If you’re trying to figure out how to check the COM port in Windows 10, you’re in the right place. Whether you’re dealing with hardware issues or setting up new devices, knowing which COM port your device is using can be quite handy. It’s easy—just follow these simple steps to check your COM ports.
The following steps will show you how to find out which COM port is being used by your devices in Windows 10. This process involves using the Device Manager tool, which is built into the Windows operating system.
Step 1: Open the Device Manager
First, open the Device Manager on your computer.
You can do this quickly by right-clicking on the Start menu and selecting «Device Manager» from the context menu. Alternatively, you can press «Windows + X» and choose it from the list.
Step 2: Expand the Ports (COM & LPT) Section
Once you’re in the Device Manager, find the section labeled «Ports (COM & LPT)» and expand it.
This section will show a list of all the COM ports currently being used by your devices. If you don’t see this section, it means no COM ports are active.
Step 3: Identify the COM Port
Look through the list of available COM ports to find the one you’re interested in.
Each device should have a name and a COM port number next to it. For example, it might say «USB Serial Device (COM3)».
Step 4: Check Device Properties
Right-click on the specific COM port and select «Properties» to get more details.
This will bring up a window with various tabs. The «General» tab will provide basic information, while the «Port Settings» tab allows you to configure the port.
Step 5: Close the Device Manager
After you’ve found the information you need, you can close the Device Manager.
Simply click the «X» in the upper right corner of the window to exit.
Once you’ve completed these steps, you’ll know exactly which COM port your device is using, and you can adjust settings or troubleshoot as necessary.
Tips for Checking COM Port in Windows 10
- Make sure your device is properly connected before checking the COM ports.
- If you don’t see the «Ports (COM & LPT)» section, try refreshing the Device Manager.
- Keep your drivers up-to-date to avoid COM port issues.
- You can also use third-party software to manage COM ports more efficiently.
- If you’re having trouble, try a different USB port on your computer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a COM port?
A COM port (short for communication port) is a serial port that allows for data transfer between devices and your computer.
Why can’t I see any COM ports in the Device Manager?
If you can’t see any COM ports, it might be because no devices are currently connected, or the necessary drivers aren’t installed.
How do I update the COM port driver?
Right-click on the COM port in the Device Manager, select «Update driver,» and follow the prompts.
Can I change the COM port number?
Yes, you can. Go to the COM port properties, click on «Port Settings,» and then «Advanced» to change the COM port number.
What should I do if my device isn’t recognized?
Try unplugging and re-plugging the device, restarting your computer, or updating the drivers.
Summary
- Open the Device Manager.
- Expand the Ports (COM & LPT) section.
- Identify the COM port.
- Check device properties.
- Close the Device Manager.
Conclusion
So there you have it—everything you need to know about how to check the COM port in Windows 10. This simple process can save you a lot of headaches, especially when you’re setting up new hardware or troubleshooting existing devices. Keeping track of your COM ports ensures that your devices are communicating effectively with your computer.
For further reading, you might want to explore topics like «How to troubleshoot COM port issues» or «Understanding Serial Communication in Windows.» Keep your system updated, and don’t hesitate to dive into the Device Manager whenever you need to check on your hardware. Happy computing!
Matt Jacobs has been working as an IT consultant for small businesses since receiving his Master’s degree in 2003. While he still does some consulting work, his primary focus now is on creating technology support content for SupportYourTech.com.
His work can be found on many websites and focuses on topics such as Microsoft Office, Apple devices, Android devices, Photoshop, and more.
Problem with checking RS-232 port activity
If you need to know how to check serial ports in the Windows operating system, you will find there are no native tools to perform this task. There is, however, a software solution that can be used for checking serial port activity and monitoring data transfer through the interfaces.
When problems arise between a serial device and an application, you need to know how to check RS232 communication. The typical method is to follow these general troubleshooting guidelines. We recommend that by developing an understanding of how serial devices work, you can save a substantial amount of time when taking down issues. A program like Serial Port Tester can be instrumental in increasing your knowledge of serial communication.
Solution: Serial Port Tester
There is an effective and efficient method of investigating issues that you may encounter during the development and testing of a serial device driver or application. COM Port Tester from Electronic Team, Inc. answers the question of how to check RS232 communication with a full-featured application which makes it easy to monitor, analyze, display, and log data from your RS232/422/485 serial ports.
