Creating a virtual drive in Windows 10 can be a breeze if you know the right steps. In essence, you’ll be making a section of your hard drive act like a separate drive, which is handy for organizing files or creating space for specific tasks. This guide will provide you with a detailed, step-by-step method to create a virtual drive in Windows 10.
We’re about to walk through the process of creating a virtual drive in Windows 10. By the end of these steps, you’ll have a new drive letter that functions just like an extra hard drive on your computer.
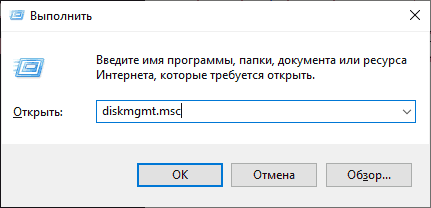
Step 1: Open Disk Management
First, right-click on the Start button and select «Disk Management.»
Disk Management is a built-in utility in Windows 10 that allows you to manage your hard drives and partitions. Opening it is the first step to creating a virtual drive.
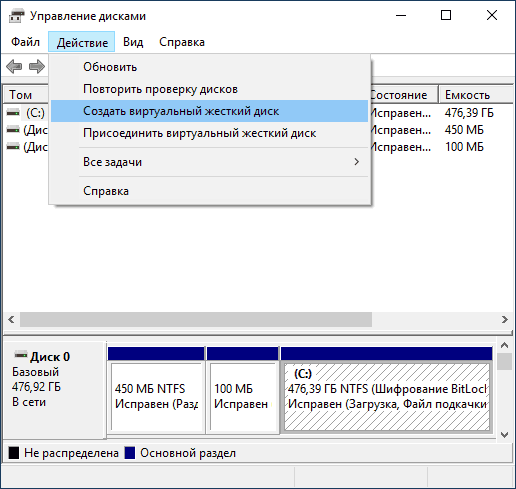
Step 2: Select Action Menu
Next, click on the «Action» menu and choose «Create VHD.»
The «Action» menu is located at the top of the Disk Management window. By selecting «Create VHD,» you begin the process of setting up a virtual hard disk.
Step 3: Specify Virtual Hard Disk Location
Choose a location on your computer to save the virtual hard disk file and click «OK.»
You’ll need to decide where you want to store your virtual hard disk file (.vhd or .vhdx). This could be any folder on your computer.
Step 4: Specify Virtual Hard Disk Size
Enter the size of your virtual hard disk and click «OK.»
You can choose how large you want your virtual drive to be. Whether it’s a few gigabytes or several hundred, make sure you have enough free space on your physical hard drive to accommodate it.
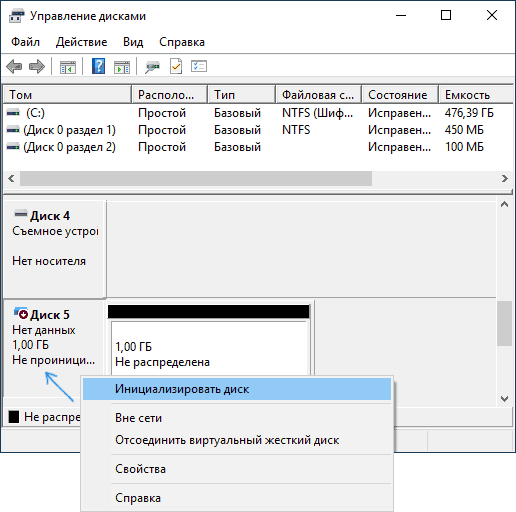
Step 5: Initialize the Virtual Disk
Right-click on the new disk that appears in Disk Management and select «Initialize Disk.»
This step prepares the virtual disk for use. You might be prompted to choose between MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (GUID Partition Table). For most users, MBR should be fine.
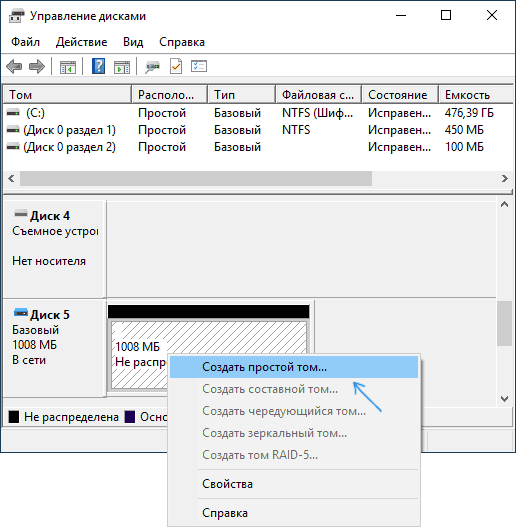
Step 6: Create a New Simple Volume
Right-click on the unallocated space of your new disk and select «New Simple Volume.»
This step will guide you through a wizard to create a new volume on your virtual disk.
Step 7: Follow the Wizard
Follow the New Simple Volume Wizard to assign a drive letter and format the virtual disk.
The wizard will ask you to assign a drive letter (like E: or F:) and format the disk with a file system (usually NTFS). Completing these steps will make your virtual drive ready for use.
After completing these steps, you’ll see your new virtual drive listed among your other drives in File Explorer. You can use it to store files, install programs, or anything else you’d use a regular hard drive for.
