Загрузить PDF
Загрузить PDF
Из данной статьи вы узнаете, как на компьютере с Windows запустить программу из командной строки. Запустить можно программу, которая хранится в папке, созданной Windows (например, на рабочем столе). Также папку с программой можно добавить в список командной строки, чтобы запустить эту программу из командной строки.
-
Щелкните по логотипу Windows в нижнем левом углу экрана. Или нажмите клавишу ⊞ Win на клавиатуре.
- В Windows 8 передвиньте указатель мыши в верхний правый угол экрана, а затем щелкните по значку в виде лупы.
-
Отобразится значок командной строки.
-
Он находится в верхней части меню «Пуск». Откроется окно командной строки.
- Если вы вошли в систему в качестве гостя, окно командной строки не откроется.
-
После команды start обязательно поставьте пробел.
-
Имеется в виду системное имя программы, а не имя ее ярлыка (например, системное имя командной строки: cmd). Ниже приведены системные имена основных программ:
- Проводник: explorer
- Блокнот: notepad
- Таблица символов: charmap
- Paint: mspaint
- Командная строка (новое окно): cmd
- Windows Media Player: wmplayer
- Диспетчер задач: taskmgr
-
Введенная команда должна выглядеть примерно так: start имя_программы. Указанная программа будет запущена в течение нескольких секунд после исполнения команды «start».
- Если выбранная программа не запустилась, скорее всего, она не включена в список программ командной строки. В этом случае перейдите к следующему разделу.
Реклама
-
Щелкните по логотипу Windows в нижнем левом углу экрана. Или нажмите клавишу ⊞ Win на клавиатуре.
-
Для этого щелкните по значку в виде папки в нижней левой части окна «Пуск».
-
Перейдите в папку с файлами программы, которую нужно открыть.
- Когда значок программы, которую необходимо запустить с помощью командной строки, отобразится в окне Проводника, значит, вы — в нужной папке.
- Если вы не знаете, где находится программа, поищите ее в папке «Program Files» на жестком диске или воспользуйтесь строкой поиска (сверху).
-
Щелкните по правой стороне адресной строки, которая находится в верхней части окна Проводника. Содержимое адресной строки будет выделено синим маркером.
-
Для этого нажмите Ctrl+C.
-
Эта папка находится в левой части окна Проводника.
-
Так будет отменено выделение любой папки внутри папки «Этот ПК», что позволит открыть свойства папки «Этот ПК».
-
Это вкладка находится в верхней левой части страницы. Откроется панель инструментов.
-
Значок этой кнопки имеет вид белого квадрата с красной галочкой. Откроется всплывающее окно.
-
Эта ссылка находится в верхней левой части окна. Откроется другое всплывающее окно.
-
Она находится в верхней части окна.
-
Эта опция находится в нижней части окна. Откроется другое окно.
-
Эта опция находится в окне «Системные переменные» в нижней части страницы.
-
Эта опция находится в нижней части страницы.
-
Эта опция находится в верхней правой части страницы «Изменить».
-
Для этого нажмите Ctrl+V.
-
Вставленный путь будет сохранен.
-
-
Введите cd в командной строке, затем поставьте пробел, нажмите Ctrl+V, чтобы ввести путь к программе, а потом нажмите ↵ Enter.
-
После команды start обязательно поставьте пробел.
-
Введите имя программы так, как оно отображается в папке с программными файлами, а затем нажмите ↵ Enter. Программа будет запущена.
- Если в названии программы есть пробелы, вместо них введите знак подчеркивания «_» (например, system_shock, а не system shock).
Реклама
Советы
- Чтобы открыть любую программу с помощью командной строки, устанавливайте программы в папку «Документы».
Реклама
Предупреждения
- Если у вас нет административного доступа к компьютеру, возможно, у вас не получится открыть окно командной строки или внести изменения в настройки пути.
Реклама
Об этой статье
Эту страницу просматривали 469 825 раз.
Была ли эта статья полезной?