Full features list of Serial Port Tester
| COM Port Tester is fully compatible with Windows 10 (32 and 64 bit). | |
| Digitally signed for safety and peace of mind. | |
| Multiple simultaneous port monitoring enabled. | |
| Ability to add additional ports to existing monitoring sessions | |
| Full support of all types of COM ports including generic onboard ports, virtual COM ports, BlueTooth serial ports, USB to Serial cradles, etc. | |
| Full monitoring and logging of data transmission. | |
| Ability to emulate data sending with advanced send dialog. Aliases can be used for faster typing and automation; send files and loop functions and commands. In the Professional / Company Edition versions of Serial Port Tester, you can change serial port parameters while a monitoring session is active. | |
| In the Professional / Company Edition you can also start and stop monitoring a serial port that is already opened by another application. | |
| All data capturing happens in real-time. | |
| All incoming and outgoing data is logged. | |
| Four different options to view data: terminal view, lne view, dump view and table view | |
| From the Terminal view you can export raw data to file. | |
| The terminal view has an automatic scroll which can be disabled if preferred. | |
| Table view offers color command highlights for ease of data analysis. | |
| Customize Quick Filters in Table view for bespoke user experience. | |
| Table view allows you to add comments to the monitoring session. | |
| IRPs in Table view include transcript hints from line view. Statistics are displayed in first to last order IRP in table view. | |
| All redirected files can be split into smaller files or you can specify a file size that suits your environment. | |
| All recorded data can also be copied to the system clipboard for quick access. | |
| Data can be redirected to file even when the monitoring session is inactive. | |
| Serial Port Tracker is able to monitor any kind of hardware/software that works on a serial port. | |
| All Input / Output control codes (IOCTLs) can be intercepted, monitored and recorded for further analysis. | |
| Monitoring sessions are fully customizable. You can adjust timestamp formats, notation scale, logging string length etc. | |
| Serial Port Tracker provides easy and flexible monitoring session management — allowing you to determine how monitored data is loaded and saved, as well as how data is exported or redirected to files. | |
| Monitored sessions can be exported in a variety of formats including HTML, ASCII text, UNICODE and Excel CSV. Data can also be automatically redirected to file. (Serial Port Monitor will add all monitored data to a file in real-time). | |
| It is possible to add data automatically before or after a packet is transmitted. | |
| Full duplex mode is supported, so the communication between sender and receiver can happen concurrently. | |
| Visualization of control line status. | |
| Large range of filter options available. | |
| Support of all baud rates. | |
| Flexibility to configure stopbits, data bits, etc. | |
| Easy user interface with no programming skills required. | |
| Data can also be filtered by port. | |
| When Serial Port Tester tries to write data to an application, that data is displayed to the user. | |
| There is an option to write data to an existing file with a new command-line option rather than overwriting existing data. |
В этой статье рассматривается проверка COM-портов на компьютере на примере преобразователя USB-COM серии UPort 1150.
Методы, описанные в этой статье, подойдут для проверки встроенных COM-портов на компьютере или COM-портов преобразователей интерфейсов, например USB-COM или USB-Ethernet, а также другого оборудования, которое требует установки драйвера виртуального COM-порта.
Содержание статьи:
- Скачать PComm Lite
- Как проверить RS-232 интерфейс?
- Схема подключения внешнего устройства с RS-232
- Как проверить RS-422 интерфейс?
- Схема подключения внешнего устройства с RS-422
- Как проверить RS-485 интерфейс?
- Схема подключения внешнего устройства с RS-485
- Подтягивающие и согласующие резисторы
- Рекомендации по устранению неисправностей
Скачать PComm Lite
Для работы с СОМ портом нужна программа, которая позволит открыть СОМ порт и отправить в него данные. MOXA предлагает воспользоваться бесплатной утилитой PComm Lite.
Для проверки RS-232 можно воспользоваться простым способом: достаточно замкнуть контакты RX и TX между собой. Тогда все переданные данные будут приняты обратно.
