From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Windows 10, version 1909 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Windows 10 November 2019 Update[1] (also known as version 1909[2] and codenamed «19H2»[3]) is the eighth major update to Windows 10 as the cumulative update to the May 2019 Update. It carries the build number 10.0.18363.[4]
The first preview was released to Insiders who opted in to the slow ring on July 1, 2019.[5] The update began rolling out on November 12, 2019.[6] Notable changes in the November 2019 Update include:[7]
- Ability to create events from the Calendar fly-out on the taskbar
- Improvements to notification management, including thumbnails demonstrating notification banners and the Action Center in application notification settings, and the ability to access per-application notification settings from their displays in Action Center
- The Start menu’s navigation sidebar icons expand into a drawer with text labels when the cursor is hovered over them
- Support for using third-party digital assistants from the lock screen
- OneDrive integration with File Explorer’s search
The update has reached end of service on May 11, 2021 for Home, Pro, Pro Education and Pro for Workstations editions.[8] The Enterprise, IoT Enterprise and Education editions have reached end of service on May 10, 2022.[9]
| Preview builds of Windows 10, version 1909 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Version | Release date(s) | Highlights |
| 10.0.18362.10000 [5] |
Slow ring: July 1, 2019 |
|
| 10.0.18362.10005 [10] |
Slow ring: July 15, 2019 |
New features in this build are turned off by default. These features are turned on by controlled feature roll-outs via the following build: 10.0.18362.10006. |
| 10.0.18362.10006 [10] |
Slow ring: July 17, 2019 |
This update is available to a select few Insiders only. New features in this build are turned on by controlled feature. |
| 10.0.18362.10012 [11] |
Slow ring: August 8, 2019 |
New features in this build are turned off by default. These features are turned on by controlled feature roll-outs via the following build: 10.0.18362.10013. |
| 10.0.18362.10013 [11] |
This update is available to a select few Insiders only. New features in this build are turned on by controlled feature. | |
| 10.0.18362.10014 [12] |
Slow ring: August 19, 2019 |
New features in this build are turned off by default. These features are turned on by controlled feature roll-outs via the following build: 10.0.18362.10015. |
| 10.0.18362.10015 [12] |
This update is available to a select few Insiders only. New features in this build are turned on by controlled feature. | |
| 10.0.18362.10019 [13] |
Slow ring: September 5, 2019 |
All introduced features in previous 19H2 builds are turned on in this build. |
| 10.0.18362.10022 [14] |
Slow ring: September 25, 2019 |
|
| 10.0.18362.10024 [1] |
Slow ring: October 16, 2019 |
|
| Version | Release date(s) | Highlights |
| Public patches of Windows 10, version 1909 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Version | Knowledge base | Release date(s) | Highlights |
| 10.0.18363.327 [3] |
KB4517245 | Release preview: August 26, 2019 |
This update is available to a select few Insiders only. |
| 10.0.18363.329 [3] |
Release preview: August 29, 2019 |
||
| 10.0.18363.385 [3] |
KB4517211 | Release preview: September 23, 2019 |
|
| 10.0.18363.387 [3] |
Release preview: September 27, 2019 |
||
| 10.0.18363.388 [3] |
KB4524147 | Release preview: October 3, 2019 |
|
| 10.0.18363.418 [3] |
KB4517389 | Release preview: October 8, 2019 |
|
| 10.0.18363.446 [1][15] |
KB4522355 | Release preview: October 17, 2019 |
|
| 10.0.18363.448 [1][16] |
Release preview: October 18, 2019 |
||
| 10.0.18363.449 [17] |
Release preview: October 23, 2019 |
||
| 10.0.18363.476 Version 1909 [18] |
KB4524570 | Release preview and public release: November 12, 2019 |
This update is no longer available from Windows Update, Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since August 5, 2021. |
| 10.0.18363.535 [19] |
KB4530684 | Release preview and public release: December 10, 2019 |
This update is no longer available from Windows Update, Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since August 5, 2021. |
| 10.0.18363.592 [20] |
KB4528760 | Release preview and public release: January 14, 2020 |
This update is no longer available from Windows Update, Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since August 5, 2021. |
| 10.0.18363.628 [21] |
KB4532695 | Release preview and public release: January 28, 2020 |
|
| 10.0.18363.657 [22] |
KB4532693 | Release preview and public release: February 11, 2020 |
This update is no longer available from Windows Update, Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since August 5, 2021. |
| 10.0.18363.693 [23] |
KB4535996 | Release preview: February 26, 2020 Public release: |
|
| 10.0.18363.719 [24] |
KB4540673 | Release preview and public release: March 10, 2020 |
This update is no longer available from Windows Update, Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since August 5, 2021. |
| 10.0.18363.720 [25] |
KB4551762 | Release preview and public release: March 12, 2020 |
This update is no longer available from Windows Update, Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since August 5, 2021. |
| 10.0.18363.752 [26][27] |
KB4541335 | Release preview: March 21, 2020 Public release: |
|
| 10.0.18363.753 [28] |
KB4554364 | Release preview and public release: March 30, 2020 |
|
| 10.0.18363.778 [29] |
KB4549951 | Release preview and public release: April 14, 2020 |
This update is no longer available from Windows Update, Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since August 5, 2021. |
| 10.0.18363.815 [30] |
KB4550945 | Public release: April 21, 2020 |
|
| 10.0.18363.836 [31] |
KB4556799 | Public release: May 12, 2020 |
This update is no longer available from Windows Update, Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since August 5, 2021. |
| 10.0.18363.900 [32] |
KB4560960 | Public release: June 9, 2020 |
This update is no longer available from Windows Update, Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since August 5, 2021. |
| 10.0.18363.904 [33] |
KB4567512 | Public release: June 16, 2020 |
|
| 10.0.18363.959 [34] |
KB4565483 | Public release: July 14, 2020 |
This update is no longer available from Windows Update, Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since August 5, 2021. |
| 10.0.18363.997 [35] |
KB4559004 | Public release: July 21, 2020 |
|
| 10.0.18363.1016 [36] |
KB4565351 | Public release: August 11, 2020 |
This update is no longer available from Windows Update, Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since August 5, 2021. |
| 10.0.18363.1049 [37] |
KB4566116 | Public release: August 20, 2020 |
|
| 10.0.18363.1082 [38] |
KB4574727 | Public release: September 8, 2020 |
This update is no longer available from Windows Update, Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since August 5, 2021. |
| 10.0.18363.1110 [39] |
KB4577062 | Public release: September 16, 2020 |
|
| 10.0.18363.1139 [40] |
KB4577671 | Public release: October 13, 2020 |
This update is no longer available from Windows Update, Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since August 5, 2021. |
| 10.0.18363.1171 [41] |
KB4580386 | Public release: October 20, 2020 |
|
| 10.0.18363.1198 [42] |
KB4586786 | Public release: November 10, 2020 |
This update is no longer available from Windows Update, Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since August 5, 2021. |
| 10.0.18363.1199 [43] |
KB4594443 | Public release: November 19, 2020 |
|
| 10.0.18363.1237 [44] |
KB4586819 | ||
| 10.0.18363.1256 [45] |
KB4592449 | Public release: December 8, 2020 |
This update is no longer available from Windows Update, Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since August 5, 2021. |
| 10.0.18363.1316 [46] |
KB4598229 | Public release: January 12, 2021 |
This update is no longer available from Windows Update, Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since August 5, 2021. |
| 10.0.18363.1350 [47] |
KB4598298 | Public release: January 21, 2021 |
|
| 10.0.18363.1377 [48] |
KB4601315 | Public release: February 9, 2021 |
This update is no longer available from Windows Update, Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since August 5, 2021. |
| 10.0.18363.1379 [49] |
KB5001028 | Public release: February 11, 2021 |
|
| 10.0.18363.1411 [50] |
KB4601380 | Public release: February 16, 2021 |
|
| 10.0.18363.1440 [51] |
KB5000808 | Public release: March 9, 2021 |
This update is no longer available from Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since September 12, 2023, although it continues to be available from Windows Update. |
| 10.0.18363.1441 [52] |
KB5001566 | Public release: March 15, 2021 |
|
| 10.0.18363.1443 [53] |
KB5001648 | Public release: March 18, 2021 |
|
| 10.0.18363.1474 [54] |
KB5000850 | Public release: March 25, 2021 |
|
| 10.0.18363.1500 [55] |
KB5001337 | Public release: April 13, 2021 |
|
| 10.0.18363.1533 [56] |
KB5001396 | Public release: April 22, 2021 |
|
| 10.0.18363.1556 [57] |
KB5003169 | Public release: May 11, 2021 |
|
| 10.0.18363.1593 [58] |
KB5003212 | Public release: May 20, 2021 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only. |
| 10.0.18363.1621 [59] |
KB5003635 | Public release: June 8, 2021 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only.