The `cmd.exe start` command is used to launch a new command prompt window or open a specific application or file from the command line.
start notepad.exe
Understanding the `start` Command
What is the `start` Command?
The `cmd.exe start` command is a powerful Windows command-line utility that initiates a separate window to run a specified program or command. This command is essential for multitasking, as it allows users to open multiple applications or commands simultaneously without affecting the ongoing tasks in the command prompt.
Syntax of the `start` Command
The basic syntax of the `start` command is as follows:
start [options] <title> <command>
- Options: These are optional flags or parameters you can use to modify the behavior of the command.
- Title: An optional string that specifies the window title. This can help differentiate between multiple windows.
- Command: The executable or command that you wish to run. This is the only required argument.

Mastering Cmd.exe Shutdown: A Handy Guide
How to Use the `start` Command
Opening Applications
Using `cmd.exe start` to open applications is straightforward. For example, to launch Notepad, you can simply type:
start notepad
Running this command opens a separate Notepad window. The beauty of this approach is its ease of use, allowing users to access applications quickly from the command line without navigating through menus.
Opening Files with Applications
You can also use the `start` command to open specific files with their associated applications. For instance, if you want to open a text file called `myfile.txt` in Notepad, the command would be:
start notepad myfile.txt
This command highlights the importance of file associations in Windows. The operating system knows which application corresponds to the file extension (like `.txt` for Notepad) and opens it accordingly. Always ensure that the file path provided is accurate, as mistakes could lead to errors.
Launching Websites
Another versatile use of the `start` command is to open web pages in your default web browser. For example, to open a website, you can use:
start https://www.example.com
This command works seamlessly, taking the URL and launching it in the browser specified as default on your system. It is a quick way to access web resources without leaving the command prompt.

Mastering Cmd.exe Switches for Efficient Commands
Advanced Usage of the `start` Command
Using Multiple Commands
The `start` command can also handle launching multiple applications at once. You can do this by chaining commands together. For example, if you want to launch both Notepad and Calculator, you can write:
start notepad & start calc
In this command, the `&` symbol indicates that both commands should be executed in sequence. Using this feature can enhance workflows by allowing several applications to be opened simultaneously.
Using the Title Option
The title option can be beneficial for organization, especially when dealing with multiple open windows. For example, if you would like to start a new command prompt window with a custom title, you can do:
start "My Custom Title" cmd
This command opens a new command prompt window with «My Custom Title» displayed at the top. Custom titles help users identify and manage various command windows more effortlessly.

Finding cmd.exe Location: A Simple Guide
Practical Examples
Example Use Cases
The `cmd.exe start` command is invaluable for automating tasks and enhancing productivity. Some typical use cases include creating batch files for repetitive tasks, enabling easy access to frequently used applications, or setting up a work environment with all necessary tools launched with a single command.
Integrated Scripts
You can integrate the `start` command into batch scripts for even greater efficiency. For example:
@echo off
start notepad
start cmd /k echo Hello World
start https://www.example.com
In this script, Notepad opens, a command prompt window displays «Hello World,» and a specified website launches—all executed in just a single script. This method is efficient for daily routines or setups that require multiple applications.

Mastering Cmd Exe Arguments for Effective Command Line Use
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Errors You Might Encounter
When using the `start` command, you may face common errors such as invalid commands or application paths. If the command cannot be recognized, double-check the spelling and ensure that the application is installed on your system. Path issues can typically occur when the specified file is not in the current directory or the path is incorrectly referenced.
Tips for Successful Command Execution
To maximize the efficiency of the `start` command:
- Always double-check your commands for typos.
- Use quotes around file paths that contain spaces to avoid errors.
- Familiarize yourself with the specific applications you are launching to ensure command effectiveness.

Mastering Cmd Exe Parameters: A Quick Guide
Conclusion
The `cmd.exe start` command is a versatile and powerful tool in the Windows command-line interface, greatly enhancing multitasking capabilities and streamlining workflows. By mastering this command, users can efficiently navigate their computing environments and automate numerous tasks, resulting in improved productivity.
