Readers help support Windows Report. We may get a commission if you buy through our links.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
The Windows 10 Temporary Internet Files folder stores all the websites you have visited online for easy reference the next time you revisit the same site.
If you want to reset the Temporary Internet Files location to default, you can do so by following our handy guide.
What are temporary Internet files?
The common name of the Temporary Internet Files is the cache. These are files saved by the device from the web.
This file is saved on your hard drive and contains vital information that reduces the time in rendering web pages you have visited before.
Your browser may store HTML, multimedia, videos, and images in this file. You should know that this file becomes bulky over time and can consume a considerable part of your storage. This means that it may slow down your computer’s performance.
Where are my temporary Internet files?
The location of this file depends on the browser you use. Below are a few popular browsers and the path of their cache:
- Google Chrome –
C:\Users{username}\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Cache - Microsoft Edge –
C:\Users{username}\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Edge\User Data\Default\Cache - Mozilla Firefox –
C:\Users{username}\AppData\Local\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles{profile folder}\cache2\entries
Do Temporary Internet Files slow down computer?
Yes, these files can slow down your devices, but it depends on the amount of storage space they take, the specific browser you use, and the number of stored files.
On older computers, a reduction in performance will be faster and more easily noticed. For top performing computers. This may never be noticed. However, from time to time, it may be good practice to empty the cache.
How can I delete Temporary Internet Files on Windows 10?
-
1. Launch Internet Explorer. You can do that simply by typing Internet Explorer in the search bar and pressing enter.
-
2. Click on the Tools icon. It is located along the top right corner and has the shape of a cog wheel.
-
3. Next, select Internet Options.
-
4. In the Internet Options window, under the General tab (shows by default) and Browsing History, click on the Setting tab.
-
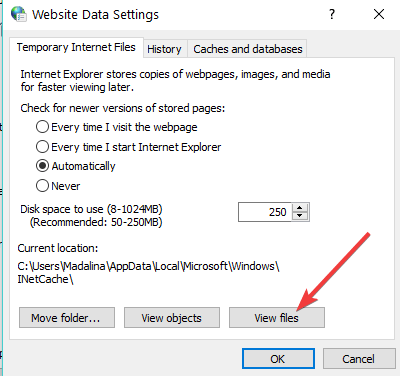
5. This will launch the Website Data Setting window. There, along the bottom right is the View Files button.
-
6. Click on View files. You will be led to a new window containing all the files pertaining to the websites you have visited before you had last deleted all your browsing history. You may now delete these.
1. Delete Temporary Internet Files from Internet Options
You can easily open and view your Temporary Internet Files by accessing Internet Settings. The Website Data Settings contain a shortcut to the folder location of the temporary files.
Also, since the content of the Temporary Internet Files folder still occupies disk space and hence can impact performance, it does make sense to get rid of those files if not needed.
Most users don’t know what to do when the Windows search box goes missing. Don’t worry; we will show you how to return it in just a few steps.
2. Delete Temporary Internet Files using Disk Cleanup
- Type Disk cleanup in the taskbar search box and select the same from the search results shown.
- Select your primary disk and hit OK.
- Select the Temporary Internet Files option.
- Finally, press OK, and that’s it. All your temporary internet files will be removed from your system.
- May 2025 Patch Tuesday finally brings Recall & other AI features to Copilot+ PCs
- Microsoft releases Windows 10 (KB5058379/ KB5058392 / KB5058383/ KB5058387) May 2025 Patch Tuesday
Is it safe to delete Temporary Internet Files in Windows 10?
Yes, deleting the Temporary Internet Files is safe for Windows 10. It comes with a few benefits, including the following:
- Performance improvement – As discussed earlier, having so much on your computer may slow it down; hence you may expect a boost after deleting these files.
- Freeing up space – After removing these files, you have more space for other things on your computer.
- Privacy protection – Since these files can contain some sensitive information, deleting them is a way to guarantee that your data is secure.
Deleting temporary files in Windows 10 is as easy as it can get using the Disk Cleanup utility. Nevertheless, problems find a way of creeping in.
If the tool suddenly decides to act out, you can stop the Disk Cleanup from crashing with a few simple tips.
