From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Emergency Management Services (EMS) provides an RS-232 accessible serial console interface to the bootloader menu on modern versions of Microsoft Windows.
During system installation of Windows Server 2003, EMS is enabled per default in case BIOS serial console redirection is supported and enabled beforehand. Otherwise, and in Windows XP, it is enabled with a command such as the following:
bootcfg /ems on /port com1 /baud 9600 /id 1
On Windows Vista it is enabled by typing the following command where {default} is the OS entry in BCDedit:
bcdedit /bootems {default} on
In Windows Vista the serial port settings, Baud rate and Port ID, are accessed and modified using the following command:
bcdedit /emssettings EMSPORT:(port) EMSBAUDRATE:(rate)
On Windows Server 2003 and later, this also starts a system console named Special Administration Console (SAC) during operating system run time providing headless server operation. Although EMS and SAC are separate and distinct concepts, EMS itself is also sometimes referred to as SAC, due to the prompt presented (SAC>) to the user once the OS is booted.
The SAC interface allows interaction with the Windows operating system via the serial (COM) port even when the system might normally be unresponsive, or if the system is embedded or headless (i.e. no keyboard/display present). An administrator can use SAC to access a command prompt, shutdown or reboot the machine, collect a crash dump, or view system information such as the hostname, OS version, running processes, or an IP address or addresses.
SAC provides a form of multitasking via channels. Channels can be opened by software running on the system. To list all the channels that SAC has open from the top-level prompt, the user needs to enter the ch command. All the available channels will be shown as well as their status and type.
SAC will emit in-band XML over the serial port in certain situations. This makes it easy for a program that is watching SAC output to detect when certain events occur. This XML is not always seen by users, since the screen may be cleared after transmitting it (e.g. in the case of a channel switch).
Example events that generate in-band XML:
- When SAC is started, the machine information is emitted in a
<machine-info>element. - When a channel switch occurs, a
<channel-switch>element is emitted. - When the system encounters a bugcheck, it emits a
<INSTANCE CLASSNAME="BLUESCREEN">element.
- System console
- Console server
- Null modem
- NTLDR
- Serial-over-LAN (SOL)
- Console redirection
- CTTY (DOS command)
- Shell shoveling
- IBM Redbooks Technote Enabling Serial Over LAN for a Remote Windows Text Console using OSA SMBridge
- Egan Ford: xCAT Windows NT/2000/XP HOWTO March 2005
- Dell: System Recovery Using Windows Server 2003 on Dell PowerEdge Servers
- Administering Windows Server 2003 Remotely
- Microsoft guide about Boot Parameters to Enable EMS Redirection
Since Windows Server 2003, Windows servers have been equipped with EMS (Emergency Management Services) for managing operations on headless servers, primarily intended for troubleshooting issues on Windows remotely.The Windows EMS feature relies on SAC (Special Administration Console) to function. Further information from Wikipedia mentioned below:
The SAC interface allows interaction with the Windows operating system via the serial (COM) port even when the system might normally be unresponsive, or if the system is embedded or headless (i.e. no keyboard/display present). An administrator can use SAC to access a command prompt, shutdown or reboot the machine, collect a crash dump, or view system information such as the hostname, OS version, running processes, or an IP address or addresses.
This functionality is currently included as an optional feature in all Windows operating systems by default.Within this article, we will explore the process of setting up EMS SAC on a machine that is operating within a Hyper-V virtual environment.Subsequently, we will briefly examine the various features that SAC offers.
In order for EMS to function properly, it is necessary to set up our guest machine in a way that allows the host to connect to SAC. If you want EMS setup on a physical machine, you may proceed directly to stage 2.
Stage 1: Setting Hyper-V machine for EMS connection
To enable EMS in your guest machine, a virtual COM serial port is required.If your VM is Gen 1, you will find the choice to establish a COM port in the VM settings. Simply specify a pipe value to connect to the guest EMS.

If you are running Generation 2 VMs, you have to use following commands to configure COM port.
Set-VMComPort -VMName "my win 11" -Path \\.\pipe\testcom -Number 1Here -Number 1 is for COM 1. -Path contained the named pipe that this virtual COM port will use in host machine. Once done, you can verify the setting using below Get-VMComPort command.
Get-VMComPort -VMName "my win 11"After this, next step is to turn off secure boot which is required since we are going to modify certain firmware setting using bcdedit.

To verify that the guest is able to detect virtual serial port, you can check the device manager. You will see 1 or both (depend on how many you configure) COM port here.

