RADIUS (Remote Authentication in Dial-In User Service) is a network protocol that provides centralized management of authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA), and designed to exchange of information between a central platform and client devices. RADIUS server can communicate with a central server for example, Active Directory domain controller) to authenticate remote dial-in clients and authorize them to access specific network services or resources.
The Network Policy Server (NPS) role implements the RADIUS server function in the Windows environment and allows you to authenticate remote clients against Active Directory. In this article, we’ll show how to configure a RADIUS server on Windows Server 2022/2019/2016, and how to configure RADIUS authentication on Cisco and MikroTic network devices (RADIUS clients) under AD user accounts.
Installing Network Policy Server (RADIUS) on Windows Server
Windows Server with the NPS (RADIUS) role forwards connecting user authentication requests to Active Directory domain controller, which performs user authentication. Therefore, the presence of an on-premises Active Directory is a mandatory requirement before the start of an NPS deployment.
Now you can to install the RADIUS server role on your Windows Server 2022/2019/2016. Open the Server Manager console, run the Add Roles and Features wizard > select the Network Policy and Access Services role.
Note. Also, you can install NPS role and management tools from an elevated PowerShell console:
Install-WindowsFeature NPAS –IncludeManagementTools
Check if the NPAS role is installed on your Windows Server host:
Get-WindowsFeature -Name NPAS

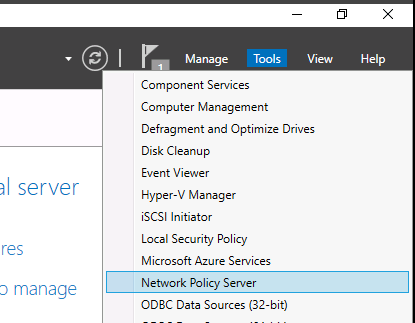
After the role installation is completed, open the Network Policy Server (nps.msc) in the Tools menu.

Right-click on a root node of the NPS console and click Register server in Active Directory.
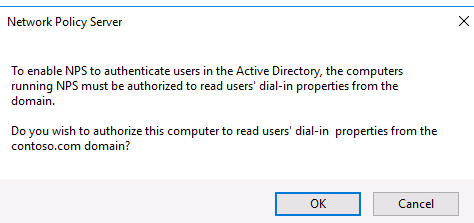
Confirm the new NPS server registration in Active Directory.

Also, you can register your NPS server in Active Directory with a command:
netsh ras add registeredserver
The AD machine account on the NPS server is given permission to read the properties Active Directory user accounts to authenticate users. Your NPS host computer account will be added to the built-in domain group RAS and IAS Servers.
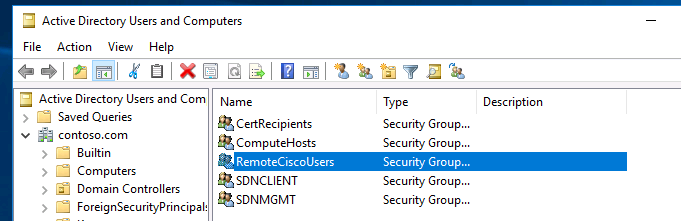
Next, create a new security group in the Active Directory domain (for example, RemoteCiscoUsers) and add all users who will be allowed to authenticate on Cisco routers and switches to this group.

The next step is to add the Radius client. Radius client is the device from which your server can receive authentication requests. This could be a Cisco router, switch, Wi-Fi access point, etc.
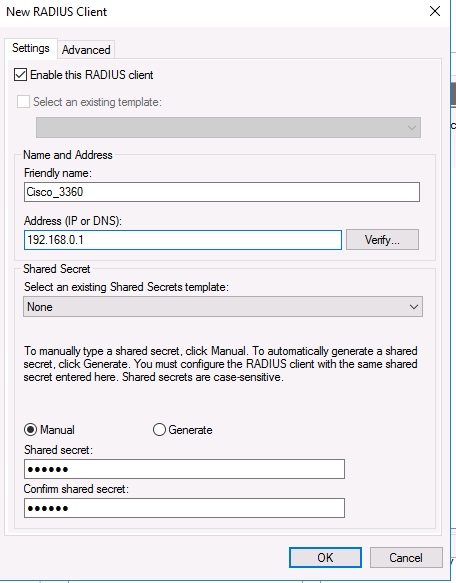
Expand the RADIUS Clients and Servers > RADIUS Clients, select New.
On the Settings tab, fill the fields Friendly name, client Address (you can specify IP address or DNS name), and Shared Secret + Confirm shared password (you will use this password in the configuration of the Cisco switch/router).
Note. The shared secret password is rarely used in large corporate networks due to the problems with the distribution of shared secrets. It is recommended to use certificates instead of shared passwords. If you have a corporate Certification Authority (CA) deployed to implement PKI infrastructure, you can request a *.p12 certificate for the Radius/NPS server. Just import the certificate to the personal certification store of the Local Machine.

In the Advanced tab, select Vendor name – Cisco.