That is how you gain access to the Temporary Internet Files Folder in Windows 10 or delete the same if not needed.
As always, for more suggestions or questions, feel free to reach out by using the comments section below.
Ivan Jenic
Windows Hardware Expert
Passionate about all elements related to Windows and combined with his innate curiosity, Ivan has delved deep into understanding this operating system, with a specialization in drivers and driver troubleshooting.
When he’s not tackling diverse driver-related problems, Ivan enjoys watching good movies and spending time hiking with his family and friends.
Download Article
View your cached web data with this easy guide
Download Article
- Microsoft Edge
- Google Chrome
- Firefox
- Windows Temp Files
- Mac Cache Files
- How do I remove temporary internet files?
- Q&A
- Tips
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This wikiHow teaches you how to find the temporary internet files for your web browser, as well as how to find other temporary files on your PC or Mac. Temporary files, or cache, are temporary data your computer uses to make operations run more smoothly. Your web browser uses temporary internet files to load websites faster. You can easily find where your browser or computer stores temporary files when you know where to look.
Where to Find Your Temporary Files
- In Microsoft Edge, temporary internet files are in «C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Edge\User Data\Default\Cache»
- To view other temporary files on Windows, press Win + R, type «%temp%», and press Enter.
- To see temporary files on your Mac, navigate to «~/Library/Containers/com.apple.Safari/Data/Library/Caches» in Finder.
-
Microsoft Edge stores your temporary internet files in «C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Edge\User Data\Default\Cache» on Windows. Use the following steps to navigate to it:[1]
- Press Win + R to open Run.
- Type «%AppData%» and press Enter.
- Click AppData in the address bar at the top.
- Open the Microsoft folder.
- Open the Edge folder.
- Open the User Data folder.
- Open the Default folder.
- Open the Cache folder.
-
The Microsoft Edge cache folder on Mac is located at «~/Library/Caches/Microsoft Edge/Default/Cache» and «~/Library/Application Support/Microsoft Edge/Default.» Use the following steps to navigate to these folders:
- Open Finder.
- Click Go.
- Hold Option and click Library.
- Open the Caches or Application Support folder.
- Open the Microsoft Edge folder.
- Open the Default folder.
- Open the Cache folder.
Advertisement
-
The Google Chrome cache folder is stored at «C:\Users\[username]\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Cache.» Use the following steps to open the Google Chrome cache folder on Windows:[2]
- Press Win + R to open Run.
- Enter %AppData% and press Enter.
- Click AppData in the address bar at the top.
- Open the Local folder.
- Open the Google folder.
- Open the Chrome folder.
- Open the User Data folder.
- Open the Default folder.
- Open the Cache folder.
-
On Mac, Google Chrome stores cache files in «~/Library/Caches/Google/Chrome» as well as «~/Library/Application Support/Google/Chrome/Default/Applications Caches.» Use the following steps to navigate to the Google Chrome cache folder:[3]
- Open Finder.
- Click Go.
- Hold Option and click Library.
- Open the Caches or Application Support folder.
- Open the Google Folder.
- Open the Chrome (stop here if you are in the «Caches» folder.)
- Open the Google folder.
- Open the Chrome folder.
- Open the Default folder.
- Open the Application Caches folder.
Advertisement
=== Safari ===
-
To find temporary internet files on your Mac, you’ll need to go to the Safari cache folder at «~/Library/Containers/com.apple.Safari/Data/Library/Caches» or «~/Library/Caches» on older versions of macOS. You can navigate to it using Finder. Click the blue smiling face icon on the bottom-left to open your Finder.
-
It’s in the menu bar at the top of the page
-
This will open your user library folder.
-
Use the following steps to navigate to the Safari cache folder:
- Open the Containers folder (or «Caches» on older versions of macOS».)
- Open the com.apple.Safari folder.
- Open the Data folder.
- Open the Library folder.
- Open the Caches folder.
Advertisement
-
This command opens and displays your temporary internet files (cache) in Firefox.
-
It’s below the «disk» heading near the middle of the page. Doing so will open a page listing all of your Firefox’s temporary internet files.
-
You can also find the Firefox cache files at «C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles\xxxxxxxx.default\cache2» on Windows. Use the following steps to navigate to it:
- Press Win + R to open Run.
