Как вариант можешь использовать DataGrip. Замечательный инструмент.
Вот навигация по DataGrip.
вкладка Database всего лишь заменит консоль от СУБД. зачем из-за неё переживать?
или просто View — Tool Windows — Database
Эта опция подходит только для Ultimate
да, но автор не указал, что у него именно Community Edition.
а мне думается, что ее мало кто ставит. 🤔
почему? У меня на всех компах обе версии (ультимейт + комюнити) + я знаю и на работе могут на коммюнити версии сидеть, если ее нашпиговать плагинами, она мало чем ультимейт уступать будет для целого ряда задач будет хватать с головой
почему? ну наш народ любит попиратить)
Качай Ultimate version тут, затем, после пробной лицензии (30 дней) читай тут.
1. Установить Ultimate версию
2. Если нужен клиент БД именно в Идее, искать плагины, например:
https://www.logicbig.com/how-to/intellij/intellij-community-edition-connecting-database.html
Эта вкладка отображает встроенный в Идею клиент БД, что это такое и как настроить знать нужно наверное, но на этапе обучения я бы советовал использовать pgAdmin/Workbench для PostgreSQL/MySQL либо же другие обособленные клиенты, поскольку они содержат ряд фишек и функционал, к которому тоже нужно привыкать. А потом уже во время работы, использовать что душе угодно, консоль, графический клиент под одну базу, клиент БД в Идее,мульти-БД клиенты и тд.
Также, тем кто только начинает тоже нужно понимать, что для того писать и запускать джава код, работающий с базами данными — вкладка Database не нужна, и не нужно настраивать Datasource, поскольку джава код и джава приложение работает с базой данных напрямую через драйвер который лежит в депенденси.
Возможно это очевидно, но иногда бывают путаются.
У меня в community версии тоже нет, а в ultimate есть.
Время на прочтение5 мин
Количество просмотров71K
Даже среди тех, кто давно и активно пользуется IntelliJ IDEA, есть немало людей, ничего не знающих о плагине, позволяющем работать с базами данных прямо из IDE. Между тем, лично для меня это — одна из самых полезных возможностей IDEA, ибо писать код я могу и в vi. Важно, насколько удобно его потом отлаживать и улучшать. Спрашивается, при чем тут Database support? Собственно, при отладке приложений я его и использую.
Рассказ про плагин Database Support будет совершенно неофициальным, я сам его использовал только в веб-разработке и в разработке под Android, но хардкорным разработчикам жесткого enterprise тоже, надеюсь, будет интересно.
История веб-разработчика
Как-то раз мне пришла в голову мысль написать веб-приложение. Был шанс, что нагрузка на него будет довольно высокой и неравномерной, так что я решил в качестве СУБД использовать PostgreSQL в надежде, что она будет работать быстрее привычной MySQL. Сказано — сделано. Прототип написан, база создана, начинаем заполнять таблицы всякой тестовой гадостью.
Через некоторое время становится ясно, что структуру таблиц надо немного подправить, да и тестовые записи в них расплодились — надо чистить. И тут выясняется, что стандартный инструмент ручной работы с PostgreSQL — pgAdmin — совсем не похож на phpMyAdmin, и вообще он — самостоятельное десктопное приложение.
Встает вопрос, есть ли какая-нибудь универсальная штука, которая может работать удобным интерфейсом к БД, причем интерфейсом, внешний вид которого не зависит от БД, с которой он работает?
В JetBrains такую штуку довольно давно придумали, это плагин Database Support, который работает с IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate, RubyMine, PyCharm Professional Edition и PhpStorm. Он довольно сложен в разработке и поддержке, так что в бесплатные IDE он не ставится.
