on October 28, 2010
In Windows OS, we can find the current logged in username from windows command line. The logged in user information is stored in environment variables. So just by printing the value in these environment variables we can get to know the login name.
To know the login name of the currently logged in user we can run the below command.
echo %username%
This works on all releases of Windows OS(Windows XP, Server 2003, Windows Vista and Windows 7).
There is another command whoami which tells us the domain name also.
whoami
Example:
c:\>whoami cmdline\administrator
Both of these options to find user name can be useful in batch files to write code in such a way that it works for every user. For example, if your batch file need to access a user specific folder, say Application data, then you can refer the directory as ‘C:\users\%username%\appdata‘.
Дерево страниц
-
Создатель Сергей Предеин, отредактировано окт 21, 2021
Узнать, под каким именем система знает текущего пользователя можно одним из следующих способов:
Способ 1: Скрипт
Скачайте и запустите файл: current_user.cmd
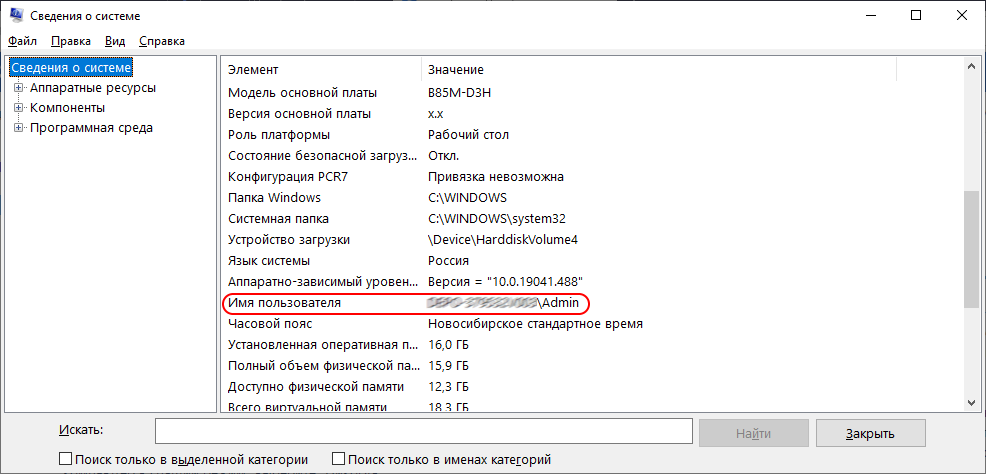
Способ 2: Сведения о системе
- Нажмите Win+R,
- введите команду
msinfo32, - нажмите «Ok».
- В открывшемся окне «Сведения о системе» найдите строку «Имя пользователя».
- Имя текущего пользователя будет находится сразу после символа «\».
Способ 3: Командная строка
- Нажмите сочетание клавиш Win+R,
- Введите в открывшемся окне
cmdи нажмите Enter, - В открывшемся окне Командной строки введите команду
%username%. - Результат работы команды — ваше текущее имя пользователя.
- Нет меток
Обзор
Инструменты контента
Download Article
See which user is currently logged into the computer
Download Article
- Using the Start Menu
- Using Command Prompt
|
This wikiHow teaches you how to see your current account’s username on a Windows computer.
- Open your computer’s Start menu.
- Type %USERNAME% into the search box.
- Press Enter.
- Find the current logged-in user in your User Accounts settings.
-
The Start menu button looks like four squares in the lower-left corner of your screen.
-
Click the search box on the Start menu, and enter this line into it. This will search and find the User Accounts application from your Control Panel.
- If %USERNAME% doesn’t bring User Accounts in the search, try searching %ACCOUNT%.
Advertisement
-
This will open your User Accounts window.
-
Your current username is displayed in your User Accounts settings.
Advertisement
-
The Run window allows you to directly open any application or document on your computer.
- You can find and open Run from the Start menu, or press the ⊞ Win+R shortcut on your keyboard.
-
-
This will open Command Prompt in a new window.
-
This command will reply with your username.
-
Your current username will be displayed in a new line.
Advertisement
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
About This Article
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 27,953 times.
Is this article up to date?
Все способы:
- Как узнать имя пользователя
- Способ 1: «Командная строка»
- Способ 2: Панель управления
- Вопросы и ответы: 5
Многие пользователи практикуют использование нескольких учётных записей на одном компьютере – например, в целях родительского контроля. Если аккаунтов много, может возникнуть путаница, поскольку не сразу понятно, под каким из них загружена система. Решить этот вопрос можно просмотром имени текущего пользователя, и сегодня мы хотим вас познакомить с методами совершения этой операции.
