При запуске новых сервисов в Windows, вы можете обнаружить что нужный порт уже занят (слушается) другой программой (процессом). Разберемся, как определить какая программ прослушивает определенный TCP или UDP порт в Windows.
Например, вы не можете запустить сайт IIS на стандартном 80 порту в Windows, т.к. этот порт сейчас занят (при запуске нескольких сайтов в IIS вы можете запускать их на одном или на разных портах). Как найти службу или процесс, который занял этот порт и завершить его?
Чтобы вывести полный список TCP и UDP портов, которые прослушиваются вашим компьютером, выполните команду:
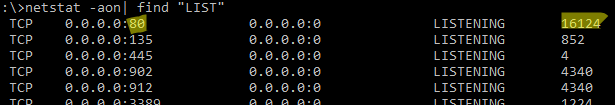
netstat -aon| find "LIST"
Или вы можете сразу указать искомый номер порта:
netstat -aon | findstr ":80" | findstr "LISTENING"
Используемые параметры команды netstat:
- a – показывать сетевые подключения и открытые порты
- o – выводить идентфикатор професса (PID) для каждого подключения
- n – показывать адреса и номера портов в числовом форматер
По выводу данной команды вы можете определить, что 80 порт TCP прослушивается (статус
LISTENING
) процессом с PID 16124.
Вы можете определить исполняемый exe файл процесса с этим PID с помощью Task Manager или с помощью команды:
tasklist /FI "PID eq 16124"
Можно заменить все указанные выше команды одной:
for /f "tokens=5" %a in ('netstat -aon ^| findstr :80') do tasklist /FI "PID eq %a"
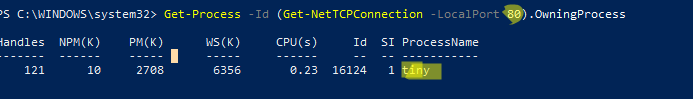
С помощью однострочной PowerShell команды можно сразу получить имя процесса, который прослушивает:
- TCP порт:
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 80).OwningProcess - UDP порт:
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetUDPEndpoint -LocalPort 53).OwningProcess
Можно сразу завершить этот процесс, отправив результаты через pipe в командлет Stop-Process:
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 80).OwningProcess| Stop-Process
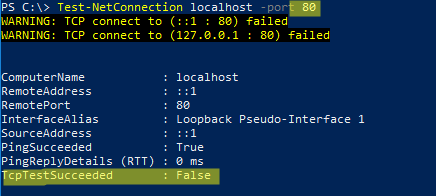
Проверьте, что порт 80 теперь свободен:
Test-NetConnection localhost -port 80
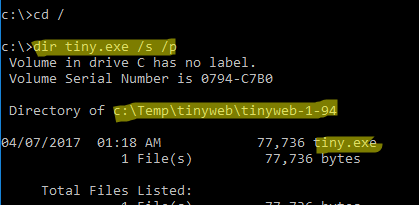
Чтобы быстрой найти путь к исполняемому файлу процесса в Windows, используйте команды:
cd /
dir tiny.exe /s /p
Или можно для поиска файла использовать встроенную команду where :
where /R C:\ tiny
В нашем случае мы нашли, что исполняемый файл
tiny.exe
(легкий HTTP сервер), который слушает 80 порт, находится в каталоге c:\Temp\tinyweb\tinyweb-1-94
Find Process ID of Process using given port in Windows
Once a while it happens that you try to start Tomcat and it complains “Port 8080 required by Tomcat v7.0 Server at localhost is already in use”. So that means there is already a process running in background that has occupied 8080 port. So how to identify the process in Windows task manager that is using port 8080? I am sure there must be a javaw.exe. But is there a better way to identify which process in windows is using a given port number? Yes…
How to Find Process ID of process that uses a Port in Windows
Our friend netstat will help us in identifying the process. netstat can list the running process and display information such as process id, port, etc. From this list we can filter the processes that has given port using findstr command.
List process by port number
Code language: Bash (bash)
netstat -ano | findstr 8080
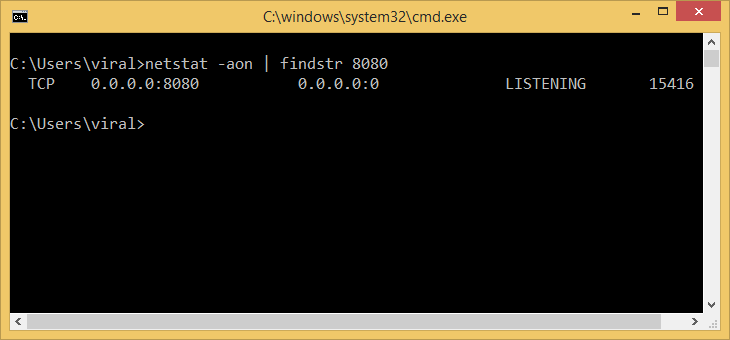
Output
Code language: Bash (bash)
Proto Local Address Foreign Address State PID TCP 0.0.0.0:8080 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 29848
-a– Displays all connections and listening ports.-o– Displays the owning process ID associated with each connection.-n– Displays addresses and port numbers in numerical form.