Посмотрим, чем же он нам может помочь. Для начала, настроим его для работы с PostgreSQL. Если у нас на компьютере еще нет драйвера JDBC для PostgreSQL, IDE нам предложит его скачать и установить. В моем случае СУБД запущена на том же компьютере, что и IDE:
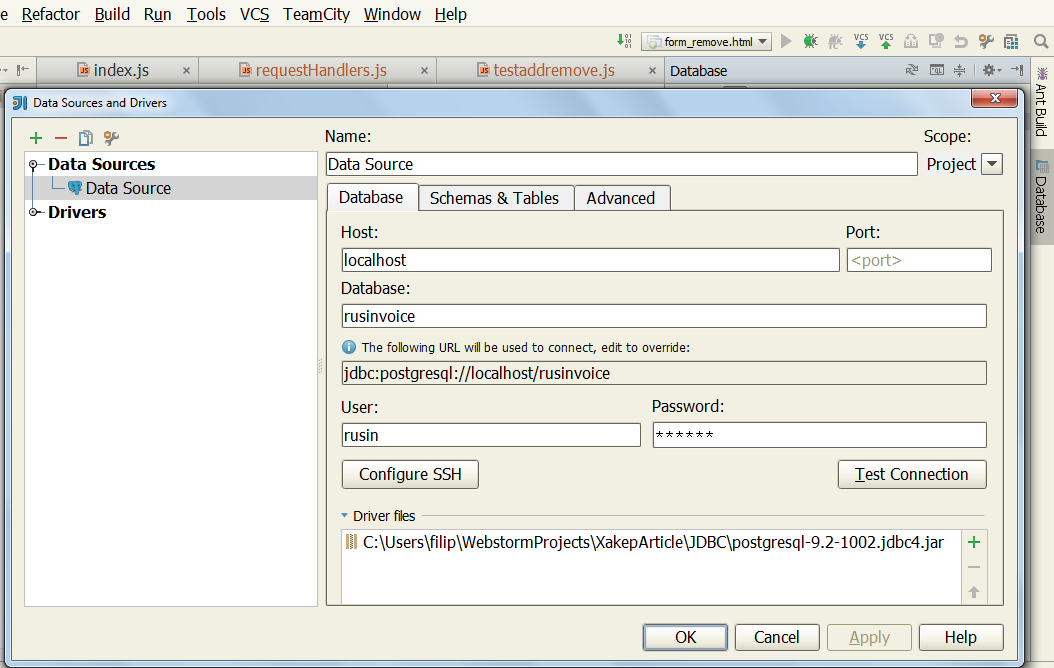
Видите вкладку Database по правому краю? Вот при нажатии на нее и открывается окно плагина Database Support (можно его открыть и через View | Tool Windows | Database, и через список окон Tool Windows):
Теперь посмотрим, что же мы можем сделать с его помощью. Во-первых, можно смотреть структуру БД в окне плагина, а если надо вывести UML-диаграмму, то и это можно (нажимаем <Ctrl+Alt+U>). Во-вторых, нам доступны просмотр и редактирование таблиц БД. Нажимаем F4 на требуемой таблице и вот она, перед нами:
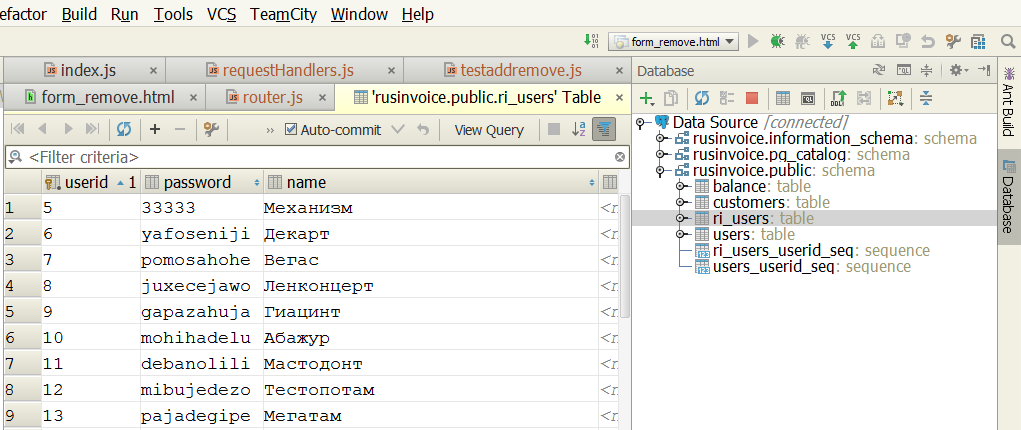
Любую ячейку мы можем редактировать, нажав F2, отметка «Auto-commit» означает, что после передачи изменений в БД будет автоматически делаться commit. Если отметку снять, то можно будет делать commit и rollback вручную.
под спойлером — коллаж, одновременно увидеть подсказки Commit и Rollback невозможно, не пытайтесь!
При сортировке таблицы (кликайте в имя столбца) изменений в БД не происходит, ибо таблица — это просто результат SELECT *, и если пока вы ее просматриваете, БД изменяется кем-то еще, вы этого не увидите.
Сортировку можно делать по разным столбцам — вначале по одному, потом по другому, а кнопка сброса сортировок (Reset columns order and visibility) появится, если окно достаточно широкое, или вы наведете мышь на двойные угловые скобки слева от настройки Auto-commit.
Нажимаем <Ctrl+F12> или используем Structure Toolwindow (<Alt+7>), и можем выбрать, какие столбцы мы хотим отображать, а какие — нет.