Как узнать имя пользователя
В более старых вариантах Виндовс псевдоним учётной записи отображался при вызове меню «Пуск», но разработчики отказались от этого в версии «окон» начиная с 8. В сборках «десятки» до 1803 эта возможность вернулась – имя можно было посмотреть через дополнительное меню «Пуска», доступное по нажатию кнопки с тремя полосками. Однако в 1803 и выше это убрали, и в новейшей сборке Windows 10 доступны иные варианты просмотра имени пользователя, приведём самые простые.
Способ 1: «Командная строка»
Множество манипуляций с системой можно совершить с помощью «Командной строки», в том числе и необходимую нам сегодня.
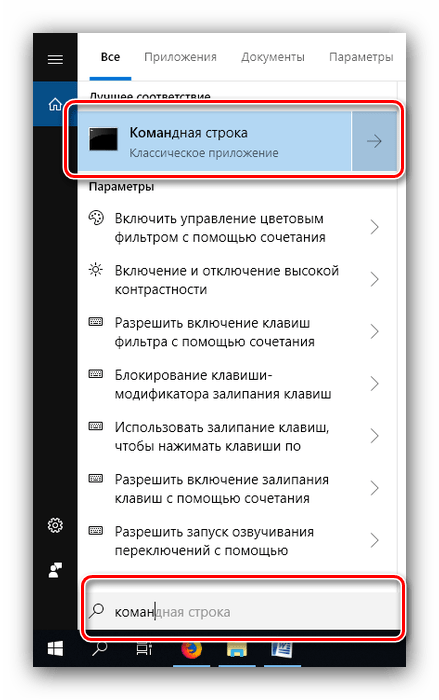
- Откройте «Поиск» и начните набирать словосочетание командная строка. В меню отобразиться нужное приложение – кликните по нему.
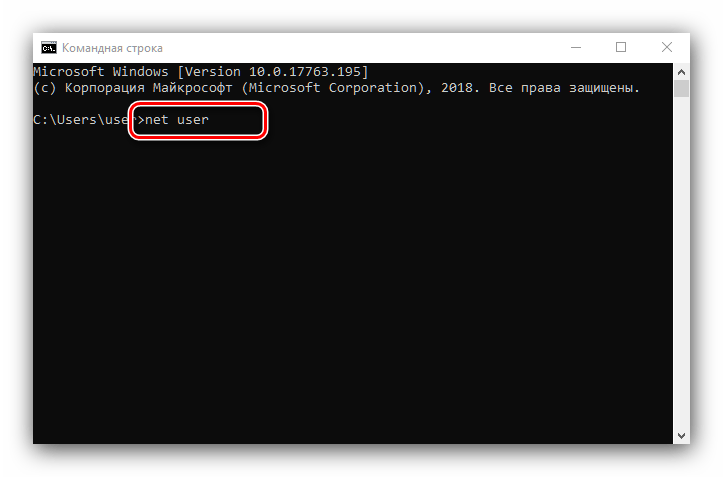
- После открытия интерфейса ввода команд укажите в нем следующий оператор и нажмите Enter:
net user - Команда выведет на экран список всех учётных записей, созданных на этой системе.
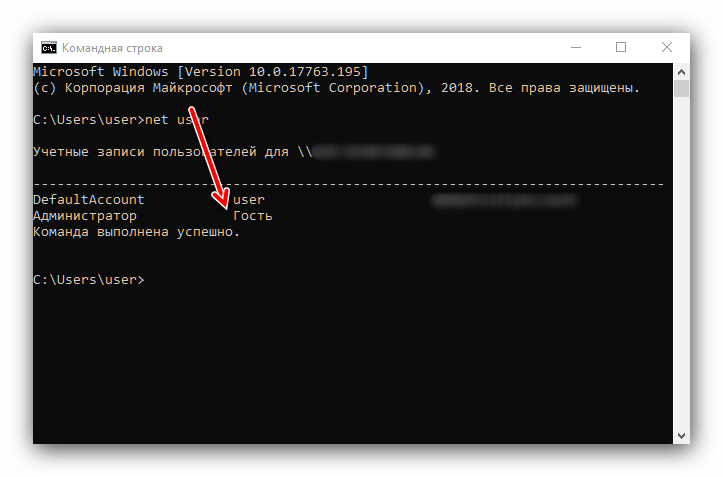
К сожалению, никакого выделения текущего пользователя не предусмотрено, поэтому этот способ подходит только для компьютеров с 1-2 учётными записями.
