-
Home
-
Partition Manager
- CMD List Drives: How to List Drives in Command Prompt? [Answered]
By Ariel | Follow |
Last Updated
Sometimes you may to need list all drives on your systems. How to list drives in CMD/PowerShell? This post of MiniTool provides a full guide on PowerShell/CMD list drives and a professional tool to manage your drives.
When formatting a drive or copying files from a drive to another drive, you may need to use the CMD or Windows PowerShell tool to list drives. However, many people don’t know how to list drives in Command Prompt or PowerShell, like a user from the superuser forum:
Is there a way to list the available drives from cmd.exe? (Other than manually typing c: d: …) and seeing which ones return errors.https://superuser.com/questions/139899/see-available-drives-from-windows-cli
How to List Drives in CMD
Command Prompt, also known as CMD, is the command-line interpreter in Windows operating system. You can input certain commands in the Command Prompt window to take corresponding actions. If you want to list drives of your systems, you can use the WMIC (Windows Management Instrumentation for Management) or Diskpart command.
List Drives CMD via WMIC:
Step 1. Press Win + R keys to open the Run dialog box, and then type cmd in it and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter keys together to open the elevated Command Prompt window.
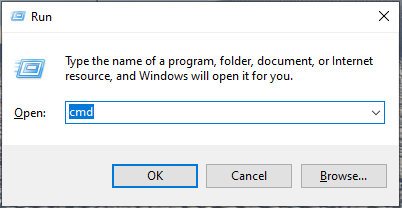
Step 2. To let CMD list drives, type one of the following commands and hit Enter.
- wmic logicaldisk get name
- wmic logicaldisk get caption
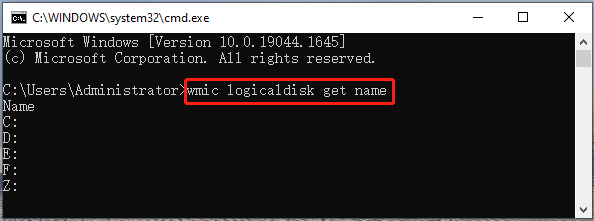
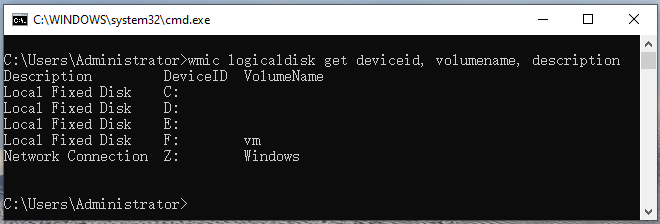
Step 3. If you want to display the Device ID and volume name, type the following command and hit Enter. Also, you can run the fsutil fsinfo drives command to list drives on your computer
wmic logicaldisk get deviceid, volumename, description
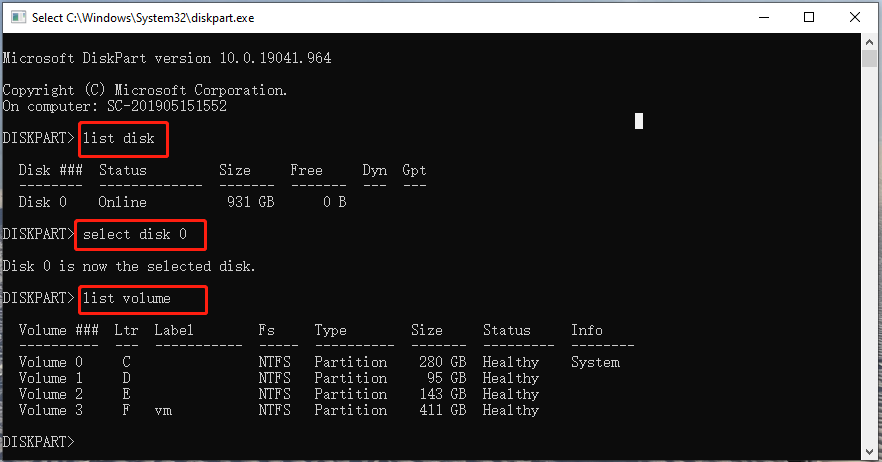
List Drives CMD via Diskpart:
DiskPart is a disk partition management tool that uses command lines to perform operations. It can be used to list drives CMD as well. Here’s how to use it.
Step 1. Open the Command Prompt window again as we explained above.
Step 2. Type the following commands in order and hit Enter after each one. Then you will see a list of drives on the disk, including partition/volume number, label, letter, file system, size, and status.
- diskpart
- list disk
- select disk *
- list volume/list partition
How to List Drives in PowerShell
PowerShell is a command-line tool like CMD. Here you can let PowerShell list drives as well. To do so, follow the steps below:
Step 1. Open the Run dialog box, and then type powershell in it and hit Enter.
Step 2. In the Windows PowerShell window, type the following command and hit Enter.
get-psdrive -psprovider filesystem
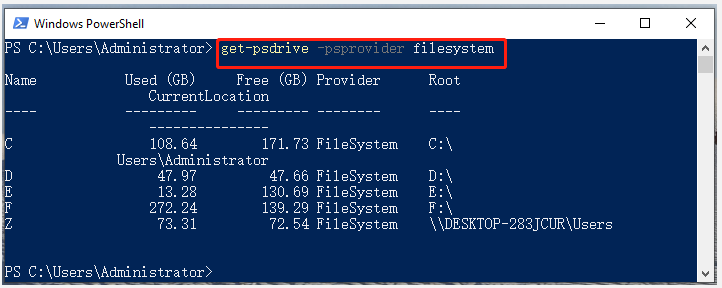
How to let PowerShell/CMD list drive letters? Now, I believe that you already have known the answer.
