This post explains how to get current date and time from command prompt or in a batch file.
How to get date and time in a batch file
Below is a sample batch script which gets current date and time
Datetime.cmd
@echo off
for /F "tokens=2" %%i in ('date /t') do set mydate=%%i
set mytime=%time%
echo Current time is %mydate%:%mytime%
When we run the above batch file
C:\>datetime.cmd Current time is 08/12/2015:22:57:24.62 C:\>
Get date from command line
To print today’s date on the command prompt, we can run date /t.
c:\>date /t Thu 05/14/2015 c:\>
Just running date without any arguments prints the current date and then prompts to enter a new date if the user wants to reset it.
c:\>date The current date is: Sat 05/16/2015 Enter the new date: (mm-dd-yy) c:\>
In addition to date command, we also have an environment variable using which we can find today’s date.
c:\>echo %date% Sun 05/17/2015
How to get only the date in MM/DD/YYYY format?
You may want to exclude the day (like ‘Sun’ in the above example) and print only the date in MM/DD/YYYY format. The below command works for the same.
for /F "tokens=2" %i in ('date /t') do echo %i
Example:
c:\>for /F "tokens=2" %i in ('date /t') do echo %i
05/14/2015
c:\>
Get time from command prompt
Similar to date command, we have the command time which lets us find the current system time. Some examples below.
c:\>time /t 11:17 PM c:\>time The current time is: 23:17:18.57 Enter the new time: c:\>
As you can see, the command prints the time in different formats. It prints in 12 hour format when /t is added and in 24 hours format without /t
We can also get the current time from environment variables.
c:\>echo %time% 23:23:51.62 c:\>
Get date and time
c:\>echo %date%-%time% Sun 05/17/2015-23:21:03.34
The «windows time cmd» commands allow users to view and modify the system time and date directly from the Command Prompt.
time
This command will prompt you to enter a new time, or if run without parameters, it will display the current system time.
Understanding the CMD Time Command
What is the CMD Time Command?
The CMD time command is a built-in command in Windows that allows users to view and modify the system’s time settings. This command plays a crucial role, especially for system administrators who need to ensure that the time settings are accurate for logging, scheduling tasks, and maintaining proper functioning of networked services. The time command is straightforward yet powerful, geared toward enhancing time management within the Windows operating environment.
How to Access CMD
Accessing the Command Prompt (CMD) is the first step in utilizing the windows time cmd capabilities. You can open CMD through several methods:
- Using Run: Press `Windows + R`, type in `cmd`, and hit Enter.
- Via Search: Click on the search icon on the taskbar, type `cmd`, and select the Command Prompt app.
- Through File Explorer: Open Windows Explorer, navigate to `C:\Windows\System32`, and double-click on `cmd.exe`.
Once the Command Prompt is visible, you are ready to start executing commands.

Mastering Windows Uptime Cmd for Quick Checks
Basic Usage of the Time Command
Displaying the Current System Time
To view the current system time, you can simply enter:
time
Upon executing this command, CMD will display the current time in hours, minutes, and seconds format. This is a quick way to check the system’s time without needing to navigate through the user interface.
Setting the Time
Changing the System Time
The ability to set the system time can be essential in multiple scenarios, particularly in an administrative context. The syntax for changing the time is as follows:
time HH:MM:SS
For instance, if you want to set the time to 2:30 PM (14:30), you would type:
time 14:30:00
When you set the time, CMD will prompt for confirmation, requiring you to debug any input errors. Ensure you use the 24-hour format to avoid confusion with AM and PM designations.
Tips for Input Format
While setting the time, it’s crucial to note the following tips to avoid common pitfalls:
- Always use the 24-hour format (e.g., 14:00 for 2 PM).
- If you attempt to set the time to an incorrect format, CMD will notify you and prompt you to re-enter.
Mastering Windows XP Cmd: Quick Commands to Enhance Your Skills
Advanced Time Command Functions
Synchronizing Time with a Time Server
Time synchronization is essential for maintaining consistency across systems, particularly in business environments. Utilization of the `net time` command makes this synchronization possible. The syntax is as follows:
net time \\time-server-name /set
Replace `time-server-name` with the actual name or address of the time server you wish to sync with. This command pulls the accurate time from the specified server, ensuring that all systems on the network maintain consistent time.
