Nowadays, most users are aware of the Command Prompt that is present in all versions of Windows. Undoubtedly this is one of the most dominant tools on the Windows Operating System. However, Windows supports another powerful application, PowerShell, to perform a wide range of operations. Just sign in as an Administrator and you may run PowerShell to handle configuration and carry out task automation.
PowerShell is a task-based mechanization and a fully developed scripting tool that can accelerate the admin job. It instructs users to manage the device from the command line. In other words, you can say that PowerShell is an advanced form of CMD. Therefore in the coming days, it is quite possible that this tool can take the place of a command prompt. So here are the five easy methods by following you can Open PowerShell as an administrator in Windows 10.
6 Ways to open PowerShell as Admin on Windows 10
Here is how to open Windows PowerShell with admin rights on your computer –
1. Using Cortana or the Search bar
You can open this tool using the Search (Win + S) bar available on the Taskbar. Here’s what you need to do –
- Click on Cortana and type PowerShell.
- Look for the option “Run as Administrator” on the right pane and click on it.

- The User Account Control window will prompt next, hit Yes to authorize opening it.
- When Windows PowerShell starts, you may run whichever command you want to execute on your PC.
2. Using Run Command
- Press the Win + R hotkey to open the Run dialog box.
- Type PowerShell and click OK.
Note: Windows PowerShell will open in normal mode.
- Type the command Start-Process Powershell -verb runAs and press the Enter key.
- Its interface will switch to administrator mode.

- There will be a confirmation line regarding this request.
- Type Y and hit Enter to confirm this action.
3. By using the Command Prompt
- Press Win + S, and type Command Prompt.
- Right-click on the result and select Run as administrator.
- Provide permission on the UAC window by clicking Yes.
- On the running Window, type PowerShell and hit Enter.

- Well, the default structure on CMD will now change to the PowerShell way. You may see the Snapshot above.
4. By using the Power menu
This method will only work if you haven’t changed Windows PowerShell to Command Prompt sometime back on your PC. Let’s see how to open PowerShell using the Power Menu (Win + X) –
- Right-click on the Start button.
- Click on Windows PowerShell (Admin).
5. By using Task Manager
- Initially open the Task Manager by pressing ctrl + shift + Esc.
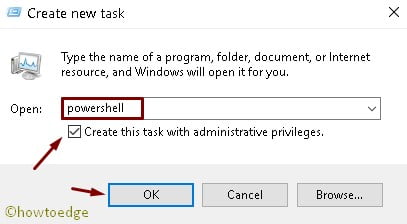
- Click on File, available in the top-left corner of the wizard.
- Hit the Run new task option.
- Now, type PowerShell in the void box and tick the checkbox below the void space.
6. By using the Start Menu
- Click on the start button; scroll down the menu list.
- Explore the drop-down menu in the Windows PowerShell folder.
- Now select this folder and it will expand.
- Right-click on the Windows PowerShell option and select Run as Administrator.

I hope you find this guide useful and all six methods also work on your computer. Let us know in the comment section if any method doesn’t work.
That would be all!
Last Updated :
01 Dec, 2023
Windows Powershell is a powerful command-line shell and scripting language devised for administrators and professionals. PowerShell with administrative privileges in Windows 11 makes it possible to carry out tasks with superior permissions. This article will discuss several ways of opening Windows PowerShell as admin.

