When using a computer, we often engage with various applications and the web, leading to the generation of temporary files. These files assist in improving performance and user experience by speeding up access to frequently visited websites and applications. The Temporary Internet Files (TIF) folder is a critical component in this process, particularly for users of Windows 10 and Windows 11. This article delves into the specifics of the Temporary Internet Files folder, its importance, how to locate it, manage its contents, and important considerations for maintaining optimal system performance.
Understanding Temporary Internet Files
Temporary Internet Files are cached copies of web pages, images, videos, and other multimedia content stored by your web browser. This caching mechanism is designed to enhance browsing speed. Instead of downloading the same content repeatedly, the browser retrieves these files from local storage, resulting in quicker load times and reduced data usage.
Why Are Temporary Internet Files Important?
-
Speed: TIF saves time by allowing faster access to frequently visited sites. Instead of retrieving all components anew, browsers can pull them from the cache.
-
Reduced Bandwidth Use: By reusing cached files, browsers decrease the amount of data transferred over the internet, which is especially helpful for users with limited data plans.
-
Offline Browsing: Some browsers enable users to access cached versions of web pages when offline, providing utility even when an internet connection is unavailable.
However, as the Temporary Internet Files accumulate, they can consume significant disk space and may lead to outdated content. Therefore, regularly managing these files is essential.
Locating the Temporary Internet Files Folder in Windows 10 and 11
The location of the Temporary Internet Files folder can vary based on your browser and Windows configuration. For the Microsoft Edge and Internet Explorer browsers, here are the usual locations:
1. Internet Explorer
For Internet Explorer, the Temporary Internet Files folder is located in the following path:
C:Users\AppDataLocalMicrosoftWindowsINetCache2. Microsoft Edge
For Microsoft Edge, temporary files are stored in a slightly different location:
C:Users\AppDataLocalMicrosoftEdgeUser DataDefaultCacheAccessing the Folder
To access these folders, follow these steps:
- Press
Windows + Rto open the Run dialog. - Type
%LocalAppData%and press Enter. - Navigate to the paths mentioned above based on the browser you are using.
3. Other Browsers
For other browsers, such as Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox, the temporary files are stored in their respective cache folders.
-
Google Chrome:
C:Users\AppDataLocalGoogleChromeUser DataDefaultCache -
Mozilla Firefox:
C:Users\AppDataLocalMozillaFirefoxProfiles\cache2
You can identify your Firefox profile by visiting about:profiles in the address bar.
Managing Temporary Internet Files
Manual Deletion
Due to potential storage overload caused by Temporary Internet Files, manual deletion can assist in reclaiming disk space and prevents old cache files from causing browsers to act erratically.
Using Disk Cleanup Tool
Windows includes a built-in tool for cleanup, which can efficiently manage disk space, including the deletion of temporary internet files. Here’s how to use it:
- Press
Windows + Sand type “Disk Cleanup”. - Open the Disk Cleanup application.
- Select the drive you want to clean (typically C:).
- In the Disk Cleanup dialog, check the box next to «Temporary Internet Files» and any other file types you wish to remove.
- Click «OK» and then «Delete Files» to confirm.
Clearing Cache through Browser Settings
Most web browsers allow you to clear the temporary internet files directly from their settings:
- Google Chrome:
- Open Chrome and click the three dots in the upper right corner.
- Go to «More Tools» > «Clear Browsing Data».
- Choose the time range and ensure that «Cached images and files» is selected.
- Click «Clear data».
- Mozilla Firefox:
- Click the menu button and choose “Options”.
- Click on «Privacy & Security» and scroll to «Cookies and Site Data».
- Click «Clear Data» and ensure «Cached Web Content» is checked, then click “Clear”.
- Microsoft Edge:
- Click on the three horizontal dots in the top right corner.
- Go to «Settings».
- Navigate to «Privacy, search, and services».
- Under «Clear browsing data», click «Choose what to clear».
- Select «Cached images and files» and click «Clear now».
Third-Party Tools
There are various third-party applications like CCleaner that can automate the process of cleaning up temporary files, including those in cache directories. However, always exercise caution while using third-party tools.
Risks and Considerations
Data Loss
While temporary files can take up unnecessary space, it’s essential to consider that some websites might store crucial data related to user sessions in the cache. Deleting these files can lead to loss of session information, logged-in status, and in some cases, shopping cart contents.