Tips for Creating a Virtual Drive in Windows 10
- Ensure you have enough free space on your physical hard drive before creating a virtual drive.
- Use an SSD for better performance if possible.
- Regularly back up important data stored on your virtual drive.
- Consider using the .vhdx format for better performance and features.
- Use descriptive names for your virtual drives to avoid confusion.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I remove a virtual drive in Windows 10?
You can remove a virtual drive by right-clicking on the virtual disk in Disk Management and selecting “Delete Volume.”
Can I expand the size of my virtual drive later?
Yes, you can expand a virtual drive by right-clicking on it in Disk Management and selecting “Extend Volume.”
Is it safe to use a virtual drive?
Yes, virtual drives are safe to use and act like regular hard drives. Just make sure not to delete the .vhd or .vhdx file accidentally.
Can I move the virtual drive file to another computer?
Yes, you can move the .vhd or .vhdx file to another computer and attach it using Disk Management.
What file system should I use for formatting the virtual drive?
NTFS is a good choice for most users, but you can choose FAT32 or exFAT depending on your needs.
Summary
- Open Disk Management.
- Select Action Menu.
- Specify Virtual Hard Disk Location.
- Specify Virtual Hard Disk Size.
- Initialize the Virtual Disk.
- Create a New Simple Volume.
- Follow the Wizard.
Conclusion
Creating a virtual drive in Windows 10 is a straightforward process that offers a ton of flexibility for organizing your files and optimizing your workflow. It can feel like adding a new room to your digital house, giving you more space to work with and keeping things tidy. Whether you’re a power user aiming to compartmentalize different projects or a casual user looking to better organize your files, a virtual drive can be a game-changer.
Remember, always back up your data and ensure you have enough physical storage before creating a virtual drive. If this guide has sparked your interest, dig deeper into Disk Management features or explore other ways to optimize your computer’s storage. Creating a virtual drive in Windows 10 isn’t just a one-off task; it’s a gateway to better file management and a more efficient digital life. So why not give it a try today?
Matt Jacobs has been working as an IT consultant for small businesses since receiving his Master’s degree in 2003. While he still does some consulting work, his primary focus now is on creating technology support content for SupportYourTech.com.
His work can be found on many websites and focuses on topics such as Microsoft Office, Apple devices, Android devices, Photoshop, and more.
Creating a Virtual Drive in Windows 11
In the ever-evolving world of computing, efficiency and adaptability are key drivers of productivity. One powerful tool available to Windows 11 users is the virtual drive. A virtual drive can simulate a physical disk, allowing users to manage files, run applications, and perform tasks without the need for additional physical storage. In this article, we will delve deep into the concept of virtual drives, the various methods to create a virtual drive in Windows 11, and practical applications for utilizing them effectively.
Understanding Virtual Drives
A virtual drive is essentially a software-based representation of a physical disk drive. It can be created from various types of disk images, such as ISO files, VHD (Virtual Hard Disk) files, and other formats commonly used for storing data. Virtual drives enable users to access and manipulate these files as if they were located on a physical drive, providing flexibility in how data and applications are managed.
There are several benefits to using virtual drives:
-
Space Management: Virtual drives allow users to minimize clutter on their physical drives. For instance, instead of keeping multiple ISO files or large applications on your hard drive, you can mount them as virtual drives and ‘unmount’ them when not in use.
-
Enhanced Security: Using virtual drives can improve security. Sensitive information can be stored in a virtual drive and encrypted, ensuring it’s only accessible when needed.
-
Convenient Access to Disk Images: Virtual drives simplify the process of accessing disk images used for installation or booting. They can be mounted directly from the File Explorer, making it easier to work with these files.
-
Testing and Development: Developers often use virtual drives to test software without affecting the physical system or operating environment. Virtual drives provide an isolated space for experimentation.
Creating a Virtual Drive in Windows 11
Now that we understand what virtual drives are and their benefits, let’s go over the various methods to create a virtual drive in Windows 11.
Method 1: Using Windows Explorer to Mount ISO Files
One of the simplest methods to create a virtual drive in Windows 11 is by using the built-in functionality to mount ISO files. Here’s how to do it:
-
Select the ISO File:
Locate the ISO file you want to mount. This could be an operating system installation image, software distribution image, or any other disk image. -
Right-Click:
Right-click on the ISO file to bring up the context menu. -
Select «Mount»:
Click on the “Mount” option. This action creates a virtual drive, and the ISO file will appear in File Explorer under «This PC» as a new drive. -
Access the Virtual Drive:
Open File Explorer and navigate to “This PC.” You will see the newly created virtual drive listed along with your physical drives. You can now access its contents just like a regular disk. -
Eject the Drive:
Once you have finished using the virtual drive, you can right-click on it in Windows Explorer and select “Eject” to unmount it.
Method 2: Using Disk Management to Create a VHD
Another option is to create a Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) using the Disk Management tool. This method allows for greater flexibility as you can define the size of the VHD and format it according to your needs.
Follow these steps:
-
Open Disk Management:
Right-click on the Start menu and select “Disk Management” or pressWin + Xand choose “Disk Management” from the menu. -
Create a VHD:
In the Disk Management window, click on the «Action» menu at the top, and select “Create VHD.” -
Set the VHD Properties:
A dialog box will appear. Here, you need to specify:- Location: Choose where you want to save the VHD file.