What is Windows PowerShell?
The Windows PowerShell is a Command Line Interface and Scripting Language based on the .NET framework. Windows is an important tool that offers an active command line interface for automation of jobs and configuration management. PowerShell can run administrative commands and as such, provide administrator access.
Method 1: Open Windows PowerShell as an Administrator Using Win + X
Step 1: To open the quick access menu, right-click on Start or use the keyboard shortcut Win + X.
Step 2: Then, from the context menu, select «Terminal (Admin)».
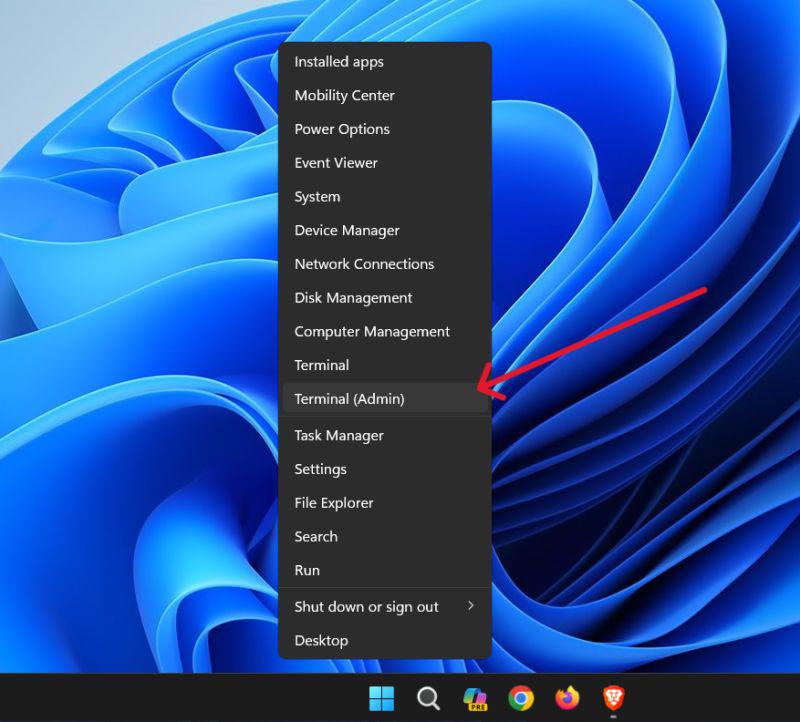
Step 3: In user account control click on «Yes«
Method 2: Run PowerShell Script as Admin from Start Menu
Step 1: Click on the start button, then the search box, and type «Windows tools».
Step 2: Then, Right-click on «Windows PowerShell» from the list.
Step 3: Choose «Run as administrator.»
Step 4: In user account control click on «Yes«
Method 3: Open PowerShell as Admin Using Windows Search
Step 1: Type «Windows PowerShell» in the Windows Search bar.
Step 2: Choose «Run as administrator» from the context menu
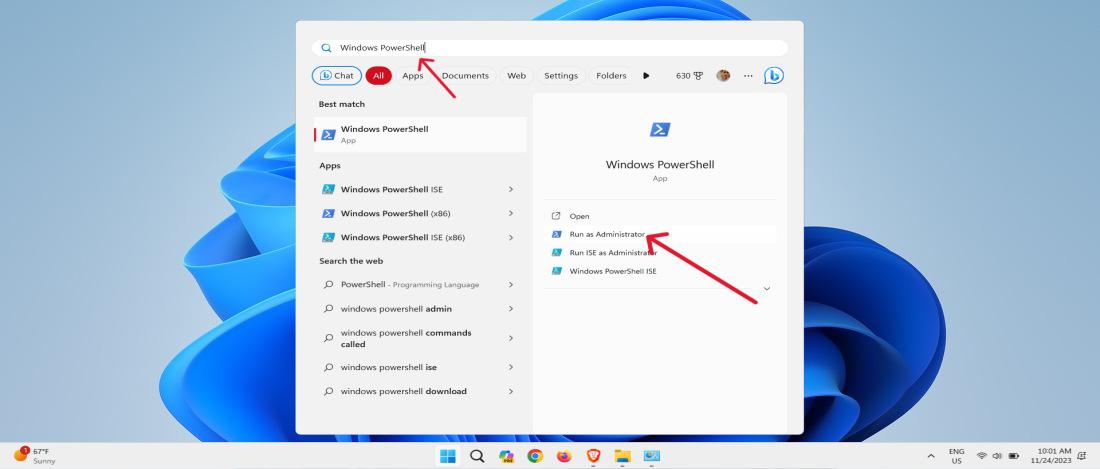
Step 3: In user account control click on «Yes«
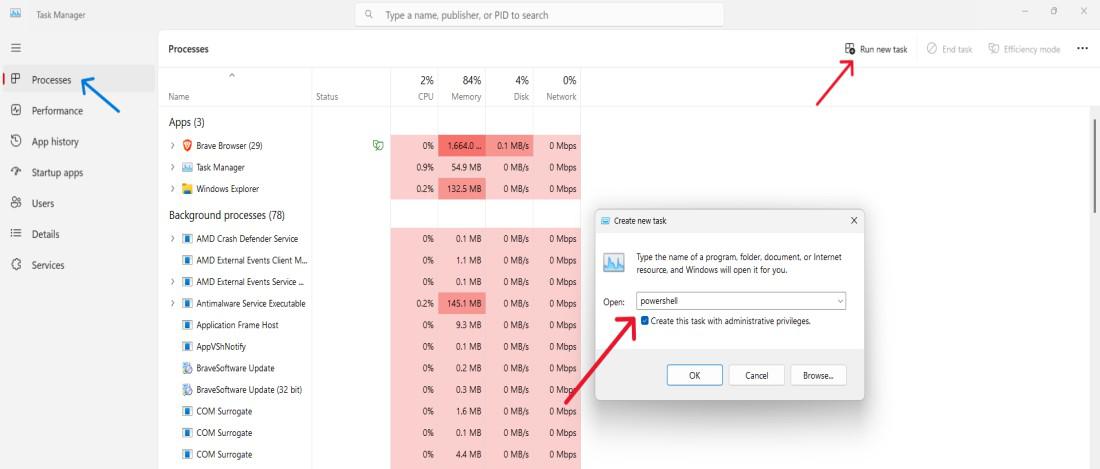
Method 4: Run Windows PowerShell Using Task Manager
Step 1: Type “Task Manager” in the search bar or press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
Step 2: Choose «Run new task.»