Mastering Cmd Start Wait: A Quick Guide to Execution
Additional Resources
To further enhance your understanding and proficient use of the `start` command and CMD in general, consider visiting the official Microsoft documentation. Explore additional CMD commands that complement the `start` command to maximize your productivity.

Mastering Cmd Exe Path: Your Quick Guide
FAQs
What happens when I don’t specify a title?
When you do not specify a title, the command will use the default window title based on the command being executed. This behavior can lead to multiple windows displaying similar titles if they’re not uniquely defined.
Can I use the start command to run scripts?
Yes, the `start` command can be used to execute scripts, including batch and PowerShell scripts. Just specify the script’s filepath following the `start` command.
How can I minimize or maximize a window using `start`?
You can specify window styles using the `start` command. For example, to open an application minimized, you can use:
start /min notepad
This command opens Notepad in a minimized state, allowing you to manage your workspace effectively.
By leveraging the `cmd.exe start` command effectively, users can enhance their command line proficiency and streamline their computing environment.
Last Updated :
08 Mar, 2025
Running any software on Windows is quite easy, but what if you have to run any.exe file using the CMD? The Command Prompt in Windows is a powerful, versatile tool that grants users direct access to the operating system’s core functionalities. While graphical interfaces (GUIs) simplify many tasks.
In this guide, we will walk you through the fundamentals of navigating CMD, as well as learn how to run or .exe files through CMD. You’ll also learn how to handle common challenges, such as specifying file paths with spaces, running programs as an administrator, and integrating EXE commands into scripts for batch processing.

What is .exe in Windows
In Windows, a file with the .exe extension denotes an executable file, which contains a program that the operating system can run directly. When you double-click an .exe file, Windows loads this program into memory and executes its instructions. This format is commonly used for software applications, installers, and system utilities.
How to Run .exe file through CMD
- Open cmd using the Run window
- Copy the file path from the Address bar.
- Paste it after the cd command to move to the directory.
- To open the executable use the command: start file_name.exe.
start chrome.exe
Note: You can also use only the file_name the extension «.exe» is optional.
Your exe file will open instantly. Let’s check out these steps with a proper demonstration.
Step 1: Open CMD Using the Run window
- Press Win + R to open the Run Dialog Box or Go to Start Menu and type «Run».
- Now type «CMD» or «Command Prompt» and hit Enter.
Step 2: Copy the File Path From the Address bar
- Go to File Location from the file explorer and click on the Address bar.
- Now, make a right-click or hit Ctrl + C to copy the location on the Address bar.
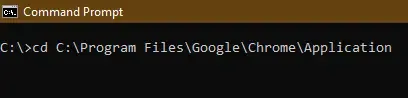
Step 3: Type ‘cd’ Followed by File Path
- Go to Command Prompt and use ‘cd’ command to navigate through the EXE file location and paste it along with the cd command (that you’ve copied)
- After entering the prompt location, now replace the file path or location with it’s actual path to the folder which contains EXE file (that you want to run)
- Hit ENTER and the path will be redirected to your desired location.
Example: cd C:\Users\GFG0388\Desktop\My folder
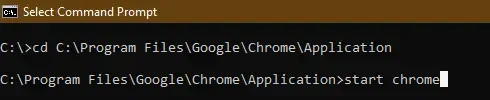
Step 4: Run an EXE File with ‘start’ Command
- Now, use the start command to execute the required EXE file by providing the file name.
- Replace the filename.exe with your EXE file (ensure that it should match your program’s file & name)
- The command instantly run the executable so beware of sudden change or window pop-up.
- Hit the ENTER key and your selected EXE file will start executing.
Example: start chrome.exe
Issues and Troubleshooting
Running executable (.exe) files through the Command Prompt (CMD) in Windows can sometimes present challenges. Here are common issues you might encounter and their potential solutions:
Executable Not Found: If you receive an error indicating that the executable isn’t recognized, it might be due to the system not knowing where to find the file.