We can use netstat to list all the processes.
List all processes by PID
Code language: Bash (bash)
netstat -ano
Kill the Process by PID
Once we identify the process PID, we can kill the process with taskkill command.
Code language: Bash (bash)
taskkill /F /PID 12345
Where /F specifies to forcefully terminate the process(es). Note that you may need an extra permission (run from admin) to kill some certain processes.
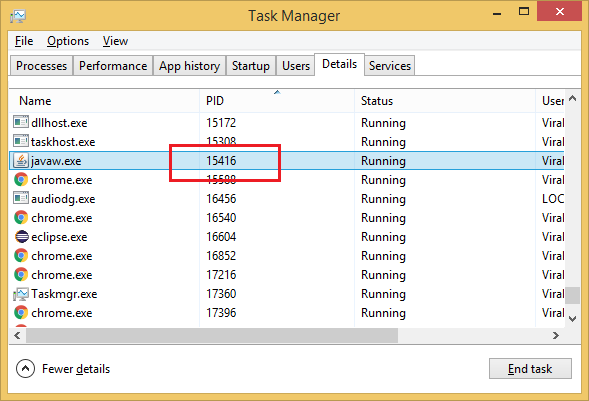
Or else you can use our old trusted Windows Task Manager to kill the process for given process id. If PID is not visible in your task manager then you can enable it by Right clicking on table header under Details tab, click Select Columns and then check PID.

If you’ve faced a blocked or in-use port, it can be frustrating. Fortunately, there are easy ways for Windows and Linux users to find which program or process is using a port and resolve conflicts.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to find the program or process that’s using a particular port on both Windows and Linux systems, and I’ll also show you the tools available to resolve port conflicts.
Why Knowing Which Process Uses a Port is Important?
Ports are essential for network communication, and multiple programs might attempt to use the same port, leading to conflicts. By finding which process is using a specific port, you can avoid these conflicts, ensure smooth network operations, and troubleshoot issues that arise from port usage.
Method 1: Using Command Prompt (Windows)
The Netstat utility on Windows can help you find which application is using a specific port. Here’s how you can use this method to track down which process is occupying a particular port:
Press the Windows key, type CMD in the search box, right-click on Command Prompt, and select Run as Administrator. Then enter the command:
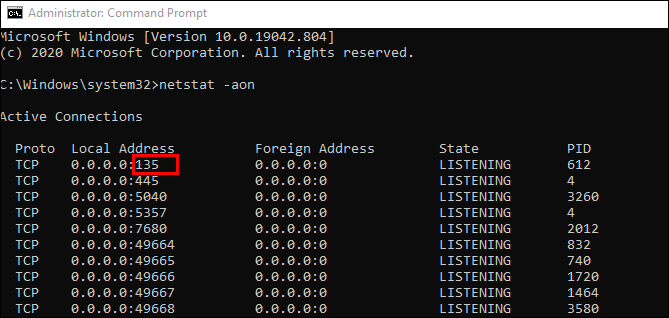
netstat -aon -p tcp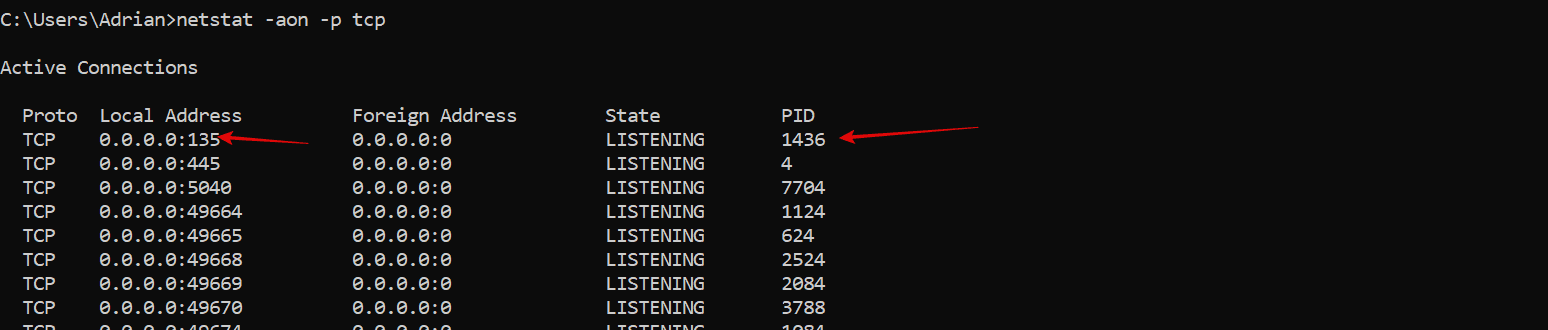
This command will display a list of all TCP connections, their local addresses, the process IDs (PIDs), and the state of each connection.