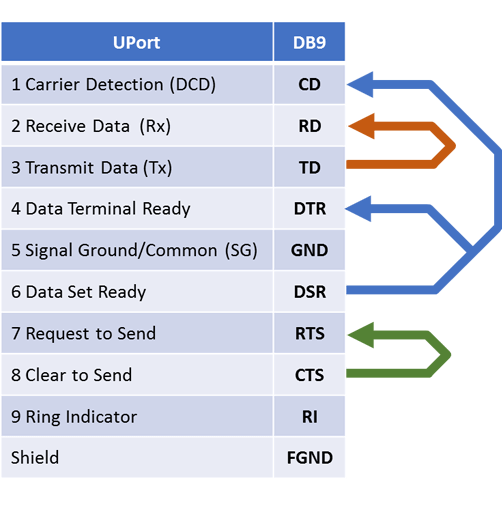
Если у вас полный RS-232 или нужно использовать аппаратный контроль за передачей данных, тогда вам нужно распаять специальную заглушку. В ней должны быть соединены между собой следующие контакты:
После этого мы можем открыть СОМ порт через программу и отправить туда любые данные. Отправленные данные должны вернуться обратно в этот же порт.
На примере PComm Lite это будет выглядеть так.
Убедитесь, что COM-порт настроен на RS-232.
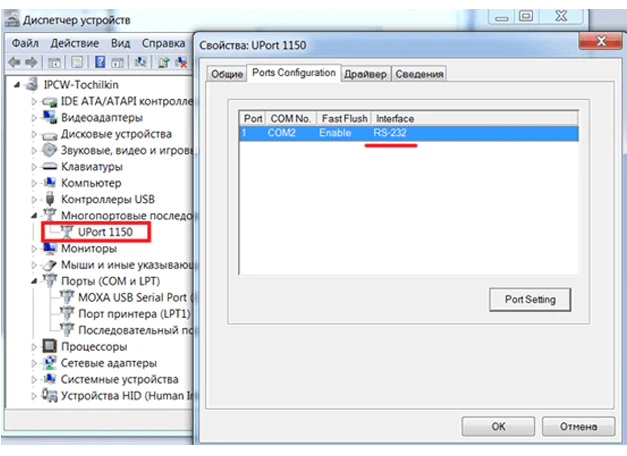
Откройте программу PComm Terminal Emulator, во вкладке Port Manager откройте СОМ порт, соответствующий вашему устройству. Скорость и другие параметры можно оставить по умолчанию.
Однако, если вы подключаете внешнее устройство к СОМ порту, эти параметры должны совпадать с параметрами внешнего устройства.
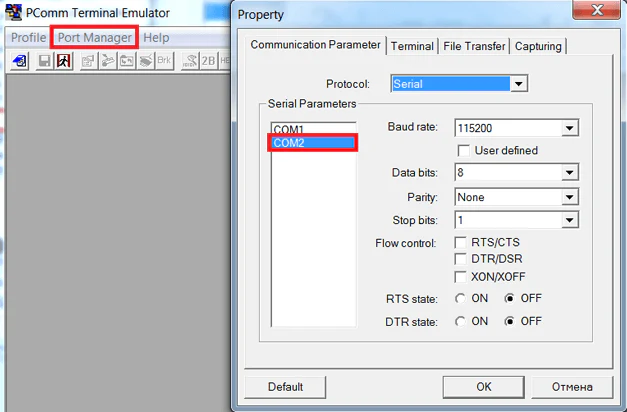
Мы отправили несколько единиц в СОМ порт и получили их обратно, также видим одинаковые значения счетчиков TX и RX, что подтверждает получение всех отправленных данных.
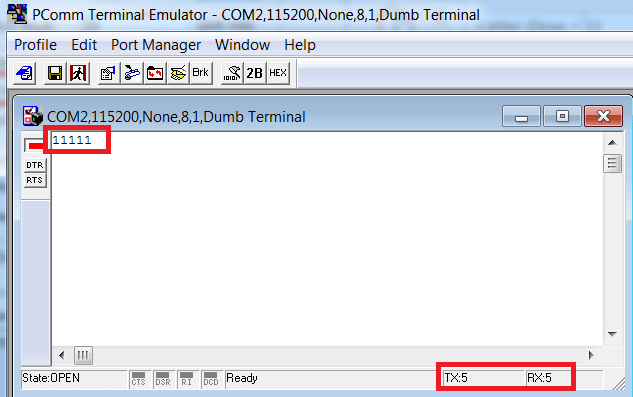
Если вы хотите отображать текст, который печатаете, то вам нужно включить функцию Local echo на вкладке Terminal при открытии порта. Важно: после включения функции Local echo, если вы замкнули TX и RX, то текст в терминале удвоится, потому что будет отображен вводимый символ и тот, который получен обратно.
