В данной статье описаны проблемы утечки памяти, которая возникает на контроллерах домена под управлением Windows Server 2012 R2 и Windows 8.1 или Windows Server 2012 R2 на компьютере с установленной ролью сервера служб Active Directory облегченного доступа к каталогам (AD LDS). Доступно исправление для устранения этой проблемы. Исправление с условием.
Симптомы
Новое выделение памяти кучи области была представлена в версии Windows Server 2012 R2 служб каталогов. Он вызывает утечку памяти в Lsass.exe (роль контроллера домена) и DsaMain.exe облегченный службы каталогов (LDS) процесса, который может использовать всю доступную память на контроллере домена Windows Server 2012 R2 или сервер LDS.
Причина
Эта проблема возникает в следующих ситуациях:
-
Повышение роли контроллера домена или Добавление LDS реплики конфигурации установки
После добавления реплики в конфигурацию, повышение роли контроллера домена или экземпляра LDS на Windows Server 2012 R2 или Windows 8.1, механизм репликации должен реплицировать каждый объект в контекстов именования, необходимые на новый экземпляр. Во время задания процесс локальной безопасности центра сертификации сервера службы (LSASS) или DsaMain.exe может привести к серьезной утечке когда он выделяет память байт выделенной виртуальной памяти, хотя реального использования очень мала. Кроме того DCpromo.log отображается следующее сообщение об ошибке:
Дата ивремя[INFO] репликация данных DC = Contoso,DC = com: XXXXXX полученных из около XXXXXX объектов и XXXXXX из приблизительно XXXXXX различающееся имя (DN) значения…Дата время [внимание] не критическую репликацию возвращается 14
Преобразует код ошибки 14 для: ERROR_OUTOFMEMORY — недостаточно памяти для завершения этой операции.
Следующее событие записывается в журнал событий, во время или dcpromo вскоре после завершения:
Журнал событий
Источник событий
ИДЕНТИФИКАТОР
Описание
Службы каталогов
Репликация
2094
Предупреждение о производительности: репликация была задержана во время применения изменений на следующий объект. Если это сообщение появляется часто, это означает, что репликация происходит медленно и что сервер может иметь трудности, придерживаясь изменения.
Объект DN: CN =имя клиента, OU =Подразделение, DC =Contoso, DC =comОбъект GUID: GUIDРазличающееся имя раздела: DC =Contoso, DC =comСервер: _msdcs DNS-запись партнера репликацииЗатраченное время (сек): XX
Действия пользователя
Распространенной причиной для просмотра Эта задержка является особенно большой объем его значения, или в число значений этого объекта. Сначала следует учитывать, можно ли изменить приложение для уменьшения объема данных, хранящихся в объекте или количество значений. Если это большой группы или списка рассылки, может потребоваться создание функциональный уровень леса до Windows Server 2003 или более поздней, так как при этом включается репликация для более эффективной работы. Необходимо выяснить ли Серверная платформа предоставляет достаточно производительности в терминах памяти и вычислительной мощности. Наконец необходимо учитывать настройки базы данных доменных служб Active Directory путем перемещения базы данных и журналов для отдельных разделов диска.
Если вы хотите изменить порог предупреждения, ниже приведены в разделе реестра. Значение 0 отключает проверку.
Дополнительные данные
Порог предупреждений (сек): XX
Ограничение реестра: System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NTDS\Parameters\Replicator ожидания для объекта обновления (сек)
Службы каталогов
KCC
кодом 1308
Средство проверки согласованности знаний (KCC) обнаружила, что последовательные попытки репликации каталогов службой последовательно не удалась.
Попыток:2Служба каталогов:CN = Параметры NTDS, CN =DC001, CN =серверы, CN =узел1, CN =сайты, CN =Конфигурация, DC =Contoso, DC =comПериод времени (в минутах):XXXXXXX
Объект подключения для данной службы каталогов будут игнорироваться и новое временное подключение будет установлено, чтобы убедиться, что репликация продолжается. После репликации с этой службой каталогов возобновляется, временное подключение будет удалено.
Дополнительные данныеЗначение ошибки:14 не хватает памяти для завершения этой операции.
Примечание. Эта проблема не возникает при установке с носителя (IFM) рекламной акции для контроллеров домена используется. Однако повышение IFM должен быть изготовлены из той же версии операционной системы.
-
Следующее событие записывается в журнал событий, во время или dcpromo вскоре после завершения:
Журнал событий
Источник событий
ИДЕНТИФИКАТОР
Описание
Службы каталогов
Репликация
2094
Предупреждение о производительности: репликация была задержана во время применения изменений на следующий объект. Если это сообщение появляется часто, это означает, что репликация происходит медленно и что сервер может иметь трудности, придерживаясь изменения.
Объект DN: CN =имя клиента, OU =Подразделение, DC =Contoso, DC =comОбъект GUID: GUIDРазличающееся имя раздела: DC =Contoso, DC =comСервер: _msdcs DNS-запись партнера репликацииЗатраченное время (сек): XX
Действия пользователя
Распространенной причиной для просмотра Эта задержка является особенно большой объем его значения, или в число значений этого объекта. Сначала следует учитывать, можно ли изменить приложение для уменьшения объема данных, хранящихся в объекте или количество значений. Если это большой группы или списка рассылки, может потребоваться создание функциональный уровень леса до Windows Server 2003 или более поздней, так как при этом включается репликация для более эффективной работы. Необходимо выяснить ли Серверная платформа предоставляет достаточно производительности в терминах памяти и вычислительной мощности. Наконец необходимо учитывать настройки базы данных доменных служб Active Directory путем перемещения базы данных и журналов для отдельных разделов диска.
Если вы хотите изменить порог предупреждения, ниже приведены в разделе реестра. Значение 0 отключает проверку.
Дополнительные данные
Порог предупреждений (сек): XX
Ограничение реестра: System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NTDS\Parameters\Replicator ожидания для объекта обновления (сек)
Службы каталогов
KCC
кодом 1308
Средство проверки согласованности знаний (KCC) обнаружила, что последовательные попытки репликации каталогов службой последовательно не удалась.
Попыток:2Служба каталогов:CN = Параметры NTDS, CN =DC001, CN =серверы, CN =узел1, CN =сайты, CN =Конфигурация, DC =Contoso, DC =comПериод времени (в минутах):XXXXXXX
Объект подключения для данной службы каталогов будут игнорироваться и новое временное подключение будет установлено, чтобы убедиться, что репликация продолжается. После репликации с этой службой каталогов возобновляется, временное подключение будет удалено.
Дополнительные данныеЗначение ошибки:14 не хватает памяти для завершения этой операции.
Примечание. Эта проблема не возникает при установке с носителя (IFM) рекламной акции для контроллеров домена используется. Однако повышение IFM должен быть изготовлены из той же версии операционной системы.
-
Преобразует код ошибки 14 для: ERROR_OUTOFMEMORY — недостаточно памяти для завершения этой операции. Следующее событие записывается в журнал событий, во время или dcpromo вскоре после завершения:
Журнал событий
Источник событий
ИДЕНТИФИКАТОР
Описание
Службы каталогов
Репликация
2094
Предупреждение о производительности: репликация была задержана во время применения изменений на следующий объект. Если это сообщение появляется часто, это означает, что репликация происходит медленно и что сервер может иметь трудности, придерживаясь изменения.
Объект DN: CN =имя клиента, OU =Подразделение, DC =Contoso, DC =comОбъект GUID: GUIDРазличающееся имя раздела: DC =Contoso, DC =comСервер: _msdcs DNS-запись партнера репликацииЗатраченное время (сек): XX
Действия пользователя
Распространенной причиной для просмотра Эта задержка является особенно большой объем его значения, или в число значений этого объекта. Сначала следует учитывать, можно ли изменить приложение для уменьшения объема данных, хранящихся в объекте или количество значений. Если это большой группы или списка рассылки, может потребоваться создание функциональный уровень леса до Windows Server 2003 или более поздней, так как при этом включается репликация для более эффективной работы. Необходимо выяснить ли Серверная платформа предоставляет достаточно производительности в терминах памяти и вычислительной мощности. Наконец необходимо учитывать настройки базы данных доменных служб Active Directory путем перемещения базы данных и журналов для отдельных разделов диска.
Если вы хотите изменить порог предупреждения, ниже приведены в разделе реестра. Значение 0 отключает проверку.
Дополнительные данные
Порог предупреждений (сек): XX
Ограничение реестра: System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NTDS\Parameters\Replicator ожидания для объекта обновления (сек)
Службы каталогов
KCC
кодом 1308
Средство проверки согласованности знаний (KCC) обнаружила, что последовательные попытки репликации каталогов службой последовательно не удалась.
Попыток:2Служба каталогов:CN = Параметры NTDS, CN =DC001, CN =серверы, CN =узел1, CN =сайты, CN =Конфигурация, DC =Contoso, DC =comПериод времени (в минутах):XXXXXXX
Объект подключения для данной службы каталогов будут игнорироваться и новое временное подключение будет установлено, чтобы убедиться, что репликация продолжается. После репликации с этой службой каталогов возобновляется, временное подключение будет удалено.
Дополнительные данныеЗначение ошибки:14 не хватает памяти для завершения этой операции.
Примечание. Эта проблема не возникает при установке с носителя (IFM) рекламной акции для контроллеров домена используется. Однако повышение IFM должен быть изготовлены из той же версии операционной системы.