This update is no longer available from Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since September 12, 2023, although it continues to be available from Windows Update. |
| 10.0.18363.1645 [60] |
KB5003698 | Public release: June 15, 2021 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only. |
| 10.0.18363.1646 [61] |
KB5004946 | Public release: July 6, 2021 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only.
This update is no longer available from Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since September 12, 2023, although it continues to be available from Windows Update. |
| 10.0.18363.1679 [62] |
KB5004245 | Public release: July 13, 2021 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only.
This update is no longer available from Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since September 12, 2023, although it continues to be available from Windows Update. |
| 10.0.18363.1714 [63] |
KB5004293 | Public release: July 29, 2021 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only. |
| 10.0.18363.1734 [64] |
KB5005031 | Public release: August 10, 2021 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only.
This update is no longer available from Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since September 12, 2023, although it continues to be available from Windows Update. |
| 10.0.18363.1766 [65] |
KB5005103 | Public release: August 26, 2021 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only. |
| 10.0.18363.1801 [66] |
KB5005566 | Public release: September 14, 2021 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only.
This update is no longer available from Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since September 12, 2023, although it continues to be available from Windows Update. |
| 10.0.18363.1830 [67] |
KB5005624 | Public release: September 21, 2021 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only. |
| 10.0.18363.1854 [68] |
KB5006667 | Public release: October 12, 2021 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only.
This update is no longer available from Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since September 12, 2023, although it continues to be available from Windows Update. |
| 10.0.18363.1916 [69] |
KB5007189 | Public release: November 9, 2021 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only.
This update is no longer available from Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since September 12, 2023, although it continues to be available from Windows Update. |
| 10.0.18363.1977 [70] |
KB5008206 | Public release: December 14, 2021 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only.
This update is no longer available from Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since September 12, 2023, although it continues to be available from Windows Update. |
| 10.0.18363.2037 [71] |
KB5009545 | Public release: January 11, 2022 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only.
This update is no longer available from Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since September 12, 2023, although it continues to be available from Windows Update. |
| 10.0.18363.2039 [72] |
KB5010792 | Public release: January 17, 2022 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only. |
| 10.0.18363.2094 [73] |
KB5010345 | Public release: February 8, 2022 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only.
This update is no longer available from Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since September 12, 2023, although it continues to be available from Windows Update. |
| 10.0.18363.2158 [74] |
KB5011485 | Public release: March 8, 2022 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only.
This update is no longer available from Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since September 12, 2023, although it continues to be available from Windows Update. |
| 10.0.18363.2212 [75] |
KB5012591 | Public release: April 12, 2022 |
This update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only.
This update is no longer available from Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since September 12, 2023, although it continues to be available from Windows Update. |
| 10.0.18363.2274 [76] |
KB5013945 | Public release: May 10, 2022 |
This final update is available for Education, Enterprise and IoT Enterprise editions only.
This update is no longer available from Microsoft Update Catalog or other release channels since September 12, 2023, although it continues to be available from Windows Update. |
| Version | Knowledge base | Release date(s) | Highlights |
- Windows 10 version history
- ^ a b c d LeBlanc, Brandon (October 10, 2019). «Getting the November 2019 Update Ready for Release». Windows Insider Blog. Archived from the original on October 11, 2019. Retrieved October 11, 2019.
- ^ «August 30, 2019—KB4512941 (OS Build 18362.329)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved August 30, 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g «Testing the throttled delivery approach for 19H2». Windows Experience Blog. 26 August 2019. Archived from the original on August 27, 2019. Retrieved August 26, 2019.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 10 Insider Preview Build 18836». Windows Experience Blog. 14 February 2019. Archived from the original on February 16, 2019. Retrieved February 16, 2019.
- ^ a b «Announcing Windows 10 Insider Preview Build 18362.10000 (19H2)». Windows Experience Blog. July 2019. Archived from the original on July 2, 2019. Retrieved July 1, 2019.
- ^ Jo Foley, Mary. «Microsoft begins the official rollout of Windows 10 1909». ZDNet. Archived from the original on November 13, 2019. Retrieved November 12, 2019.
- ^ «How to get the Windows 10 November 2019 Update». Windows Experience Blog. 2019-11-12. Archived from the original on 13 November 2019. Retrieved November 13, 2019.
- ^ «Windows 10, version 1909 end of servicing (Home and Pro)». Microsoft Learn. February 11, 2021. Retrieved June 15, 2024.
- ^ «Windows 10, version 1909 end of servicing (Enterprise and Education)». Microsoft Learn. February 11, 2022. Retrieved June 15, 2024.
- ^ a b «Announcing Windows 10 Insider Preview Build 18362.10005 (19H2)». Windows Experience Blog. 15 July 2019. Archived from the original on July 16, 2019. Retrieved July 19, 2019.
- ^ a b «Announcing Windows 10 Insider Preview Build 18362.10012 & 18362.10013 (19H2)». Windows Experience Blog. 8 August 2019. Archived from the original on August 9, 2019. Retrieved August 9, 2019.
- ^ a b «Announcing Windows 10 Insider Preview Build 18362.10014 & 18362.10015 (19H2)». Windows Experience Blog. 19 August 2019. Archived from the original on August 20, 2019. Retrieved August 19, 2019.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 10 Insider Preview Build 18362.10019 (19H2)». Windows Experience Blog. 5 September 2019. Archived from the original on September 5, 2019. Retrieved September 5, 2019.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 10 Insider Preview Build 18362.10022 (19H2)». Windows Experience Blog. 25 September 2019. Archived from the original on September 26, 2019. Retrieved September 25, 2019.