Схема подключения внешнего устройства с RS-232:
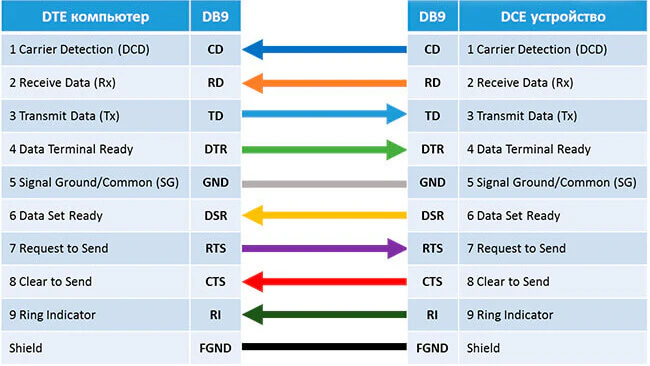
Прямой кабель DTE-DCE (компьютер-модем)
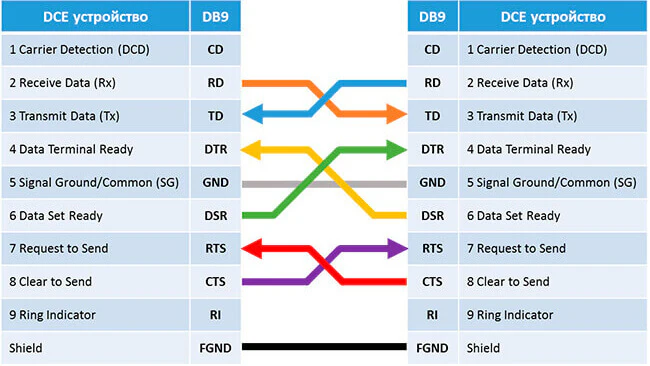
Нуль-модемный кабель DCE-DCE (модем-модем)
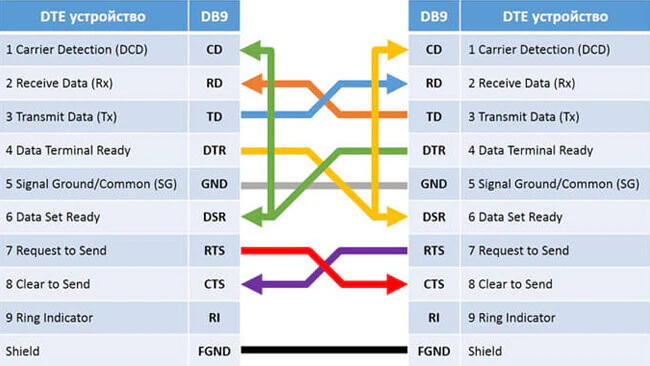
Нуль-модемный кабель DTE-DTE (компьютер-компьютер)
Как проверить RS-422 интерфейс?
Для проверки RS-422 можно также воспользоваться простым способом: достаточно замкнуть контакты TD+ на RD+ и TD- на RD-. Тогда все переданные данные будут приняты обратно.
Убедитесь, что COM-порт настроен на RS-422.
В терминале видны данные, которые мы отправили в СОМ порт.

Схема подключения внешнего устройства с RS-422:
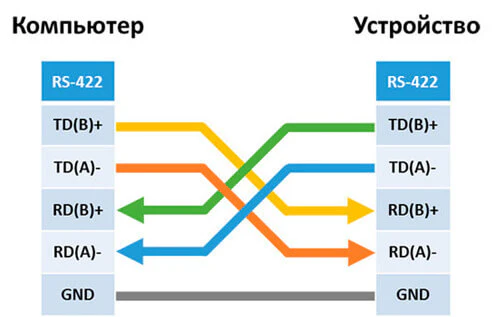
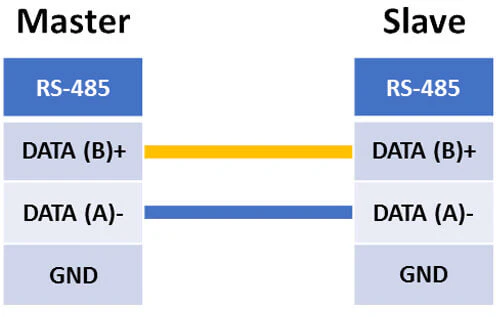
Как проверить RS-485 интерфейс?
Интерфейс RS-485 может быть реализован на 2 или 4 контактах.