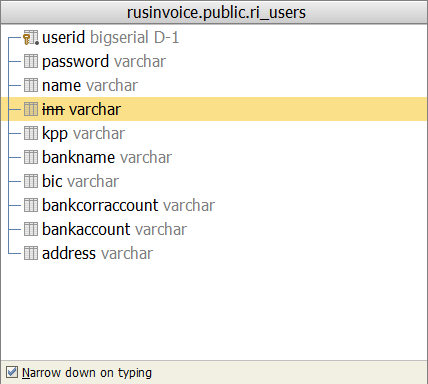
В этом же окне выбора отображается, в каком порядке сортируются столбцы (A — ascending, по возрастанию, D — descending, по убыванию). Если шрифт вашего look and feel позволяет, то вместо A и D вы увидите красивые стрелочки вверх и вниз. Выбирать столбцы для просмотра можно пробелом.
Сортировку можно делать как в таблице на стороне IDE, так и заранее — на стороне базы. Последнее делается кнопкой ORDER BY, а с помощью View Query можно посмотреть, какой именно запрос IDEA отправляет в базу:
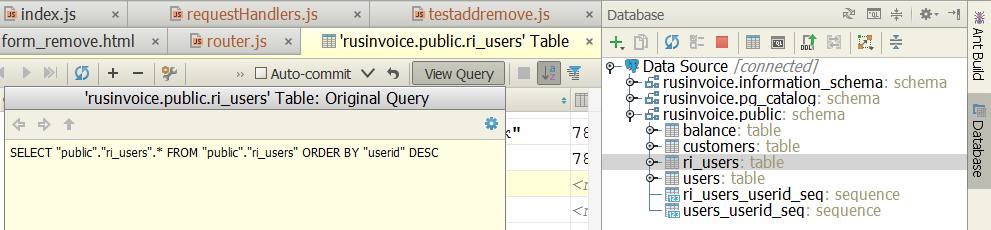
Из неочевидных возможностей стоит отметить недавно — в EAP 13-й версии — появившееся транспонирование строк (в IDEA 12 такого не было): если столбцов так много, что строка не умещается на экран, то двойным <Ctrl+Q> ее можно получить в виде столбца, и стрелочками еще бегать вверх-вниз по таблице с длинными строками. С содержимым базы, разумеется, при этом ничего не происходит, оно остается прежним.

Пока что мы работали с Table View базы. Однако поддерживается и режим консоли (нажимаем на значок консоли над tree view в окне Databases):
Теперь мы можем общаться с базой напрямую, отдавая ей SQL-команды, причем в SQL полностью поддерживается знакомый нам autocompletion по <Ctrl+пробел>.
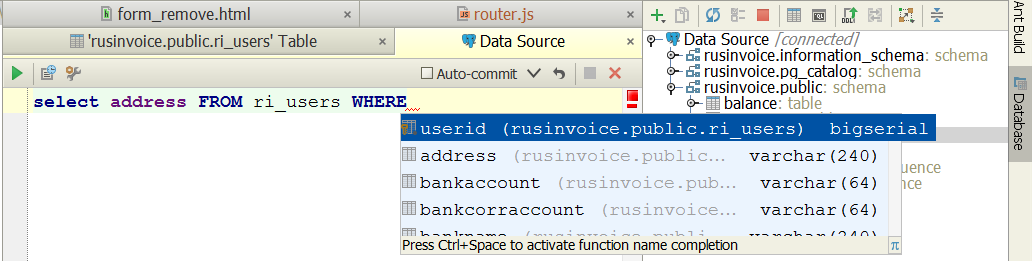
В консольном режиме тоже есть настройка «Auto-commit». Как и раньше, она означает, что после передачи изменений в БД транзакция будет подтверждаться автоматически. Если отметку снять, то справа от нее активируются кнопки для ручного commit и rollback.
Результаты запросов, если таковые ожидаются (например, при SELECT’ах) будут показаны в отдельной таблице внизу экрана, и их можно просматривать также, как и табличное представление базы, вызванное по F4.
Естественно, что с помощью этого плагина можно менять не только значения полей в таблицах, но и структуру таблиц, для этого легко использовать контекстные меню в дереве БД справа.
История разработчика под Андроид
Если бы поддержкой традиционных БД дело и ограничивалось, то статья на Хабр могла бы и не попасть: в работе с БД с JDBC есть много удобств, но для хабрастатьи не хватало финального аккорда. Аккорд случился осенью 2013-го, когда я пришел к моему коллеге, пишущему всю поддержку Android в JetBrains.