- ^ Popa, Bogdan (October 18, 2019). «Windows 10 Cumulative Update KB4522355 (1903/1909) Now Available for Testing». Softpedia. Archived from the original on October 18, 2019. Retrieved October 18, 2019.
- ^ Brink (October 19, 2019). «KB4522355 Windows 10 Build 18362.448 19H1 and 18363.448 19H2 — Oct. 18». Windows 10 Forums. Archived from the original on October 19, 2019. Retrieved October 19, 2019.
- ^ Popa, Bogdan (October 24, 2019). «Windows 10 Cumulative Update KB4522355 Re-Released for Version 1903, 1909». Softpedia. Archived from the original on October 24, 2019. Retrieved October 24, 2019.
- ^ «November 12, 2019—KB4524570 (OS Build 18362.476 and 18363.476)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved November 12, 2019.
- ^ «December 10, 2019—KB4530684 (OS Builds 18362.535 and 18363.535)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved December 10, 2019.
- ^ «January 14, 2020—KB4528760 (OS Builds 18362.592 and 18363.592)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved January 14, 2020.
- ^ «January 28, 2020—KB4532695 (OS Builds 18362.628 and 18363.628)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ^ «February 11, 2020—KB4532693 (OS Builds 18362.657 and 18363.657)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 11, 2020.
- ^ «February 27, 2020—KB4535996 (OS Builds 18362.693 and 18363.693)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 29, 2020.
- ^ «March 10, 2020—KB4540673 (OS Builds 18362.719 and 18363.719)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved March 10, 2020.
- ^ «March 12, 2020—KB4551762 (OS Builds 18362.720 and 18363.720)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved March 14, 2020.
- ^ «March 24, 2020—KB4541335 (OS Builds 18362.752 and 18363.752)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved March 25, 2020.
- ^ «Windows 10 v1909 18363.752 and v1903 18362.752 (KB4541335, RP)». Winaero. March 21, 2020. Retrieved March 21, 2020.
- ^ «March 30, 2020—KB4554364 (OS Builds 18362.753 and 18363.753)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 2, 2020.
- ^ «April 14, 2020—KB4549951 (OS Builds 18362.778 and 18363.778)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 15, 2020.
- ^ «April 21, 2020—KB4550945 (OS Builds 18362.815 and 18363.815)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 22, 2020.
- ^ «May 12, 2020—KB4556799 (OS Builds 18362.836 and 18363.836)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved May 13, 2020.
- ^ «June 9, 2020—KB4560960 (OS Builds 18362.900 and 18363.900)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved June 10, 2020.
- ^ «June 16, 2020—KB4567512 (OS Builds 18362.904 and 18363.904)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved June 19, 2020.
- ^ «July 14, 2020—KB4565483 (OS Builds 18362.959 and 18363.959)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved July 15, 2020.
- ^ «July 21, 2020—KB4559004 (OS Builds 18362.997 and 18363.997) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved July 24, 2020.
- ^ «August 11, 2020—KB4565351 (OS Builds 18362.1016 and 18363.1016)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved August 12, 2020.
- ^ «August 20, 2020—KB4566116 (OS Builds 18362.1049 and 18363.1049) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved August 21, 2020.
- ^ «September 8, 2020—KB4574727 (OS Builds 18362.1082 and 18363.1082)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved September 9, 2020.
- ^ «September 16, 2020—KB4577062 (OS Builds 18362.1110 and 18363.1110) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- ^ «October 13, 2020—KB4577671 (OS Builds 18362.1139 and 18363.1139)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved October 14, 2020.
- ^ «October 20, 2020—KB4580386 (OS Builds 18362.1171 and 18363.1171) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved October 21, 2020.
- ^ «November 10, 2020—KB4586786 (OS Builds 18362.1198 and 18363.1198)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved November 11, 2020.
- ^ «November 19, 2020—KB4594443 (OS Builds 18362.1199 and 18363.1199) Out-of-band». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved November 20, 2020.
- ^ «November 19, 2020—KB4586819 (OS Builds 18362.1237 and 18363.1237) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved November 20, 2020.
- ^ «December 8, 2020—KB4592449 (OS Builds 18362.1256 and 18363.1256)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved December 9, 2020.
- ^ «January 12, 2021—KB4598229 (OS Build 18363.1316)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved January 13, 2021.
- ^ «January 21, 2021—KB4598298 (OS Build 18363.1350) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved January 22, 2021.
- ^ «February 9, 2021—KB4601315 (OS Build 18363.1377)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 10, 2021.
- ^ «February 11, 2021—KB5001028 (OS Build 18363.1379) Out-of-band». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 12, 2021.
- ^ «February 16, 2021—KB4601380 (OS Build 18363.1411) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 18, 2021.
- ^ «March 9, 2021—KB5000808 (OS Build 18363.1440)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved March 10, 2021.
- ^ «March 15, 2021—KB5001566 (OS Build 18363.1441) Out-of-band». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved March 16, 2021.
- ^ «March 18, 2021—KB5001648 (OS Build 18363.1443) Out-of-band». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved March 18, 2021.
- ^ «March 25, 2021—KB5000850 (OS Build 18363.1474) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved March 29, 2021.
- ^ «April 13, 2021—KB5001337 (OS Build 18363.1500)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 14, 2021.
- ^ «April 22, 2021—KB5001396 (OS Build 18363.1533) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 25, 2021.
- ^ «May 11, 2021—KB5003169 (OS Build 18363.1556)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved May 12, 2021.
- ^ «May 20, 2021—KB5003212 (OS Build 18363.1593) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved May 21, 2021.
- ^ «June 8, 2021—KB5003635 (OS Build 18363.1621)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved June 9, 2021.
- ^ «June 15, 2021—KB5003698 (OS Build 18363.1645) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved June 16, 2021.
- ^ «July 6, 2021—KB5004946 (OS Build 18363.1646) Out-of-band». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ^ «July 13, 2021—KB5004245 (OS Build 18363.1679)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ «July 29, 2021—KB5004293 (OS Build 18363.1714) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved July 31, 2021.
- ^ «August 10, 2021—KB5005031 (OS Build 18363.1734)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved August 11, 2021.
- ^ «August 26, 2021—KB5005103 (OS Build 18363.1766) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved August 28, 2021.
- ^ «September 14, 2021—KB5005566 (OS Build 18363.1801)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved September 16, 2021.
- ^ «September 21, 2021—KB5005624 (OS Build 18363.1830) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved September 23, 2021.
- ^ «October 12, 2021—KB5006667 (OS Build 18363.1854)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved October 13, 2021.
- ^ «November 9, 2021—KB5007189 (OS Build 18362.1916)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved November 10, 2021.
- ^ «December 14, 2021—KB5008206 (OS Build 18363.1977)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved December 14, 2021.
- ^ «January 11, 2022—KB5009545 (OS Build 18363.2037)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved January 12, 2022.
- ^ «January 17, 2022—KB5010792 (OS Build 18363.2039) Out-of-band». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved January 18, 2022.
- ^ «February 8, 2022—KB5010345 (OS Build 18363.2094)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 9, 2022.
