- Can Windows 10 read ReFS?
- Is ReFS faster than NTFS?
- Why can’t ReFS be used to boot a Windows operating system?
- How do I install Windows 10 directly?
- Should I use ReFS or NTFS?
- Which file system is best for Windows 10?
- What are the advantages of ReFS over NTFS?
- Does Windows 10 use NTFS?
- Can Linux read ReFS?
- Do ReFS support deduplication?
- Is NTFS outdated?
- How do ReFS work?
Can Windows 10 read ReFS?
As part of the Windows 10 Fall Creators Update, we will fully support ReFS in Windows 10 Enterprise and Windows 10 Pro for Workstation editions. All other editions will have the ability to read and write but will not have the creation ability.
Is ReFS faster than NTFS?
NTFS theoretically provides a maximum capacity of 16 exabytes, while ReFS has 262,144 exabytes. Thus, ReFS is more easily scalable than NTFS and ensures an efficient storage performance. … However, ReFS provides support for longer file names and file paths by default.
Why can’t ReFS be used to boot a Windows operating system?
Windows cannot boot from a ReFS file system, and requires NTFS. ReFS also omits other features NTFS includes, including file system compression and encryption, hard links, extended attributes, data deduplication, and disk quotas. … On Windows Server 2016, you can choose to format volumes with ReFS instead of NTFS.
How do I install Windows 10 directly?
How to install Windows 10
- Make sure your device meets the minimum system requirements. For the latest version of Windows 10, you’ll need to have the following: …
- Create installation media. Microsoft has a tool specifically for creating installation media. …
- Use the installation media. …
- Change your computer’s boot order. …
- Save settings and exit BIOS/UEFI.
Should I use ReFS or NTFS?
ReFS has staggeringly higher limits, but very few systems use more than a fraction of what NTFS can offer. ReFS does have impressive resilience features, but NTFS also has self-healing powers and you have access to RAID technologies to defend against data corruption. Microsoft will continue to develop ReFS.
Which file system is best for Windows 10?
Use NTFS file system for installing Windows 10 by default NTFS is the file system use by Windows operating systems. For removable flash drives and other forms of USB interface-based storage, we use FAT32. But the removable storage larger than 32 GB we use NTFS you can also use exFAT your choice.
What are the advantages of ReFS over NTFS?
Other NTFS-only functions include an encrypting file system, hard links, and extended attributes. ReFS was designed to provide a better file performance system, and one advantage of ReFS over NTFS is mirror-accelerated parity [https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/storage/refs/mirror-accelerated-parity].
Does Windows 10 use NTFS?
Windows 10 uses the default file system NTFS, as does Windows 8 and 8.1. … All hard drives connected in Storage Space are using the new file system, ReFS.
Can Linux read ReFS?
Open-source users can’t access ReFS volumes on Linux systems due lack of appropriate file system driver. ReFS for Linux solves this issue, allowing full read and write access to ReFS (1. x) volumes on Linux. The software supports SMP kernels and ReFS (1.
Do ReFS support deduplication?
ReFS in Windows Server 2019 now supports deduplication and provides an extremely effective use case for Hyper-V environments running VDI or other highly duplicated virtual environments.
Is NTFS outdated?
Which begs the question, have we stuck with NTFS for too long? The first version was introduced all the way back in 1993, and while it certainly has been updated a ton, it looks like it’s very core is just pretty outdated now.
How do ReFS work?
ReFS seeks to eliminate any torn writes by using the Allocate on Write method, which does not update metadata in-place, but rather writes it using an atomic operation. This means that the file is written and read in a single instruction.
Накопительное обновление Creators Update, привнёсшее в систему Windows 10 много новых возможностей, в их числе реализовало официальную поддержку современной файловой системы REFS — преемницы NTFS, ныне используемой в операционных системах от Microsoft. Особой шумихи этот факт не вызвал, поскольку REFS – далеко не новая наработка софтверного гиганта. Её и раньше можно было использовать в среде Windows 10, но только для создаваемых средствами системы дисковых пространств (программных RAID). Для обычных разделов диска эта возможность не предусматривалась, однако её и в Windows 10, и в Windows 8.1 (в 64-битных редакциях) можно было реализовать путём ручной правки системного реестра или внесения изменений с помощью REG-файлов, выложенных на форумах для компьютерных гиков.
Что это за файловая система, чем она отличается от NTFS, каковы её реальные выгоды для обычных пользователей, и к каким сюрпризам нужно быть готовым при работе с ней – обо всём этом ниже.
{banner_google1}
REFS – это аббревиатура от Resilient File System, что по-русски обозначает отказоустойчивая файловая система. Это, как упоминалось выше, преемница NTFS, но пока что в далёком, плохо обозримом будущем. Новая файловая система компанией Microsoft представлена миру ещё в 2012 году. Все эти годы она проходила «обкатку» на серверных редакциях Windows, начиная с версии Server 2012. 6 лет её тестирования привели лишь к скромной участи быть альтернативой для несистемных разделов диска в последней версии клиентской операционной системы. Впрочем, если взглянуть на историю внедрения NTFS, получается, что в случае с REFS всё идёт своим чередом. Ведь NTFS на клиентские Windows компания Microsoft внедряла долгих 7 лет.
Новая файловая система – не просто преемница NTFS, она базируется на последней, но устраняет её недостатки и открывает новые возможности. Ключевая особенность REFS – отказоустойчивость, защита от потери данных, что обеспечивается рядом механизмов поддержки их целостности. Microsoft настолько уверена в своей наработке, что для отформатированных в REFS разделов диска даже убрала из их свойств возможность запуска проверки на предмет наличия ошибок файловой системы.

