on November 25, 2010
Windows has two command line utilities to copy files/directories from command line. Copy command can be used to copy files from one folder to another folder. It can’t be used to copy a complete folder to another location on the disk. Xcopy allows us to do this. Let’s see how we can copy a directory along with all the files and sub directories to another location.
Xcopy /E /I SourceFolder DestinationFolder
Let’s say we need to copy a directory called C:\dir1\sourcedir to a location named D:\data\destinationdir.
Now you can run the below command to copy the complete sourcedir to D:\data\destination
Xcopy /E /I C:\dir1\sourcedir D:\data\destinationdir
In the above command we can also use relative paths of the folders with respect to the current directory.
Understanding the command
/E – This option makes sure that empty subfolders are copied to the destination.
/I – Avoids prompting if the destination is a folder or file. Not required if you are adding a trailing ‘\’ to the destination folder, like below.
Xcopy /E C:\dir1\sourcedir D:\data\destinationdir\
/S – This option is not required if you are using /E. /E ensures that all subfolders are also copied to the destination.
To copy a folder in Windows using the command prompt, you can use the `xcopy` command, which allows you to copy entire directories with their contents.
xcopy "C:\source\folder" "D:\destination\folder" /E /I
Understanding CMD and Its Capabilities
What is CMD?
CMD, or Command Prompt, is a command-line interpreter in Windows that allows users to execute commands to interact with their operating system. Unlike graphical user interfaces (GUIs) that require mouse clicks, CMD uses text-based commands, enabling users to run scripts, manage files, and automate tasks efficiently.
Why Use CMD for Copying Folders?
Using CMD to copy folders presents several advantages over traditional GUI methods. CMD allows for faster execution of commands, especially when dealing with large directories or repeated tasks. This is particularly useful for batch processing or when managing multiple files across different systems. Furthermore, CMD gives users the ability to script their processes, enabling automation and reducing human error.
Copy Folder Cmd: A Quick Guide to Mastering Copying Folders
Basic CMD Syntax for File Operations
Understanding Command Structure
Understanding the basic structure of CMD commands is crucial. Most commands will follow a syntax that includes the command itself, followed by options that modify its behavior and then the source or destination paths. Familiarity with these components is essential for effective usage.

Mastering Windows MySQL Cmd in Simple Steps
How to Copy a Folder Using CMD
Using the Copy Command
The `copy` command in CMD is mainly designed for copying files rather than folders. It’s less suited for copying entire directories. However, if a user needs to copy specific files from one folder to another, the command can be helpful.
Example Command:
copy "C:\SourceFolder\*.*" "D:\DestinationFolder"
This command attempts to copy all files from `C:\SourceFolder` to `D:\DestinationFolder`. Note that this will not copy subdirectories; only files will be transferred.
Using the Xcopy Command
The `xcopy` command is specifically designed for copying files and directories, including all subdirectories and files. It’s far more flexible than the basic copy command.
Example Command:
xcopy "C:\SourceFolder" "D:\DestinationFolder" /E /I
Here, the `/E` flag tells Xcopy to copy all subdirectories, including empty ones, while the `/I` flag assumes the destination is a directory if it doesn’t already exist. Using Xcopy is essential when working with complex directory structures.
Using the Robocopy Command
Robocopy stands for «Robust File Copy» and is a command that provides advanced capabilities compared to both copy and xcopy. Robocopy is designed to handle large-scale copying jobs and includes features like resuming interrupted copies and mirroring directories.
Example Command:
robocopy "C:\SourceFolder" "D:\DestinationFolder" /E
In this command, the `/E` option again ensures all subdirectories are copied. Robocopy can also resume after interruptions, making it an excellent choice for copying large datasets.

Mastering Windows Recovery Cmd: A Quick Guide
Additional Methods to Copy Folders in CMD
Copying a Folder with the Copy Command
While you can use the `copy` command on folders, its functionality is limited. It can only copy files, and users will typically prefer Xcopy or Robocopy for entire folders.
The Xcopy Alternative
Xcopy allows you to refine your copying tasks with a variety of options. For instance, if you want to copy all files and directories within a specified directory while ensuring that you can define whether to include subdirectories or not, Xcopy is the way to go.
