Applies ToWindows 11 Windows 10
Чтобы узнать, сколько ядер и логических процессоров имеет процессор на устройстве с Windows, выполните следующие действия.
-
Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши меню Пуск и выберите Диспетчер задач.
Совет: При нажатии клавиш CTRL + SHIFT + ESC на клавиатуре также открывается диспетчер задач.
-
Когда откроется окно диспетчера задач , выберите вкладку Производительность в левой части окна, а затем убедитесь, что выбран параметр ЦП .
-
Количество ядер и логических процессоров на устройстве с Windows указано рядом со следующими значениями:
-
Ядер:
-
Логические процессоры:
-
Нужна дополнительная помощь?
Нужны дополнительные параметры?
Изучите преимущества подписки, просмотрите учебные курсы, узнайте, как защитить свое устройство и т. д.
Как узнать сколько ядер у процессора
Если по какой-то причине у вас возникли сомнения по поводу количества ядер CPU или просто одолело любопытство, в этой инструкции подробно о том, как узнать сколько ядер процессора на вашем компьютере несколькими способами.
Заранее отмечу, что не следует путать количество ядер (cores) и потоков или логических процессоров (threads): часть современных процессоров имеют по два потока (своего рода «виртуальных ядер») на одно физическое ядро и в итоге, заглянув в диспетчер задач вы можете увидеть диаграмму с 8-ю потоками для 4-х ядерного процессора, аналогичная картинка будет и в диспетчере устройств в разделе «Процессоры». См. также: Как узнать сокет процессора и материнской платы.
Способы узнать количество ядер процессора
Посмотреть, сколько физических ядер и сколько потоков у вашего процессора можно различными способами, все они достаточно простые:
- Во встроенной утилите Windows «Сведения о системе»
- С помощью командной строки Windows 10, 8.1 и Windows 7
- В диспетчере задач Windows 10 (в предыдущих версиях в диспетчере задач можно посмотреть лишь число «логических процессоров», т.е. потоков)
- На официальном сайте производителя процессора
- С помощью сторонних программ
Думаю, что это не полный список возможностей, но вероятнее всего их окажется достаточно. А теперь по порядку.
Сведения о системе
В Windows последних версий присутствует встроенная утилита для просмотра основных сведений о системе. Запустить её можно, нажав клавиши Win+R на клавиатуре и введя msinfo32 (затем нажать Enter).
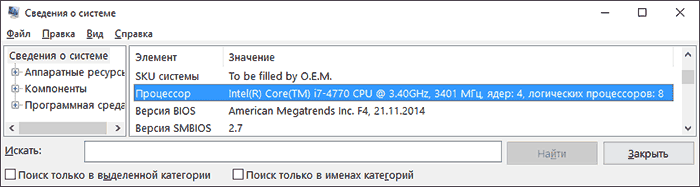
В разделе «Процессор» вы увидите модель вашего процессора, количество ядер (физических) и логических процессоров (потоков).
Узнаем, сколько ядер у CPU компьютера в командной строке
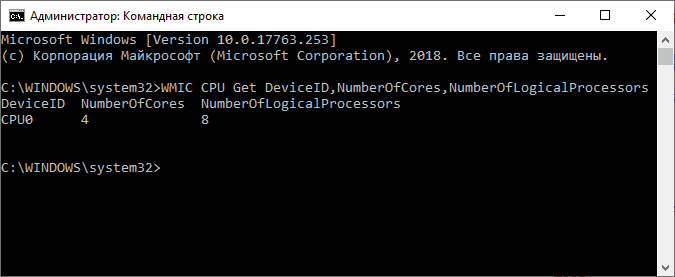
Не все знают, но посмотреть информацию о количестве ядер и потоков можно и с помощью командной строки: запустите её (не обязательно от имени Администратора) и введите команду
WMIC CPU Get DeviceID,NumberOfCores,NumberOfLogicalProcessors
В результате вы получите список процессоров на компьютере (обычно — один), количество физических ядер (NumberOfCores) и количество потоков (NumberOfLogicalProcessors).