От NTFS новая файловая система унаследовала:
- Списки контроля доступа ACL;
- Журнал USN;
- Символьные ссылки;
- Точки монтирования, соединения и повторной обработки;
- Технологию шифрования BitLocker.
В REFS упразднены невостребованные возможности NTFS:
- Шифрование на уровне файлов EFS;
- DOS-совместимые короткие имена файлов 8.3;
- Жёсткие ссылки;
- Дисковые квоты.
В числе возможностей REFS, отсутствующих у NTFS:
- Предотвращение потери данных – сведение к минимуму случаев возникновения ошибок файловой системы, изоляция повреждённых секторов, профилактические меры во избежание повреждения данных;
- Как заверяют разработчики, увеличенная производительность;
- Оперативное проведение проверки дисков на предмет наличия ошибок;
- Прочие возможности, приведённые ниже в таблице сравнения с NTFS.

Что из описанных выше преимуществ есть хорошо для обычных пользователей? Которым и предельные возможности NTFS кажутся астрономическими за неимением возможности реализовать их.
Увы, в сухом остатке получим только возможность больше не томиться в ожидании, наблюдая на экране предзагрузки мельтешащие циферки прогресса проверки файловой системы на ошибки, если работа Windows завершится некорректно. Ну и ещё меньшую вероятность потери ценных данных. Меньшую, но не 100%-ную. Отказоустойчивая файловая система – это очень хорошо, но она, естественно, решает только свои проблемы. Какая-бы файловая система ни использовалась, пользовательским данным по-прежнему угрожает теоретическая вероятность выхода из строя жёсткого диска, упредить которую – задача самих пользователей. Конечно, REFS может решить эту задачу за пользователей, но только в рамках использования технологии дисковых пространств и создания пула носителей по типу зеркального RAID 1 (как минимум).

В этом случае связка «надёжная файловая система + надёжное хранилище», бесспорно, даст наибольшие гарантии. Вот только что такого ценного должно храниться на диске обывателя, чтобы он заморачивался и финансово вкладывался в RAID вне зависимости от технологии его реализации?
А что же с заявленным улучшением производительности REFS? Это в большей степени касается использования той самой технологии дисковых пространств. Новая файловая система изначально предусматривает запись данных на более быстрый жёсткий диск. А во время простоя компьютера большие файлы будут перемещаться на более медленный жёсткий диск.
На что могут рассчитывать обычные пользователи, на борту компьютера которых установлен единственный HDD? Увы, ни на что. В ходе тестирования REFS и её сравнения с NTFS на обычном разделе HDD улучшений в производительности отметить не удалось. В одинаковых условиях тестирования – с одним и тем же размером тестового файла, с одинаковым числом циклов чтения и записи, на одном и том же разделе диска — программа Crystal Disk Mark зафиксировала примерно одинаковые показатели. Значимые для быстродействия случайные чтение и запись мелких файлов у REFS на мизер превысили скорости NTFS.