Better Choice Than PowerShell/CMD List Drives
Although both of the two Windows tools can help you list drives, you may encounter some limitations to further managing drives/disks with them. For example, you can’t format a drive larger than 32GB to FAT32 using CMD. If you want to manage your hard disk or partitions more effectively, it’s highly recommended that you use a professional tool like MiniTool Partition Wizard.
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
It is a popular partition manager trusted by millions of users around the world. With this tool, you can not only obtain the drive information easily but do many other powerful tasks, including create/extend/move/format/wipe partition, convert NTFS to FAT32 without data loss, convert MBR to GPT, migrate OS, rebuild MBR, recover data, etc.
About The Author
Position: Columnist
Ariel has been working as a highly professional computer-relevant technology editor at MiniTool for many years. She has a strong passion for researching all knowledge related to the computer’s disk, partition, and Windows OS. Up till now, she has finished thousands of articles covering a broad range of topics and helped lots of users fix various problems. She focuses on the fields of disk management, OS backup, and PDF editing and provides her readers with insightful and informative content.
To list all disks in Command Prompt (cmd), you can use the Diskpart utility followed by the ‘list disk’ command. Here’s how to do it:
diskpart
list disk
Understanding CMD Commands
What is CMD?
The Command Prompt (CMD) is a powerful tool in Windows that allows users to execute commands to perform advanced administrative tasks, troubleshoot issues, and configure system settings. It offers a text-based interface, enabling users to communicate directly with their operating system.
Using CMD is crucial for anyone looking to manage their computer efficiently, as it can speed up tasks that may take longer through the graphical interface. For advanced users, it encompasses a myriad of functions, including file management, network configuration, and disk management.
The Role of Disk Management in CMD
Disk management is a vital aspect of maintaining a healthy computer system. It involves overseeing and configuring storage devices like hard drives and solid-state drives while ensuring they function correctly. With CMD, you can easily manage your disks, including formatting, partitioning, and listing disks connected to your machine.

Mastering The List Disk Cmd Command In Minutes
Listing Disks in CMD
What Does «List Disks» Mean?
To list disks refers to checking the disks that are currently connected to your computer. This capability is particularly helpful for system administrators and advanced users who need to monitor disk usage, check disk status, and manage disk partitions. Knowing the disks connected helps you identify storage limitations or potential issues that may impact your system’s performance.
How to Access Command Prompt
Accessing Command Prompt is the first step to listing disks. Here’s how you can do it:
- Using Windows Search: Type “cmd” or “Command Prompt” in the Windows search bar. Click on it to open.
- Accessing through the Run Dialog: Press `Windows + R`, type `cmd`, and hit Enter.
- Opening CMD as an Administrator: Right-click on the Command Prompt icon in the search results and select “Run as administrator” for full privileges.

List Disk Cmd Windows: Quick Guide to Disks Management
Using the Diskpart Command
Introduction to Diskpart
Diskpart is a built-in Windows utility for disk management. It provides more comprehensive features than the standard graphical interface and allows users to manage disks, partitions, and volumes directly through commands. The command-line environment of Diskpart is especially beneficial when dealing with multiple disks or when you encounter issues that require a more hands-on approach.
Command to List Disks
To list disks in CMD, you can use the Diskpart utility. Here’s how you can do it:
- Open Command Prompt as an Administrator.
- Launch Diskpart by typing the following command:
diskpart
- Once in the Diskpart environment, type the next command to list all disks:
list disk
Example of Listing Disks
After executing the `list disk` command, you will see an output that resembles the following structure:
Disk ### Status Size Free Dyn Gpt
-------- ------------- ------- ------- --- ---
Disk 0 Online 476 GB 50 GB *
Disk 1 Online 931 GB 0 B
In this output:
- Disk Number: Identifies the individual disk (e.g., Disk 0, Disk 1).
- Status: Indicates whether the disk is online or offline.
- Size: Displays the total capacity of the disk.
- Free Space: Shows the amount of unallocated space available.
- Dynamic/Basic: Designates the type of disk configuration (if applicable).
List Users in Cmd: A Quick Guide for Beginners
Additional Disk Management Commands
Show Additional Disk Information
Once you have listed the disks, you might want to retrieve more detail about a specific disk. This can be done using two commands in Diskpart:
select disk [number]
detail disk
For example, if you want to see details of Disk 0, you would execute:
diskpart
select disk 0
detail disk
This will provide comprehensive information about the selected disk, including its partitions, serial number, and more.
Exploring Diskpart Further
In addition to `list disk`, Diskpart includes numerous commands for advanced disk management:
- `list volume`: Displays all available volumes.
- `list partition`: Shows partitions on the selected disk.
- `create partition primary`: Creates a new primary partition.
Understanding these commands allows you to manage your disk configuration extensively.