В диспетчере задач
Диспетчер задач Windows 10 отображает информацию о количестве ядер и потоков процессора вашего компьютера:
- Запустите диспетчер задач (можно через меню, которое открывается по правому клику на кнопке «Пуск»).
- Перейдите на вкладку «Производительность».

На указанной вкладке в разделе «ЦП» (центральный процессор) вы увидите информацию о ядрах и логических процессорах вашего CPU.
На официальном сайте производителя процессора
Если вы знаете модель вашего процессора, которую можно увидеть в сведениях о системе или открыв свойства у значка «Мой компьютер» на рабочем столе, вы можете узнать его характеристики на официальном сайте производителя.
Обычно достаточно просто ввести модель процессора в любой поисковик и уже первый результат (если пропустить рекламные) будет вести на официальный сайт Intel или AMD, где можно получить технические характеристики вашего CPU.
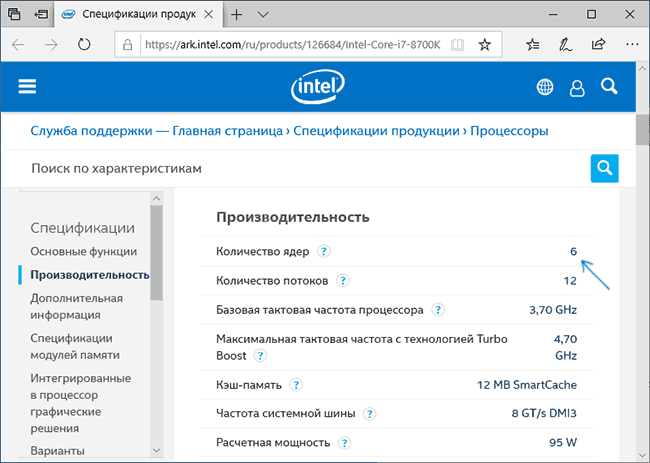
Технические характеристики включают в себя в том числе и информацию о количестве ядер и потоков процессора.
Информация о процессоре в сторонних программах
Большинство сторонних программ для просмотра аппаратных характеристик компьютера показывают, в том числе, и сколько ядер имеет процессор. Например, в бесплатной программе CPU-Z такая информация располагается на вкладке CPU (в поле Cores — количество ядер, в Threads — потоков).

В AIDA64 в разделе ЦП также можно получить информацию о количестве ядер и логических процессоров.
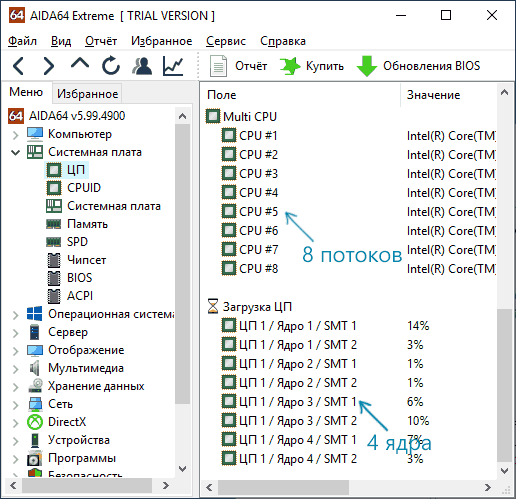
Подробнее о таких программах и где их скачать в отдельном обзоре Как узнать характеристики компьютера или ноутбука.
How To Find CPU Cores In Windows
When it comes to maximizing the potential of your computer, understanding its hardware capabilities is essential. One of the core features of a CPU (Central Processing Unit) that plays a significant role in performance is the number of cores it has. This article will guide you through the process of finding the number of CPU cores in Windows, elaborating on the importance of CPU cores, methods to obtain this information, and additional tips related to CPU performance.
Understanding CPU Cores
Before we delve into how to find the number of CPU cores in your Windows system, it’s vital to grasp what CPU cores are and why they matter.
A CPU core is an individual processing unit within the CPU. Modern CPUs often come with multiple cores, allowing them to perform tasks more efficiently than older single-core processors. Each core can process its own thread of instructions, meaning tasks can be split between multiple cores, which significantly enhances multitasking capabilities and performance.