Step 3: Select Powershell, and tick administrative privilege.
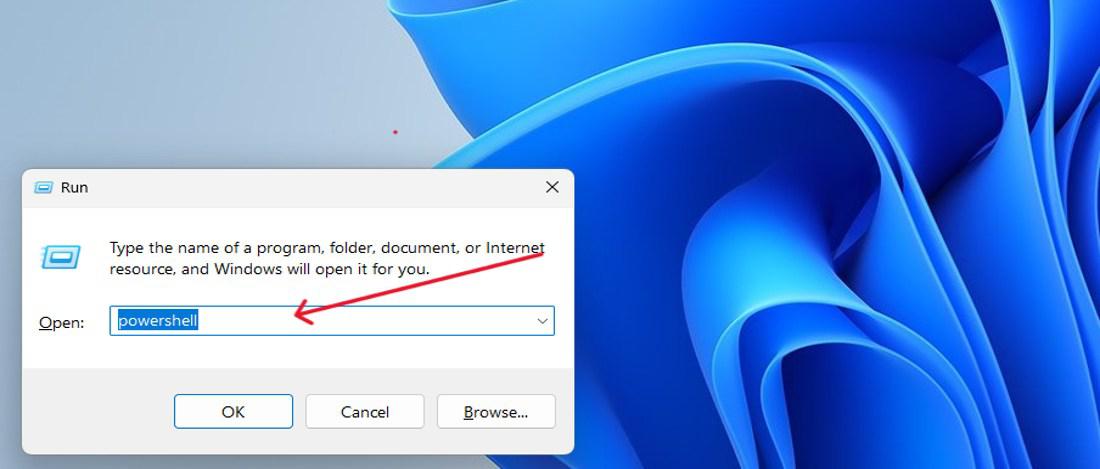
Method 5: Open PowerShell as Admin Using Run Dialog
Step 1: Press Win + R to open the Run dialog.
Step 2: Type «PowerShelland » and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to run as administrator. Do not click on OK button
Step 3: In user account control click on «Yes«
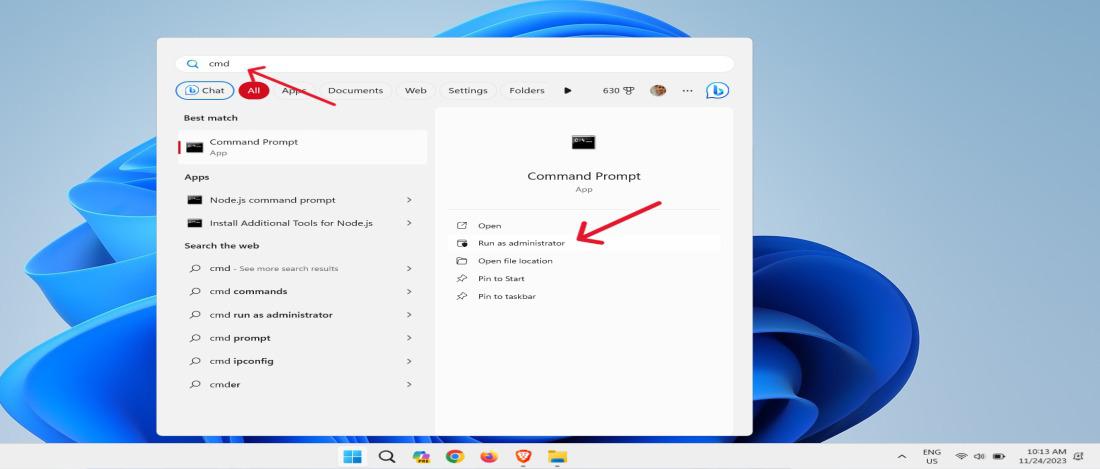
Method 6: Run Windows PowerShell as Admin from CMD
Step 1: Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
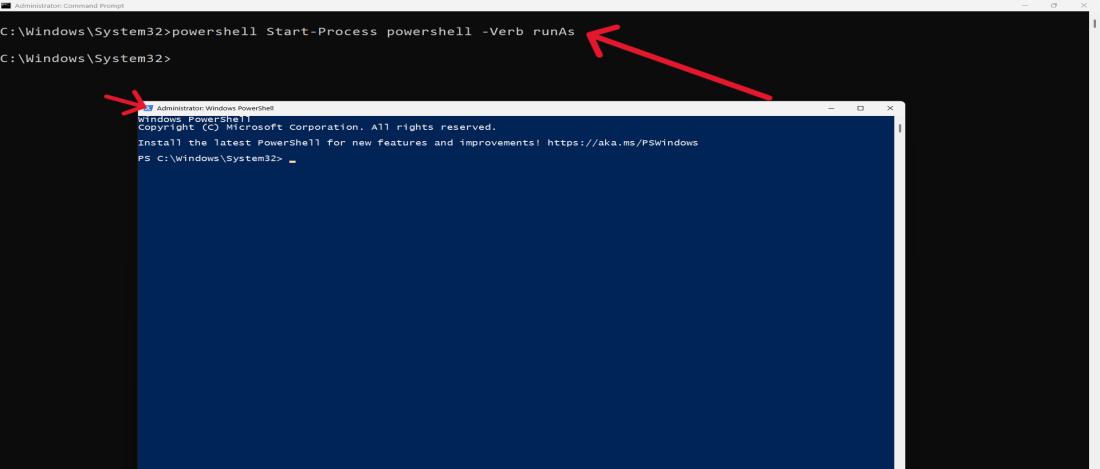
Step 2: In user account control click on «Yes«
Step 3: Type
powershell Start-Process powershell -Verb runAs
Method 7: Open PowerShell as Admin Using Windows File Explorer
Step 1: Open file explores by using the shortcut Win + E or type «File Explorer» on search bar
Step 2: Type the command in the File Explorer address bar and press Enter.
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\
Step 3: Right click on Powershell then click on «run as administrator».
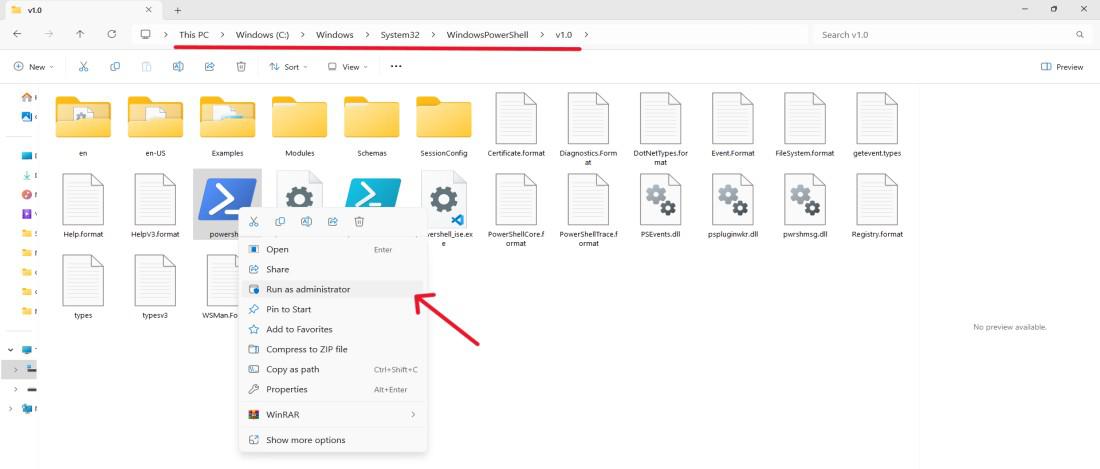
Step 4: In user account control click on «Yes»
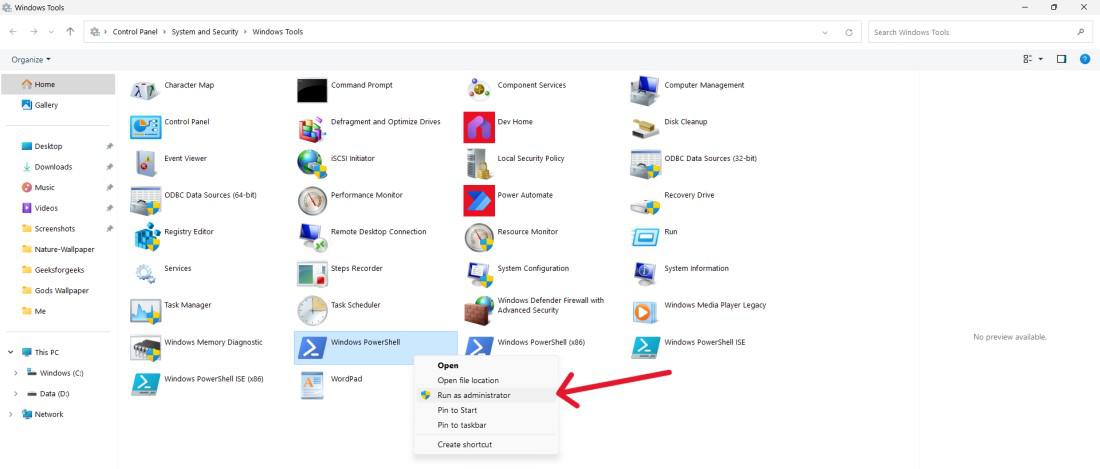
Method 8: Open PowerShell as Admin Using Control Panel
Step 1: Open the Control Panel.
Step 2: Go to «System and Security» > «Windows Tools.»
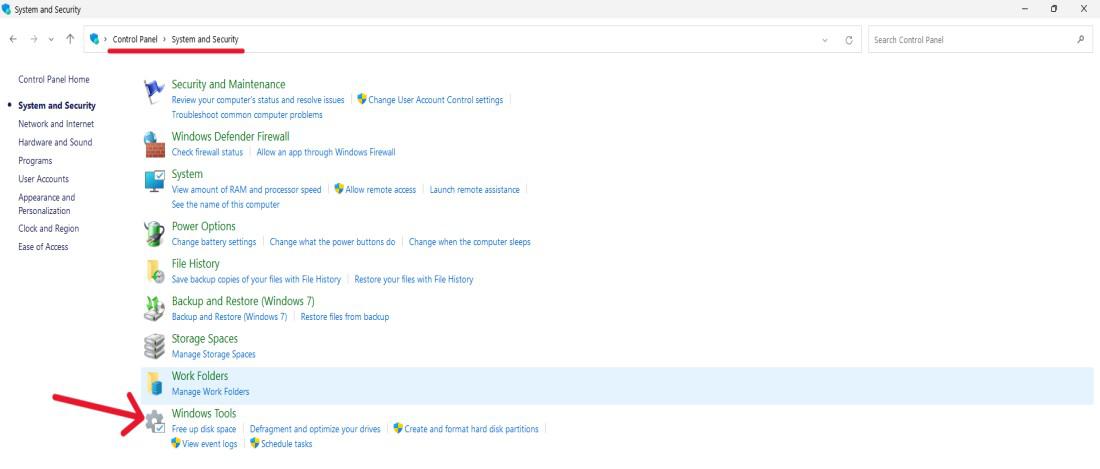
Step 3: Right-click on «Windows PowerShell ISE (x86)» or «Windows PowerShell» with administrative privileges.