List Files Cmd Windows: A Simple Guide
Listing Disk Drives in CMD
Using WMIC to List Disk Drives
An alternative to Diskpart for listing disks is using WMIC (Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line). This command can be executed directly in CMD, providing a concise overview of disk drives:
wmic diskdrive list brief
Running this command will produce an output similar to the one below, which highlights the manufacturer and size of each disk:
DeviceID Model Size
----------- -------------------------- --------
\\.\PHYSICAL0 Samsung SSD 970 EVO 500GB 500107862016
\\.\PHYSICAL1 Seagate HDD 1TB 1000204886016
Advantages of Using WMIC
WMIC can be advantageous for users who prefer a simpler and more straightforward syntax. Its output is often easier to interpret for users who aren’t accustomed to more complex command-line structures found in Diskpart. Additionally, it can provide quick insights without needing to navigate through Diskpart’s menus.
List Folders in Cmd: A Quick Guide to Navigation
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common Mistakes When Listing Disks
While executing commands to list disks in CMD, some common errors include:
- Incorrect command usage: Ensure there are no typographical errors in your commands.
- Lack of administrator privileges: Always run CMD as an Administrator when executing Diskpart or other system-level commands.
Resolving Errors in CMD
If you encounter issues, you can troubleshoot as follows:
- Restart CMD as Administrator: If you didn’t run CMD as Administrator, exit and relaunch it with elevated privileges.
- Check Disk Connections: Ensure that the disks are properly connected to your system.
- Use the `diskpart` command: If you’re unsure, retype `diskpart` to ensure are in the right environment to start executing Diskpart commands.

How to List Drives in Cmd: A Quick Guide
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
In this guide, you’ve learned how to list disks in CMD using various methods, including the Diskpart and WMIC commands. Understanding how to monitor and manage disks is crucial for effective system management.
Next Steps for CMD Enthusiasts
I encourage you to practice using CMD commands regularly. Explore other commands, such as those for managing files, network settings, and user accounts. The more you familiarize yourself with these utilities, the more adept you will become at troubleshooting and configuring your system.

Mastering Strings Cmd: A Quick Guide to String Manipulation
Call To Action
Join Our Community
Interested in learning more about CMD commands? Join our community to receive updates, tips, and resources geared towards mastering CMD and enhancing your technical skills.
Feedback Request
We would love to hear from you! Share your experiences or suggest topics for our future posts to help us provide the best content for you.
If you need to obtain a list of all disk drives on a Microsoft Windows system
from a
command line interface (CLI), e.g., a command prompt window, you can do so using
Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line (WMIC). You can obtain
a list of drives by opening a
command prompt window and then issuing a wmic logicaldisk get command followed by parameters relevant to the information you
wish to see. You can see a list of parameter options by issuing the command
wmic logicaldisk get /?.
C:\>wmic logicaldisk get /? Property get operations. USAGE: GET [<property list>] [<get switches>] NOTE: <property list> ::= <property name> | <property name>, <property list> The following properties are available: Property Type Operation ======== ==== ========= Access N/A N/A Availability N/A N/A BlockSize N/A N/A Caption N/A N/A Compressed N/A N/A ConfigManagerErrorCode N/A N/A ConfigManagerUserConfig N/A N/A Description N/A N/A DeviceID N/A N/A DriveType N/A N/A ErrorCleared N/A N/A ErrorDescription N/A N/A ErrorMethodology N/A N/A FileSystem N/A N/A FreeSpace N/A N/A InstallDate N/A N/A LastErrorCode N/A N/A MaximumComponentLength N/A N/A MediaType N/A N/A Name N/A N/A NumberOfBlocks N/A N/A PNPDeviceID N/A N/A PowerManagementCapabilities N/A N/A PowerManagementSupported N/A N/A ProviderName N/A N/A Purpose N/A N/A QuotasDisabled N/A N/A QuotasIncomplete N/A N/A QuotasRebuilding N/A N/A Size N/A N/A Status N/A N/A StatusInfo N/A N/A SupportsDiskQuotas N/A N/A SupportsFileBasedCompression N/A N/A VolumeName N/A N/A VolumeSerialNumber N/A N/A The following GET switches are available: /VALUE - Return value. /ALL(default) - Return the data and metadata for the attribute. /TRANSLATE:<table name> - Translate output via values from <table name>. /EVERY:<interval> [/REPEAT:<repeat count>] - Returns value every (X interval) se conds, If /REPEAT specified the command is executed <repeat count> times. /FORMAT:<format specifier> - Keyword/XSL filename to process the XML results. NOTE: Order of /TRANSLATE and /FORMAT switches influences the appearance of outp ut. Case1: If /TRANSLATE precedes /FORMAT, then translation of results will be follo wed by formatting. Case2: If /TRANSLATE succeeds /FORMAT, then translation of the formatted results will be done. C:\>
For example, the results from issuing the command on a Windows 10
system to display the device ID, volume name, and description are shown
below:
C:\>wmic logicaldisk get deviceid, volumename, description Description DeviceID VolumeName Local Fixed Disk C: OS CD-ROM Disc D: CD-ROM Disc E: Removable Disk F: EMTEC C:\>
In the above example, drive C: is the internal disk drive in the system
and drive F: is an 8 GB USB 2.0
flash
drive. If I only want to see a particular type of drive, e.g., only
internal disk drives or only removeable
USB-attached
drives, I can add a «where»
argument to the command and specify a drive type. The
values that can be used to specify drive types are shown below:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | Unknown |
| 1 | No Root Directory |
| 2 | Removable Disk |
| 3 | Local Disk |
| 4 | Network Drive |
| 5 | Compact Disc |
| 6 | RAM Disk |
For instance, if I only wanted to see local disks, e.g., the internal disk
drive in the system, I could use the command below, which would only show
drive C:
C:\>wmic logicaldisk where drivetype=3 get deviceid, volumename, description Description DeviceID VolumeName Local Fixed Disk C: OS C:\>
If I only wanted to see removable disks, such as
USB flash drives, attached to the system, I could use the command below:
C:\>wmic logicaldisk where drivetype=2 get deviceid, volumename, description Description DeviceID VolumeName Removable Disk F: EMTEC C:\>
If I use a drive type of 5, instead, I should see
compact disc (CD) drives.