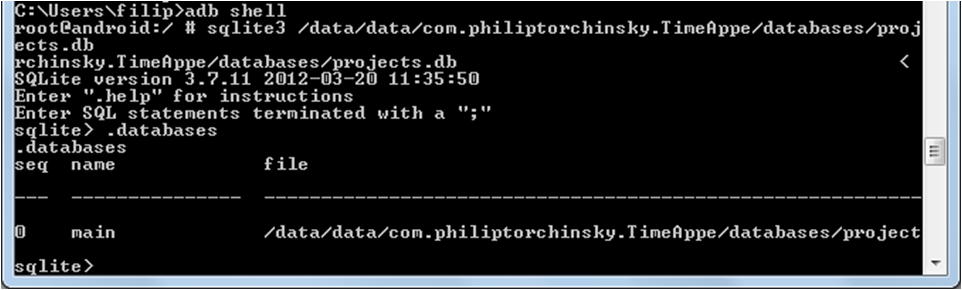
Разработчик под Android легко узнает свои мучения в скриншоте командной строки ниже. Для того, чтобы поработать с базой SQLite на устройстве или эмуляторе напрямую, без приложения, приходится звать adb shell, потом вызывать sqlite3, и просить его открыть базу по адресу, в который входит полное имя пакета приложения. А имя может быть длинным. И autocompletion к adb shell не прилагается.
Поэтому мой визит был жестом отчаяния: даже для того, чтобы сказать DROP DATABASE, когда в таблицах набралось достаточно ненужных тестовых данных, приходилось тратить время на рутинный набор длинных строк.
Любимое дело разработчиков в JetBrains — борьба с рутиной, так что мои горячие просьбы что-нибудь с этим сделать хорошо легли в русло добрых намерений, уже проложенное пятьюдесятью голосами за эту фичу в нашем трекере. Несмотря на тучу других задач, поддержку SQLite в Android допилили за две недели. Решение получилось элегантным: база SQLite вытягивается на компьютер из устройства или эмулятора прозрачно для пользователя, затем с локальной копией можно работать как с обычной БД, а затем ее можно залить в устройство обратно, вызвав Upload из контекстного меню.
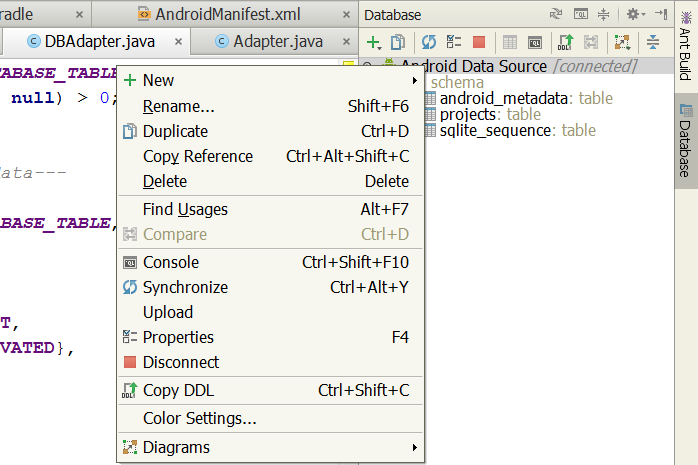
Для уверенности в том, что вы работаете с актуальной копией БД, можно синхронизироваться с нею на устройстве, нажав кнопку Syncronize или <Ctrl+Alt+Y>:
В остальном работа с БД при разработке под Android аналогична работе с обычным SQL-сервером.
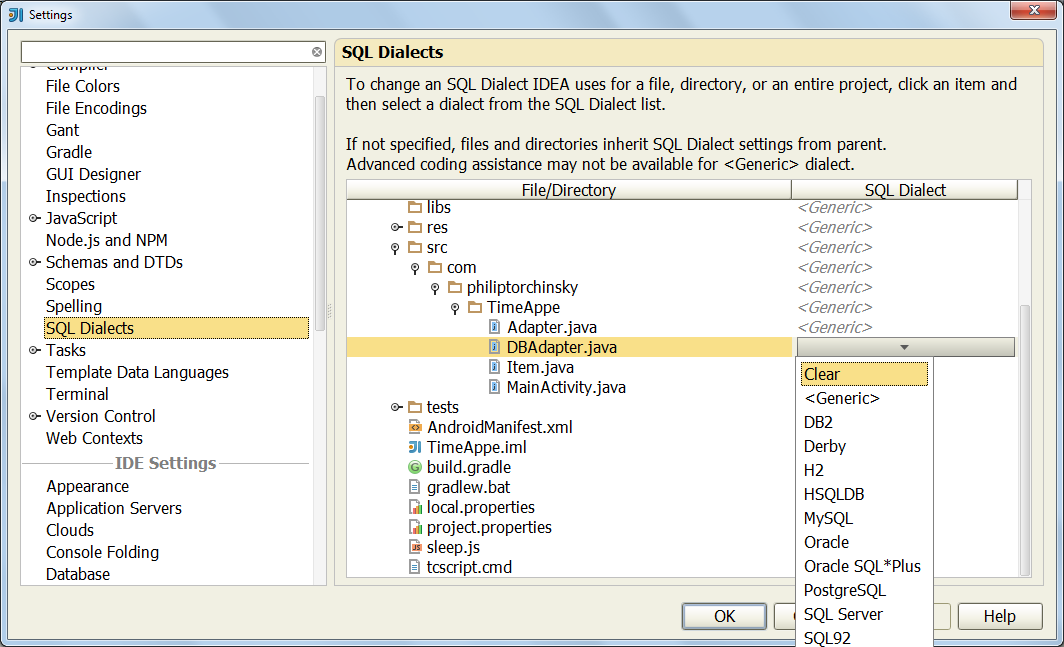
В заключение остается сказать, что плагин Database Support поддерживает все СУБД, для которых существуют драйверы JDBC (а это практически все популярные СУБД на рынке), и понимает 12 диалектов SQL. Какой именно диалект вы хотите использовать (и иметь соответствующее автодополнение и прочие фишечки к нему), можно указать в настройках IDE: Settings | SQL Dialects.