Step 4: In user account control click on «Yes«
Method 9: Open PowerShell as Admin With a Desktop Shortcut
Step 1: Right-click on the desktop.
Step 2: Choose «New» > «Shortcut.»
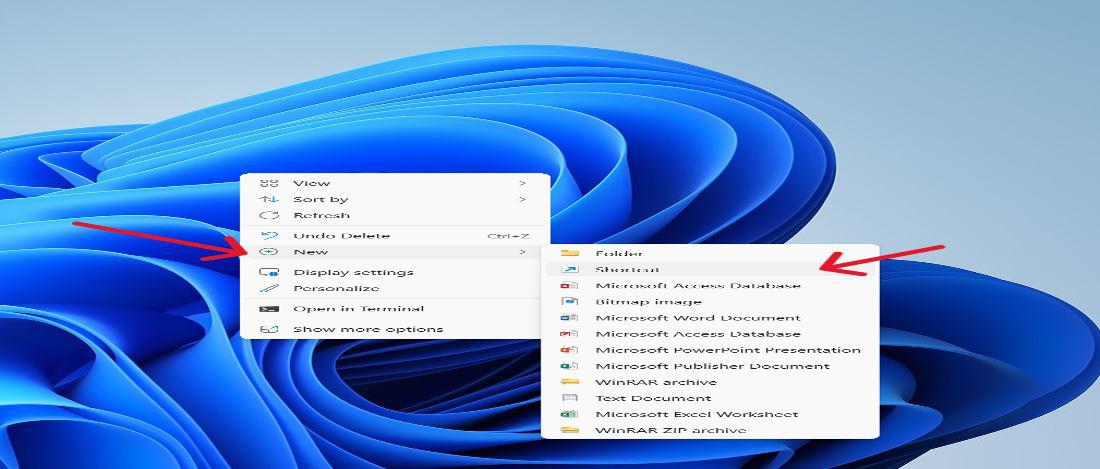
Step 3: Enter «powershell.exe» as the location.
Step 4: Click «Next» and give your shortcut a name.
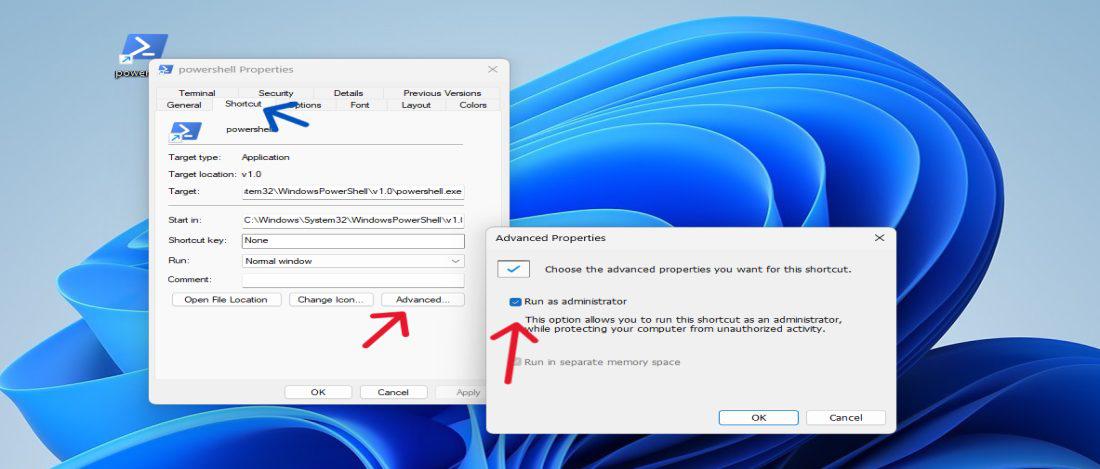
Step 5: Right-click on the shortcut, go to «Properties,» and under the «Shortcut» tab, click «Advanced» and check «Run as administrator.»
Conclusion
There are different ways to launch Windows PowerShell with administrative rights in Windows 11 such that you may choose what best suits you. You can use different approaches through which the PowerShell is executed with its administrative access. These means include the use of keyboard shortcuts and the Start Menu among others since it’s an elevated command used in system-level tasks. Adopt these processes within your workflow to simplify your administrative duties in Microsoft Windows 11.
Also Read
- How to Change Your User Name on Windows 11?
- How To Merge Folders in Windows?
- How to Disable Background Apps in Windows 11?
- How to Clear the Windows Command Prompt Screen?
Quick Tips
- Utilize the search bar. Hit the Windows key + S > type PowerShell > right-click the result > select Run as administrator.
- Press Win + R > type powershell > hold Ctrl + Shift + Enter to launch with admin rights.
- Need another way? Press the Windows key + X and select Terminal (Admin).
Method 1. Using Windows Search
Step 1: Press the Windows key and type PowerShell in the search box.
Step 2: Click on Run as Administrator from the right pane.
Step 3: You will get a UAC prompt asking for your consent; click Yes.
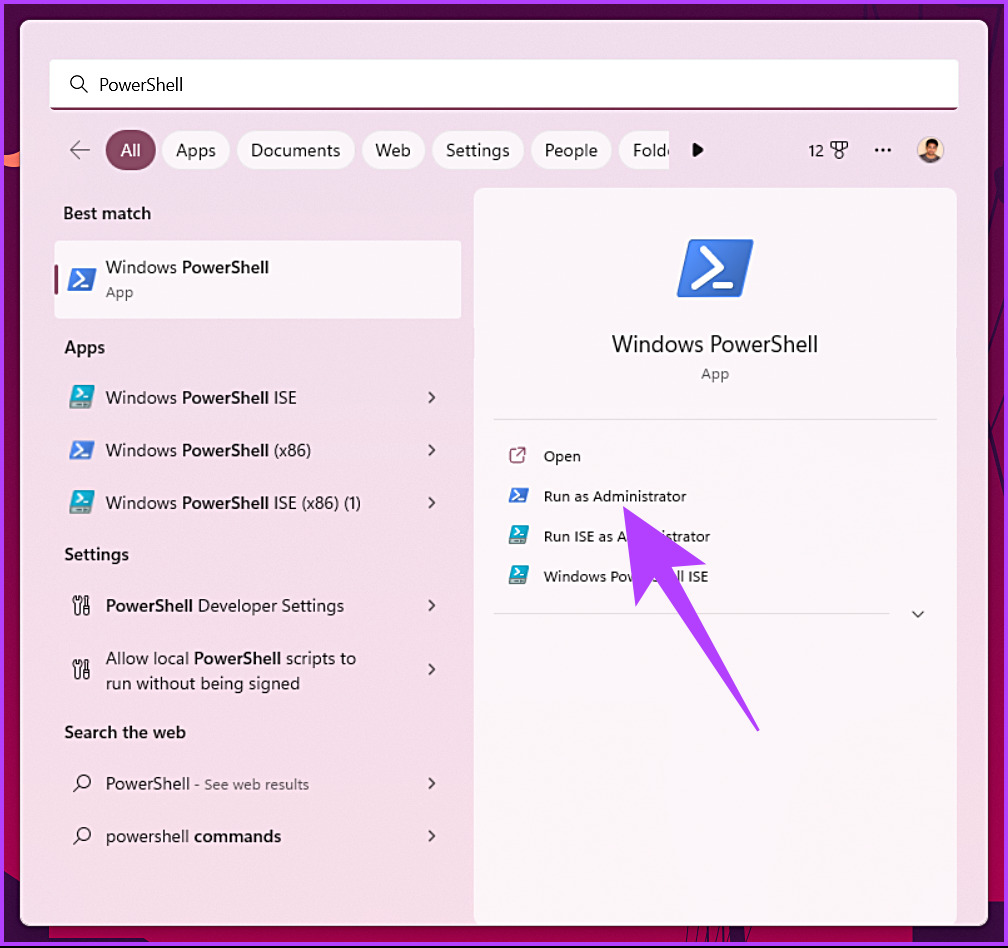
That’s it. The PowerShell will open as administrator. If you don’t want to use the Windows Search feature to find and open PowerShell, you can do the same with the help of the Windows context menu. Keep reading.
Method 2. Using WinX
Step 1: Press the Windows key + X on your keyboard.
Step 2: From the context menu, select Terminal (Admin).
Step 3: In the UAC prompt, click Yes.