C:\>wmic logicaldisk where drivetype=5 get deviceid, volumename, description Description DeviceID VolumeName CD-ROM Disc D: CD-ROM Disc E: C:\>
In the example above, thought the output shows two
CD-ROM
drives, the system doesn’t actually have any CD-ROM drives in it nor
externally attached to it. Instead, an Android phone is connected to the
Dell laptop by a USB cable and is being reported as drives D: and E:,
though if I attempt to view the contents of those drives, I see «the device
is not ready.»
C:\>dir d: The device is not ready. C:\>dir e: The device is not ready. C:\>
You can, of course, specify other parameters on the command line. E.g.,
you can request the media type be displayed by including mediatype as a parameter. The output will then show the type of media currently
present in the logical drive. The value may not be exact for removable drives
if currently there is no media in the drive. E.g.:
C:\>wmic logicaldisk where drivetype=2 get deviceid, volumename, description, mediatype Description DeviceID MediaType VolumeName Removable Disk F: EMTEC C:\>wmic logicaldisk where drivetype=3 get deviceid, volumename, description, mediatype Description DeviceID MediaType VolumeName Local Fixed Disk C: 12 OS C:\> C:\>wmic logicaldisk where drivetype=5 get deviceid, volumename, description, mediatype Description DeviceID MediaType VolumeName CD-ROM Disc D: 11 CD-ROM Disc E: 11 C:\>
The media type values are listed below:
- Format is unknown (0)
- 5¼-Inch Floppy Disk (1)
-
5 1/4-Inch Floppy Disk — 1.2 MB — 512 bytes/sector
- 3½-Inch Floppy Disk (2)
-
3 1/2-Inch Floppy Disk — 1.44 MB -512 bytes/sector
- 3½-Inch Floppy Disk (3)
-
3 1/2-Inch Floppy Disk — 2.88 MB — 512 bytes/sector
- 3½-Inch Floppy Disk (4)
-
3 1/2-Inch Floppy Disk — 20.8 MB — 512 bytes/sector
- 3½-Inch Floppy Disk (5)
-
3 1/2-Inch Floppy Disk — 720 KB — 512 bytes/sector
- 5¼-Inch Floppy Disk (6)
-
5 1/4-Inch Floppy Disk — 360 KB — 512 bytes/sector
- 5¼-Inch Floppy Disk (7)
-
5 1/4-Inch Floppy Disk — 320 KB — 512 bytes/sector
- 5¼-Inch Floppy Disk (8)
-
5 1/4-Inch Floppy Disk — 320 KB — 1024 bytes/sector
- 5¼-Inch Floppy Disk (9)
-
5 1/4-Inch Floppy Disk — 180 KB — 512 bytes/sector
- 5¼-Inch Floppy Disk (10)
-
5 1/4-Inch Floppy Disk — 160 KB — 512 bytes/sector
- Removable media other than floppy (11)
- Fixed hard disk media (12)
- 3½-Inch Floppy Disk (13)
-
3 1/2-Inch Floppy Disk — 120 MB — 512 bytes/sector
- 3½-Inch Floppy Disk (14)
-
3 1/2-Inch Floppy Disk — 640 KB — 512 bytes/sector
- 5¼-Inch Floppy Disk (15)
-
5 1/4-Inch Floppy Disk — 640 KB — 512 bytes/sector
- 5¼-Inch Floppy Disk (16)
-
5 1/4-Inch Floppy Disk — 720 KB — 512 bytes/sector
- 3½-Inch Floppy Disk (17)
-
3 1/2-Inch Floppy Disk — 1.2 MB — 512 bytes/sector
- 3½-Inch Floppy Disk (18)
-
3 1/2-Inch Floppy Disk — 1.23 MB — 1024 bytes/sector
- 5¼-Inch Floppy Disk (19)
-
5 1/4-Inch Floppy Disk — 1.23 MB — 1024 bytes/sector
- 3½-Inch Floppy Disk (20)
-
3 1/2-Inch Floppy Disk — 128 MB — 512 bytes/sector
- 3½-Inch Floppy Disk (21)
-
3 1/2-Inch Floppy Disk — 230 MB — 512 bytes/sector
- 8-Inch Floppy Disk (22)
-
8-Inch Floppy Disk — 256 KB — 128 bytes/sector
Related articles:
-
Obtaining the model number and serial number for a HDD from the command line
Date: October 13, 2015
MoonPoint Support -
Using wmic to get disk drive information
Date: July 10, 2015
MoonPoint Support
References:
-
Win32_LogicalDisk class
Microsoft Develper Network
Одним из основных принципов, которым следовали разработчики Windows Server 2008, является возможность управлять многими компонентами операционной системы из командной строки. Если вам понадобится создать массив RAID, как правило, легче всего это выполнить, используя консоль управления дисками, но это при условии, что Вам нужно выполнить такую операцию на одной машине, и эта машина имеет интерфейс GUI. Если вам необходимо выполнить эти действия на множестве машинах, лучше написать для этих целей скрипт (сценарий). Кроме того, если вы используете в своей среде Server Core 2008, у вас может и не быть другого выбора, кроме управления дисковой подсистемой из командной строки.