Повторное тестирование файловых систем проводилось в других условиях – с большим размером тестового файла, с большим числом циклов чтения и записи, с самым медленным разделом HDD. Здесь у REFS и вовсе в целом наблюдался спад производительности.

А это значит, что новая файловая система никак не оптимизирована с целью уменьшения числа движений головок HDD. И, соответственно, никак не решит проблемы винчестеров, давно уже просящихся остаться в прошлом компьютерных технологий.
Но по части производительности есть и хорошие новости, правда, не совсем для обычных пользователей, скорее для продвинутых, работающих с гипервизором от Microsoft Hyper-V. Если виртуальные машины расположить на разделе, отформатированном в REFS, процессы их клонирования и слияния с контрольными точками будут проходить в разы быстрее. Поскольку для новой файловой системы достаточно записать новые метаданные и сослаться на записанные на диске данные, но не проводить их физическое копирование.
Также REFS умеет быстро записывать в большой файл нули, а это значит, что при создании виртуальных дисков с фиксированным размером нужно будет подождать несколько секунд, а не минут, как это происходит в NTFS. И это весомый прорыв. NTFS не только долго создаёт фиксированные виртуальные диски, она ещё и нагружает HDD, не давая возможности параллельно работать с другими программами. При тестировании создания 60-гигабайтного VHD-файла фиксированного размера на разделе с REFS этот процесс занял 1 секунду. Тогда как на разделе с NTFS создание точно такого же VHD-файла длилось почти 7 минут с загрузкой диска на 99%.
Предполагается, что эти возможности будут реализованы и при работе с виртуальными машинами VMware и VirtualBox.
С плюсами REFS разобрались, а что же с недостатками? Они есть, но если Microsoft примет решение по активному внедрению новой файловой системы, часть недостатков со временем устранится. Пока что же имеем то, что имеем — REFS:
- Можно использовать только для несистемных разделов диска, а для раздела с Windows – нельзя;
- Можно использовать только для внутренних носителей, а для внешних – нельзя;
- В неё нельзя преобразовать NTFS-раздел без потери данных, только форматировать, что обуславливает необходимость временного переноса данных куда-то;
- С ней работают не все сторонние программы, в частности, это касается реаниматоров удалённых данных.
Ну и главный сюрприз: друзья, узнаёте версию Windows?

А эту?

Вот так и храни данные в новых файловых системах. Не то что Windows 7, даже Windows 8.1 не видит раздел с REFS. В случае с Windows 8.1 была совершена попытка дать шанс новой файловой системе быть распознанной, и в системный реестр внеслась правка, которая обеспечила поддержку REFS. Но реализовалась только возможность форматирования новых разделов в среде Windows 8.1.

Наряду с отформатированным в REFS новым разделом старый раздел, форматирование которого в ту же REFS осуществлялось в среде Windows 10, по-прежнему остался значиться как не распознанный.

Ещё один неприятный сюрприз, но на фоне предыдущего он кажется таким малозначимым.

Сыровато, конечно… Впрочем, а было ли когда-то по-другому с интеграцией новинок от Microsoft?
Использовать или нет новую файловую систему от Microsoft, друзья, решайте сами. Дам лишь совет на случай, если что-то случится с ценными данными: восстановить их поможет программа R-Studio, её разработчиком заявлена поддержка REFS.
Форматирование раздела в REFS осуществляется только из проводника Windows 10, а также в командной строке.
Выбираем пустой раздел, в контекстном меню кликаем «Форматировать».