In the Database tool window (View | Tool Windows | Database), you can work with databases and DDL data sources. You can view and modify data structures in your databases, and perform other associated tasks. To view a table, double-click the table. For more information about different viewing modes, see View data.
- Where is the Database tool window in IntelliJ?
- How do I open a Database in IntelliJ?
- How do I open the build tool window in IntelliJ?
- How do I open the persistence tool window in IntelliJ?
- How do I get database options in IntelliJ Community Edition?
- How do I open the toolbar in IntelliJ?
- What is tool window?
- How do I open the JPA structure in IntelliJ?
- What is Spring Data JPA?
Where is the Database tool window in IntelliJ?
As of intellij version 2017.1, search for the plugin «Database navigator» in Settings -> Plugins. Then you can open the db browser from View -> Tool Windows -> DB Browser.
How do I open a Database in IntelliJ?
To add a new database connection (called a data source in IntelliJ), open the Database window View -> Tool Windows -> Databases, then click the + sign and select Data Source and then MySQL from the sub-menu.
How do I open the build tool window in IntelliJ?
From the main menu, select Build | Build Project Ctrl+F9 . Check the results in the Build tool window.
How do I open the persistence tool window in IntelliJ?
Right-click a module or a persistence unit, point to Generate Persistence Mapping and select By Database Schema. Select the source and output options and click OK.
How do I get database options in IntelliJ Community Edition?
Intellij community edition doesn’t come with a database browser, but we can install Database Navigator plugin. Open Setting dialogs and search for plugin: Select MarketPlace tab and type database: In the right panel (which shows Database Navigator) click on install and then click on restart IDE.
How do I open the toolbar in IntelliJ?
The main toolbar with buttons for opening and saving files, undo and redo actions is hidden by default. To show it, select View | Appearance | Toolbar.
What is tool window?
Tool windows provide access to development tasks: viewing your project structure, running and debugging your application, integration with version control systems and other external tools, code analysis, search, navigation, and so on. By default, tool windows are attached to the bottom and sides of the main window.
How do I open the JPA structure in IntelliJ?
Open the JPA console
in the toolbar or press Ctrl+Shift+F10 .
What is Spring Data JPA?
Spring Data JPA is an add-on
It provides a framework that works with JPA and provides a complete abstraction over the Data Access Layer. Spring Data JPA brings in the concept of JPA Repositories, a set of Interfaces that defines query methods. The Repository and Entity Bean represent the DAO layer in the application.
Database · December 12, 2024
IntelliJ IDEA is a powerful integrated development environment (IDE) that supports a variety of programming languages and frameworks. One of its standout features is the ability to connect to various databases, making it an excellent tool for developers who need to manage and interact with data. In this article, we will guide you step by step on how to connect IntelliJ IDEA to MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and Redis databases.
Prerequisites
- IntelliJ IDEA installed on your machine.
- Database server (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, or Redis) running locally or remotely.
- Database credentials (username, password, database name, etc.).
Connecting to MySQL
Step 1: Install MySQL JDBC Driver
To connect to a MySQL database, you need the MySQL JDBC driver. Follow these steps:
- Open IntelliJ IDEA and navigate to File > Project Structure.
- Select Libraries and click on the + icon to add a new library.
- Choose From Maven and search for
mysql:mysql-connector-java. - Select the latest version and click OK.
Step 2: Create a Database Connection
- Go to the Database tool window (View > Tool Windows > Database).
- Click on the + icon and select Data Source > MySQL.
- In the connection settings, enter your database credentials:
- Host: localhost (or your server IP)
- Port: 3306
- User: your_username
- Password: your_password
- Database: your_database_name
- Click on Test Connection to ensure everything is set up correctly.
- If successful, click OK to save the connection.
Connecting to PostgreSQL
Step 1: Install PostgreSQL JDBC Driver
Similar to MySQL, you need the PostgreSQL JDBC driver:
- Open Project Structure and go to Libraries.
