The Local Group Policy Editor enables a power user to control a large number of settings in Windows. You can control the sign-in and shutdown processes, the features and the apps that users are allowed to access, and you can do so using a simple interface that offers lots of information. The tool itself is rather hidden from view and before using it, you obviously need to know how to get to Local Group Policy Editor in Windows 10 and Windows 11. We have put together a comprehensive list of methods for accessing it, so that you can choose the one that is most convenient:
Where is the Local Group Policy Editor in Windows? I can’t find it!
The Local Group Policy Editor is a tool aimed at power users of Windows. You can find lots of information about using the tool in this article: What is the Local Group Policy Editor, and how do I use it?
If you try the methods below and the Local Group Policy Editor doesn’t show up, you may have a version of Windows that doesn’t come with the tool. By default, you can find the editor only in:
- Windows 11 Pro and Windows 11 Enterprise
- Windows 10 Pro and Windows 10 Enterprise
- Windows 7 Professional, Windows 7 Ultimate, and Windows 7 Enterprise
- Windows 8.1 Professional and Windows 8.1 Enterprise
Although the process isn’t covered in this article, there are ways to install the Local Group Policy Editor on Windows Home editions as well. If you do not know your Windows version, read this tutorial: How to tell what Windows I have (11 ways).
NOTE: This article covers Windows 11 and Windows 10. Still, many of the methods described below are valid for older versions of Windows as well.
Editing policies globally versus editing policies for specific users or groups
If you have other users on your Windows computer (for example other family members), you can control what kinds of changes they can make and what applications they can run. Before you open the Local Group Policy Editor, you first need to decide whether you want the changes to apply to all users (including yourself) or only to specific users or groups of users (for example non-administrators) on your computer. The process of opening the Local Group Policy Editor is going to be very different, depending on your objective.
First, let’s see how you can open the editor if you want to apply the changes to all users.
NOTE: You need to have administrative privileges in order to be able to access the Local Group Policy Editor. If you try opening it as a regular user, you get this error:
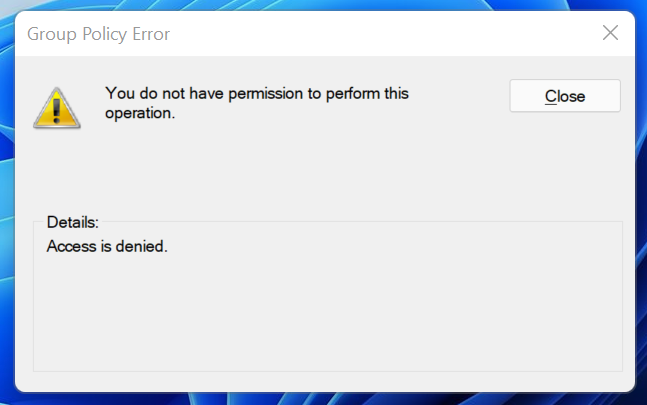
Only users with administrative rights can use the Local Group Policy Editor
Opening the Local Group Policy Editor to change settings for all users
If you want the settings that you modify to affect all users of the computer (or if you want to modify settings related to the computer itself), here are all the ways you can open the Local Group Policy Editor:
1. Open Local Group Policy Editor using Windows Search
The first method of opening the Local Group Policy Editor is pretty simple: you have to search for it by name or by the name of its executable file: gpedit.msc. For Windows 11, press Windows + S on your keyboard or click/tap on the magnifier icon on your taskbar to open the Search window. Then, type either gpedit or group policy, and the result should show up as you type. Click or tap on the “Edit group policy” result.
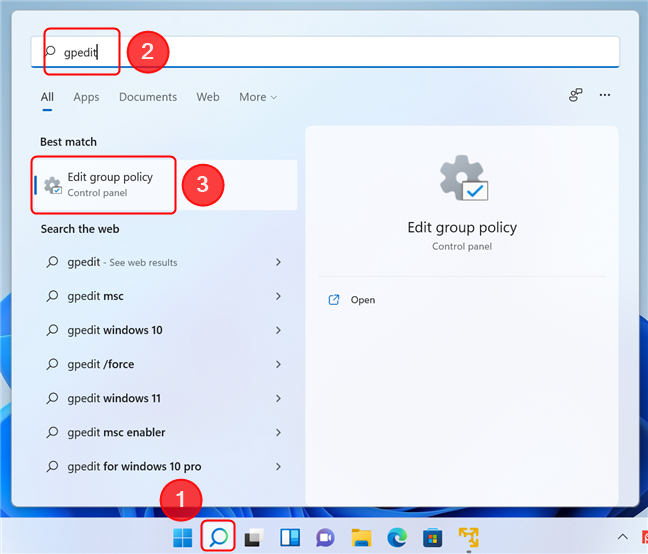
Open the Local Group Policy Editor using Search in Windows 11
Are you wondering how to find Local Group Policy Editor In Windows 10? Well, the process is even simpler in this case, since this popular operating system has a search field in its taskbar. Just click or tap on the input field (or press Windows + S) and then type gpedit or group policy. In the results list, click or tap on “Edit group policy.”
TIP: You can use the Start Menu to initiate a search, as well. Simply open it by pressing the Windows key or clicking the Start Menu icon on the taskbar, then start typing the keyword.
2. Open the Local Group Policy Editor from Settings
Open the Local Group Policy Editor using Search in Windows 10
You can also access the Local Group Policy Editor from the Settings app in Windows 11 or Windows 10. First, open Settings (one way to do it is by pressing Windows + I on your keyboard), then type gpedit in the search box and select the “Edit group policy” result. Here’s how it looks on Windows 11:
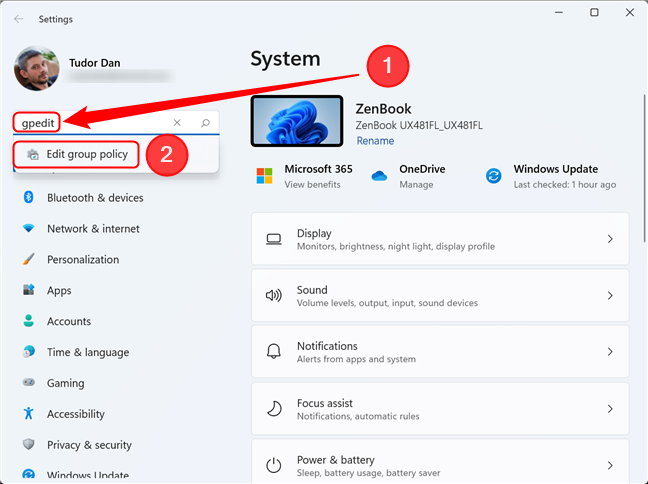
Open the Local Group Policy Editor from Settings in Windows 11
…and here’s how it looks on Windows 10. Very similar.
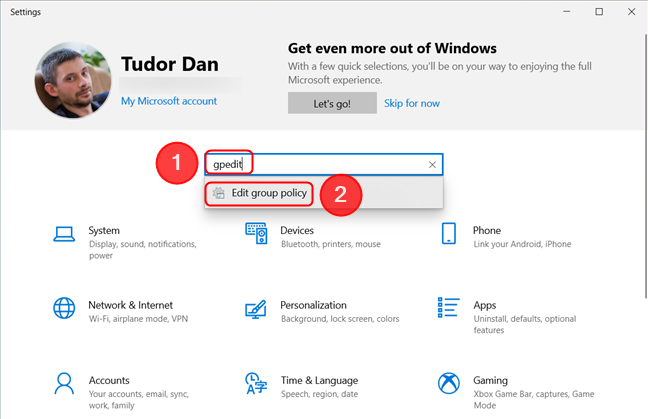
Open the Local Group Policy Editor from Settings in Windows 10