Из перечня доступных файловых систем выбираем, соответственно, REFS.
Сначала в Windows Server, а теперь и в Windows 10 появилась современная файловая система REFS (Resilient File System), в которой вы можете отформатировать жесткие диски компьютера или созданные системными средствами дисковые пространства.
В этой статье — о том, что представляет собой файловая система REFS, о её отличиях от NTFS и возможных применениях для обычного домашнего пользователя.
Что такое REFS
Как уже было отмечено выше, REFS — новая файловая система, недавно появившаяся в «обычных» версиях Windows 10 (начиная с версии Creators Update ее можно использовать для любых дисков, ранее — только для дисковых пространств). Перевести на русский можно примерно как «Устойчивая» файловая система.
REFS была разработана для того, чтобы устранить некоторые недостатки файловой системы NTFS, повысить устойчивость, минимизировать возможные потери данных, а также работать с большим количеством данных.
Одна из главных особенностей файловой системы REFS — защита от потери данных: по умолчанию, на дисках хранятся контрольные суммы для метаданных или файлов. При операциях чтения-записи данные файлов сверяются с хранимыми для них контрольными суммами, таким образом, в случае повреждения данных есть возможность сразу «обратить на это внимание».
Изначально REFS в пользовательских версиях Windows 10 была доступна только для дисковых пространств (см. Как создать и использовать дисковые пространства Windows 10).
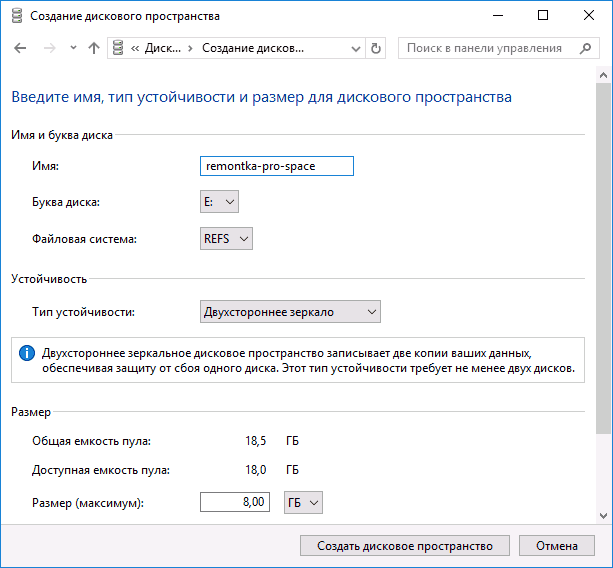
В случае с дисковыми пространствами её особенности могут быть наиболее полезными при обычном использовании: например, если вы создаете зеркальные дисковые пространства с файловой системой REFS, то при повреждении данных на одном из дисков, поврежденные данные сразу будут перезаписаны неповрежденной копией с другого диска.
Также новая файловая система содержит другие механизмы проверки, поддержки и исправления целостности данных на дисках, причем они работают в автоматическом режиме. Для обычного пользователя это означает меньшую вероятность повреждения данных в случаях, например, внезапного отключения питания при операциях чтения-записи.
Отличия файловой системы REFS от NTFS
Помимо функций, связанных с поддержкой целостности данных на дисках, REFS имеет следующие основные отличия от файловой системы NTFS:
- Обычно более высокая производительность, особенно в случае использования дисковых пространств.
- Теоретический размер тома 262144 экзабайта (против 16 у NTFS).
- Отсутствие ограничения пути к файлу в 255 символов (в REFS — 32768 символов).
- В REFS не поддерживаются имена файлов DOS (т.е. получить доступ к папке C:\Program Files\ по пути C:\progra~1\ в ней не получится). В NTFS эта возможность сохранялась в целях совместимости со старым ПО.
- В REFS не поддерживается сжатие, дополнительные атрибуты, шифрование средствами файловой системы (в NTFS такое есть, для REFS работает шифрование Bitlocker).
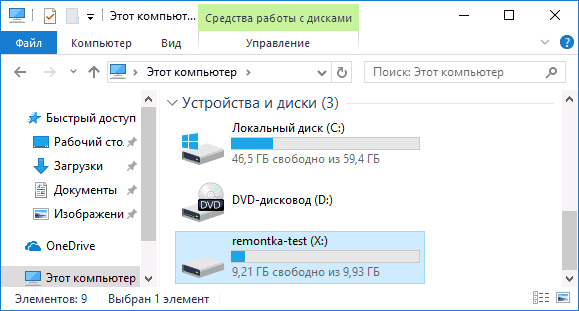
В настоящий момент времени нельзя отформатировать системный диск в REFS, функция доступна только для не системных дисков (для съемных дисков не поддерживается), а также для дисковых пространств, и, пожалуй, только последний вариант может быть действительно полезным для обычного пользователя, которого беспокоит сохранность данных.
Обратите внимание, что после форматирования диска в файловой системе REFS, часть места на нем сразу будет занято контрольными данными: например, для пустого диска 10 Гб это около 700 Мб.
Возможно, в будущем REFS может стать основной файловой системой в Windows, однако на данный момент этого не произошло. Официальная информация по файловой системе на сайте Майкрософт: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/storage/refs/refs-overview
For a little over a decade, Microsoft has been working on a file system to succeed NTFS, which has been used in Windows since the introduction of the Windows NT kernel in the 1990s. This file system, called ReFS has been around for quite some time, but for most of us, it’s still new, considering Microsoft has gradually been adding new features that make the file system more viable in more scenarios.
Today, you can boot Windows 11 off of an ReFS drive, but it takes some work to set up properly since Microsoft doesn’t make this option very visible. Still, I decided to try it out, so here’s how it went.