- Size: Specify the size of the virtual hard disk. Ensure it’s enough for your intended use.
- VHD Type: Choose between “VHD” (for older systems) or “VHDX” (for modern systems with potential for larger sizes and better reliability).
- Format: You can choose from fixed size or dynamically expanding. A fixed size allocates the entire amount immediately, while dynamically expanding allocates space as needed.
-
Initialize the VHD:
After creating the VHD, it will appear as an uninitialized disk in Disk Management. Right-click on the graphical representation of the newly created VHD and choose “Initialize Disk.” Select the partition style (MBR or GPT) based on your requirements. -
Create a New Volume:
Right-click again on the unallocated space of the VHD and select “New Simple Volume.” Follow the prompts to format the volume and assign a drive letter. -
Access the VHD:
The VHD will now appear in File Explorer as a separate drive. You can now use it to store files, applications, or media. -
Detach the VHD:
When you are finished using the VHD, you can return to Disk Management, right-click on the VHD, and select “Detach VHD.” This option allows you to keep the VHD file intact on your disk for future use.
Method 3: Using Third-Party Software
If you require more advanced features or prefer a more user-friendly interface, third-party software may be the way to go. Popular applications for creating and managing virtual drives include Daemon Tools, WinCDEmu, and Virtual CloneDrive. These tools typically offer additional functions, such as creating and managing multiple virtual drives simultaneously, customizing settings, and enhanced support for various image formats.
Let’s consider a brief example using Daemon Tools:
-
Download and Install: Download Daemon Tools from the official website. Proceed with the installation by following the installed prompts.
-
Launch the Application: Open Daemon Tools after installation.
-
Mount an Image: Click on the “Quick Mount” option. From here, select the image file you want to mount. The software will create a virtual drive automatically.
-
Access the mounted image: Navigate to File Explorer, and the newly created drive will appear, similar to the previous methods.
-
Dismount the Image: To dismount the image, right-click the virtual drive in Daemon Tools and select “Dismount.”
Practical Applications of Virtual Drives
Having created virtual drives using the various methods mentioned, the next step is to understand how to leverage them in practical applications.
Game Installation and Management
Many PC gamers use ISO files to store game installations for easy access. By mounting these ISO files as virtual drives, players can install games without needing to keep a physical copy or cluttering their hard drive with multiple installers.
Software Testing and Development
For software developers, virtual drives can provide an isolated environment to test applications. Instead of relying on multiple physical machines or partitions, developers can create a VHD to test new features or releases while maintaining the integrity of the main system.
Backing Up Data
Backups are crucial for data security. Virtual drives can be used to store backups of essential files. By using dynamic VHDs or even encrypted virtual drives, users can create a secure, easily manageable backup solution.
Running Multiple Operating Systems
Virtual drives allow users to experiment with multiple operating systems without making changes to their main installation. Using virtualization tools (like Hyper-V), users can create VHDs for various operating systems and test applications or learn new skills without affecting their primary setup.
Temporary Storage and File Sharing
Virtual drives can serve as temporary storage solutions. If you’re sharing files with others or transitioning between systems, you can create a virtual drive, mount it, and fill it with necessary items that can be easily carried over and detached when complete.
Conclusion
Creating and managing virtual drives in Windows 11 offers a plethora of benefits, enhancing productivity and organization for professionals and casual users alike. Whether you’re accessing application disk images, creating isolated testing environments, or simply decluttering your physical drives, virtual drives provide a versatile solution.
In mastering the creation of virtual drives using built-in Windows functions or leveraging third-party tools, users can implement these efficient solutions to meet their unique needs, ultimately leading to a more organized and effective computing experience. As software and technology continue to evolve, mastering these tools will remain essential for getting the most out of your digital workspace.
Creating a virtual disk or drive in Windows 7, 8, 8.1 and 10 no longer requires the use of external applications, just a few simple steps.
Creating a virtual drive
Under “Start -> Search programs and files, type in diskmgmt.msc”. The Disk Management window will open. Another way to access this window is by right-clicking on “PC” and then on “Manage”. The Computer Management window will open and then Disk Management can be accessed.
In the Disk Management window, click on the “Action” menu and then on “Create VHD”.
The location of the virtual disk is specified in this new window, to do this, click on «Browse» and select the folder (a new one should be created), assign a name to the file and save it, thus creating the virtual hard disk as a VHD file extension.
The next step is to specify the capacity for the virtual hard disk in the «Virtual disk size» field, by typing in a figure in MB (megabytes), GB (gigabytes) or TR (terabytes).
Next, the format of the disk is specified, either “Dynamically expanding” or “Fixed size”. Windows 7, 8, 8.1 and 10 recommend the “Fixed size” option. The corresponding option is chosen and the window is accepted.
At this point, the creation process will begin, after which the virtual hard disk will be visible in the Disk Manager.