-
Распространения дескриптор безопасности
Утечка памяти может возникнуть, когда изменение безопасности для объекта контейнера (корневой домен или подразделение (OU)) наследуется на множество дочерних объектов или подчиненных подразделений хотя SD распространения. В зависимости от записи управления доступом (ACE) может быть изменен размер и количество объектов (например, 500 000) распространение может занять много времени. В течение этого времени процесса LSASS или DsaMain процесс может постоянно выделять фиксировано байт.
-
Долго выполняющиеся запросы
Неожиданно потребление высокой виртуальной памяти во время длительных запросов Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) на серверах под управлением Windows 8.1 LDAP или Windows Server 2012 R2 может привести сбои памяти. Длительные запросы потребляют память, получая кучи для дескриптор безопасности каждого объекта, который был затронут.
При достижении фиксировано байт числа байтов, доступных в этих случаях система непригодна к использованию и может даже перестать.
Решение
Чтобы устранить эту проблему, установите исправление, описанное в следующем разделе.
Для использования исправления в контексте продвижения контроллера домена (DCPROMO), выполните следующие действия.
-
Установка роли доменных служб Active Directory или AD LDS.
-
Установите это обновление или установку новых обновлений Windows Server 2012 R2 и обновлений безопасности, которые содержат одинаковые Ntdsai.dll двоичных как они носят накопительный характер.
-
Повысьте уровень компьютера статус контроллера домена.
Важно. Если установить языковой пакет после установки данного исправления, необходимо переустановить это исправление. Таким образом, рекомендуется установить все языковые пакеты, которые прежде чем установить данное исправление. Дополнительные сведения содержатся в статье Установка языковых пакетов для Windows.
Сведения об исправлении
Существует исправление от корпорации Майкрософт. Однако данное исправление предназначено для устранения проблемы, описанной в этой статье. Применяйте данное исправление только в тех системах, которые имеют данную проблему.
Если исправление доступно для загрузки, имеется раздел «Исправление загрузки доступно» в верхней части этой статьи базы знаний. Если этого раздела нет, отправьте запрос на получение исправления в службу технической поддержки и поддержки.
Примечание. Если наблюдаются другие проблемы или необходимо устранить неполадки, вам может понадобиться создать отдельный запрос на обслуживание. Затраты на обычные службы поддержки будет применяться к Дополнительные вопросы и проблемы, с которыми не данным исправлением, оплачиваются. Полный список телефонов поддержки и обслуживания клиентов корпорации Майкрософт или создать отдельный запрос на обслуживание посетите следующий веб-узел корпорации Майкрософт:
http://support.microsoft.com/contactus/?ws=supportПримечание. В форме «Пакет исправлений доступен для скачивания» отображаются языки, для которых доступно исправление. Если нужный язык не отображается, это потому, что исправление не поддерживается для этого языка.
Предварительные условия
Для установки этого исправления необходимо иметь апреля 2014 накопительный пакет обновления для Windows RT 8.1, Windows 8.1 и Windows Server 2012 R2 (2919355) установлен в Windows Server 2012 R2 или Windows 8.1.
Сведения о реестре
Применяя данное исправление, вам не потребуется вносить какие-либо изменения в реестр.
Необходимость перезагрузки
Может потребоваться перезагрузить компьютер после установки данного исправления.
Сведения о замене исправлений
Это исправление не заменяет ранее выпущенные исправления.
Статус
Корпорация Майкрософт подтверждает, что это проблема продуктов Майкрософт, перечисленных в разделе «Относится к».
Дополнительные сведения
Если включен уровень «9 Внутренняя обработка» NTDS\Diagnostics 2, как описано в статье базы знаний Майкрософт 314980, могут появиться следующие события ActiveDirectory_DomainService. Эти события показывают SD распространение продолжительной задачи.
События 1257 -, с которой начинается распространение SDВнутреннее событие: распространение события, начиная с следующий контейнер обрабатывает задачу распространения дескриптора безопасности.Контейнер: OU = Подразделение, DC = Contoso, DC = com
События 2007 -, показывающее ход выполнения распространения SD, войти в каждые 5 минутВнутреннее событие: достигнут следующий контейнер и продолжит распространение задачу распространения дескриптора безопасности.Контейнер: OU = Подразделение, DC = Contoso, DC = comЧисло объектов, проанализированной на данный момент: XXXXXX
1258 события -, указывающее конец распространения SD, через несколько часовВнутреннее событие: задача распространения дескриптора безопасности завершил обработку события распространения начиная с следующий контейнер.Контейнер: OU = Подразделение, DC = Contoso, DC = comКоличество обработанных объектов: ПППППП
После репликации Active Directory на контроллерах домена под управлением Windows Server 2012 R2 или LDS экземпляров в домене та же проблема может возникать SD передача выполняется локально.
Вы не увидите, что утечка памяти в Active Directory сборщик набор отчетов, так как он показывает только байт. Тем не менее, можно использовать созданный производительности данных ЖРНАЛ проверки файлов счетчиков объекта: процесса монитора, экземпляр: Lsass, счетчик: Private Bytes и объект: памяти, счетчик: Committed Bytes.
Для более наблюдения разработки утечки «Граф с образцом свойства элементов графа, монитор производительности» можно использовать каждые 60 секунд. Длительность: 15 000 секунд (> 4 часа).
Увеличение выделения можно также наблюдать в диспетчере задач, вкладка производительностьпамяти, выделенныйэлемент. Это отображается в списке Зафиксировано/доступно гигабайт (ГБ).
Ниже перечислены индикаторы состояния ошибки.
Возвращает repadmin /showrepl:
Недостаточно памяти для завершения этой операции.
Ошибка события 1699 журналы службы каталогов:
Службе каталогов не удалось получить изменения, запрошенные для следующего раздела каталога. В результате не удается отправить запросы на изменение в службе каталогов по следующему адресу сети.Расширенный код запроса: 0Дополнительные данныеЗначение ошибки: 8446 операции репликации не удалось выделить память.
Всплывающее окно приложения:
Windows — недостаточно виртуальной памяти: системе не хватает виртуальной памяти. Чтобы обеспечить нормальную работу Windows, увеличьте размер файла подкачки виртуальной памяти. Дополнительные сведения см.
Ссылки
Дополнительные сведения о терминологии , которую корпорация Майкрософт использует для описания обновлений программного обеспечения.
Сведения о файлах
Английская (США) версия данного обновления программного обеспечения устанавливает файлы, атрибуты которых указаны в приведенных ниже таблицах. Дата и время для этих файлов указаны в формате общего скоординированного времени (UTC). Имейте в виду, что дата и время для этих файлов на локальном компьютере отображаются в местном времени с вашим текущим смещением летнего времени. При выполнении определенных операций с файлами даты и время могут изменяться.
Важно. Windows Server 2012 R2 исправления и исправления Windows 8.1 включаются в тех же самых пакетов. Однако исправления на странице запроса исправлений перечислены под обеими операционными системами. Для получения пакета исправлений, который применяется к одной или обеих операционных систем, установите исправления, перечисленные в разделе «Windows 8.1 / Windows Server 2012 R2» на странице. Всегда смотрите раздел «Информация в данной статье относится к следующим продуктам» статьи для определения фактических операционных систем, к которым применяется каждое исправление.
Примечания
-
Файлы, относящиеся к определенному продукту, этапу разработки (RTM, SPn) и обслуживания (LDR, GDR) можно определить по номерам версий, как показано в следующей таблице.
Версия
Продукт
Контрольная точка
Направление поддержки
6.3.960 0.18 xxx
Windows 8.1 и Windows Server 2012 R2
RTM
GDR
-
Выпуски обновлений GDR содержат только те исправления, которые выпускаются повсеместно и предназначены для устранения распространенных критических проблем. В обновления LDR входят также специализированные исправления.
-
Файлы MANIFEST (.manifest) и MUM (.mum), устанавливаемые для каждой среды, перечислены в разделе «Сведения о дополнительных файлах». MUM, MANIFEST и связанные файлы каталога безопасности (.cat) очень важны для поддержания состояния обновленных компонентов. Файлы каталога безопасности, для которых не перечислены атрибуты, подписаны цифровой подписью корпорации Майкрософт.