Для варианта RS-485 с 4 контактами проверка сводится к тем же действиям что и в RS-422 с таким же подключением контактов TD+ на RD+ и TD- на RD.
Для варианта RS-485 с 2 контактами нужно использовать внешнее устройство для проверки работы. Это может быть второй порт UPort или заведомо исправное устройство с RS-485.
Убедитесь, что COM-порт настроен на RS-485 и правильно указано количество контактов.
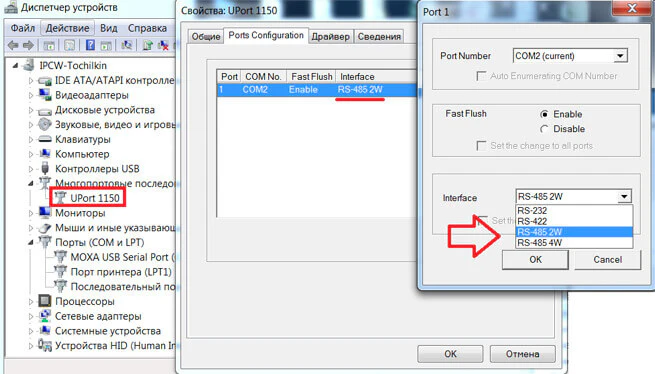
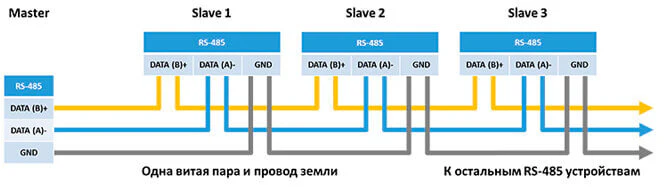
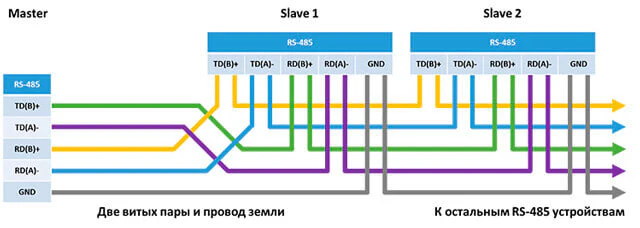
Схема подключения внешнего устройства с RS-485:
Подтягивающие и согласующие резисторы
В некоторых моделях оборудования есть встроенные резисторы, которые обеспечивают правильную работу линий RS-422/485.
Согласующий резистор или терминатор 120 Ом – ставится в начале и конце линии для предотвращения отражения сигнала от конца линии и искажения полезного сигнала в RS-422/485.
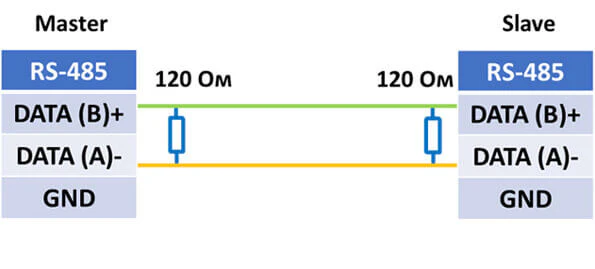
При большой длине линии связи (более 100 метров) возникают эффекты длинных линий, которые связаны с индуктивностью и ёмкостью кабеля. Получается, что сигнал, переданный в линию с одной стороны, начинает искажаться по мере распространения в другую сторону. Поскольку на практике кабель на всей длине имеет одинаковые параметры погонной ёмкости и индуктивности, это свойство кабеля характеризуют волновым сопротивлением. Поэтому, если на приёмном конце кабеля использовать резистор с сопротивлением, равным волновому сопротивлению кабеля, то негативные резонансные явления значительно ослабляются.
Подтягивающие резисторы (pull high/low resistors) – предназначены для ограничения тока, протекающего по сигнальным цепям, и чтобы сделать состояние цифрового входа по умолчанию высоким или низким.