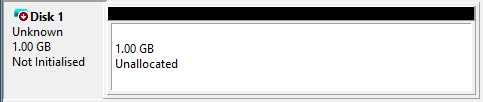
Assigning volume to the disk
As shown in the figure above, the disk has already been created, but a volume or label must be assigned to it, i.e. a letter that does not coincide with any other physical or virtual unit on the system. To do this, right-click on the part where «Disk Unknown» is displayed and choose the «Initialise disk» option, which will display the following window:
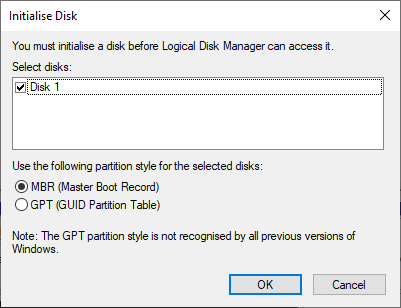
Select the “MBR” or “GPT” partition style and accept the dialogue box. Now, the virtual disk will no longer be displayed as “Unknown” but as “Basic”.

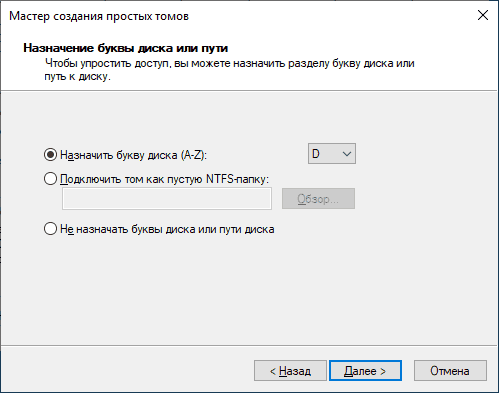
Lastly, right-click on the section where «Unallocated» is shown and select the «New simple volume» option. This will open a wizard:
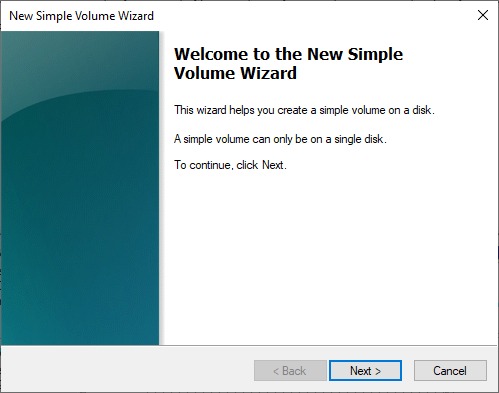
Where the following steps will be carried out:
- The final size of the drive (the same size chosen when creating the VHD should be chosen) is set.
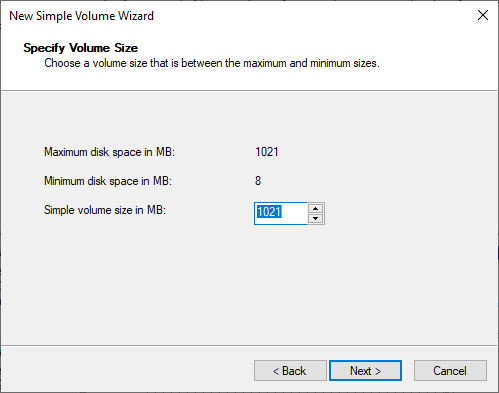
- The drive letter or path is assigned:
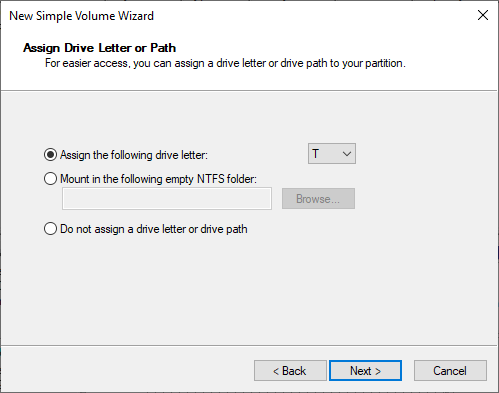
- Whether or not the partition is formatted, and a name or label is defined for the new unit.
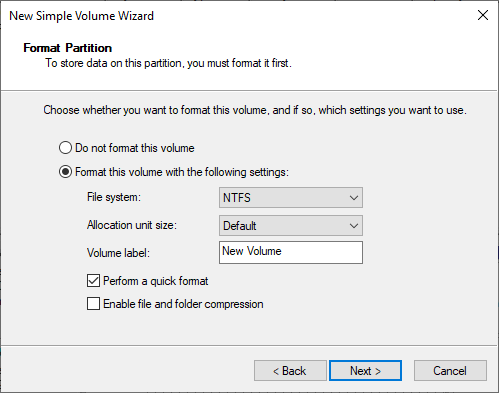
- Lastly, the wizard is finished:
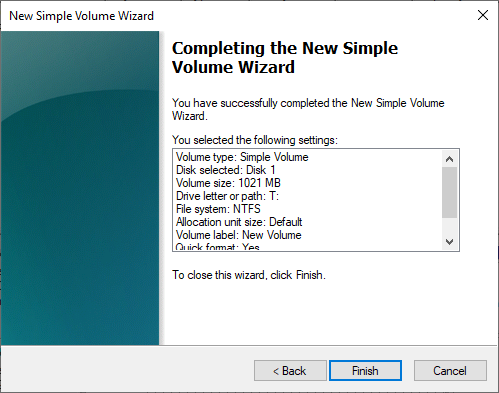
The definition of the virtual hard disk is now complete.