- ^ «March 8, 2022—KB5011485 (OS Build 18363.2158)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved March 9, 2022.
- ^ «April 12, 2022—KB5012591 (OS Build 18363.2212)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 13, 2022.
- ^ «May 10, 2022—KB5013945 (OS Build 18363.2274)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Retrieved May 11, 2022.
Are you contemplating the Windows 10 1909 update but concerned about how much space it will occupy on your device? The mystery of how many gigabytes (GB) this update requires can be a significant factor in your decision-making process. Understanding the storage implications of the Windows 10 1909 update is crucial for ensuring a smooth and efficient transition to the latest version of the operating system.
In this article, we will delve into the specifics of the Windows 10 1909 update size, decoding the mystery surrounding the GB requirements. By unraveling this crucial information, you will be equipped with the knowledge needed to confidently navigate the updating process and make informed decisions about managing your device’s storage space.
Quick Summary
The Windows 10 1909 update typically ranges from 2 to 3 GB in size. The exact size may vary depending on your system configuration and the updates already installed on your computer. It is recommended to have sufficient free disk space to accommodate the update and ensure a smooth installation process.
Understanding The Windows 10 1909 Update
The Windows 10 1909 update, also known as the November 2019 update, is a significant release from Microsoft aimed at improving system stability and performance. This update brings various enhancements, bug fixes, and new features to Windows 10 users. It is a part of Microsoft’s strategy to provide regular updates that include security patches and improvements to keep the operating system up to date.
In addition to performance improvements, the Windows 10 1909 update focuses on refining the user experience by introducing subtle changes to the interface and functionality of the operating system. The update is designed to be lightweight, meaning it does not require a large amount of storage space to install. Users can expect a smoother and more efficient Windows experience after installing this update, as it addresses many of the issues found in previous versions of Windows 10. Overall, the Windows 10 1909 update is a valuable addition to the operating system, offering both performance enhancements and new features for users to enjoy.
Minimum Hardware Requirements For The Update
To successfully install the Windows 10 1909 update, your system must meet specific minimum hardware requirements. The update requires a 1 GHz processor or faster, at least 1 GB of RAM for 32-bit systems or 2 GB for 64-bit systems, and a minimum of 16 GB of available hard disk space. Additionally, a DirectX 9 compatible graphics card with a WDDM 1.0 driver is necessary for running the update smoothly.
Furthermore, your device should have a display with at least a 800×600 resolution to ensure compatibility with the Windows 10 1909 update. It is important to note that these are the basic hardware requirements to install the update, and having more powerful hardware may result in better performance and user experience. Before initiating the update, it is recommended to review your system specifications to confirm that your device meets these minimum requirements to avoid any installation issues.
Factors Affecting The Required Storage Space
When determining the storage space needed for the Windows 10 1909 update, several factors come into play. One of the primary considerations is the existing storage capacity on your device. If your device is already running low on storage space, the update may require additional room for temporary files and installation processes.
The type of update you choose to install also influences the required storage space. For instance, a major feature update like the Windows 10 1909 update will typically need more storage compared to a minor security update. Additionally, the architecture of your current Windows installation, including the number of installed applications and system files, can impact the amount of space needed for the update.
Moreover, the update process itself may temporarily use additional space for backup purposes or in case any issues arise during installation. It is advisable to have sufficient free space on your device before initiating the Windows 10 1909 update to ensure a smooth and successful installation without any storage-related complications.
Managing Storage Space Before Updating
Before updating to the Windows 10 1909 version, it is crucial to manage your storage space efficiently. This ensures a smooth and successful update process without any hindrances. Start by conducting a thorough audit of your current storage usage to identify and delete any unnecessary files or applications that are taking up valuable space on your device.
Consider transferring large files or documents to an external hard drive or cloud storage to free up space on your internal storage. It is also recommended to clean up your temporary files and empty your Recycle Bin to create additional room for the update. By managing your storage space effectively before initiating the update, you can prevent any potential issues such as update failures due to insufficient storage capacity.
Furthermore, organizing your files and folders can contribute to a more streamlined update process. Categorize and prioritize your data to optimize storage utilization, making it easier to identify redundant files that can be safely removed. Taking these proactive steps can help ensure a successful update to the Windows 10 1909 version without encountering storage-related complications.
Ways To Free Up Space For The Update
To create space for the Windows 10 1909 update, begin by clearing out unnecessary files and programs. One effective way is to use the Disk Cleanup tool provided by Windows, which helps identify and remove temporary files, system files, and other items that can be safely deleted. Uninstalling unused applications can also free up valuable space on your system.
Another strategy is to move files to an external storage device or cloud storage service. This includes transferring large media files, documents, or downloads to an external hard drive or utilizing cloud solutions like OneDrive, Google Drive, or Dropbox to store files remotely. By offloading data from your device, you can make room for the update without permanently deleting files.
Furthermore, disabling hibernate mode and reducing the size of the System Restore allocation can help reclaim space on your system. Additionally, you may consider running a storage space analysis tool to identify large files or folders that can be safely deleted or moved to an alternative storage location. By implementing these space-saving techniques, you can prepare your device for the Windows 10 1909 update and ensure a smoother installation process.
Installation Process And Storage Allocation
When initiating the installation process for the Windows 10 1909 update, users should be prepared for the storage allocation requirements. The update typically requires a substantial amount of disk space to complete the installation successfully. Adequate free space is necessary to accommodate the temporary files and system requirements during the update process.
During the installation, Windows 10 will allocate a portion of the available storage for the update. It is crucial to ensure that the device has enough free space to avoid any interruptions or errors during the installation. Users may need to clear up additional space on their hard drive to meet the storage allocation demands of the update and facilitate a smooth and efficient installation process. Remember to check your storage capacity beforehand to prevent any complications during the update.
Common Issues Related To Storage Requirements
Common issues related to storage requirements when it comes to the Windows 10 1909 update include running out of disk space during the update process. Users with limited storage space may encounter challenges in completing the update due to the large size of the files involved. This can lead to errors or interruption of the update process, requiring users to free up disk space before proceeding.
Another common issue is the need for temporary files and additional space to accommodate the installation process. The update may require extra storage for buffering and storing files before they are fully integrated into the system. Users should be aware of these storage requirements and ensure they have enough free space on their devices to prevent any disruptions or errors during the update installation.
By understanding and addressing these common storage-related issues, Windows 10 users can ensure a smooth and successful update process without encountering storage-related obstacles. Proper planning and maintenance of disk space are essential to avoid any complications and to enjoy the benefits of the latest Windows updates seamlessly.
Tips For Smooth Update Experience
To ensure a smooth Windows 10 1909 update experience, it is recommended to back up your important files and create a restore point before initiating the update process. This precautionary step will safeguard your data in case any unexpected issues arise during the installation. Additionally, make sure your device has sufficient free disk space available to accommodate the update files comfortably.
Before starting the update, consider disabling any third-party antivirus software temporarily. This can help prevent compatibility issues that may arise during the update process. It is also advisable to uninstall any unnecessary programs or applications to streamline the update and reduce the chance of conflicts. Lastly, ensure your device is connected to a stable internet connection to prevent interruptions during the download and installation of the update files. By following these simple tips, you can enhance the likelihood of a successful and hassle-free Windows 10 1909 update.