You can use the PowerShell command instead of the NPS GUI to add a new RADIUS client. In this case, you can use the New-NpsRadiusClient PowerShell cmdlet:
New-NpsRadiusClient –Address "192.168.31.1" –Name "cisco2960" –SharedSecret "Zb+kp^JUy]v\ePb-h.Q*d=weya2AY?hn+npRRp[/J7d"
Note. On Windows Server Datacenter edition you can add RADIUS clients to NPS by IP address range. This allows to add a large number of RADIUS clients (such as wireless access points) rather than adding them individually. You can specify the IP range using the format 10.1.0.0/22.
By default, NPS uses the following UDP ports to send and receive RADIUS traffic: 1812, 1813, 1645, and 1646. When you install the NPS role on Windows Server, rules for these ports are automatically created and enabled in Windows Defender Firewall. You can list these Windows Firewall rules using PowerShell:
Get-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "Network Policy Server"
If your RADIUS client is located in a DMZ network or an external security perimeter, you must create the appropriate firewall rules on your network firewall.
Configure NPS Policies on the RADIUS Server
NPS policies allow you to authenticate remote users and grant them access permissions configured in the NPS role. NPS access policies allow you to associate the RADIUS client to the domain security group that determines the user privileges on CISCO devices.
There are two types of policy on a RADIUS server:
- Connection request policies — determine which RADIUS servers should authenticate and authorize connection requests received from RADIUS clients;
- Network policies — allow you to specify who is authorized to connect to your network and a list of assigned privileges.
In our case, we will use only the NPS Network policies. Expand the Policies > Network Policies branch and select New:
Specify the Policy name, the type of network access server should remain unchanged (Unspecified).

In the Specify conditions step, you need to add the conditions under which this RADIUS policy will be applied. Let’s add two conditions — the authorized user must be a member of a specific domain security group, and the device you want to access has a specific name. Use the Add option to create a new condition by selecting the Windows Group type (add the RemoteCiscoUsers group) and specifying the Client Friendly Name (Cisco_*).
Note. The Client Friendly Name field may differ from the DNS name of your device. We will need it in the further steps to identify a specific network device when creating a Remote Access Policy. For example, you can use this name to specify a mask through which several different RADIUS clients are processed by a single access policy.

On the next screen, select Access Granted.

My Cisco switch only supports Unencrypted authentication methods (PAP, SPAP), so I’ve disabled all other options.

Skip the next configuration Constraints step.
In the Configure Settings section, go to the RADIUS Attributes > Standard section. Delete the existing attributes there and click the Add button.
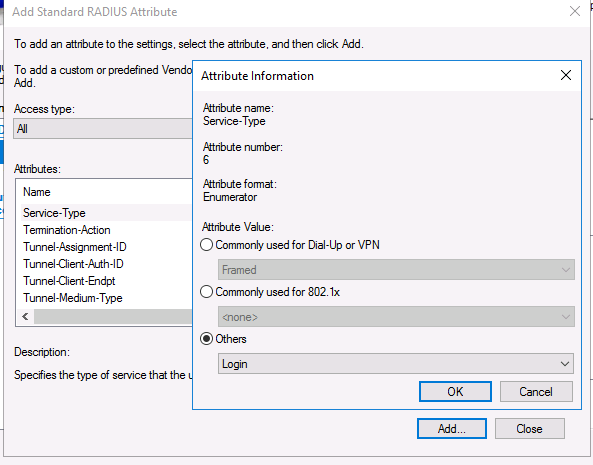
Select Access type > All, then Service-Type > Add. Specify Others = Login.

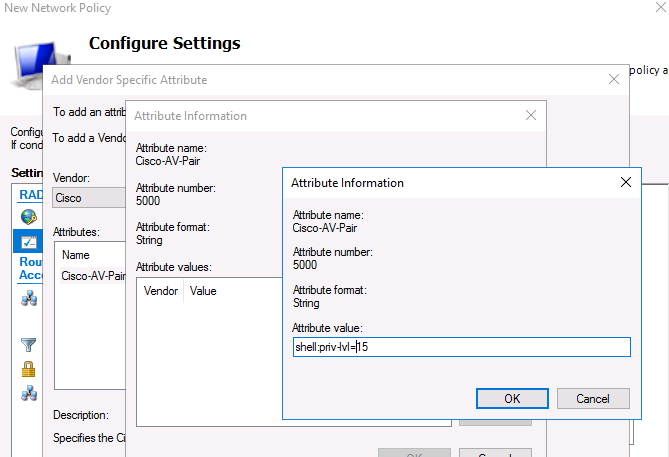
Now add a new attribute in the RADIUS Attributes > Vendor Specific section. Under Vendor, select Cisco, and click Add. Here you need to add information about the attribute. Click Add and specify the following value:
shell: priv-lvl = 15
This value means that the user authorized by this policy will be granted a maximum (15) administrative access privileges on the Cisco device.