Creating a Batch File for Time Management
Automating time display using a batch file can streamline various tasks. Here’s a simple example of how to create a batch file that displays the current system time at regular intervals.
- Open Notepad and paste the following script:
@echo off
:start
echo Current Time: %time%
timeout /t 60
goto start
- Save the file with a `.bat` extension, such as `show_time.bat`.
This script will display the current time and refresh every 60 seconds. It utilizes the `timeout` command to wait before displaying the time again. This automation can be handy for monitoring time-sensitive tasks.
Mastering Windows 10 Cmd: Quick Tips for Power Users
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Error Messages When Using Time Command
While using the windows time cmd, you may encounter error messages related to incorrect formats or insufficient permissions. Common error messages include «Invalid time» and «Access Denied.» When faced with such messages, verify your command syntax and ensure you have the necessary permissions to make changes to the system time.
Permissions Required for Setting Time
Changing the system time typically requires administrative privileges. If you receive «Access Denied» messages, try running CMD as an Administrator:
- Search for `cmd` in the start menu.
- Right-click on Command Prompt and select «Run as Administrator.»
This will grant the necessary permissions to set the system time without restrictions.
Mastering Windows 10 Cmd Prompt: A Quick Guide
Practical Applications of the CMD Time Command
Synchronizing Time for Networked Systems
In corporate environments, where multiple computers operate in a network, it’s vital to maintain time consistency. Time discrepancies can lead to issues with file timestamps, logging, and scheduling tasks. Using the windows time cmd to establish synchronization with a reliable time server prevents these issues and promotes operational fluidity.
Time Stamping for Documentation
Incorporating timestamps into your documentation is crucial for maintaining accurate records. You can easily timestamp log entries with a simple command:
echo [%date% %time%] Log Entry >> logfile.txt
This command appends a new log entry to `logfile.txt`, complete with the current date and time. This practice can be extremely useful for tracking changes, debugging information, or maintaining records of transactions and activities.

Windows 10 Cmd Recovery: Quick Guide for Every User
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Schedule Time Commands?
You can schedule CMD commands, including the time command, to run at specific intervals using Task Scheduler. By creating a scheduled task, you can automate operations that require time checks or adjustments regularly.
Are There Limitations to the Time Command?
Yes, while the time command is quite useful, it does have limitations, such as not supporting time zone changes directly. Instead, adjustments usually need to be handled through the system settings.
Can I Use the Time Command in PowerShell?
The time command is native to CMD; however, you can execute similar commands in PowerShell. For example, getting the current time can be done with `Get-Date`. The versatility of CMD and PowerShell allows you to choose the tool best suited to your workflow.

Mastering Windows 11 Cmd Commands: A Quick Guide
Conclusion
The windows time cmd command provides a fundamental yet robust tool for managing system time within a Windows environment. Understanding its basic usage, advanced functions, and various applications can significantly enhance your system management capabilities. Whether you’re a novice eager to learn or an experienced administrator refining your skills, mastering the time command will undoubtedly contribute to your efficiency and effectiveness in various tasks.
Вывести в текстовый файл текущую дату и время
Иногда требуется программно вывести дату и время в файл текстового формата *.txt, *.dat или с любым другим расширением для последующей обработки. Для этих целей можно использовать средства операционной системы, в частности командную строку Windows и глобальные переменные содержащие время с датой.