Команда Diskpart
Windows Server 2008 содержит утилиту командной строки Diskpart.exe, которая позволяет управлять дисковой подсистемой сервера из командной строки. Чтобы использовать эту команду, просто откройте окно командной строки и введите команду DiskPart.exe. После этого вы попадете в командную оболочку Diskpart. Отсюда вы можете запускать различные команды для управления дисковой подсистемы.
Cинтаксис команды Diskpart
Типичная команда Diskpart состоит из глагола и существительного. Глагол говорит какие действия нужно выполнить, и существительное указывает объект, с которым вы хотите выполнить действие. Одним из простейших примеров команд Diskpart является команда List Disk. В этом примере List — глагол, а Disk это существительное. После ввода этой команды, Windows отобразит список всех физических дисков, установленных на сервере.
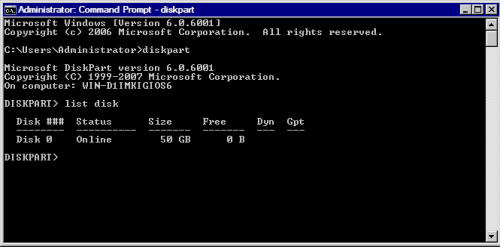
Обратите внимание на вышеприведенный рисунок, на нем видно, что каждому диску присваивается номер. Если вам необходимо выполнить операции с конкретным диском, вы должны указать диск, введя команду Select. Например, чтобы выполнить операцию с диском 0, нужно набрать Select Disk 0.
Во многих случаях, управление дисками включает в себя создание отказоустойчивых томов, и вы можете легко создать их с помощью команды Diskpart. Например, в вашей системе 4 жестких диска, и эти жесткие диски пронумерованы как 0, 1, 2 и 3. Также будем считать, что диск 0 – это наш системный диск, а диски 1, 2 и 3 пустые жесткие диски, которые мы хотим превратить в том RAID 5.
Прежде чем мы сможем создать том RAID 5, мы должны убедиться, что каждый из дисков подключен как динамический диск. Если посмотреть на рисунок, можно увидеть, что команда List Disk отображает, является ли диск динамическим или нет. Предполагая, что ни один из дисков не является динамическими, вы можете конвертировать их из основных в динамические, введя следующие команды:
Select Disk 1
Convert Dynamic
Select Disk 2
Convert Dynamic
Select Disk 3
Convert Dynamic
Теперь, когда мы переконвертировали наши диски, мы можем создать том RAID 5, введя следующие команды:
Select Disk 1
Create Volume RAID Disk 1, 2, 3
Введя команду List Volume, вы убедитесь, что том RAID был создан. Обратите внимание, что каждому тому присваивается номер.
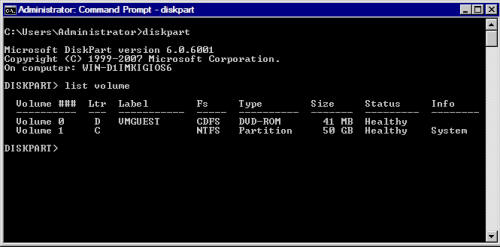
Последнее, что мы должны сделать, это отформатировать том и присвоить ему букву. Это можно выполнить, набрав следующие команды:
Select volume 2
Format FS=NTFS Label=MyNewVolume
Assign Letter=F
С помощью команды List Volume, можно удостовериться, что том отформатирован и ему присвоена буква. Наконец, введите команду Exit, чтобы выйти из оболочки Diskpart.
Содержание статьи:
- Перечень «сподручных» команд // CMD // Таблицы
- Для просмотра характеристик устройства, сведений о системе
- Для работы с сетью
- Для работы с дисками / флешками
- Для загрузки и восстановления Windows
- Общие операции
- 📌Дополнения
- Вопросы и ответы: 10
Доброго времени!
Ни для кого не секрет, что очень многие операции в Windows можно выполнять с помощью командной строки (на англ.: CMD). А в некоторых случаях — это, пожалуй, вообще единственный вариант решить вопрос!
Я в своих заметках тоже нередко обращаюсь к ней за помощью. 😉 И в сегодняшней статье, как раз, решил собрать все самые необходимые и популярные команды (думаю, в качестве небольшого сподручного материала, чтобы было куда сослаться «в трудную минуту», — она точно не помешает на блоге).
Заранее предупрежу:
- я не ставлю целью разобрать все команды! Только основное, что часто приходиться делать;
- часть нижеперечисленных команд нужно выполнять с правами администратора (если оных прав не будет — вместо результата увидите сообщение похожее на «недостаточно прав, или настроена групповая политика»)!
*
*
Перечень «сподручных» команд // CMD // Таблицы
Для просмотра характеристик устройства, сведений о системе
👉 Также в помощь!