Look through the list for the port you’re concerned about (e.g., port 135 in the above screenshot).
Find the PID number associated with that port in the last column. i.e; 1436 there.
To match the PID with the program name, use the following command in the same Command Prompt window:
tasklist | find "PID_number"For example, if the PID number from the previous command was 1400, you would run: tasklist | find “1436”
This will show you the name of the application using that port (e.g., FileZilla Server, SQL Server, etc.).

Method 2: Using Resource Monitor (Windows)
If you prefer a more visual approach, Windows’ Resource Monitor tool can provide a detailed view of the programs using specific ports.
- Press the Windows key and type resource monitor or resmon in the search box. Click on Resource Monitor to open the tool.
- In Resource Monitor, navigate to the Network tab.
In the Listening Ports section, you’ll see a list of all open ports and the applications that are using them.
You can check the PID column to match the process IDs with the applications.

Method 3: Command Line on Linux
If you’re using Linux, the process is quite similar, but instead of Command Prompt, you’ll use the Terminal to run the necessary commands.
- Open a terminal on your Linux machine.
- Enter the following NetStat command to get a list of active connections:
sudo netstat -ano -p tcpThis will show all TCP connections with their corresponding PIDs.
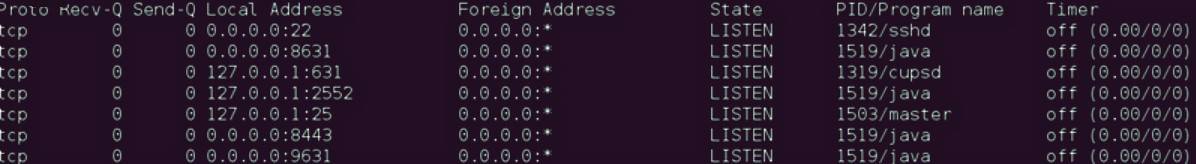
Similar to Windows, locate the specific port number and note the associated PID.
Once you have the PID, you can use the following command to find more details about the process:
ps -ef | grepThis will display the program name and other details related to the process ID.
Additional Tips:
How to Interpret the netstat Command:
You can customize the netstat command with different flags to refine the results:
| -a | Displays all active connections and listening ports. |
| -n | Shows addresses and port numbers in numerical form (instead of resolving them to hostnames). |
| -o | Displays the PID associated with each connection. |
| -p | Displays the protocol (TCP, UDP, etc.). |
Task Manager PID Column:
If you’re using Windows Task Manager to match a PID, ensure the PID column is visible. To do this, click on the View menu, select Select Columns, and check the box for PID (Process Identifier).
Knowing which application is using a port is essential for troubleshooting network and application conflicts. By following the methods above, you can easily find which program or process is using a particular port on both Windows and Linux systems. Whether you prefer using the command line or a graphical interface, there are plenty of ways to resolve port conflicts efficiently.
Take Control with cPanel
Manage every aspect of your website with our intuitive cPanel. From email setup to file management, enjoy complete control. Experience reliable hosting with robust features.
Explore cPanel Plans
Related Blogs:
Содержание статьи:
- Типовые задачи и их решение
- Вариант 1: смотрим список прослушиваемых портов + приложение (общий случай)
- Вариант 2: а если наоборот — по названию приложения узнать порт
- Вариант 3: исп-ем спец. приложения (более информативнее и быстрее)
- Вопросы и ответы: 0
Доброго времени!
При запуске некоторого ПО/сервисов можно столкнуться с тем, что определенный порт в системе уже занят… какой-нибудь другой программой (скажем, настраиваете вы апач — и возникает конфликт порта 80. Например, на нем может «висеть/слушать» Skype…). Незадача…?
Собственно, в заметке приведу неск. способов, как можно относительно быстро узнать «кем» и «чем» заняты определенные порты — а это позволит быстро изменить их настройки и разрешить вопрос! (разумеется, приводить советы посмотреть описание установленного софта, в котором разработчики указывают порты — я не буду: ибо это долго, и не всегда продуктивно… 🙂).