FAQs
What Is The Typical Size Of The Windows 10 1909 Update In Gigabytes?
The typical size of the Windows 10 1909 update is around 3 to 4 gigabytes. This size may vary depending on the specific system and the updates already installed on the computer. It is recommended to ensure you have sufficient free space on your device before initiating the update process to avoid any issues.
Are There Any Differences In The Required Storage Space For Different Versions Of Windows 10?
There are some differences in the required storage space for various versions of Windows 10. The 32-bit version of Windows 10 requires a minimum of 16 GB of storage space, while the 64-bit version needs at least 20 GB. Additionally, certain editions like Windows 10 Home or Pro may require more storage space for updates and additional features, compared to the Windows 10 S mode, which is designed to be more streamlined and lightweight. Overall, the storage space needed can vary depending on the specific version and edition of Windows 10 being used.
How Can Users Check If They Have Enough Available Storage For The Update?
To check if you have enough available storage for an update, go to your device settings and navigate to the storage section. Here, you can see how much storage space is currently used and how much is available. Compare the available storage with the size of the update to ensure you have enough space to download and install it. Additionally, you can delete unnecessary files or apps to free up storage if needed.
Are There Any Ways To Reduce The Size Of The Windows 10 1909 Update To Save Storage Space?
One way to reduce the size of the Windows 10 1909 update is to use the Disk Cleanup tool built into Windows. This tool allows you to remove temporary files and other unnecessary data that may be taking up space. Additionally, you can consider uninstalling unused applications or transferring files to an external storage device to free up more space on your computer. Regularly cleaning up your system and optimizing storage usage can help reduce the overall size of the update and save storage space.
Will Installing The Update Impact The Performance Of My Device Due To Increased Storage Requirements?
Installing updates may slightly increase the storage requirements on your device, but it shouldn’t have a significant impact on performance. Most updates are designed to optimize system resources and improve overall performance rather than cause slowdowns. However, it’s always a good idea to periodically check and manage your device’s storage to ensure smooth operation. If storage space is a concern, consider deleting unnecessary files or apps before installing the update to free up space and minimize any potential impact on performance.
Conclusion
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, understanding the storage requirements of Windows 10 updates is crucial for ensuring smooth system performance. The analysis of the Windows 10 1909 update sheds light on the approximate storage space needed for a hassle-free installation process. By comprehending these storage needs, users can proactively manage their device’s storage capacity and make informed decisions when upgrading their operating system. As technology continues to rapidly evolve, being informed about software updates and their associated storage requirements is essential for optimizing the functionality and longevity of our devices. Stay knowledgeable and stay ahead in the digital realm.
Advertisement
Space required to install Windows 10
If you’re looking to install Windows 10 on your computer or are about to fresh Install Windows 10 but are concerned about how much space Windows 10 take after installation. This short guide will give you an estimated idea of whether you have recommended space to install and run windows 10 on your computer. Check the following points to decide whether you should install Windows 10 or not.
Windows 10 and Windows 11 are updated yearly as of the current schedule. Windows 10 is set to expire somewhere in 2025. While the latest version works just fine on newer machines, old machines usually face issues when upgrading. To avoid all the mess created during the update process,
We recommend that you clean-install Windows 11 every 6 months.
This makes your PC clean and fast.
Windows 11 storage occupied after install
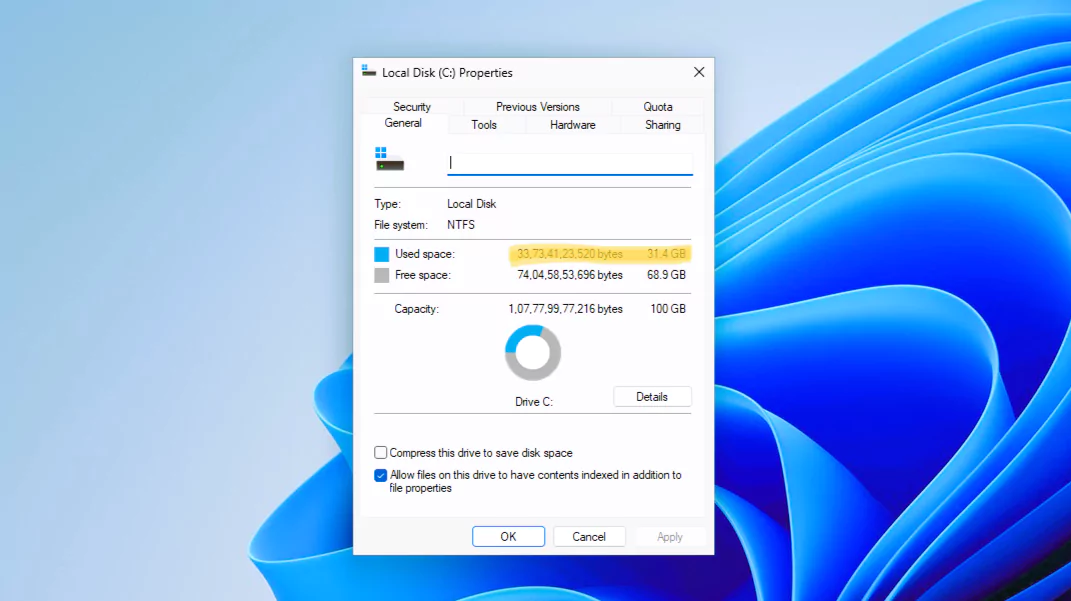
Windows 11 Pro English language version 22H2 takes little more than 30GB. While this is similar to the storage space Windows 10 takes. But remember once you enable the internet connection, Windows automatic update will run in the background and download and install all the patches and updates, which can quickly fill up your free space. If you have recently upgraded to a new year Windows 11 version here is how you can free up space.
Windows 10 Install size on Storage
Test 1 C:/ Drive is 20GB or less. Tested with: Windows 10 Nov 2019 update.
A clean or fresh Windows 10 installation size took 11.6 GB, though recommended free space is 16 GB for 32-bit OS and 20 GB for 64-bit OS, it is advisable to have a partition with more free space so that you can install more software and games. For this test, we also installed Windows 10 on a partition that was 12GB in size and it occupied around 11.6GB leaving just 300MB.
^^ This will applies to you when Windows is installed on C:/ drive which is just 20GB.
