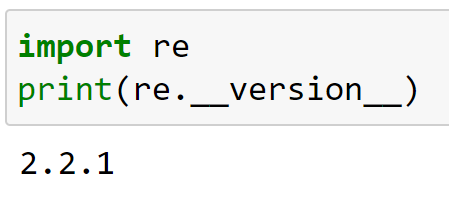
An output like the above suggests that Python’s re module is compatible with your current Python version.
If you’d like to learn how to switch to the latest version of Python, check out our quick and easy guide on how to update Python.
2. Cross-platform Verification
To find where Python is installed on your system, you can use the following Python code snippet for a cross-platform solution:
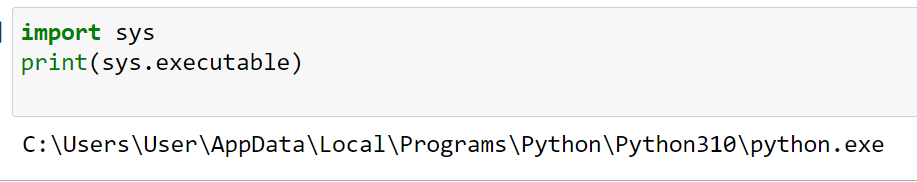
import sys
print(sys.executable)
This code will print the location of the Python interpreter executable. Depending on your operating system, this might differ.
The output is given below:
By knowing this location, you can ensure that you are using the correct Python interpreter for your projects.
Troubleshooting Common Python Issues
In this section, we’ll talk about some common issues that you may face when working with Python paths.

Let’s get into it!
1. Path-related Problems
For beginners, one common problem when using Python is related to file paths.
When Python is installed, its location may not be added automatically to the system environment variables PATH.
This could result in the “Python not found” error when trying to run Python scripts or access the Python shell.
To troubleshoot this issue, you can:
- Ensure Python is installed correctly by checking the installation folder, typically found in:
- Windows: C:\Python{version}
- macOS and Linux: /usr/local/bin/python{version}
- Add Python to the PATH variable to make it accessible system-wide:
- Windows: Open the Control Panel, navigate to System and Security > System > Advanced system settings > System Environment Variables, and edit the PATH variable to include the Python installation folder.
- macOS and Linux: Open the terminal and add the Python installation directory to the PATH variable using the export command, such as export PATH=/usr/local/bin/python{version}:$PATH.
- Save and restart the terminal or Command Prompt to apply the changes.
After following the steps above correctly, you’ll no longer run into any errors with running Python files.
2. Version Compatibility
Different Python versions might lead to version compatibility issues, especially when working with third-party modules and libraries.
To overcome this, you can:
- Check your Python version by running python –version in the terminal or Command Prompt.
- Verify the compatibility of a package by checking its documentation or the PyPI page. Packages usually list compatible Python versions.
- Use a virtual environment to manage and isolate dependencies for different projects.
By addressing path-related problems and ensuring version compatibility, you can resolve some of the most common Python issues.
To learn more about error resolution in Python, check the following video out:
Final Thoughts
Understanding where Python is installed on your system is a fundamental aspect of becoming an efficient programmer.
It allows you to manage your programming environment effectively and is key when dealing with using multiple versions of Python versions or when installing modules.
It also helps you in cases when you want to use specific versions for different projects, or when you need to install packages globally or just for one project.
Furthermore, knowing the path of your Python installation can also help you troubleshoot issues related to your environment setup or version conflicts and fine-tune your coding environment to your liking.
It’s an essential step in setting up an integrated development environment, and it makes using code editors or Python-related software smoother and more efficient!
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we’ve listed some frequently asked questions that most beginners have related to the Python installation directory.

Where is Python install location on Windows?
Python is installed in the default location C:\PythonXY where XY represents the version number.
For example, C:\Python39 for Python 3.9. It might also get installed under C:\Users\YourUsername\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\PythonXY for per-user installations.
How to find Python location in CMD?
To find the Python installation path in CMD, you can use the following command:
python -c
import os, sys
print(os.path.dirname(sys.executable))This command imports the os and sys modules and prints the directory of the Python executable.
Where is Python’s location in Windows 10?
On Windows 10, Python’s default location is C:\PythonXY or C:\Users\YourUsername\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\PythonXY for per-user installations.