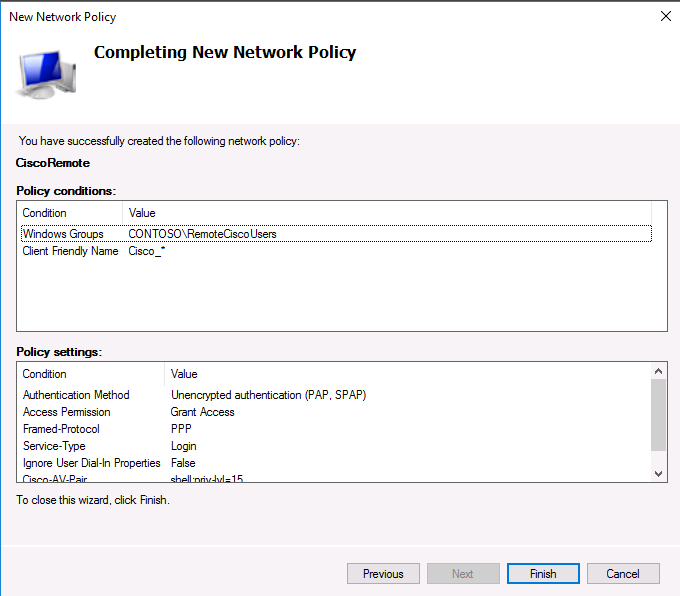
The last screen displays all selected NPS policy settings. Click Finish.

If you have created several network policies in the NPS console, please note that they are processed from top to bottom, so the order of the policies is important. Further processing will stop if all conditions in the next policy are met. You can change the priority of policies in the NPS console using the Processing Order value.

By default, all AD accounts can be used to authenticate using RADIUS. You can check this using the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in (dsa.msc). Open any user properties, go to the Dial-In tab, and check that the Control access through NPS Network Policy option in enabled in the Network Access Permission section.

Configuring RADIUS Authentication on Cisco Devices
Once you have created the NFS policy, you can proceed to configure your Cisco routers or switches for authentication on the newly installed RADUIS server.
As it is insecure to send unencrypted user credentials over the network, you should disable the Telnet protocol on your Cisco devices. To disable Telnet and enable SSH, use the following commands in Configuration Mode on the Cisco device:
configure terminal crypto key generate rsa modulus 1024 ip ssh version 2
You should create a local user on your Cisco device to avoid losing access to it if the RADIUS server or AD is unavailable. Create a local user with the following command:
username cisco_local password $UPerrP@ssw0rd
To make the use of SSH mandatory and disable remote access using Telnet, execute the following commands:
line vty 5 15 transport input ssh
Below is an example of the configuration for authorizing a Radius server for the Cisco Catalyst Switch:
aaa new-model aaa authentication login default group radius local aaa authorization exec default group radius if-authenticated radius-server host 192.168.1.16 key Sfs34e#sf #Specify your RADIUS server IP address and key for encryption (the shared secret that we specified on the RADIUS server) service password-encryption # Enable password encryption
If you have several Radius servers, add them to the group:
aaa group server radius radius_srv_group server 192.168.1.16 server 192.168.101.16
This completes the minimum switch configuration and you can try to check Radius authentication on your Cisco device.
How to Enable MikroTik (RouterOS) User Authentication via RADIUS
In this part, we will show you how to configure RADIUS authentication for VPN user connections on a MikroTik router (RouterOS based).
Open the Network Policy Server console (nps.msc) and create a new Radius client.
Select New RADIUS Client and configure the following settings:
- Enable this RADIUS Client;
- Friendly Name — enter the name of your MikroTik router;
- Address — specific the IP address of the MikroTik router;
- Specify your Pre-shared secret key.
Create a new Network Policy with the following settings:
- User Groups — specify the name of the domain user group that is allowed to authenticate on your MikroTik router;
- Authentication Type — MS-CHAPv2;
- Tunnel Type — Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP);
- Access Permissions — Access granted;
- In the Configure Authentication Methods window, leave only MS-CHAPv2 and allow users to change expired passwords (User can change password after it has expired option);
- Multilink and Bandwidth Allocation Protocol (BAP) – Do not allow Multilink connections;
- In the Standard section, remove Service-Type – Framed and leave only Framed-Protocol PPP;
- Encryptions — leave only the strongest encryption (MPP 128-bit) method.

Once you have created a new policy, open the Network Policy Server settings.
Leave only the following UDP ports for the RADIUS server communications:
- Authentication — 1812;
- Accounting — 1813.

Check if these UDP ports are open in Microsoft Defender Firewall Rules. If not, open them manually.
Now you need to configure the connection settings for Windows Server RADIUS in the MikroTik configuration (we assume that PPP VPN Server is already configured on RouterOS).
Check in the PPTP server settings that only mschap2 is allowed to use for authentication.
Now we need to configure the connection to Radius NPS server. Select New Radius Server and specify the following options:
- Service: ppp;
- Address: IP address of the RADIUS server;
- Secret: pre-shared key that you specified in the network policy settings;
- Src/ Address: MikroTik IP address from which traffic will be sent to NPS;
- Authentication Port: 1812;
- Accounting Port: 1813.
Add appropriate access rules to MikroTik Firewall.
Then go to Secrets > PPP Authentication and Accounting and enable the Use Radius option.
It remains to configure a PPTP VPN connection to your MikroTik VPN on users’ computers. Users can use their Active Directory account credentials to authenticate against Mikrotik (accounts must be added to the AD group that you have specified when creating the MiktoTik Network Policy on NPS).
How to View the NPS/RADIUS Event Logs on Windows?
To enable NPS Server Radius Authentication logging, you need to enable the Network Policy Server audit policy via the local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc). Go to Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Advanced Audit Policy Configuration > Audit Policies > Logon/Logoff > Audit Network Policy Server and check the option to audit both success and failure logon attempts.
Now you can open the Event Viewer console (eventvwr.msc), go to the Windows Logs > Security, and filter the event by the Event ID 6272.
Network Policy Server granted access to a user.