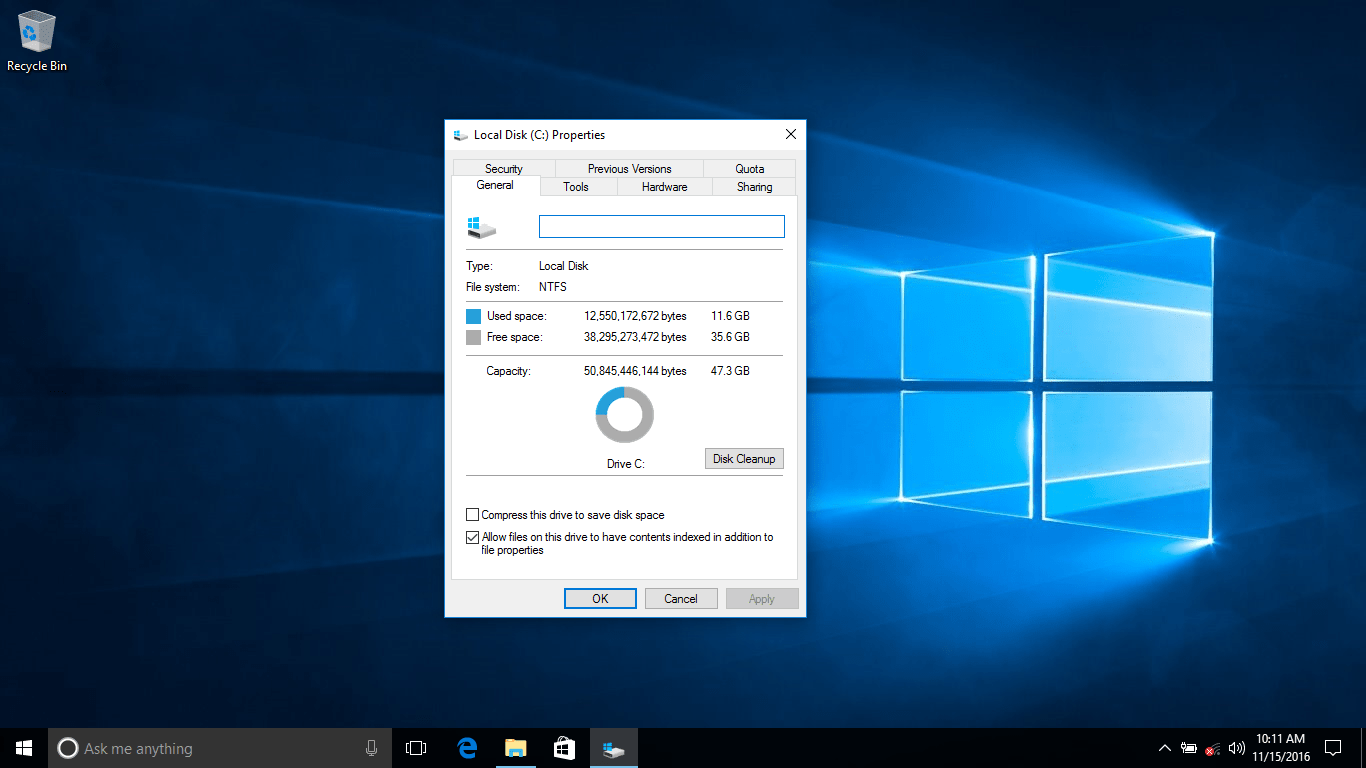
Test 2 C:/ is 50GB+. Tested with: Windows 10 Nov 2019 update.
We installed Windows 10 on C:/ with 50GB+ Free Space and it took roughtly 25GB (24.4GB to b exact.
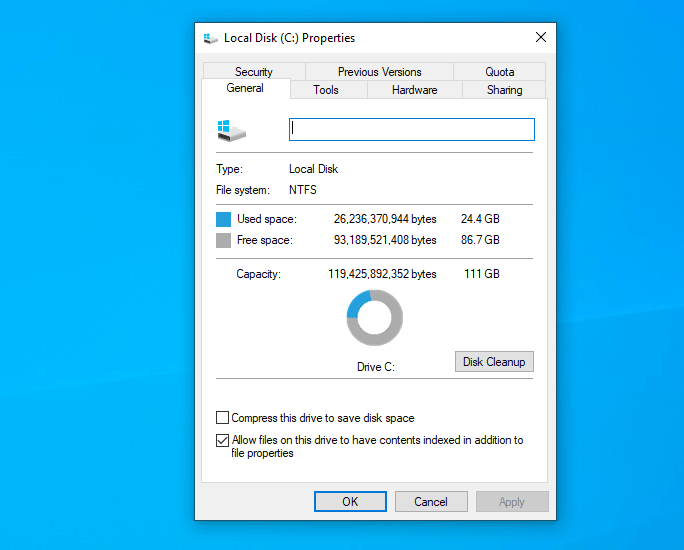
We also tested Windows 10 version 2004 (Pro edition 64-bit) on M.2 SSD it took similarly around 24.5GB and 25GB with Google Chrome installed.
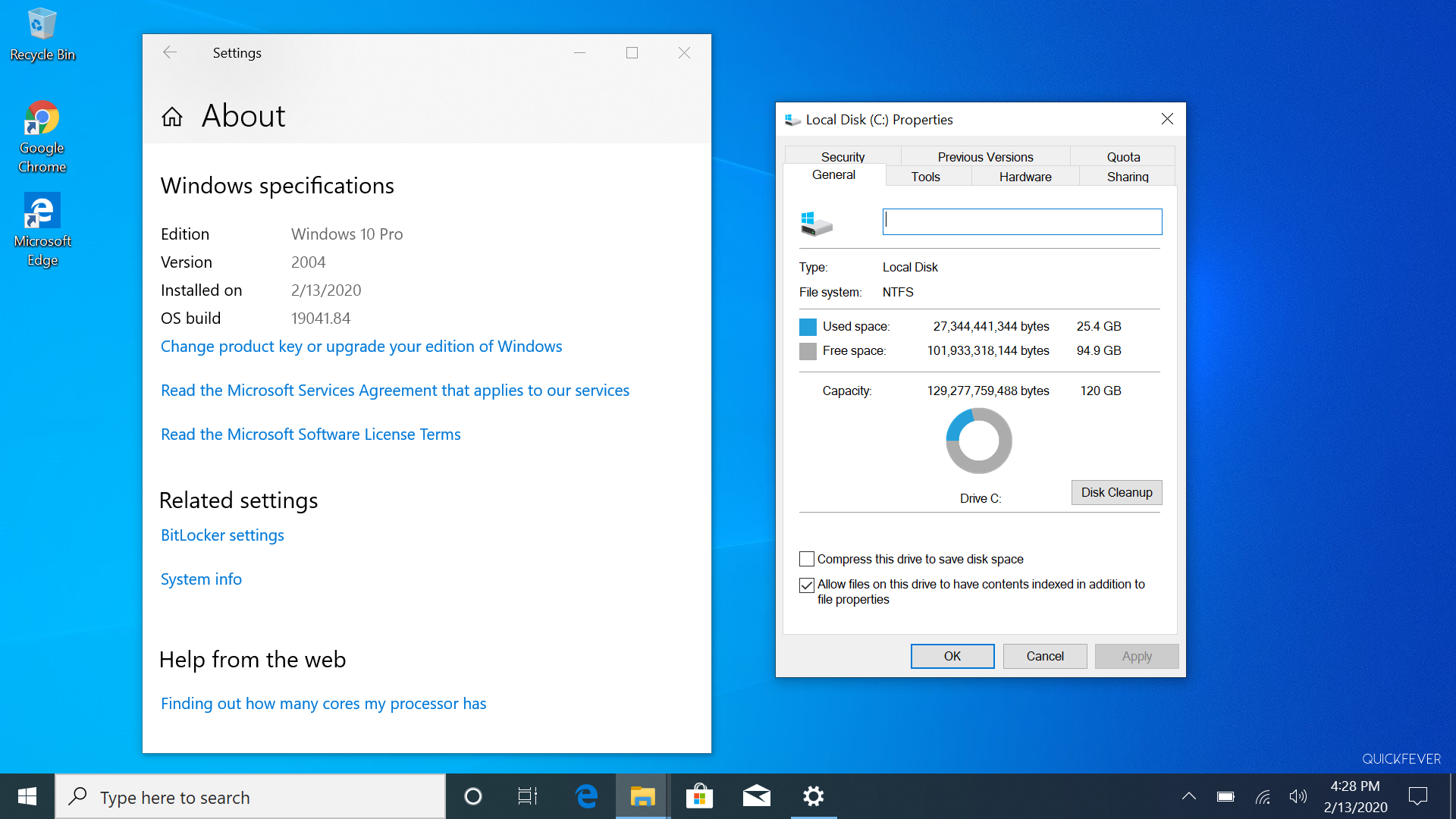
At least 20+ GB will be used on your windows installation partition. But if a partition has near 20-30 GB and on storage limits, Windows 10 has a special feature** that will automatically compress some system files to keep working fine. But you can also do this manually, in a rough figure this feature is likewise able to compress 5GB into 3GBb but that’s the limit. You can not compress everything in the windows directory.