Example Command:
xcopy "C:\SourceFolder\*" "D:\DestinationFolder\" /S /E /I
In this example, `/S` copies all non-empty subdirectories, while `/E` allows for copying of empty ones. This makes Xcopy a powerful tool for any user needing to manage directory structures.
The Power of Robocopy
Robocopy provides many advanced features that are not available with Xcopy or the basic copy command.
Basic Command Syntax:
robocopy "C:\SourceFolder" "D:\DestinationFolder" /E /Z /R:5 /W:5
Here, `/Z` enables restartable mode, which is particularly useful for network paths. The `/R:5` option specifies that Robocopy should retry up to 5 times on failed copies, with `/W:5` setting a wait time of 5 seconds between each retry.

Mastering Windows Uptime Cmd for Quick Checks
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Error Messages During Copying
When using CMD, users may encounter several common error messages. It’s essential to pay close attention to these messages as they often provide context on what went wrong. Common issues include «Access Denied,» indicating permission-related problems, and «Path Not Found,» indicating an incorrect directory path.
Permission Issues
To resolve permission-related issues, ensure that CMD is running with administrator privileges. Right-click on the CMD icon and select «Run as administrator» to gain elevated permissions. This can help in ensuring you have the necessary rights to copy files or folders across protected directories.
Mastering Windows Shell Cmd: Quick Tips and Tricks
Best Practices for Using CMD to Copy Folders
Regular Backup Strategies
Creating regular backups of important folders should be a part of any user’s workflow. CMD commands can be particularly effective in automating these backups. Setting a recurring schedule for the `xcopy` or `robocopy` command can significantly reduce the chances of data loss.
Scripting for Automation
Creating batch scripts can help automate the folder copying process. Automating these tasks minimizes human error and saves time.
Example Batch Script for Daily Folder Copying:
@echo off
set source=C:\SourceFolder
set destination=D:\DestinationFolder
robocopy "%source%" "%destination%" /E
This script sets defined source and destination paths and executes the Robocopy command. You can schedule this script using Task Scheduler to run at specified intervals, providing an excellent mechanism for consistent backups.

Mastering Windows Time Cmd: A Quick Guide
Conclusion
In conclusion, utilizing the Windows copy folder cmd commands can greatly enhance your file management productivity. Whether you’re aiming for basic file transfers with `copy`, enhanced directory copying with `xcopy`, or robust, reliable transfers using `robocopy`, understanding these commands will empower you to manage your data more effectively. Familiarizing yourself with these techniques will not only streamline your processes but also prepare you for more complex CMD tasks in the future.
Mastering Windows XP Cmd: Quick Commands to Enhance Your Skills
Additional Resources
For further reading on CMD commands and their applications, consider checking out online tutorials, official documentation, or community forums dedicated to Windows command line use. Practicing these commands will solidify your understanding and expose you to additional features and options.

In this tutorial, we will learn how to copy files and folders in the Windows Command prompt.
We are going to look at two cmd commands: Copy and Xcopy.
Note that the copy command has some limitations compared to the xcopy. For example, to copy directories or hidden files, you have to use the xcopy command.
Copy Command
On Windows, we can use the copy command to copy one or more files from one location to another:
copy C:\data\sales.doc C:\backupThe preceding command will copy sales.doc from C:\data\ to C:\backup.
Use the /y switch to overwrite duplicate files without confirmation:
copy /y C:\data\sales.doc C:\backupWe can also save a file to a different name. For example, the following command saves file1.txt as file2.txt in the same directory:
copy file1.txt file2.txtYou can also use wildcards to copy multiple files:
copy /y C:\data\* C:\backup
copy /y C:\data\*.doc C:\backupThe first command copies all files in the C:\data\ directory to C:\backup. The second command copies all files with a .doc extension to the C:\backup.

We can also combine several files into one:
copy file1+file2 file3
copy error* C:\backup\report.txtIn the first line, file1 and file2 are combined to make one file named file3. In the second line, all files whose names start with «error» are copied to the C:\backup, as a single file called report.txt.
You can get a list of all available options with the copy /? command.
Xcopy Command
The xcopy command offers more features. For example, with xcopy, we can copy directories and subdirectories, as well as hidden files.