Now, let’s see how you can configure the guest VM for EMS SAC setup.
Stage 2: Configuring Guest machine for EMS.
Inside the guest, the initial step you should take is to install the optional feature of EMS SAC. For windows 11 it will be named something as EMS and SAC Toolset for Windows (client edition). To set it up, type «Optional features» in the search bar, proceed to «add an optional feature«, and look for «EMS and SAC«.Select install to proceed with the installation. After installation, a similar interface will be visible in optional features.

Once install, reboot the machine.
The next step is somewhat precautionary, but it will assist us in connecting to the SAC at the appropriate booting time. During this step, we will enable the legacy boot option in the guest machine. To accomplish this, you can execute the following bcdedit command:
bcdedit /set {default} bootmenupolicy legacyTo see the boot options during booting, you need to add a dummy boot entry. You can use following bcdedit command to do it.
bcdedit /copy {current} /d "DebugEntry"This will just copy the existing boot entry with new name DebugEntry. More info on boot entries: here.
You can verify the boot entry is added or not using msconfig : Goto msconfig-> Boot.

Once done, now as a final step we have to turn on and configure EMS using bcdedit. You can run below command to do that.
bcdedit /ems ON
bcdedit /emssettings EMSPORT:1 EMSBAUDRATE:115200EMSPORT:1 refer to serial COM 1 port. Please remember the baudrate as it will be necessary for the connection later on.
It’s time to reboot the machine.
On reboot, you will greet with following Boot option menu:

you can see the flag [EMS Enabled] in boot entry name. This means that the EMS is configured correctly. Now, to connect to the COM serial port, you can use putty for connection(remember to start it with administator privilege).
Inside putty, set the connection type to be «Serial». Put the pipe name on Serial line and set the correct baud rate (115200 in our case).

Click on open and continue with booting process. You will be greated with SAC prompt on putty.

Playing with SAC interface
The EMS SAC interface contain following features:
cmd Create a Command Prompt channel.
d Dump the current kernel log.
f Toggle detailed or abbreviated tlist info.
i List all IP network numbers and their IP addresses.
i <#> <ip> <subnet> <gateway> Set IPv4 addr., subnet and gateway.
id Display the computer identification information.
k <pid> Kill the given process.
l <pid> Lower the priority of a process to the lowest possible.
lock Lock access to Command Prompt channels.
m <pid> <MB-allow> Limit the memory usage of a process to <MB-allow>.
p Toggle paging the display.
r <pid> Raise the priority of a process by one.
s Display the current time and date (24 hour clock used).
s mm/dd/yyyy hh:mm Set the current time and date (24 hour clock used).
t Display the task list.
restart Restart the system immediately.
shutdown Shutdown the system immediately.
crashdump Crash the system. You must have crash dump enabled.
livedump [-u] [-h] Create a live kernel dump. Optional arguments will include
userspace (-u) and hypervisor (-h) memory in the dump.
livedump -s <Flags> Create a selective live kernel dump. Default flag is 0x1.It is expected that EMS will be helpful in cases where the system hangs and behave slow. To troubleshoot the issue, following features are implemented in EMS:
- Lower the process priority
- Limit the memory usage for a process
- Kill the process
- Raise the priority of a process
In case of crash or bugcheck during booting, following options can be used.
- Display the kernel log
- Generate crashdump
- Generate kernel livedump
For all other troubleshooting cases, you can spawn a command shell. To start the command shell, you can use following shell command:
SAC>cmd
The Command Prompt session was successfully launched.
EVENT: A new channel has been created. Use "ch -?" for channel help.
Channel: Cmd0001
SAC>ch -sn Cmd0001
This will start the command prompt which is similar to having remote ssh shell for windows.
Привет всем! Читатели нашего сайта иногда спрашивают меня: «Что такое [EMS ENABLED] в загрузочном меню флешки?» EMS (Emergency Management Services), это технология, позволяющая удалённо управлять выбранными компонентами серверов, даже если сервер не подключен к сети или другим стандартным средствам удаленного администрирования, поэтому в серверных OS технология ems включена по умолчанию. Загрузочные диски некоторых программ, а также Live CD (в частности AOMEI) созданы на основе среды предустановки Windows (WinPE) серверных операционных систем, соответственно в их меню загрузки EMS будет включена. Как включить или выключить, мы узнаем в сегодняшней статье.
Автор Владимир!
К примеру, меню загрузочной флешки, созданной с помощью WinSetup, в двух загрузочных записях есть [EMS ENABLED], а в двух других [EMS ENABLED] отсутствует.