1) Программы для проверки и мониторинга температуры процессора, видеокарты, диска
2) Как узнать характеристики компьютера, ноутбука
| № | Команда (скопировать в окно CMD и нажать Enter) | Описание команды / результат ее выполнения |
| 1 | systeminfo | Покажет информацию о системе: версию ОС Windows, модель компьютера (ноутбука), владельца, версию BIOS, кол-во ОЗУ, домен (рабочую группу), имя ПК, сетевые адаптеры и пр. |
| 2 | wmic cpu get name | Узнать модель ЦП (примерный ответ: «AMD Ryzen 3 5300U with Radeon Graphics.»). Др. способы. |
| 3 | wmic bios get serialnumber | Серийный номер устройства (ноутбука, например). |
| 4 | wmic baseboard get product
wmic baseboard get version |
Модель мат. платы / ее версия. |
| 5 | wmic bios get SMBIOSBIOSVersion | Версия BIOS. |
| 6 | wmic path win32_VideoController get name | Название видеокарты (др. способы). |
| 7 | wmic path win32_VideoController get VideoModeDescription | Разрешение экрана, цвета. |
| 8 | wmic OS get Caption,OSArchitecture,Version | Информация о Windows. |
| 9 | wmic DISKDRIVE get Caption | Информация о накопителях. |
| 10 | wmic /namespace:\\root\wmi PATH MSAcpi_ThermalZoneTemperature get CurrentTemperature | Посмотреть температуру ЦП (для перевода в градусы Цельсия — полученное значение нужно разделить на 10 и отнять 273,15). |
| 11 | Winver
или Ver |
Показать окно с версией установленной системы.
-//- Отобразить версию ОС прямо в окне CMD. |
| 12 | Hostname | Узнать текущее имя ПК. |
| 13 | wmic path softwarelicensingservice get OA3xOriginalProductKey | Команда покажет текущий лиценз. ключ Windows. |
| 14 |
|
Отображение сведений о лицензии (подробно, кратко). |
*
Для работы с сетью
👉 В помощь!
Коллекция заметок по настройки сети и интернета на компьютере.
| № | Команда (скопировать в окно CMD и нажать Enter) | Описание команды / результат ее выполнения |
| 1 | ipconfig /all | Показывает сетевые настройки для сетевых адаптеров (IP-адрес, MAC-адрес, и пр.). |
| 2 | ping ya.ru
или ping ya.ru -t |
Определение пинга до ресурса www.ya.ru (разумеется, адрес можно указать свой).
Примечание: второй вариант команды (с наличием на конце -t) запускает безостановочную проверку. |
| 3 | GETMAC | Посмотреть MAC-адрес. |
| 4 | nslookup ya.ru | Покажет IP-адрес по доменному имени. |
| 5 | netsh wlan set autoconfig enabled=no interface=»Wi-Fi»
Обратная операция: netsh wlan set autoconfig enabled=yes interface=»Wi-Fi» |
Выключает авто-поиск сетей по Wi-Fi (в некоторых случаях это увел. скорость работы Wi-Fi подключения, и снижает пинг!).
Примечание: вместо «Wi-Fi» нужно указать название своего адаптера, используемого для подключения по Wi-Fi. |
| 6 | netcfg -d
или
|
Сброс сетевых настроек.* |
| 7 | netsh wlan show all | Просмотреть всю информацию о беспроводных устройствах. |
| 8 | netsh wlan show drivers | -//- о драйверах. |
| 9 | netstat -abno | Информация о текущих подключениях и состоянии портов. |
*
Для работы с дисками / флешками
👉 В помощь!
1) Восстановление работы флешки (прошивка) / восстановление пропавших и удаленных файлов с флешки/диска;
2) Лучшие программы для работы с накопителями (флешками, HDD, SSD и пр.).
| № | Команда (скопировать в окно CMD и нажать Enter) | Описание команды / результат ее выполнения |
| 1 | chkdsk v: /f | Проверка диска на ошибки (вместо V — нужно указать свою букву диска).
Рекомендуется запускать после некорректного выключения ПК, при ошибках чтения и пр. |
| 2 | diskmgmt.msc | Вызвать встроенную утилиту «управление дисками». |
| 3 | format E: /FS:exFAT /Q /V:fleska | Форматирование диска/флешки (быстрое). Где:
|
| 4 |
или
|
Запуск утилиты Diskpart (для работы с дисками) и просмотр информации о дисках (томах).
Первая команда покажет наличие всех физических дисков, вторая — всех томов на них. (для просмотра разделов: List Partition) |
| 5 | Вводить последовательно (по одной!)
|
Второй пример с Diskpart: смотрим все тома на дисках, выбираем первый из них (цифра «1» заменяема!), и присваиваем ему букву «R». |
| 6 | Вводить последовательно (по одной!)
|
Еще один пример с Diskpart: просмотр томов, выбор одного из них и полная его очистка. Будьте аккуратны с этой последовательностью команд, она удаляет информацию!
Кстати, после очистки диска (Diskpart, list disk, select disk 1, clean) его можно конвертировать: convert gpt (или convert mbr). |
| 7 | defrag /A /C /U /V | Анализ дисков на фрагментацию. |
| 8 | defrag C: /W /V | Дефрагментация диска «C», и вывод отчета по операции. |
| 9 | DEL /F «C:\111\Новый текстовый документ.txt» | Принудительное удаление файла * (нужно указать правильный путь до него).