Command Options
| /Y | Prompt before overwriting an existing file. |
| /H | Copy hidden files/system files. |
| /S | Copy directories and subdirectories. Empty directories are not included by default (use /e for that). |
| /E | Include empty directories. |
| /I | Create the destination folder if it does not exist. Use this option when you want to copy the parent folder itself. |
| /T | Copy directory tree without files. Empty directories are not included by default. Use /e option to include empty folders. |
| /P | Prompt for confirmation before creating each file. |
| /Q | Quiet mode. |
| /exclude | Specify a text file that contains a list of files to exclude. See the examples. |
| /Z | Resume mode. Use this option when copying files over a network. |
| /D:m-d-y | Copies files changed on or after the specified date. |
Examples of Using the Xcopy Command
Copy sales.doc from the current directory to C:\backup:
xcopy sales.doc C:\backupCopy C:\data\accounts (all files including subdirectories) to C:\backup:
xcopy /s /e /h /i /y C:\data\accounts C:\backup\accounts
In the following example (without /I switch), the contents of the folder are copied but not the folder itself:
xcopy /s /e /h /y C:\data\accounts C:\backup\Copy the directory structure of C:\OneDrive to the backup directory:
xcopy /s /e /t /y C:\OneDrive C:\backup\You can use wildcard characters to match patterns. The following command copies all files with a .jpg extension:
xcopy /s /h /y C:\data\*.jpg C:\backupUsing for loop to copy multiple files:
for %i in (sales.doc, products.doc) do xcopy /y %i C:\backupExcluding files with xcopy
With the /exclude, we can provide a text file that contains items we want to exclude.
xcopy /s /e /h /y /exclude:C:\Users\user1\files-to-exclude.txt C:\data\ C:\backup\The files-to-exclude.txt may look like the following:
.doc
sales*In this example, we exclude items with the .doc extension and files whose name starts with sales.
You can get a list of all available options with the xcopy /? command.
Last Updated :
23 Sep, 2024
The xcopy command in Windows is a powerful tool for copying files and directories. It extends the functionality of the standard copy command by allowing the copy of entire directories along with their subdirectories and files all at once. This makes xcopy highly useful for tasks such as backing up files, migrating data, or automating file management tasks. In this article, we will cover what the xcopy command is how to use it, and provide some common use cases with examples.
Table of Content
- What is the Xcopy Command?
- How to Use the xcopy Command?
- 1. Copy Files
- 2. Copy Entire Directory
- 3. Copy Directory Including Empty Folders
- 4. Copy and Overwrite Files
- 5. Copy Files Based on Date
- 6. Copy Files in Quiet Mode
- 7. Copy Files with Attributes
- 8. Copy Files and Verify
- 9. Copy Files Without Prompting for Destination Confirmation
- Common xcopy Options
- How to Use the Xcopy Command in Windows — FAQs
What is the Xcopy Command?
The xcopy (extended copy) command is used to copy files and directories including the subdirectories and files within them. Unlike the basic copy command, xcopy can handle large-scale directory copying making it perfect for backups, migrations, and file replication.
Basic Syntax:
xcopy [source] [destination] [options]
- [source]: The path to the file or directory we want to copy.
- [destination]: The path to where we want to copy the files.
- [options]: The Various flags that control how the xcopy command behaves.
How to Use the xcopy Command?
1. Copy Files
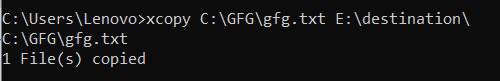
To copy a file from one location to another using xcopy the basic syntax is:
xcopy C:\source\file.txt D:\destination\
This command copies file.txt from the C:\source directory to the D:\destination directory.
Example:
2. Copy Entire Directory
To copy an entire directory including all its subdirectories and files we can use the /s switch:
xcopy C:\source\ D:\destination\ /s
The /s option copies all directories and subdirectories except empty ones.
Example:
3. Copy Directory Including Empty Folders
If we also want to include the empty directories in the copy use the /e switch:
xcopy C:\source\ D:\destination\ /e
The /e switch copies all subdirectories including the empty ones.
Example:
4. Copy and Overwrite Files
If files in the destination already exist and we want to overwrite them we can use the /y option:
xcopy C:\source\ D:\destination\ /y
The /y option suppresses the prompt that asks if we want to overwrite the file.