3. Create a shortcut for Local Group Policy Editor
If you want to access the editor very frequently but prefer to use desktop shortcuts, then you can create one for Local Group Policy Editor. In the Create Shortcut wizard, type gpedit.msc in the Location field. If you don’t know how to create shortcuts, read this article: How to create shortcuts for files, folders, apps, and web pages in Windows.
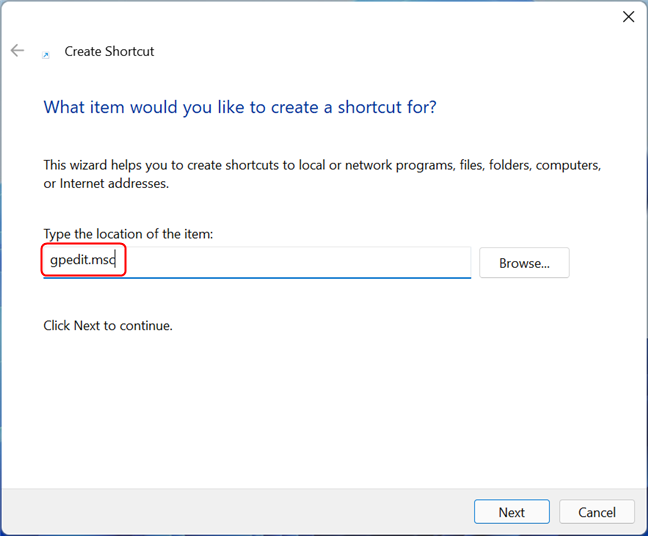
Create a shortcut to the Local Group Policy Editor in Windows
After creating it, you can open Local Group Policy Editor by double-clicking or double-tapping on the shortcut.
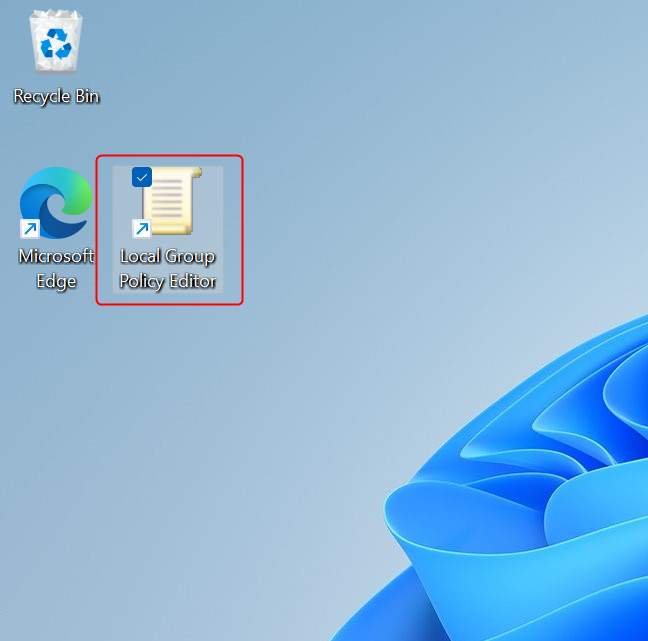
The Local Group Policy Editor shortcut
4. Pin the Local Group Policy Editor to the taskbar or the Start Menu
If you use the Local Group Policy Editor frequently, you can pin it to the taskbar or the Start Menu, but first, you need to create a shortcut for the editor. After creating it, in Windows 11, right-click or tap and hold the icon. Next, access the old right-click menu by selecting “Show more options”. Then, click or tap on one of the two actions, depending on what you want to do.
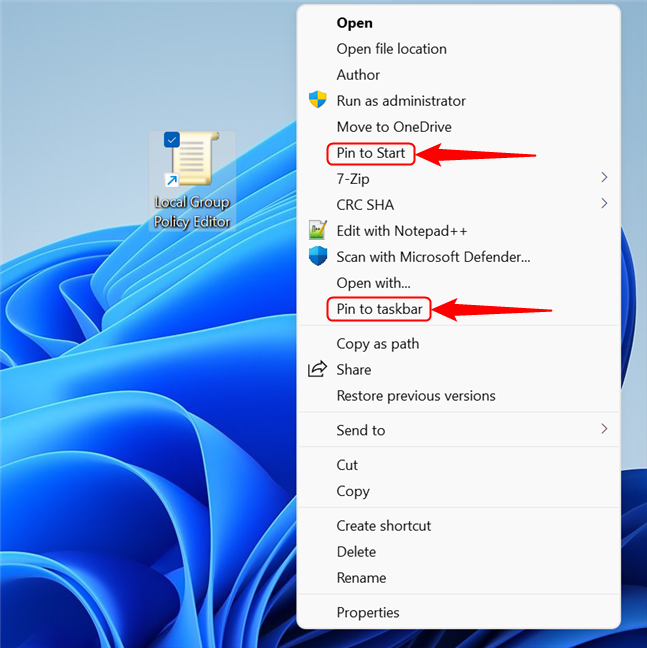
Select one of the two options if you want to pin the shortcut in Windows 11
In Windows 10, since the classic right-click menu is the default, simply right-click (or tap and hold) on the shortcut and select Pin to Start or Pin to taskbar.
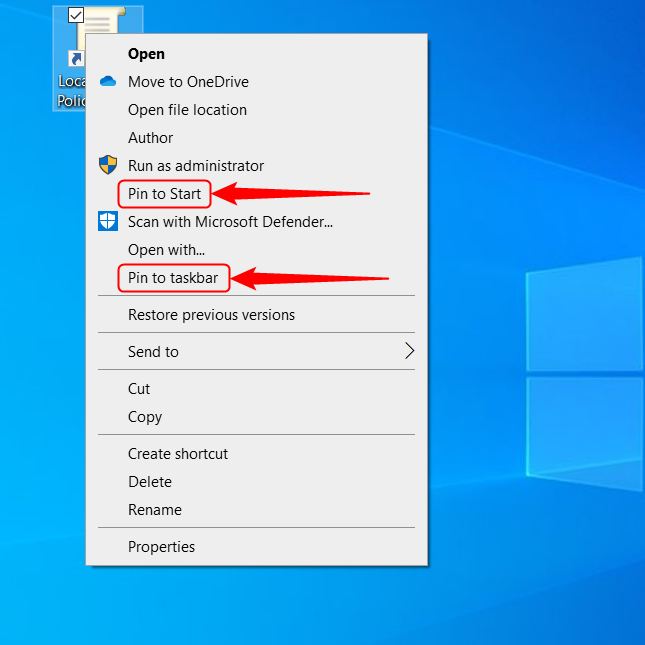
Pinning the Local Group Policy editor is easier in Windows 10
From now on, you can open Local Group Policy Editor from the Start Menu or the taskbar.
5. Opening the Local Group Policy Editor from Control Panel
Local Group Policy Editor is also available through the Control Panel. First, open the Control Panel. Then, click on the search box, type “group policy” and click or tap on Edit group policy in the results list.
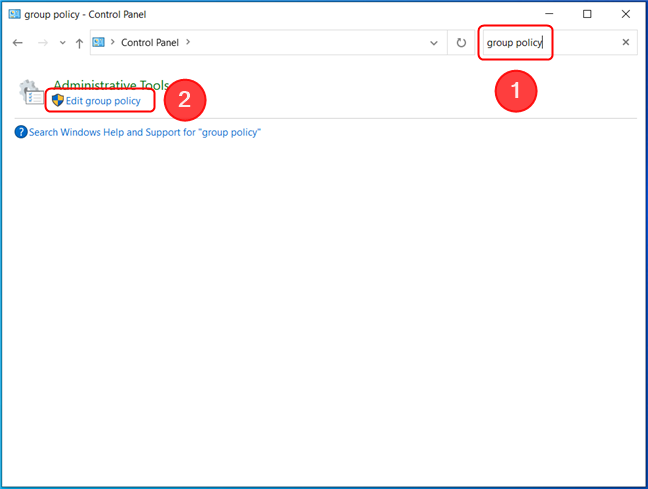
Open Local Group Policy Editor from the Control Panel
NOTE: Although Windows lists the search result under Administrative tools (in Windows 10) or Windows tools (in Windows 11), if you open the location, the Edit group policy shortcut is not there. Thus, the only way to reach it in the Control Panel is to use the search feature.
6. Open Local Group Policy Editor by using the Run window
Here’s another way to open Local Group Policy Editor: Press Windows + R on the keyboard to open the Run window. Then, type gpedit.msc and press Enter on the keyboard or click OK.
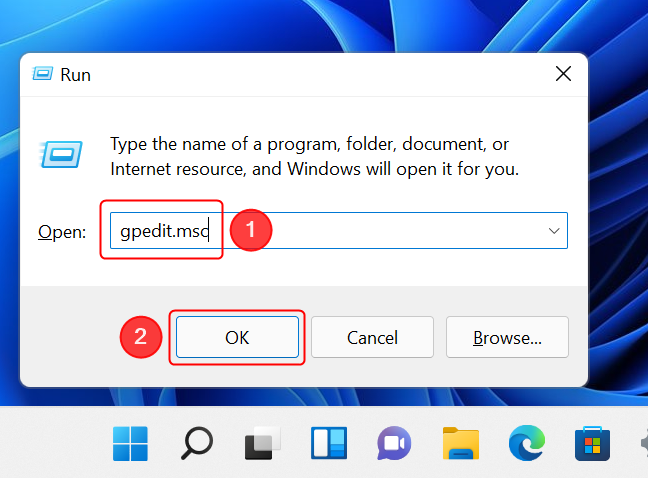
Open the Local Group Policy Editor using Run
7. Open Local Group Policy Editor by using Command Prompt, PowerShell or Windows Terminal
You can also use Command Prompt, PowerShell, or Windows Terminal to open the editor. In any of these apps, type gpedit.msc in the command line and press Enter.
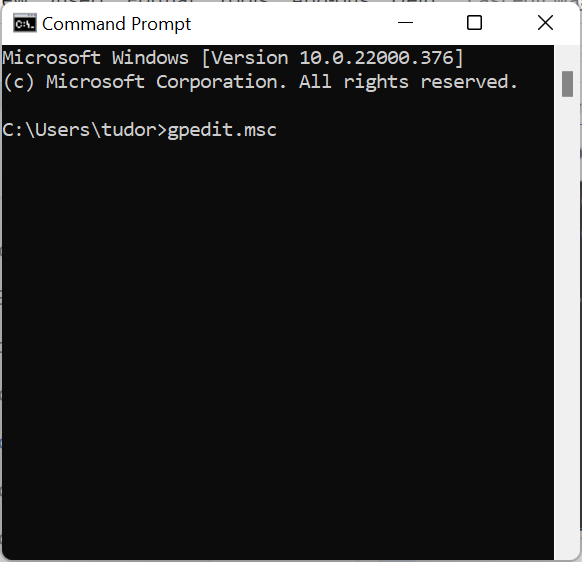
The command is identical for Command Prompt and PowerShell
8. Open Local Group Policy Editor by using Task Manager
You can open Local Group Policy Editor using the Task Manager. Launch Task Manager (a quick way to do it is by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard). If you are presented with the compact view of the Task Manager, press More details in the bottom-left corner. Next, open the File menu and click or tap “Run new task”.
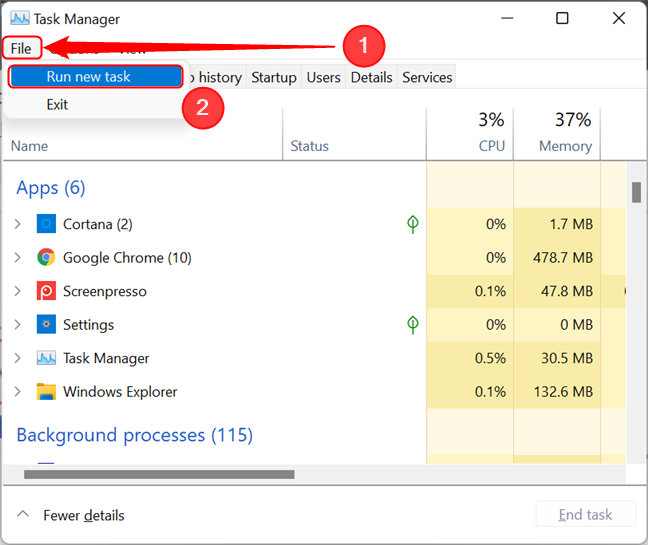
Run a new task in Task Manager
Now, type gpedit.msc in the Open field of the “Create new task” window. Press Enter or OK to run the command.
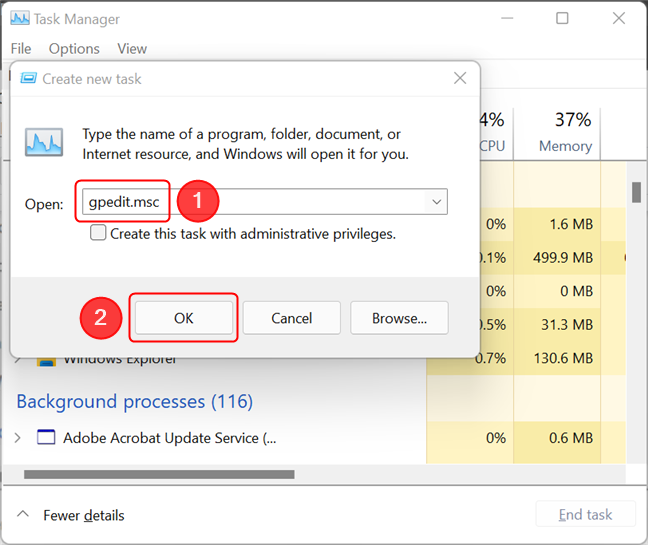
Opening the Local Group Policy Editor from the Task Manager
9. Open Local Group Policy Editor by using File Explorer
The File Explorer from Windows 11 and Windows 10 is another convenient way to start the Local Group Policy Editor. Simply open File Explorer, then type gpedit.msc in the address bar and press Enter on the keyboard.
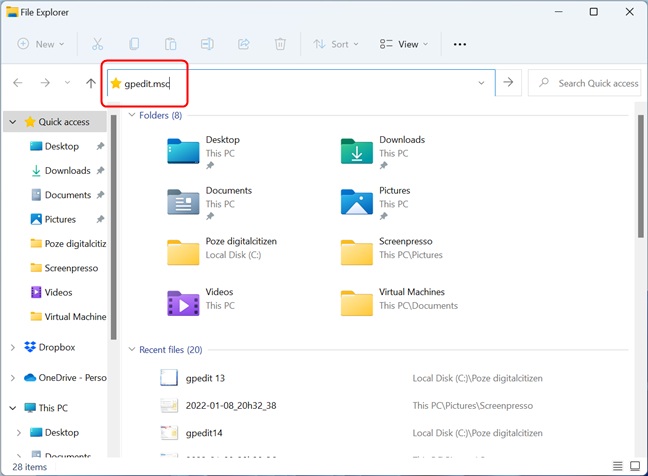
Run the Local Group Policy Editor from File Explorer in Windows 11 and Windows 10
10. Open Local Group Policy Editor by running its executable file
On both Windows 11 and Windows 10, the Local Group Policy Editor executable file is found in the System32 subfolder of the Windows folder. Navigate to “C:\Windows\System32” and look for a file named gpedit. If you hover your mouse cursor over the file, its description should be “Microsoft Common Console Document”. Once you identified the correct file, double-click or double-tap on it.
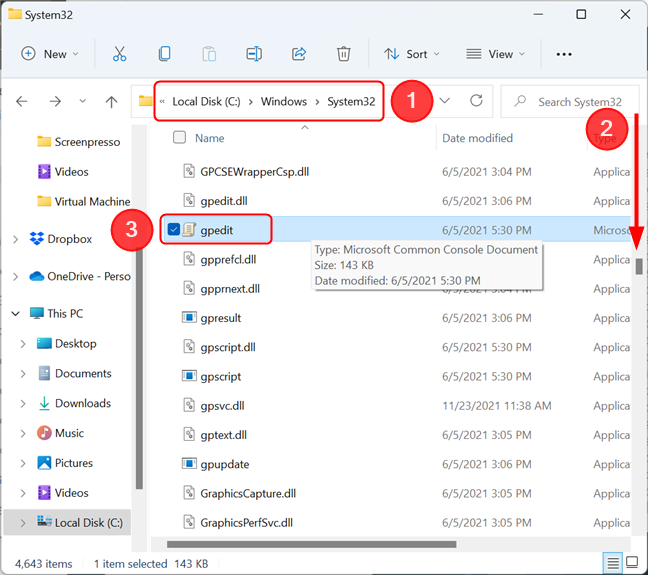
The file is located in the System32 folder
Opening the Local Group Policy Editor to change settings for specific users or groups