How to check if Python is installed?
To check if Python is installed, open a command prompt or terminal and type in:
python --versionIf Python is installed, the command will display the version of Python.
If it’s not installed, you’ll get an error or the Microsoft Store may open for Python installations in certain cases on Windows.
How to find Python package’s installation location?
Python packages are generally installed in a subfolder of the Python installation. The specific location depends on whether you’re using a virtual environment or not.
To find the installation location of a package, open a terminal or command prompt and type:
pip show package-nameReplace “package-name” with the name of the package you want to find the location for. The output will show the package’s location along with other information.
-
Understanding the Default Install Location
-
Verifying Your Python Installation
-
Managing Python with Git
-
Setting Up Virtual Environments
-
Conclusion
-
FAQ

Installing Python on Windows is a straightforward process, but finding the default install location can sometimes be a bit tricky. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or a beginner looking to dive into programming, understanding where Python resides on your system is crucial. This knowledge not only helps in managing your Python projects effectively but also aids in troubleshooting and environment setup.
In this tutorial, we will explore the default installation location of Python on Windows, how to verify your installation, and how to manage your Python environment using Git commands. Let’s get started!
Understanding the Default Install Location
When you install Python on a Windows machine, it typically defaults to a specific directory. The most common locations include:
C:\Users\<YourUsername>\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python<version>C:\Program Files\Python<version>
The exact location may vary based on the version of Python you are installing and your installation choices. Knowing the default install location can help you navigate your system more efficiently, especially when dealing with multiple projects or environments.
Verifying Your Python Installation
To confirm that Python is installed and to find its location, you can use the command line. Open Command Prompt and type the following command:
Output:
C:\Users\<YourUsername>\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python<version>\python.exe
This command will display the path to the Python executable. If you see a path similar to the one above, it means Python is successfully installed. If not, you may need to check your installation or add Python to your system’s PATH variable.
Verifying your Python installation is crucial, especially if you plan to work with virtual environments or multiple Python versions. Knowing where Python is installed allows you to manage your projects effectively and ensures that you’re using the correct version for your development needs.
Managing Python with Git
If you’re using Git for version control, it’s essential to integrate it with your Python projects seamlessly. Here’s a simple method to create a new Git repository for your Python project:
- Navigate to your project directory using Command Prompt.
- Initialize a new Git repository:
Output:
Initialized empty Git repository in C:/Path/To/Your/Project/.git/
This command creates a new .git directory in your project folder, allowing Git to track changes.
Next, you can add your Python files to the repository:
Output:
This command stages all your files, making them ready for committing. Finally, commit your changes:
git commit -m "Initial commit"
Output:
[master (root-commit) 1234567] Initial commit
3 files changed, 30 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 file1.py
create mode 100644 file2.py
create mode 100644 file3.py
Using Git with your Python projects not only helps you keep track of changes but also allows you to collaborate effectively with others. By initializing a Git repository, adding your files, and committing your changes, you establish a solid foundation for version control.
Setting Up Virtual Environments
Managing dependencies in Python projects is crucial, especially when using different libraries. A virtual environment is a self-contained directory that contains a Python installation for a particular version of Python, plus several additional packages. Here’s how to set one up using Git:
- First, navigate to your project directory:
cd C:\Path\To\Your\Project
- Create a virtual environment:
Output:
Created virtual environment 'venv' in C:\Path\To\Your\Project\venv
This command creates a new directory named venv in your project folder, which contains the Python executable and a copy of the pip library.
- Activate the virtual environment:
Output:
(venv) C:\Path\To\Your\Project>
You’ll notice that your command prompt now shows the name of the virtual environment, indicating that it’s active. While activated, any Python packages you install will be confined to this environment, preventing conflicts with other projects.
- To deactivate the virtual environment, simply type:
Output:
Setting up a virtual environment is a best practice in Python development. It ensures that your projects remain isolated and that dependencies do not interfere with one another. By integrating this with Git, you can maintain a clean and organized project structure.
Conclusion
Understanding the default install location of Python on Windows is essential for effective project management and troubleshooting. By verifying your installation and using Git to manage your Python projects, you can streamline your development process. Creating virtual environments further enhances your workflow by isolating dependencies. As you continue your Python journey, these practices will help you maintain a structured and efficient coding environment.