Related
Setting up was time-consuming
Using ReFS isn’t exactly straightforward
This was my first time ever trying to use ReFS to boot Windows 11, and suffice it to say, it’s not exactly a straightforward path. Documentation online around ReFS is still not easy to come across and even Microsoft’s own documentation is outdated, and I had to fumble around for a bit to get things working. There’s a relatively easy way to create an ReFS partition on Windows 11 by creating a Dev Drive, but I’m not sure if this partition would be bootable afterward.
The best way I found to do this if you don’t want to use a Windows Insider build is to bring up the Command Prompt during the Windows 11 setup process and formatting your drive to ReFS using the command:
format c: /fs:refs
You’ll need to specify the drive you want to format with the correct letter, which may also require some messing around with Diskpart to make sure you have the right labels and everything. Then, proceed with the installation as normal and you should be booting from ReFS. Do note that you can’t erase your existing partitions if you plan to do it this way, since creating a new partition would still create it as an NTFS partition.
If you do feel comfortable using Windows Insider builds, though, the latest builds in the Dev channel let you create ReFS partitions more easily through the UI, which makes the process feel a bit less daunting.
Related
How to reformat an SSD in Windows: A step-by-step guide
Windows makes it effortlessly easy to reformat your SSD
Windows 11 just runs
It definitely works like a computer
Once you get through the hurdle of installing Windows 11, there really isn’t a whole lot to ReFS that’s going to be immediately noticeable just by using Windows 11 as normal. The operating system will boot as usual and you can do all the things you usually do.
The big benefits of ReFS have to do with resiliency and durability of the data on the drive, as well as speed for specific features such as managing virtual hard disks, which will perform much better. That resiliency is at the heart of ReFS, so much so that that’s where the name comes from. It uses automatic and continuous error-checking technology to ensure that data isn’t lost easily and less downtime is required to fix corrupted data. The ReFS partitions are also better for managing Storage Spaces across multiple drives, but again, that’s a different thing entirely.
As far as I can tell, though, nothing was really broken by having ReFS as the main boot partition, which is to be expected. If Microsoft does intend to replace NTFS altogether, it would have to work as normal. Features like BitLocker still worked as they always do, so there isn’t much to note in terms of problems.