Solution: Navigate to the directory containing the executable using the cd command before running it. Alternatively, add the executable’s directory to the system’s PATH environment variable to allow it to be run from any location.
Corrupted File Association: Sometimes, .exe files might not open correctly due to corrupted registry settings or interference from third-party applications or malware.
Solution: Modify the registry to restore the default configuration for running .exe files. Detailed instructions can be found in Microsoft’s support article.
Insufficient Permissions: Certain executables require administrative privileges to run.
Solution: Run the Command Prompt as an administrator by right-clicking on the CMD shortcut and selecting «Run as administrator.» Then, execute the .exe file.
Executable Opens and Closes Immediately: Some console applications might execute and close too quickly to read any output.
Solution: Run the executable directly within the Command Prompt to keep the window open and view the output. Alternatively, create a batch file that runs the executable followed by the pause command to prevent the window from closing immediately.
Command Prompt Not Working: If CMD itself isn’t functioning correctly, it can hinder running executables.
Solution: Troubleshoot the Command Prompt by restarting your computer, checking for system file corruption using tools like SFC (System File Checker), or modifying environment variables. A comprehensive guide is available to address this issue.
System Conflicts or Malware: Malware or system conflicts can prevent executables from running properly.
Solution: Perform a thorough malware scan using reputable antivirus software. Additionally, consider restoring your system to a previous state using System Restore if the problem started recently.
Conclusion
Being able to run an exe through CMD gives you greater control over your applications and can simplify certain tasks that might be cumbersome through a graphical interface. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you’ll be able to confidently execute exe files using Command Prompt in various scenarios, whether you’re running a setup program, launching a game, or automating a task.
Also Read
- How to Execute C# Program on cmd (command-line)?
- How to Abort a Command Execution in Command Prompt?
- How to Find the Wi-Fi Password Using CMD in Windows 11/10?
- SS64
- CMD
- How-to
Start a program, command or batch script, opens in a new/separate Command Prompt window.
Syntax
START "title" [/D path] [options] "command" [parameters]
Key:
title Text for the CMD window title bar (required.)
path Starting directory.
command The command, batch file or executable program to run.
parameters The parameters passed to the command.
Options:
/MIN Start window Minimized.
/MAX Start window Maximized.
/W or /WAIT Start application and wait for it to terminate.
(see below)
/LOW Use IDLE priority class.
/NORMAL Use NORMAL priority class.
/ABOVENORMAL Use ABOVENORMAL priority class.
/BELOWNORMAL Use BELOWNORMAL priority class.
/HIGH Use HIGH priority class.
/REALTIME Use REALTIME priority class.
/B Start application without creating a new window. In this case
Ctrl-C will be ignored - leaving Ctrl-Break as the only way to
interrupt the application.
/I Ignore any changes to the current environment, typically made with SET.
Use the original environment passed to cmd.exe
/NODE The preferred Non-Uniform Memory Architecture (NUMA)
node as a decimal integer.
/AFFINITY The processor affinity mask as a hexadecimal number.
The process will be restricted to running on these processors.
Options for running 16-bit Windows programs, on Windows 10 only:
/SEPARATE Start in separate memory space. (more robust) 32 bit only.
/SHARED Start in shared memory space. (default) 32 bit only.
Always include a TITLE this can be a simple string like «My Script» or just a pair of empty quotes «»
According to the Microsoft documentation, the title is optional, but depending on the other options chosen you can have problems if it is omitted.
If command is an internal cmd command or a batch file then the command processor CMD.exe is run with the /K switch. This means that the window will remain after the command has been run.
In a batch script, a START command without /wait will run the program and just continue, so a script containing nothing but a START command will close the CMD console and leave the new program running.
Document files can be invoked through their file association just by typing the name of the file as a command.
e.g. START «» MarchReport.docx will launch the application associated with the .docx file extension and load the document.