- Type %AppData% and press Enter.
- Click AppData in the address bar at the top.
- Open the Local folder.
- Open the Mozilla folder.
- Open the Firefox folder.
- Open the Profiles folde.r
- Open the folder that has an 8-digit string of characters followed by «.default».
- Open the cache2 folder.
-
The location of the cache folder for Firefox on Mac is «~/Library/Application Support/Firefox/Profiles.» Use the following steps to navigate to it:
- Open Finder.
- Click Go.
- Hold Option and click LIbrary.
- Open the Application Support folder.
- Open the Firefox folder.
- Open the Profiles folder.
Advertisement
-
There are two types of temp files on Windows: Windows temp files, which are used by the operating system, and local user temp files, which are used by the apps you run. You can use File Explorer to find your Windows temp files.
-
On most computers, this will be the «OS C:» drive. You can find it in the menu bar to the left, or under «This PC.»
-
These are the general temp files that Windows creates. They are usually located at «C:\Windows\Temp.» You may need administrative access to access these files. Use the following steps to navigate to the Windows temp files.
- Click Windows.
- Scroll down and click Temp.
-
You can use Run to quickly navigate to your local user temp files. These are where most of your applications store their temp files. Use the keyboard shortcut to open Run.
-
This will open the local temp folder in File Explorer. The location of the local user temp folder is usually «C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Temp.»
- You will see a bunch of free-floating files as well as a few folders for various programs.
Advertisement
-
Your Mac stores temporary files (other than those from your web browser) in folders for each app. Click the blue smiling face icon on the bottom-left to open your Finder.
-
It’s in the menu bar at the top of the page
-
This will open your user library folder.
- The Library option only shows up when you press down the Option/Alt key.
-
This folder contains the temp files for all the applications on your Mac.
-
Most temp folders on a Mac have a name like «com.apple.safari.» Here you can find the temp folders for various applications on your Mac.
Advertisement
-
- Microsoft Edge: Click the three dots at the top-right corner and select Delete browsing data. Check the box next to «Cached images and files,» and remove the checkmarks from all other boxes. Select All time from the «Time range» menu and click Clear now to delete your cache.
- Google Chrome: Click the three dots at the top-right corner and select Delete browsing data. Check the box next to «Cached images and files,» uncheck all other boxes, select All time from the «Time range» menu, and then click Delete data.
- Safari: First, enable the Develop menu in Safari > Settings > Advanced. Then, click the Develop menu, followed by Empty Caches.
- Firefox: Click the three-line menu and go to Settings > Privacy & Security. Click Clear Data…, check the box next to «Temporary cached files and pages,» and remove all other checkboxes. Select Everything from the When menu, then click Clear.
Add New Question
-
Question
How do I delete temporary Internet files in Chrome?
Within Chrome:
CTRL-H
Click on Clear Browsing Data
Check what you want deleted and select how far back
Then click Clear Browsing Data
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
-
Temporary internet files can be anything from copies of the images and icons one finds on any website to files containing pieces of website code.
-
Neither Chrome nor Firefox stores usable files on your computer.
-
Some temporary Internet files will be impossible to open without the context of the website for which they were designed.
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
References
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Open Finder.
2. Press the Option key and click Go.
3. Click Library.
4. Double-click Caches.
5. Double-click com.apple.Safari.
6. Double-click fsCachedData.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 581,537 times.
Reader Success Stories
-
«This was a good, thorough article with nice detail.»
Is this article up to date?
If your computer feels sluggish or your browser’s acting up, it might be time to clear out those temporary internet files. This process frees up space and can make your system run smoother. In Windows 10, it’s a straightforward task that anyone can handle.
Deleting temporary internet files will free up space on your computer and potentially improve performance. Follow these steps to make it happen.
Step 1: Open the Settings App
To start, open the Settings app by clicking on the Start Menu and selecting the gear icon.
In Windows 10, the Settings app is your go-to for most system adjustments. Think of it as the control room of your computer.
Step 2: Go to System Settings
Next, click on “System” in the Settings menu.
The System section is like the brain of your Settings. It holds all the important settings related to your computer’s performance and storage.