Related
Is it any faster?
It’s slower, actually
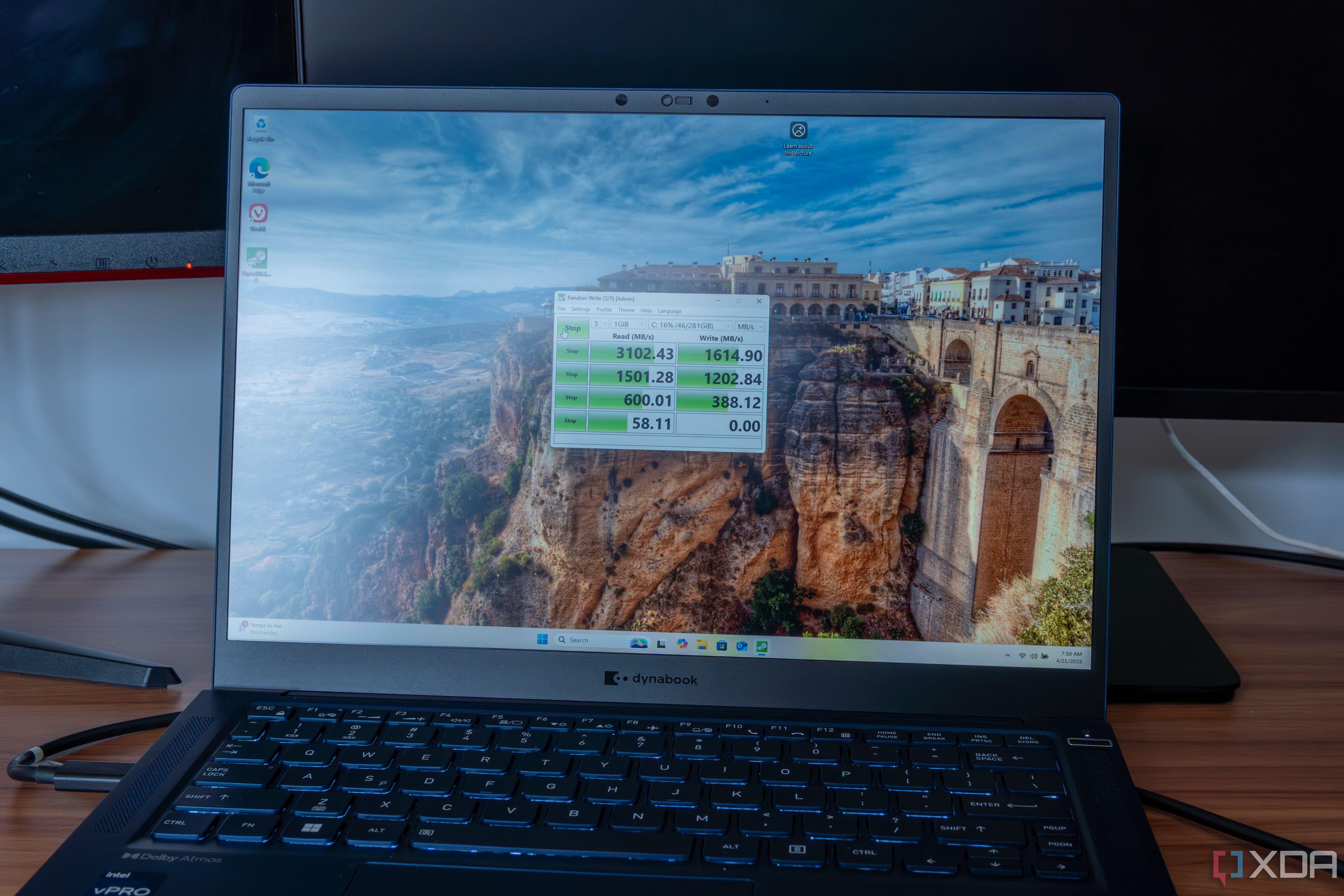
Of course, if you’re thinking about using ReFS, you have to see some tangible benefits. Resiliency is great, but is ReFS going to make any difference for performance on Windows 11? Well, that shouldn’t be the main reason you’re making the switch to ReFS, especially if you’re not working with virtual hard drives or Storage Spaces. ReFS features like block clone can greatly help with performance in situations like managing VMs, but it’s not something most users are going to need often.
I did try running a disk speed test with CrystalDiskMark to see if any notable differences would appear. I ran the test three times on two partitions on the same disk, one formatted as NTFS and the other as ReFS. Between each test, the computer was rebooted. Here are the average scores from both:
|
NTFS |
ReFS |
Difference (%) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Read SEQ1M Q8T1 |
3104.32 |
2532.06 |
-18.43% |
|
Read SEQ1M Q1T1 |
1516.51 |
1192.76 |
-21.35% |
|
Read RND4K Q32T1 |
594.84 |
546.07 |
-8.2% |
|
Read RND4K Q1T1 |
57.91 |
49.27 |
-14.92% |
|
Write SEQ1M Q8T1 |
1801.75 |
1711.52 |
-5.01% |
|
Write SEQ1M Q1T1 |
1307.65 |
1203.62 |
-7.96% |
|
Read RND4K Q32T1 |
510.72 |
442.34 |
-13.39% |
|
Read RND4K Q1T1 |
166.38 |
163.52 |
-1.72% |
Somewhat surprisingly, ReFS actually seems to perform worse across the board, and in some ways, fairly significantly. This is just one benchmark, though, and there are other use cases that could yield different results. Again, VMs and virtual drives are prime use cases for taking advantage of ReFS.