** run Compact.exe /CompactOS:always in CMD to free up about 2GB space by compacting Windows file.
Test 3. 150+GB Storage and installed a few recommended software.
We ran another test and installed Google Chrome, and a few other tools (recommended here). The occupied space quickly grows into 42+GB.
How big is windows 10 (ISO and system images)
A Windows 10 Pro edition would be around 3 to 5GB with standard install.wim file.
- x86 English Windows 10 ISO = 3.xx GB
- x64 English Windows 10 ISO = 5.xx GB
Windows 10 Single language home edition saves a few MB in file size.
- x86 Single Edition English Windows 10 ISO = 3.x GB
- x64 Single Edition English Windows 10 ISO = 4.x GB
Though size may vary but not much. You can get official Windows 10 ISO using this guide. If you build a multi-edition ISO file it will take more space. For a single 32-bit + 64-bit the ISO will be around 3 to 5GB in space with the compressed install.esd while install.wim file could be more than 5GB. ESD has a better compression ratio but it takes longer to build one.
Windows 10 version 21H1
UUP files = 2.9 GB (x64) Download Windows 10 UUP files.
- With standerd Install.WIM Size = 3.7GB
- With compress Install.ESD Size = 2.7 GB
- ISO with Install.esd = 3.35GB
Installing Windows 10 on SSD:
Roughly around the same as required on normal hard disks. As SSD (Solid-state drive) are faster so is windows 10 when you have an SSD. Having a solid-state drive will help the operating system to boot faster and work flawlessly. When tested on both ADATA SSD (C:/ 50GB) and M.2 Silicon power (C:/ 100GB) both were filled 20GB.
On the other hand, if drive, C;/ is just 20GB then windows 10 manages to get installed in just 12 GB.
Installing from USB
Making a bootable USB from a Windows 10 ISO depends on its architecture. BTW a 4GB USB drive is enough for both 32-bit and 64-bit ISO. However, in the case of multiple edition ISO, you may need at least an 8GB USB drive.
Windows 10 Minimum Requirments.
New device: 2 gigabytes (GB) RAM for 32-bit or 64-bit
Update: 1 gigabyte (GB) for 32-bit or 2 GB for 64-bit
| Processor: | 1 gigahertz (GHz) or faster processor or System on a Chip (SoC) |
| RAM: | 1 gigabyte (GB) for 32-bit or 2 GB for 64-bit |
| Hard drive space: | 16 GB for 32-bit OS 32 GB for 64-bit OS |
| Graphics card: | DirectX 9 or later with WDDM 1.0 driver |
| Display: | 800×600 |
Processor: Pentium 8th Genration
RAM: 2GB
Storage: 100GB SSD
Graphics Card: Windows 10 requires at least DirectX 9 or later with a WDDM 1.0 driver and display with a resolution of 800×600.
Windows 10 Recommended Requirments.
Processor: Pentium 8th Generation
RAM: 2GB
Storage: 100GB SSD
Graphics Card: Windows 10 requires at least DirectX 9 or later with a WDDM 1.0 driver and display with a resolution of 800×600.
→ If you think your computer can not run Windows 10, you should try once to install windows 10. If Windows 10 is not your cup of coffee your computer needs a lightweight operating system.
→ If you are new to Windows 10, Click here to read windows 10 Guides, Tips and How To’s.
Personal Note: this section is as on my own case.
Test #1: Windows 10 Pro, x64 System, 16 GB RAM, installed on 100GB M.2 SSD drive.

My Windows 10 installation took around ~20 GB despite the fact that I’ve installed around 20 programs. You can also use the Disk Cleanup tool to gain some free space on the Windows installation partition.
Test #2. Specs: Windows 10 Pro, x64 System, 16 GB RAM, installed on 100GB SSD

This time Windows 10 (1903) installation took around ~20GB, with all the drivers up to date. You can also use the Disk Cleanup tool to gain some free space on the Windows installation partition.
When You Don’t have Required Space to Install Windows 10.
It is very unlikely because today an average computer has around 500 GB Hard Disk. Maybe you have files on your disk or you Installed Windows 10 over any older windows. This might leave a Windows.old folder inside the Windows installation directory. You can clear the folder by going to Disk Cleanup > Clean System Files > Tick Old windows backup > Clean it.
Additionally, you enable the ‘Compress this drive to disk space‘ in Local Disk (C:)’s properties. This may make the program’s execution a bit slower than usual.
Are you ready to install Windows 10?
Windows 10 is the best, perfect and flexible windows Yet. However, we are not forcing, but you should experience it. Windows 10 has everything new. New UI, New keyboard shortcuts, Windows Hello and more.
Windows 10 1909, or the November 2019 Update, is expected to be released to the public next week on Patch Tuesday. While you can already install this new version before everyone, as usual we wouldn’t recommend doing that unless you are sure you can deal with any unknown bugs.
As for the basic system requirements for this upcoming feature update, since introducing Windows 10 in 2015, Microsoft hasn’t made any significant changes. The Windows maker introduced some storage changes to these requirements with the release of Windows 10 May 2019 Update aka version 1903 earlier this year. However, a few weeks after the release, the company clarified that even those machine that do not meet these storage requirements will be able to run version 1903.
Since Windows 10 1909 aka the November 2019 Update is nothing but an extension of version 1903, bringing no major features and focusing entirely on performance improvements and bug fixes, the same requirements apply to this version too. Do, however, note that Microsoft had shared some processor requirements for its OEM partners.
System requirements for installing Windows 10 1909
| RAM | 1GB for 32 bit, 2GB for 64 bit |
| Hard disk space | — For Windows 10 1809 and earlier: 16 GB for 32 bit and 20 GB for 64 bit — For Windows 10 1903: 32 GB or greater |
| CPU | 1 gigahertz (GHz) or faster processor or SoC that meet the following requirements:
— Compatible with the x86 or x64 instruction set. |
| Screen resolution | 800 x 600 |
| Graphics | Microsoft DirectX 9 or later with WDDM 1.0 driver |
| Internet Connection | Required |
For the hardware requirements, you can check our earlier coverage over here.