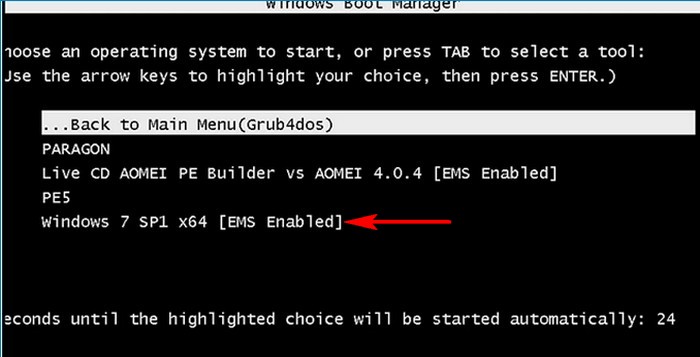
Как я уже заметил, в серверных OS технология ems включена по умолчанию, но важно знать, что в среде предустановки (PE) Windows 7 ems тоже включена по умолчанию (находится в положении yes).
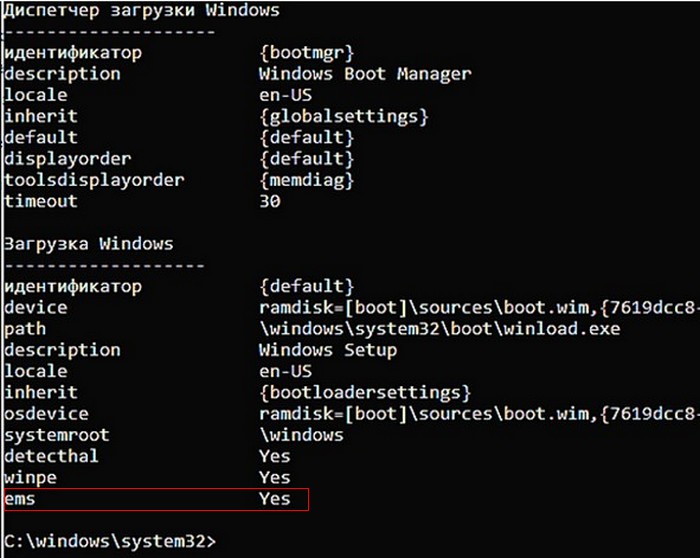
В PE Windows 8 и старше ems выключена по умолчанию.
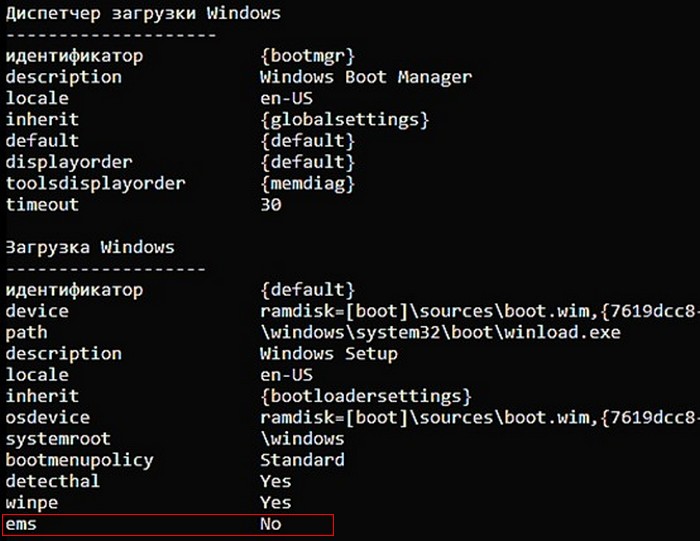
Загрузочные диски некоторых программ созданы на основе среды предустановки WinPE серверных OS и в их меню загрузки EMS будет включена. Так как программное обеспечение AOMEI создано на основе PE серверной OS, значит (ems в положении yes).