Related
ReFS may well be the future
Just from this quick hands-on experience, ReFS already seems to be a viable alternative to NTFS, though if you’re looking some kind of improvement in usability, you’re not going to see much of that here, at least not in a way you can quantify right off the bat. The biggest and most important feature — resilience — is only going to show itself over time. Performance is also major, but only if you have specific workloads that involve a lot of operations with VMs. Still, the fact that ReFS is completely usable is a good sign. I wouldn’t be surprised to see it become the default file system for Windows in the next few years, assuming the performance differences can be made up.
With the arrival of the Windows Server 2022 RTM version, the history that ReFS cannot be used as a system disk to run Windows has passed. However, because currently only Windows Server 2022 has reached the RTM stage among all systems that can support ReFS booting, the release of this tutorial is only conducted with the official version of Windows Server 2022 Build 20348 for actual operational testing.
ReFS starts Windows Server 2022 preview screenshot:

Of course, in the future, I will continue to update and supplement this hidden function that even Microsoft has never mentioned. It will be developed for future versions of Windows and help you solve other minor problems encountered when running ReFS as a system disk. Just like before, now I also decided to publish a complete and ultra-detailed installation tutorial on the entire network again, so let us witness the new future for the next-generation Windows file system.
Overview of Recoverable File System (ReFS)

ReFS is the latest file system developed by Microsoft. As the next-generation successor to NTFS, ReFS was originally introduced with Windows Server 2012. It aims to solve the ever-expanding demand for massive data storage and lay the foundation for future storage technology innovations.
A summary table of the compatibility between the versions of ReFS and the Windows version is currently known:

New functions and features brought by ReFS:
-
Supports ultra-large volume capacity (1YB), single file (16EB) and number of file directories (2^64), ensuring high scalability without negatively affecting its performance
-
Retain and strengthen log file records, and ensure the robustness of the file system to the maximum extent through independent storage of 64-bit metadata checksum
-
At the same time, it is optimized for both NVMe solid state drives and SMR mechanical hard drives, which greatly improves the hard drive IO performance
-
Intelligently adjust the data distribution strategy according to the different storage structures of SSD and HDD to extend their service life
-
Proactively verify data integrity, and can automatically correct errors. No need to manually run Chkdsk. Downtime for maintenance
-
RefsUtil can provide data salvage to severely damaged ReFS volumes to recover lost data
-
Seamless integration and provide storage space through real-time layer optimization
-
Enhanced data repairability in RAID mirroring mode
-
Optimize the fault tolerance and load balancing of the shared storage pool
-
Provide storage pool mirroring to accelerate parity
-
Provides a flexible redundancy mechanism to prevent bit attenuation
-
Provide virtual machine.VHD(X) performance optimization
-
Support copy-on-write (COW)
-
Support file Ghosting
-
Support integrity flow
-
Support sparse VDL
-
Support block cloning
-
Support stream snapshot
The above is a list of known new features of the latest ReFS 3.7 version relative to NTFS. In the future, as the ReFS version continues to upgrade, more new features will be introduced.
Features that ReFS plans to add in the future:
-
EFS encryption
The above functions are still in the development stage and have not been completed, and will be supported in future ReFS version updates.
Features that have been removed or downgraded in ReFS:
-
No longer support NTFS 8.3 short file name, completely incompatible with MS-DOS operating system
-
The TFAT passive protection mechanism of exFAT is no longer supported and has been replaced by more powerful active data error correction
The above are the functions that have been permanently removed from the initial version of ReFS 1.1, and will not be introduced again with future upgrades of the ReFS version.
Precautions:
-
ReFS installs and starts the Windows system. It is recommended to use it with storage media such as NVMe solid state drives or SMR mechanical hard drives. It is not recommended for removable storage devices unless there is a special need.
-
Compared with the almost unrestricted exFAT startup, Microsoft imposes stricter artificial restrictions on ReFS startup:
-
ReFS startup only supports Windows 10 Build 20185 and later systems, systems below this version do not support ReFS startup, so don’t try again.
-
Currently ReFS only supports UEFI boot, Legacy boot is not supported.
-
Currently, only the 64-bit version of the system can boot from the ReFS partition, and the 32-bit version of the system does not support it.
-
Currently, the bootable feature only supports ReFS v3 of Windows 10, and does not support ReFS v1 of Windows 8.
Installation ideas
Because Microsoft’s Sysprep has a bug, when the original system is installed directly to the ReFS partition, it will get stuck in the system OOBE interface when it starts to report an error that the initialization cannot be completed.
The correct installation method is to first install the system in the NTFS partition and manually complete the OOBE initialization phase, enter the desktop, then import the registry that prohibits the system from automatically upgrading the ReFS version number, and then package the entire system under WinPE and back it up as a WIM or ESD file. (GHOST cannot be used) Unzip and release it to the exFAT partition to start the transfer to confirm that there is no problem, and finally re-package the entire system under WinPE and back it up as a WIM or ESD file (cannot use GHOST) and then unzip it and release it to the ReFS partition to start. .
For the existing system that has been installed on the exFAT partition and can be used, you can directly back up WIM/ESD under WinPE and format the original exFAT volume as ReFS and then release the system files to test the boot. If you encounter problems, you can also manually complete it. Revert back to the state before the test.
Because there are currently as many as 8 different minor versions in the major version of ReFS v3, there are currently two installation schemes according to the functional differences of different version numbers:
-
We categorize them into two groups according to whether they support the hard link feature. Among them, the five versions of ReFS v3.0 to 3.4 that do not support the hard link feature will be classified as the third group, and the ReFS v3.5 to 3.7 that support the hard link feature. These 3 versions will be grouped into the second group. Note that hard link support is only available for newly formatted ReFS v3.5 or higher volumes. If the volume is upgraded from ReFS v3.4 or lower, hard links cannot be used.
-
If you are using the group ReFS version, you must use exFAT to do a secondary transfer process to remove the unsupported hard link, otherwise an error will be reported when the image is released and cannot continue, but the advantage is that the lower version of ReFS v3.0 is relatively compatible Good, it can be recognized by Windows 10 internal version 10586 or later; if you are using the second set of ReFS version, you don’t need to do the transfer processing through exFAT, but the disadvantage is that the compatibility of the higher version of ReFS v3.7 will be relatively poor , Cannot be recognized by Windows 10 internal version 19044 or lower systems. This tutorial uses ReFS 3.0 version to install the Server 2022 system as a benchmark for actual combat operations.
-
(Actually, as long as you can learn to use the more complicated ReFS v3.0 installation system, then the simpler operation ReFS v3.7 installation system will naturally be enough, but it does not rule out that the future ReFS v4 can support directly without bugs. Install the system without transiting through NTFS and exFAT, resulting in a simpler third installation program.)
Preparation tools
Steps
1. Download the Windows system image to be installed, here is an example of using Windows Server 2022 RTM version.