Step 3: Select Storage
Now, click on “Storage” from the side menu.
Storage settings show you how much space is being used and what’s taking up that space. It’s your map for navigating disk usage.
Step 4: Temporary Files
Under Storage, find and click on “Temporary files.”
This section gathers all the files that your computer doesn’t need to run. It’s like finding a junk drawer you didn’t know you had.
Step 5: Delete Temporary Internet Files
Check the box next to “Temporary Internet Files” and click “Remove files.”
This step is like taking out the trash. You’re getting rid of stuff that’s just sitting there, taking up space.
Once you complete these steps, you should notice a bit more free space on your hard drive. Your computer might even run a bit smoother.
Tips for Deleting Temporary Internet Files in Windows 10
- Use Disk Cleanup: This built-in tool can also help you delete temporary files.
- Schedule Cleanups: Set a reminder to delete temp files regularly.
- Use Third-Party Tools: Apps like CCleaner can help automate the process.
- Monitor Storage: Keep an eye on your storage for unusual spikes.
- Browser Settings: Many browsers have their own options for clearing cache and cookies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are temporary internet files?
Temporary internet files are files saved by your browser to help web pages load faster. They can pile up and take up significant space over time.
Can deleting temporary internet files cause any problems?
Generally, no. Deleting these files frees up space and can improve performance. However, some websites may load slower the first time after deletion.
How often should I delete temporary internet files?
It depends on your usage. If you use your computer heavily, consider doing it once a month.
Are there any risks involved in deleting temporary files?
There’s minimal risk. You might lose some saved website preferences, but it’s nothing that will harm your system.
Can I recover deleted temporary internet files?
Not easily. Once they’re deleted, they’re gone for good. Make sure you don’t need any saved data before you delete them.
Summary of Steps
- Open the Settings app.
- Go to System settings.
- Select Storage.
- Click on Temporary files.
- Delete Temporary Internet Files.
Conclusion
Clearing out temporary internet files in Windows 10 is a simple yet effective way to keep your computer running smoothly. Over time, these files can accumulate and take up precious storage space, slowing down your system’s performance. By following the steps mentioned above, you can easily free up space and potentially improve how your computer runs.
Remember, regular maintenance is key to a healthy computer. Make it a habit to check and delete temporary files periodically. If you’re often on the web, consider using third-party tools to automate the cleanup process. And don’t forget to explore other areas of your computer that might need a little tidying up.
So, take a few minutes now to clear out those temporary internet files. Your computer will thank you for it!
Matthew Burleigh has been writing tech tutorials since 2008. His writing has appeared on dozens of different websites and been read over 50 million times.
After receiving his Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees in Computer Science he spent several years working in IT management for small businesses. However, he now works full time writing content online and creating websites.
His main writing topics include iPhones, Microsoft Office, Google Apps, Android, and Photoshop, but he has also written about many other tech topics as well.
Read his full bio here.
Understanding Temporary Internet Files Folder Location in Windows 11/10
In the realm of computing, browsing the internet has become an intrinsic part of our daily lives. As we surf the web, our device accumulates various data to enhance user experience, including the Temporary Internet Files (TIF) folder. These files serve essential functions in speeding up browsing processes and saving crucial data. However, knowing where to locate these files is crucial for managing storage and maintaining your privacy. This article delves deep into the Temporary Internet Files folder’s location in Windows 10 and 11, alongside user management practices, implications for performance, and privacy considerations.
What are Temporary Internet Files?
Before exploring the exact locations of Temporary Internet Files (TIF), it’s essential to understand what they are. Temporary Internet Files are cached files stored on your hard drive by your web browser. They consist of various elements as you navigate the internet, including web pages, images, scripts, and multimedia content. The caching process enables your browser to load frequently visited websites more swiftly, thereby conserving bandwidth and improving loading times.
Purpose of Temporary Internet Files
Temporary Internet Files serve multiple purposes, which can be summarized as follows:
-
Speeding Up Browsing: By storing data locally, browsers can retrieve it quickly without needing to re-download files.
-
Reducing Bandwidth Usage: Cached content minimizes the amount of data that has to be downloaded, making browsing more efficient, especially for users with limited internet connectivity.