As for the 32GB requirement, we had noted at the time that it could very well be because of the operating system now reserving 7GB exclusively for Windows updates and system use. But that isn’t happening for every machine that’s upgrading to version 1903. [You can confirm using steps shared in this guide.] Even without this feature, people had often asked the company to upgrade these minimum storage requirements to make sure devices can actually run Windows 10 and not just install it.
Since the release of Windows 10 October 2018 Update, version 1809, last year, Microsoft has been trying to come up with strategies that could help the company earn back user trust in its update process. Windows 10 May 2019 Update proved to be a much stable update but then was hit by bugs brought by cumulative updates. The adoption rate is finally going up now that Microsoft has cleared all the bugs and people are rushing to upgrade to it before the next version drops.
As for the next update, Windows 10 1909 will be a small update delivered like a monthly cumulative update to those running version 1903, causing minimal, if any, disruption. The company is focusing on the development of Windows 10 20H1 for new features, hopefully delivering bug-free feature updates that don’t push users to actively avoid them because of compatibility and performance issues.
— Can’t wait? Here’s how to get version 1909 before everyone else! | reminder: Windows 7 breathing its last; 2.5 months left to upgrade for free
Source: Microsoft
Официально для Windows 10 версии 2004 потребуется ПК, который соответствует следующим спецификациям:
Эти системные требования унаследованы Windows 10 версий 1909 и 2004.
- Процессор: 1 гигагерц (ГГц) или более быстрый процессор или SoC
- Оперативная память: 1 гигабайт (ГБ) для 32-разрядных или 2 ГБ для 64-разрядных
- Место на жестком диске: 32 ГБ для 64-битной и 32-битной ОС
- Видеокарта: с поддержкой DirectX 9
- Разрешение экрана: 800 x 600, минимальный размер диагонали для основного дисплея 7 дюймов или больше.
Любой, кто пытается использовать Windows 10 на таком оборудовании, может подтвердить, что эти системные требования весьма оптимистичны. 2 ГБ оперативной памяти — ничто для ОС, а обычный жесткий диск сильно влияет на ее производительность.
Кроме того, контроллеры хранилища, используемые в устройствах под управлением Windows 10 для настольных версий, должны соответствовать следующим требованиям:
- Контроллеры хранилища должны поддерживать загрузку с использованием расширяемого интерфейса микропрограмм (EFI) и реализовывать пути к устройствам, как определено в EDD-3.
- Контроллеры и адаптеры хоста хранения должны соответствовать требованиям к используемому протоколу устройства и любым требованиям, связанным с типом шины хранения устройства.
- Контроллеры, подключенные к шине, должны реализовывать правильный код класса / подкласса, как указано в спецификации PCI Codes and Assignments v1.6.
Другой официальный документ, проливает свет на то, какое оборудование Microsoft считает подходящим для своего продукта. Как видно из документа, у вас должно быть 8 ГБ ОЗУ или лучше 16 ГБ, и SSD / NVMe играет важную роль в конфигурации устройства.
В документе упоминаются эти требования с точки зрения безопасности.
«Если вы принимаете решение о приобретении новых устройств и хотите включить наилучшую возможную конфигурацию безопасности, ваше устройство должно соответствовать или превышать эти стандарты»
Другие известные требования к оборудованию включают в себя процессоры:
| Windows 10 1909 | До следующих процессоров Intel 9-го поколения (Intel Core i3 / i5 / i7 / i9-9xxxK) и Intel Xeon E-21xx [1], Intel Atom (J4xxx / J5xxx и N4xxx / N5xxx), процессоров Celeron и Pentium |
Вплоть до следующих процессоров AMD 7-го поколения (A-Series Ax-9xxx и E-Series Ex-9xxx и FX-9xxx); Процессоры AMD Athlon 2xx, AMD Ryzen 3/5/7 2xxx, AMD Opteron [2] и AMD EPYC 7xxx [2] |
Qualcomm Snapdragon 850 |
| Windows 10 2004 |
До следующих процессоров Intel 10-го поколения (Intel Core i3 / i5 / i7 / i9-10xxx) и Intel Xeon E-22xx [1], Intel Atom (J4xxx / J5xxx и N4xxx / N5xxx), процессоров Celeron и Pentium |
До следующих процессоров AMD 7-го поколения (A-Series Ax-9xxx и E-Series Ex-9xxx и FX-9xxx); Процессоры AMD Athlon 2xx, AMD Ryzen 3/5/7 4xxx, AMD Opteron [2] и AMD EPYC 7xxx [2] |
Qualcomm Snapdragon 850 и 8cx |
[1] Процессоры Intel Xeon поддерживаются только в Windows 10 Pro для рабочих станций и Windows 10 Enterprise.
[2] Процессоры AMD Opteron и AMD EPYC поддерживаются только в Windows 10 Pro для рабочих станций и Windows 10 Enterprise.
Требования к размеру жесткого диска.
Ранее было достаточного 16 Гб дискового пространства для Windows 10 32-бита и 20 ГБ для 64 -бита, теперь компания подняла его в обеих версиях до 32 ГБ оперативной памяти. Это означает, что производители оборудования (OEM), которые предварительно устанавливают настольную версию Windows 10 теперь нужно комплектовать устройство по крайней мере, жестким диском 32 Гб.
Это имеет смысл — 16 ГБ на некоторых устройствах было недостаточно и вызывало проблемы с обновлениями. Тем более, в Windows 10 1903 была добавлено «Зарезервированное хранилище». Небольшая часть дискового пространства, которая будет зарезервирована для использования обновлениями, приложениями, временными файлами, а также системным кешем.
Требования к размеру хранилища для устройств под управлением Windows 10 для настольных изданий:
| Архитектура ОС | Версия ОС | Емкость накопителя |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 10, версия 1809 и ранее | 32-бита | 16 ГБ или больше |
| 64-бита | 20 ГБ или больше | |
| Windows 10, версия 1903 / 2004 | 32-бита и 64-бита | 32 ГБ или больше |
| Windows 10 IoT Enterprise, версия 2004 и более ранние | 32-бита | 16 ГБ или больше |
| 64-бита | 20 ГБ или больше |
Оптимальная аппаратная конфигурация для Windows 10 выглядит как минимум следующим образом:
- Процессор: Intel 8-го поколения (Intel i3 / i5 / i7 / i9-7x), Core M3-7xxx, Xeon E3-xxxx и Xeon E5-xxxx, AMD 8-го поколения (A-серии Ax-9xxx, E-Series Процессоры Ex-9xxx, FX-9xxx) или ARM64 (Snapdragon SDM850 или более поздняя версия)
- Оперативная память: 4 гигабайта (ГБ) для 32-битной или 16 ГБ для 64-битной
- SSD / NVMe: не менее 128 ГБ для 64-битной и 32-битной ОС
- Видеокарта: DirectX 9 или более поздняя
- Разрешение экрана: 800 x 600, минимальный размер диагонали для основного дисплея 7 дюймов или больше.
Источник: microsoft.com
Вам может быть интересно: Cистемные требования для обновления и запуска Windows 11