Performance Impact
While cache plays a vital role in enhancing performance, excessive size can lead to the opposite effect. Browsers may start to crawl or crash if overwhelmed with too many temporary files. Regularly clearing the cache can actually enhance your browser’s overall performance.
Privacy Concerns
Temporary Internet Files can potentially store sensitive data like login credentials and browsing history. Regularly clearing your cache can help mitigate privacy concerns, particularly on shared or public systems.
Conclusion
In summary, the Temporary Internet Files folder plays a significant role in maintaining the performance and efficiency of web browsing in Windows 10 and 11. Understanding how to locate, manage, and delete these files is crucial for all users, particularly those who often browse the web.
By effectively managing temporary files, you not only reclaim storage space but also enhance your browsing experience, maintain privacy, and ensure that outdated files do not affect browser functionality. Regular maintenance of the Temporary Internet Files folder should be part of any user’s routine to keep their system running smoothly.
In an era of increasing focus on privacy and data management, staying informed about your system’s temporary files can help you achieve a better balance between performance, privacy, and storage management. By practicing regular clean-up routines and being cautious with browser settings and third-party tools, users can ensure their online habits are not only efficient but also secure.
Reset the temp files folder location or view temporary files
Microsoft Internet Explorer (IE) uses temporary internet files to store copies of web content on a local hard drive. While it’s useful for improving network performance, it can quickly fill the hard drive with large amounts of unwanted data. If your computer has random images and other temporary internet files from Internet Explorer, delete them to clean up space and maybe speed up IE.
IE Temporary Internet Files Location
Internet Explorer has a default location where temporary internet files are stored. Depending on your operating system, temp files should be in one of these locations:
- C:\Users\[username]\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\INetCache: This temp files location is relevant in Windows 10 and Windows 8.
- C:\Users\[username]\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Temporary Internet Files: This is where temporary internet files are stored in Windows 7 and Windows Vista.
- C:\Documents and Settings\[username]\Local Settings\Temporary Internet Files: This is where Windows XP IE temp internet files are stored.
- C:\Windows\Downloaded Program Files: This is where downloaded program files are stored.
Replace [username] in the folder locations with your Windows username.
These locations display temporary internet files and files downloaded from the web. You can sort these lists by file name, address, file extension, size, and various dates.
However, if you don’t see these folders, it’s possible that they’ve been changed. You can see which folders your computer is using by accessing the settings described below.
How to Access the Settings for Temp Internet Files
The temporary internet file settings can be accessed through the Internet Explorer Internet Options screen. Use these options to change the temporary internet files folder location, set how often IE checks for cached website pages, and adjust the amount of storage reserved for temp files.
-
Use one of these methods to open Internet Options:
- Open Control Panel, then select Network and Internet > Internet Options.
- In the Run dialog box or from Command Prompt, enter the inetcpl.cpl command.
- From Internet Explorer, select Tools > Internet options.
-
Select the General tab, then go to the Browsing history section and select Settings.
-
Select the Temporary Internet Files tab to access more options to deal with temp files in Internet Explorer.
Other Ways to Deal With Temp Files in Internet Explorer
In the Temporary Internet Files tab, select Check for newer versions of stored pages to choose how often Internet Explorer looks in the temporary internet files folder for cached pages. More frequent checks speed up access to websites. The default option is Automatically but you can change it to Every time I visit the webpage, Every time I start Internet Explorer, or Never.
Another option you can change is how much storage space is allowed for temporary internet files. Choose any size between 8 MB and 1,024 MB (1 GB), but Microsoft recommends setting the disk space usage between 50 MB and 250 MB.
You can change the folder in which IE keeps temporary internet files. Change the folder to store cached pages, images, and other files on a different hard drive that has more space, such as an external hard drive. To do that, select Move folder and then choose which folder to use for temp files.
The other buttons on this screen are for viewing the objects and files that IE has stored. These are the folders mentioned above.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
The Temporary Internet Files folder in Windows 10 is a hidden folder that stores website files, images, scripts, and other elements that are downloaded while browsing the internet. Locating this folder can be helpful for various reasons, such as troubleshooting browser issues, clearing cache, or accessing specific temporary files. Here’s how you can find the Temporary Internet Files folder in Windows 10:
1. Open File Explorer: You can do this by clicking on the folder-shaped icon on the taskbar or by pressing the Windows key + E on your keyboard.
2. Enable the display of hidden files and folders: By default, the Temporary Internet Files folder is hidden. To view it, click on the «View» tab at the top of the File Explorer window, then check the box next to «Hidden items» in the «Show/hide» section. This will reveal hidden folders and files.