-
Offline Browsing: Temporary Internet Files allow users to access previously visited websites even without an internet connection, provided that the content is stored in the cache.
-
User Convenience: Websites often load faster as your browser fetches files from the cache rather than reloading them from the server.
Location of Temporary Internet Files in Windows 10/11
The location of the Temporary Internet Files folder can differ slightly between Windows versions and the browser being used. Typically, these files are stored in specific directories.
In Windows 10
For Microsoft Edge (the default browser in Windows 10):
-
Open File Explorer: Right-click on the Start menu and select ‘File Explorer’.
-
Navigate to the Folder: The Temporary Internet Files are usually found at:
C:Users\AppDataLocalMicrosoftWindowsINetCache -
Access the AppData Folder: You might not see the
AppDatafolder because it is hidden by default. To make it visible:- Click on the ‘View’ tab at the top of File Explorer.
- Check the box for ‘Hidden items’.
For Mozilla Firefox:
- Open File Explorer.
- Navigate to the following path:
C:Users\AppDataLocalMozillaFirefoxProfiles - Locate the appropriate profile folder and look for ‘cache2’.
For Google Chrome:
- Open File Explorer.
- Navigate to:
C:Users\AppDataLocalGoogleChromeUser DataDefaultCache
In Windows 11
The folders in Windows 11 are quite similar to those in Windows 10, owing to the shared architecture. Here’s where you can find Temporary Internet Files in different browsers:
For Microsoft Edge:
- Open File Explorer.
- Navigate to:
C:Users\AppDataLocalMicrosoftWindowsINetCache
For Firefox:
- Open File Explorer.
- Navigate to:
C:Users\AppDataLocalMozillaFirefoxProfiles - Within your profile folder, find the ‘cache2’ directory.
For Google Chrome:
- Open File Explorer.
- Navigate to:
C:Users\AppDataLocalGoogleChromeUser DataDefaultCache
Understanding Folder Structures
Each of these paths leads to a folder where your browser stores temporary files. Here’s a brief breakdown of what you’ll find in some of the common folders:
-
INetCache: This is primarily utilized by Microsoft Edge and Internet Explorer to store cached webpage data.
-
Cache and Cache2: Most browsers store cached elements in these directories. You’ll find an assortment of files here, often non-descript in title.
-
Profiles: Browsers like Firefox and Chrome maintain user profile folders, which contain all user-specific cached items.
Managing Temporary Internet Files
Over time, the accumulation of temporary internet files can lead to various issues, from consuming valuable storage space to complications in browser performance. Understanding how to manage these files properly is essential for maintaining optimal performance on your system.
Clear Temporary Internet Files
It’s a good practice to periodically clear these files. Here’s how to do it across the most common browsers:
-
Microsoft Edge:
- Open Edge.
- Click on the three-dot menu in the top right corner.
- Go to ‘Settings’ > ‘Privacy, search, and services’.
- Under ‘Clear browsing data’, click ‘Choose what to clear’.
- Check the ‘Cached images and files’ box and click ‘Clear now’.
-
Google Chrome:
- Open Chrome.
- Click on the three-dot menu and select ‘More tools’ > ‘Clear browsing data’.
- Choose the time range and check ‘Cached images and files’.
- Click on ‘Clear data’.
-
Mozilla Firefox:
- Open Firefox.
- Click on the three-line menu and select ‘Options’.
- Go to ‘Privacy & Security’.
- Scroll down to ‘Cookies and Site Data’, then click on ‘Clear Data’.
- Make sure to check ‘Cached Web Content’ and click ‘Clear’.
Automated Cleanup Tools
Using built-in tools or third-party applications can further ease the management of Temporary Internet Files. Windows provides a Disk Cleanup tool that efficiently removes unwanted files, including Temporary Internet Files.
-
Disk Cleanup:
- Type ‘Disk Cleanup’ in the Start menu search bar and open the application.
- Select the drive you wish to clean, typically the C: drive.
- After scanning, check the box for ‘Temporary Internet Files’ and any other categories you wish to delete.
- Click ‘OK’ to begin the cleanup.
-
Third-Party Tools:
- Applications like CCleaner offer more control and options for cleaning up Temporary Internet Files and other unnecessary data regularly.