If the user has entered an incorrect password or is not authorized to log on through the RADIUS Client, Event ID 6272 is displayed:
Network Policy Server denied access to a user.
If the user has entered an incorrect user name and password, an event will be displayed in the Event Viewer:
Authentication failed due to a user credentials mismatch
If the user is not a member of the correct security group, or if Network Access Permission= Deny is set in the AD user properties on the Dial-in tab, the following event will occur:
The Network Access Permission setting in the dial-in properties of the user account in Active Directory is set to Deny access to the use
If a user enters an incorrect password multiple times, their account will be locked out in accordance with your Account Lockout Policy in AD.
Event ID: 6279
Network Policy Server locked the user account due to repeated failed authentication attempts.
If you need to find all NPS authorizations events for the specific user (Richard.Doe in this example), use the next PowerShell script:
$Query = @"
<QueryList>
<Query Id="0" Path="Security">
<Select Path="Security">
*[EventData[Data[@Name='SubjectUserName'] and (Data=theitbros\richard.doe')]] and
*[System[(EventID='6272')]]
</Select>
</Query>
</QueryList>
"@
$events = Get-WinEvent -FilterXML $Query
$ipaddr = @{ label="IP"; Expression={$_.properties[9].value} }
$events | select $ipaddr | group "IP" | format-table Count, Name -autosize
В этой статье мы покажем, как настроить сервер централизованной аутентификации, авторизации и аккаунтинга (RADIUS) на операционной системе Windows Server 2016, а также как настроить Radius-аутентификацию на Cisco устройствах с помощью службы Политики сети и доступа (Network Policy Server).
RADIUS (англ. Remote Authentication in Dial-In User Service) — протокол для реализации аутентификации, авторизации и сбора сведений об использованных ресурсах, разработанный для передачи сведений между центральным севером и различными сетевым оборудованием и клиентами.
В первую очередь создайте в домене Active Directory группу безопасности AllowRemoteCiscoUsers, в которую нужно добавить пользователей, которым будет разрешена аутентификации на маршрутизаторах и коммутаторах Cisco.
Далее нужно установить на сервере, с помощью которого будет выполнятся аутентификация клиентов и назначаться права доступа, роль RADIUS сервера. Для этого на сервере Windows Server 2016 откройте оснастку Server Manager и вызовите мастер добавления ролей — Add Roles and features.
В открывшемся мастере на шаге выбора ролей отметьте роль Network Policy and Access Services. На шаге выбора служб роли в нашей ситуации достаточно будет выбрать только службу Network Policy Server.
Протокол Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) в Windows Server 2016 включен в состав роли Network Policy Server.
В консоли Server Manager выберите меню Tools и откройте консоль Network Policy Server (nps.msc).
Для полноценного использования NPS-сервера в домене необходимо зарегистрировать его в домене Active Directory. В оснастке на NPS, щелкните ПКМ по вашему NPS узлу и выберите Register server in Active Directory.
Подтвердите регистрацию сервера в Active Directory:
При этом мы должны предоставите серверу полномочия на чтение свойств учётных записей пользователей, касающихся удалённого доступа. Сервер при этом будет добавлен во встроенную доменную группу RAS and IAS Servers.
Теперь можно добавить клиента Radius. Для этого в дереве консоли NPS разверните раздел RADIUS Clients and Servers и на элементе RADIUS Clients выберите пункт New.
На вкладке Settings заполните поля Friendly name, Client address (можно указать IP адрес или DNS имя подключающегося сетевого устройства) и пароль — Shared Secret + Confirm shared (этот пароль вы будете использовать в настройках коммутатора или маршрутизатора Cisco для установления доверительных отношений с Radius сервером).
Во вкладке Advanced выберите в поле Vendor name — Cisco.
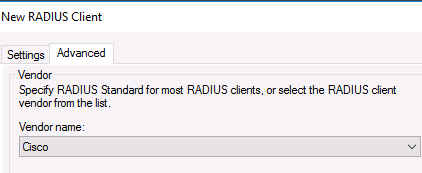
Теперь нужно создать политики доступа на сервере RADIUS. С помощью политик доступа мы свяжем клиента Radius и доменную группу пользователей.
Раскройте ветку Policies —> Network Policies, и выберите пункт меню New:
Укажите Имя политики (Policy name). Тип сервера доступа к сети (Type of network access server) оставьте без изменения (Unspecified):
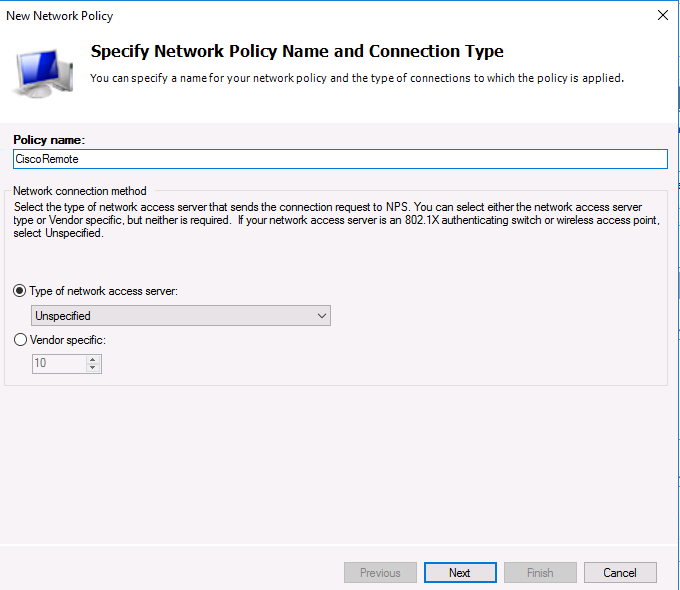
На следующем шаге Specify conditions нам нужно добавить условия, при которых будет применяться данная политика RADIUS. Добавим два условия: вы хотите, что для успешной авторизации пользователь входил в определенную доменную группу безопасности, и устройство, к которому осуществляется доступ, имело определённое имя. С помощью кнопки Add добавим сначала условие, выбрав тип Windows Group (добавьте группу RemoteCiscoUsers) и укажите Client Friendly Name (Cisco_*).
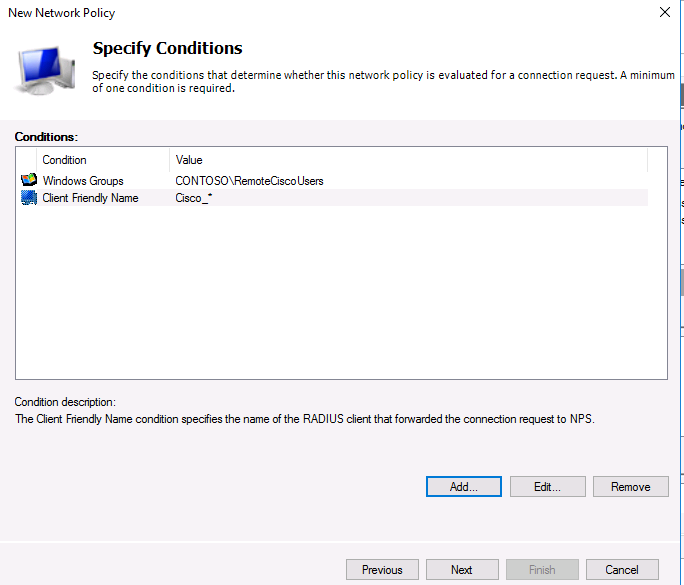
На следующем выберите значение Доступ разрешен (Access Granted).
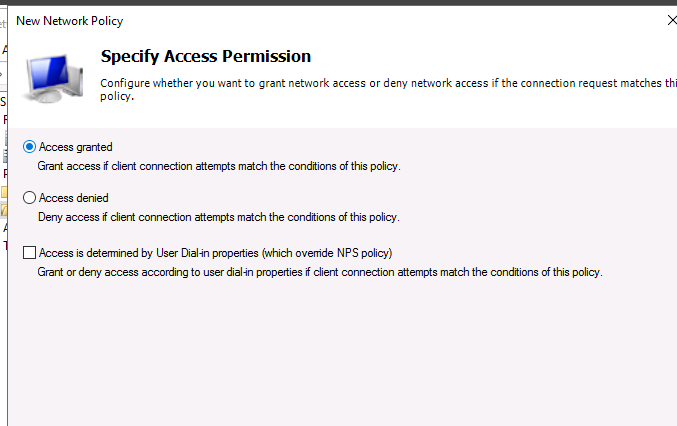
Т.к. наш коммутатор Cisco поддерживает только метод аутентификации Unencrypted authentication (PAP, SPAP), снимите все остальные флажки.
Следующий шаг настройки ограничений (Constraints) мы пропустим.
В разделе Configure Settings перейдите секцию RADIUS Attributes -> Standard. Удалите имеющиеся там атрибуты и нажмите кнопку Add.
Выберите Access type -> All, затем Service-Type->Add. Укажите Others=Login.
Теперь в секции RADIUS Attributes -> Vendor Specific добавьте новый атрибут. В пункте Vendor, найдите Cisco и нажмите Add. Здесь нужно добавить сведения об атрибуте. Нажмите Add и укажите следующее значение атрибута:
shell: priv-lvl = 15
На последнем экране будут указаны все созданные вами настройки политики NPS. Нажмите Finish:
При создании и планировании политик обратите внимание на то, что имеет значение их порядок. Политики обрабатываются сверху вниз, и все условия очередной политике соблюдены, эта политика применяется к клиенту, а дальнейшая обработка других политик прекращается. То есть с точки зрения безопасности и разрешения конфликтов между политиками правильнее будет располагать политики в порядке возрастания административных полномочий.
После создания политики, можно переходить к настройке маршрутизаторов и коммутаторов Cisco для аутентификации на сервере Radius NPS.
AAA работает таким образом, что, если не получен ответ от сервера, клиент предполагает, что аутентификация не выполнена. Чтобы не потерять доступ к своим сетевым устройствам, которые вы переключаете на авторизацию на Radius сервера, обязательно создайте локальных пользователей на случай если RADIUS сервер станет недоступен по какой-либо причине.
Ниже пример конфигурации для авторизации на Radius (NPS) сервере для коммутатора Cisco Catalyst:
aaa new-model
aaa authentication login default group radius local
aaa authorization exec default group radius if-authenticated
radius-server host 192.168.1.16 key R@diu$pa$$
service password-encryption
На этом минимальная настройка коммутатора закончена и можно испытать новый механизм аутентификации и авторизации в действии.
The secret is out: pre-shared key-backed networks do not provide enough defense against hackers and data thieves. A survey found that 74% of IT decision-makers whose data had been breached in the past say the hack involved privileged access credential abuse. Even complex credentials are susceptible to over-the-air credential theft.
Backing your network with a RADIUS server can help close these security gaps. NPS is a common RADIUS solution for Windows.
Using NPS as a RADIUS Server
A RADIUS server authenticates users’ identities and authorizes them for network use. A user becomes authorized for network access after enrolling for a certificate from the PKI ( Public Key Infrastructure) or confirming their credentials. Each time the user connects, the RADIUS confirms they have the correct certificate or credentials and prevents any unapproved users from accessing the network. Check out how a SecureW2 client upgraded their network infrastructure to eliminate any risk of MITM attacks with a RADIUS-backed network.