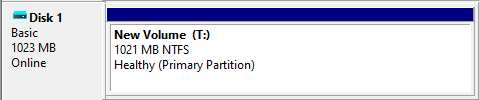
Automatically start the virtual disk when booting
Windows 7, 8, 8.1 and 10 do not automatically start the virtual hard disk every time the computer is booted, so Disk Management would have to be accessed again and the VHD would have to be selected each time. To avoid this, a .bat file can be created to perform this task automatically. The process is as follows:
1.1. A .txt file is created in Notepad with the following:
seselect vdisk file=C:\Path\VirtualDiskx.vhd
attach vdisk
exit
2. Another .bat file is created in Notepad. To do this, the File -> Save option is used and in “Type”, “All files” is selected, allowing the .bat extension to be included in the file name. The contents of the file will be as follows:
diskpart /s C:\Path\previous_text_file.txt
NOTE: the text shown in bold in the described files means that each user must change the locations of the virtual disk and the text file for their own particular case in the aforementioned commands.
3. Finally, this .bat file can be run each time the computer is booted in order to start the disk or a shortcut of this file can be created and located in “Start -> All programs -> Startup” to run this file when starting Windows 7, 8, 8.1 and 10.
Windows 10, 8.1 и Windows 7 позволяют создать виртуальный жесткий диск встроенными средствами системы и использовать его практически как обычный HDD, что может пригодиться для самых разных целей, начиная с удобной организации документов и файлов на компьютере и заканчивая установкой операционной системы. В следующих статьях я подробно опишу несколько вариантов использования.
Виртуальный жесткий диск представляет собой файл с расширением VHD или VHDX, который при монтировании в системе (для этого не требуются дополнительные программы) виден в проводнике как обычный дополнительный диск. В чем-то это схоже со смонтированными файлами ISO, но с возможностью записи и иных вариантов использования: например, вы можете установить шифрование BitLocker на виртуальный диск, получив таким образом зашифрованный файловый контейнер. Еще одна возможность — установка Windows на виртуальный жесткий диск и загрузка компьютера с данного диска. Учитывая, что виртуальный диск доступен и в виде отдельного файла, вы с легкостью можете перенести его на другой компьютер и использовать там.
Как создать виртуальный жесткий диск
Создание виртуального жесткого диска ничем не отличается в последних версиях ОС, разве что в Windows 10 и 8.1 имеется возможность смонтировать файл VHD и VHDX в системе просто дважды кликнув по нему: он тут же будет подключен как HDD и ему будет назначена буква.
Для создания виртуального жесткого диска, выполните следующие простые шаги
- Нажмите клавиши Win+R, введите diskmgmt.msc и нажмите Enter. В Windows 10 и 8.1 можно также нажать правой кнопкой мыши по кнопке Пуск и выбрать пункт «Управление дисками».
- В утилите управления дисками в меню выберите «Действие» — «Создать виртуальный жесткий диск» (кстати, тут же имеется и пункт «Присоединить виртуальный жесткий диск», он пригодится в Windows 7, если требуется перенести VHD с одного компьютера на другой и подключить его).
- Запустится мастер создания виртуальных жестких дисков, в котором необходимо выбрать расположение файла диска, тип диска — VHD или VHDX, размер (не менее 3 Мб), а также один из доступных форматов: динамически расширяемый или с фиксированным размером.
- После того, как вы задали настройки и нажали «Ок», в управлении дисками появится новый, не инициализированный диск, также при необходимости будет установлен драйвер адаптера шины виртуального жесткого диска Microsoft.
- Следующим шагом, кликните правой кнопкой мыши по новому диску (по его заголовку слева) и выберите пункт «Инициализировать диск».
- При инициализации нового виртуального жесткого диска потребуется указать стиль разделов — MBR или GPT (GUID), для большинства применений и небольших размеров дисков подойдет MBR.
- И последнее, что потребуется — создать раздел или разделы и подключить виртуальный жесткий диск в Windows. Для этого кликните по нему правой кнопкой мыши и выберите пункт «Создать простой том».
- Нужно будет указать размер тома (если оставить рекомендуемый размер, то на виртуальном диске будет один единственный раздел, занимающий все его пространство), задать параметры форматирования (FAT32 или NTFS) и указать букву диска.
По завершении операции вы получите новый диск, который будет отображаться в проводнике и с которым можно работать точно также, как с любым другим HDD. Однако помните, где в действительности хранится файл виртуального жесткого диска VHD, так как физически все данные хранятся именно в нем.
В дальнейшем, если вам потребуется отключить виртуальный диск, просто нажмите по нему правой кнопкой мыши и выберите пункт «Извлечь».
-
Home
-
Partition Manager
- A Full Guide to Create a Virtual Disk on Windows 10/8/7
By Ariel | Follow |
Last Updated
Virtual disk can be used to store the files, the operating system and other data like a normal hard disk. A great number of users consult google about how to create a virtual disk on Windows 10/8/7. In today’s article, MiniTool Solution will walk you through a full guide about how to create a virtual disk.
What Is a Virtual Drive
A virtual disk enables you to make full use of storage space like an actual disk storage device. With a virtual disk drive, you can store the files, the operating system and other important data. After the virtual hard drive is mounted, you can use it as a normal hard drive or removable storage device.
In addition, virtual disk drives can be used as shared storage on your network. In other words, sending and receiving files between the virtual disk drive and the computer become easier without getting access to your physical hard drive.
Well, the more important thing is about how to create a virtual disk. Please keep reading the following part to view this full tutorial.