x86 Windows 8.1
|
Имя файла |
Версия файла |
Размер файла |
Дата |
Время |
Платформа |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ntdsa.mof |
Неприменимо |
227,765 |
18-Jun-2013 |
12:21 |
Неприменимо |
|
Ntdsai.dll |
6.3.9600.18116 |
2,583,552 |
03-Nov-2015 |
02:41 |
x86 |
64-разрядная (x64) Windows 8.1 и Windows Server 2012 R2
|
Имя файла |
Версия файла |
Размер файла |
Дата |
Время |
Платформа |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ntdsa.mof |
Неприменимо |
227,765 |
18-Jun-2013 |
14:45 |
Неприменимо |
|
Ntdsai.dll |
6.3.9600.18116 |
3,676,160 |
03-Nov-2015 |
02:54 |
x64 |
x86 Windows 8.1
|
Свойства файла |
Значение |
|---|---|
|
Имя файла |
Update.mum |
|
Версия файла |
Неприменимо |
|
Размер файла |
1 600 |
|
Дата (UTC) |
04-Nov-2015 |
|
Время (UTC) |
05:53 |
|
Платформа |
Неприменимо |
|
Имя файла |
X86_532408894ea01e6280e568d78cbfbc21_31bf3856ad364e35_6.3.9600.18116_none_70de56a241809c7b.manifest |
|
Версия файла |
Неприменимо |
|
Размер файла |
712 |
|
Дата (UTC) |
04-Nov-2015 |
|
Время (UTC) |
05:53 |
|
Платформа |
Неприменимо |
|
Имя файла |
X86_microsoft-windows-d..toryservices-ntdsai_31bf3856ad364e35_6.3.9600.18116_none_85b3851fd48201e8.manifest |
|
Версия файла |
Неприменимо |
|
Размер файла |
3,352 |
|
Дата (UTC) |
03-Nov-2015 |
|
Время (UTC) |
05:09 |
|
Платформа |
Неприменимо |
64-разрядная (x64) Windows 8.1 и Windows Server 2012 R2
|
Свойства файла |
Значение |
|---|---|
|
Имя файла |
Amd64_1c835b965fc6e60c22f413386606599e_31bf3856ad364e35_6.3.9600.18116_none_b800a1506ce79afa.manifest |
|
Версия файла |
Неприменимо |
|
Размер файла |
716 |
|
Дата (UTC) |
04-Nov-2015 |
|
Время (UTC) |
05:53 |
|
Платформа |
Неприменимо |
|
Имя файла |
Amd64_microsoft-windows-d..toryservices-ntdsai_31bf3856ad364e35_6.3.9600.18116_none_e1d220a38cdf731e.manifest |
|
Версия файла |
Неприменимо |
|
Размер файла |
3,356 |
|
Дата (UTC) |
03-Nov-2015 |
|
Время (UTC) |
06:04 |
|
Платформа |
Неприменимо |
|
Имя файла |
Update.mum |
|
Версия файла |
Неприменимо |
|
Размер файла |
2,061 |
|
Дата (UTC) |
04-Nov-2015 |
|
Время (UTC) |
05:53 |
|
Платформа |
Неприменимо |
На компьютерах и серверах Windows могут возникать проблемы с исчерпанием свободной памяти, вызванной утечкой некого системного драйвера, хранящего свои данные в невыгружаемом пуле памяти системы. Невыгружаемый пул памяти (Non-paged memory) – это данные в оперативной памяти компьютера, используемые ядром и драйверами операционной системой, которая никогда не выгружается на диск (в своп/ файл подкачки), т.е. всегда находится в физической RAM памяти.
Текущий размер невыгружаемого пула памяти можно увидеть в диспетчере задач Windows на вкладке Perfomance (Производительность) в разделе Memory (Память). На скриншоте ниже видно, что практически вся память на сервере занята, и большая часть ее относится к невыгружаемому пулу 4,2 Гб (Non-paged pool / Невыгружаемый пул). В нормальном состоянии размер невыгружаемого пула редко превышает 200-400 Мб. Большой размер невыгружаемого пула часто указывает на наличии утечки памяти в каком-то системном компоненте или драйвере.
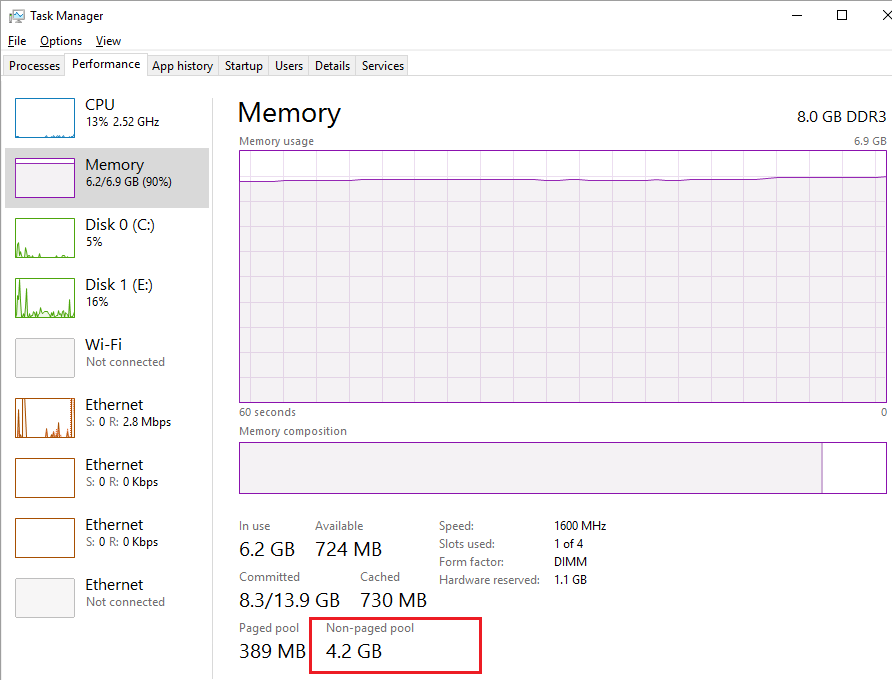
При утечке памяти в невыгружаемом пуле на сервере, в системном журнале событий появится события:
Event ID: 2019
Source: Srv
Description:
The server was unable to allocate from the system nonpaged pool because the pool was empty
В подавляющем большинстве случаев причиной такой утечки памяти является проблема со сторонними драйверами, установленными в Windows. Как правило, это сетевые драйвера. Обратите внимание, как ведет себя пул при скачивании больших файлов (скорее всего он при этом быстро растет).
Максимальный размер невыгружаемого пула в Windows:
- Windows x64 до 128 Гб и не более 75% физической памяти
- Windows x86 до 2 Гб и не более 75% RAM
Для очистки пула помогает только перезагрузка, и, если для домашнего компьютера это еще может быть приемлемо, то на круглосуточно работающем сервере желательно найти нормальное решение.
Содержание:
- Установка последних версий драйверов сетевых адаптеров
- Отключение драйвера мониторинга сетевой активности Windows
- Отключение роли Hyper-V
- Поиск драйвера, вызвавшего утечку памяти с помощью Poolmon
Установка последних версий драйверов сетевых адаптеров
Попробуйте скачать и установить последние версии драйверов ваших сетевых адаптеров с сайта производителя.
Если у вас в Windows включено автоматическое обновление драйверов, убедитесь не начались ли проблемы после установки новых драйверов. Попробуйте откатить версию драйвера на более старую и проверить, воспроизводится ли проблема. Если проблема решилась, отключите авто обновление драйверов.
Отключение драйвера мониторинга сетевой активности Windows
Достаточно часто причиной утечки памяти в невыгружаемый пул является несовместимость драйвера мониторинга сетевой активности (Network Data Usage — NDU, %WinDir%\system32\drivers\Ndu.sys) с драйверами сетевого адаптера компьютера (чаще всего конфликтуют драйвера для сетевых карт Killer Network и MSI). Данный сервис можно отключить без особых потерь функционала Windows.
Службу можно остановить командной:
sc config NDU start= disabled
Либо через реестр:
- Откройте редактор реестра regedit.exe
- Перейдите в ветку HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\Ndu\
- Измените значения параметра Start на 4.
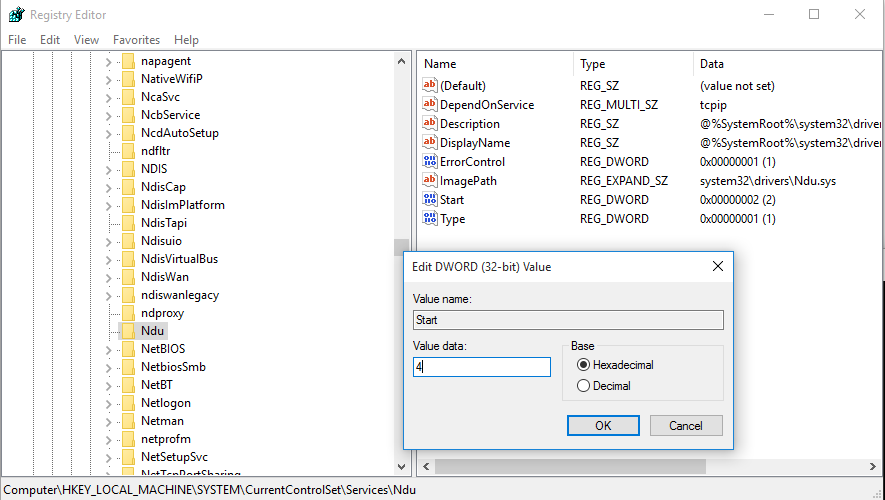
После внесения изменений нужно перезагрузить компьютер
Отключение роли Hyper-V
В некоторых случаях утечку памяти в невыгружаемый пул вызывает установленная роль Hyper-V. Если эта роль не нужна, рекомендуем отключить ее.
В Windows Server Hyper-V роль можно отключить командой:
Remove-WindowsFeature -Name Hyper-V
Команда для Windows 10:
Disable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V-All
Поиск драйвера, вызвавшего утечку памяти с помощью Poolmon
Если описанные выше способы не помогли, можно попробовать определить драйвер, который вызвал утечку памяти в невыгружаемый пул.
Для этого нам понадобится консольная утилита Poolmoon.exe, входящая в комплект разработки Windows Driver Kit (WDK). Скачайте с сайта Microsoft и установите WDK для вашей версии Windows и запустите утилиту Poolmon.exe (в WDK для Windows 10 утилита находится в каталоге
C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Tools\
).