3. Access the AppData folder: In the File Explorer window, navigate to the «C:» drive, which is typically where your operating system is installed. From there, open the «Users» folder, followed by your specific username.
4. Locate the AppData folder: Within your user folder, you need to find the «AppData» folder. However, this folder is also hidden by default. To access it, click on the «View» tab again, and this time, check the box next to «Hidden items» in the «Show/hide» section if it’s not already selected.
5. Find the Temporary Internet Files folder: Open the «AppData» folder, then go into the «Local» folder. Inside the «Local» folder, you’ll find a «Microsoft» folder. Open it and locate the «Windows» folder. Finally, within the «Windows» folder, you’ll find the «Temporary Internet Files» folder.
Please note that the exact path may vary slightly based on system configuration, user profiles, or modifications made to Windows settings. The steps provided should give you a general idea of how to locate the Temporary Internet Files folder on Windows 10.
Video Tutorial: Should I delete temporary internet files Windows 10?
What are Temporary Internet Files and can I delete them?
Temporary Internet Files, also known as cache files, are temporary data stored on your device when you visit a website. These files store elements of a webpage such as images, videos, scripts, and other downloadable content. The purpose of these files is to speed up subsequent visits to the same website by retrieving the stored data locally instead of downloading it again from the internet.
Here’s why you might consider deleting temporary internet files:
1. Free up storage space: Temporary Internet Files can accumulate over time and consume a significant amount of storage on your device. Deleting them can free up space and allow for better overall performance.
2. Privacy concerns: Temporary Internet Files can contain sensitive information like login credentials, browsing history, and cached pages. Clearing these files can help protect your privacy by removing potential traces of your online activity.
3. Resolve website loading issues: In some cases, outdated or corrupted cache files may interfere with website functionality, causing pages to load improperly or not at all. Deleting the cache files can resolve such issues and improve your browsing experience.
How to delete Temporary Internet Files:
1. Clearing cache in a web browser: Each browser has its own process for clearing cache files. Here are general steps for popular browsers:
– Google Chrome: Settings > Privacy and security > Clear browsing data > Select «Cached images and files» > Clear data.
– Mozilla Firefox: Options > Privacy & Security > Cookies and Site Data > Clear Data > Check «Cached Web Content» > Clear.
– Safari: Preferences > Privacy > Manage Website Data > Remove All.
– Microsoft Edge: Settings and more (three-dot menu) > Settings > Privacy, search, and services > Clear browsing data > Choose «Cached images and files» > Clear.
2. Using a system cleaning tool: You can also use third-party system cleaning tools that offer cache clearing functionalities. These tools can scan and remove temporary internet files from various browsers and system locations.
Remember that deleting Temporary Internet Files will clear your browsing history, so if there are specific websites you want to revisit easily, consider bookmarking them before clearing the cache.
In summary, Temporary Internet Files are stored on your device to enhance website loading speed. However, you can delete them to free up storage space, protect your privacy, and resolve website loading issues. Different web browsers have specific steps to clear cache, and third-party system cleaning tools can also assist in this process.
Are Temporary Internet Files stored on the hard drive?
Yes, Temporary Internet Files are stored on the hard drive. When you browse the internet, your web browser stores various files to enhance your browsing experience. These files, known as temporary internet files or cache files, are saved on your computer’s hard drive.
Here are the steps to locate and clear Temporary Internet Files:
1. Open your web browser (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, or Safari).
2. Access the browser’s settings or preferences. This is usually found in the menu bar or the three-dot/three-line icon.
3. Look for the «Privacy» or «History» section in the settings.
4. Within the privacy or history settings, you should find an option to clear browsing data or delete cache files.
5. Select or check the «Temporary Internet Files» or «Cache» option. You may also choose to clear other types of browsing data like cookies or history.
6. Click on the «Clear» or «Delete» button to remove the temporary internet files from your hard drive.
Clearing temporary internet files can help free up disk space, improve browsing speed, and ensure privacy. It’s recommended to periodically clear these files to maintain optimal browser performance.
Remember that the steps to clear temporary internet files may slightly vary depending on the web browser and its version you are using.
Windows 10 Temporary Internet Files are stored in a specific location on your computer’s hard drive. Here’s how you can find them:
1. Open File Explorer on your Windows 10 computer. You can do this by clicking on the folder icon in the taskbar or pressing the Windows key + E on your keyboard.
2. In the File Explorer window, navigate to the following path:
C:\Users\\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\INetCache\
Replace «» in the path above with your actual Windows username.