If you want to adjust settings only for a specific user account or user group on your Windows PC, launching the Local Group Policy Editor is more complicated and begins with launching the Microsoft Management Console. The quickest way to do this is by pressing Windows + R to open the Run window, typing mmc and pressing Enter. If you get a UAC warning, press Yes to continue. In the MMC window that appears, open the File menu, then click or tap on Add/Remove Snap-in.
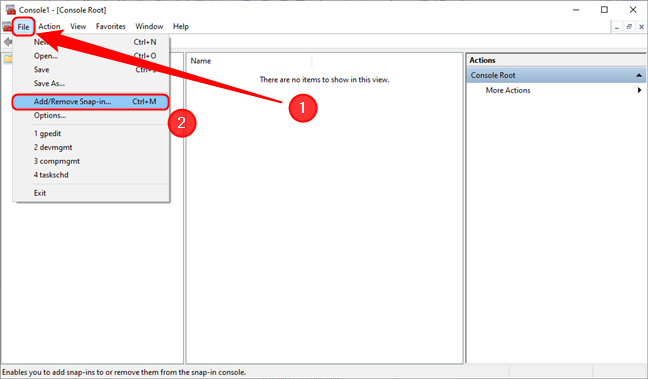
Add a snap-in in the Microsoft Management Console
The Add or Remove Snap-ins window appears. Here, click or tap on Group Policy Object Editor, then press Add. Alternatively, you can double-click the Group Policy Object Editor snap-in.
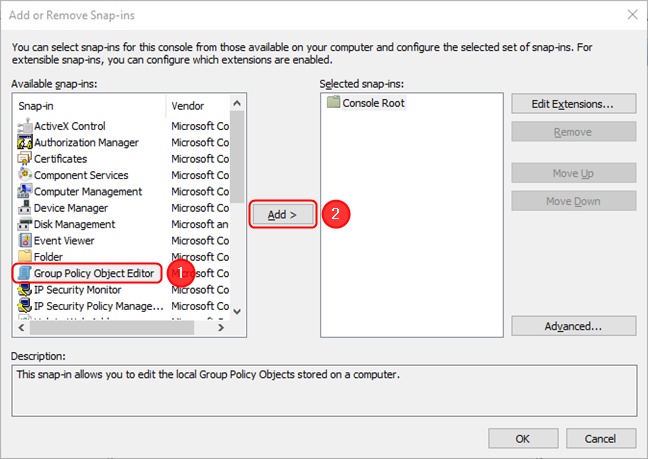
Select the Group Policy Object Editor, then press Add
This opens the Select Group Policy Object wizard. Click or tap on Browse to continue.
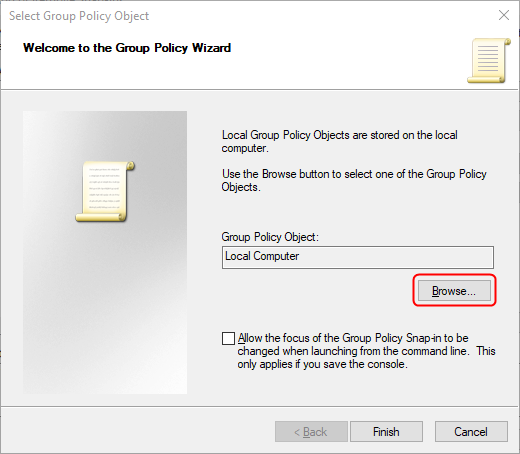
Hit Browse in the wizard
In the next window, go to the Users tab, select the user or the group of users for which you want to make changes (we selected the Non-Administrators group), then click or tap on OK afterward. Finally, press Finish.
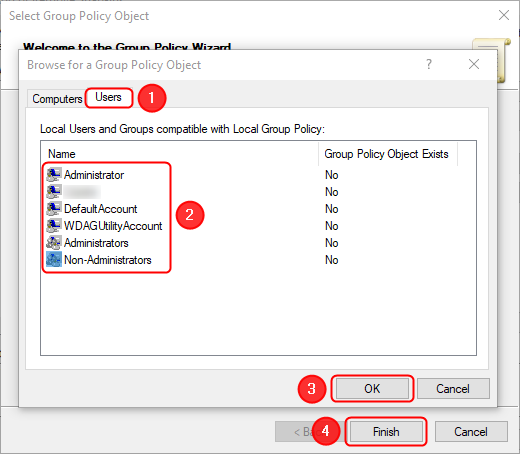
Selecting the user or the group for which you want to change settings
The Add or Remove Snap-ins window comes into focus. Press the OK button in the lower-right. This opens the settings tree applicable to the selected user/group.
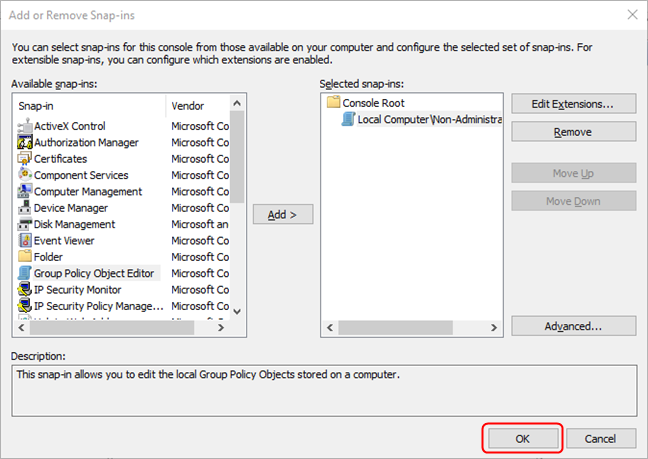
Press OK and the Editor will appear
If you plan on changing the settings frequently, in order to bypass this lengthy process, you can save the console settings. Open the File menu, then click or tap on Save as.
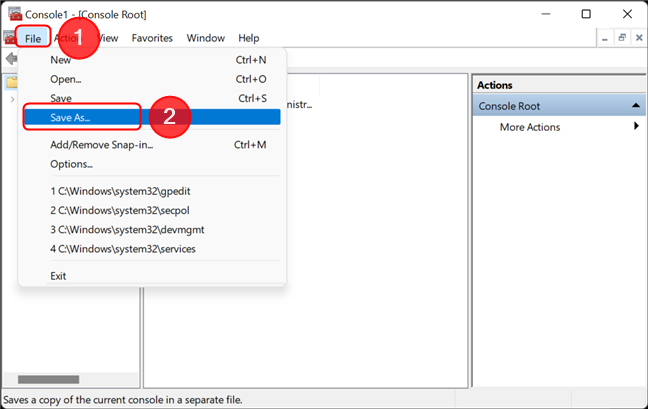
Save the console configuration for the Local Group Policy Editor
Next, navigate to the location where you want a shortcut to the console to be created, rename the shortcut, and click or tap on Save.
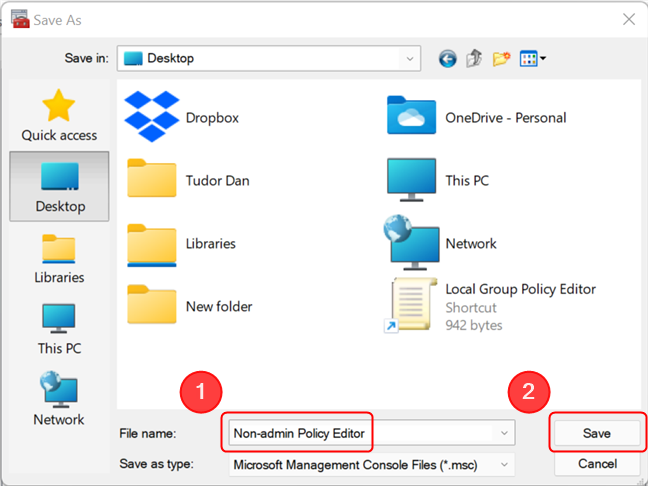
Rename the shortcut and place it in a folder of your choosing
The next time you want to modify the settings for the same user or group, simply double-click or double-tap the newly-created icon.
NOTE: The settings you alter in the Local Group Policy Editor will be enforced and will override the user’s preferences. For example, you can enforce a certain wallpaper, in which case the user will have no way of changing it (unless it has access to Local Group Policy Editor).
What do you plan to change in the Local Group Policy Editor?
Local Group Policy Editor is a powerful tool designed for power users and IT administrators. You get to control many aspects of how the other users access and use your Windows PC. What do you plan to change in the Local Group Policy Editor? Let us know your preferences in a comment below. Also, if you know any other ways of opening the editor, share them with us and we will update the article.
The Local Group Policy Editor is a powerful tool for administrating Windows 11 Pro and Enterprise editions. It grants granular control over system settings, allowing you to fine-tune user experience, security policies, and more. But with great power comes the question: how do you access it? This guide equips you with 10 methods to open the Local Group Policy Editor in Windows 11, ensuring you can use its potential when needed.
There are a couple of reasons why you might need multiple methods to access something like the Local Group Policy Editor:
- User Convenience: Different people prefer different ways of interacting with their computers. Multiple methods provide options for launching the tool in a way that feels most natural to the user.
- Accessibility: Not everyone interacts with computers in the same way. Having multiple methods ensures someone with motor skill limitations or using a screen reader can still access the tool.
- Contingency Plans: If one method is unavailable due to a bug, shortcut malfunction, or permission issues, having alternative methods allows you to bypass the obstacle and access the tool anyway.
Page Contents
Here are 10 different methods for opening the Local Group Policy Editor. Choose the approach that best suits your workflow and needs!
Method 1: Run Command
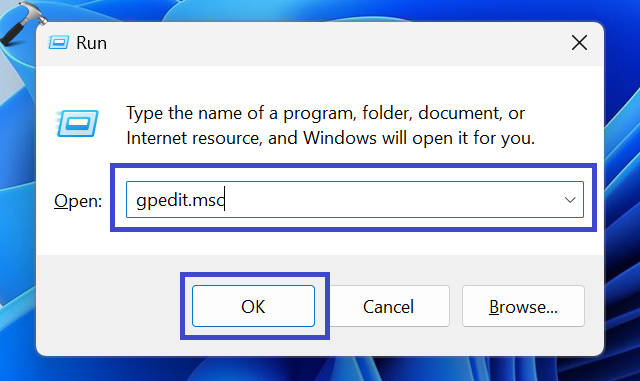
1. Press the Windows key + R.
2. Type “gpedit.msc” and click OK.
Method 2: Settings App
Open Settings App. In the search bar, type “edit group policy“. Click on the search result to open the local group policy editor.
Note: The Local Group Policy Editor isn’t directly accessible through the Settings app in Windows 11. The functionality is only available in Windows 11 Pro and Enterprise editions, not the Home version.
Method 3: Windows Search
1. Click on the Windows icon to open the search menu.