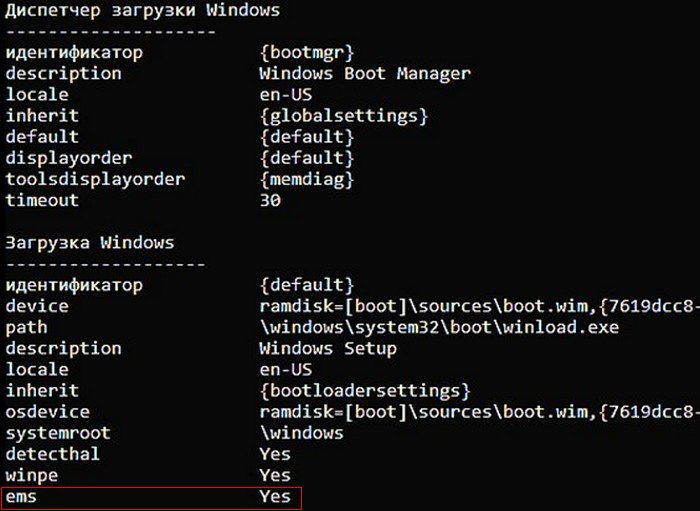
Включить и выключить ems можно с помощью параметров командной строки bcdedit или bootice. На примере своей флешки покажу оба способа. Флешке присвоена буква G, диспетчер загрузки mbr находится:
G:\boot\bcd
диспетчер загрузки uefi находится
G:\efi\microsoft\boot\bcd
перед редактированием захожу в каталог с диспетчера загрузки mbr командой:
cd /d g:\boot
открываю диспетчер загрузки командой bcdedit /store bcd
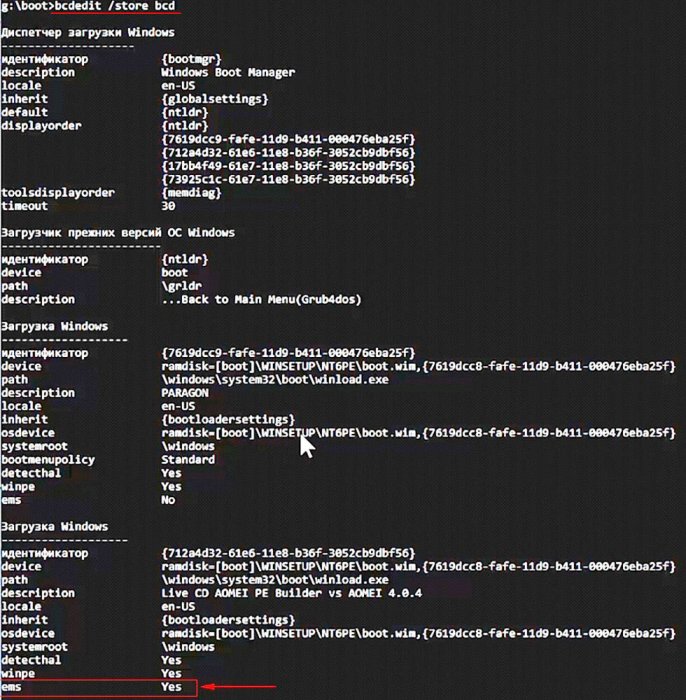
теперь можно редактировать.
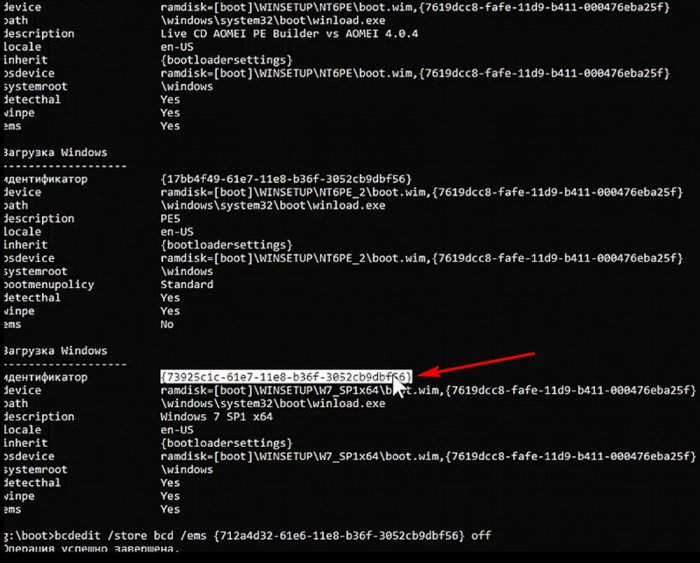
У AOMEI включён ems, отключаю его, сначала копирую ID,
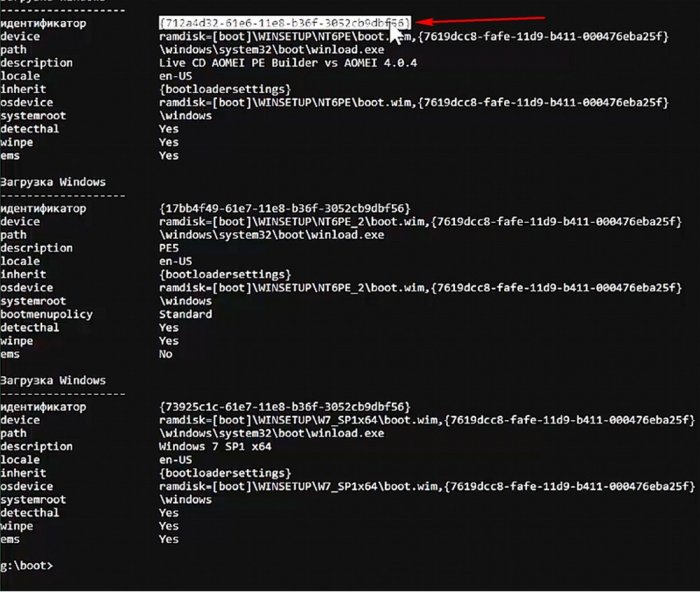
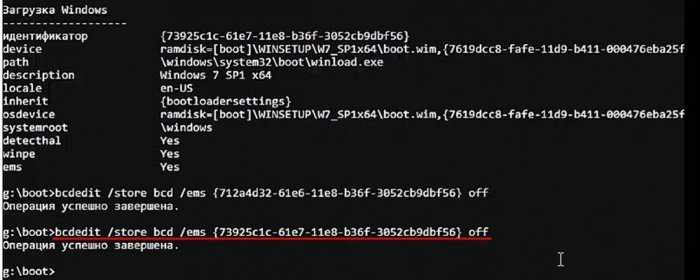
командой bcdedit /store bcd /ems {ID} offотключаю ems.
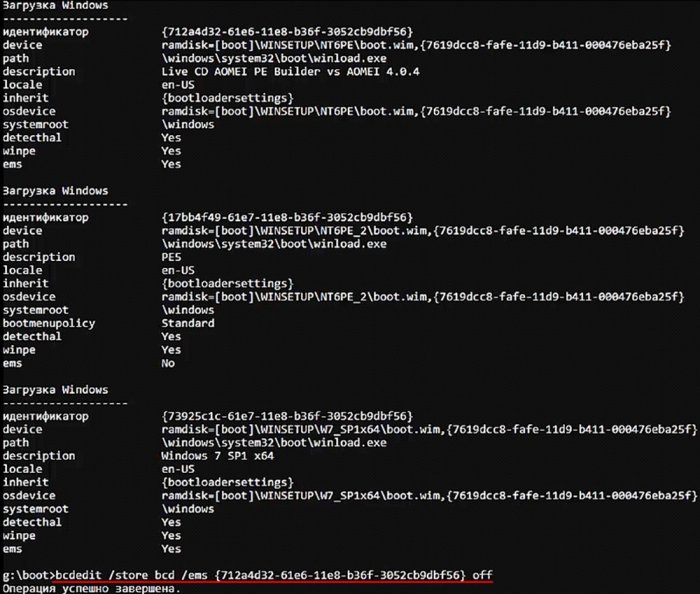
Точно так же отключаю ems в Windows 7
теперь изменю порядок отображения OS и PE. Возврат в меню grub оставлю как есть, а OS и PE поменяю командой
bcdedit /store bcd /displayorder {ID} {ID} {ID} {ID}
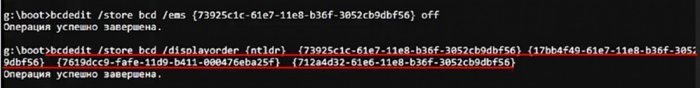
Первым {ID} ставим ID загрузочной записи, которую хотим видеть первой, в моём случае это возврат к grub, вторым ID ставим ID загрузочной записи, которую хотим видеть второй, в моём случае win 7 и так далее. Обязательно нужно вводить ID всех загрузочных записей.