RADIUS servers are typically implemented through NPS (Network Policy Server) if you’re using Windows. Originally created to enforce network access policies, NPS is frequently used as a RADIUS server.
NPS allows you to authenticate clients using Active Directory (AD) through a wide variety of access points, including the following:
- 802.1x switches
- Wi-Fi
- VPN
- Dial-up
- Router-to-router
While the integration between NPS and AD is more or less manageable, it’s an aging technology that is difficult to integrate into more modern infrastructures. This is especially noteworthy if you’re working in the cloud, which Microsoft doesn’t offer a RADIUS solution.
How To Set Up Windows RADIUS with NPS
This walkthrough will guide you through installing RADIUS server roles in Windows server 2019.
1. Set up a Security Group
In the Active Directory domain, create a security group. Add all of the users that will authenticate through your new RADIUS.
2. Add Network Policy and Access Services Role
The Server Manager console contains the Add Roles and Features wizard. That wizard handles the installation and configuration of all of the optional Windows Server features, including NPS. Select the Network Policy and Access Services role.
After the role installation is completed, open the Network Policy Server (nps.msc) in the Tools menu.
3. Snap-In NPS to AD
Find the root labeled “NPS (Local)” and right-click on it. Choose “Register server in Active Directory”.
Select OK in the confirmation dialogue box that pops up.
4. Add RADIUS Client to NPS
In your NPS console tree, there should be a RADIUS Clients and Servers folder. To add the new RADIUS client, expand the RADIUS Clients and Servers section in the NPS console tree and select New on the RADIUS Clients item.
On the Settings tab, fill the following fields. “Friendly Name” is your client nickname, “Address” can be the IP or DNS name, and “Shared Secret” should have been determined when you configured the access point.
Note: Shared secrets are a weak form of authentication security. Digital certificates offer the best security. Certificates are similarly easy to authorize. Add your access point certificate to the personal certification store on the Local Machine, then request and import the certificate to the NPS server.
SecureW2 allows you to easily generate a custom private CA and export the .p12 to then import into NPS. Or, you can import your AD CS certificates and use SecureW2 to enroll end-user devices to self-service themselves for client certificates for your AD CS Certificate Authority.
If you’re using a major access point vendor, such as Aruba or Cisco, navigate to the advanced tab and select the vendor from the “Vendor Name” list.
Your Windows Server RADIUS is now ready to go! Users will need to be manually added and removed from the security group unless you use an onboarding solution like the one offered by SecureW2. Click here to check out our world-class automatic enrollment suite JoinNow.
Cloud RADIUS + Windows: A Better Solution
A major issue with NPS is that using it essentially locks you into using Windows as your vendor. NPS is only compatible with Active Directory through the LDAP protocol. While you can use third-party vendors to overcome this hurdle, it creates unnecessary complications for your infrastructure, putting your network at risk.
Furthermore, NPS was designed to be used as an on-premise solution with AD because it was made long before cloud solutions became prevalent. There is no native ability to connect NPS with cloud directories, and it doesn’t even work with Microsoft’s own cloud platform, Azure.
Forward-thinking companies know that the future is in the cloud, so your RADIUS should be, too.
Cloud RADIUS is a turnkey solution that allows you to bridge the gap between on-prem and cloud without the expensive forklift upgrade you would need with Azure. SecureW2’s RADIUS and Managed PKI Services integrate seamlessly with every major vendor. We’ve worked with countless organizations to migrate to an all-cloud environment using Azure with Cloud RADIUS. Check out our pricing page to see how we can help you.
Eytan Raphaely
Eytan Raphaely is a digital marketing professional with a true passion for writing things that he thinks are really funny, that other people think are mildly funny. Eytan is a graduate of University of Washington where he studied digital marketing. Eytan has diverse writing experience, including studios and marketing consulting companies, digital comedy media companies, and more.
Need a solution for your network authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) requirements? RADIUS has been around for decades, used by thousands of organizations. Without a RADIUS server, authentication would have to occur at the access point (this would require some pretty powerful APs), such as in the case of PSK (pre-shared key) authentication. PSK authentication only requires a single password to be remembered, so it is simple to implement.
But is PSK secure enough? An attacker can easily read a device’s wireless settings and view the pre-shared key in plain text. It is no secret that a PSK network is vulnerable to various attacks,74% of Data Breaches start with privileged credential abuse.
A RADIUS network eliminates this risk of leak of the private information of your organization to snooping outsiders by enabling individual users to authenticate with unique credentials.
If you’re using Windows 2022/2019/2016, you already have RADIUS capability. Before using the third-party servers, look into the Network Policy Server (NPS) as a RADIUS solution.
NPS as a RADIUS Server
In Windows, RADIUS servers are implemented through Network Policy Server (NPS). NPS allows the creation of both access policies for connection requests and configures Network Access Servers (NAS) to forward connection requests to remote RADIUS servers, which helps load-balancing the connection requests.
NPS performs AAA services for the connection requests from:
- Wireless network
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) remote access
- 802.1x switches
- Dial-up
- Router to router connections
NPS is designed for on-premise infrastructure, so it may not be a suitable choice for organizations looking for cloud solutions. Also, it doesn’t blend well in a non-Windows environment. With the rise in cloud computing, compatibility with the cloud is a must for any technology seeking longevity in this industry.
Pre-requisites for Configuring a Microsoft RADIUS Server
Before you configure RADIUS, please check for the below requirements:
- Windows 2022 Installation
- Here are step-by-step instructions.
- Windows 2022 Desktop Experience
- Devices that support WPA2-Enterprise
- An activated Domain Controller for Windows
- Active Directory installed on your Windows
- Here are step-by-step instructions.
- NPS Installation
- Follow the instructions in the guide
Step 1 – Create a New Group on AD
To facilitate the users with permission to access your network, create a group in the Active Directory Domain. Add all of the users that will authenticate through your new RADIUS.
- Click on “Active Directory Users and Computers” under Tools in Server Manager:
source
- Now to create a new group, right click on “Users”, followed by “New” to choose “Group”:
- Name the AD group under “Group name”:
- Right click on the the user (here user1) you want to authenticate throught the new group (here VpnAuthorisedUsers):
- Now select the newly created group (VpnAuthorisedUsers):
Step 2 – Add Network Policy and Access Services Role
- Add Roles and Features in the Server Manager console:
- Select the type to install roles and features:

- Select the server where you want the role to be installed:
- Now add Network Policy and Access Services:
- Then add the features you need in the wizard.
- Add role services, select “Network Policy Server”:
- Confirm and finish the installation:
Step 3 – Configure RADIUS using NPS
Follow the pictorial instructions and you will have RADIUS configured.
- Select “Network Policy Server” for the server you installed the role (server is added under NAP):
- Snap-In NPS to AD:
- Create a new Radius Client under the option “RADIUS Clients and Servers”.
- Give a name and IP for the device that will forward the authentication request to the RADIUS. Also, a password(shared secret) for the network:
source

- Radius is now configured.
Microsoft RADIUS Security Concerns
Shared secrets are a weak form of authentication security. The server generates a keypair and is copied to every client machine. When connecting to the server, the client will check that the public key presented matches the one they have cached for that server.
An attacker can easily harvest the server’s private key and can act as an authenticated server. The client believes it is talking to an authentic server and there is nothing that can be done to prevent this because pre-shared secrets have no revocation mechanism.
Digital certificates offer the best security. Certificates are similarly easy to authorize. Part of the authentication process involves the RADIUS server checking a Certificate Revocation List (CRL) to ensure the certificate is not revoked or expired. If an admin realizes that a certificate has been compromised, they add it to the CRLand all clients will immediately know because the online revocation checks will fail. The revocation mechanism is very important and is one of the major advantages of certificates.
SecureW2 allows you to easily generate a custom private CA and export the .p12 to then import into NPS. Or, you can import your AD CS certificates and use SecureW2 to enroll end-user devices to self-service themselves for client certificates for your AD CS Certificate Authority.
Your Windows Server RADIUS is now ready to go! Users will need to be manually added and removed from the security group unless you use an onboarding solution like the one offered by SecureW2. Click here to check out our world-class automatic enrollment suite JoinNow.
Cloud RADIUS: A Great Replacement for Microsoft RADIUS Server