In contemporary computing, having multiple cores is essential for demanding applications, including video editing, gaming, and software development. Knowing the number of cores your CPU has can help you determine if your computer is capable of handling specific workloads, or whether it may be time for an upgrade.
Methods to Find CPU Cores in Windows
Here are several effective ways to check the number of CPU cores on your Windows machine.
1. Using the Task Manager
The Task Manager in Windows is a powerful tool that can be utilized for various monitoring purposes, including checking your CPU cores.
Steps:
- Press
Ctrl + Shift + EscorCtrl + Alt + Deleteand select Task Manager. - If Task Manager opens in compact view, click on “More details” at the bottom.
- Navigate to the ‘Performance’ tab.
- Click on ‘CPU’ on the left sidebar.
- In the right pane under the «CPU» section, you’ll see information about your processor, including its core count listed as “Cores” and “Logical processors.”
This method provides an easy-to-read overview of your CPU, allowing you not only to see the core count but also other relevant information such as clock speed and utilization.
2. Using System Information
Windows has a built-in tool called System Information that details your system’s hardware components, including CPU cores.
Steps:
- Press
Windows + Rto open the Run dialog box. - Type
msinfo32and press Enter. - The System Information window will open. On the left sidebar, click on “System Summary.”
- Scroll down in the right pane, and look for «Processor.» Here you will find information about your CPU, including the number of cores.
System Information provides a concise summary of system components, making it easy to locate specific details about your CPU.
3. Using Command Prompt
For those who prefer command-line tools, using the Command Prompt is another straightforward way to find out your CPU core count.
Steps:
- Press
Windows + Xand select «Command Prompt» or «Windows PowerShell.» -
Type the following command and press Enter:
wmic cpu get NumberOfCores,NumberOfLogicalProcessors
This command will display the number of cores as well as the number of logical processors (threads). Logical processors may be more than your physical cores due to technologies like Hyper-Threading, which allows each core to handle two threads simultaneously.
4. Using PowerShell
PowerShell provides a more sophisticated command-line interface that can be utilized to gather information about system hardware.
Steps:
- Press
Windows + Xand select «Windows PowerShell.» -
Type the following command and hit Enter:
Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_Processor | Select-Object NumberOfCores, NumberOfLogicalProcessors
This command will output similar information as the Command Prompt command, but with a more PowerShell-specific formatting. You’ll get a clear view of your CPU core count, along with additional processor details.
5. Using Third-Party Software
While Windows provides several built-in tools to check the number of CPU cores, sometimes third-party applications offer a more user-friendly experience. Software like CPU-Z, Speccy, or HWiNFO can provide detailed specifications of your CPU without much hassle.
Steps:
- Download and install a third-party tool like CPU-Z.
- Launch the application, and navigate to the ‘CPU’ tab.
- There you will find detailed information about your processor, including its core count.
Using third-party applications can give you more than just core count; you can see real-time performance stats, temperatures, and various other details that can aid in making informed decisions about your computer’s performance.
Significance of Knowing CPU Cores
Understanding how many cores your CPU has can help in various scenarios:
-
Multitasking and Performance: If you often run multiple applications simultaneously or perform resource-intensive tasks, knowing your CPU’s core count helps you understand how effectively your system can handle those tasks.
-
Software Compatibility: Certain software applications, particularly those used for video editing, 3D rendering, and gaming, have specific requirements related to CPU cores. Knowing your system’s limits ensures you don’t attempt to run programs that exceed your CPU’s capabilities.
-
Upgrades and Compatibility: When considering an upgrade, knowing your core count can influence your decision. If you find your current setup lacking in performance due to limited cores, you might choose to invest in an upgrade that provides more processing power.
-
Optimizing System Performance: By understanding your CPU’s specifications, you can tweak settings for better performance. For instance, you can prioritize tasks and allocate resources based on core availability to improve software performance.
Additional CPU Performance Tips
Beyond knowing how to find CPU cores, there are several other considerations to optimize your CPU performance:
-
Monitor Temperatures: High temperatures can adversely affect performance. Use tools like Core Temp or HWMonitor to keep an eye on your CPU temperature. Ensure that your cooling solution, such as fans or liquid cooling, is functioning correctly to maintain optimal performance.