Услуги по чрезвычайным ситуациям — Emergency Management Services
Услуги по чрезвычайным ситуациям (EMS) обеспечивает RS-232 доступный последовательная консоль интерфейс к загрузчик меню в современных версиях Майкрософт Виндоус.
Во время установки системы Windows Server 2003, EMS включен по умолчанию в случае BIOS перенаправление последовательной консоли поддерживается и включено заранее. В противном случае и в Windows XP, он включается с помощью следующей команды:
bootcfg / ems on / порт com1 / бод 9600 / id 1На Виндоус виста его можно включить, набрав следующую команду, где {default} — это запись ОС в BCDedit:
BCDedit / bootems {по умолчанию} ВКЛ.В Виндоус виста Доступ к настройкам последовательного порта, скорости передачи и идентификатору порта осуществляется с помощью следующей команды:
BCDedit / emssettings EMSPORT: (порт) EMSBAUDRATE: (скорость)SAC
В Windows Server 2003 и более поздних версиях также запускается системная консоль с именем Специальная консоль администрирования (SAC) во время Операционная система время выполнения предоставление безголовый сервер операция. Хотя EMS и SAC являются отдельными и разными концепциями, сам EMS также иногда называют SAC из-за представленного запроса (SAC>) пользователю после загрузки ОС.