How to Create a Virtual Disk on Windows 10/8/7
The full guide given below to create a virtual disk can work with Windows 10/8/7. Here we take Windows 10 for an example.
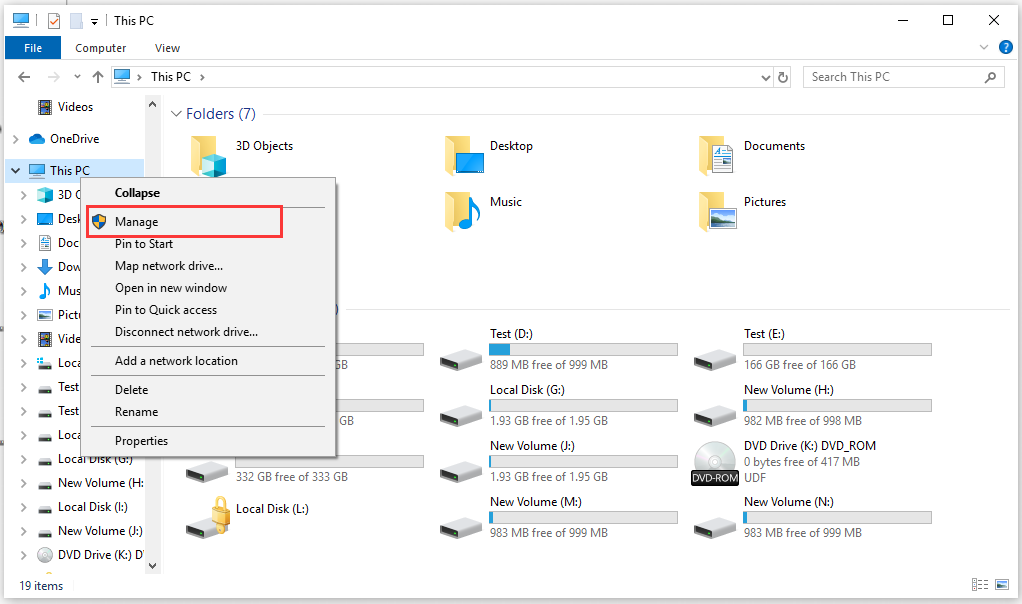
Step 1. Open your Windows File Explorer, then right-click on My Computer (Windows 7) or This PC (Windows 10/8) and select Manage.
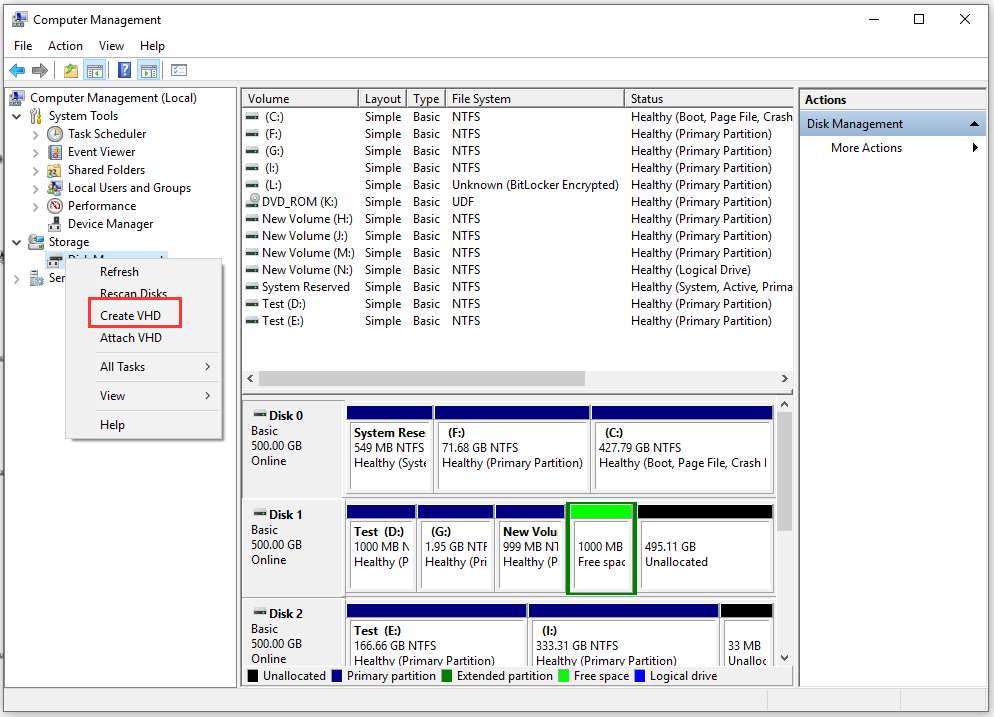
Step 2. Navigate to Disk Management inside the Computer Management (Local) window. Then right-click Disk Management and click on Create VHD button.
Step 3. In the pop-up window, you can specify the virtual hard disk location on the machine. Click the Browse button to choose a drive and determine how much disk space you need to take from it for the virtual disk creation. After the virtual disk drive settings are finally configured, click on OK. This process will take some time to complete.
Note: If you want to create a virtual disk with the VHD format, the maximum size of the hard drive should not be higher than 2040 GB, which should be large enough for most users. Well, if you want to create a virtual disk drive with more storage space, the VHDX format is a good choice.