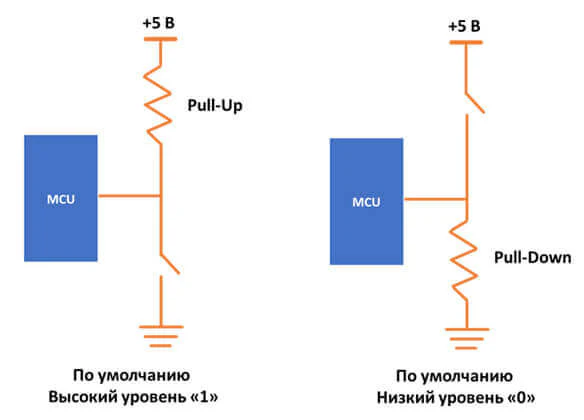
Цифровой вход нельзя напрямую подключить к питанию без ограничения тока, а также нельзя оставлять вход без подключения к чему либо, т.к. возможны ложные изменения состояния входа из-за внешних наводок.
Цепь с подтягивающим резистором можно представить в виде делителя напряжения из двух резисторов — одного подтягивающего и другого на месте кнопки.
Логический вход имеет ёмкость относительно земли, что влияет на время нарастания или спада сигнала при размыкании кнопки. Время спада или нарастания — это время между размыканием кнопки и достижением сигнала порогового напряжения, при достижении которого логическим входом фиксируется изменение логического состояния с высокого «1» на низкий «0» или наоборот.
Время спада и нарастания — зависит от произведения сопротивления, ёмкости и коэффициента, который учитывает пороговое напряжение. При подключении различных устройств значение ёмкости изменяется, это ведет к изменению формы сигнала, что может негативно сказаться на правильном определении уровня сигнала.
Поэтому иногда требуется подстройка значений подтягивающих резисторов, для восстановления формы сигнала. Ниже пример того, как может выглядеть сигнал при разном значении подтягивающего резистора:
Обычно значения подтягивающих резисторов по умолчанию оптимальны, но если форма сигнала сильно искажена или данные передаются с ошибками, то вам следует изменить значения подтягивающих резисторов.
Ниже показан пример расположения переключателей для изменения значений подтягивающих резисторов.
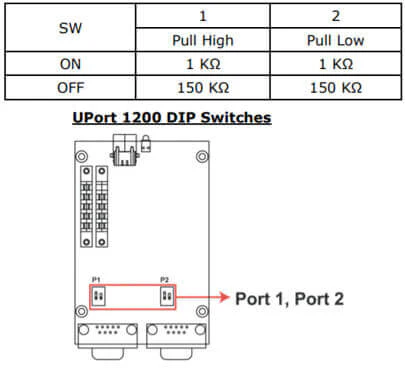
Рекомендации по устранению неисправностей
Структурная схема подключения устройства с СОМ портом к ПК выглядит так:

Схема подключения на примере UPort
- Если вы настроили подключение, но оно у вас не работает, убедитесь, что ваш конвертер работает и настроен правильно. Рекомендации по проверке RS-232/422/485 даны выше.
- Проблема может быть в подключении к конечному устройству, проверьте распиновку конвертера и конечного устройства.
- Проблема может быть в отличающихся параметрах СОМ порта на конвертере и конечном устройстве: скорости, четности, типе интерфейса, протоколе данных и т.д.
- Также можно изменить номинал подтягивающих резисторов и добавить согласующий резистор (для RS-422/485).
- Проблема может быть в программном обеспечении, попробуйте использовать другое ПО для проверки, например PComm Lite.
You may need to test serial ports for a variety of reasons. One situation to consider is when you are not receiving an expected data flow. Perhaps you have data acquisition software that should be getting information from a device connected to your computer’s COM port. Unfortunately, there is no data being transmitted and you suspect you may have a communication issue. You want to identify the issue and will need to test the COM port. Now you just need to know how to test serial ports.
Serial Port Tester enables you to test serial ports in Windows 10/8/7 to see exactly what is going on with your serial communication, This enables you to troubleshoot and diagnose communication issues. The first step is to download the RS232 tester software.
Here’s how to check if the RS232 port is working when you have problems with the data flow while using COM Port Tester.
Set the serial port details
Before you can use the serial port tester you need to provide details about the device you are attaching to your computer.
Gather all the device’s details such as the baud rate, the number of serial ports to which it is connected, data bits, and parity. You can use a value of 2 for the top bits if you don’t know how many are in use. This will not cause any harm except to possibly slightly slow down data transmission. You can query and monitor the status of current connections to your machine with Serial Port Tester’s COM Port Status window.
Note: Detailed information concerning each setting can be obtained by reviewing the device’s documentation.