There you go. You have launched PowerShell in administrator mode. If you landed on some Command Prompt or in any other terminal, click on the Chevron (arrow) icon at the top and select PowerShell.
We will be using Windows Tools to execute this method.
Step 1: Press the Windows key on your keyboard > click on All apps.
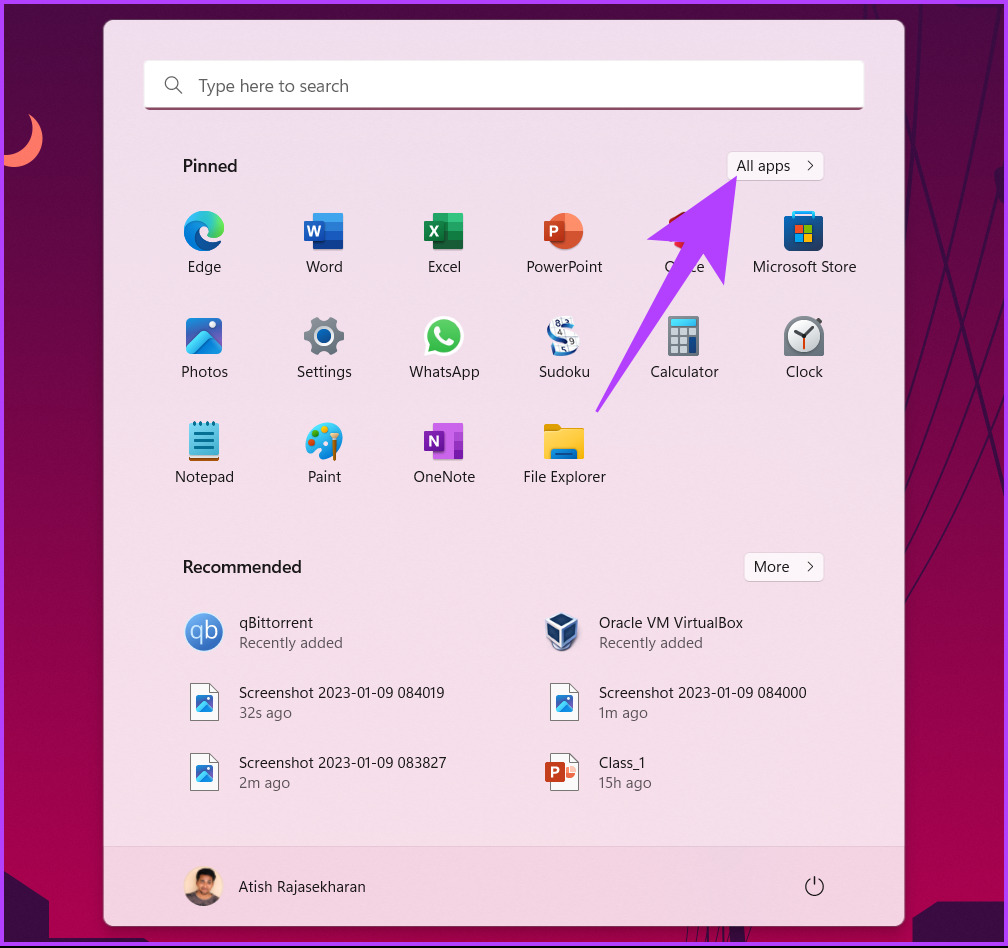
Step 2: Scroll down and click on Windows Tools.
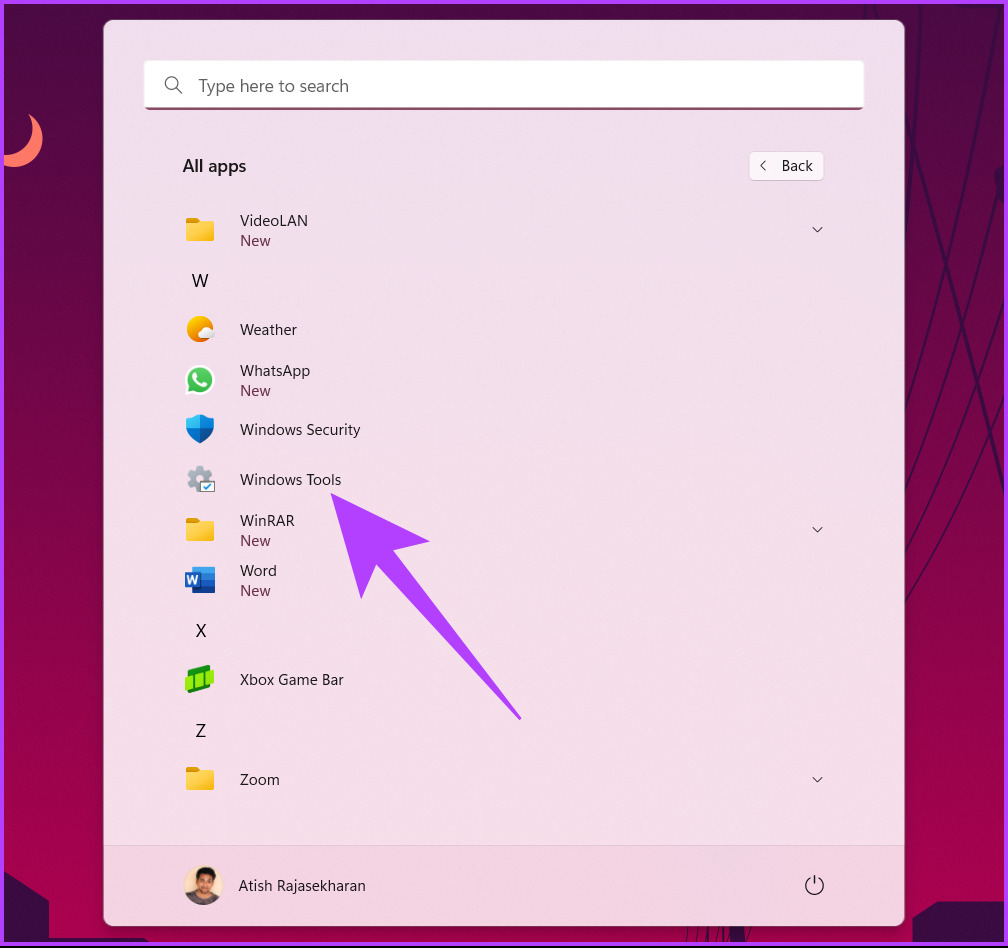
Step 3: In the Windows Tools window, scroll down and right-click on Windows PowerShell.
Step 4: From the context menu, select Run as administrator.