После запуска утилиты Poolman.exe нажмите клавиши P. Во втором столбце останутся теги процессов, которые используют невыгружаемую память (атрибут Nonp) Затем нажмите клавишу B, чтобы выполнить сортировку по столбцу Bytes.
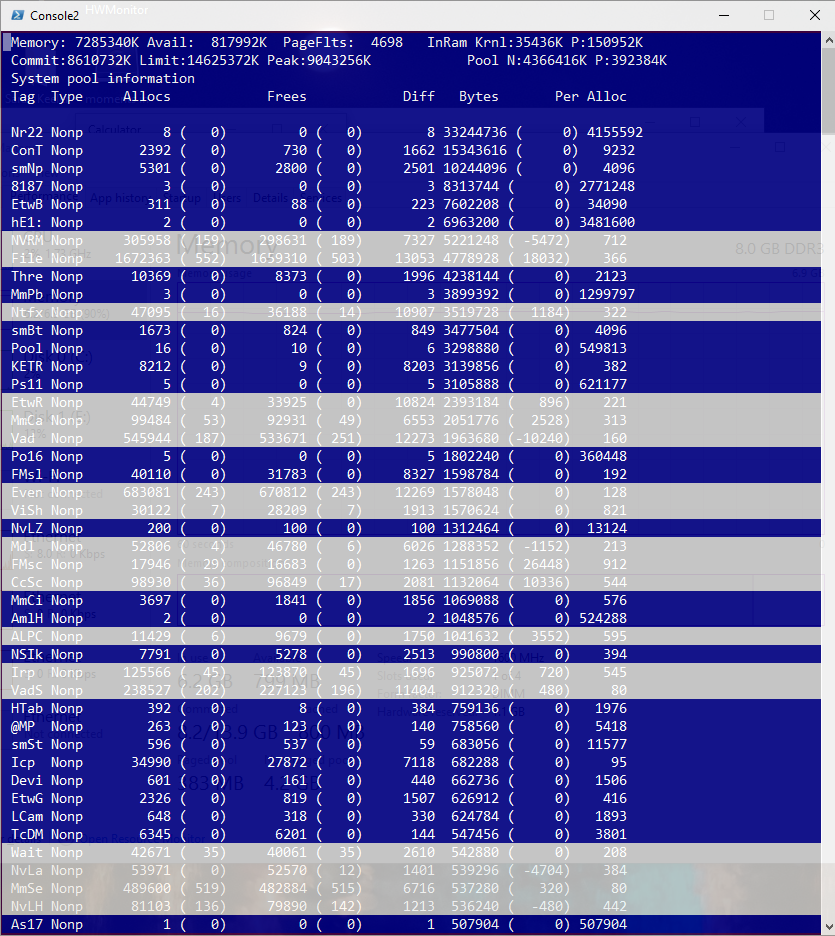
В левом столбце указаны теги драйверов. Ваша задача определить файл драйвера, использующего этот тег. В нашем примере видно, что больше всего RAM в невыгружаемом пуле используют драйвера с тегами Nr22, ConT и smNp.
Вы должны проверить драйвера на наличие найденных тегов с помощью утилиты strings.exe (от Sysinternals), с помощью встроенной команды findstr или с помощью PowerShell.
Следующие команды должны найти файлы драйверов, связанные с найденными вами тегами. данными процессами можно командами:
findstr /m /l /s Nr22 %Systemroot%\System32\drivers\*.sys
findstr /m /l /s ConT %Systemroot%\System32\drivers\*.sys
findstr /m /l /s smNp %Systemroot%\System32\drivers\*.sys
Также можно воспользоваться PowerShell:
Set-Location "C:\Windows\System32\drivers"
Select-String -Path *.sys -Pattern "Nr22" -CaseSensitive | Select-Object FileName -Unique
Select-String -Path *.sys -Pattern "Py28" -CaseSensitive | Select-Object FileName -Unique
Select-String -Path *.sys -Pattern "Ne40" -CaseSensitive | Select-Object FileName –Unique
Вы можете отобразить файлы драйверов непосредственно в poolmon.exe. Для этого убедитесь, что в каталоге утилиты находится файл pooltag.txt. Его можно скопировать из каталога установки WDK или найти в GitHub. Запустите утилиту:
Poolmon /g
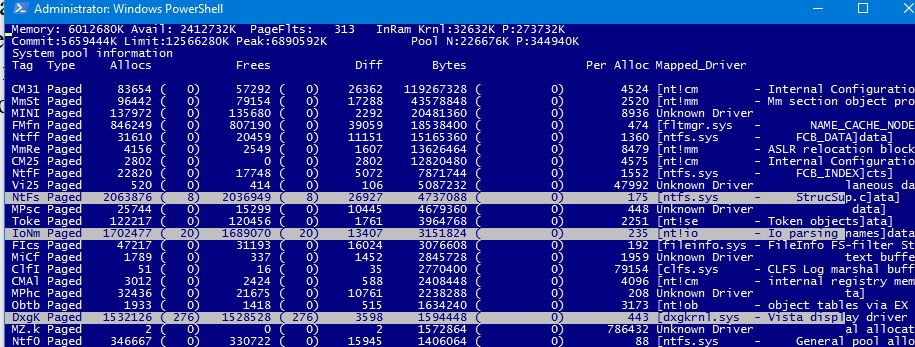
Обратите внимание, что имя драйвера теперь отображается в столбце Mapped_driver.
Если поиск не дал результатов, проверьте возможно утечка памяти вызвана не системным процессом. Запустите Task Manager, перейдите на вкладку Details, добавьте колонку NP Pool и найдите процессы с большим размером памяти в невыгружаемом пуле.
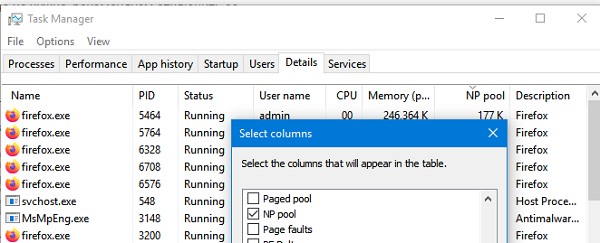
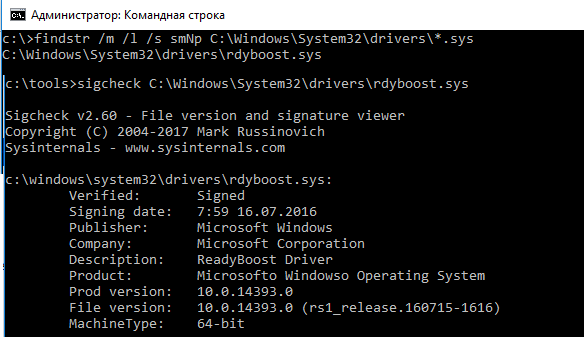
Таким образом, мы получили список файлов драйверов, которые могут оказаться причиной проблемы. Теперь по именам файлов нужно определить, к каким драйверам и системным компонентам они относятся. Для этого можно воспользоваться утилитой sigcheck от Sysinternals.
sigcheck C:\Windows\System32\drivers\rdyboost.sys
Утилита возвращает имя драйвера, его свойства и информацию о версии.
Теперь можно попытаться удалить/обновить/переустановить проблемный драйвер или службу.
Если утечка памяти привела к BSOD, вы можете определить проблемный драйвер по файл дампа памяти.
- Загрузите дамп памяти в отладчик Windbg;
- Выполните команду:
!vm - Если значение NonPagedPool Usage больше чем Max, это говорит о том, что невыгружаемый пул исчерпан;
- Проверьте содержимое пула командой (результаты будут отсортированы по использованию невыгружаемого пула):
!poolused 2 - После получение тега драйвера найдите файл с помощью findstr или strings как описано выше.
Данная инструкция применима как для Windows Server 2019/2016/2012R2, так и для клиентских Windows 10, 8.1.
The Non-paged pool use system memory, basically it is use in kernel and drivers of machine operating system. You can never transfer the load of non-paged pool memory to system hard drive partition, that we can do for paged pool (paging file).
If your machine operating system consume extra memory then you must see the size of operating system memory elements on task manager performance tab that are mention below.
1. Non-paged pool.
2. Paged Pool.
3. Cached.
Here we will discuss only how fix non-paged pool memory leak on Windows Server 2012 R2, this procedure also applicable for other windows operating system.
To check how much memory is consume by non-paged pool click on performance tab on task manager.
To check processes that consume memory click on processes tab on task manager.
In the above image you can see that the Microsoft SQL Server is consuming too much random access memory.
To check the system configuration take the properties of computer. In the below image you can see windows edition and system details.
Normally non paged pool consume memory 150MB to 500MB, In our case it is consuming 28.4GB. To fix non paged pool memory consumption we need to modify two registry settings.
First modify the registry entry «NonPagedPoolSize«, to modify the registry entry «NonPagedPoolSize» follow the below mention path.
HEKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE à SYSTEM à CurrentControlSet à Control à Session Manager à Memory Management
nonPagedpoolSize
à Modify à Decimal (192)
In the above image you can see that we have modify the registry entry «NonPagedPoolSize«, instructions is mention below.
Value name: NonPagedPoolSize
Value Data: 192
Base: Decimal
Second modify the registry entry «Start«, to modify the registry entry «Start» follow the below mention path.
HEKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE à SYSTEM à ControlSet001 à Services à Null à
Start à Modify à Hexadecimal (4)
In the above image you can see that we have modify the registry entry «Start«, instructions is mention below.