3. In the INetCache folder, you should be able to see the Temporary Internet Files stored by Windows 10. These files typically have names with random characters and various file extensions.
It’s worth noting that the AppData folder is a hidden folder by default, so you may need to enable the option to show hidden files and folders. You can do this by going to the View tab in File Explorer, and checking the «Hidden items» checkbox in the Show/hide section.
By accessing the Temporary Internet Files folder, you can manage the stored files, clear the cache, or delete specific files if necessary. It’s important to bear in mind that deleting these files may affect your browsing experience on websites you visit frequently, as some elements may need to be re-downloaded.
Remember to exercise caution when modifying system files, and always have a backup of important data to avoid any unintended consequences.
How to delete locked Temporary Internet Files in Windows 10?
To delete locked Temporary Internet Files in Windows 10, you can follow these steps:
1. Close all web browsers: Before attempting to delete Temporary Internet Files, ensure that all web browsers are closed, as they may be accessing these files.
2. Open the Run dialog box: Press the Windows key + R on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box.
3. Enter the file path: Type «%temp%» (without quotes) in the Run dialog box and press Enter. This will open the Temporary Files folder.
4. Close any open files: If any files or folders are open within the Temporary Files folder, close them before proceeding.
5. Select the locked files: Look for files starting with «Temporary Internet Files» or «Content.IE5«. To select multiple files, hold the Ctrl key while clicking on them. If there are many files, you can sort them by date modified to locate the ones you want to delete.
6. Delete the files: Once the desired files are selected, right-click on any of them and choose «Delete» from the context menu. Confirm the deletion if prompted.
7. Skip locked files: If there are any locked files that cannot be deleted, Windows will prompt you with a message. Choose the «Skip» option to continue deleting the remaining unlocked files.
8. Empty the Recycle Bin: Once you have deleted the temporary internet files, empty your Recycle Bin to permanently remove them from your system.
It’s worth noting that some files within the Temporary Internet Files folder may be in use by other processes, preventing their deletion. In such cases, restart your computer and try deleting the files again before any applications or processes have a chance to access them.
Are temporary internet files stored on the hard drive?
Yes, temporary internet files are stored on the hard drive of a computer. These files are also known as cache files or browser cache, and they serve to improve the performance and speed of web browsing. When you visit a website, your browser downloads and stores various elements of the web page, such as images, scripts, and stylesheets, in a temporary folder on your hard drive.
There are several reasons why temporary internet files are stored on the hard drive:
1. Faster Retrieval: By storing website data locally, subsequent visits to the same website can be faster since the browser can retrieve certain elements from the cache instead of downloading them again from the internet.
2. Offline Access: Temporary internet files allow for offline access to web pages that you have previously visited. If your browser has cached the web page, you can view it even without an internet connection.
3. Reduced Bandwidth Usage: Since the browser can retrieve certain website elements from the cache instead of downloading them, it helps reduce bandwidth usage, especially when visiting frequently accessed websites.
4. Enhanced User Experience: By storing temporary internet files, browsers can display web pages more quickly and smoothly, providing a better overall user experience.
To clear temporary internet files from your hard drive, you can follow these steps:
1. Open your web browser’s settings or preferences.
2. Look for the «Clear browsing data» or «Clear cache» option. It might be located under a «Privacy,» «Advanced,» or «History» section.
3. Select the option to clear temporary internet files or cache. Make sure to uncheck any data you want to keep, such as saved passwords.
4. Choose the time range or duration for which you want to delete the cache. You can select «All time» to remove all temporary internet files.
5. Click on the «Clear» or «Delete» button to initiate the process.
6. Wait for the browser to clear the cache, and then restart your browser for the changes to take effect.
Remember that clearing temporary internet files will remove locally stored data and may require websites to re-download certain elements on subsequent visits, resulting in slightly slower loading times initially.
Temporary Internet Files in Windows 10 are stored in a specific location on your computer. Here’s how you can find them:
1. Open File Explorer: You can do this by pressing the Windows key + E on your keyboard or by clicking on the File Explorer icon in the taskbar.
2. In File Explorer, navigate to the following path:
C:\Users\[Your Username]\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\INetCache
Note: Replace «[Your Username]» with your actual username.
3. Once you’re in the INetCache folder, you should see various folders with randomly generated names. These folders contain the temporary internet files.
It’s important to note that the AppData folder is hidden by default. If you don’t see it, you need to enable hidden files and folders in File Explorer.