Example:
5. Copy Files Based on Date
We can use the /d option to only copy files that have changed after a specific date or if they are newer than the destination files.
xcopy C:\source\ D:\destination\ /d
This ensures that only new or modified files are copied saving time and disk space.
Example:
6. Copy Files in Quiet Mode
To suppress output and avoid unnecessary prompts use the /q option:
xcopy C:\source\ D:\destination\ /q
This copies files quietly without listing each file.
Example:
7. Copy Files with Attributes
To copy system or hidden files we can use the /h option:
xcopy C:\source\ D:\destination\ /h
Normally, hidden and system files are not copied. The /h switch forces the xcopy command to the include them.
Example:
8. Copy Files and Verify
To ensure that files are copied correctly we can use the /v option which verifies each file after copying:
xcopy C:\source\ D:\destination\ /v
Example:
9. Copy Files Without Prompting for Destination Confirmation
Sometimes, xcopy will prompt to confirm whether the destination is a directory or a file. To avoid this we can add the /i option:
xcopy C:\source\ D:\destination\ /i
The /i option assumes the destination is a directory and automatically continues.
Example:
Common xcopy Options
Here are some commonly used xcopy options:
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
/s |
The Copies directories and subdirectories except empty ones. |
|
/e |
The Copies of all subdirectories including the empty ones. |
|
/y |
Overwrites files without prompting for confirmation. |
|
/d |
Copies files that have changed since the last copy. |
|
/v |
The Verifies each file after copying to ensure accuracy. |
|
/h |
The Copies hid and system files. |
|
/q |
The Copies files in quiet mode suppressing output. |
|
/i |
Assumes the destination is a directory if it’s unclear. |
|
/f |
It displays the full source and destination of each file copied. |
Conclusion
The xcopy command is a versatile and powerful tool in Windows allowing you to perform advanced file-copying tasks with ease. Whether we’re backing up directories copying only newer files or handling large sets of files across different drives, xcopy offers a range of options to suit your needs. By mastering this command we can save time streamline your file management tasks and ensure that data is efficiently copied with accuracy and precision.
При работе в командной строке (cmd) часто возникает необходимость скопировать файл или целую папку. Также консольные команды для копирования могут использоваться в BAT-файлах для резервного копирования и других задачах.
В этой статье мы расскажем о том, как скопировать файл или папку в командной строке Windows. Статья будет актуальной для всех версий Windows, включая самые новые Windows 11 и Windows 10.
Содержание
Как скопировать файл через командную строку Windows
Для копирования файлов в командной строке Windows нужно использовать команду «copy». Данная команда позволяет скопировать один или несколько файлов из одной папку в другую. Обратите внимание, команда «copy» копирует только файлы. Для копирования вложенных папок нужно использовать команду «xcopy», которую мы рассмотрим ниже.