Value name: Start
Value Data: 4
Base: Hexadecimal
After modify the registry entries check non paged pool memory consumption, click on performance tab on task manager.
In the above image you can see that current memory consumption of non paged pool has changed from 28.4GB to 237MB.
To again check processes that consume memory click on processes tab on task manager.
In this given information you can resolve the issue of non paged pool memory consumption, but the actual cause of non paged pool memory consumption are kernel and drivers of machine operating system. In Our case Microsoft SQL Server is misbehaving, In your case it may different. Keep continue to troubleshoot to find the actual cause.
Thanks for Read this Article
Главная
> Active Directory, Microsoft, Troubleshooting, Windows > Утечка памяти на контролере домена WIndows Server 2012 R2
Обнаружил странное. На контролере домена Windows Server 2012 R2 практически вся память кончилась Осматриваем список процессов — ничего подозрительного. Мало того, суммарно не набирается по процессам тот объем, что истрачен. Память утекла. Перезагрузка помогает но лишь на время — потом память опять утекает. Расследование показало, что после построения Custom view лога безопасности (security log) память начинает утекать и не высвобождается до перезагрузки. Дальше больше -было выявлено, что память утекает и без всяких кастомных вьюх. Дальнейшие манипуляции привели к тому, что если скопировать файл журнала security log куда-нибудь — память высвобождается прямо в процессе копирования. Как будто кэш сбрасывается из памяти на диск.
Теперь временное решение известно. Причина пока не ясна.
Рубрики:Active Directory, Microsoft, Troubleshooting, Windows
Метки: Active Directory, Память, Утечка памяти, EventLog, Microsoft, Security Log, Troubleshooting, Windows

-
Microsoft Support & Malware Removal
-
BSOD Crashes, Kernel Debugging
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Server 2012 R2 possible memory leak?
-
Thread starter
Thread starterbascotie
-
Start date
Start date
- Joined
- Feb 14, 2021
- Posts
- 206
-
-
#1
So I don’t know if this 100% classifies as a BSOD, it’s a bit of a long story and I’ll summarize it as succinctly as possible.
— It’s a 2012 R2 Server which hosts AD/DNS/SQL/RDS. It’s mainly used for a rental program called Point of Rentals so we have anywhere from 30-60 people on an average day remoted into the server mostly to use that program which is SQL based (we have sql management studio installed on the server). The server has 112GB RAM
— A few months ago, the server crashed (BSOD, I assume, and wouldn’t boot. Boot repair didn’t work, but a chkdsk got it booting again)
— 2 months later, a similar issue except this time we had to restore the most recent backup image to get it working.
— To my dismay, a week later, it happens again. A tech finds that the RAID card in the Dell server is extremely hot / looks loose so we replace it.
— Things work pretty well for a while, but then we start running into issues where the server gets very slow. Sometimes, it’ll be slow but only showing 65% memory usage, but many others times, it’ll show 97% or so memory usage, even though in task manager the most consuming process is SQL which is using about 65GB (which is the limit we set for it, we’ve tried other limits as well for testing)
— Rebooting the server fixes this for a couple days, or more, then it happens again.
— I’ve checked with Dell Openmanage and everything checks out (no failing drives, etc). This past weekend, I updated the RAID drivers (but could not update bios and RAID firmware remotely) so we’ll see if that has any impact. I also cleared out and ran chkdsk on some drives and all looks good for the most part. sfc scan found one error it couldn’t fix but a DISM restorehealth looked to have fixed it.
I’m technically testing it right now, but I’m trying to be proactive so I collected some logs a few days ago in hopes that we might get a hint of what it may be in case it happens again.
Attached is the sysnative log zip.
Also, I’ve run poolmon while the server was hitting high memory usage last week and here are some screenshots (keep in mind, this is with task manager saying SQL was the top offender with 65GB of RAM, and everything else didn’t seem to use much at all)
Here’s a snapshot of task manager during this climbing memory usage:
I tried running this command to see which drivers CM31 and MmSt were tied to , but I assume it couldn’t find it because it was paged memory?
Any help is appreciated and this is also a precious learning experience for me. Thank you
Attachments
-
SysnativeFileCollectionApp.zip
SysnativeFileCollectionApp.zip
- Joined
- Oct 2, 2015
- Posts
- 919
-
-
#2
a) BSOD
b) There were no collected dump files
c) Multiple drive file system corruptions including the MFT and page file
A corruption was discovered in the file system structure on volume C:
The Master File Table (MFT) contains a corrupted file record. The file reference number is 0x17a000000002c45. The name of the file is "\pagefile.sys".
A corruption was discovered in the file system structure on volume F:
A corruption was found in a file system index structure. The file reference number is 0x60000003bff6e. The name of the file is "\SecondPor\POR\Attachments". The corrupted index attribute is ":$I30:$INDEX_ALLOCATION".
A corruption was discovered in the file system structure on volume New Volume.1) Run chkdsk switches on all drives.
Find downtime so that you can run chkdsk switches on the Windows drive.
2) Modify the startup and recovery system failure settings from small memory dump to automatic or kernel memory dump.
3) Reevaluate computer instability / stability after all chkdsk reports display no corruption.
Open administrative command prompt and type or copy and paste:
chkdsk /r /v
This may take hours to run so plan to run overnight.
Run on all drives using the syntax: chkdsk /r /v C: or chkdsk /r /v D: changing the drive letter to the applicable drive.
C:\Windows\system32>chkdsk /r /v
The type of the file system is NTFS.
Cannot lock current drive.
Chkdsk cannot run because the volume is in use by another
process. Would you like to schedule this volume to be
checked the next time the system restarts? (Y/N)
Type: Y
reboot
After running chkdsk switches:
Download ListChkdskResult.exe (by SleepyDude) from Here, save the file to your desktop.
https://www.dropbox.com/s/xfsr4yyg5yun3k1/ListChkdskResult.exe?dl=1
Once the file has been downloaded please go to your desktop and double click on ListChkdskResult.exe.
This scan only takes a few seconds to run, once the scan is complete a pop-up will open with all the CHKDSK from the most recent scan plus any previous scans.
Event[8972]:
Log Name: System
Source: Ntfs
Date: 2021-02-12T12:39:03.755
Event ID: 55
Task: N/A
Level: Error
Opcode: Info
Keyword: N/A
User: S-1-5-18
User Name: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
Computer: ENTERPRISE.RENTAL.LOCAL
Description:
A corruption was discovered in the file system structure on volume C:.
The exact nature of the corruption is unknown. The file system structures need to be scanned online.
Event[8971]:
Log Name: System
Source: Ntfs
Date: 2021-02-12T12:39:06.377
Event ID: 55
Task: N/A
Level: Error
Opcode: Info
Keyword: N/A
User: S-1-5-18
User Name: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
Computer: ENTERPRISE.RENTAL.LOCAL
Description:
A corruption was discovered in the file system structure on volume F:.
The exact nature of the corruption is unknown. The file system structures need to be scanned online.
Event[8624]:
Log Name: System
Source: Ntfs
Date: 2021-02-12T20:52:39.583
Event ID: 55
Task: N/A
Level: Error
Opcode: Info
Keyword: N/A
User: S-1-5-18
User Name: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
Computer: ENTERPRISE.RENTAL.LOCAL
Description:
A corruption was discovered in the file system structure on volume New Volume.
The exact nature of the corruption is unknown. The file system structures need to be scanned online.
Event[34304]:
Log Name: System
Source: Ntfs
Date: 2021-01-04T13:32:38.780
Event ID: 55
Task: N/A
Level: Error
Opcode: Info
Keyword: N/A
User: S-1-5-18
User Name: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
Computer: ENTERPRISE.RENTAL.LOCAL
Description:
A corruption was discovered in the file system structure on volume New Volume.
The exact nature of the corruption is unknown. The file system structures need to be scanned online.
Event[33687]:
Log Name: System
Source: Ntfs
Date: 2021-01-05T06:20:42.823
Event ID: 55
Task: N/A
Level: Error
Opcode: Info
Keyword: N/A
User: S-1-5-18
User Name: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
Computer: ENTERPRISE.RENTAL.LOCAL
Description:
A corruption was discovered in the file system structure on volume F:.
The exact nature of the corruption is unknown. The file system structures need to be scanned online.
Event[32811]:
Log Name: System
Source: Ntfs
Date: 2021-01-05T20:40:38.016
Event ID: 55
Task: N/A
Level: Error
Opcode: Info
Keyword: N/A
User: S-1-5-18
User Name: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
Computer: ENTERPRISE.RENTAL.LOCAL
Description:
A corruption was discovered in the file system structure on volume F:.
A corruption was found in a file system index structure. The file reference number is 0x60000003bff6e. The name of the file is "\SecondPor\POR\Attachments". The corrupted index attribute is ":$I30:$INDEX_ALLOCATION".
Event[12728]:
Log Name: System
Source: Ntfs
Date: 2021-02-09T20:45:37.710
Event ID: 55
Task: N/A
Level: Error
Opcode: Info
Keyword: N/A
User: S-1-5-18
User Name: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
Computer: ENTERPRISE.RENTAL.LOCAL
Description:
A corruption was discovered in the file system structure on volume OS.
The Master File Table (MFT) contains a corrupted file record. The file reference number is 0x17a000000002c45. The name of the file is "\pagefile.sys".