Способ 2: Панель управления
Второй метод, с помощью которого можно узнать имя пользователя – инструмент «Панель управления».
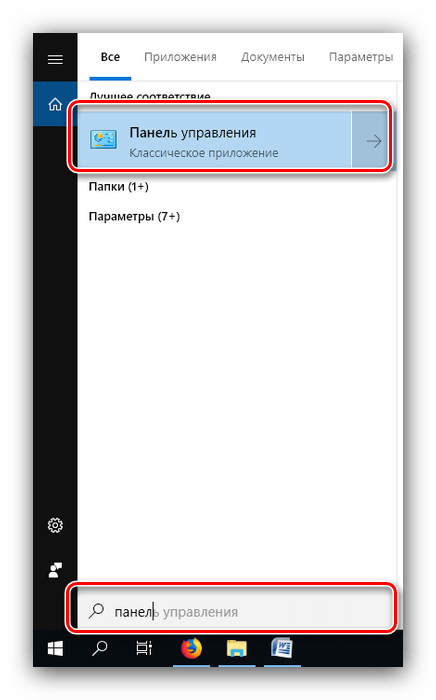
- Откройте «Поиск», наберите в строке панель управления и кликните по результату.
- Режим отображения значков переключите в «Крупные» и воспользуйтесь пунктом «Учётные записи пользователей».
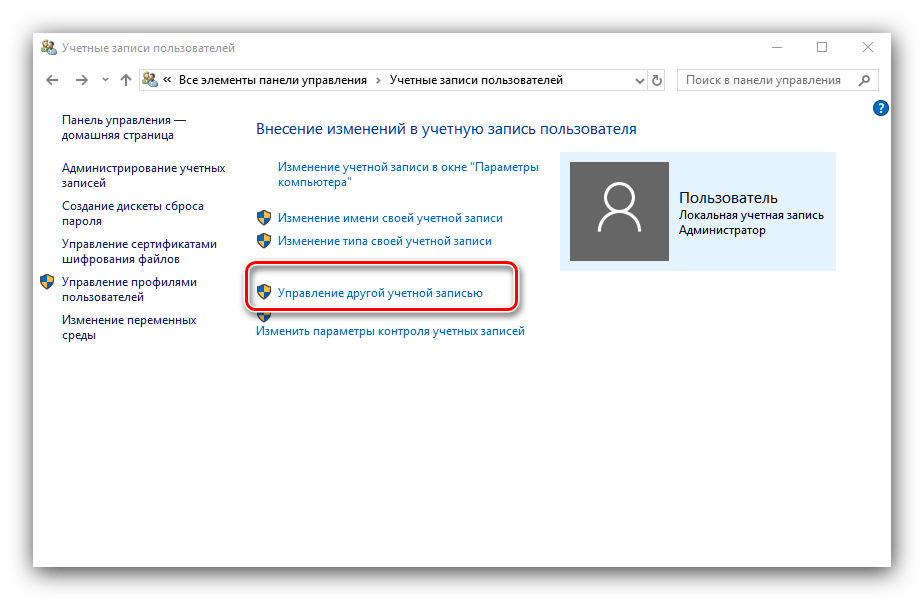
- Щёлкните по ссылке «Управление другой учётной записью».
- Откроется окно, в котором можно просмотреть все учётные записи, существующие на этом компьютере – справа от аватаров каждой из них можно увидеть имена.


Такой способ удобнее, чем задействование «Командной строки», поскольку применять его можно на любой учётной записи, и информацию указанная оснастка отображает более наглядно.
Мы рассмотрели способы, которыми можно узнать имя пользователя компьютера на Windows 10.
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
The `whoami` command in CMD displays the username of the currently logged-in user, helping you quickly identify the account under which the command prompt session is running.
whoami
Understanding the `whoami` Command
The `whoami` command is a powerful utility within CMD (Command Prompt) that allows users to quickly identify their currently logged-in user account. It’s a simple yet essential command, especially in multi-user environments or scenarios where user permissions are critical. The primary purpose of this command is to provide immediate feedback about the identity of the user currently active in the command line interface.