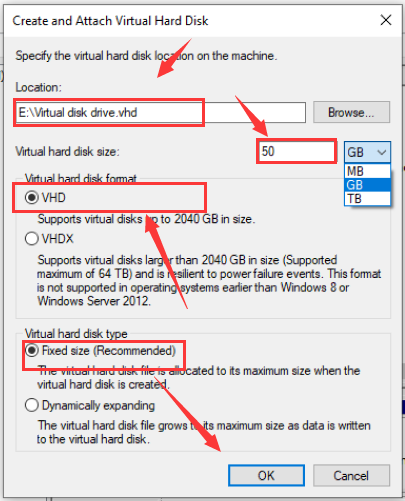
There are two options of virtual hard disk size: Fixed Size recommended and dynamically increase the size of the virtual hard drive you can choose.
- If you choose the fixed size, the size allocated for the virtual hard drive will be reserved right away after you create a virtual disk.
- If you choose dynamically expanding, the size allocated for the virtual hard drive will increase as you add files to it. Here you can choose the appropriate settings based on your requirements.
- Then you need to mount the virtual hard drive after creating a virtual disk as we mentioned at the beginning.
There are detailed steps to mount a virtual disk on Windows 10/8/7:
Step 1. In Disk Management, you will see a virtual disk you just created. Now navigate to the virtual disk you created by scrolling down in the list of storage devices and right-click it to click on Initialize Disk.
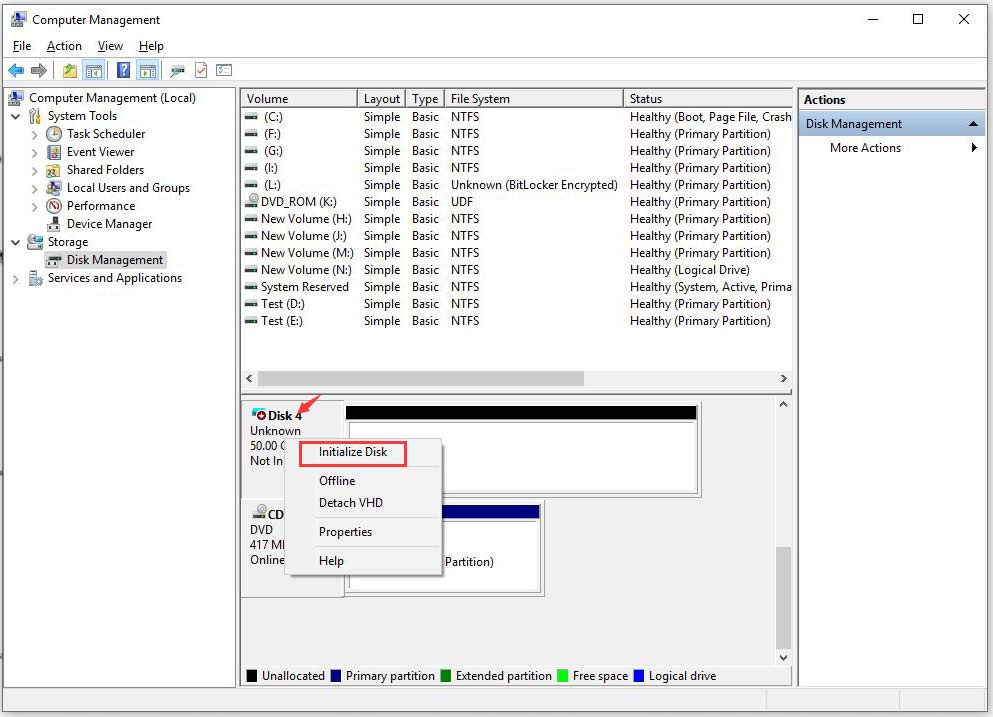
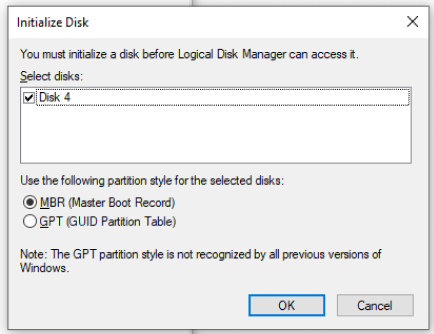
Step 2. Then a new window pops up, there are two options MBR or GPT disk you can create, just choose the one depending on your requirements. Here we choose MBR as an example and click OK.