FAQ
-
Where can I find the default installation path of Python on Windows?
You can typically find Python installed inC:\Users\<YourUsername>\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python<version>orC:\Program Files\Python<version>. -
How do I verify if Python is installed on my system?
You can verify the installation by opening Command Prompt and typingwhere python. This command will show the path to the Python executable. -
What is a virtual environment in Python?
A virtual environment is a self-contained directory that contains a Python installation for a specific version, along with its own set of libraries and packages. -
How do I create a virtual environment in Python?
You can create a virtual environment by navigating to your project directory and runningpython -m venv venv. -
Why should I use Git with my Python projects?
Using Git allows you to track changes, collaborate with others, and manage different versions of your code efficiently.
Enjoying our tutorials? Subscribe to DelftStack on YouTube to support us in creating more high-quality video guides. Subscribe

В процессе работы с различными проектами разработчики часто сталкиваются с необходимостью обеспечения правильной конфигурации их рабочей среды. Настройка окружения, включая добавление программных языков в системные переменные, может стать важным аспектом подготовки к эффективной разработке. Правильная интеграция инструментов и утилит обеспечивает бесперебойное исполнение кода, независимо от операционной системы, будь то Linux или Windows.
Довольно часто встает задача добавления интерпретатора языка программирования в системные параметры, чтобы можно было работать с ним из командной строки. Независимо от того, используете вы Linux или Windows, такая настройка облегчает запуск скриптов и автоматизацию процессов. Задача сводится к простым действиям, но может немного отличаться в зависимости от операционной системы, что требует внимательного подхода и следования ряду важных шагов.
В среде Linux, например, достаточно отредактировать файл конфигурации оболочки. Пример команды для этого:
echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/путь/к/каталогу' >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc
На Windows же система предложит несколько иной подход, требующий вмешательства в графический интерфейс и редактирование переменных среды через панель управления. Здесь важно следовать инструкции по выбору нужных переменных и аргументов, чтобы избежать ошибок в настройке.
Расширение системных возможностей путем корректировки переменных окружения позволяет сделать работу более гибкой и удобной, независимо от используемой платформы. Прочтите подробное руководство и настройте ваше окружение должным образом, чтобы избежать возможных трудностей в процессе разработки.
Понимание PATH и его значение
Когда мы говорим о PATH, речь идет о неявной указке для операционной системы, которая подсказывает, где находить нужные приложения и скрипты. Эта концепция связана с системной переменной, позволяющей упрощать запуск и управление программами. Осознание значения этой переменной важно для всех, кто работает в командах разработки и сталкивается с необходимостью взаимодействия между различными программными средами.
Переменная PATH используется системами Windows и Linux для определения тех директорий, где нужно искать исполняемые файлы. Если вы неоднократно задавались вопросами об ошибках в командной строке, то скорее всего сталкивались с этой переменной. Она автоматически определяет места нахождения часто используемых команд, значительно упрощая работу с программным обеспечением без необходимости постоянного указания полного пути к программам.
На платформе Windows управлять этой переменной можно через системную панель управления. С другой стороны, пользователи Linux взаимодействуют с ней через текстовые файлы, например, .bashrc или .profile. В обоих случаях, процесс установки и настройки понятийно идентичен, но детали варьируются.
Рассмотрим краткие примеры управления переменной PATH в системах Windows и Linux:
| Операционная система | Способ изменения |
|---|---|
| Windows |
Используется системная утилита для настройки окружения. Команда: |
| Linux | Редактируется файл конфигурации, например, .bashrc:export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/newapp |
Правильная настройка и понимание variable PATH экономит время и ресурсы при интеграции и использовании новых программ. Убедитесь в добавлении и хранении правильных путей в этой переменной для ускорения взаимодействия с командной строкой и скриптами без лишнего вмешательства.
Установка Python на компьютере
Windows
В операционной системе Windows установка начинается с загрузки установочного файла с официального сайта. После этого:
- Запустите загруженный инсталлятор.
- В появившемся окне выберите опцию для установки, удостоверившись, что отмечена галочка для добавления в системную переменную.
- Следуйте инструкциям мастера по установке, выбирая необходимые опции.