Step 5: In the prompt, click Yes.
There you go. You can now work on PowerShell with administrator privileges. If you want to know another way, jump to the next method.
Method 4. Using Task Manager
Step 1: Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open Task Manager.
Step 2: Click on the Run new task button. It will open a Create new task dialog box.
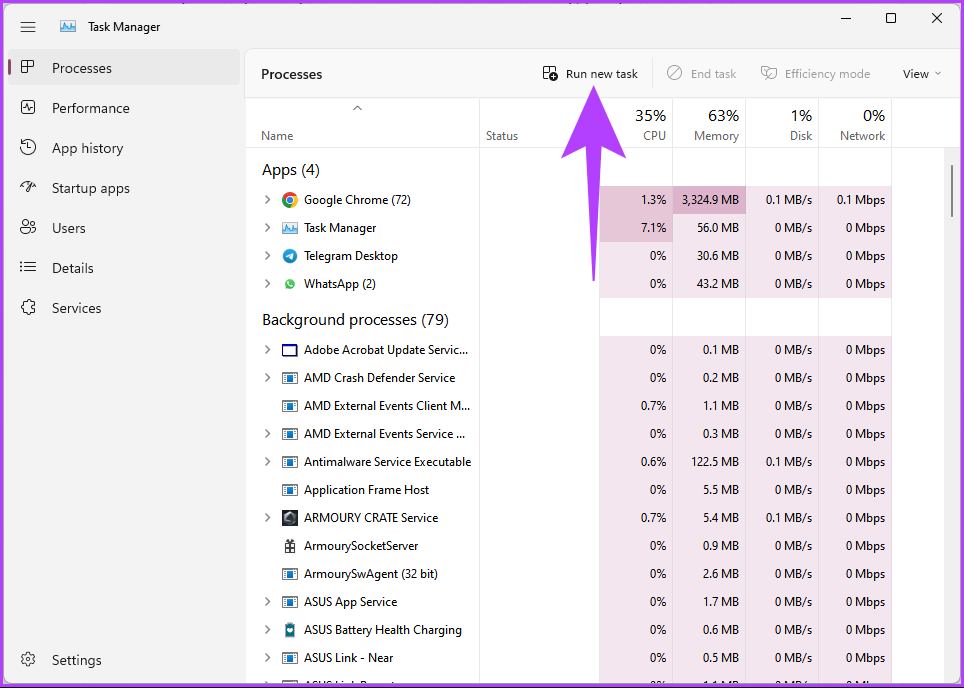
Step 3: Type PowerShell in the text field > check the box for Create this task with administrative privileges > click OK.