*
Примечание:
- заметка носит информативный характер, и не явл. инструкцией в последней инстанции. Дело в том, что нередко встречаются не офиц. резервируемые порты… и, разумеется, точности здесь никакой быть не может;
- если у вас не получается подключиться к сетевым играм, есть проблемы с раздачей/загрузкой торрентов и пр. — ознакомьтесь с заметкой про проброс портов на роутере (это немного не по теме, но когда речь заходит об этом — очень часто приходится ссылаться на сию заметку).
*
Типовые задачи и их решение
Вариант 1: смотрим список прослушиваемых портов + приложение (общий случай)
По умолчанию в Windows есть консольная утилита netstat. Она позволяет посмотреть активные соединения протокола TCP/IP (в т.ч. там есть и порты).
*
Чтобы вывести полный список портов (TCP, UDP) нужно:
1) Запустить 📌командную строку от имени администратора.
2) Ввести команду Netstat –ao и нажать Enter.
(можно ее слегка изменить и использовать такую: netstat -aon| find «LISTENING»)
Примечание:
- «-a» – см. все соединения и порты.
- «-o» – см. числовые идентификаторы процесса, отвечающего за конкретное соединение (Process ID, сокращенно: PID).
- «-n» – см. номера портов в числовом формате»;
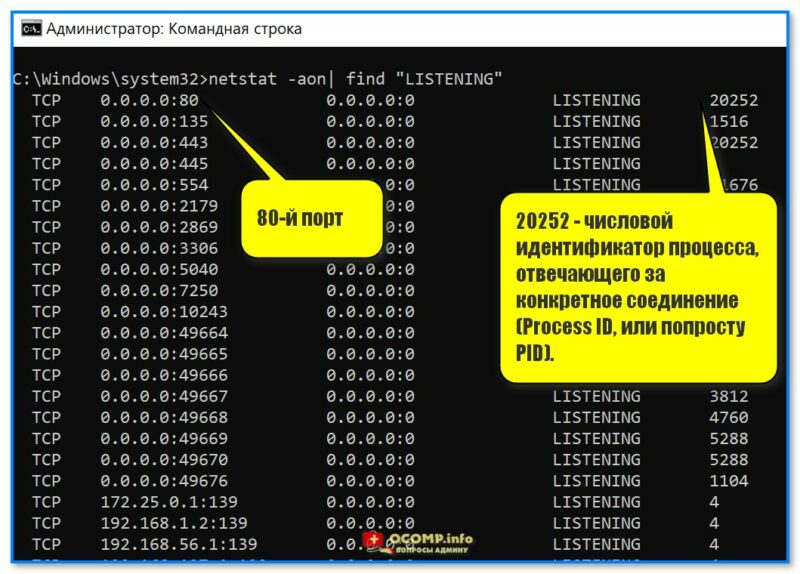
Где тут порт и идентификатор, см. скрин, я выделил // пример работы с командной строкой, команда netstat
📌 Для справки!
В списке, который предоставит нам команда Netstat, есть строки с аббревиатурами: «ESTABLISHED» и «LISTENING». В чем разница:
- «ESTABLISHED» — означает, что в данный момент установлено соединение;
- «LISTENING» — означает, что сокет ожидает соединения (в режиме прослушивания).
Причем, и тот и другой порты открыты, но один ожидает соединения, а другой уже установил соединение!
Например, протокол HTTP (это порт 80-й) находится в режиме прослушивания («LISTENING») до тех пор, пока кто-нибудь не зайдет на сервер. В тот момент, когда кто-нибудь будет загружать страницу — режим поменяется на «ESTABLISHED».
3) Например, понадобилось нам узнать какой процесс занял порт с идентификатором (PID) «5288» — вводим в командной строке tasklist | find «5288» и нажимаем Enter;
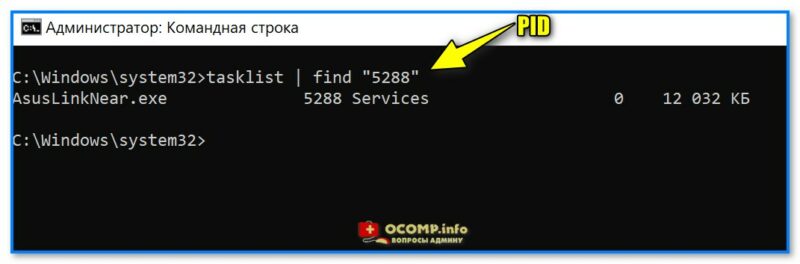
Вводим PID и смотрим название процесса
4) Почти сразу же узнаем, что это фирменная утилита от производителя ноутбука ASUS (шла вместе с операционной системой Windows // инсталлируется автоматически при установке драйверов).