To enable hidden files and folders:
1. In File Explorer, click on the «View» tab at the top.
2. Check the «Hidden items» box in the «Show/hide» section.
Now you should be able to see the AppData folder and navigate to the Temporary Internet Files folder as mentioned above.
Temporary Internet Files are used by web browsers like Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, and Mozilla Firefox to store website content such as images, HTML files, CSS files, and scripts. These files help in loading websites faster upon revisits or when browsing pages with similar content.
However, it’s important to regularly clear these files to free up storage space on your computer and maintain privacy. Clearing Temporary Internet Files can also resolve browser-related issues or conflicts.
To clear Temporary Internet Files in Windows 10:
1. Open your preferred web browser (e.g., Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox).
2. Access the browser’s settings or preferences menu. This is typically done by clicking on the three-dot icon (usually located in the upper-right corner) and selecting «Settings» or «Options.«
3. Look for the «Privacy» or «Clear browsing data» section within the settings menu.
4. Click on the option to clear or delete temporary files, cache, or browsing history. The wording may vary slightly depending on the browser you’re using.
5. Select the appropriate time range for which you want to clear the files. You can choose options like «Last hour,» «Last 24 hours,» «Last 7 days,» or «All time.«
6. Make sure the «Temporary Internet Files» or «Cache» option is checked.
7. Click on the «Clear» or «Delete» button to remove the temporary internet files from your computer.
Remember, clearing Temporary Internet Files regularly can improve browser performance, protect your privacy, and free up storage space on your device.
Video Tutorial:What happens if I delete all temporary files Windows 10?
Where is IE cache stored?
The cache is a temporary storage location on your device that helps web pages load faster by saving frequently accessed data. In the case of Internet Explorer (IE), the cache is stored in a specific location on your computer’s hard drive. Here are the steps to locate the IE cache:
1. Open File Explorer on your computer. You can do this by right-clicking the Start button and selecting «File Explorer» from the menu that appears.
2. In the File Explorer window, navigate to the main system drive where Windows is installed. This is typically the C: drive.
3. Once you are in the root directory of the system drive, locate and open the «Users» folder.
4. Inside the Users folder, you will find a list of user profiles. Open the folder corresponding to the user account you are currently logged in with.
5. Within the user profile folder, locate and open the «AppData» folder.
6. Inside the AppData folder, you might find many subfolders. Open the «Local» folder.
7. Within the Local folder, find and open the «Microsoft» folder.
8. Inside the Microsoft folder, locate and open the «Windows» folder.
9. Finally, within the Windows folder, you should find a folder named «Temporary Internet Files.» This is where the IE cache is stored.
Note: The location of the IE cache may vary slightly depending on the version of Windows you are using. However, the general path mentioned above should work for most Windows versions.
It’s important to note that manually accessing and modifying the cache files can have unintended consequences and may lead to system instability or data loss. Therefore, it is recommended to clear the cache through the Internet Options settings in Internet Explorer or using the built-in clearing options provided by the browser.
Is temporary Internet files a folder?
Temporary Internet Files is a folder that stores copies of web pages, images, and media files that are downloaded from the Internet while browsing. This folder is used by web browsers to store this data temporarily, allowing for quicker access to previously visited websites and reducing the need to download the same files repeatedly.
To answer your question, yes, Temporary Internet Files is a folder on a computer. It is typically located in the user’s profile directory, under the «AppData» folder, within the web browser’s specific folder. The exact location may vary depending on the browser and the operating system being used.
Windows users can access the Temporary Internet Files folder by following these steps:
1. Open the File Explorer by pressing the Windows key + E.
2. In the file explorer’s address bar, type «%localappdata%» (without quotes) and hit Enter.
3. Navigate to the folder corresponding to your web browser. For example, for Google Chrome, the folder will be «Google\Chrome\User Data\Default«.
4. Within the browser’s folder, you should find the «Cache» subfolder, which contains the Temporary Internet Files.
Mac users can access the Temporary Internet Files folder for different browsers by following these steps:
1. Open a Finder window.
2. Click on the «Go» menu at the top of the screen.
3. Press and hold the Option key while the «Go» menu is open.
4. You should see the «Library» option appear. Click on it.
5. Within the «Library» folder, navigate to the «Caches» directory.
6. Look for the folder corresponding to your web browser, such as «com.apple.Safari» for Safari or «com.google.Chrome» for Chrome.