В самом простом случае команда для копирования файлов выглядит так:
copy [исходный файл] [новый файл или папка назначения]
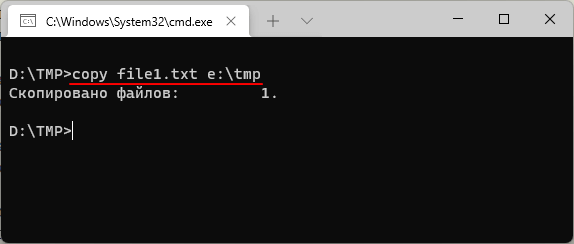
Например, чтобы скопировать файл «file1.txt» из текущего каталога в папку «e:\tmp» нужно выполнить:
copy file1.txt e:\tmp
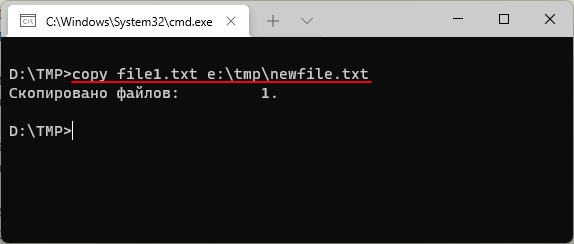
При необходимости для копируемого файла можно указать новое название в папке назначения. Например, чтобы скопировать «file1.txt» из текущего каталога в папку «e:\tmp» и при этом назвать его «newfile.txt» нужно выполнить:
copy file1.txt e:\tmp\newfile.txt
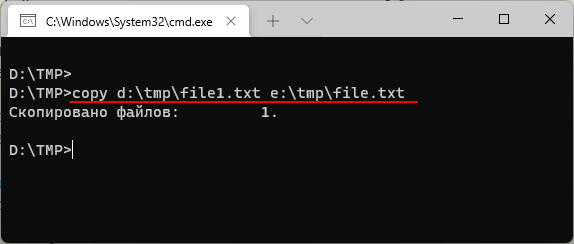
С указанием полных путей команда копирования будет выглядеть так:
copy d:\tmp\file1.txt e:\tmp\file.txt
Для копирования большого количества файлов в названиях можно использовать маски. Символ звездочка (*) обозначает любое количество любых символов, а знак вопроса (?) – один любой символ. Например, чтобы скопировать все документы с расширением TXT из текущего каталога в папку «e:\tmp\» нужно выполнить следующее:
copy *.txt e:\tmp\
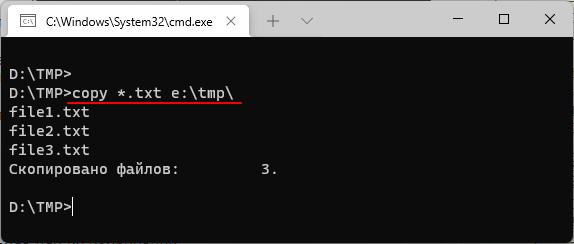
Также с помощью команды «copy» можно скопировать все содержимое одной папки в другую. Например, в случае копирования всех файлов из папки «d:\tmp\» в папку «e:\tmp» команда будет выглядеть так:
copy d:\tmp\ e:\tmp
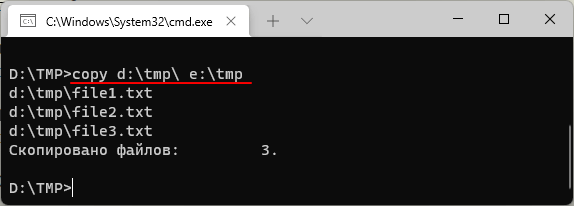
В данном случае из папки «d:\tmp\» будут скопированы только файлы. Для копирования вложенных папок нужно использовать «xcopy».
Полный синтаксис команды «copy» выглядит так:
copy [/d] [/v] [/n] [/y | /-y] [/z] [/a | /b] <source> [/a | /b] [+<source> [/a | /b] [+ ...]] [<destination> [/a | /b]]
Полный список параметров для команды «copy»:
| Параметр | Описание |
| /d | Сохранение копируемых зашифрованные файлов в расшифрованном виде в месте назначения. |
| /v | Проверка правильности записи скопированных файлов. |
| /n | Использование короткого имени файла (если доступно) при копировании файла с именем длиннее восьми символов или с расширением длиннее трех символов. |
| /y | Подавление запроса на подтверждение перезаписи. |
| /-y | Вывод запроса на подтверждение перезаписи. |
| /z | Копирует сетевые файлы в перезапускаемом режиме. |
| /a | Копирование текстового файла ASCII. |
| /b | Копирование двоичного файла. |
| <source> | Указывает расположение, из которого необходимо скопировать один или несколько файлов. Обязательный параметр. |
| <destination> | Указывает расположение, в которое необходимо скопировать файл или несколько файлов. Обязательный параметр. |
| /? | Отображение справки в командной строке. |
Большинство параметров указываются в начале, сразу после команды «copy». Например, для того чтобы подавить вывод запросов на перезапись существующих файлов можно добавить параметр «/y».
copy /y file1.txt file2.txt
Как скопировать папку через командную строку Windows
Для копирования папок с вложенными папками и файлами в командной строке Windows нужно использовать команду «xcopy». Данная команда позволяет скопировать папку из одного расположение в другое с сохранением структуры каталогов. Фактически «xcopy» — это более продвинутая версия команды «copy».