Следуйте инструкции ниже чтобы записать в файл локальное текущее дату и время
Выводим текущую дату и время в файл
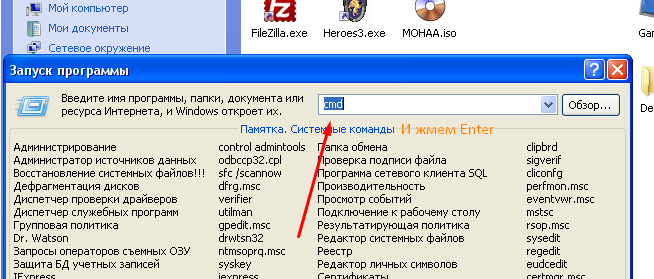
- Откройте консоль «CMD» нажатием на Пуск->Выполнить->пишем cmd и жмем клавишу «Enter». Откроется черное окошко, это консоль Windows. Прописываем команду «echo Local date: %date% — Time: %time%>C:\date.txt
Открываем консоль CMD
«
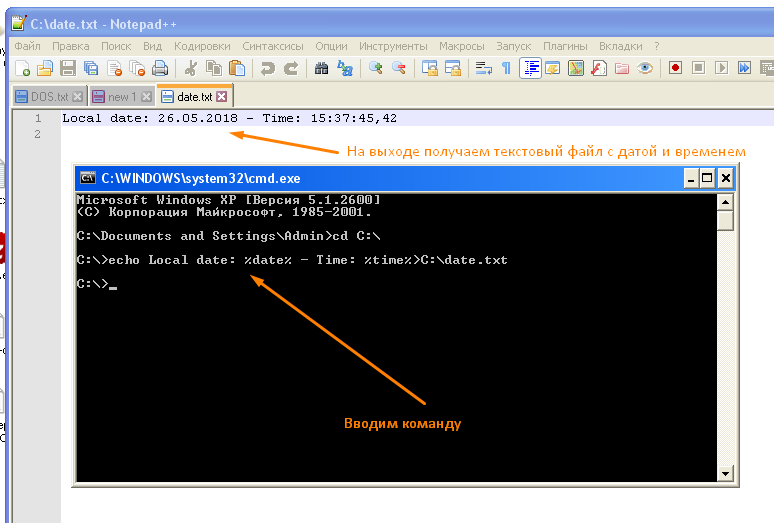
- Команда, которую мы прописали, создает текстовый файл на диске «C:\» и записывает в него локальное текущее время и дату вида: «Local date: 26.05.2018 — Time: 15:23:05,12»
Ввод команды и просмотр файла с данными
Для вывода мы используем глобальные переменные вида %date% и %time%, первая переменная содержит дату, вторая соответственно время с миллисекундами.
Вы можете поменять путь, где будет создаваться текстовый файл, а так же сменить расширение и отформатировать строку по-своему желанию. Помните что переменные нужно обрамлять текстом на латинице, если хотите записать в файл кириллицу, для этого перед основной командой используйте команду «chcp 1251» для смены кодировки, в противном случае русский текст будет превращен в непонятные символы.
You can use the date and
time commands on a Microsoft Windows system to
display current date and time information:
C:\Users\Lila>date /t Sat 08/26/2017 C:\Users\Lila>time /t 02:07 PM C:\Users\Lila>
Placing /t after the commands results in the current date
and time information being displayed without an accompanying prompt to change
the current settings.
You can display the information in a different format using
the
Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line (WMIC) command shown below:
C:\Users\Lila>wmic path win32_utctime get * /format:list Day=26 DayOfWeek=6 Hour=18 Milliseconds= Minute=16 Month=8 Quarter=3 Second=19 WeekInMonth=4 Year=2017 C:\Users\Lila>
The output will show the day and the number for the day of the week,
e.g., 6 for Saturday (the numbering starts with Monday as the first day of
the week). The WMIC command also shows the number of seconds, the quarter of
the year, and the week in the current month, which are not shown by the time
command.
The hour is displayed in
24-hour clock time, aka «military time.» In the example above, since
the local time is 2:07 PM, the hour value is 18, because two o’clock is
14:00 in 24-hour clock time with 4 hours added to the number of hours to make
the value 18, since the system is in the
Eastern Time Zone
, currently Eastern Daylight Time (EDT), in the United States, which is
currently 4 hours behind
Coordinated
Universal Time, which is abbreviated as UTC. There is a 5 hour time
difference when Eastern Standard Time (EST) applies. You can see the
current U.S. time zones at
Time Zones Currently Being Used in United States.