It’s important to note that manually modifying or deleting files within the Temporary Internet Files folder can have unintended consequences and is generally not recommended unless you are troubleshooting specific issues or trying to free up disk space. Most browsers have built-in options to clear the cache and manage temporary files, which are safer to use for regular maintenance.
In conclusion, Temporary Internet Files is a folder on a computer that stores temporary copies of web pages, images, and media files for faster access and efficient browsing.
Temporary Internet files, also known as cache or browser cache, are files stored on your computer by web browsers while you browse the internet. These files are created to enhance your browsing experience by speeding up the loading of websites you frequently visit, as they can be retrieved locally instead of downloading them every time you access a website.
In the context of Windows 10, temporary Internet files are specifically associated with the default web browser, Microsoft Edge. Here’s how temporary Internet files work on Windows 10:
1. Caching Web Content: When you visit a website using Microsoft Edge, the browser temporarily stores elements of that website, such as HTML files, stylesheets, images, and multimedia files, in a designated folder on your computer called the «cache» or «Temporary Internet Files» folder. This helps speed up subsequent visits to the same website, as the browser can retrieve those files from the cache instead of downloading them again.
2. Offline Browsing: Temporary Internet files enable offline browsing capabilities. For instance, if you load a webpage with Microsoft Edge while connected to the internet, a copy of that webpage’s content may be saved in the cache. This allows you to access and view that webpage even when you’re offline, as long as the cached version is still available.
3. Privacy Considerations: It’s important to note that temporary Internet files may store cookies, which are small text files that contain website-specific data, such as login information or preferences. While cookies serve various useful purposes, they can also be used to track your browsing activities. Clearing temporary Internet files can help maintain your privacy and reduce the chance of certain websites accessing your personal information.
4. Managing Temporary Internet Files: To manage temporary Internet files on Windows 10, you can follow these steps in Microsoft Edge:
a. Open Microsoft Edge and click on the three-dot menu button in the top-right corner.
b. From the dropdown menu, select «Settings.«
c. Scroll down and click on «Privacy, search, and services.«
d. Under the «Clear browsing data» section, click on «Choose what to clear.«
e. Check the box labeled «Cached images and files» (and any other options you wish to clear).
f. Click on the «Clear» button to remove the selected temporary Internet files.
Remember, clearing temporary Internet files regularly can help maintain the performance of your browser and protect your privacy by removing potentially sensitive information stored in the cache.
What are Temporary Internet Files and can I delete them?
Temporary Internet Files, also known as cache files or browser cache, are files stored on your computer’s hard drive when you visit websites. These files are created by your web browser to improve the loading speed of web pages and enhance your browsing experience. They typically include images, videos, scripts, and other website elements.
Deleting temporary internet files can have several benefits:
1. Free up storage space: Over time, the cache files can accumulate and take up a significant amount of space on your hard drive. Deleting them can help free up storage and improve your computer’s performance.
2. Resolve webpage issues: Sometimes, outdated or corrupted cache files may cause problems when accessing certain websites. Deleting the cache can force your browser to retrieve fresh copies of website files, potentially resolving any loading or display issues.
3. Enhance privacy: Temporary Internet Files can also store information about your browsing history, cookies, and other tracking data. By deleting these files, you can enhance your privacy and reduce the chances of websites tracking your online activities.
To delete temporary internet files, follow these steps:
1. Open your web browser (e.g., Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge).
2. Access the browser settings or options—usually found by clicking on the three-dot icon or the menu button.
3. Look for the «Privacy,» «Browsing Data,» or similar section within the settings.
4. Find the option to clear or delete browsing data.
5. Make sure to select the appropriate time range, such as «All time» or «Everything» if you want to delete all cache files.
6. Check the box or boxes next to «Cached images and files,» «Browser cache,» or similar terminology.
7. Click on the «Clear Data» or «Delete» button to remove the temporary internet files.
Please note that the steps might vary slightly depending on the web browser and its version you are using. It’s a good practice to review the options available in your specific browser’s settings for clearing cache or browsing data.
Keep in mind that deleting temporary internet files will also log you out of any websites you are currently signed into and may cause some websites to load slightly slower initially, as the browser rebuilds the cache. However, these are temporary inconveniences and can be easily resolved.
Where do I find my temporary Internet files?
As a tech blogger, I would be glad to provide guidance on locating temporary Internet files. Temporary Internet files are typically stored on your computer to speed up webpage loading and enhance your browsing experience. In order to find these files, you can follow the steps below:
1. Open your preferred web browser: Whether you are using Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, or Safari, the process to find temporary Internet files is quite similar across different browsers.