2. Type “gpedit.msc” in the search bar.
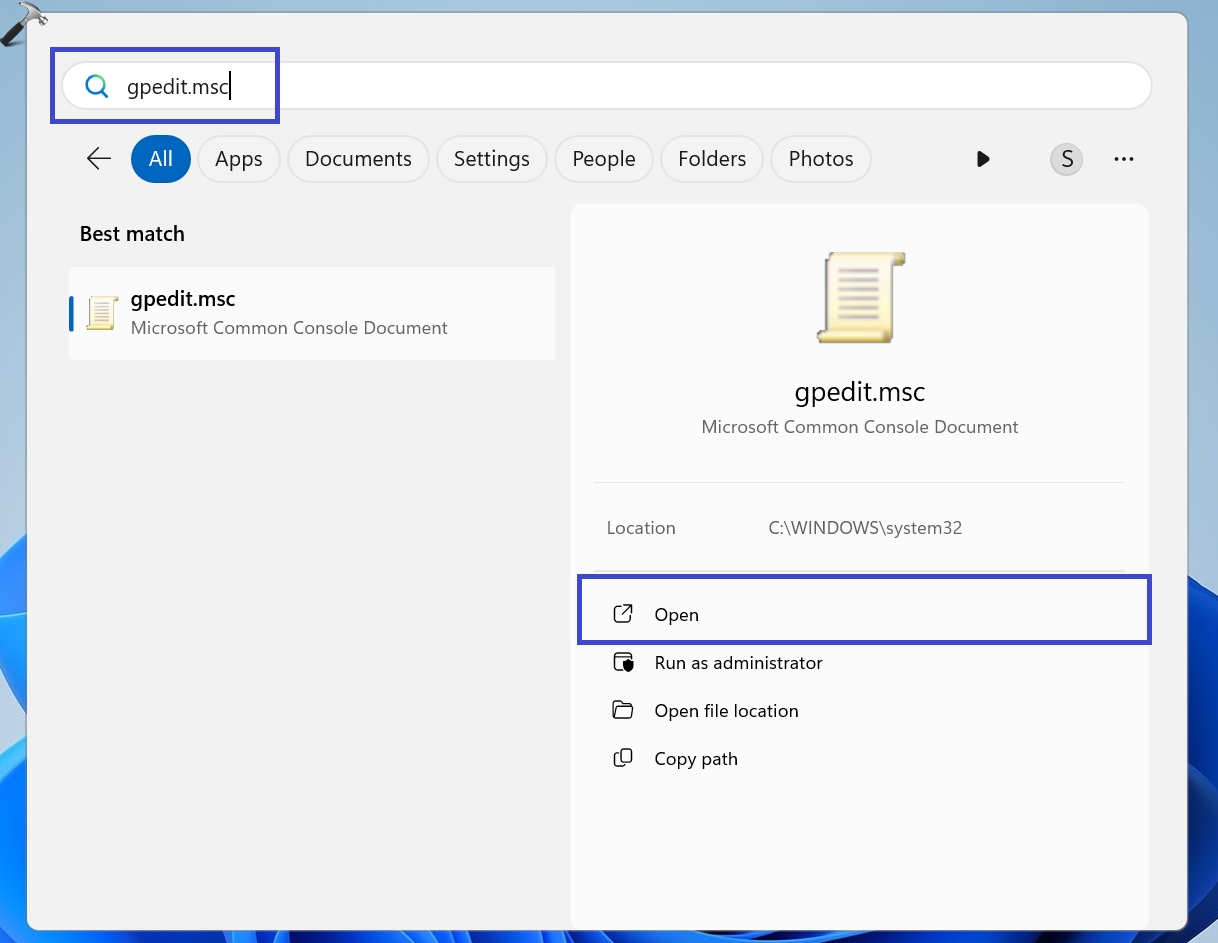
3. Click “Open” to open it.
Method 4: Windows Copilot
1. Press the WIndows key + C to open Windows Copilot.
2. Type “Open the local group policy editor” and press Enter.