Performance Implications of Temporary Internet Files
A well-managed cache can lead to improved browser performance, while a bloated cache may hinder it. Additional benefits include increased system performance, faster loading speeds, and decreased chances of encountering errors while browsing.
However, Temporary Internet Files can also contribute to system slowdowns if too many cached files accumulate. Here are a few performance implications to consider:
-
Enhanced Speed: Properly managed Temporary Internet Files can drastically decrease loading times for frequently visited websites.
-
Increased Scrutiny on Performance: Browsers may slow down as the cache grows larger, causing lags or long loading times on less optimized machines.
-
Potential Corruption: Sometimes, outdated or corrupt cached files can lead to display issues or errors. Regularly clearing them helps mitigate this problem.
Privacy Concerns and Temporary Internet Files
Temporary Internet Files also present potential risks concerning user privacy. As these files store sensitive data, it’s crucial to understand how they can be exploited and what you can do to protect your information.
-
Data Retention: Every time you access a website, files related to that visit are stored. This includes cookies, login information, and personal settings.
-
Potential for Data Leakage: If someone has access to your machine, they could retrieve sensitive information from cached files, making regular cleaning a necessity.
-
Incognito Mode: Consider using incognito or private browsing modes on browsers, which do not save Temporary Internet Files once the session ends.
Conclusion
Understanding the location and management of Temporary Internet Files in Windows 10 and 11 is crucial for efficient browser performance and privacy management. Navigating the folders and cleaning unwanted files can significantly enhance your browsing experience while safeguarding your sensitive information.
In today’s fast-paced digital world, an organized cache not only speeds up your browsing but also provides you with better control over your data’s privacy. By familiarizing yourself with cache management tools and practices, you can ensure a smoother and more secure internet experience that aligns seamlessly with your computing needs. Regular maintenance encourages optimal performance, creating an efficient balance in the experience of modern web browsing.
When it comes to optimizing your computer’s performance, deleting temporary internet files should be at the top of your list. These files take up valuable space on your hard drive and can slow down your browsing experience. So, why not take a few minutes to learn how to delete temporary internet files on Windows 10?
Deleting temporary internet files on Windows 10 is a simple process that can help improve your computer’s speed and overall performance. By clearing out these files, you can free up storage space and ensure that your internet browser is running smoothly. In fact, it’s estimated that deleting temporary files can free up as much as 4 GB of space on your hard drive.
To delete temporary internet files on Windows 10, follow these simple steps:
- Open the «Settings» app.
- Select «System» and then click on «Storage».
- Click on «Temporary files».
- Check the box next to «Temporary Internet Files».
- Click on «Remove files» to delete them.

Introduction: Why Delete Temporary Internet Files in Windows 10?
In the age of the internet, browsing the web has become an integral part of our daily lives. Whether it’s for work, research, or leisure, we rely on our web browsers to access information and explore the digital realm. As we browse different websites and interact with online content, our web browsers store temporary internet files to enhance our browsing experience. These files, however, can accumulate over time and consume valuable storage space on our computers.
Deleting temporary internet files in Windows 10 is important for several reasons. Firstly, it helps to free up storage space on your computer, allowing it to run more efficiently. Secondly, deleting these files can improve your browsing speed by removing unnecessary clutter from your browser’s cache. Lastly, it enhances your privacy and security by removing traces of your online activities that may be stored within these files. In this article, we will guide you through the process of deleting temporary internet files in Windows 10.
Step 1: Accessing the Internet Options
To begin the process of deleting temporary internet files in Windows 10, you need to access the Internet Options. Follow the steps below:
- Open your preferred web browser (e.g., Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge).
- Click on the Gear icon or the three-dot menu icon located at the top-right corner of the browser window.
- From the drop-down menu, select «Settings» or «Options.»
- In the settings or options menu, navigate to the «Privacy & Security» or «Privacy» section.
- Look for the «Clear browsing data,» «Clear cache,» or «Delete temporary files» option. The specific wording may vary depending on the browser you are using.
- Click on this option to access the Internet Options.
Once you have accessed the Internet Options, you can proceed to the next step.