To minimise any chance of the wrong exectuable being run, specify the full path to command or at a minimum include the file extension: START «» notepad.exe
If you START an application without a file extension (for example WinWord instead of WinWord.exe)then the PATHEXT environment variable will be read to determine
which file extensions to search for and in what order.
The default value for the PATHEXT variable is: .COM;.EXE;.BAT;.CMD
Start — run in parallel
The default behaviour of START is to instantiate a new process that runs in parallel with the main process. For arcane technical reasons, this does not work for some types of executable, in those cases the process will act as a blocker, pausing the main script until it’s complete.
In practice you just need to test it and see how it behaves.
Often you can work around this issue by creating a one line batch script (runme.cmd ) to launch the executable, and then call that script with START runme.cmd
Start /Wait
The /WAIT option should reverse the default ‘run in parallel’ behaviour of START but again your results will vary depending on the item being started, for example:
Echo Starting START /wait "job1" calc.exe Echo DoneThe above will start the calculator and wait before continuing. However if you replace calc.exe with Winword.exe, to run Word instead, then the /wait will stop working, this is because Winword.exe is a stub which launches the main Word application and then exits.
A similar problem will occur when starting a batch file, by default START will run the equivalent of CMD /K which opens a second command window and leaves it open. In most cases you will want the batch script to complete and then just close its CMD console to resume the initial batch script. This can be done by explicitly running CMD /C …
Echo Starting START /wait "demojob" CMD /c demoscript.cmd Echo DoneAdd /B to have everything run in a single window.
In a batch file, an alternative is to use TIMEOUT to delay processing of individual commands.
START vs CALL
Starting a new process with CALL, is very similar to running START /wait, in both cases the calling script will (usually) pause until the second script has completed.
Starting a new process with CALL, will run in the same shell environment as the calling script. For a GUI application this makes no difference, but a second ‘called’ batch file will be able to change variables and pass those changes back to the caller.
In comparison START will instantiate a new CMD.exe shell for the called batch. This will inherit variables from the calling shell, but any variable changes will be discarded when the second script ends.
Run a program
To start a new program (not a batch script), you don’t have to use CALL or START, just enter the path/file to be executed, either on the command line or within a batch script. This will behave as follows:
- On the command line, CMD.EXE does not wait for the application to terminate and control immediately returns to the command prompt.
- Running a program from within a batch script, CMD.EXE will pause the initial script and wait for the application to terminate before continuing.
- If you run one batch script from another without using either CALL or START, then the first script is terminated and the second one takes over.
Search order:
- Running a program from CMD will search first in the current directory and then in the PATH.
- Running a program from PowerShell will search first in the PATH and then in the current directory.
- The Windows Run Line (win+r) will search first in App Paths [defined in HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\App Paths] and then the PATH
Multiprocessor systems
Processor affinity is assigned as a hex number but calculated from the binary positions (similar to NODRIVES)
Hex Binary Processors
1 00000001 Proc 1
3 00000011 Proc 1+2
7 00000111 Proc 1+2+3
C 00001100 Proc 3+4 etcSpecifying /NODE allows processes to be created in a way that leverages memory locality on NUMA systems. For example, two processes that communicate with each other heavily through shared memory can be created to share the same preferred NUMA node in order to minimize memory latencies. They allocate memory from the same NUMA node when possible, and they are free to run on processors outside the specified node.
start /NODE 1 app1.exe
start /NODE 1 app2.exeThese two processes can be further constrained to run on specific processors within the same NUMA node.
In the following example, app1 runs on the low-order two processors of the node, while app2 runs on the next two processors of the node. This example assumes the specified node has at least four logical processors. Note that the node number can be changed to any valid node number for that computer without having to change the affinity mask.
start /NODE 1 /AFFINITY 0x3 app1.exe
start /NODE 1 /AFFINITY 0xc app2.exe
Running executable (.EXE) files
When a file that contains a .exe header, is invoked from a CMD prompt or batch file (with or without START), it will be opened as an executable file. The filename extension does not have to be .EXE. The file header of executable files start with the ‘magic sequence’ of ASCII characters ‘MZ’ (0x4D, 0x5A) The ‘MZ’ being the initials of Mark Zibowski, a Microsoft employee at the time the file format was designed.