Asus
5) Кстати, если вам неудобно пользоваться командной строкой — то узнать название процесса и его расположение по PID можно в 📌диспетчере задач (Ctrl+Alt+Del): достаточно перейти во вкладку «Подробности».👇
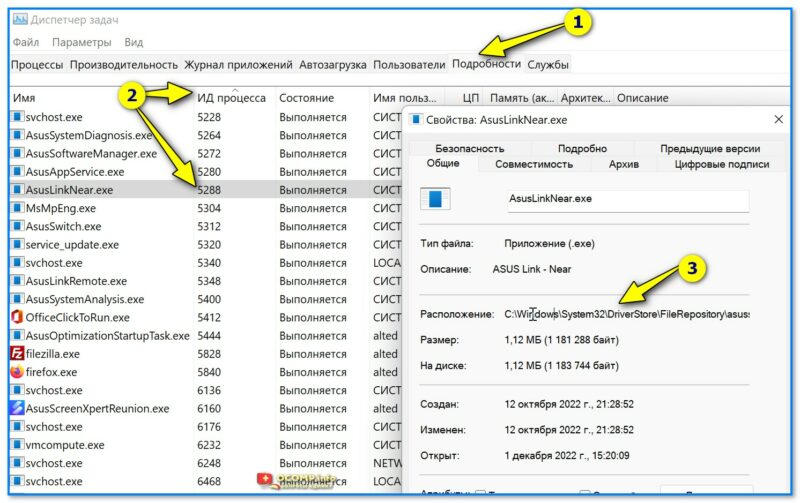
Диспетчер задач — подробности — сортировка по ИД процессу
*
Вариант 2: а если наоборот — по названию приложения узнать порт
Относительно просто!
Находим нужный процесс в 📌диспетчере задач (вкладка «Подробности» для Windows 11). Узнаем его ИД (в моем случае 6216, взял для примера uTorrent).
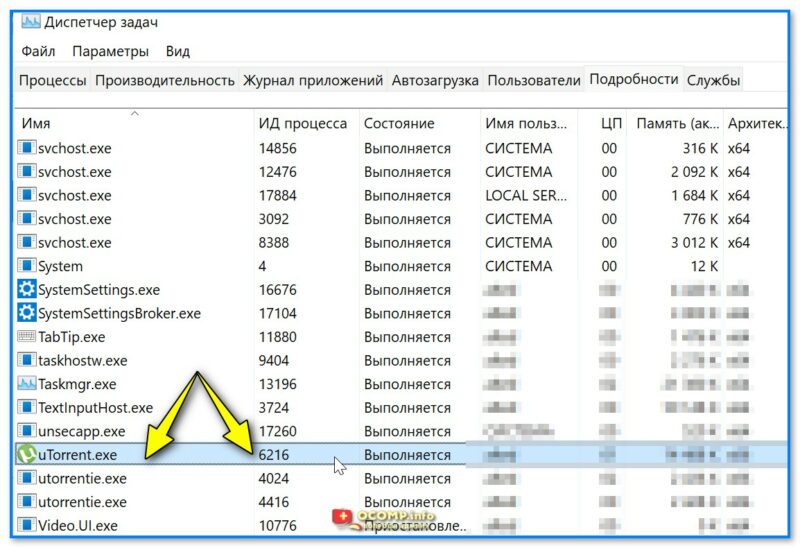
uTorrent — ИД 6216
Далее в комодной строке набираем следующее:
netstat -aon| find «6216»
где вместо «6216» нужно указать свой ИД.
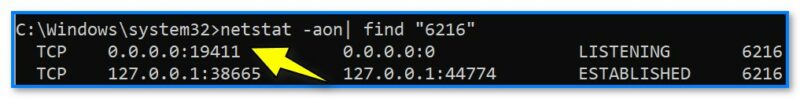
19411 порт, используемый uTorrent
В результате определяем, что uTorrent слушает порт 19411…
Кстати, в настройках uTorrent (если запустить саму программу) — можно тоже узнать и изменить этот порт на какой-нибудь другой.