3. Click “Yes, proceed” option to confirm.

Method 5: System 32 Folder
1. Open File Explorer and navigate to “C:> Windows”.
2. Click on “System32“.

2. Click “gpedit.msc” to open the local group policy editor.

Method 6: Task Manager
1. Press the Windows key + X and select “Task Manager“.
2. Click on “Run new task“.

3. A create new task prompt box will appear. Type “gpedit.msc” and click OK.

Method 7: Desktop Shortcut
1. Right-click on the blank space on the Desktop. Click on “New => Shortcut“.

2. Copy and paste the following local group policy editor location and click Next.
%windir%\System32\gpedit.msc

3. Under the “Type a name for this shortcut“, type “gpedit.msc”.

4. Click “Finish“.
Method 8: File Explorer
1. Open File Explorer. Type “gpedit.msc” in the search box.

Press Enter.
Method 9: Control Panel
1. Open the Control Panel. Type “edit group policy” or “gpedit.msc” in the search box.

2. Click on “Edit group policy“.
Note: This method only works if using Windows 11 Pro or Enterprise. If you’re on the Home edition, you won’t see the “Edit group policy” option within the Control Panel.
Method 10: Command Prompt / PowerShell
1. Open the Command prompt pr PowerShell and type the following command:
gpedit.msc
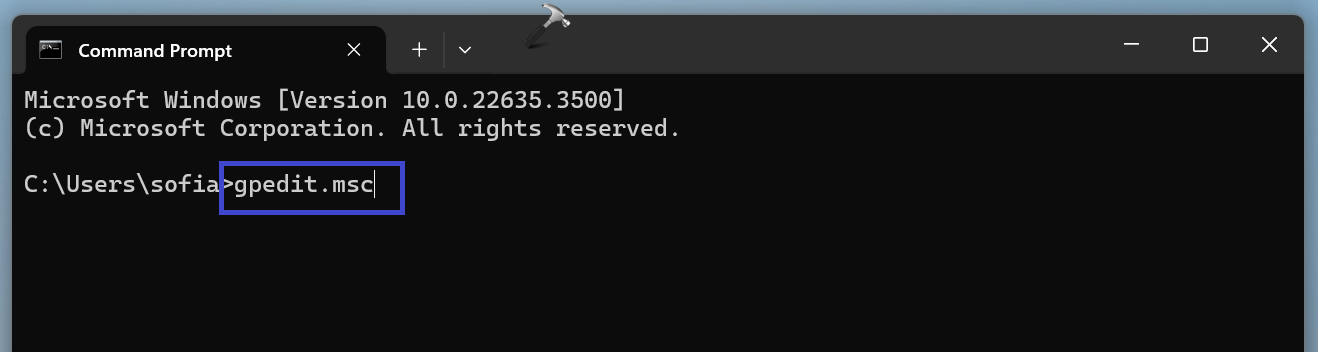
2. Press Enter
That’s It!
Related: Group Policy Update Hangs In Windows
RELATED ARTICLES
Table of contents
- What Is the Group Policy on Windows?
- What Is the Group Policy Editor?
- Components of the Group Policy Editor
- Components of the Local Group Policy Editor
- What Can You Do with the Group Policy Editor
- How to Access the Group Policy Editor in Windows 10/11
- Open the Local Group Policy Editor via Run
- Open the Local Group Policy Editor via the Command Prompt
- Open the Local Group Policy Editor via the search
- Open the Local Group Policy Editor via Control Panel
- Open the Local Group Policy Editor via PowerShell
- How to Use Group Policy Settings
- How to configure a security policy
- How to Use Group Policies with PowerShell
- The Group Policy on Windows: All You Need to Know
- FAQ
Sometimes, you may need to configure advanced system settings that are not in Control Panel or the Settings app. This is where the Local Group Policy Editor comes in.
The Group Policy Editor (or gpedit.msc) is a system tool that gives you administrative privileges to view and edit Group Policy settings.
This can be beneficial if you’re an administrator. This article will walk you through accessing and using the Local Group Policy Editor in Windows 10 and 11.
What Is the Group Policy on Windows?
The Group Policy is a Windows feature that contains different levels of advanced settings specifically designed for network administrators.
Administrators can use the Group Policy to configure settings in an Active Directory system on several computers.
In other words, you can configure various Windows settings for every computer on the network from this central location.
This Windows tool prevents people from changing predefined settings. For example, you can define a standard homepage for all network computers or restrict access to particular areas of Control Panel .
What Is the Group Policy Editor?
The Group Policy Editor helps you to work with Group Policy Objects to customize your PC’s functions and user experience. Unlike the Group Policy discussed above, which is mainly used for network-wide settings, the Group Policy Editor can modify settings on a single computer. You can change Windows settings you can’t access via the graphical interface, like customizing the login screen. For example, the Group Policy Editor allows you to lock down a computer in network scenarios, limit disk access, enforce password requirements, or limit program access.
There’s a difference between the Local Group Policy Editor (LGPE) and Group Policy Editor (GPE). The LGPE allows you to control settings and policies specific to a single computer that only apply to that device.
On the other hand, the GPE is a more complete tool for managing policies throughout a whole network domain within an Active Directory environment.
It enables centralized configuration and enforcement of policies for several computers and user accounts.
Components of the Group Policy Editor
The Group Policy Editor is made up of multiple parts that work together to control settings and policies within a network domain.
These components are the following:
- Group Policy Template (GPT): The GPT stores policy settings on individual client computers.
- Group Policy Client (GPC): It’s in charge of applying policies to client computers.
- Group Policy Objects (GPOs): They hold the actual policy settings.
- Group Policy Management Console (GPMC): The GPMC is a management tool for creating, editing, and linking GPOs.
- Group Policy Infrastructure: It consists of the Group Policy Service (GPSvc), which processes policy settings and applies them to client computers, and Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS), which maintains GPOs.
Components of the Local Group Policy Editor
The Local Group Policy Editor consists of multiple components:
- Group Policy Engine: It processes and applies policy settings to the local computer.
- Local Security Authority (LSA): The LSA imposes local security policies and settings.
- Local Group Policy Objects (LGPOs): LGPOs hold the policy settings unique to the local computer.
- MMC-based interface: It offers a user-friendly environment for viewing and configuring local policies.
These components allow you to use the Local Group Policy Editor to alter user preferences, security settings, and system behavior on specific machines.
What Can You Do with the Group Policy Editor
Group policies set password restrictions and regulate which versions of network protocols are available.
Establishing and upholding a strict Group Policy enhances IT security for corporations. Here are some things you can do with the Group Policy Editor in Windows 11 or 10:
- Restrict the apps employees can download and use on their business devices under management.
- Disable insecure network protocols such as TLS 1.0 to enforce more secure protocols.
- Turn off removable devices, such as USB drives.
- Limit the Control Panel’s settings that a user can change. For example, the GPE helps users adjust the screen resolution but doesn’t let them change the VPN settings .
How to Access the Group Policy Editor in Windows 10/11
There are several ways to open the Group Policy Editor. Let’s go through them:
Open the Local Group Policy Editor via Run
Here’s how to open the Local Group Policy Editor:
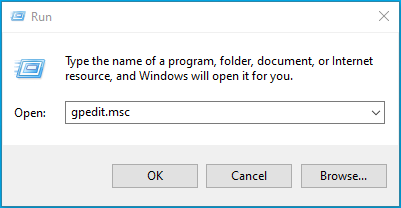
- Type
Windows + Rto open the Run dialog box. - Type
gpedit.mscinto the text field and press “ OK.”
Open the Local Group Policy Editor via the Command Prompt
You can also open the Local Group Policy Editor using the Command Prompt . Here’s how to do it:
- Open the Command Prompt using the search bar.
- Type
gpedit.msc, and press “ Enter.”
Open the Local Group Policy Editor via the search
- Open the search toolbar.
- Type
gpeditin the search bar and select “ Edit group policy.”
Open the Local Group Policy Editor via Control Panel
- Open Control Panel from the Start menu.
- Type “ group policy” or
gpeditin the search field. - Click on “ Edit group policy.”
Open the Local Group Policy Editor via PowerShell
- Type “ PowerShell” in the search bar to open.
- Type
gpeditand press “ Enter.”
Question
What does it mean when I receive the error message “ gpedit.msc not found” on my Windows 10/11?
The error message “ gpedit.msc not found” on Windows 10 and 11 usually occurs when you try to access the Group Policy Editor, but it’s unavailable or can’t be located.
The causes of the issue with gpedit.msc not found in Windows 11 and 10 could range from corrupt or missing files, third-party interruptions, and a lack of administrative privileges.
How to Use Group Policy Settings
Here’s how to apply Group Policy settings:
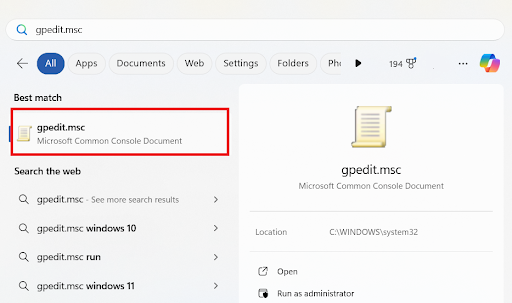
- You can launch the Group Policy Management tool by typing
gpedit.mscin the Windows search bar.
- Search for your preferred organizational unit (OU). You can apply the Group Policy at the OU, domain, or site level.
- Go to the default domain policies. Right-click on your preferred GPO to edit.
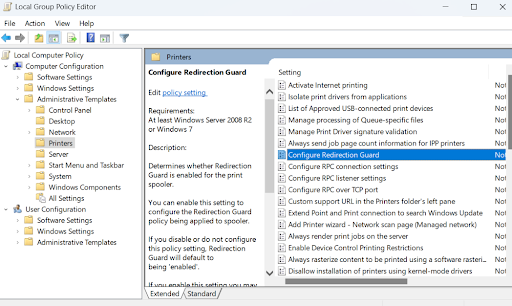
Every Group Policy Object has two fundamental configurations: computer and user configuration. Each of these configurations has policies and preferences.
Choose the configuration you want to change and save them.
How to configure a security policy
Let’s take an example. If you want to change a security policy in the Group Policy Management, follow the steps below:
- Type
gpedit.mscsearch bar and click to open - Click Windows Settings > Security Settings > Password Policy.
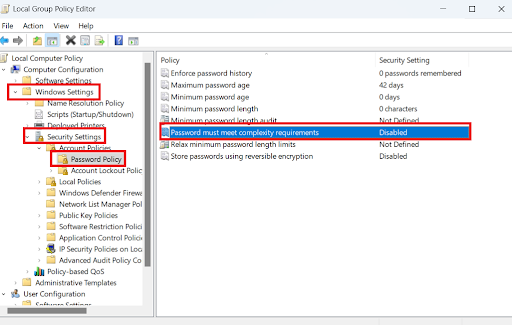
- Double-click on “ Password must meet complexity requirements.”
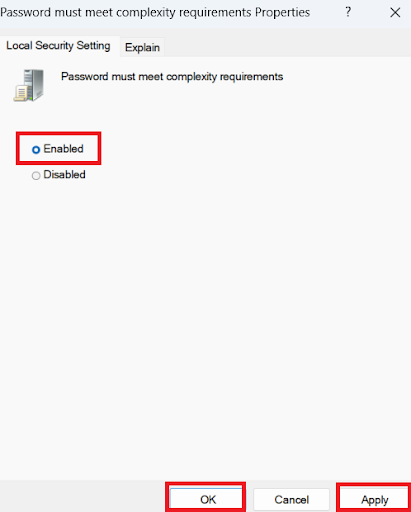
- Click “ Enabled,” select “ Apply,” and then “ OK.”
How to Use Group Policies with PowerShell
Here are examples of the PowerShell GroupPolicy cmdlets: New-GPO: This cmdlet creates a new, unassigned GPO. The new GPO allows you to choose a name, owner, domain, and additional parameters. Get-GPResultantSetOfPolicy: This cmdlet generates an XML file containing the results and returns the whole Resultant Set of Policy (RSoP) for a user, computer, or both. It’s a useful method for researching GPO-related problems. The only method to determine whether another GPO has overridden a policy set to a particular value is to know the actual values applied to a particular user or computer. Get-GPOReport: This cmdlet creates an XML or HTML file containing all or the specified GPOs in a domain.
- Invoke-GPUpdate: This cmdlet helps you to update the GPOs on a PC.
When you use PowerShell to configure the Group Policy Editor, you gain advantages such as automation, flexibility, and remote management.
You can remotely manage GPOs, automate processes, and change configurations with PowerShell.
Many IT workers choose PowerShell because of its scripting capabilities and version control, which make configuration management and troubleshooting easier.
The Group Policy on Windows: All You Need to Know
Throughout this guide, we’ve discussed the Group Policy Editor, the differences between the Local Group Policy Editor and the Group Policy Editor, and how to access the GPE on Windows 10 and 11.
We hope this guide has given you a basic understanding of the GPE and how to use it effectively.
You can use the PowerShell commands to implement policies without using the Group Policy interface.
Was this article helpful? Share it with your friends who might need it, and share your thoughts in the comments below!
FAQ
What is the Local Group Policy?
The Local Group Policy is a collection of configurations and settings applied to a single user account or computer. It allows administrators to regulate several aspects of user preferences, security settings, and system behavior inside a particular Windows environment. Usually, these rules are implemented locally on each device rather than controlled centrally over a network. Local Group Policy settings can support efficient resource management, user experience customization, and security measure enforcement.
How do I access the Group Policy Editor on my Windows computer?
To access gpedit.msc , Press the Windows key + R combo on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box. Then, type “gpedit.msc” into the text field and press “Enter.” This will open the Local Group Policy Edito r window, where you can navigate various Group Policy settings and configurations.
Is the Group Policy Editor available in all editions of Windows?
The Windows edition you are using determines whether the Group Policy Editor is available. Windows professional and enterprise editions, such as Windows 10 Pro, Windows 10 Enterprise, and similar versions, typically include the Group Policy Editor. However, basic versions of Windows, like Windows 10 Home, don’t usually come with it.
How can I run the Group Policy Editor as an administrator on my Windows computer?
Here’s how to open the Local Group Policy Editor as an administrator. Press Windows key + X and select “Computer Management.” Next, expand “Local Users and Groups” and click “Groups.” Double-click on the “Administrators group” and click “Add.” Then, type your username and select “OK.” After adding the username, close the “Computer Management” window. This will give the Group Policy Management administrative privileges.
The Group Policy Editor in Windows 11 and Windows 10 is a Microsoft Management Console that allows users access to the Computer and User Management Settings that could be changed. One can access settings such as changing the processes a user on the computer could open, manage the apps, and a lot more. Not to be visible to an average user, this option is hidden. So if you are interested in opening it, Here’s how you can open a Group Policy Editor on Windows 11/10.
Note: Group Policy Editor is not available for Windows 11/10 Home version. To enable it, follow this guide.

This tool is not meant for beginners, and thus so the location of the tool is hidden and is not directly available through the Start Menu. Here’s the list of methods we will be following in the below guide to open Group Policy Editor on Windows 10
- Search Box
- Settings Panel
- Control Panel
- Run Dialog
- Command Prompt
- Create a Shortcut for Group Policy Editor on Windows.
Group Policy can enable or disable many things in Windows, so make sure you understand what you plan to change on the computer. Also, Group Policy Editor creates an entry in the registry and is a safer way instead of directly changing via a registry entry.
1] Search Box

The Search Box is used for searching files across the drive and could perform our required function as well. To open the Windows Group Policy Editor via the Search Box, Fire up the search box by either clicking the ‘Windows’ Logo or clicking on it.
Next, Search for Edit Group Policy or gpedit.msc would bring up the Group Policy Editor as the main result. Tap on the required application, and you are good to go.
2] Run Dialog

We all do use the Run Dialog to launch applications or a specified location quickly. We could also use the Run Dialog in this case. Here’s how:
Quickly launch the Run Dialog by pressing the Win + R button simultaneously or head over to the search box and open it via there. Next, in the Run Dialog, type in gpedit.msc and press Enter to run it.
3] Command Prompt

While you can use the Command Prompt for executing queries and commands, here’s how you can use it to complete our required function of opening the Windows Group Policy Editor.
Fire up the Command Prompt or a Powershell window using the Search Box, the Run Dialog, or any other method. Next, In the command line, type in gpedit.msc and press Enter to run the command.
4] Windows Settings

As discussed earlier, you can also use the Group Policy Editor on Windows 11/10 to change/modify the settings, and hence as the name suggests, it could be accessed from the Settings Panel. To do so, Open the Settings Panel either via the Search Box or directly from the Start Menu. In the Search Box, type in Group Policy Editor and select the main listed result.
5] Control Panel

Another way to access the Group Policy Editor on Windows 11/10 is via the classic Control Panel. So, open the Control Panel first. At the top right corner, click on the search box, and search for Group Policy Editor. In the results, under the Administrative Tools menu, you’ll find the result for the Edit Group Policy, click on it, and you’re good to go.
A point here to be noted is, although the Windows Group Policy Editor is available under the Administrative Menu in the search results, if you open the Control Panel and head over to the Administrative Menu directly, you won’t be in a position to find it. So, the only method to access it via the Contol Panel is using the Search Box.
6] Create a Shortcut to the Group Policy Editor on the Desktop