-
Optimize Power Settings: Windows power settings can considerably impact CPU performance, especially in laptops. Set your power plan to “High Performance” to ensure the CPU operates at its full potential when plugged in.
-
Keep Software Updated: Regularly updating your operating system and drivers can enhance performance. Updates often include performance improvements and optimizations that can help utilize your CPU better.
-
Limit Background Processes: Too many active processes can detract from performance. Monitor your CPU usage in Task Manager and close unnecessary applications and processes to allocate more resources to your primary workload.
-
Consider Overclocking: If you’re familiar with hardware tweaks, overclocking your CPU can provide a significant performance boost. However, this should be approached with caution, as it can lead to overheating and stability issues if not managed correctly.
-
Invest in Quality Hardware: If your tasks demand high performance, consider upgrading to a CPU with more cores, higher clock speeds, or support for newer technologies like DDR5 memory and PCIe 4.0.
Conclusion
Understanding your CPU’s core count is crucial in optimizing your overall computing experience. Whether you’re using integrated tools like Task Manager or System Information, command-line utilities in Command Prompt or PowerShell, or opting for third-party applications, the methods outlined in this article enable you to assess your CPU effectively. Knowing these details can significantly impact your workflow, system upgrades, and performance optimization strategies.
As technology continues to evolve, keeping an eye on your system’s capabilities ensures you are well-prepared to tackle increasingly demanding applications and use cases. With the right knowledge and tools at your disposal, you can harness the full potential of your CPU and improve your overall computing experience.
January 31, 2019 updated by
Leave a reply »
How to find out how many physical cores and logic cores your CPU has? Need to check the CPU core before you buy a new laptop? In this tutorial we’ll show you 4 simple ways to find number of physical cores and logical cores in your CPU on Windows 10.
Physical Core VS. Logical Core
A physical core is an actual physical processor core in your CPU. Each physical core has its own circuitry and its own L1 (and usually L2) cache can read and execute instructions separately (for the most part) from the other physical cores on the chip. A CPU with two physical cores is called a dual-core processor and four physical cores is called a quad-core processor.
A logical core (also known as logical processors) is more of a programming abstraction than an actual physical entity. Logical cores are the abilities of a single physical core to run multiple tasks or threads simultaneously. For example, if you have a quad core CPU and each of its physical cores can run two threads at a time, then you have 8 logical cores.
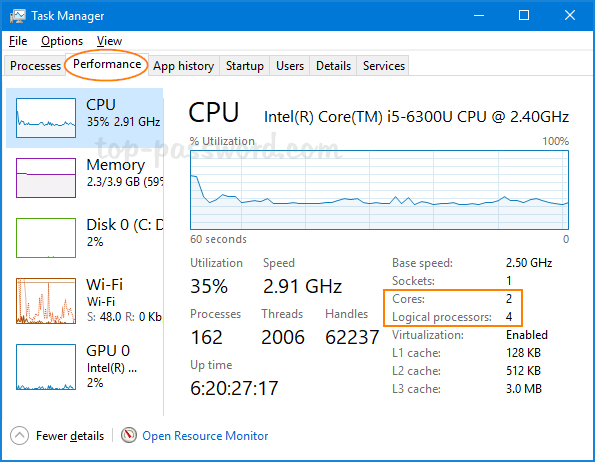
Method 1: Check Number of CPU Cores Using Task Manager
Press the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys simultaneously to open the Task Manager. Go to the Performance tab and select CPU from the left column. You’ll see the number of physical cores and logical processors on the bottom-right side.
Method 2: Check Number of CPU Cores Using msinfo32 Command
Press the Windows key + R to open the Run command box, then type msinfo32 and hit Enter.
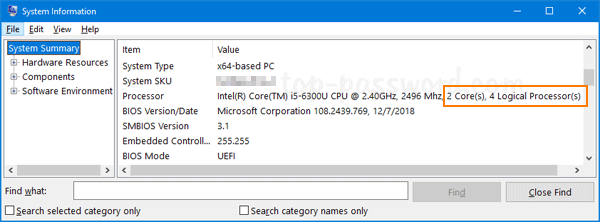
It should open up the System Information app. Select Summary and scroll down until you find Processor. The details will tell you both how many cores and logical processors your CPU has.