Command Extensions
If Command Extensions are enabled, external command invocation through the command line or the START command changes as follows:
Non-executable files can be invoked through their file association just by typing the name of the file as a command. (e.g. example.docx would launch the application associated with the .docx file extension). This is based on the setting in HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\FileExts\.ext\OpenWithList, or if that is not specified, then the file associations — see ASSOC and FTYPE.
When executing a command line whose first token is the string CMD without an extension or path qualifier, then CMD is replaced with the value of the COMSPEC variable. This prevents picking up CMD.EXE from the current directory.
When executing a command line whose first token does NOT contain an extension, then CMD.EXE uses the value of the COMSPEC environment variable. This prevents picking up CMD.EXE from the current directory.
When executing a command line whose first token does NOT contain an extension, then CMD.EXE uses the value of the PATHEXT environment variable to determine which extensions to look for and in what order. The default value for the PATHEXT variable is: .COM;.EXE;.BAT;.CMD Notice the syntax is the same as the PATH variable, with semicolons separating the different elements.
When searching for an executable, if there is no match on any extension, then looks to see if the name matches a directory name. If it does, the START command launches the Explorer on that path. If done from the command line, it is the equivalent to doing a CD /D to that path.
Errorlevels
If the command is successfully started ERRORLEVEL =unchanged, typically this will be 0 but if a previous command set an errorlevel, that will be preserved (this is a bug).
If the command fails to start then ERRORLEVEL = 9059
START /WAIT batch_file — will return the ERRORLEVEL specified by EXIT
START is an internal command.
Examples
Start a program in the current directory:
START «Demo Title» example.exe
Start a program giving a fulll path:
START «Demo 2» /D «C:\Program Files\ACME Corp\» «example.exe»
Alternatively:
START «Demo 2» «C:\Program Files\ACME Corp\example.exe»
or:
CD /d «C:\Program Files\ACME Corp\»
START «Demo 2» «example.exe»
Start a program and wait for it to complete before continuing:
START «Demo 3» /wait autocad.exe
Open a file with a particular program:
START «Demo 4» «C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Winword.exe» «D:\Docs\demo.txt»
Run a minimised Login script:
CMD.exe /C START «Login Script» /Min CMD.exe /C Login.cmd
In this example the first CMD session will terminate almost immediately and the second will run minimised.
The first CMD is required because START is a CMD internal command. An alternative to this is using a shortcut set to open minimised.
Open Windows Explorer and list the files in the current folder (.) :
C:\any\old\directory> START .
Open a webpage in the default browser, note the protocol is required (https://):
START
https://ss64.com
Open a webpage in Microsoft Edge:
%windir%\explorer.exe microsoft-edge:https://ss64.com
or with a hard-coded path:
«C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Edge\Application\msedge.exe»https://ss64.com"%windir%\explorer.exe shell:Appsfolder\Microsoft.MicrosoftEdge_8wekyb3d8bbwe!MicrosoftEdge" https://ss64.com
Connect to a new printer: (this will setup the print connection/driver):
START \\print_server\printer_name
Start an application and specify where files will be saved (Working Directory):
START /D C:\Documents\ /MAX «Maximised Notes» notepad.exe
“Do not run; scorn running with thy heels” ~ Shakespeare, The Merchant of Venice
Related commands
WMIC process call create «c:\some.exe»,»c:\exec_dir» — This method returns the PID of the started process.
CALL — Call one batch program from another.
CMD — can be used to call a subsequent batch and ALWAYS return even if errors occur.
TIMEOUT — Delay processing of a batch file/command.
TITLE — Change the title displayed above the CMD window.
RUN commands Start ➞ Run commands.
How-to: Run a script — How to create and run a batch file.
How-to: Autoexec — Run commands at startup.