If you are a person, who keeps accessing the Group Policy Editor often, we would recommend you create a shortcut on the Desktop using the method attached to save some time. On the Desktop, in a blank space, make a Right-Click. In the menu that pops up, Under the New options, select Create New Shortcut.
This will open a new menu to create a shortcut. In the menu, type in gpedit.msc and click Next. This will create a shortcut on the Desktop.
I hope the post was useful, and you were able to learn multiple ways to open Group Policy Editor in Windows 11/10.
How do I edit Group Policy in Windows?
Once the Policy editor is open, locate the policy. Then you can choose between Not configured, enabled, or disabled. Click on Finish to commit the changes.
Does Windows Home have Group Policy Editor?
It is not enabled by default for the Home version. However, it is still possible to enable it using a built-in tool. It will download the Group Policy Editor, and you can then find and launch it.
Why Does Gpedit MSC Not Work?
Make sure to launch it with admin permission if the tool doesn’t show the UAC prompt when you open it.
How Do I Fix Setup Blocked by Group Policy?
- Open the Group Policy Editor.
- Navigate to User Configuration > Administrative Templates > System.
- Locate the Don’t run specified Windows applications policy.
- Click on the Show button.
- Remove the blocked program or application from the disallowed list.
- Relaunch the program.
Related: How to launch a program with advanced run options with a right-click with admin permission.
A long-standing Windows fan, Photographer, and Tech Enthusiast who loves to write about Smartphones and Technology.
Групповая политика — это способ настройки параметров компьютера и пользователя для устройств, которые присоединены к доменным службам Active Directory (AD), а также к учетным записям локальных пользователей. Она контролирует широкий спектр параметров и может использоваться для принудительного применения и изменения настроек по умолчанию для соответствующих пользователей. Локальная групповая политика — это базовая версия групповой политики для компьютеров, не входящих в домен. Параметры локальной групповой политики хранятся в следующих папках:
- C:\Windows\System32\GroupPolicy
- C:\Windows\System32\GroupPolicyUsers.
Когда в Windows 10 вам необходимо открыть редактор локальной групповой политики, для этого вы можете использовать командную строку, команду выполнить, поиск на панели задач, меню Пуск или с помощью консоли управления (MMC).
Рассмотрим самые простые варианты:
- C помощью меню Пуск.
- C помощью команды Выполнить.
- C помощью Проводника Windows.
- С помощью командной строки или PowerShell
- Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики в качестве оснастки консоли управления.
- Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики в Windows 10 Home.
Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики с помощью меню «Пуск».
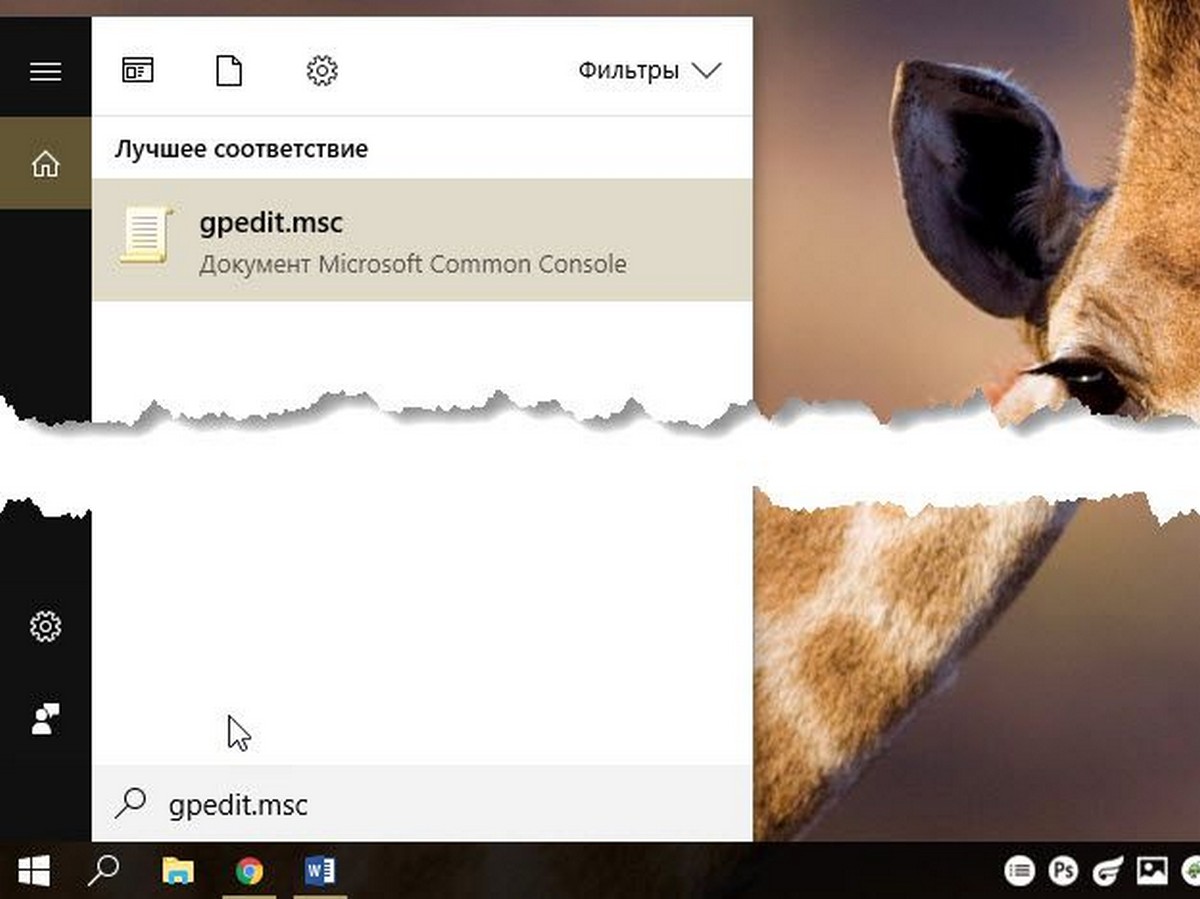
- Откройте меню «Пуск» и введите gpedit.msc в верхней части меню появится значок, при клике, на котором, откроется редактор политики.
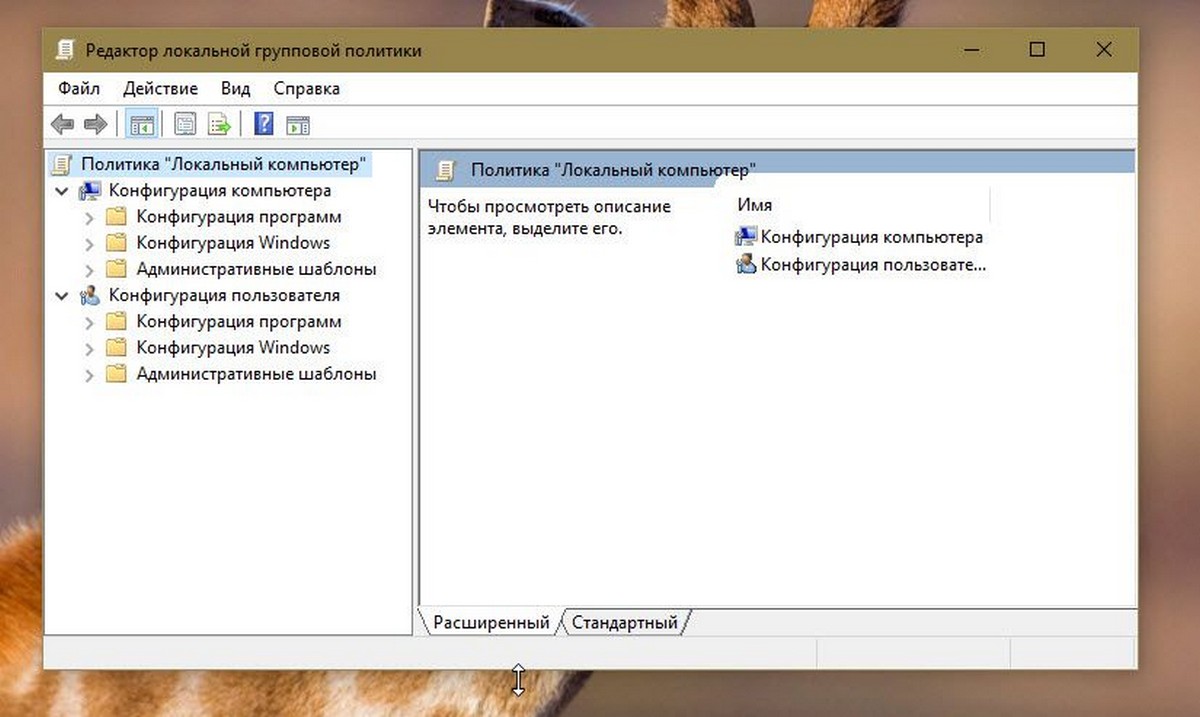
Чтобы просмотреть все применяемые политики в разделе «Конфигурация компьютера», перейдите в раздел «Конфигурация компьютера \ Административные шаблоны \ Все параметры»
Чтобы просмотреть все применяемые политики пользовательской настройки, перейдите в раздел «Конфигурация пользователя \ Административные шаблоны \ Все параметры».
Примечание: вы можете использовать поиск на панели задач.
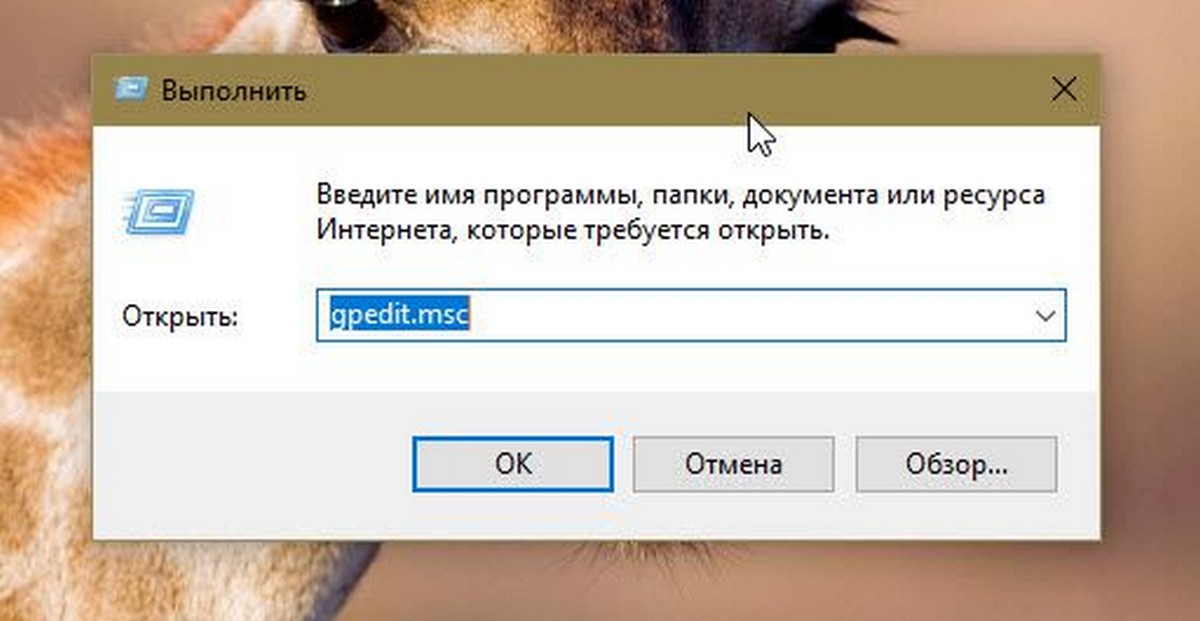
Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики с помощью команды «Выполнить».
- Нажмите сочетание клавиш Win + X или кликните правой кнопкой мыши на меню «Пуск».
- В открывшемся меню выберите Выполнить.
- В строке «Открыть» введите — gpedit.msc и нажмите кнопку «ОК».
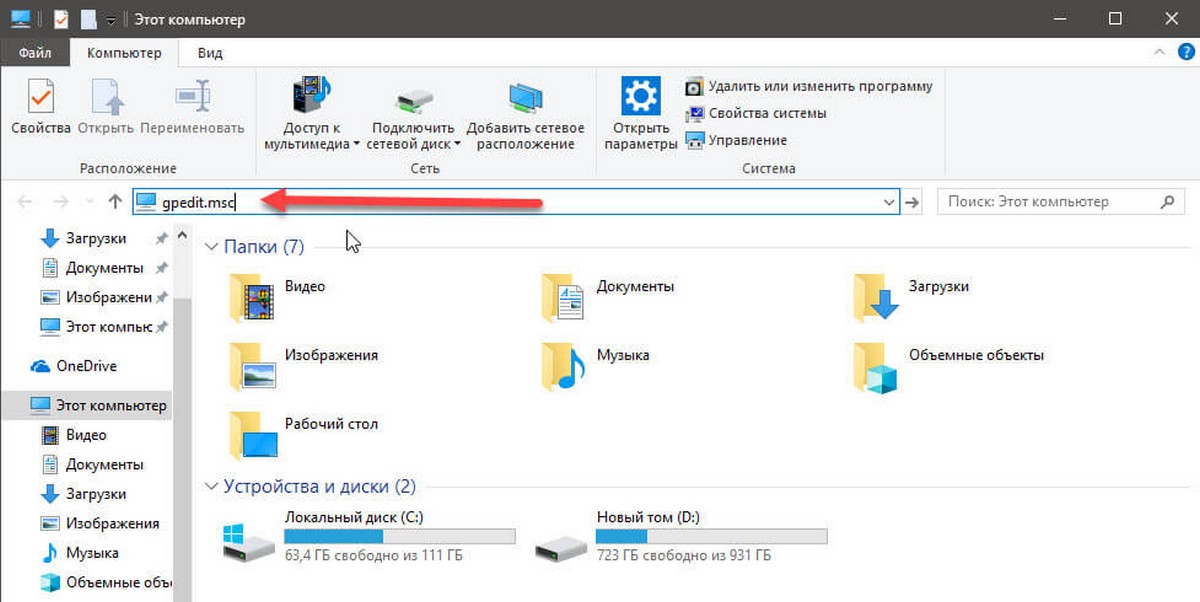
Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики с помощью Проводника Windows.
- Откройте Проводник с помощью ярлыка на панели задач или просто нажав сочетание клавиш Win + E
- В адресную строку проводника введите или скопируйте и вставьте:
gpedit.msc
- Нажмите Enter
Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики из командной строки или PowerShell
- Откройте Командную строку или вы можете открыть новый экземпляр PowerShell.
- Введите: gpedit.msc и нажмите клавишу Enter.
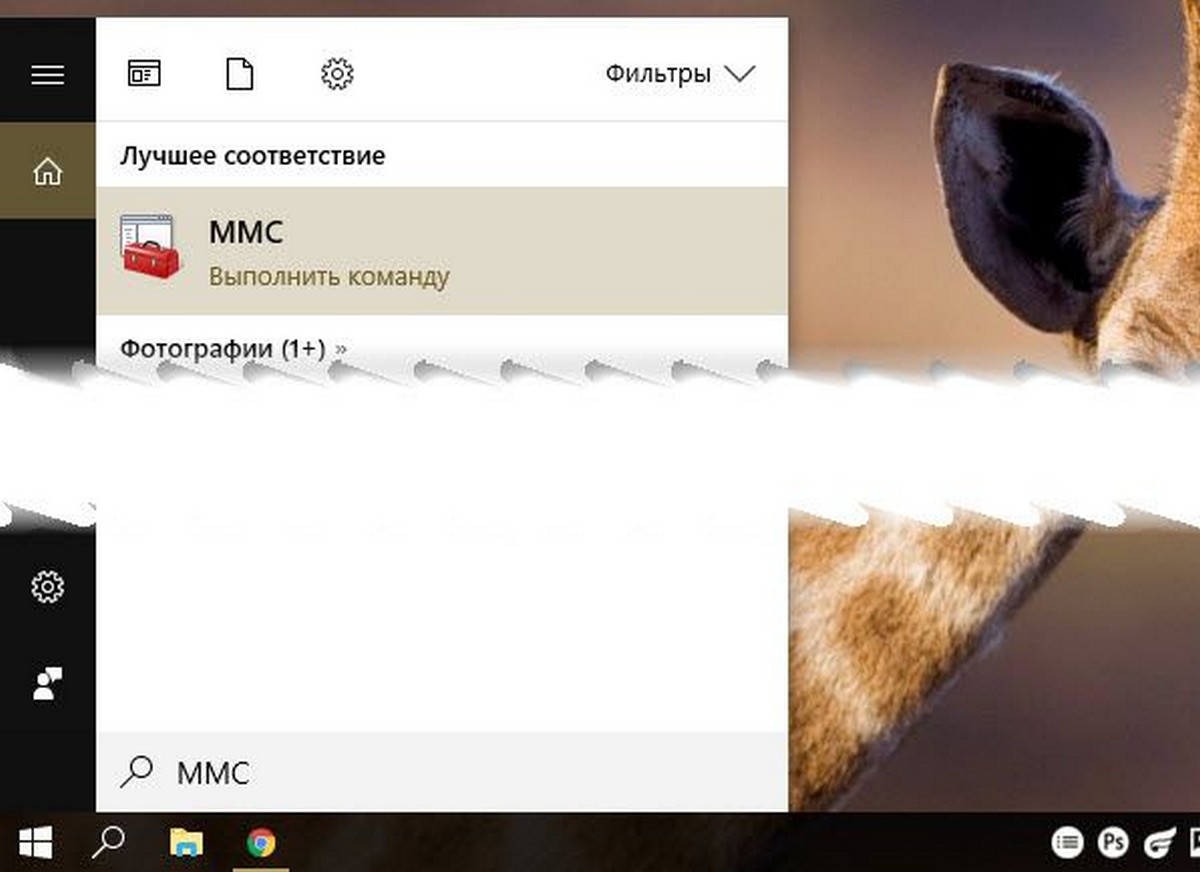
Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики в качестве оснастки консоли управления.
- Откройте консоль управления MMC. (Нажмите кнопку «Пуск», введите mmc и нажмите клавишу Enter).
- В меню Файл выберите пункт Добавить или удалить оснастку.
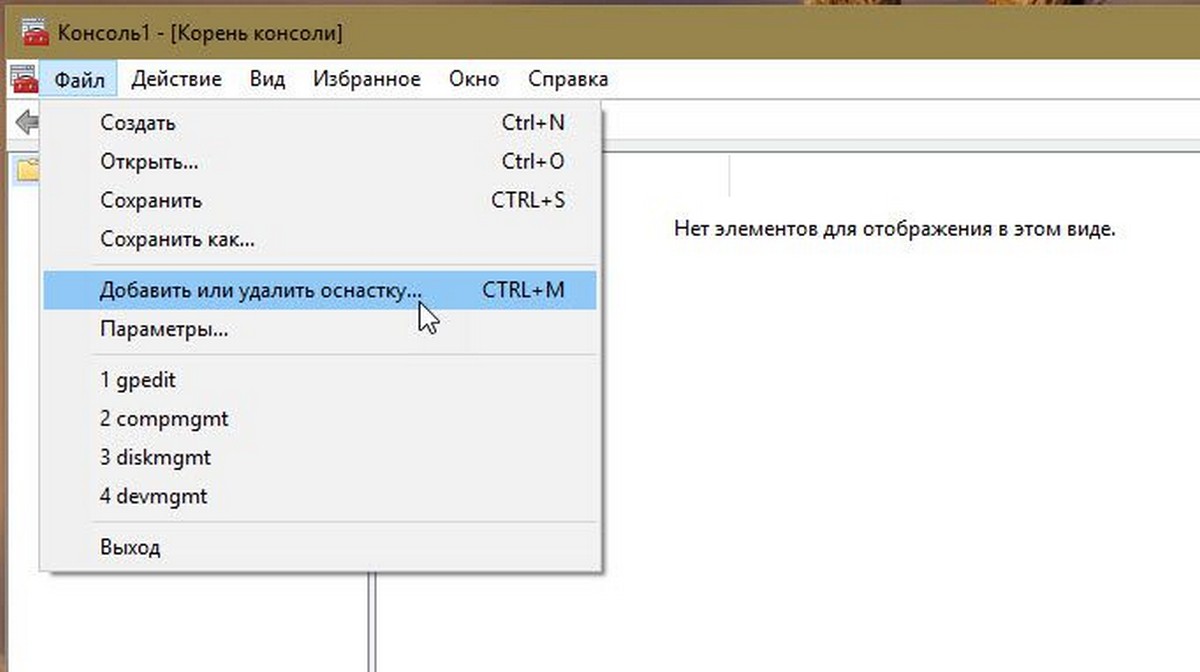
- В открывшимся диалоговом окне, дважды кликните «Редактор объектов групповой политики» и нажмите кнопку «Готово» и «ОК».
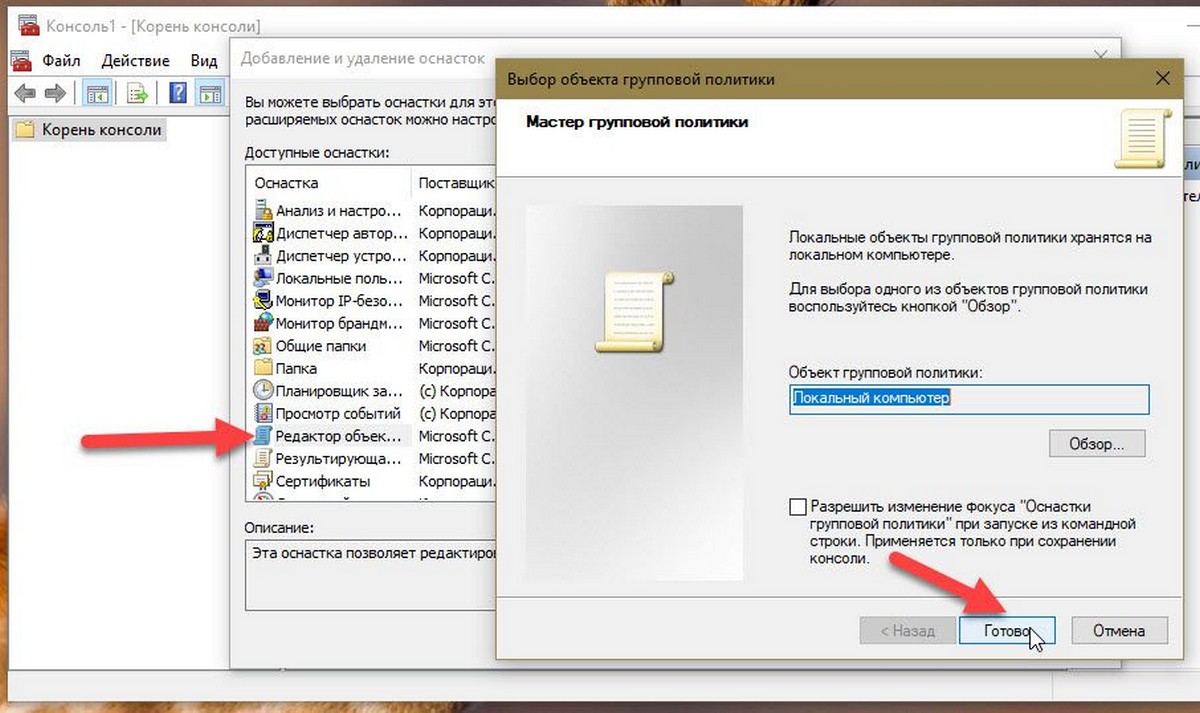
Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики в Windows 10 Home.
Как вы уже знаете, приложение Редактора локальной групповой политики доступно в Windows 10 Pro, Enterprise или Education. Пользователи Windows 10 Home не имеют доступа к gpedit.msc из-за ограничений ОС. Вот простое и элегантное решение, которое позволяет разблокировать его без установки сторонних приложений.
Существует простой способ включить Редактор локальных групповых политик в Windows 10 Home запустив всего лишь один пакетный файл.
Чтобы включить Gpedit.msc (групповая политика) в Windows 10 Home
- Загрузите следующий ZIP-архив: Скачать ZIP-архив.
- Распакуйте его содержимое в любую папку. Он содержит только один файл, gpedit_home.cmd
- Кликните правой кнопкой мыши по файлу.
- Выберите в контекстном меню «Запуск от имени администратора».