Method 3: Check Number of CPU Cores Using Command Prompt or PowerShell
Open the Command Prompt or PowerShell. Type the following command and press Enter:
WMIC CPU Get DeviceID,NumberOfCores,NumberOfLogicalProcessors
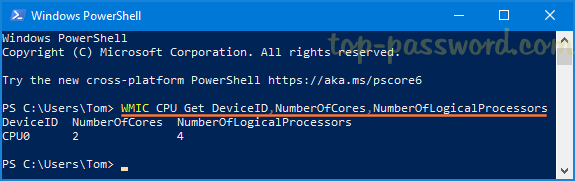
The output of the command tells you how many cores and how many logical processors are found in each CPU on your computer.
Method 4: Check Number of CPU Cores Using Third-Party Software
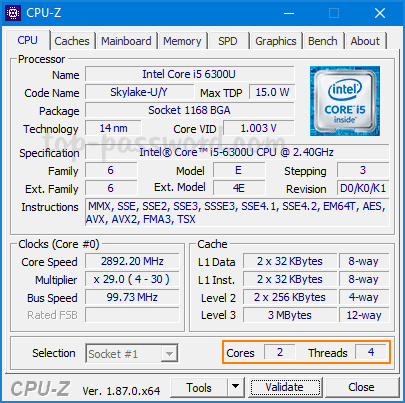
If you would like to find out the detail information about your CPU, try the third-party freeware CPU-Z. After running the app, you can see the number of physical cores and threads (logical cores) at the bottom.
That’s it!
- Previous Post: VMware: How to Boot a VM from USB Stick
- Next Post: Fix: Duplicate User Names on Windows 10 Login Screen
Привет, друзья. В этой публикации рассмотрим такой вопрос: как узнать количество ядер процессора. Как узнать, сколько ядер, и сколько потоков у процессора, если он поддерживает гиперпоточность. В среде Windows делается это очень просто её же системными средствами. Также для получения такой информации можно использовать специальные программы для диагностики компьютерных комплектующих. Давайте рассмотрим все средства решения поставленной задачи.
Итак, ядра и потоки процессоров, это два неразрывно связанных понятия. Ядра – аппаратные, т.е. физические, они обеспечивают выполнение задач, возложенных на процессор по обработке информации. Некоторые процессоры Intel поддерживают технологию гиперпоточности Hyper-Threading, это значит, что у таких процессоров физические ядра имеют по два логических потока, которые помогают ядрам более эффективно (на 30%) справляться со своими задачами. Узнаем же, сколько ядер и потоков при наличии последних имеется у нашего процессора.
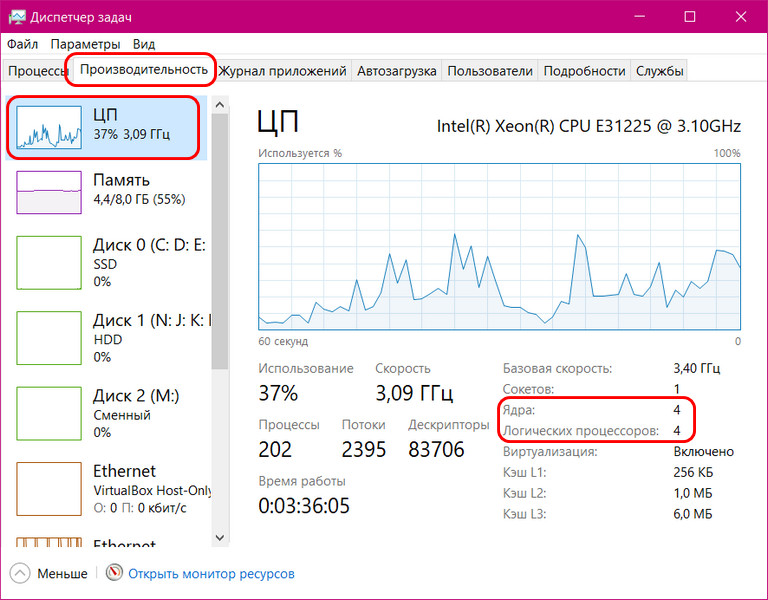
В Windows 10 и 8.1 можем использовать системный диспетчер задач, вызывается клавишами Shift+Ctrl+Esc, либо опциями в контекстном меню на панели задач или меню по клавишам Win+X. Во вкладке «Производительность» переключаемся на раздел «ЦП» и смотрим графы:
- «Ядра», где будет указано число ядер процессора;
- «Логических процессоров», где будет указано число потоков.