В упрощенном виде синтаксис команды «xcopy» будет выглядеть так:
xcopy [исходная папка или файл] [папка назначения или файл] [параметры]
Для копирования папок с вложенными папками и файлами нужно использовать параметр «/s» или «/e». Без этих параметров команда будет работать только с одним каталогом.
| Параметр | Описание |
| /s | Копирование каталогов с подкаталогами (исключая пустые) |
| /e | Копирование каталогов с подкаталогами (включая пустые). |
Например, для того чтобы скопировать все файлы и вложенные папки (включая пустые) из папки «d:\tmp» в папку «e:\tmp» нужно выполнить:
xcopy d:\tmp e:\tmp /e
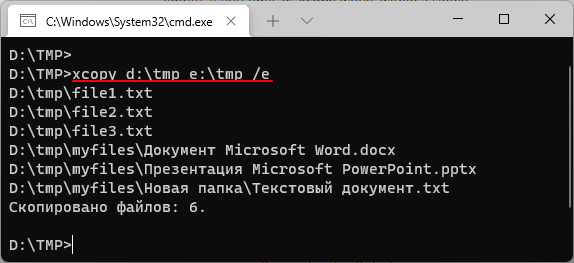
Полный синтаксис команды «xcopy» выглядит так:
xcopy <Source> [<Destination>] [/w] [/p] [/c] [/v] [/q] [/f] [/l] [/g] [/d [:MM-DD-YYYY]] [/u] [/i] [/s [/e]] [/t] [/k] [/r] [/h] [{/a | /m}] [/n] [/o] [/x] [/exclude:FileName1[+[FileName2]][+[FileName3]]] [{/y | /-y}] [/z] [/b] [/j]
Полный список параметров для команды «xcopy» можно посмотреть на сайте Майкрософт. Здесь же приведены только некоторые самые базовые:
| Параметр | Описание |
| /s | Копирование каталогов с подкаталогами (исключая пустые) |
| /e | Копирование каталогов с подкаталогами (включая пустые). |
| /w | Вывод запроса на подтверждения начала копирования. |
| /p | Запрос подтверждение при создании каждого нового файла. |
| /c | Пропуск ошибок. |
| /v | Проверка всех скопированных файлов на соответствие его исходнику. |
| /q | Скрывает вывод информации от команды xcopy. |
| /f | Вывод имен в процессе копирования. |
| /l | Вывод списка копируемых файлов. |
| /g | Сохранение новых файлов в незашифрованном виде. |
| /d[:мм-дд-гггг] | Копирование файлов, которые были измененные не ранее указанной даты. Если не указать дату (мм-дд-гггг), то команда xcopy будет копировать все файлы, которые новее существующих. |
| /u | Обновление только существующих файлов в папке назначения. |
| /y | Подавление запроса на подтверждение перезаписи. |
| /-y | Вывод запроса на подтверждение перезаписи. |
| /z | Копирует сетевые файлы в перезапускаемом режиме. |
| /h | Копирование скрытых и системных файлов. |
| /r | Перезапись файлов с атрибутом «только для чтения». |
| /t | Создание структуры каталогов без копирования файлов. Пустые каталоги не включаются в структуру. Для включения пустых каталогов нужно добавить параметр /E. |
| <source> | Указывает расположение, из которого необходимо скопировать один или несколько файлов. Обязательный параметр. |
| <destination> | Указывает расположение, в которое необходимо скопировать файл или несколько файлов. Обязательный параметр. |
| /? | Отображение справки в командной строке. |
Параметры указываются в конце команды. Например, для того чтобы скопировать все файлы (включая скрытые, системные и только для чтения) и вложенные папки (включая пустые) из папки «d:\tmp» в папку «e:\tmp» нужно выполнить:
xcopy d:\tmp e:\tmp /e /h /r
Посмотрите также:
- Выключение компьютера через командную строку
- Как перезагрузить компьютер через командную строку
- Как вызвать командную строку в Windows 7
- Как поменять дату в Windows 7
- Как выключить компьютер через определенное время
Автор
Александр Степушин
Создатель сайта comp-security.net, автор более 2000 статей о ремонте компьютеров, работе с программами, настройке операционных систем.
Остались вопросы?
Задайте вопрос в комментариях под статьей или на странице
«Задать вопрос»
и вы обязательно получите ответ.