Serial port control information is displayed as a collection of 4 or 5 items, each separated by a dash. In the fling list, a leading “n” indicates a numeric item and a “c” designates a character item.
nBaudRate:
Defines the serial port baud rate or transmission speed. Possible values are: 110, 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 14400, 19200, 38400, 56000, 57600, 115200, 128000 and 256000. If no value is set, a default of 110 is used.
cParity:
Parity can be defined with one of these values: (E)ven, (O)dd, (M)ark, (S)pace, or (N)one. (N)one is the default.
cHandflow:
Defines the flow control used in the connection. It can be set to Hardware (P), Xon/Xoff (X) and None. The default setting is None.
nDataLength:
Defines the length of a data packet. Possible values are 5, 6, 7 and 8. The default is 7 bits.
nStopBits:
Defines the number of stop bits. Possible values are: “1”, “1,5” and “2”. Default value is “1”.
How to check serial port communication with Serial Port Tester
Using a quality software tool can help you identify and address issues quickly. Electronic Team’s Serial Port Tester offers an excellent solution that provides users with an advanced feature set for diagnosing serial communication problems. Its versatility and flexibility make this a valuable addition to the software tools available to individuals working with serial applications and devices.
Follow these steps to initiate a new testing session after you have defined the settings for the connection.
- Launch the RS232 test software.
- Choose “Session >>> New session” from the main menu. Clicking “New” on the main toolbar or using “CTRL+N” are alternative methods of starting a session.
- The “New monitoring session” window will be displayed.
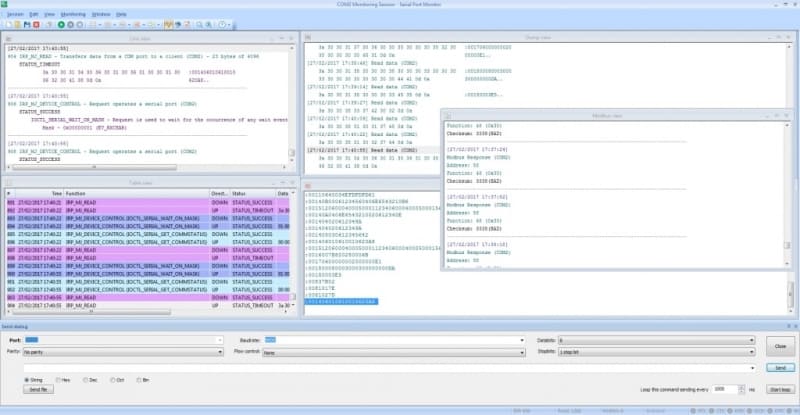
- Choose how the session’s data will be displayed by selecting from among these visualizers:
- ■ Line view concentrates on a specific serial line and provides detailed information regarding any requests it receives.
- ■ Dump view displays all sent and received data transmitted through a serial line.
- ■ Terminal view uses an ASCII text console to display the data that is received through a line.
- ■ Modbus view displays received and sent Modbus data and support both the RTU and ASCII variation of the protocol.
- ■ Table view employs a table format to present the recorded IRPs.
You can control how a new monitoring session begins with the “Start monitoring now” and “Start in new window” checkboxes.
Select the capture options from these choices: Create/Close, Read/Write, and Device Control.
Click the “Start monitoring” button to start the new session after all the options have been set.
- A new monitoring window is opened using the visualizers previously selected.
- You save a session with the “Session >>> Save session/Save session As” option from the app’s main menu. Alternately you can use the CTRL+S keyboard shortcut or “Save” on the main toolbar.
Specify a file name at the prompt so you can reload the session later to work with it further.
Serial cable testing
DTE equipment may require you to use a null-modem adapter to conduct a serial port test. Rewiring the cable connector is another option that more technically proficient users might attempt.
- First, you need to connect the ground, RXD, and TXD wires.
- Next, connect the wire that carries the device’s output data signal to the computer’s RXD. The documentation that comes with the device might guide you in finding this wire.
- The next step in performing a serial cable test is to connect the device’s input line to the computer’s TXD. Signal labels can be deceiving so be careful. Depending on the type of device, input or output wires can use the same signal.
Note: At times it can be difficult to identify the type of device in question. The documentation is often sketchy and you may need to use your deductive powers by looking at the device’s other signals. Devices such as modems have a DSR as an output and use the DTR as a counter.
Other manufacturers reverse this labeling, making it challenging to figure out the device’s signals.
With correctly named signals you end up with:
- a Computer to Computer link connecting TXD to RXD and RXD to TXD;
- a Computer to modem link that connects TXD to TXD and RXD to RXD.