Event[330]:
Log Name: System
Source: Ntfs
Date: 2021-02-25T16:28:48.800
Event ID: 55
Task: N/A
Level: Error
Opcode: Info
Keyword: N/A
User: S-1-5-18
User Name: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
Computer: ENTERPRISE.RENTAL.LOCAL
Description:
A corruption was discovered in the file system structure on volume F:.
The exact nature of the corruption is unknown. The file system structures need to be scanned online.
Event[972]:
Log Name: System
Source: Ntfs
Date: 2021-02-25T04:07:56.959
Event ID: 55
Task: N/A
Level: Error
Opcode: Info
Keyword: N/A
User: S-1-5-18
User Name: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
Computer: ENTERPRISE.RENTAL.LOCAL
Description:
A corruption was discovered in the file system structure on volume New Volume.
The exact nature of the corruption is unknown. The file system structures need to be scanned online.------------------------
Disk & DVD/CD-ROM Drives
------------------------
Drive: C:
Free Space: 95.7 GB
Total Space: 570.7 GB
File System: NTFS
Model: DELL PERC H730P Adp SCSI Disk Device
Drive: D:
Free Space: 30.4 GB
Total Space: 285.6 GB
File System: NTFS
Model: DELL PERC H730P Adp SCSI Disk Device
Drive: F:
Free Space: 28.1 GB
Total Space: 1907.2 GB
File System: NTFS
Model: DELL PERC H730P Adp SCSI Disk Device
Drive: H:
Free Space: 37.0 GB
Total Space: 953.7 GB
File System: NTFS
Model: ST1000DM003-1ER162
Drive: I:
Free Space: 50.8 GB
Total Space: 1907.7 GB
File System: NTFS
Model: Dell Portable SCSI Disk Device
Drive: E:
Model: PLDS DVD-ROM DH-16D8S
Driver: c:\windows\system32\drivers\cdrom.sys, 6.03.9600.18878 (English), 12/5/2017 07:24:08, 165376 bytesLast edited by a moderator:
- Joined
- May 7, 2013
- Posts
- 10,406
-
-
#3
- Joined
- May 7, 2013
- Posts
- 10,406
-
-
#4
I tried running this command to see which drivers CM31 and MmSt were tied to , but I assume it couldn’t find it because it was paged memory?
They’re pool tags and not driver names. You can find them in the pooltag.txt file.
8: kd> !pooltag CM31
Pooltag CM31
Description: Internal Configuration manager allocations
Driver!Module: nt!cm8: kd> !pooltag MmSt
Pooltag MmSt
Description: Mm section object prototype ptes
Driver!Module: nt!mm— Things work pretty well for a while, but then we start running into issues where the server gets very slow. Sometimes, it’ll be slow but only showing 65% memory usage, but many others times, it’ll show 97% or so memory usage, even though in task manager the most consuming process is SQL which is using about 65GB (which is the limit we set for it, we’ve tried other limits as well for testing)
By slow, do you mean the entire server or just the SQL server instance? As in, are queries taking a long time to process?
- Joined
- Oct 2, 2015
- Posts
- 919
-
-
#5
@zbook some of those logs are almost two months old, the rest are several weeks old. The OP has mentioned that they’ve ran chkdsk.
Many of the log findings from January and February reported that switches that had been used left unfixed drive problems during the two months:
Windows has examined the list of previously identified potential issues and found problems.Windows cannot perform an online scan on the volume because it is in the "Full Chkdsk Needed" state.Windows has examined the list of previously identified potential issues and found problems.Windows cannot perform an online scan on the volume because it is in the "Full Chkdsk Needed" state.Windows has examined the list of previously identified potential issues and found problems.Windows has found problems that must be fixed offline.
Please run chkdsk /spotfix to fix the issues.Windows has examined the list of previously identified potential issues and found problems.
Please run chkdsk /scan to fully analyze the problems and queue them for repair.
axe0
Administrator,
BSOD Academy Instructor,
Security Analyst
- Joined
- May 21, 2015
- Posts
- 3,671
- Location
-
Holland
-
-
#6
- Joined
- Feb 14, 2021
- Posts
- 206
-
-
#7
@BlueRobot : It seems like the whole server gets slow when this happens. They especially have complained about being able to remote into their sessions since this is primarily what they use. I have personally been in the server during one of these issues, and it feels like it takes a while for various things to respond.
BTW, is there a way to tag users on replies besides using the reply/quote feature?
Attachments
-
SysnativeFileCollectionApp.zip
SysnativeFileCollectionApp.zip
- Joined
- Oct 2, 2015
- Posts
- 919
-
-
#8
The new log collector on 3/1 reported:
F:
CHKDSK discovered free space marked as allocated in the volume bitmap.
Windows has made corrections to the file system.I:
Windows has scanned the file system and found no problems.Please run each as per the earlier post:
chkdsk /r /v C:
chkdsk /r /v D:
chkdsk /r /v H:
Typically the non-windows drives can be performed without impacting server downtime.
Plan to check C: when downtime can be planned.
- Joined
- Feb 14, 2021
- Posts
- 206
-
-
#9
The opening post log collector started on 2/25.
The new log collector on 3/1 reported:F: CHKDSK discovered free space marked as allocated in the volume bitmap. Windows has made corrections to the file system.I:
Windows has scanned the file system and found no problems.Please run each as per the earlier post:
chkdsk /r /v C:
chkdsk /r /v D:
chkdsk /r /v H:Typically the non-windows drives can be performed without impacting server downtime.
Plan to check C: when downtime can be planned.
I’ll try that this weekend since they have some downtime between sat night and sunday morning. That’ll also give me a chance to see how the week goes. Thanks!
- Joined
- Oct 2, 2015
- Posts
- 919
-
-
#10
The BIOS: Version/Date Dell Inc. 1.3.6, 6/8/2015
1) Upgrade the BIOS: 1.3.6 > 2.11
Challenge Page
Support for PowerEdge T630 | Drivers & Downloads | Dell US
2) Change startup and recovery system failure write debugging information to kernel or automatic memory dump
Version 2.12.1
Enhancements:
- Enhancement to address the security vulnerabilities (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures - CVE) such as CVE-2020-0592, CVE-
2020-8696, CVE-2020-8698, CVE-2020-8705, CVE-2020-8749, and CVE-2020-8755.
- Updated the Intel Management Engine firmware to version SPS_E5_03.01.03.079.0_GR_WBG_REL.
- Updated the Intel SINIT to v3.1.4_20191029.
Version 2.11.0
Fixes
- Fixed an issue where the system stops responding when trying to boot from a PXE.
- Fixed an issue in EFI_RESET_SYSTEM runtime service that resulted in the Oracle VM having kernel dump record after system reboot.
- Removed the Correctable Error Warning threshold SEL event.
Enhancements
- Enhancement to address the security vulnerabilities (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures-CVE) such as CVE-2019-0124 and CVE-2019-0151.
- Updated the Intel SINIT to v3.1.3_20190718.
Version 2.10.5
Enhancements
- Enhancement to address the security vulnerabilities (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures-CVE) such as CVE-2018-12126, CVE-2018-12127, CVE-2018-12130, CVE-2019-11091, and CVE-2019-0089.
- Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v4 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x0b000038.
- Updated the Xeon Processor E5-2600 v3 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x43.
- Updated the Intel Management Engine firmware to version SPS_E5_03.01.03.072.0_GR_WBG_REL.
- Support for the iDRAC8 2.70.70.70 version.
Fixes
- When booting to RHEL 8, the following message is displayed:
Kernel panic - not syncing: Fatal hardware error!
Version 2.9.1
Fixes
- Fixed an issue pertaining to the PCR2 measurement. When TPM is enabled, the PCR2 values were sometimes inconsistent when the CSIOR was enabled.
Enhancements
- Enhanced the BIOS security protection features.
- Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v4 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x0B000033.
- Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v3 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x41.
Version 2.8.0
Fixed issues (this release)
- For memory sizes less than 1 TB, updated the MTRR algorithm to the same behavior as 2.4.2 and earlier BIOS versions.
New and enhanced features
- Enhancement to address security vulnerability CVE-2018-3639 (https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-3639).
- Enhancement to address security vulnerability CVE-2018-3640 (https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-3640).
- Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v4 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x0b00002E.
- Updated the Xeon Processor E5-2600 v3 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x3D.
- Added setup option QPI Link L1 Power Management. Default is set to Enabled.
- Added setup option Lower Memory Mapped I/O Base to 512 GB. Default is set to Disabled.
- Added proper identification for maximum DIMM speed of 2666 MHz.
Version 2.7.1
Fixes
- None
Enhancements
- Updated the Intel Xeon Processor Microcode to address CVE-2017-5715 (http://www.cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=2017-5715)
- Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v4 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x0b00002A.
- Updated the Xeon Processor E5-2600 v3 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x3C.
- CVE-2017-5753 and CVE-2017-5754 are addressed by Operating System & Hypervisor updates.
- Please see more information at http://www.dell.com/support/article/SLN308588
Version 2.6.0
Fixes
- Added a workaround to fix false Multibit memory errors after a CPU IERR.
Enhancements
-N/A
Version 2.5.4
Fixes
- Added workaround to address the uncorrectable errors on RDIMMs with specific vendor or the rev Register Clock Driver (RCD).
- Updated ECRC (end-to-end CRC checking) to prevent the OS from changing the BIOS settings.
- Fixed CPU machine check issue when the Write Data Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) is enabled.