ScriptRunner — Run one or more scripts in sequence.
Q162059 — Opening Office documents.
Equivalent PowerShell: Start-Process — Start one or more processes.
Equivalent bash command (Linux) : open — Open a file in it’s default application.
Equivalent macOS command: open — Open a file in a chosen application.
Copyright © 1999-2025 SS64.com
Some rights reserved
Start a program, command or batch script (opens in a new window.)
Syntax
START "title" [/D path] [options] "command" [parameters]
Key:
title Text for the CMD window title bar (required.)
path Starting directory.
command The command, batch file or executable program to run.
parameters The parameters passed to the command.
Options:
/MIN Start window Minimized.
/MAX Start window Maximized.
/W or /WAIT Start application and wait for it to terminate.
(see below)
/LOW Use IDLE priority class.
/NORMAL Use NORMAL priority class.
/ABOVENORMAL Use ABOVENORMAL priority class.
/BELOWNORMAL Use BELOWNORMAL priority class.
/HIGH Use HIGH priority class.
/REALTIME Use REALTIME priority class.
/B Start application without creating a new window. In this case
Ctrl-C will be ignored - leaving Ctrl-Break as the only way to
interrupt the application.
/I Ignore any changes to the current environment.
Use the original environment passed to cmd.exe
/NODE The preferred Non-Uniform Memory Architecture (NUMA)
node as a decimal integer.
/AFFINITY The processor affinity mask as a hexadecimal number.
The process will be restricted to running on these processors.
Options for 16-bit WINDOWS programs only
/SEPARATE Start in separate memory space. (more robust) 32 bit only.
/SHARED Start in shared memory space. (default) 32 bit only.
Always include a TITLE this can be a simple string like “My Script” or just a pair of empty quotes “”
According to the Microsoft documentation, the title is optional, but depending on the other options chosen you can have problems if it is omitted.
If command is an internal cmd command or a batch file then the command processor is run with the /K switch to cmd.exe. This means that the window will remain after the command has been run.
In a batch script, a START command without /wait will run the program and just continue, so a script containing nothing but a START command will close the CMD console and leave the new program running.
Document files can be invoked through their file association just by typing the name of the file as a command.
e.g. START “” MarchReport.DOC will launch the application associated with the .DOC file extension and load the document.
To minimise any chance of the wrong exectuable being run, specify the full path to command or at a minimum include the file extension: START “” notepad.exe
If you START an application without a file extension (for example WinWord instead of WinWord.exe)then the PATHEXT environment variable will be read to determine which file extensions to search for and in what order.
The default value for the PATHEXT variable is: .COM;.EXE;.BAT;.CMD
Start /Wait
The behaviour of START /Wait will vary depending on the item being started, for example
Echo Starting START /wait "demo" calc.exe Echo Done
The above will start the calculator and wait before continuing. However if you replace calc.exe with Winword.exe, to run Word instead, then the /wait will stop working, this is because Winword.exe is a stub which launches the main Word application and then exits.
A similar problem will occur when starting a batch file, by default START will run the equivalent of CMD /K which opens a second command window and leaves it open. In most cases you will want the batch script to complete, then just close it’s CMD console and resume the initial batch script. This can be done by explicitly running CMD /C …
Echo Starting START /wait "demo" CMD /c demoscript.cmd Echo Done
Add /B to have everything run in a single window.
In a batch file, an alternative is to use TIMEOUT to delay processing of individual commands.
START vs CALL
Starting a new process with CALL, is very similar to running START /wait, in both cases the calling script will (usually) pause until the second script has completed.
Starting a new process with CALL, will run in the same shell environment as the calling script. For a GUI application this makes no difference, but a second ‘called’ batch file will be able to change variables and pass those changes back to the caller.
In comparison START will instantiate a new CMD.exe shell for the called batch. This will inherit variables from the calling shell, but any variable changes will be discarded when the second script ends.
Run a program
To start a new program (not a batch script), you don’t have to use CALL or START, simply enter the path/file to be executed, either on the command line or within a batch script.