Полезно в тех случаях, когда файл не удается удалить из проводника. |
| 9.1 | del /q /f /s %SYSTEMDRIVE%\*.log | Удаление всех Log-файлов с системного диска (вместо «.log» можно использовать и др. расширения). |
| 10 | RD /S «C:\111» | Удаление папки * (также нужно указать путь до нее). |
| 11 | VOL D: | Вывод серийного номера и названия диска. |
| 12 | wmic logicaldisk get name, VolumeName, Size, FileSystem, NumberOfBlocks, description | Получить информацию по всем подключенным дискам (объем, имя, тип и пр.). Более подробно тут. |
*
Для загрузки и восстановления Windows
📌 Примечание: если у вас не загружается Windows — командную строку можно вызвать с установочной флешки.
| № | Команда (скопировать в окно CMD и нажать Enter) | Описание команды / результат ее выполнения |
| 1 | chkdsk /x/f/r
можно и так: chkdsk D: /f |
Проверка текущего сист. диска на ошибки (/ либо проверка указанного диска). |
| 2 | sfc /scannow | Проверка целостности системных файлов. |
| 3 | BCDEDIT | Диспетчер загрузки Windows |
| 4 |
Затем, узнав том с Windows, использовать: bcdboot d:\windows |
Сначала узнаем том, на котором установлена Windows, затем восстанавливаем файлы загрузки. |
| 5 |
Затем ввести: bcdboot D:\windows /s Z: /f UEFI |
Сначала узнаем все тома дисков в системе.
Далее выбираем «ESP» том, он в 99-512 МБ (FAT32) (важно: вместо «2» нужно будет выбрать свой том). Затем присваиваем ему букву Z. Далее указываем букву тома с Windows (вначале мы узнали и ее тоже) и восстанавливаем файлы загрузки. |
| 6 | rstrui | Запуск утилиты для отката системы (если есть точки восстановления). |
| 7 | sysdm.cpl | Создать точку восстановления ОС в окне «Защита системы». |
| 8 | wmic.exe /Namespace:\\root\default Path SystemRestore Call CreateRestorePoint “MyRestorePoint”, 100, 7 | Создать точку восстановления системы в авто-режиме (без лишних вопросов). |
| 9 | bcdedit /set {default} safeboot minimal
или bcdedit /set {default} safeboot network |
Загрузка безопасного режима (можно вводить, загрузившись с установочной флешки). Полезная команда, если в обычном режиме Windows не загружается («лагает»).
—//— C поддержкой сети. * Важно: чтобы отменить загрузку в безопасном режиме — в рабочей Windows используйте команду: bcdedit /deletevalue {default} safeboot |
| 10 | msconfig | Конфигурация системы (здесь можно настроить запуск служб, автозагрузку ПО, режим загрузки ОС). |
| 11 | dism /online /export-driver /destination:F:\MyDrivers
Dism /online /Add-Driver /Driver:F:\MyDrivers /Recurse |
Первая команда создает копию драйверов, вторая — восстанавливает их из копии. Работает в Windows 10/11 (Net Framework 3.5). |
*
Общие операции
| № | Команда (скопировать в окно CMD и нажать Enter) | Описание команды / результат ее выполнения |
| 1 | Pause | Ставит на «паузу» выполнение последовательности команд, и ждет нажатия одной из кнопок клавиатуры. |
| 2 | net start | Просмотр списка запущенных служб. |
| 3 | net start WlanSvc
или net stop WlanSvc |
Запустить службу WlanSvc / остановить службу -//- |
| 4 | ASSOC | Просмотреть таблицу: расширение (например, «.RAR») / программа, которая его открывает. |
| 5 | DATE | Просмотр и установка даты (полезно, когда не работают параметры ОС).
В помощь: настройка даты и времени в Windows. |
| 6 | shutdown.exe -r -f -t 20 | Перезагрузка компьютера через 20 сек.
Прим.: время задается в секундах. В 1 часе = 3600 сек.! |
| 7 | shutdown /s /t 60 | Выключение компьютера через минуту.
Прим.: время задается в секундах. |
| 8 | TASKLIST
и доп. в помощь taskkill /F /IM explorer.exe & start explorer |
Просмотр всех выполняемых программ и служб.
Завершение процесса explorer.exe (проводник), и его запуск. Удобная штука, когда диспетчер задач «лагает», или вы в нем не можете «поймать» проводник. |
| 9 | wmic computersystem where name=»%computername%» call joindomainorworkgroup name=»homework» | Сменить рабочую группу текущему компьютеру (вместо «homework» — напишите свое название).
Необходима перезагрузка ПК! |
| 10 | wmic computersystem where name=»%computername%» call rename name=»newpc» | Сменить имя компьютеру (вместо «newpc» задайте свое имя ПК).
Необходима перезагрузка ПК! |
| 11 | powercfg -a
еще доп.: powercfg -h on powercfg -h off |
Просмотр режимов выкл. ПК (гибернация, сон и пр.).
*** Вкл. / откл. гибернацию. |
| 12 | start /high /D «C:\Games\World of Warcraft Classic» wow.exe | Запуск приложения с нужным приоритетом (в моем случае — высокий приоритет, который чаще всего и нужен). Часто помогает снизить тормоза в играх.
Более подробно о приоритетах тут. |
| 13 | xcopy C:\Games D:\backup /f /i /y /s | Копирует один каталог в другой (без лишних вопросов; с перезаписью файлов!).
Удобно использовать для создания резервных копий нужных папок. |
| 14 | dir C:\Fraps /B /S > initial_c.txt
dir c:\initial_c.txt /w/o/s/p |
Все файлы из папки C:\Fraps запишет в файл initial_c.txt.