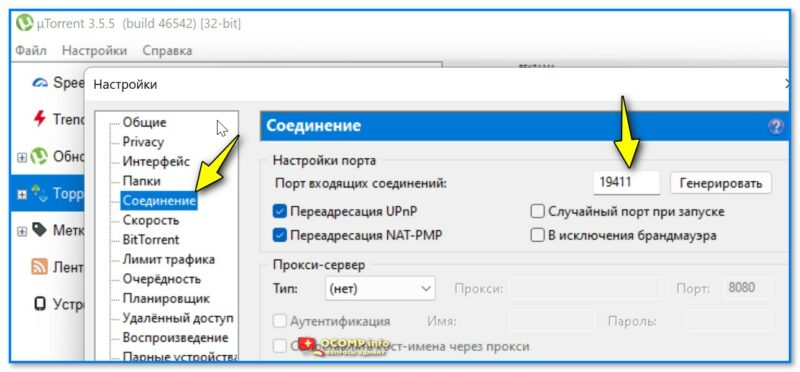
Настройки uTorrent — выбор порта
*
Вариант 3: исп-ем спец. приложения (более информативнее и быстрее)
📌 TCPView
Ссылка на сайт Microsoft: https://learn.microsoft.com/ru-ru/sysinternals/downloads/tcpview
TCPView — небольшая спец. утилита (не требующая установки), позволяющая очень быстро узнать список всех сетевых соединений, с информацией о портах, IP-адресах и пр.
Причем, список можно отсортировать по нужному вам столбцу + отфильтровать по какой-нибудь аббревиатуре. В общем, вещи удобная! См. скрин ниже. 👇
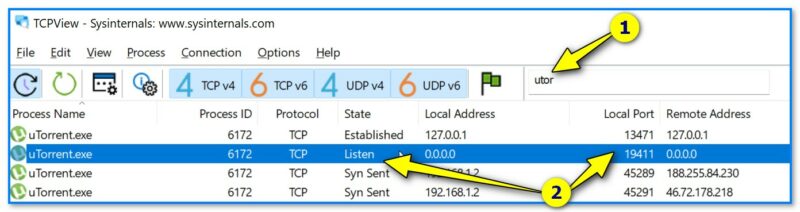
TCPView — список приложений, смотрим все необходимые свойства
📌 CurrPorts
Ссылка на офиц. сайт: https://www.nirsoft.net/utils/cports.html#DownloadLinks
CurrPorts — еще одна сетевая утилита для просмотра сетевых подкл. В установке программа не нуждается, по информативности не уступает первой. Кстати, у утилиты есть рус. перевод (но скачать его нужно отдельно, есть на офиц. сайте).
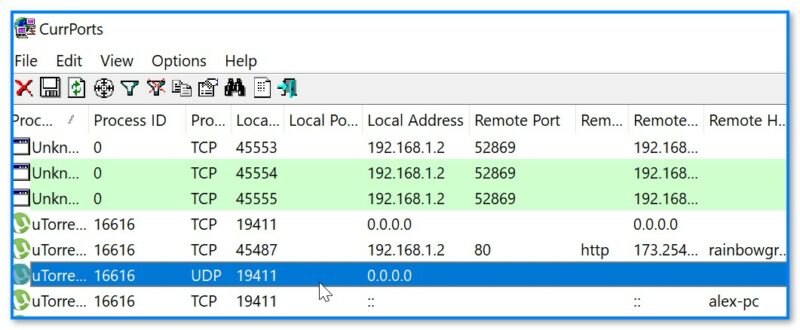
CurrPorts — пример использования
*
Дополнения по теме — приветствуются!
Успехов!
👋
3 minute read
Can’t use a specific port? Here’s how to check which port is in use in Windows with simple commands and apps like currports and tcpview.
Windows has many applications connected or trying to connect to the internet at any point in time. With all those applications, it is only natural that they use many network ports.
Two or more applications may need the same port to work from time to time. When that specific port is already in use by one application, the other application cannot use that port, and it may show a warning message, error out, or crash entirely.
In those situations, it is better to know which ports are used and which application is using that specific port. That way, you can either change the port or terminate the problem-causing application so that the other one works as it should.
The good thing is that it is pretty easy to know which port is used by which application in Windows. So, without further ado, let me show the steps to find which ports are used in Windows 10 and 11 operating systems.
Note: The methods shown below work in Windows 7, 8, 10, and 11.
Command to check ports in
Using a single command, you can get a list of all the ports in use by various programs. This method is quite helpful if you want to take a quick glance at the ports in use.
-
Search for “cmd” in the start menu, right-click on the Command Prompt and select “Run as Administrator.” This option lets you open the command prompt with admin rights.
- In the elevated command prompt window, execute the below command. You can copy and paste the command into the Command Prompt window by right-clicking inside it.
- You will see the port number right next to the IP address (ex: 192.168.42.198:50943) in the output result. You can see the highlighted portion of the attached image for better representation.
Keep in mind that the list will not be refreshed automatically. You have to execute the command again when you need an updated list. If you want the used port list to be updated automatically, follow one of the two methods illustrated below.