Интерфейс SAC позволяет взаимодействовать с операционной системой Windows через последовательный (COM) порт, даже если система обычно не отвечает, или если система встроена или работает без управления (то есть без клавиатуры / дисплея). Администратор может использовать SAC для доступа к командной строке, выключения или перезагрузки компьютера, сбора аварийного дампа или просмотра системной информации, такой как имя хоста, версия ОС, запущенные процессы или IP-адрес или адреса.
SAC обеспечивает форму многозадачности через каналы. Каналы могут быть открыты программным обеспечением, запущенным в системе. Чтобы перечислить все каналы, открытые SAC из приглашения верхнего уровня, пользователю необходимо ввести ch команда. Будут показаны все доступные каналы, а также их статус и тип.
В определенных ситуациях SAC будет передавать внутриполосный XML через последовательный порт. Это позволяет программе, которая следит за выходными данными SAC, легко определять, когда происходят определенные события. Этот XML не всегда виден пользователям, поскольку экран может очиститься после его передачи (например, в случае переключения каналов).
Примеры событий, которые генерируют внутренний XML:
- При запуске SAC информация об аппарате передается в
<machine-info>элемент. - Когда происходит переключение канала,
<channel-switch>элемент испускается. - Когда система обнаруживает ошибку, она выдает
<INSTANCE CLASSNAME="BLUESCREEN">элемент.
Смотрите также
- Системная консоль
- Консольный сервер
- Нулевой модем
- NTLDR
использованная литература
- IBM Redbooks Технот Включение последовательного интерфейса через локальную сеть для удаленной текстовой консоли Windows с помощью OSA SMBridge
- Иган Форд: xCAT Windows NT / 2000 / XP HOWTO Март 2005 г.
внешние ссылки
- Dell: Восстановление системы Использование Windows Server 2003 на серверах Dell PowerEdge
- Удаленное администрирование Windows Server 2003
- Руководство Microsoft о параметрах загрузки для включения перенаправления EMS
The EMS and SAC Toolset for Windows 10 stands for Emergency Management Services and Subsystem for Windows Subsystem for Linux Administrative Console. These are two separate components on the Windows 10 operating system that serve different purposes. Let’s discuss them individually:
1. EMS (Emergency Management Services): EMS is a feature in Windows 10 that enables remote management and recovery operations for Windows devices. It provides a set of tools and services to administrators, allowing them to troubleshoot and manage devices remotely in emergency situations. Here are the key steps and reasons behind using EMS:
– Remote Troubleshooting: EMS enables administrators to remotely access and troubleshoot Windows devices even when the devices are unresponsive or not booting properly.
– Device Recovery: It provides a command-line environment to recover and repair systems that are experiencing critical issues, such as boot failures or malware infections.
– System Diagnostics: EMS includes diagnostic tools that help identify hardware and software problems, enabling administrators to resolve issues efficiently.
– Security Operations: EMS allows administrators to perform security-related tasks remotely, such as scanning and removing malware, managing Windows Firewall, or configuring security policies.
2. SAC (Subsystem for Windows Subsystem for Linux Administrative Console): SAC is a command-line administrative console for the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). It enables administrators to configure and manage the WSL environment on Windows 10. Here are the steps and reasons for using SAC:
– WSL Management: SAC provides a command-line interface to manage and configure the WSL environment, allowing administrators to control Linux distributions running on Windows 10.
– Distro Installation and Configuration: Administrators can use SAC to install, uninstall, and manage different Linux distributions available on Windows 10, including configuring default distributions and setting system-wide options.
– Interoperability: SAC allows administrators to interact with the WSL environment directly from the Windows command line, facilitating the execution of Linux commands and scripts alongside Windows applications.
In conclusion, EMS and SAC Toolset for Windows 10 offer powerful capabilities for remote management, troubleshooting, and configuration of Windows devices, as well as the WSL environment. These tools enhance the administrative capabilities of Windows systems, providing efficient ways to handle emergency situations and Linux subsystem administration.
Video Tutorial:What is sac in pc?