Если процессор не поддерживает Hyper-Threading, потоков будет указано столько же, сколько и ядер.
Друзья, в принципе максимум информации о своём процессоре – ядра, потоки, частоты, поддерживаемые технологии и т.п. – можно узнать на его страничке спецификаций на сайте производителя, т.е. на сайте компаний Intel и AMD. Вам для этого нужно загуглить запрос нечто «модель процессора + сайт». А модель своего процессора в среде Windows узнать можно узнать элементарно – с помощью системного диспетчера устройств. Запустить его можно в Windows 10 и 8.1 в меню по клавишам Win+X, во всех системах Windows – с помощью ввода в системный поиск непосредственно названия диспетчера или технического названия его приложения:
devmgmt.msc
В диспетчере устройств, в разделе «Процессоры» и увидим название модели нашего процессора. Кстати, процессоров здесь будет числиться столько, сколько у него ядер или потоков.
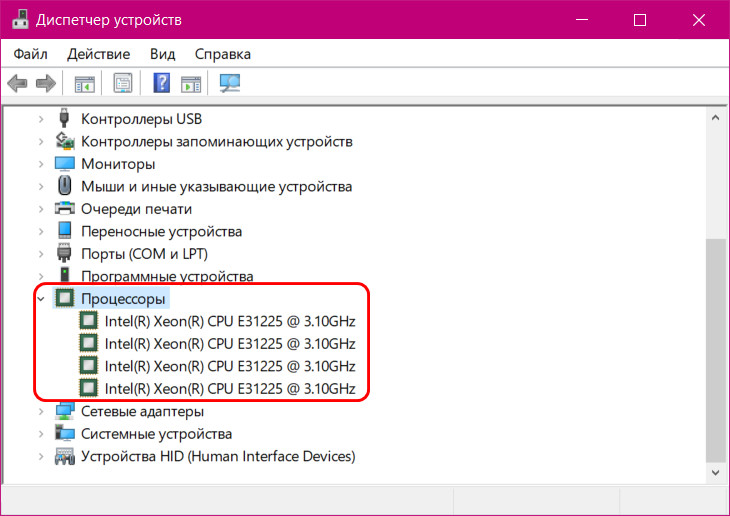
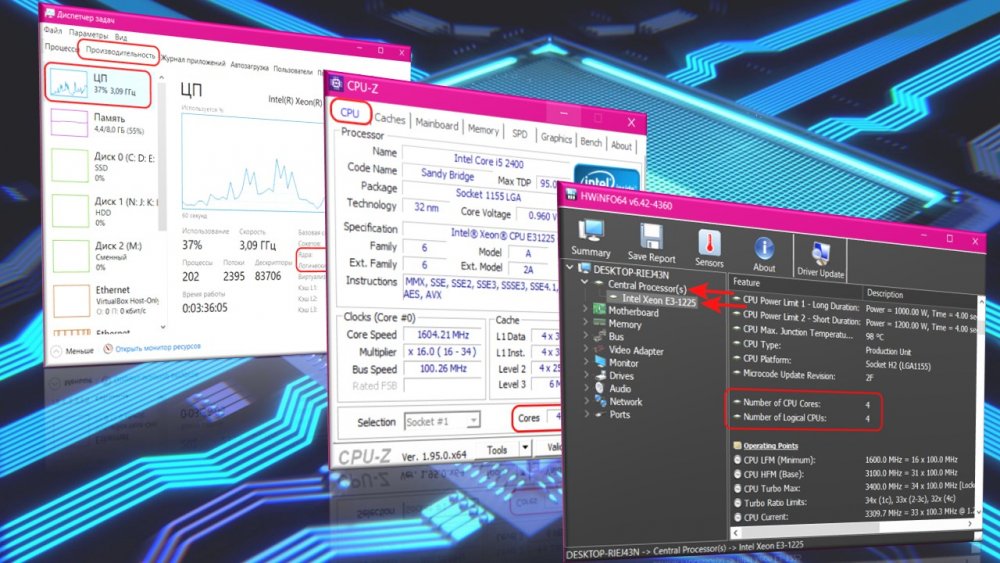
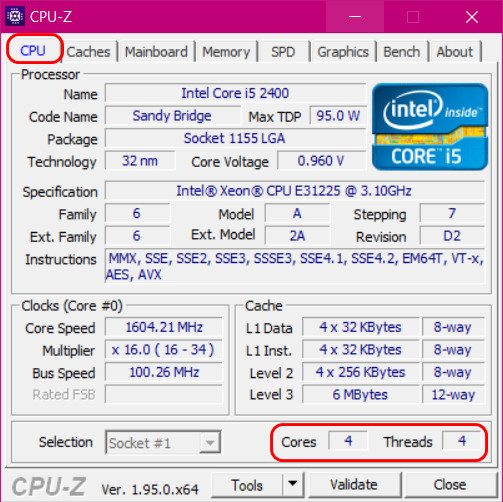