2. Access the browser settings: Look for the settings menu, usually represented by three dots or lines located in the upper-right or lower-right corner of the browser window. Click on it to open the settings menu.
3. Find the browsing history settings: Once you have opened the settings menu, look for an option called «History» or «Browsing history.» Click on it to proceed.
4. Locate the temporary Internet files: Within the browsing history settings, you should find an option for «Clear browsing data» or «Delete browsing history.» Click on it to access further settings.
5. Specify the desired time range: In the subsequent menu, you will be prompted to select the time range of the browsing data you wish to delete or manage. If you are specifically interested in locating temporary Internet files, ensure that this option is selected or marked.
6. View the temporary Internet files: After selecting the appropriate time range, you may find a list of various types of browsing data, including temporary Internet files. Typically, these files are labeled as «Cache» or «Cached files.» Within this list, you will be able to identify the amount of data associated with temporary Internet files.
Please keep in mind that the exact wording and settings placement might differ slightly across browsers and versions. However, by following these general steps, you should be able to locate and manage your temporary Internet files efficiently.
При работе программ, игр, а также при процедурах обновления системы, установки драйверов и подобных вещах Windows 10 создаются временные файлы, при этом они не всегда и не все удаляются автоматически. В этой инструкции для начинающих пошагово о том, как удалить временные файлы в Windows 10 встроенными средствами системы. Также в конце статьи информация о том, где в системе хранятся временные файлы и видео с демонстрацией всего описанного в статье. Обновление 2017: В Windows 10 Creators Update появилась автоматическая очистка диска от временных файлов.
Отмечу, что описываемые ниже способы позволяют удалить лишь те временные файлы, которые система смогла определить как таковые, однако в некоторых случаях на компьютере могут быть и другие ненужные данные, подлежащие очистке (см. Как узнать чем занято место на диске). Преимущество описанных вариантов в том, что они полностью безопасны для ОС, но если нужны более действенные методы, можете ознакомиться со статьей Как очистить диск от ненужных файлов.
Удаление временных файлов с помощью опции «Хранилище» в Windows 10
В Windows 10 появился новый инструмент для анализа содержимого дисков компьютера или ноутбука, а также их очистки от ненужных файлов. Найти его можно, зайдя в «Параметры» (через меню Пуск или нажав клавиши Win+I) — «Система» — «Хранилище».
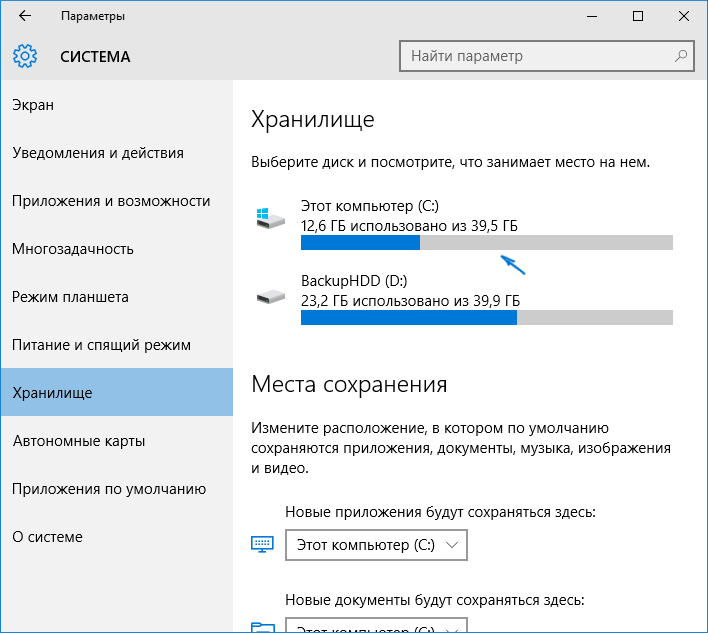
В этом разделе будут отображаться подключенные к компьютеру жесткие диски или, вернее, разделы на них. При выборе любого из дисков, вы сможете изучить, чем занято место на нем. Для примера выберем системный диск C (так как именно на нем в большинстве случаев и располагаются временные файлы).