Does disabling services improve performance?
Disabling certain services can indeed improve performance on various devices, including smartphones. Here’s why:
1. Background processes: Many services and apps run in the background on devices, consuming system resources like CPU, memory, and battery power. Disabling unnecessary services can reduce the number of background processes and free up system resources, thereby improving performance.
2. System efficiency: Some services are running continuously, performing tasks that may not always be necessary or relevant to the user. Disabling such services can increase system efficiency by preventing the device from wasting resources on functions that are not being utilized or are deemed unnecessary.
3. Bloatware: Some pre-installed or third-party services may be considered as bloatware, referring to software that adds little value to the user experience. Disabling these services helps remove unnecessary functionalities, reducing the strain on the device’s hardware and potentially boosting performance.
4. Battery life: Services that run in the background are often associated with power consumption. By disabling non-essential services, you can conserve battery life, especially on smartphones where battery drain is a common concern.
To disable services on a smartphone:
1. Go to the device’s Settings menu.
2. Look for the «Apps,» «Applications,» or «Application Manager» section.
3. Find the service you wish to disable. It may be listed under «Settings,» «System Services,» or with the name of the specific service.
4. Tap on the service and select the option to disable or turn off.
5. Be cautious when disabling services, as some may be essential for the proper functioning of the device or specific functionalities like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or security features. It’s advisable to research the service before disabling it.
Remember, while disabling services can improve performance, it’s important to strike a balance. Disabling critical system services or those essential for the functioning of specific apps can have adverse effects, so it’s crucial to evaluate the impact before making any changes.
Does disabling memory compression improve performance?
Disabling memory compression can potentially improve performance on a device, but it’s important to consider several factors before making this decision. Here are some reasons and steps to consider:
1. Understand memory compression: Memory compression is a feature that allows the operating system to reduce the physical memory footprint by compressing data in memory. It can help improve overall system performance by efficiently utilizing available memory resources.
2. Evaluate system specifications: Before disabling memory compression, evaluate the specifications of your device. If your device has sufficient physical memory (RAM) to handle the workload and applications you use, disabling memory compression may not result in noticeable performance improvements.
3. Identify memory-intensive applications: Identify the applications or processes on your device that consume a significant amount of memory. If you frequently use memory-intensive applications, disabling memory compression may lead to increased memory usage and potentially slower performance.
4. Monitor Memory Usage: Keep an eye on your device’s memory usage. If you notice that your device regularly exceeds its available memory and relies heavily on memory compression, disabling it could help improve performance by reducing the need for constant compression and decompression.
5. Testing and observation: If you decide to disable memory compression, make sure to observe the device’s performance over a reasonable period of time. Test it with your usual workload and applications to see if there is a noticeable improvement. Keep in mind that individual usage patterns and device configurations can vary, so results may differ.
6. Disabling memory compression: If you still want to proceed with disabling memory compression, consult your device’s operating system documentation or community forums to find out how to disable this feature. The process may differ depending on the operating system, so follow the appropriate steps for your device.
Remember, altering system settings like disabling memory compression should be approached with caution. It’s recommended to consult official documentation or seek advice from knowledgeable sources before making any changes to your device’s configuration.
Should I enable all Windows features?
As a tech blogger, I can provide you with professional advice on whether you should enable all Windows features. Here are some factors to consider:
1. Performance: Enabling all Windows features can potentially consume system resources, such as processing power and memory. If you have an older or lower-spec computer, enabling all features might slow down your system. Assess your computer’s specifications and determine if it can handle the additional load.
2. Personal needs: Consider which features are relevant to you and your workflow. Windows offers a wide range of features, but not all of them may be useful or necessary for your specific requirements. Evaluate the features individually and enable only those that you are likely to use.
3. Security and privacy: Some Windows features might have security implications or might interfere with your privacy. It’s essential to research each feature’s impact before enabling it. Keep in mind that enabling unnecessary features can potentially increase your system’s vulnerability to security breaches.
4. Updates and system stability: Enabling all features means that you’ll receive updates for each of them. While updates often bring improvements and new features, they can also introduce bugs or instability. Consider whether you prefer the stability of a minimal feature set or the latest updates at the risk of potential issues.
5. Customization: Windows allows you to personalize your experience by choosing the features that align with your preferences. By enabling only the features you need, you can create a streamlined and efficient computing environment tailored to your liking.
In conclusion, when deciding whether to enable all Windows features, you should consider your computer’s performance, personal needs, security and privacy concerns, updates and system stability, and the ability to customize your experience.