- Add a new library by searching for
org.postgresql:postgresql. - Select the latest version and click OK.
Step 2: Create a Database Connection
- Open the Database tool window.
- Click on the + icon and select Data Source > PostgreSQL.
- Fill in the connection details:
- Host: localhost (or your server IP)
- Port: 5432
- User: your_username
- Password: your_password
- Database: your_database_name
- Click Test Connection and then OK to save.
Connecting to MongoDB
Step 1: Install MongoDB Driver
To connect to MongoDB, you need the MongoDB driver:
- Go to Project Structure > Libraries.
- Add a new library by searching for
org.mongodb:mongodb-driver-sync. - Select the latest version and click OK.
Step 2: Create a Database Connection
- Open the Database tool window.
- Click on the + icon and select Data Source > MongoDB.
- Enter the connection string in the format:
mongodb://your_username:your_password@localhost:27017/your_database_nameConnecting to Redis
Step 1: Install Redis Driver
For Redis, you will need a specific driver:
- Go to Project Structure > Libraries.
- Add a new library by searching for
redis.clients:jedis. - Select the latest version and click OK.
Step 2: Create a Database Connection
- Open the Database tool window.
- Click on the + icon and select Data Source > Redis.
- Enter the connection details:
- Host: localhost (or your server IP)
- Port: 6379
- Password: your_password (if applicable)
- Click Test Connection and then OK to save.
Summary
In this article, we have provided a comprehensive guide on how to connect IntelliJ IDEA to MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and Redis databases. By following these steps, you can efficiently manage your database connections directly from your IDE. For developers looking for reliable infrastructure to host their applications, consider exploring USA VPS Hosting solutions that can enhance your development experience.
To issue a query to a database, you must create a data source connection. Data source is the location of your data and can be a server or a DDL file. The data source includes a name and connection settings that are dependent on the data source type.
Amazon Redshift
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select Amazon Redshift.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
From the Connection type list, select a type of connection that you want to use:
-
Default: connect by using Host, Port, and Database.
-
IAM cluster/region: connect by using Database, Region, and Cluster.
-
URL only: connect by using the JDBC URL that you can copy in settings of your Amazon Redshift cluster.
-
-
From the Authentication list, select an authentication method.
-
pgpass: by using the PGPASS file. You can store this file in the user’s home directory (for example, /Users/jetbrains/.pgpass). You can read more about the password file in The Password File at postgresql.org.
-
User & Password: by using your login and password.
-
AWS profile: by using a named profile. A named profile is a collection of settings and credentials that you can use for authentication. Named profiles are stored in CREDENTIALS files. Default directories for these files are ~/.aws/credentials (Linux and macOS) and %USERPROFILE%\.aws\credentials (Windows).
-
-
In your Redshift dashboard, create a Redshift cluster.
For more information about the Amazon Redshift cluster, read Getting Started with Amazon Redshift.
-
In settings of the Redshift cluster, copy the JDBC URL.
-
Paste the JDBC URL from the Redshift cluster settings to the URL field in IntelliJ IDEA.
-
In User and Password fields, specify your Redshift credentials.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
Apache Cassandra
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select Apache Cassandra.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
Apache Derby
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select Apache Derby.
-
From the Driver list, select the type of the JDBC driver that you want to use. For remote connections, select Apache Derby (Remote). For embedded databases, select Apache Derby (Embedded).
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
Apache Hive
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select Apache Hive.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
Azure SQL Database
Microsoft Azure supports PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, and other Database Management Systems (DBMS). If you want to connect to these data sources, create data source connections that correspond to these DMBS. In IntelliJ IDEA, these connections already include necessary JDBC drivers. So, if you want to connect to the Azure database for PostgreSQL, create the PostgreSQL connection.
-
In your Microsoft Azure account, create an SQL data source. For more information about the Azure SQL Database, read Azure SQL Database documentation at docs.microsoft.com.
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select Azure SQL Database.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link.
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
To use Azure Active Directory Authentication, select Azure Active Directory password from the Authentication list. You might need to download additional libraries for Active Directory Authentication. To use SQL authentication, select User & Password.
BigQuery
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select Azure SQL Database.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
Specify information about the project to which you want to connect.
-
Project ID:: a unique identifier for your project.