There you have it. It will open PowerShell with administrative privileges without any complications.
Method 5. Using the Run Command Box
Step 1: Press the Windows key + R on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box.
Step 2: Type PowerShell > click OK. This will open Windows PowerShell with the rights of the current user.

Step 3: To switch from normal (current user) mode to administrator mode, type the below command and press Enter.
Start-Process powershell -Verb runAs
Step 4: In the UAC prompt, click Yes.

Method 6. Using CMD
Step 1: Press the Windows key > type Command Prompt > click Run as administrator. In the prompt, click Yes.
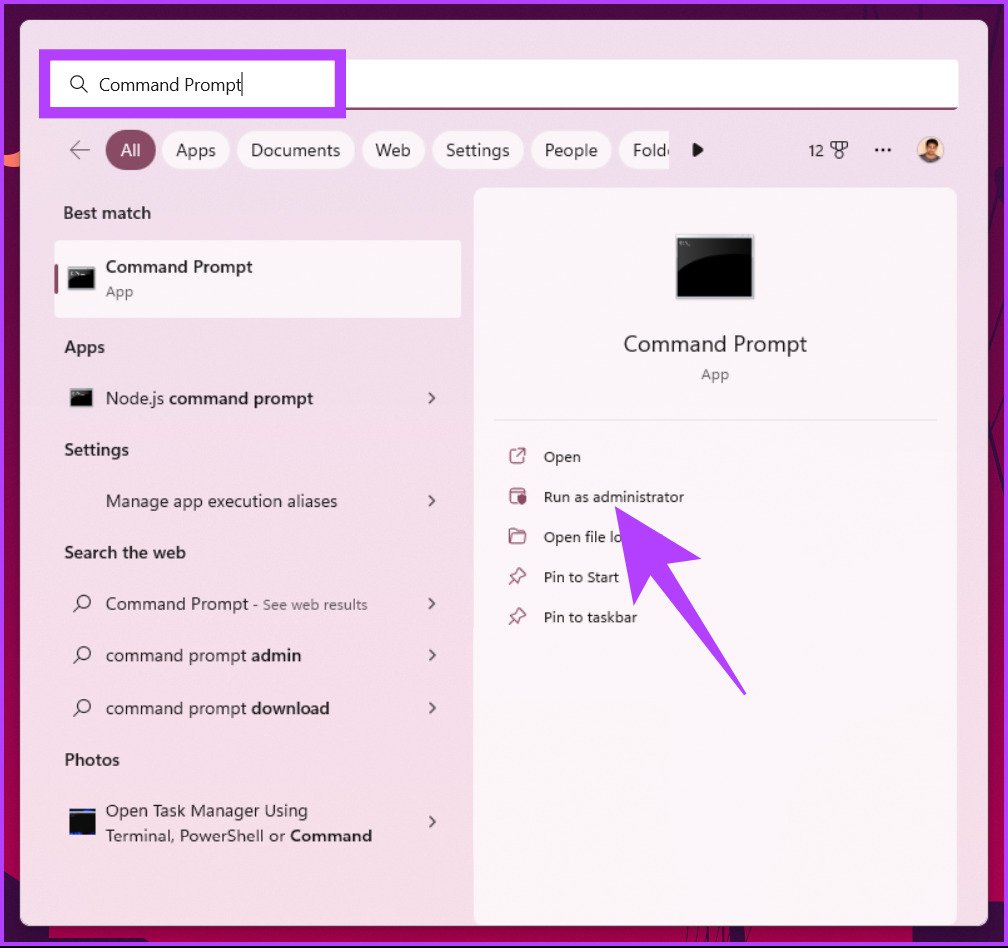
Step 2: In the Command Prompt window, type PowerShell > press Enter.
FAQs
1. Does Windows PowerShell run in administrator mode by default?
Windows PowerShell does not run in administrator mode by default. When you launch PowerShell, it runs with the permissions of the currently logged-in user.
2. How do I know if PowerShell is running as an administrator?
There are several ways to determine if PowerShell is running as an administrator. One is to check the PowerShell window title or the PowerShell execution policy. Another is to check the user account control (UAC) prompt.
Was this helpful?
Thanks for your feedback!
The article above may contain affiliate links which help support Guiding Tech. The content remains unbiased and authentic and will never affect our editorial integrity.
Whether you’re just starting out with PowerShell or you already know how to run commands, there are times when you must use PowerShell to ‘run as administrator’ Why? Because sometimes, any activity you do inside of PowerShell will require elevated privileges.
In this tutorial, you’re going to learn just about every way possible to run PowerShell as administrator from the perspective of an end-user, a command-line junkie, or an IT admin!
This tutorial has many sections each showcasing how to run PowerShell as administrator. Feel free to click on whichever method you prefer in the Table of Contents.
Prerequisites
This article will be a hands-on tutorial. If you’d like to follow along, please be sure you have:
- A Windows 10 PC – Although Windows 10 was used as an example for this article, most of the methods provided will work with Windows 7+.
- An account with administrator privileges. If you don’t already have one, learn how to create one here.
- PowerShell – Most of these methods will work with Windows PowerShell 5.1 or PowerShell 7.
Running PowerShell as Administrator with a Right-Click
One of the simplest ways to run PowerShell as administrator is with a right-click. There are a few different areas where you can right click on PowerShell and run it. Let’s run through them.
Using the Search Bar
The Search Bar is practically one of the easiest ways to run most of the programs installed on your computer. It’s also an easy way to run any program as administrator, including PowerShell.
To run PowerShell, specifically, as administrator from the search bar:
- Click on the search box at the taskbar and type powershell. This action will bring up the PowerShell edition of your preference.
- Look for Windows PowerShell or just PowerShell, if using PowerShell Core, from the search result.
- Right-click on the menu item and select Run as administrator.
You can see these steps demonstrated in the screenshot below.

If you pin a program to the start menu or taskbar, you can also right-click on the menu item there as well. With this method, Windows 10 creates a shortcut for PowerShell that is more accessible to you at the start menu or the taskbar.
To run PowerShell as administrator on a pinned item:
- Find the PowerShell icon in the search box again.
- Right-click on the PowerShell icon and select Pin to Start or Pin to Taskbar.

- Click on the Start button
- Look for Windows PowerShell (or PowerShell Core) on the right side of the Start Menu.
- Right-click on the menu item and choose Run as administrator.

Running PowerShell as Administrator Using File Explorer
Are you in Windows’ File Explorer, you can fire up PowerShell as administrator there too!
- Open up File Explorer by using Win Key + E shortcut keys or by simply clicking the icon at the taskbar as you can see on the screenshot below.
2. Once in File Explorer, click on File → Open Windows PowerShell → Open Windows PowerShell as administrator as shown below.

Using the PowerShell Executable
Whether you’re using a 32-bit or 64-bit operating system, you can run PowerShell as administrator from its respective location.
- In File Explorer, navigate to one of the folders below.
- For 32-bit OS: C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0
- For 64-bit OS: C:\Windows\SysWOW64\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0
- Find the powershell.exe file.
- Right-click on powershel.exe and select Run as Adminstrator.

Creating a Shortcut for PowerShell on the Desktop
If you’d like an easy way to invoke PowerShell, you can also create a Windows shortcut for it.
- Once you’ve got the Create Shortcut process started, provide the path to the PowerShell executable. For Windows PowerShell, that path is:
- For 32-bit OS: C:\Windows\SysWOW64\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
- For 64-bit OS: C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe

2. Provide the shortcut a handy name (PowerShell Admin for example).

3. Find the shortcut you just created and right-click on it and choose Properties as shown below.

4. Click on Shortcut tab and then on the Advanced button and the Advanced Properties window will pop-up.
5. In the Advanced Properties window, select the Run as administrator checkbox and click OK.
6. Back to the Shortcut Properties, click OK to apply the changes and you’re all set.
Another way to easily access PowerShell is via the Win-X menu as shown in the following screenshot. This menu was never given an official name but was widely referred to as Win-X (or power user menu) as the shortcut to access it is Win Key + X.
Once the menu is up, simply click on Windows PowerShell (Admin) and you’re off to th races.

Using the Run Command Window
The Run Command Window is a powerful tool that lets you run programs without searching for them using the SearchBar, Start Menu or File Explorer. To run PowerShell as administrator via the Run command window:
- Press Win Key + R. A a small window will pop up as shown in the screenshot below.
- Type in powershell and press Ctrl+Shift+Enter or press and hold Ctrl+Shift.
- Click OK to make PowerShell run as administrator.
You’re now running PowerShell as administrator.
Using Task Manager
Task Manager is a tool that lets you monitor or end a process of the programs and services that are currently running on your computer. You can also use it to execute a task such as running PowerShell as administrator manually.
To run PowerShell as administrator via the task manager:
- Open the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc keys on your keyboard or as you see in the screenshot below
You can alternatively right-click on the Task Bar and select Task Manager to bring up Task Manager.
2. Once Task Manager opens, go up to File and click on Run new task as shown below.

3. You should then see a window pop up that looks similar to the Run window described earlier.
4. Type in powershell ensuring you also check the Create this task with administrative privileges checkbox and click OK to make PowerShell run as administrator.
Running PowerShell as Administrator with the Command Line
If you regularly find yourself on the command line, don’t fret, you can run PowerShell as administrator there too!
If you already have cmd. exe open running as adminstrator using the same techniques described in this article, you can simply run start powershell and it will be running as adminstrator.
If you’re running a command prompt not as administrator yet, that’s not a problem. Invoke the Start-Process cmdlet with PowerShell from cmd. exe using the -Verb runas parameter.
powershell Start-Process powershell -Verb runAsIf you’re already in a PowerShell window, you can run Start-Process powershell -Verb runas directly to open a new PowerShell instance running as administrator
Creating a Batch File to Run PowerShell as Administrator
So you now know how to invoke PowerShell as administrator from a command prompt. If you already know how to do that, you can create a batch file to automate it!
Open up your favorite text editor, paste in the following line and save the file as PowerShell as admin.bat anywhere you’d like.
Powershell.exe -Command "& {Start-Process Powershell.exe -Verb RunAs}"Run the batch file and you’ll notice up comes a PowerShell window running as administrator!
Creating a Scheduled Task to Run PowerShell as Administrator
Task Scheduler is a built-in app on Windows 10 that lets you virtually run automated tasks. Hence, you can also use it to create a task that runs PowerShell as administrator each time you logon to your computer, for example.
Start up the Create Taskbox and specify the file to run as one of the below:
- For 32-bit OS: C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
- For 64-bit OS: C:\Windows\SysWOW64\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
In the Create Task windows, provide the values to all of the menu items shown below ensuring the Run with highest privileges checkbox is checked.