Теперь для проверки корректности инсталляции откройте командную строку и выполните:
python --version
При успешной установке командная строка должна отобразить версию. Если версия не отображается, проверьте настройки системных переменных.
Linux
Большинство дистрибутивов Linux имеют предустановленную версию интерпретатора, но для установки последней версии потребуется выполнить несколько команд в терминале:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python3
Эти действия обновят системные пакеты и установят последнюю версию. Проверить корректность установки можно при помощи команды:
python3 --version
Если появится номер версии, установка прошла успешно.
Теперь ваш компьютер готов к работе с интерпретатором, и вы можете насладиться разработкой проектов. Обратите внимание на то, что Process инсталляции может немного варьироваться в зависимости от особенностей операционной системы и используемой версии.
Проверка текущих системных переменных
Прежде чем вносить изменения, важно убедиться в текущем состоянии системных переменных на вашем устройстве. Это поможет избежать ошибок и обеспечит правильную настройку среды. В данном разделе разобраны способы проверки переменных окружения на разных операционных системах, что позволит вам осознанно управлять изменениями.
Для пользователей Windows определить текущие системные переменные не составляет труда. Откройте командную строку, введя cmd в поиске и запустив соответствующее приложение. В открывшемся окне наберите команду:
echo %PATH% set
На системах, работающих под управлением Linux, используйте терминал для проверки. Выполните следующую команду:
echo $PATH
Результат команды покажет все пути, зарегистрированные в PATH. Если необходимо просмотреть прочие переменные окружения, используйте команду:
printenv
Эти команды дают обширную информацию о текущих настройках среды выполнения. Понимание текущего состояния системных переменных позволит легко управлять и, если нужно, адаптировать их для удовлетворения ваших потребностей. Такие проверки особенно полезны при конфигурации новых инструментов или при устранении неполадок.
Пошаговое добавление Python в PATH
Настройка в Windows
- Перейдите в Этот компьютер и выберите Свойства через контекстное меню.
- Откройте Дополнительные параметры системы и перейдите на вкладку Дополнительно.
- Щелкните Переменные среды.
- В списке Системные переменные найдите строку с именем Path и выберите Изменить.
- Нажмите Создать и введите путь к каталогу, где установлена ваша версия Python, например:
C:\Python39\. - Нажмите ОК для сохранения изменений.
Настройка в Linux
- Откройте терминал.
- Используйте текстовый редактор, чтобы открыть файл
~/.bashrcили~/.bash_profile:nano ~/.bashrc. - Добавьте в файл следующую строку:
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/bin/python3. - Сохраните изменения, нажав
Ctrl + O, затемEnter, и выйдите из редактора с помощьюCtrl + X. - Примените изменения командой:
source ~/.bashrc.
Проверка переменных
После установки убедитесь, что новая директория корректно добавлена. Для проверки наберите в командной строке:
python --version
Если команда показывает установленную версию, значит, все сделано верно. Теперь вы можете легко использовать команду в терминале без указания полного пути до исполняемого файла.
Проверка корректности изменений PATH
После модификации системной переменной PATH важно проверить, что изменения выполнены правильно. Это позволяет убедиться, что ваш компьютер распознаёт и без ошибок использует изменённые параметры, и вы сможете эффективно работать с установленными программами.
Первым шагом к проверке обновлённой переменной будет использование командной строки. Откройте консоль в вашей системе Windows. Это можно сделать, введя в строке поиска меню Пуск слово cmd и выбрав соответствующее приложение. После открытия консоли, введите команду:
echo %PATH%
Эта команда покажет текущие значения переменной PATH. Пробегитесь взглядом по списку значений, чтобы убедиться, что необходимый путь был успешно добавлен. Если путь отсутствует, это может свидетельствовать о неправильном процессе добавления.
Ещё одним способом проверки является запуск необходимой программы из консоли без указания полного пути к файлу. Введите в командной строке название программы и нажмите Enter. Если программа запускается без ошибок, это значит, что системная переменная настроена корректно и все необходимые изменения были успешно применены.
Для дополнительной проверки вызываемых команд или сценариев на корректность выполненной операции, попробуйте дополнительно использовать отладочную информацию или встроенные функции диагностики самого Microsoft Windows, которые могут указать на возможные проблемы в конфигурации переменных.