Найдет все файлы на диске «C:» с названием «initial_c.txt». Найдет все файлы на диске «C:» с расширением «.txt». |
| 15 | more c:\Users\initial_c.txt
type c:\Users\initial_c.txt |
Прочитать и вывести содержимое текстового файла на экран. |
| 16 |
|
|
| 17 | HELP | Выводит справку по всем командам Windows. |
| 18 | EXIT | Выход из CMD. |
*
📌Дополнения
Показ скрытых файлов
Полезные команды для проводника (позволят отображать скрытые расширения, скрытые и системные файлы):
reg add «HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced» /v HideFileExt /t REG_DWORD /d 00000000 /f
reg add “HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced” /v Hidden /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
reg add “HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced” /v ShowSuperHidden /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
После выполнения команд — не забудьте перезагрузить проводник (ПК).
*
Как автоматизировать выполнение определенных команд
Например, вам требуется постоянно запускать игру с нужным приоритетом (чаще с высоким), или очищать какие-то папки от мусора (определенных файлов), или еще что…
В этом случае можно сделать так:
- создать 📌BAT-файл с нужными вам командами (по ссылке привел все нюансы его создания + примеры) и проверить — оценить, всё ли выполняется правильно после его запуска;
- настроить 📌планировщик заданий в Windows, чтобы запускать этот BAT-файл в нужное вам время, например, при каждом включении ПК / или в определенное время (скажем, по вторникам и четвергам с 14-00 до 16-00).
*
Что делать, если не загружается Windows
📌Вариант 1: воспользоваться другим рабочим компьютером и записать установочную флешку с Windows. Также не помешает и LiveCD-флешка (эта «штуковина» позволит загружать «полноценную» Windows с флешки, и, само собой, работать с командной строкой… Для восстановления загрузчика Windows — обратите внимание на эту табличку).
*
📌Вариант 2: воспользоваться телефоном (под Android) и записать на нем установочную флешку. Далее подключить ее к ПК, и загрузиться…
*
📌Кстати, открыть окно командной строки можно и с установочной флешки с Windows: достаточно загрузиться с нее и нажать сочетание Shift+F10. Далее можно выполнить многое из таблиц выше…
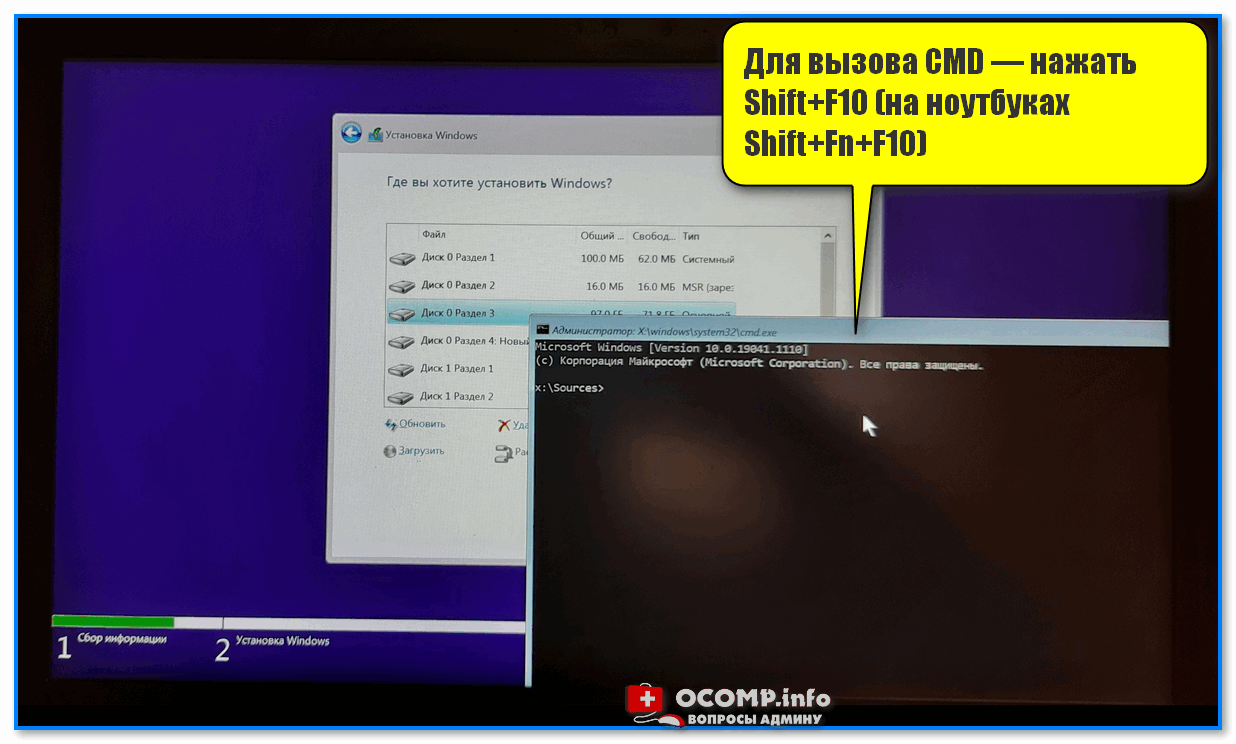
Установка Windows — запуск командной строки
*
📌 Рекомендую! Коллекция аварийных флешек, которую нужно иметь на экстренный случай (как раз, когда не загружается Windows).
*
На сим пока всё, дополнения приветствуются!
Успехов!
👋