You can find the time zone the Windows system is in with the command shown
below:
C:\>systeminfo | find "Time Zone:" Time Zone: (UTC-05:00) Eastern Time (US & Canada) C:\>
The command above shows there is a 5 hour difference between the time zone
the system is in and UTC time, aka Zulu time or GMT, but that is only the
case when Eastern Standard Time (EST) is in effect, not when Eastern Daylight
Time (EDT) is in effect.
If you omit the /format:list parameter at the end of the
wmic path win32_utctime get * command, all of the values will be
displayed on one line:
C:\>wmic path win32_utctime get * Day DayOfWeek Hour Milliseconds Minute Month Quarter Second WeekInMonth Year 26 6 18 32 8 3 11 4 2017 C:\>
You can also specify the particular values you are interested rather than
getting all values with the asterisk. E.g.:
C:\>wmic path win32_utctime get hour, minute, second Hour Minute Second 18 34 47 C:\>wmic path win32_utctime get quarter Quarter 3 C:\>wmic path win32_utctime get weekinmonth WeekInMonth 4 C:\>wmic path win32_utctime get hour, minute, second Hour Minute Second 18 35 13 C:\>
If I want to know whether
daylight saving
time (DST) is currently in effect, I can open a
PowerShell
window and use the command shown below:
PS C:\Users\Lila> Get-CimInstance Win32_TimeZone | select * Caption : (UTC-05:00) Eastern Time (US & Canada) Description : (UTC-05:00) Eastern Time (US & Canada) SettingID : Bias : -300 DaylightBias : -60 DaylightDay : 2 DaylightDayOfWeek : 0 DaylightHour : 2 DaylightMillisecond : 0 DaylightMinute : 0 DaylightMonth : 3 DaylightName : Eastern Daylight Time DaylightSecond : 0 DaylightYear : 0 StandardBias : 0 StandardDay : 1 StandardDayOfWeek : 0 StandardHour : 2 StandardMillisecond : 0 StandardMinute : 0 StandardMonth : 11 StandardName : Eastern Standard Time StandardSecond : 0 StandardYear : 0 PSComputerName : CimClass : root/cimv2:Win32_TimeZone CimInstanceProperties : {Caption, Description, SettingID, Bias...} CimSystemProperties : Microsoft.Management.Infrastructure.CimSystemProperties PS C:\Users\Lila>
The StandardHour, StandardDay,
StandardDayOfWeek, and StandardMonth values tell me
when standard time goes into effect on this system. Since
StandardMonth is 11, I know that it takes effect in November. The
StandardDayofWeek value is zero, which indicates the change occurs
on the first day of the week, i.e., Sunday and the StandardDay
value of 1 indicates that the change occurs on the first Sunday of
StandardMonth, i.e., the first Sunday in November. The
StandardHour value of 2 tells me the time change takes place
at 2:00 AM on that day, i.e., the change occurs on the first Sunday in
November at 2:00 AM.
Likewise, I can examine the «Daylight» values to determine when daylight
savings time begins:
DaylightDay : 2 DaylightDayOfWeek : 0 DaylightHour : 2 DaylightMillisecond : 0 DaylightMinute : 0 DaylightMonth : 3
I can see from the above that, for this system, daylight savings time
begins on the second Sunday of March at 2:00 AM EST when clocks are
advanced one hour to 3:00 AM EDT, leaving a one hour gap. The mnemonic
for the time changes is «spring forward, fall back.» You can see the
calendar dates for daylight saving time for recent years and future years at
Daylight saving time in the United States.
You can select individual values by specifying the value you are interested
in instead of using an asterisk after «select». E.g.:
PS C:\Users\Lila> Get-CimInstance Win32_TimeZone | select DaylightName DaylightName ------------ Eastern Daylight Time PS C:\Users\Lila> Get-CimInstance Win32_TimeZone | select DaylightName, StandardName DaylightName StandardName ------------ ------------ Eastern Daylight Time Eastern Standard Time PS C:\Users\Lila>
Related articles:
-
WMIC Share Get
-
Determining S.M.A.R.T disk drive status from a command prompt
-
Show all drives from Windows command prompt
References:
-
Check for Daylight Savings Time by Using PowerShell
By:
The Scripting Guys
Date: October 23, 2012Hey, Scripting Guy! Blog