Mastering Cmd Whois: A Quick Guide to Domain Lookups
How to Use the `whoami` Command
The basic syntax is straightforward:
whoami
When executed, this command reveals the username of the currently logged-in user. For example, if your Windows username is «john_doe,» running `whoami` will output:
john_doe
Common Use Cases for `whoami`
One common scenario where you might use the `whoami` command is when working on a shared machine. In such situations, efficiently establishing your identity can save time and prevent mistakes, especially when permissions and roles differ for multiple users.
Another essential use case appears during troubleshooting sessions. Sometimes, knowing which user is operating can help determine whether the right permissions are in place to execute specific commands or access certain files.

Mastering Cmd Choice: Quick Guide to Conditional Logic
Advanced Options for `whoami`
The `whoami` command comes with several parameters that broaden its functionality and applications. Here are some advanced options:
Displaying User SID
The Security Identifier (SID) is a unique identifier used to represent users or groups. To display the SID associated with your user account, you can use the following command:
whoami /user
When you run this command, you’ll receive output containing both your username and its corresponding SID. This is particularly useful in environments where user access needs to be tightly controlled or audited.
Displaying Group Memberships
Understanding which groups the current user belongs to is crucial for managing permissions effectively. To check group memberships, use:
whoami /groups
This will generate a list of groups along with their respective attributes, including group SIDs and attributes such as «Mandatory Group» or «Enabled Group.» Knowing your group memberships helps you understand your access level across different systems.
Displaying Token Information
If you need to dive deeper into user privileges, the following command provides detailed information about the security token associated with the user account:
whoami /priv
Executing this command reveals the privileges that the user has on the system, which can be invaluable for security audits and troubleshooting issues related to permission errors.
Unlocking The Power Of Windows Cmd Whois
Practical Examples of Using `whoami`
Example 1: Quick User Check
In situations where you may forget your user identity, a simple execution of `whoami` serves as a quick reminder. This can particularly help when multiple users are logged into a system, ensuring you are aware of which account you are operating under.
whoami
Example 2: Security Audits
A more involved use case involves security audits. When examining whether users have appropriate access permissions, you could run:
whoami /priv
This output allows you to examine your privileges and determine if there are any unnecessary rights assigned to your account, helping to maintain a secure environment.
Example 3: Troubleshooting
Combining various `whoami` commands can streamline troubleshooting efforts. For instance, running this combined command will give you clear insights into both group memberships and privilege levels:
whoami /groups && whoami /priv
By analyzing both outputs, you can quickly diagnose access-related issues or validate user configurations.

Cmd Home Group: Mastering Group Management in Cmd
Practical Tips for Using `whoami` Effectively
Understanding Output Format
When you execute the `whoami` command or its parameters, the output is structured in a readable format. Familiarizing yourself with these formats will help you interpret the information more effectively. For example, when checking group memberships, take note of the attributes listed alongside group names, as these provide context about your permissions.
Using `whoami` in Batch Scripts
If you find yourself needing to check user identities frequently, consider automating this process with batch scripts. Here’s a simple script that uses `whoami`:
@echo off
echo Current User:
whoami
echo Permission levels:
whoami /priv
This script will output the current user and their permissions every time it’s executed, saving time and effort.
Combining with Other CMD Commands
The power of the `whoami` command can be enhanced by pairing it with other CMD commands. For instance, you can dynamically display the current user along with a message by using the following syntax (in a supported shell):
echo You are logged in as: $(whoami)
This can be particularly useful in scripts or when automating tasks.

Explore Fun Cmd Games for Quick Command Mastery
Conclusion
The `whoami` command in CMD is more than just a simple utility for identifying your user account; it is a versatile tool that plays a significant role in managing user permissions, enhancing security, and facilitating troubleshooting. By understanding its functionality and incorporating its various options into your workflow, you can significantly improve your command line efficiency. Don’t hesitate to explore further CMD commands for a more robust toolset that empowers your computing experience.

Mastering Cmd Comment: Quick Tips and Tricks
Additional Resources
For further learning, seek out related CMD tutorials that delve into other useful commands. Engage with community forums or consult official documentation to enhance your understanding of CMD commands and their practical applications. Remember, mastery of CMD can significantly streamline your workflow and improve your technical skill set.