Step 2: Deleting Temporary Internet Files
Now that you have accessed the Internet Options, you can delete your temporary internet files. Follow the steps below:
- In the Internet Options window, navigate to the «General» or «Browsing history» tab.
- Under the «Browsing history» section, you will find a button labeled «Delete» or «Clear.»
- Click on this button to open the «Delete Browsing History» or «Clear browsing data» window.
- In this window, you will see various checkboxes representing different types of data you can delete.
- Select the checkbox next to «Temporary Internet Files» or «Cached images and files.» You can also choose to select other types of data to delete, such as cookies or browsing history, if desired.
- Once you have selected the appropriate checkboxes, click on the «Delete» or «Clear» button to delete your temporary internet files.
- Wait for the process to complete, which may take a few moments depending on the size of your cache.
- Once the files are deleted, you can close the Internet Options window.
Congratulations! You have successfully deleted your temporary internet files in Windows 10. This will help improve your computer’s performance and enhance your browsing experience.
Additional Considerations
While deleting temporary internet files is beneficial, it is important to note that doing so will remove certain data that can be useful in certain situations. For example, cached images and files can help web pages load faster upon revisiting them. Additionally, deleting cookies may sign you out of websites or remove personalized settings.
Before deleting all your temporary internet files, consider the following:
- If you are experiencing issues with a specific website, try clearing the cache specifically for that website before deleting all temporary files.
- If you want certain websites to remember your login information or other preferences, make sure to deselect the checkboxes for cookies or other site-specific data.
- Regularly clearing temporary internet files is recommended for optimal performance, but you can also adjust your browser settings to automatically clear the cache at specified intervals.
By considering these factors, you can strike a balance between maintaining optimal browsing performance and preserving certain convenience features provided by temporary internet files.
Exploring Alternative Methods
In addition to the method outlined above, there are alternative methods for deleting temporary internet files in Windows 10. Depending on your preference or specific requirements, you may find these methods more suitable:
Method 1: Using Disk Cleanup
Windows 10 provides a built-in tool called Disk Cleanup, which can be used to delete temporary files and free up disk space. Follow the steps below to use Disk Cleanup:
- Open the Start menu and search for «Disk Cleanup.»
- Click on the «Disk Cleanup» application from the search results. You may need to provide administrator permissions to proceed.
- In the Disk Cleanup window, select the disk drive where Windows is installed (usually the C: drive).
- Click on the «OK» button to initiate the scanning process.
- After the scan is complete, you will see a list of files that can be deleted.
- Scroll down the list and select the checkbox next to «Temporary Internet Files» or «Temporary files.»
- Click on the «OK» button to start the cleanup process.
- Confirm the deletion by clicking on the «Delete Files» button.
- Wait for the process to complete, which may take a few moments depending on the size of the temporary files.
Once the process is complete, you will have successfully deleted temporary internet files using Disk Cleanup.
Method 2: Using Third-Party Cleaning Tools
There are also third-party cleaning tools available that specialize in removing temporary files and optimizing disk space. These tools often offer additional features and customization options compared to the built-in Windows methods. Popular examples of such tools include CCleaner, BleachBit, and Wise Disk Cleaner. To use these tools:
- Download and install your preferred third-party cleaning tool from a trusted source.
- Launch the tool and navigate to the section dedicated to cleaning temporary files or internet cache.
- Select the appropriate checkboxes for temporary internet files or other types of temporary files you wish to delete.
- Click on the «Clean» or «Start» button to initiate the cleaning process.
- Follow any additional prompts or instructions provided by the tool.
- Wait for the process to complete, which may take longer than the built-in Windows methods depending on the tool and your system’s specifications.
By using third-party cleaning tools, you can gain more control over the deletion process and potentially access advanced features for optimizing your computer’s performance.
Conclusion
Deleting temporary internet files in Windows 10 is essential for maintaining optimal performance, freeing up disk space, and enhancing security and privacy. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can easily delete these files through the Internet Options or explore alternative methods such as using Disk Cleanup or third-party cleaning tools. Remember to consider the trade-offs between convenience and performance when deleting temporary internet files, and find a balance that suits your browsing habits and system requirements.