Enhancements
- Updated the Intel Processor and Memory Reference Code (MRC) to PLR11.
- Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v4 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x21.
- Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v3 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x3A.
- Secure MOR change to support the Windows 2016 R3 server version.
- Added support for the Redfish management interfaces.
- Added improvements to Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe).
- Added improvements to the Secure Boot Custom Policy settings.
- Added improvements to the S130 storage.
Version 2.0.2
Fixes
- Fixed an issue where iSCSI boot got disabled when configuration of connection2 setting failed under the UEFI boot mode.
- Fixed the system unexpected issues if running warm reset from iDRAC after BIOS setup change.
- Fixed an issue where mouse device trail is seen while moving cursor quickly in the HII browser.
Enhancements
- Updated the Intel processor and memory reference code to version 3.0.0.
- Added support for Intel Xeon processor E5-2600 V4 product family.
- Updated the Intel Management Engine (ME) firmware to SPS_E5_03.01.03.021.0_WBG_REL.
- Updated PERC S130 option ROM (OPROM) and Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) drivers to version 4.2.0-0009.
- Added support for a new PM1725 category.
- Improved NVMe version 1.1 export log.
- Updated NVMe Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) driver to version 2.5.
- Updated to Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) 2.4 support.
- Added Global Slot Boot Driver Disable option.
Version 2.4.2
Fixes
- Export log issues in the Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) Human Interface Infrastructure (HII).
- Rarely, the system may stop responding because of a power failure during the boot process.
Enhancements
- Updated the Intel Processor and Memory Reference Code to PLR8.
- Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v4 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x1F.
- Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v3 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x39.
Version 2.2.5
Enhancements:
- Updated the Intel Processor and Memory Reference Code to PLR4.
- Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v4 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x1E.
- Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v3 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x38.
- Updated the Intel Trusted Execution Technology (Intel TXT) BIOS and SINIT Authenticated Code Module (ACM) to version 3.1.0.
- The Intel TXT feature is supported with Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 2.0.
- Updated TPM version 2.0 support.
- Updated the integrated Dell Remote Access Controller (iDRAC) Human Interface Infrastructure (HII) to version 2.40.40.05.
- Updated text in the BIOS Setup menu help content.
- Changed the default setting of BIOS Setup option In-System-Characterization to Disabled.
Fixes:
- The boot order may change after updating the BIOS version.
- The cause of system internal error (IERR) is not getting logged.
Version 2.1.5
Enhancements
- Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v3 Product Family Processor Microcode to 0x37.
- Updated the Intel Management Engine (ME) firmware to SPS_E5_03.01.03.030.0_WBG_REL.
- Updated the Intel Trusted Execution Technology (Intel TXT) BIOS and SINIT Authenticated Code Module (ACM) to version v3.0.5.
- Added support to JEDEC serial present detect (SPD) 1.1.
- Added support for memory module with 128 GB DIMM size.
- Updated text in the BIOS Setup Menu help content.
Fixes
- Intermittent PCIe slot training errors.
- While rebooting, server that used E5-2603 or 2609 processor (6-core Low Core Count (LCC) processor) displayed the Red Screen of Death (RSOD) error.
- After importing a platform key, the Secure Boot feature is forced to get enabled.
- Unused DIMM clocks are not disabled for E5-2600 v3 CPU-based system.
- Watchdog timer event log is missing from the ELog and Windows Event Log.
- CPU is not frequently polling the DIMM temperature sensor.
- System cannot boot by using DVD or HDD.
- During the POST stage on the console redirection, an option to press the F12 key is not displayed on the monitor.
Version 2.0.3
Fixes
- None.
Enhancements
- Updated the Intel Processor and Memory Reference Code to MR2.
- Added support for Intel Xeon processor E5-2600 V4 Product Family processor Microcode to 0x17.
Version 1.5.4
Fixes
- Fixed an issue where sometimes systems with Intel SSD drives freeze at PXE boot.
- Fixed an issue where hotkeys are still available after abnormal exit from Life Cycle Controller.
- Fixed an issue where execution of "Ctrl-p" command fails through Serial-Over-Lan.
- Fixed some HII display issues for NVMe PCIe SSDs in System Setup menu.
Enhancements
- Updated the Intel processor and memory reference code to PLR9.1.
- Updated the Intel Xeon processor E5-2600 V3 product family processor microcode to 0x36.
- Updated the Intel Management Engine (ME) firmware version to SPS_E5_03.00.07.173.0_PLR9-G_WBG_REL.
- Added the new I/O Non-Posted Prefetch option in System Setup that can be used to control the PCIe throughput by enabling or disabling the PCI IO non-posted prefetch mode.
- Added the new Form Factor field for NVMe PCIe SSDs in the HII menu.
- Added TPM2 support.
- Joined
- Feb 14, 2021
- Posts
- 206
-
-
#11
The BIOS is old (approximately 13 missed updates).The BIOS: Version/Date Dell Inc. 1.3.6, 6/8/2015
1) Upgrade the BIOS: 1.3.6 > 2.11
Challenge Page
Support for PowerEdge T630 | Drivers & Downloads | Dell US2) Change startup and recovery system failure write debugging information to kernel or automatic memory dump
Version 2.12.1 Enhancements: - Enhancement to address the security vulnerabilities (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures - CVE) such as CVE-2020-0592, CVE- 2020-8696, CVE-2020-8698, CVE-2020-8705, CVE-2020-8749, and CVE-2020-8755. - Updated the Intel Management Engine firmware to version SPS_E5_03.01.03.079.0_GR_WBG_REL. - Updated the Intel SINIT to v3.1.4_20191029. Version 2.11.0 Fixes - Fixed an issue where the system stops responding when trying to boot from a PXE. - Fixed an issue in EFI_RESET_SYSTEM runtime service that resulted in the Oracle VM having kernel dump record after system reboot. - Removed the Correctable Error Warning threshold SEL event. Enhancements - Enhancement to address the security vulnerabilities (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures-CVE) such as CVE-2019-0124 and CVE-2019-0151. - Updated the Intel SINIT to v3.1.3_20190718. Version 2.10.5 Enhancements - Enhancement to address the security vulnerabilities (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures-CVE) such as CVE-2018-12126, CVE-2018-12127, CVE-2018-12130, CVE-2019-11091, and CVE-2019-0089. - Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v4 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x0b000038. - Updated the Xeon Processor E5-2600 v3 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x43. - Updated the Intel Management Engine firmware to version SPS_E5_03.01.03.072.0_GR_WBG_REL. - Support for the iDRAC8 2.70.70.70 version. Fixes - When booting to RHEL 8, the following message is displayed: Kernel panic - not syncing: Fatal hardware error! Version 2.9.1 Fixes - Fixed an issue pertaining to the PCR2 measurement. When TPM is enabled, the PCR2 values were sometimes inconsistent when the CSIOR was enabled. Enhancements - Enhanced the BIOS security protection features. - Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v4 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x0B000033. - Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v3 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x41. Version 2.8.0 Fixed issues (this release) - For memory sizes less than 1 TB, updated the MTRR algorithm to the same behavior as 2.4.2 and earlier BIOS versions. New and enhanced features - Enhancement to address security vulnerability CVE-2018-3639 (https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-3639). - Enhancement to address security vulnerability CVE-2018-3640 (https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-3640). - Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v4 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x0b00002E. - Updated the Xeon Processor E5-2600 v3 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x3D. - Added setup option QPI Link L1 Power Management. Default is set to Enabled. - Added setup option Lower Memory Mapped I/O Base to 512 GB. Default is set to Disabled. - Added proper identification for maximum DIMM speed of 2666 MHz. Version 2.7.1 Fixes - None Enhancements - Updated the Intel Xeon Processor Microcode to address CVE-2017-5715 (http://www.cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=2017-5715) - Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v4 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x0b00002A. - Updated the Xeon Processor E5-2600 v3 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x3C. - CVE-2017-5753 and CVE-2017-5754 are addressed by Operating System & Hypervisor updates. - Please see more information at http://www.dell.com/support/article/SLN308588 Version 2.6.0 Fixes - Added a workaround to fix false Multibit memory errors after a CPU IERR. Enhancements -N/A Version 2.5.4 Fixes - Added workaround to address the uncorrectable errors on RDIMMs with specific vendor or the rev Register Clock Driver (RCD). - Updated ECRC (end-to-end CRC checking) to prevent the OS from changing the BIOS settings. - Fixed CPU machine check issue when the Write Data Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) is enabled. Enhancements - Updated the Intel Processor and Memory Reference Code (MRC) to PLR11. - Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v4 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x21. - Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v3 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x3A. - Secure MOR change to support the Windows 2016 R3 server version. - Added support for the Redfish management interfaces. - Added improvements to Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe). - Added improvements to the Secure Boot Custom Policy settings. - Added improvements to the S130 storage. Version 2.0.2 Fixes - Fixed an issue where iSCSI boot got disabled when configuration of