On the command line, CMD.EXE does not wait for the application to terminate and control immediately returns to the command prompt.
Within a command script CMD.EXE will pause the initial script and wait for the application to terminate before continuing.
If you run one batch script from another without using either CALL or START, then the first script is terminated and the second one takes over.
Multiprocessor systems
Processor affinity is assigned as a hex number but calculated from the binary positions (similar to NODRIVES)
Hex Binary Processors 1 00000001 Proc 1 3 00000011 Proc 1+2 7 00000111 Proc 1+2+3 C 00001100 Proc 3+4 etc
Specifying /NODE allows processes to be created in a way that leverages memory locality on NUMA systems. For example, two processes that communicate with each other heavily through shared memory can be created to share the same preferred NUMA node in order to minimize memory latencies. They allocate memory from the same NUMA node when possible, and they are free to run on processors outside the specified node.
start /NODE 1 app1.exe start /NODE 1 app2.exe
These two processes can be further constrained to run on specific processors within the same NUMA node.
In the following example, app1 runs on the low-order two processors of the node, while app2 runs on the next two processors of the node. This example assumes the specified node has at least four logical processors. Note that the node number can be changed to any valid node number for that computer without having to change the affinity mask.
start /NODE 1 /AFFINITY 0x3 app1.exe start /NODE 1 /AFFINITY 0xc app2.exe
Running executable (.EXE) files
When a file that contains a .exe header, is invoked from a CMD prompt or batch file (with or without START), it will be opened as an executable file. The filename extension does not have to be .EXE. The file header of executable files start with the ‘magic sequence’ of ASCII characters ‘MZ’ (0x4D, 0x5A) The ‘MZ’ being the initials of Mark Zibowski, a Microsoft employee at the time the file format was designed.
Command Extensions
If Command Extensions are enabled, external command invocation through the command line or the START command changes as follows:
Non-executable files can be invoked through their file association just by typing the name of the file as a command. (e.g. WORD.DOC would launch the application associated with the .DOC file extension). This is based on the setting in HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\FileExts\.ext\OpenWithList, or if that is not specified, then the file associations – see ASSOC and FTYPE.
When executing a command line whose first token is the string CMD without an extension or path qualifier, then CMD is replaced with the value of the COMSPEC variable. This prevents picking up CMD.EXE from the current directory.
When executing a command line whose first token does NOT contain an extension, then CMD.EXE uses the value of the COMSPEC environment variable. This prevents picking up CMD.EXE from the current directory.
When executing a command line whose first token does NOT contain an extension, then CMD.EXE uses the value of the PATHEXT environment variable to determine which extensions to look for and in what order. The default value for the PATHEXT variable is: .COM;.EXE;.BAT;.CMD Notice the syntax is the same as the PATH variable, with semicolons separating the different elements.
When searching for an executable, if there is no match on any extension, then looks to see if the name matches a directory name. If it does, the START command launches the Explorer on that path. If done from the command line, it is the equivalent to doing a CD /D to that path.
Errorlevels
If the command is successfully started ERRORLEVEL =unchanged, typically this will be 0 but if a previous command set an errorlevel, that will be preserved (this is a bug).
If the command fails to start then ERRORLEVEL = 9059
START /WAIT batch_file – will return the ERRORLEVEL specified by EXIT
Examples
Run a minimised Login script:START "My Login Script" /Min Login.cmd
Start a program and wait for it to complete before continuing:START "" /wait autocad.exe
Open a file with a particular program:START "" "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Winword.exe" "D:\Docs\demo.txt"
Open Windows Explorer and list the files in the current folder (.) :C:\any\old\directory> START .
Connect to a new printer: (this will setup the print connection/driver )START \\print_server\printer_name
Start an application and specify where files will be saved (Working Directory):
START /D C:\Documents\ /MAX "Maximised Notes" notepad.exe
START is an internal command.



