Use CurrPorts to find ports in use
Nirsoft Utilities has a pretty neat and lightweight tool called CurrPorts. It shows all the ports used by Windows and other programs. Let me show you how to use the application to get the information you need.
A quick note: In case you don’t know, Nirsoft has a lot of small and portable apps that are pretty useful in day-to-day life. If you’ve never used Nirsoft Utilities, browse the developer site and find many interesting little tools.
-
First, download CurrPorts from the official website. Being a portable application, you don’t have to install it. After downloading, extract the exe file from the zip file and double-click the file to open it.
-
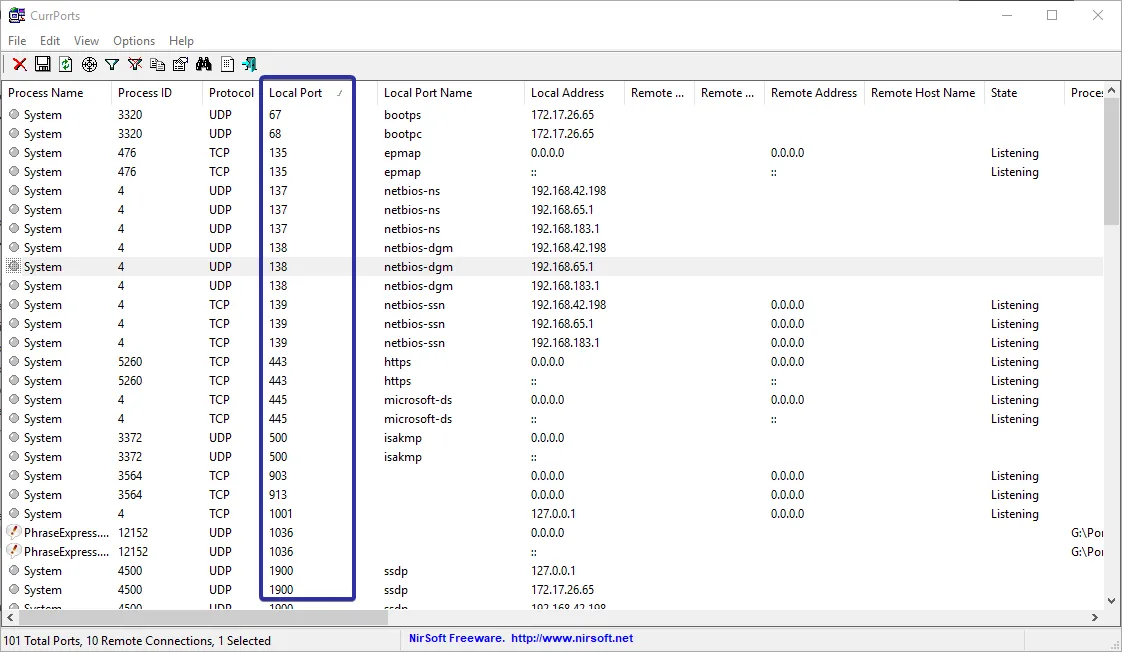
As soon as you open the window, the application will list all the connections and their ports. You can find the port number under the Local Port section.
-
Being a dedicated port monitoring application, it offers quite a few options to manage the applications and ports. Right-click on any option, and you will see appropriate options like the ability to close the TCP connection, copying properties, application properties, etc.
-
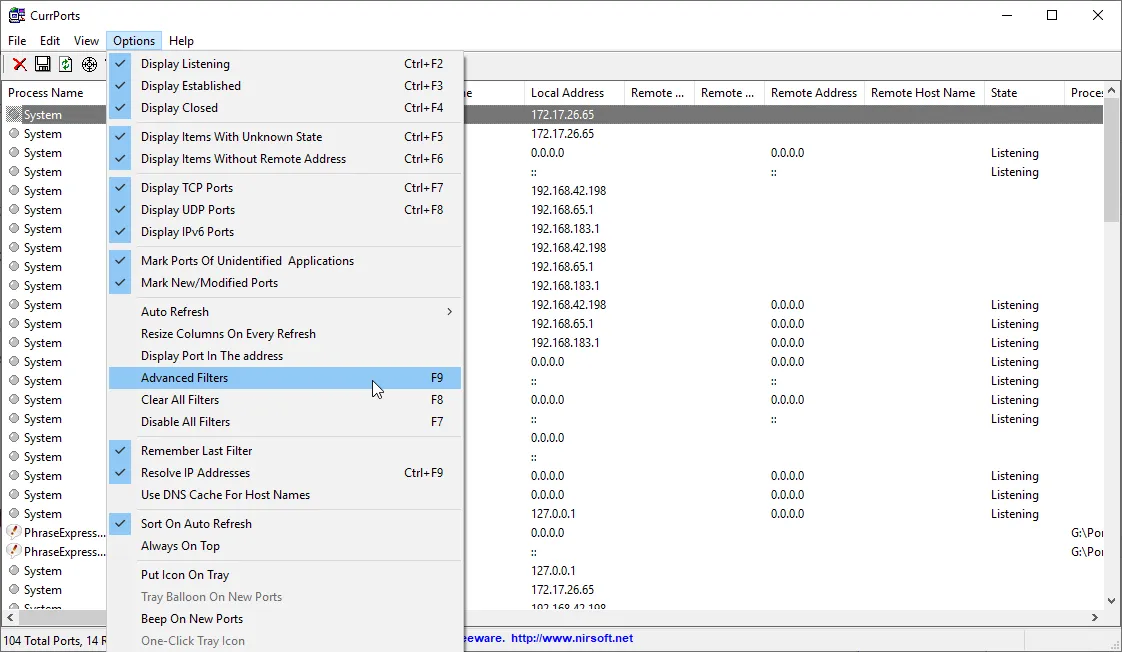
If you want finer control, you can create your own filters to narrow down the search. To do that, select “Options -> Advanced Filters” option.