connection2 setting failed under the UEFI boot mode. - Fixed the system unexpected issues if running warm reset from iDRAC after BIOS setup change. - Fixed an issue where mouse device trail is seen while moving cursor quickly in the HII browser. Enhancements - Updated the Intel processor and memory reference code to version 3.0.0. - Added support for Intel Xeon processor E5-2600 V4 product family. - Updated the Intel Management Engine (ME) firmware to SPS_E5_03.01.03.021.0_WBG_REL. - Updated PERC S130 option ROM (OPROM) and Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) drivers to version 4.2.0-0009. - Added support for a new PM1725 category. - Improved NVMe version 1.1 export log. - Updated NVMe Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) driver to version 2.5. - Updated to Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) 2.4 support. - Added Global Slot Boot Driver Disable option. Version 2.4.2 Fixes - Export log issues in the Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) Human Interface Infrastructure (HII). - Rarely, the system may stop responding because of a power failure during the boot process. Enhancements - Updated the Intel Processor and Memory Reference Code to PLR8. - Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v4 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x1F. - Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v3 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x39. Version 2.2.5 Enhancements: - Updated the Intel Processor and Memory Reference Code to PLR4. - Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v4 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x1E. - Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v3 Product Family Processor Microcode to version 0x38. - Updated the Intel Trusted Execution Technology (Intel TXT) BIOS and SINIT Authenticated Code Module (ACM) to version 3.1.0. - The Intel TXT feature is supported with Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 2.0. - Updated TPM version 2.0 support. - Updated the integrated Dell Remote Access Controller (iDRAC) Human Interface Infrastructure (HII) to version 2.40.40.05. - Updated text in the BIOS Setup menu help content. - Changed the default setting of BIOS Setup option In-System-Characterization to Disabled. Fixes: - The boot order may change after updating the BIOS version. - The cause of system internal error (IERR) is not getting logged. Version 2.1.5 Enhancements - Updated the Intel Xeon Processor E5-2600 v3 Product Family Processor Microcode to 0x37. - Updated the Intel Management Engine (ME) firmware to SPS_E5_03.01.03.030.0_WBG_REL. - Updated the Intel Trusted Execution Technology (Intel TXT) BIOS and SINIT Authenticated Code Module (ACM) to version v3.0.5. - Added support to JEDEC serial present detect (SPD) 1.1. - Added support for memory module with 128 GB DIMM size. - Updated text in the BIOS Setup Menu help content. Fixes - Intermittent PCIe slot training errors. - While rebooting, server that used E5-2603 or 2609 processor (6-core Low Core Count (LCC) processor) displayed the Red Screen of Death (RSOD) error. - After importing a platform key, the Secure Boot feature is forced to get enabled. - Unused DIMM clocks are not disabled for E5-2600 v3 CPU-based system. - Watchdog timer event log is missing from the ELog and Windows Event Log. - CPU is not frequently polling the DIMM temperature sensor. - System cannot boot by using DVD or HDD. - During the POST stage on the console redirection, an option to press the F12 key is not displayed on the monitor. Version 2.0.3 Fixes - None. Enhancements - Updated the Intel Processor and Memory Reference Code to MR2. - Added support for Intel Xeon processor E5-2600 V4 Product Family processor Microcode to 0x17. Version 1.5.4 Fixes - Fixed an issue where sometimes systems with Intel SSD drives freeze at PXE boot. - Fixed an issue where hotkeys are still available after abnormal exit from Life Cycle Controller. - Fixed an issue where execution of "Ctrl-p" command fails through Serial-Over-Lan. - Fixed some HII display issues for NVMe PCIe SSDs in System Setup menu. Enhancements - Updated the Intel processor and memory reference code to PLR9.1. - Updated the Intel Xeon processor E5-2600 V3 product family processor microcode to 0x36. - Updated the Intel Management Engine (ME) firmware version to SPS_E5_03.00.07.173.0_PLR9-G_WBG_REL. - Added the new I/O Non-Posted Prefetch option in System Setup that can be used to control the PCIe throughput by enabling or disabling the PCI IO non-posted prefetch mode. - Added the new Form Factor field for NVMe PCIe SSDs in the HII menu. - Added TPM2 support.
So I forgot to mention in response to blue’s post that the reason I changed from auto dump to small was we were not getting any bsod dumps the couple times it happened last year.
I’ve changed it now to kernel dump.
Also, according to dell open manage, we had a bad ram stick which we have since changed out a couple months ago.
Also, I tried to update bios and the raid firmware as well but both of them failed when I try to update from Windows so I will have to set a time to do this in person
axe0
Administrator,
BSOD Academy Instructor,
Security Analyst
- Joined
- May 21, 2015
- Posts
- 3,671
- Location
-
Holland
-
-
#12
BTW, is there a way to tag users on replies besides using the reply/quote feature?
There is, you almost nailed it too. For x BlueRobot you missed the ‘x’ and ‘ ‘ (space).
Tagging/mentioning a user works as follows
@<full username>
e.g.
@axe0
Not a shortened name, no @BlueRobot or @blue (blue is a different user here), but the full username. It’s strict in this because the username works like an ID. If you know the ID of a user and the bbcode for tagging/mentioning, then you can use shortened names.
BBcode = [USER=9865]@axe0[/USER]
jcgriff2
Co-Founder / Admin
BSOD Instructor/Expert
Microsoft MVP (Ret.)
-
-
#13
So I forgot to mention in response to blue’s post that the reason I changed from auto dump to small was we were not getting any bsod dumps the couple times it happened last year.I’ve changed it now to kernel dump.
That setting will just produce a full kernel memory dump only — \windows\memory.dmp — no minidumps. The full kernel memory dump is overwritten with each BSOD. Windows stores up to 50 minidumps as of Windows 7 or Windows 8/8.1. Prior to that, the number of minidumps Windows retained was unlimited.
Change system crash setting to Automatic. This setting results in Windows producing a full kernel dump and a mini kernel dump.
You likely got no dumps because one of the earlier messages re: page file corruption —
The Master File Table (MFT) contains a corrupted file record. The file reference number is 0x17a000000002c45. The name of the file is «\pagefile.sys».
When a BSOD occurs, kernel memory is written to the page file. That is what is occurring while the countdown screen is displayed. Upon system reboot after BSOD, Windows uses the page file data to create the kernel memory dumps (both full kernel dump and mini kernel dump if the system crash setting is «Automatic»). If the data in the page file is corrupted, I would think that no dumps would be produced. There should be evidence of this in one of the Event Viewer files (usually, anyway) — System or Application log; forget which one.
If chkdsk cannot fix the corrupted MFT file record/ page file, delete and reallocate the page file — (11) Deletion + Reallocation of the Page File (Windows 10, 8.1, 8, 7 & Vista) | Sysnative Forums
You can check/verify that your system can produce a dump by doing this — Forcing a System Crash from the Keyboard — Windows drivers | Microsoft Docs
Regards. . .
John
axe0
Administrator,
BSOD Academy Instructor,
Security Analyst
- Joined
- May 21, 2015
- Posts
- 3,671
- Location
-
Holland
-
-
#14
If the data in the page file is corrupted, I would think that no dumps would be produced. There should be evidence of this in one of the Event Viewer files (usually, anyway)
Then the data won’t be written to the pagefile to prevent issues on the drive because it’s unknown where this corruption started when the data is written. This is in the event logs something like ‘dump file creation failed due to error during dump file creation’.
jcgriff2
Co-Founder / Admin
BSOD Instructor/Expert
Microsoft MVP (Ret.)
-
-
#15
- Joined
- Feb 14, 2021
- Posts
- 206
-
-
#16
1) Ran chkdsk on a couple drives previous to posting this
2) This last weekend, I did another chkdsk on some other drives which came up clean
3) We upgraded raid firmware and drivers. Unfortunately, we could not upgrade bios no matter which version or method we tried. Both from Windows, and via the lifecycle controller would not work .Skipped that for now
4) Got some advice on another forum on cleaning up SQL indexes and tweaking those settings which we did.
5) added more RAM.
Technically, things were okay week one but adding all that made things better. Just keeping an eye on it but I think we can mark this as solved! Thanks so much guys
- Joined
- Oct 2, 2015
- Posts
- 919
-
-
#17
- Joined
- Feb 14, 2021
- Posts
- 206
-
-
#18
Please upload new Sysnative log collector results.
Gathering the new logs now. It always takes a very long time on network statistics. Any way to speed it up? It’s usually a matter of hours before that phase finishes in the sysnative program
- Joined
- Oct 2, 2015
- Posts
- 919
-
-
#20
There were no new collected BSOD.
And there were no BSOD seen in the collected logs.
Chkdsk C: displayed cleaning
chkdsk /r /v D: no results seen
chkdsk /r /v H: no results seen
BIOS upgrade failures:
1.5.4
1.5.4
2.0.3
2.4.2
2.4.2
These txt files may have additional information:
C:\ProgramData\Dell\UpdatePackage\log\\BIOS_P8KHV_WN64_1.5.4.txt
C:\ProgramData\Dell\UpdatePackage\log\\BIOS_PRY6P_WN64_2.0.3.txt
C:\ProgramData\Dell\UpdatePackage\log\\BIOS_GK2F7_WN64_2.4.2.txt
There were application crashes, one had dump files:
03/06/2021 10:03 PM 91,345,739 MEMORY~1.HDM memory.hdmp
03/06/2021 10:03 PM 297,991 TRIAGE~1.DMP triagedump.dmpRecent app crashes:
araavl.exe
databaseedits.exe
dsm_sa_datamgr64.exe
biosie.exe
chipsetdriver.exe
psdup.exe
See if reinstalling the Intel chipsetdrivers makes any difference:
Downloads for Chipsets
For the computer sluggishness you can try clean boot:
How to perform a clean boot in Windows
Has Sysnative Forums helped you? Please consider donating to help us support the site!
-
Microsoft Support & Malware Removal
-
BSOD Crashes, Kernel Debugging