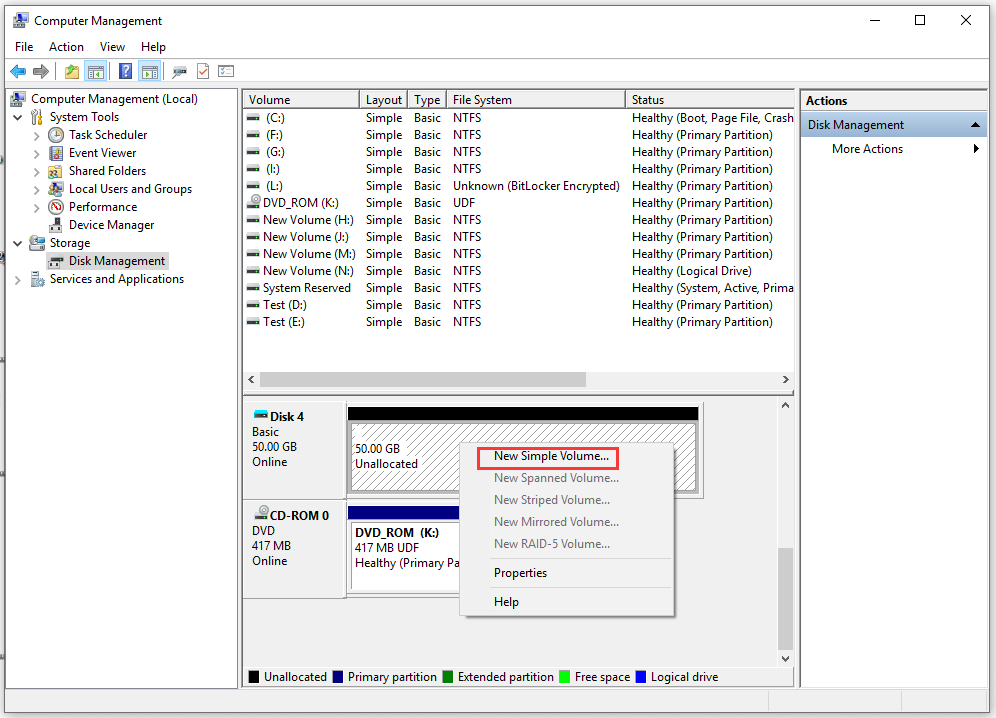
Step 3. Now a virtual disk drive is created. You can right-click the unallocated space and select New Simple Value to create a partition in this virtual disk.
Step 4. Inside the new window, assign a drive letter and format the virtual hard drive by following the prompts. Here it is recommended to format the disk in the NTFS file system.
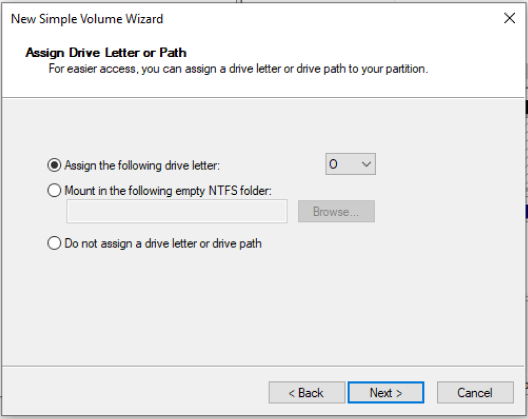
Step 5. After the virtual disk drive is created, you can find this virtual disk drive as a removable storage device within This PC.
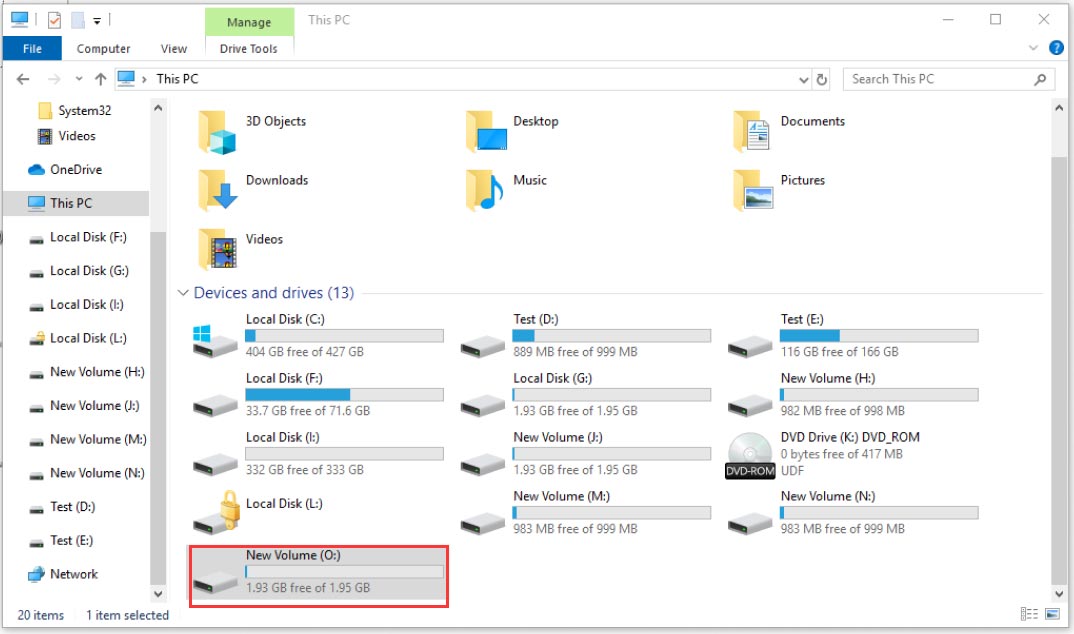
Well, all about how to create a virtual disk and mount the virtual disk are told to you. Now, it’s your turn to have a try.
About The Author
Position: Columnist
Ariel has been working as a highly professional computer-relevant technology editor at MiniTool for many years. She has a strong passion for researching all knowledge related to the computer’s disk, partition, and Windows OS. Up till now, she has finished thousands of articles covering a broad range of topics and helped lots of users fix various problems. She focuses on the fields of disk management, OS backup, and PDF editing and provides her readers with insightful and informative content.