-
OAuthType:: an option that specifies how the driver obtains or provides the credentials for OAuth 2.0 authentication. You can select between the following options:
-
Google Service Account: authenticate the connection with a Google service account. In the URL field, add the following options:
OAuthServiceAcctEmail(a Google service account email address),OAuthPvtKeyPath(the full path to a private key file for the service account), andOAuthType=0. Consider the following example JDBC URL.jdbc:bigquery://https://www.googleapis.com/bigquery/v2:443;
ProjectId=ConnectToBigQuery;
OAuthType=0;
OAuthServiceAcctEmail=my_google_service_account@connect-to-bigquery.iam.gserviceaccount.com;
OAuthPvtKeyPath=/Users/jetbrains/DatagripProjects/keyFile.p12; -
Google User Account: authenticate the connection with a Google user account. You must provide your Google user account credentials to connect to the server.
jdbc:bigquery://https://www.googleapis.com/bigquery/v2:443;
ProjectId=ConnectToBigQuery;
OAuthType=1; -
Pre-Generated Access and Refresh Tokens: authenticate the connection using access or refresh tokens that have already been generated from the Google Authorization Server. In the URL field, add the following options:
OAuthAccessToken(an access token),OAuthClientId(a refresh token),OAuthClientSecret(a client secret), andOAuthType=2. If you are using a refresh token, set theOAuthClientIdproperty to to your client ID and set theOAuthClientSecretproperty to your client secret. For more information about tokens, see Using OAuth 2.0 to Access Google APIs at developers.google.com.jdbc:bigquery://https://www.googleapis.com/bigquery/v2:443;
OAuthType=2;
ProjectId=ConnectToBigQuery;
OAuthAccessToken=FI1vf0PSMMu9;
OAuthRefreshToken=@3GANwIJk2n3lk3n5g2k45;
OAuthClientId=234k5j23l4kf;
OAuthClientSecret=lkegjle+2435mn; -
Application Default Credentials: authenticate the connection using credentials obtained through Application Default Credentials (ADC). For more information about ADC and how to obtain them, see Authenticating as a service account at cloud.google.com.
jdbc:bigquery://https://www.googleapis.com/bigquery/v2:443;
OAuthType=3;
ProjectId=ConnectToBigQuery;
-
-
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
ClickHouse
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select ClickHouse.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
Couchbase Query
IntelliJ IDEA supports the Couchbase Query Query service, not the Couchbase Query Analytics service.
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select Couchbase Query.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
You can skip the port field or set the port number to 11210 that is the default port for the Couchbase Query Query Service.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
Exasol
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select Exasol.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
Greenplum
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select Greenplum.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
From the Authentication list, select an authentication method.
-
pgpass: by using the PGPASS file. You can store this file in the user’s home directory (for example, /Users/jetbrains/.pgpass). You can read more about the password file in The Password File at postgresql.org.
-
User & Password: by using your login and password.
-
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
H2
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select H2.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
From the Connection type list, select the connection mode: Remote, In-memory, Embedded. For more information about these modes, see the official H2 documentation.
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
HSQLDB
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select HSQLDB.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
IBM Db2 LUW
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select IBM Db2 LUW.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
From the Connection type list, select the connection mode that you want to use: Type 2 or Type 4. For more information about driver architectures, see the IBM documentation for IBM Db2 LUW.
In the user interface, if compared to Type 2, Type 4 has Host and Port fields.
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
MariaDB
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select MariaDB.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
Microsoft SQL Server
For more information about configuring Microsoft SQL Server, Windows domain authentication, and user permissions, see How to connect to MS SQL server in the IntelliJ IDEA documentation.
For more information about connecting to LocalDB, see How to connect to SQL Server Express LocalDB in the DataGrip documentation.
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select Microsoft SQL Server.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
(Optional) To use Azure Active Directory Authentication, you can select Azure Active Directory password or Azure Active Directory interactive options from the Authentication list.
If you select the Azure Active Directory password option, you need to specify your username and password for the Azure Active Directory in User and Password fields, respectively.
To authorize your connection from the browser, select Azure Active Directory interactive. In this case, you will be redirected to login.microsoftonline.com, where you need to authorize with your Active Directory (AD) account. Then the browser will send the authentication information to the IDE.
You might need to download additional libraries for Azure Active Directory Authentication. To use SQL authentication, select User & Password.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
MongoDB
In MongoDB, for authentication, you must provide a username, password, and the authentication database that is associated with this username. If the authentication database differs from the database to which you want to connect, specify the authentication database with the authSource parameter in the URL. If no authentication database is specified, MongoDB uses the admin database by default.
For example, you want to connect to the local database but your authentication database is admin. In this case, the connection URL will look like: mongodb://localhost:27017/local?authSource=admin.
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select MongoDB.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
From the Connection type list, select your connection type:
-
default: standard connection string format (for example,
mongodb://localhost:27021/admin). Read more about standard connection string format in Standard Connection String Format at docs.mongodb.com. -
MongoDB Atlas (SRV protocol): DNS seedlist connection format (for example,
mongodb+srv://unit1.test.net:27121,unit2.test.com:27021). Read more about standard connection string format in DNS Seedlist Connection Format at docs.mongodb.com.