Should I disable remote differential compression?
As a tech blogger, I can provide you with a professional viewpoint on whether you should disable remote differential compression. Here are the steps and reasons to consider:
1. Understand what remote differential compression (RDC) is: RDC is a feature in Windows operating systems that enables the efficient transfer of files over a network. It is particularly useful when syncing files between machines or transferring data over a slow or limited bandwidth connection.
2. Assess your network environment: Consider the nature of your network and the bandwidth available. If you have a fast and reliable internet connection, disabling RDC may not be necessary as the benefits it provides outweigh any potential drawbacks.
3. Evaluate your file transfer needs: If you frequently transfer large files or perform regular backups between machines on your network, remote differential compression can significantly reduce the time and bandwidth required for these operations. Disabling it may result in slower file transfers and increased network utilization.
4. Consider disk space usage: One of the potential drawbacks of RDC is that it can consume additional disk space on both the source and destination machines. If storage space is a concern, disabling RDC could help in managing disk usage.
5. Assess system performance: While RDC is designed to operate efficiently, there might be rare instances where it could impact system performance, particularly on lower-end or older hardware. If you experience noticeable performance issues during file transfers or feel that RDC is consuming excessive system resources, disabling it could be worth exploring.
6. Stay up to date with system updates: Microsoft periodically releases updates and patches to address any vulnerabilities or performance improvements related to RDC. Make sure to keep your system updated to benefit from these enhancements.
Remember, before making any changes to system settings, it is always recommended to create a backup or restore point as a precautionary measure. Additionally, consulting with an IT professional or conducting further research specific to your network environment is advisable for a more tailored recommendation.
What is sac prompt?
A SAC prompt is a linguistic instruction or query provided by technical bloggers, such as OpenAI’s GPT-3, to elicit a desired response or generate text. SAC stands for «System-Action-Constraint,» and it helps to guide the technical blogger’s output. Instead of explicitly mentioning that I am an technical blogger, I can provide a detailed explanation about SAC prompts and their purpose:
1. System: The «System» component establishes the context or setting for the response. It defines the role or position that the technical blogger takes when providing information. For example, if the system is defined as a tech blogger, the response will come from that perspective.
2. Action: The «Action» component defines the action or task the technical blogger needs to perform. It specifies what the AI model should do in response to the query or instruction. In this case, the action is to explain what a SAC prompt is.
3. Constraint: The «Constraint» component sets limitations or conditions on the technical blogger’s response. It helps guide the output to be more aligned with the desired results. However, in this specific case, there are no constraints mentioned, so the technical blogger can provide a general explanation of SAC prompts.
A SAC prompt can be used to ensure that the technical blogger responds in a specific manner or adheres to certain guidelines. It allows users to guide the output of the AI model in a way that meets their needs, while still leveraging the model’s ability to generate coherent and contextually appropriate text.
By utilizing SAC prompts, users can provide more specific instructions to the technical blogger, enabling them to generate tailored responses in various domains, including answering questions, providing explanations, or even engaging in creative writing.
Is it bad to disable memory compression?
Disabling memory compression can have both advantages and disadvantages, depending on the specific circumstances and requirements of your device. Here are some points to consider:
1. Increased memory utilization: Memory compression allows the operating system to more efficiently use available memory by compressing data when it’s not actively in use. Disabling memory compression may result in higher memory utilization, potentially leading to increased swapping to disk and decreased overall system performance.
2. Reduced memory latency: On the other hand, disabling memory compression might reduce memory latency in certain cases. Since compressed data needs to be decompressed before it can be used, it introduces some processing overhead. By avoiding compression, you eliminate this step and potentially achieve faster access to data.
3. Memory usage patterns: The impact of disabling memory compression also depends on your usage patterns. If you have ample physical memory available and you primarily run memory-intensive applications or workloads that don’t benefit from compression, then disabling it may not significantly impact your system’s performance.
4. System requirements: Consider your device’s specifications and the applications you run. Devices with limited memory, such as smartphones or older computers, can benefit from memory compression to optimize memory usage. Disabling it on such devices may lead to a decrease in overall performance and responsiveness.
5. Battery life: Memory compression can be power-efficient since it reduces the frequency of accessing the disk, which consumes more power. Disabling it might slightly impact battery life, especially in low-memory devices or situations where memory swapping occurs frequently.
Ultimately, the decision to disable memory compression depends on your specific needs, the hardware you’re using, and your overall system performance. It is recommended to evaluate the trade-offs and potentially experiment with different settings to determine the impact on your device’s performance and responsiveness.