Узнать количество ядер процессора можно с помощью бесплатной программы-диагноста CPU-Z. Она отображает характеристики базовых комплектующих компьютера, с её помощью можно много чего узнать о начинке своего ПК или ноутбука. В первой вкладке «CPU» этой программы будет содержаться информация о процессоре. И в самом низу увидим:
- В графе «Cores» число ядер процессора;
- В графе «Threads» число потоков для процессоров, у которых есть поддержка Hyper-Threading.
Опять же, если процессор без технологии гиперпоточности, потоков для него будет указано столько, сколько ядер.
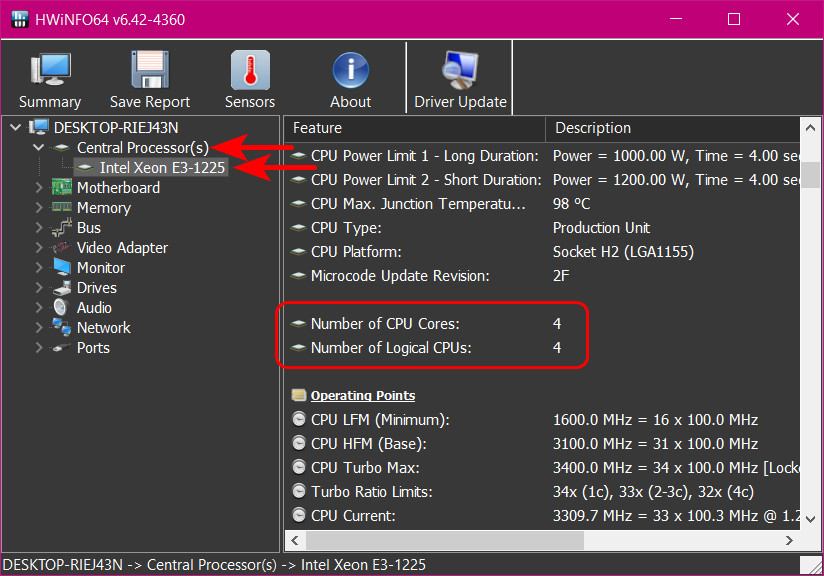
Ну и ещё одна программа, показывающая сколько ядер у процессора, не могу, друзья, не упомянуть лишний раз о ней – HWiNFO. Совершенно бесплатная, при этом по уровню детализации информации о комплектующих компьютера сравнима с известной AIDA64, пригодится во многих случаях. В программе HWiNFO идём в раздел «Central Processor(s)», и там будут графы:
- «Number of CPU Cores», показывающая число ядер;
- «Number of Logical CPUs», показывающая число потоков для процессоров с технологией гиперпоточности.
И здесь также, если процессор без гиперпоточности, его число потоков будет таким же, как и число ядер.