-
-
Specify database connection details: a login, a password, and the database that you want to connect to. To set an empty password, right-click the Password field and select Set empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
MySQL
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select MySQL.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
Oracle
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select Oracle.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
From the Connection type list, select a connection type:
-
SID: to use a unique name of an Oracle instance (a process that runs on the workstation).
To use a correct value, check the environment variable
ORACLE_SIDon the server host, or contact your database administrator. Commonly-used values areXEorORCL. -
Service name: to use an alias to an Oracle instance (or many instances).
-
TNS: to use tnsnames.ora configuration file. In the TNSADMIN field, specify a path to the folder with tnsnames.ora. In the TNS name field, specify what service name to use (see a value of
net_service_namein tnsnames.ora) if you have more than one service.For more information about tnsnames.ora, see Local Naming Parameters in the tnsnames.ora file.
-
URL only: to use the JDBC URL.
-
-
From the Driver list, specify the driver type. For more information about driver types, see Oracle JDBC FAQ.
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
PostgreSQL
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select PostgreSQL.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
From the Authentication list, select an authentication method.
-
pgpass: by using the PGPASS file. You can store this file in the user’s home directory (for example, /Users/jetbrains/.pgpass). You can read more about the password file in The Password File at postgresql.org.
-
User & Password: by using your login and password.
-
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
Snowflake
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select Snowflake.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
From the Authentication list, select an authentication method.
-
Authenticator: the authenticator to use for verifying user login credentials. For more information about the authenticator, see the Snowflake documentation at docs.snowflake.com.
-
User & Password: by using your login and password.
-
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
SQLite
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select SQLite.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
To connect to an existing SQLite database, specify a file path to the database file in the File field.
To create a new SQLite database, change the default name of the database if needed
identifier.sqliteand click OK.Also, to create a database, you can drag an SQLite DB file to the Database tool window.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
Sybase ASE
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select Sybase ASE.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
From the Authentication list, select an authentication method.
-
Domain credentials: by using domain authentication.
-
User & Password: by using your login and password.
-
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
Vertica
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
On the Data Sources tab in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select Vertica.
-
At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. As you click this link, IntelliJ IDEA downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. To decrease the size of the installation package and keep driver versions up-to-date, drivers are not bundled with the IDE.
You can specify your own drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
Other
Currently, IntelliJ IDEA supports vendors that are mentioned previously. The support includes such features as enhanced code completion and better retrieval of database objects (introspection). If your vendor is not in the list, you still can connect to the database with a JDBC driver.
Create a connection to a database with a JDBC driver
If you cannot find a name of a database vendor in the list of data sources, download a JDBC driver for the database management system (DBMS), and create a connection in IntelliJ IDEA. With the JDBC driver, you can connect to DBMS and start working.
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
In the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select Driver and Data Source.
-
Click the User Driver link.
-
In the Driver files pane, click the Add icon () and select Custom JARs.
-
Navigate to the JAR file of the JDBC driver, select it, and click OK.
-
In the Class field, specify the value that you want to use for the driver.
-
Click Apply.
-
Return to the created data source connection.
-
Specify database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
To delete a password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click Test Connection.
Specify a library path for a driver
To work properly, some JDBC drivers require a path to library files along with the driver.
For example, to determine if the application should operate in the Instant Client mode, Oracle Instant Client (OCI) applications look for library files in the runtime library search path (LD_LIBRARY_PATH on Linux or PATH on Windows). You can set these paths in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog.
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
In the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the driver entry to which you want to add a path to library files.
-
(Optional) Add a driver for which you want to add library files. If the existing driver does not meet the requirements, replace the existing driver. To delete the existing driver entry, select the driver and click Remove. For more information about adding a driver, see Create a connection to a database with a JDBC driver.
-
In the Driver files pane, click the Add icon () and select Native Library Path.
-
Navigate to the folder with library files. Ensure that the driver version corresponds to the version of these library files. For example, if you use the driver version 19.6, the attached library files must also have the 19.6 version.
DDL data source
SQL files that contain data definition language statements (DDL statements) can be used as data sources. As a result, you can reference all tables, columns and other objects defined in such files in the editor.
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
In the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select DDL Data Source.
-
In the DDL Files pane, click the Add button .
-
In the file browser, navigate to the SQL file or files with DDL statements and click Open.
-
Click Apply.
-
In the SQL Dialects dialog, select a dialect that you want to use for the added SQL file.
-
Apply settings and click OK.
Productivity tips
Create a data source from the JDBC URL
-
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon .
-
In the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon () and select Data Source from URL.
-
In the URL field, paste the JDBC URL.
-
From the Driver list, select the necessary driver for the data source.
-
In the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, enter credentials.
-
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.

Last modified: 27 May 2021