Рекомендуется перезапустить систему после изменения системных переменных, чтобы изменения гарантированно вступили в силу во всех приложениях и сессиях. Таким образом, можно добиться уверенности, что изменения PATH применены успешно и корректно работают в любом контексте работы с файлами и программами.
Устранение возможных ошибок и проблем
Настройка переменных окружения может иногда вызывать различные затруднения, особенно у начинающих пользователей. Ошибки могут возникать по ряду причин: вследствие неправильно заданных параметров, путей к директориям или нарушений в системных настройках.
Одной из частых ошибок является опечатка в строке переменных. Например, если неверно указать путь до исполняемого файла, система не сможет его обнаружить. Важно удостовериться, что вы используете правильный синтаксис. На операционных системах на основе UNIX (таких как Linux) дополнительно проверяйте учет регистра, так как он имеет значение.
Некоторые пользователи могут столкнуться с проблемами, связанными с конфликтами между версиями. Проверьте, что путь указывает именно на ту версию, которая вам необходима. Для этого можно использовать команду which в терминале Linux, чтобы увидеть путь к текущей версии.
На Windows ошибки могут возникнуть, если значения переменных были изменены неадекватно. В этом случае вам может понадобиться открыть Редактор системных переменных и восстановить значение переменной вручную. Просто убедитесь, что все пути корректны и там нет лишних пробелов.
Еще одна возможная проблема – операционная система не обновляет переменные окружения после изменений. Перезагрузите компьютер или завершите сеанс пользователя, чтобы удостовериться, что обновления вступили в силу.
Продвинутое устранение неполадок может включать отладку скриптом. Напишите небольшой скрипт на языке программирования, который вы используете, чтобы вывести значение переменных окружения и убедиться, что они изменены правильно. Например, на Python это можно сделать с помощью:
import os print(os.environ['PATH'])
Если вы проверили все возможные источники ошибок, но проблема осталась нерешенной, возможно, стоит обратиться к документации вашей операционной системы или к сообществу пользователей на форумах.
Комментарии
Python’s interpreter, libraries, and scripts can reside in multiple locations on a system. So, finding where Python is installed helps with:
- Locating the
pythonexecutable to launch the interpreter - Editing module files under the Python install’s
site-packages - Modifying scripts under the
scriptsfolder of a Python environment - Switching between multiple Python versions using virtual environments
- Troubleshooting issues related to Python installations
The methods for finding Python’s install location vary across operating systems. In detail, we’ll explore platform-specific techniques on Windows, Linux/Unix, and macOS. Let’s jump right in
Finding Python Location on Windows
There are several easy methods to find where Python is installed on Windows. Using the where command or checking Python’s sys path returns the location.
Also read: Pipenv: The New Packaging Tool For Python
Using the where Command
The easiest way is to use the where command within the Command Prompt (CMD). Simply open CMD and type:
Here’s an example output showing the path to the Python interpreter:
C:\Users\gurpreet\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python310\python.exe
So for the sample product data table we imported earlier, we can launch Python from this location:
C:\Users\gurpreet\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python310\python.exe
import pandas as pd
print(pd.read_csv('products.csv'))
The where command also works in PowerShell:
PS C:\> where python C:\Users\gurpreet\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python310\python.exe
On Windows, Python gets added to your system’s PATH environment variable. So running python launches the interpreter from any location.
But where python returns the actual install location on disk.
Also read: [Fix] Bash: Python3: command not found When Installing discord.py on Windows
Checking Python’s sys.executable
Another method is using Python’s built-in sys module to print the path to the currently running executable:
import sys print(sys.executable)
Output:
C:\Users\gurpreet\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python310\python.exe
You can also directly run this oneliner from CMD or PowerShell instead of launching Python first:
python -c "import sys; print(sys.executable)"
So, if you have multiple Python versions installed (eg. Python 2.7, 3.7, 3.10 etc), sys.executable points to the specific executable.
This helps when switching between Python installs using virtual environments.
Additional Ways of Finding Python Path on Windows
Some other methods for locating where Python is installed on Windows include:
- Searching for
python.exeusing Windows search - Running
pip listto see packages installed in Python’ssite-packages - Checking the start menu Python folder’s location
- Using
Get-Command pythonin PowerShell
So in summary, where python, sys.executable, and Windows search makes finding Python installs easy on Windows.