Все!
Пакетный файл вызовет DISM для активации редактора локальной групповой политики. Подождите, пока командный файл не завершит свою работу.
Помните, что некоторые политики не будут работать в Windows Home. Некоторые политики жестко заданы для версий Windows Pro. Кроме того, если вы активируете gpedit.msc с помощью предоставленного пакетного файла, изменение политик для отдельных пользователей не вступит в силу. Они по-прежнему требуют настройки реестра.
Вы можете самостоятельно создать пакетный файл. Прежде чем начать, рекомендуем создать точку восстановления системы, и вы могли в любой момент отменить произведенные изменения в системе.
- Откройте текстовый редактор, например «Блокнот».
- Скопируйте и вставьте следующие строки:
@echo off
pushd "%~dp0"
dir /b %SystemRoot%\servicing\Packages\Microsoft-Windows-GroupPolicy-ClientExtensions-Package~3*.mum >List.txt
dir /b %SystemRoot%\servicing\Packages\Microsoft-Windows-GroupPolicy-ClientTools-Package~3*.mum >>List.txt
for /f %%i in ('findstr /i . List.txt 2^>nul') do dism /online /norestart /add-package:"%SystemRoot%\servicing\Packages\%%i"
pause
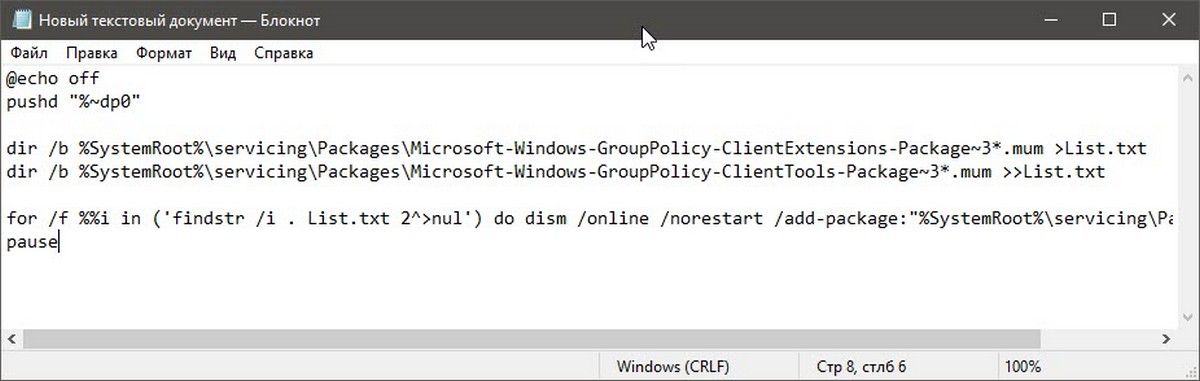
- В меню «Файл» текстового редактора выберите «Сохранить как» в диалоговом окне в строке «Имя файла» введите — gpedit.bat и нажмите кнопку «Сохранить».
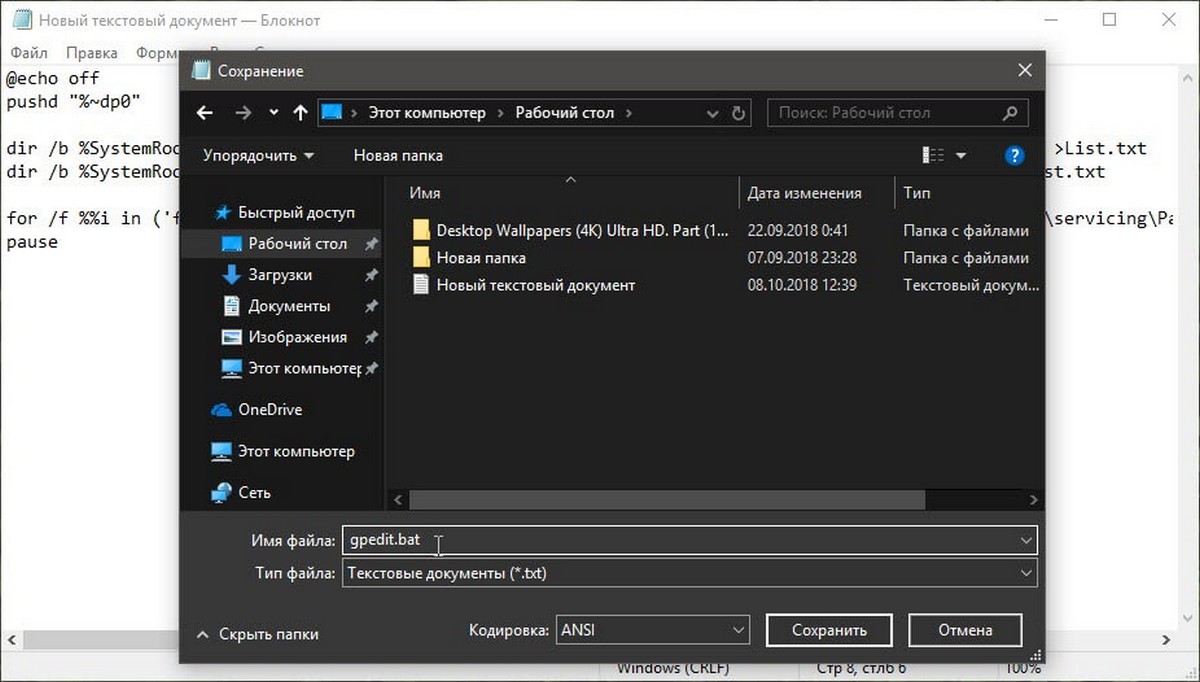
- Запустите от имени Администратора полученный пакетный файл gpedit.bat
- При запросе фильтра Windows SmartScreen, нажмите «Подробнее», затем нажмите кнопку «Выполнить в любом случае».
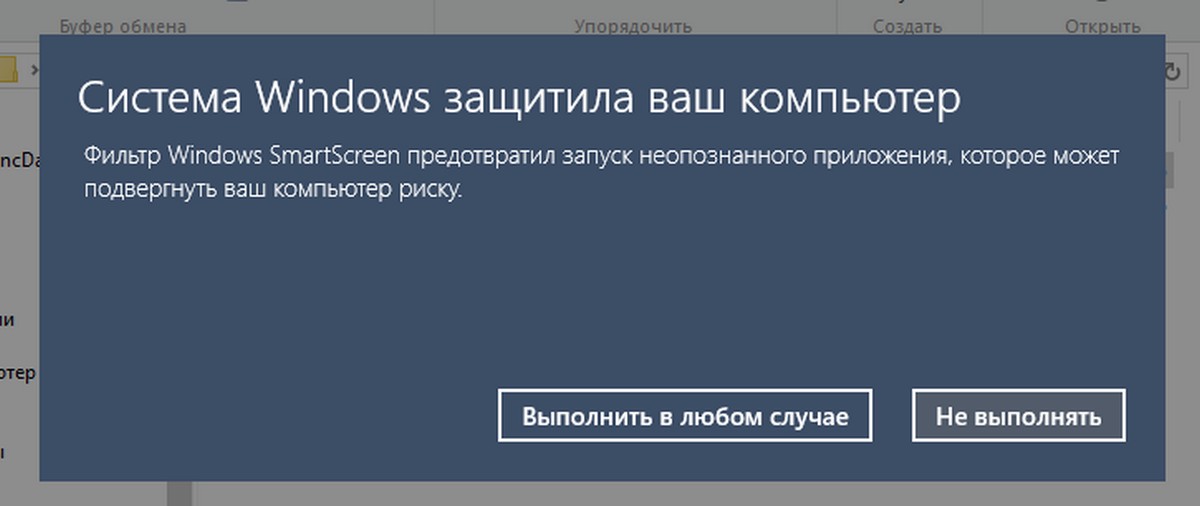
- В окне Контроля учетных записей, нажмите кнопку «Да».
- Дождитесь пока утилита DISM внесет изменения и закройте окно.
Все! Редактор локальных групповых политик (gpedit.msc) включен и теперь Вы можете его запустить любым из описанных выше способов.
Policy Plus
Существует хорошая альтернатива встроенному приложению gpedit.msc, которое называется Policy Plus. Это стороннее приложение с открытым исходным кодом: PolicyPlus
Policy Plus предназначен для того, чтобы сделать параметры групповой политики доступными для всех.
- Редактор работает на всех выпусках Windows, не только на Pro и Enterprise
- Полностью соблюдает условия лицензирования
-
Просмотр и редактирование политик на основе реестра в локальных объектах групповой политики, объектах групповой политики для отдельных пользователей, отдельных файлах POL, автономных кустах пользователей реестра и действующем реестре
- Переход к политикам по идентификатору, тексту или отдельным записям реестра.
- Просмотр дополнительной технической информации об объектах (политики, категории, продукты)
- Удобные способы изменить и импортировать настройки политики
Рекомендуем:
- Как Windows 10 вернуть настройки локальной групповой политики по умолчанию.
- 12 способов открыть редактор локальной групповой политики в Windows 11