Use Sysinternals TCPView to check ports in use
Sysinternals TCPView is a Microsoft tool that makes it easy to view all the TCP connections and ports used in Windows 10 and 11. The tool is very similar to CurrPorts.
-
Download TCPView from the Sysinternals website, extract the exe file to your desktop, and double-click on it.
-
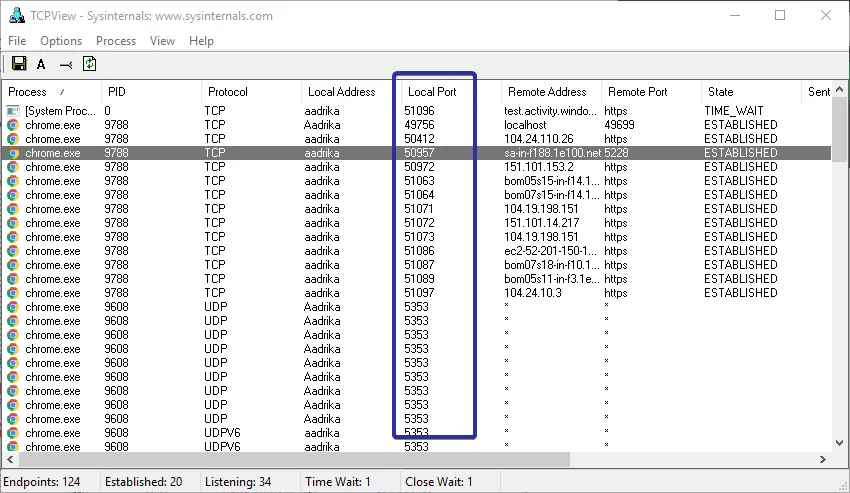
As soon as you open the application, you will see a user agreement. Agree to the agreement, and you will instantly see all the TCP connections and ports in use. You will find the port numbers under the Local Port section.
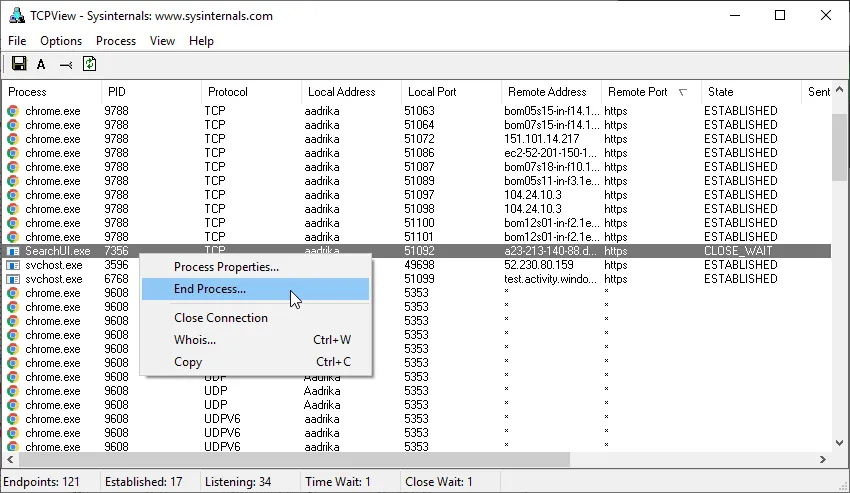
-
You can end the connection and free the port if you want to. To do that, right-click on the connection and select “End Process.” This will terminates the process.