Now when the scheduled task is invoked, it will execute PowerShell as administrator!
Further Reading
- PowerShell Objects, Properties and Methods
- How to Set Up and Manage Scheduled Tasks with PowerShell
To run a PowerShell script as an administrator, you can right-click on the PowerShell icon and select «Run as administrator,» or use the following code snippet to elevate your script programmatically:
Start-Process powershell -ArgumentList '-NoProfile -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File "C:\Path\To\YourScript.ps1"' -Verb RunAs
Understanding PowerShell Scripts
What is a PowerShell Script?
A PowerShell script is a text file containing a series of PowerShell commands that automate processes and tasks. Typically, these scripts are used for system administration tasks, such as managing user accounts, configuring network settings, or performing batch processing of files. The power of PowerShell scripts lies in their ability to interact directly with the Windows operating system and perform administrative tasks efficiently.
Why Run PowerShell Scripts as Administrator?
Running a PowerShell script as an administrator is essential when the script needs elevated permissions to perform specific actions. Certain tasks require administrative privileges, such as modifying system files, changing configurations, or accessing sensitive areas of the system. Understanding the need for admin rights will enable you to effectively manage your environment and automate tasks securely.
Run PowerShell Script as Administrator Without Prompt: A Guide
Prerequisites for Running PowerShell Scripts as Administrator
Checking Your PowerShell Version
To ensure compatibility with your scripts and features, it’s vital to verify your PowerShell version. Here’s how you can do it:
- Open PowerShell (you can search for it in the Start menu).
- Type the following command and press Enter:
$PSVersionTable.PSVersion
This command outputs the version number, allowing you to confirm you are using a supported version.
User Account Control (UAC) and Administrative Permissions
User Account Control (UAC) is a security feature that helps prevent unauthorized changes to your operating system. It may prompt you when you attempt to run PowerShell as an administrator. To check if your user account has administrative privileges, follow these steps:
- Go to Control Panel > User Accounts > User Accounts.
- Look for the label «Administrator» under your username.
If administrative privileges are necessary for running your scripts, it’s crucial to ensure you have the proper rights before executing commands.

How to Run PowerShell Script From Command Line Effortlessly
Methods to Run a PowerShell Script as Administrator
Using the Context Menu
One of the easiest ways to execute a PowerShell script as an administrator is through the context menu. Simply locate your script file, then:
- Right-click on the script (.ps1) file.
- Select «Run with PowerShell».
- If prompted by UAC, click Yes to allow it to run.
This method is straightforward and works well for ad-hoc script execution.
Code Snippet Example:
# Sample Script: MyScript.ps1
Write-Host "Hello, Administrator!"
Running PowerShell from the Start Menu
You can also open PowerShell directly from the Start menu with elevated privileges:
- Search for PowerShell in the Start menu.
- Right-click on the Windows PowerShell option.
- Select «Run as Administrator».
- Once the PowerShell window is open, navigate to the script location, and execute it using:
.\MyScript.ps1
This method allows you to run your scripts in an elevated session directly from the command line.
Creating a Desktop Shortcut to Run as Administrator
Creating a shortcut to run a PowerShell script as an administrator simplifies the process for future execution. Here’s how to set it up:
- Right-click on your desktop and select New > Shortcut.
- In the location field, enter:
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File "C:\path\to\MyScript.ps1" - Name your shortcut and click Finish.
- After creating the shortcut, right-click it and select Properties.
- Under the Shortcut tab, click Advanced… and check Run as administrator.
Now, double-clicking this shortcut will automatically run your script with elevated permissions.
Using the Command Line
If you prefer working from the Command Prompt, you can execute your PowerShell script as an admin with this command:
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type the following command:
powershell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File "C:\path\to\MyScript.ps1"
This allows you to run the script without opening a PowerShell window first.
Task Scheduler
For running PowerShell scripts automatically with administrative rights, you can utilize Task Scheduler. Here’s how:
- Open Task Scheduler from the Start menu.
- Click Create Basic Task.
- Follow the wizard to name your task and select a trigger (e.g., daily).
- Under Action, select «Start a program». For the program/script, enter:
powershell.exe - In the Add arguments section, add:
-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File "C:\path\to\MyScript.ps1" - Finally, in the Conditions tab, check «Run with highest privileges».
Your script will now run automatically with administrative rights at scheduled times.
Run PowerShell Script as Administrator from Batch File Explained
Best Practices for Running PowerShell Scripts as Admin
Ensuring Script Safety
Before running a script as an administrator, it is vital to validate its content and sources. Malicious scripts can compromise your system. Always:
- Review the script for potentially harmful commands.
- Run scripts from trusted sources only.
- Use a text editor to examine scripts before execution.
Logging and Monitoring Scripts
Logging script execution is crucial when performing administrative tasks. It helps in auditing what commands were run and by whom. You can enable logging in PowerShell by adding the following line at the beginning of your script:
Start-Transcript -Path "C:\path\to\logfile.txt"
This command will create a transcript of all command outputs and errors, aiding in any troubleshooting efforts.

Understanding Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.Internal.Format.FormatStartData
Troubleshooting Common Issues
UAC Prompt Issues
If you’re facing persistent UAC prompts each time you run a script, consider adjusting UAC settings or using Task Scheduler, as discussed earlier, to bypass repeated confirmations.
Script Errors
Common errors might occur when running scripts as an administrator. If an error arises, PowerShell provides mechanisms for exception handling. Utilize a try-catch block for better control:
try {
# Your script code here
} catch {
Write-Host "An error occurred: $_"
}
This not only handles errors gracefully but also gives you insight into what went wrong.
Unlocking Windows PowerShell Scriptomatic For Quick Tasks
Conclusion
Understanding how to run PowerShell scripts as admin is crucial for effective system management. By following the outlined methods and best practices, you can leverage the power of PowerShell scripts while maintaining security and compliance. Experiment and practice with PowerShell to enhance your administrative skills, and remember to validate your scripts for safety!
Handy PowerShell Scripts for Everyday Tasks
Additional Resources
- Always refer to the official PowerShell documentation for in-depth information and updates on new features.
- Engage with online forums and communities to learn from other PowerShell users and share your experiences.