Next, let’s look at Linux/Unix systems.
Finding Python on Linux/Unix
On Linux and Unix-based operating systems like Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS etc, there are simple terminal commands for finding where Python is installed.
The which, type -a, and readlink commands come in handy here.
Using the which Command
Most Linux/Unix systems have Python pre-installed and available globally via the shell.
You can find where it’s located by using which python:
which python3 /usr/bin/python3
This returns the path to the global Python executable in use.
For our product data example, we can run:
/usr/bin/python3
import pandas as pd
print(pd.read_csv('products.csv'))
To find all installed Python versions, use:
which -a python /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/python3 /usr/local/bin/python /home/preet/virtualenvs/analytics/bin/python
So which python helps locate not just the active Python interpreter, but also all available versions on your Linux/Unix system.
Using type -a
Another option is using the type command with the -a flag:
type -a python python is /usr/bin/python python is /usr/bin/python3 python is /usr/local/bin/python python is /home/preet/virtualenvs/analytics/bin/python
This displays all commands matching the name python across directories in your $PATH.
Using readlink
Sometimes Python executables are symbolically linked in the /usr/bin or /usr/local/bin folders to their actual location.
For example:
which python3 /usr/bin/python3
We can find where this symlink points to using readlink:
readlink -f /usr/bin/python3 /usr/local/lib/python3.8/bin/python3
This shows the actual install location to be /usr/local/lib/python3.8/.
In summary, using which, type, and readlink allows locating both global and virtual environment Python installs on Linux and Unix.
Finding Python on macOS
On macOS, Python generally gets installed into the /Library/ or ~/Library/ folders.
The Finder app provides an easy way to find these locations.
You can also use terminal commands like which and sys.executable covered earlier.
Let’s go through the Finder approach first.
Using Finder
To find where Python is installed on your Mac:
1. Launch Finder and hit Command + Shift + G
This opens the Go to Folder dialog box.
2. Enter paths like /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework or ~/Library/Python
The /Library path contains Python versions installed system-wide for all users. This includes major versions like:
/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.11 /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7
While the ~/Library path has Python installs scoped to your user account. Typically, you’ll find virtual environments here:
~/Library/Python/3.11/bin
3. Drill down the folders to see the bin/ directory containing python3.
So using Finder provides a graphical way to explore Python install locations on macOS.
Additional Ways of Finding Python
As on Linux/Unix, which python finds the active Python version:
which python3 /usr/local/bin/python3
And sys.executable prints the currently running one:
python3 -c "import sys; print(sys.executable)" /Users/preet/virtualenvs/analytics/bin/python
These terminal commands work the same on macOS as on Linux.
In summary, Finder and shell commands both provide easy methods for finding Python on macOS.
Quick Reference of All Methods By OS
Here’s a quick comparison table summarizing the different techniques across operating systems:
| Operating System | Method | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Windows | where python | where python |
| Windows | sys.executable | python -c “import sys; print(sys.executable)” |
| Windows | Get-Command | Get-Command python |
| Linux/Unix | which python | which python3 |
| Linux/Unix | type -a python | type -a python |
| Linux/Unix | readlink -f | readlink -f /usr/bin/python |
| macOS | Finder (Ctrl + Shift + G) | /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework |
| macOS | which python | which python3 |
| Cross-platform | sys.executable | python -c “import sys; print(sys.executable)” |
This covers some easy, go-to approaches for finding Python installs across different OS environments.
Summary
Finding where Python is installed is essential for managing multiple versions and virtual environments.
We learned platform-specific techniques for locating Python on Windows, Linux/Unix and macOS systems:
- Windows – Using
where python, PowerShell’sGet-Command, andsys.executable - Linux/Unix – Leveraging the
which,type -a, andreadlinkterminal commands - macOS – Finding Python through Finder and shell commands like
which
These methods help pinpoint the exact folder containing Python installs.
Knowing the install location allows running Python or its packages, modifying installed scripts, switching between environments, and debugging issues, if any.
Whether you just started with Python or have been using it for a while, finding where Python lives on your OS is an important troubleshooting skill.
So next time you need to locate Python, use this guide to find its path across Windows, Linux and macOS platforms.
References: StackOverflow