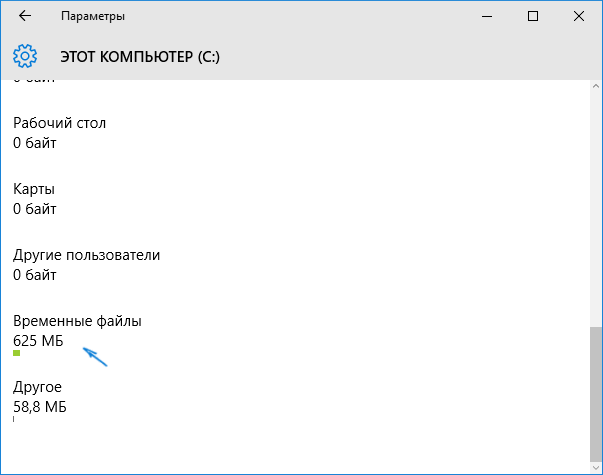
Если пролистать список с элементами, хранящимися на диске, до конца, вы увидите пункт «Временные файлы» с указанием занимаемого места на диске. Нажмите по этому пункту.
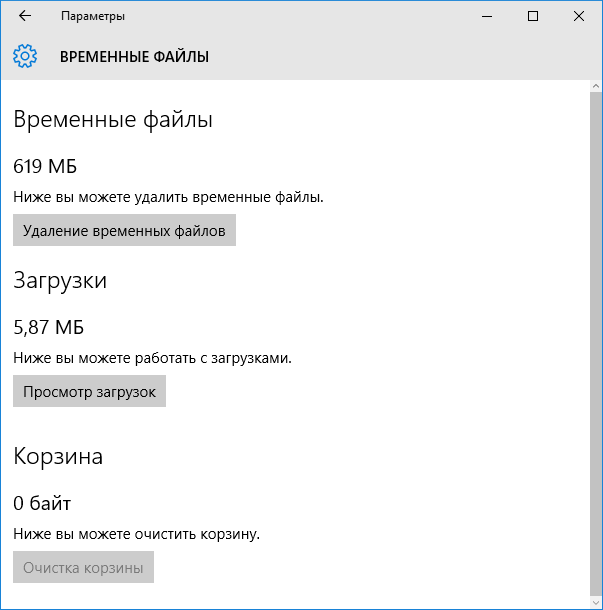
В следующем окне вы можете отдельно удалить временные файлы, изучить и очистить содержимое папки «Загрузки», узнать, сколько места занимает корзина и очистить ее.
В моем случае, на почти идеально чистой Windows 10 нашлось 600 с лишним мегабайт временных файлов. Нажимаем «Очистить» и подтверждаем удаление временных файлов. Начнется процесс удаления (который никак не демонстрируется, а просто написано «Мы удаляем временные файлы») и через короткое время они исчезнут с жесткого диска компьютера (при этом держать окно очистки открытым необязательно).
Использование утилиты очистки диска для удаления временных файлов
В Windows 10 также имеется встроенная программа «Очистка диска» (которая присутствует и в предыдущих версиях ОС). Она может удалить и те временные файлы, которые доступны при очистке с помощью предыдущего способа и некоторые дополнительные.
Для ее запуска можно использовать поиск или нажать клавиши Win+R на клавиатуре и ввести cleanmgr в окно «Выполнить».
После запуска программы, выберите диск, который нужно очистить, а затем элементы, которые нужно удалить. Среди временных файлов здесь представлены «Временные файлы Интернета» и просто «Временные файлы» (те же, что удалялись предыдущим способом). Кстати, вы также безопасно можете удалить и компонент RetailDemo Offline Content (это материалы, для демонстрации Windows 10 в магазинах).
Для начала процесса удаления нажмите «Ок» и дождитесь завершения процесса очистки диска от временных файлов.
Удаление временных файлов Windows 10 — видео
Ну и видео инструкция, в котором все шаги, связанные с удалением временных файлов из системы показаны и рассказаны.
Где в Windows 10 хранятся временные файлы
Если вы хотите удалить временные файлы вручную, то найти их можно в следующих типичных расположениях (но могут быть и дополнительные, используемые некоторыми программами):
- C:\Windows\Temp\
- C:\ Users\ Имя_пользователя\ AppData\ Local\ Temp (папка AppData по умолчанию скрыта. Как показать скрытые папки Windows 10.)
С учетом того, что данная инструкция предназначена для начинающих, думаю, достаточно. Удалив содержимое указанных папок вы, почти гарантированно, ничего не повредите в Windows 10. Возможно, вам также пригодится статья: Лучшие программы для очистки компьютера. Если же остались какие-то вопросы или непонимание, спрашивайте в комментариях, постараюсь ответить.