NPS may be a good option for the Windows environment but there are major shortcomings you must consider before you decide.
NPS is an on-premise server. On-prem infrastructures have various vulnerabilities ranging from intruders to calamities. One of the most frequent and severe threats is a zero-day attack, Mandiant Threat Intelligence observed roughly 80% of successful cybersecurity breaches stem from zero-day attacks.
Cloud Radius networks are typically much better protected and highly resilient compared to their on-premise counterparts. End users and IT admins alike value both the convenience and versatility of cloud computing services and its quickly overtaking on-site servers.
There is no native ability to connect NPS with cloud directories. It doesn’t even work with Microsoft’s own cloud platform, Azure AD (Microsoft Entra ID), without workarounds and proxy servers. This means that NPS may not be a suitable choice for organizations looking for cloud-based solutions.
Cloud RADIUS is a turnkey solution that allows you to bridge the gap between on-prem and cloud without expensive forklift upgrades. SecureW2’s RADIUS and Managed PKI Services integrate seamlessly with every major vendor. We’ve worked with countless organizations to migrate to an all-cloud environment using Azure with Cloud RADIUS.
Check out our pricing page to see how we can help you.
Learn about this author
Shantha Meena
Shantha Meena is a content writer with a passion for creative writing and poetry that captures momentary emotions and insights. She originally was a Software Engineer at Juniper Networks and started writing out of a desire to further her creative aspirations and her technical knowledge
В данной статье опишу конфигурацию Радиус сервера, для подключения к нему Mikrotik в качестве клиента.
Данная функция полезна, если у вас есть собственный домен на базе Active Directory, и вы не хотите каждый раз заводить VPN пользователей в ручную. Так же с помощью RADIUS сервера, можно настроить аутентификацию непосредственно на сам Mikrotik с помощью доменных учеток или аутентификацию на Wi-Fi
В общем, штука полезная.
Во время написания статьи все указанные настройки проводил на Windows Server 2019, но думаю она так же актуальна и для Windows Server 2016
Первое что нам нужно — сам Windows Server, в данной статье не описываю его установку. Думаю, раз вы дошли до этого материала, то развернуть WinSrv и выполнить базовую настройку Mikrotik вы в состоянии.
К делу.
Переходим к добавлению компонентов
- Диспетчер серверов — Добавить роли и компоненты
- Далее — Установка Ролей и Компонентов — Выбрать целевой сервер — Службы политики сети и доступы — (Копмпоненты) Далее — Установить
После установки переходим к настройке:
- Средства — сервер политики сети
- ПКМ на NPS — Зарегистрировать сервер в Active Directory