The crossed connections described define a null-modem configuration. When deciding how to test a serial port, you may need to purchase an adapter to implement this connection.
Set Handshaking or Flow Control
Set Hardware Handshaking
You are ready to test RS232 ports once you have the signal wires connected correctly. If you are still not successful in receiving data, you might need to investigate the handshaking lines in order to test serial ports.
A handshaking arrangement is done for one of two reasons:
- To allow a computer that is not ready to receive data to stop a device from transmitting any;
- To enable a device to hold up communication from a computer if the device is not yet ready to receive the data.
Handshaking does not need to be implemented just because a device has the capability to do so. In many cases, manufacturers put the signals on the plug as they are easily available from the unit’s processor. If you choose to use handshaking, it is advisable to start with lines carrying fixed voltages. This minimizes any effects on the equipment’s operation. In cases where resistors are tied to handshake lines, you do not need to connect them.
There are some indicators that lead to the conclusion that handshaking should be implemented.
- If an input buffer overflow causes the computer to miss part of a message, handshaking may solve the issue.
- Similarly, a device can miss part of a message which will impact its ability to function correctly.
If you choose to implement handshaking with your RS232 tester, you should know that Serial Port Tester supports DTR / CTS handshaking. Using the tool, the computer employs its DTR output to indicate it is available to receive data. Devices can take advantage of the CTS input to limit the data flow from the computer.
The only time that the computer’s CTS input is important is when you are performing hardware handshaking. If you are not using hardware handshaking the CTS is ignored, but a high level is maintained on the DTR so you can use it to tie unused inputs to the device.
Removing handshaking will enable you to keep the RTS high and the DTR low. Here’s how to do it:
- Connect pins 8 and 7 (i.e. CTS drives RTS).
- Connect pins 1, 4, and 6. This should maintain the DTR line in the correct state, by connecting it to DCD and DSR.
This change should be performed on the device’s end of the cable. After making the modification, ensure that data is still flowing through the cable.
Set Software Handshaking
A software protocol that enables Xon \ Xoff handshaking can also be used to control the flow of data between a computer and a connected device.
The protocol works by a device sending an Xoff character when it cannot receive any more data. Transmission is halted until an Xon character is sent and received by the computer which informs it to restart the communication. Xon and Xoff characters can be sent by the device or computer.
Software handshaking is supported by COM Port Tester if it is required by the device you are using.
Return to the Serial Port Tester
Once serial communication issues have been solved by the previously outlined steps, you can return to step one and check the status of your serial port lines.
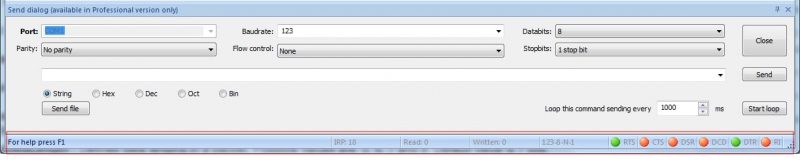
Below the main table, the states of the serial control lines are displayed.
- DSR: Data Send Ready line indicator
- DCD: Data Carrier Detect line indicator
- DTR: Data Terminal Ready line indicator
- RTS: Request to Send line indicator
- CTS: Clear to Send line indicator
- RI: Ring line indicator
The RS232 port test is facilitated by a graphical display of the status of the lines. A green circle indicates a high level with red representing a low level and gray pointing to a line with an undetermined state.
It can be hard to pinpoint the cause of serial communication problems. Some of the more common methods of diagnosing the issue have been discussed in the article.
Key takeaways for effective troubleshooting
In conclusion, testing serial ports can be essential when troubleshooting communication issues between your computer and connected devices. By using Serial Tester Software, you gain visibility into the details of your serial communication and can methodically identify and resolve problems. Key steps in the testing process include setting up serial port details, understanding and adjusting baud rates, data lengths, and handshaking options, and using specific diagnostic modes within the tester software, such as Dump view or Modbus view, for real-time feedback on the data flow.
In some cases, additional configurations like null-modem adapters or fine-tuning handshaking lines may be necessary to establish or maintain proper communication. Whether using hardware or software handshaking, these settings can prevent data loss and improve the reliability of the serial connection. With a clear understanding of these tools and techniques, users can efficiently test, diagnose, and ultimately improve their serial port communication setups, ensuring smooth data transfer and system functionality.