Deleting Temporary Internet Files in Windows 10
In Windows 10, temporary internet files are stored in a specific location on your computer to improve browsing speed and load frequently visited websites faster. However, over time, these files can accumulate and take up valuable disk space. To optimize your computer’s performance, it is important to regularly delete temporary internet files. Here’s how:
Method 1: Using the Settings App
- Open the Start menu and click on «Settings».
- Go to the «System» category and select «Storage».
- Scroll down and click on «Temporary files».
- Check the box next to «Temporary Internet Files» and click on «Remove Files».
Method 2: Using Internet Options
- Open Internet Explorer or Microsoft Edge.
- Click on the «Settings» icon and select «Internet Options».
- In the «General» tab, under «Browsing history», click on «Delete».
- Check the box next to «Temporary Internet Files» and click on «Delete».
By following these steps, you can easily delete temporary internet files in Windows 10 and free up valuable disk space. Regularly performing this maintenance task will help improve your computer’s performance and ensure smoother browsing experiences.
Key Takeaways:
- Deleting temporary internet files on Windows 10 is essential for improving performance and protecting privacy.
- You can delete temporary internet files through the «Disk Cleanup» utility in Windows 10.
- Clearing temporary internet files can free up storage space on your computer.
- Deleting temporary internet files can help resolve issues related to website loading or access.
- Regularly deleting temporary internet files can help prevent malware and security threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
Deleting temporary internet files in Windows 10 is an essential maintenance task to improve system performance. Here are some common questions and answers related to deleting temporary internet files in Windows 10.
1. What are temporary internet files in Windows 10?
Temporary internet files are files that are saved by your web browser while you browse the internet. These files include web page content, images, scripts, and other media files. The purpose of these files is to improve your browsing experience by storing data locally, so the next time you visit a website, it can load faster.
In Windows 10, temporary internet files are stored in a specific folder called the «Temporary Internet Files» folder.
2. Why should I delete temporary internet files in Windows 10?
There are several reasons why you should regularly delete temporary internet files in Windows 10:
- Free up disk space: Temporary internet files can take up a significant amount of disk space over time. Deleting them can help free up space on your hard drive.
- Improve browser performance: As the number of temporary internet files increases, your browser may start to slow down. Deleting these files can help improve your browser’s performance.
- Privacy and security: Temporary internet files may contain sensitive information, such as login credentials or browsing history. Deleting them can help protect your privacy and prevent unauthorized access to your personal information.
3. How can I delete temporary internet files in Windows 10?
You can delete temporary internet files in Windows 10 by following these steps:
- Open the «Settings» app by clicking on the «Start» button and selecting «Settings» (gear icon).
- In the Settings window, click on «System.»
- Under System, click on «Storage.»
- In the Storage settings, click on «Temporary files.»
- You will see a list of file types. Check the box next to «Temporary Internet files» and any other file types you want to delete.
- Click on the «Remove files» button to delete the selected temporary internet files.
4. Is there a way to automatically delete temporary internet files in Windows 10?
Yes, you can configure Windows 10 to automatically delete temporary internet files. Here’s how:
- Open the «Settings» app by clicking on the «Start» button and selecting «Settings» (gear icon).
- In the Settings window, click on «Network & Internet.»
- Under Network & Internet, click on «Proxy.»
- Scroll down to the «Manual setup» section and toggle the switch under «Automatically delete temporary files» to turn it on.
- Windows 10 will now automatically delete temporary internet files periodically.
5. Will deleting temporary internet files affect my browsing experience?
Deleting temporary internet files should not affect your browsing experience negatively. On the contrary, it may even improve your browsing speed and performance. However, deleting temporary internet files will remove any stored website data, such as login information or website preferences. You may need to re-enter login information or adjust website preferences after deleting these files.
To summarize, deleting temporary internet files on Windows 10 is essential for maintaining the performance and security of your computer. By following a few simple steps, you can easily clear out these files and free up valuable storage space.
First, navigate to the «Settings» menu, and select «System» followed by «Storage.» From there, choose the drive where your temporary files are stored, typically the C: drive. Click on «Temporary files» and check the box next to «Temporary Internet Files.» Finally, click «Remove files» and Windows 10 will delete these files, improving your computer’s speed and protecting your privacy.