- ПКМ на RADIUS-клиенты — Новый документ
- Устанавливаем флаг «Включит этот RADIUS-клиент»
- Понятное имя — Указываем понятное имя
- Адрес (IP или DNS) — указываем IP адрес или DNS имя Mikrotik.
- Общий секрет — Генерируем и сохраняем себе секретный ключ для обмена Mikrotik и RADIUS-сервера. Или используйте свой вариант ключа.

- Развернуть политики — пкм на «Сетевые политики» — Создать новый документ
Задаем имя политики

- Далее — Добавить
- Условие — Группы пользоватей — Добавить группы — Выбираем группу — Доступ разрешен
На самом деле, условий там масса, можете выбрать под свои цели. Самое частое всё таки «группы пользователей», ведь основная задача разгрузить логику добавления пользователей. В соответствии с данным условием — все пользователи, которые являются членами группы openvpn_users будут иметь возможность пользоваться openvpn
Тип Шифрования ms-chap можно отключить, как устарешвий. Оставить только MS_CHAP_V2
Однако есть нюанс, MS_CHAP_V2 работает только с RouterOS начиная с версии 6.43, если у вас версия моложе — или обновляйтесь, или используйте в политике шифрование PAP

- Далее — Тип порта NAS — Асинхронная (модем)

- Далее — Оставляем только Service-Type = Login

- На последнем окошке проверяем что указали правильные параметры и нигде не ошиблись. Клацаем Готово
- Настраиваем Брандмауэр
- Правила для входящих подключений — Предопределенные — Сервер политики сети

- Выбираем правила с портами 1813/udp и 1812/udp

- Далее — Разрешить подключение.
Переходим к настройке Mikrotik
- PPP — Secrets — PPP Authentication & Accounting – Use Radius
/ppp aaa
set use-radius=yesВ терминале

- Переходим в меню Radius и устанавливаем адрес сервера и секретный ключ
/radius
add address=192.168.X.YYY secret=Radius-PASS service=pppВ терминале

На этом настройка завершена. Теперь для подключения VPN можно использовать доменную учётку.
Другие стати по теме:
- Генерация сертификатов на Mikrotik для OpenVPN
- Настройка OpenVPN Server на Mikrotik RouterOS
- Сборка opvn.conf для клиента Mikrotik
- Howto
- Mikrotik
- Radius
- WindowsSrv
