Большинству администраторов Windows, знакомых с темой PKI, известна утилита MakeCert.exe, с помощью которой можно создать самоподписанный сертификат. Эта утилита включена в состав Microsoft .NET Framework SDK и Microsoft Windows SDK. В современных версиях Windows 11/10/8.1 и Windows Server 2022/2019/2016/2012R2 вы можете создать самоподписанный сертификат с помощью встроенных командлетов PowerShell без использования дополнительных утилит.
Содержание:
- New-SelfSignedCertificate: создать самоподписанный SSL сертификат в PowerShell
- Как сгенерировать SAN (SubjectAltName) сертификат с помощью PowerShell?
- Экспорт самоподписаного сертификата в Windows
- Сгенерировать сертификат для подписи кода типа Code Signing
- Создать самоподписанный SSL сертификат SHA-256 для IIS
New-SelfSignedCertificate: создать самоподписанный SSL сертификат в PowerShell
Для создания самоподписанного сертификата в PowerShell нужно использовать командлет New-SelfSignedCertificate, входящий в состав модуля PKI (Public Key Infrastructure).
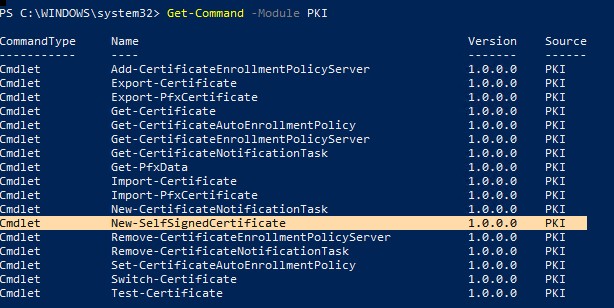
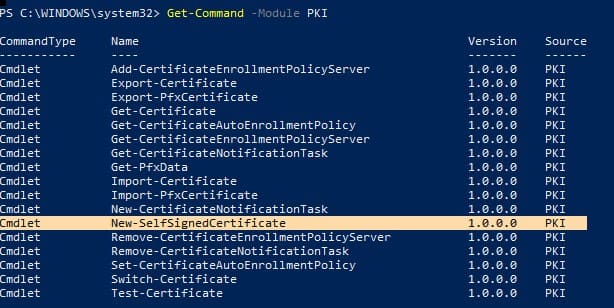
Чтобы вывести список всех доступных командлетов в модуле PKI, выполните команду:
Get-Command -Module PKI
Самоподписанные SSL сертификаты рекомендуется использовать в тестовых целях или для обеспечения сертификатами внутренних интранет служб (IIS, Exchange, Web Application Proxy, LDAPS, ADRMS, DirectAccess и т.п.), в тех случая когда по какой-то причине приобретение сертификата у внешнего провайдера или разворачивание инфраструктуры PKI/CA невозможны.
Совет. Не забывайте, что вы можете использования полноценные бесплатные SSL сертификаты от Let’s Encrypt. Например, вы можете SSL сертификат Let’s Encrypt и привязать его к сайту IIS.
Для создания сертификата нужно указать значения -DnsName (DNS имя сервера, имя может быть произвольным и отличаться от имени localhost) и -CertStoreLocation (раздел локального хранилища сертификатов, в который будет помещен сгенерированный сертификат).
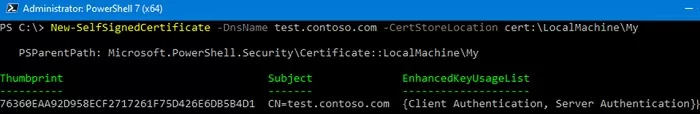
Чтобы создать новый SSL сертификат для DNS имени test.contoso.com (указывается FQDN имя) и поместить его в список персональных сертификатов компьютера, выполните команду:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName test.contoso.com -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My
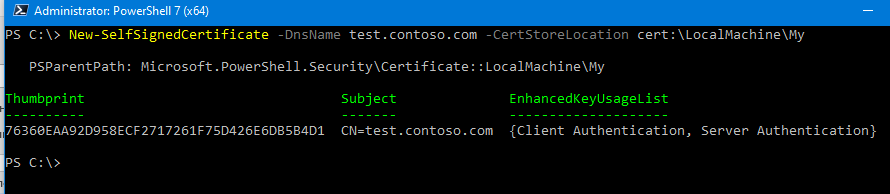
Команда вернет отпечаток нового сертификата (Thumbprint), Subject и EnhancedKeyUsageList. По умолчанию такой сертификат можно использовать для аутентификации клиента Client Authentication (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2) или сервера Server Authentication (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1).
Если вы запустите эту команду в PowerShell без прав администратор, появится ошибка:
New-SelfSignedCertificate : CertEnroll::CX509Enrollment::_CreateRequest: Access denied. 0x80090010 (-2146893808 NTE_PERM)
Если вы указали нестандартный криптографический провайдер CSPs (например, с помощью параметров
-KeyAlgorithm "ECDSA_secP256r1" -Provider 'Microsoft Smart Card Key Storage Provider'
), убедитесь, что он установлен на компьютере (по умолчанию используется CSP Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider). Иначе появится ошибка:
New-SelfSignedCertificate: CertEnroll::CX509Enrollment::_CreateRequest: Provider type not defined. 0x80090017 (-2146893801 NTE_PROV_TYPE_NOT_DEF).
По-умолчанию генерируется самоподписанный сертификат со следующим параметрами:
- Криптографический алгоритм: RSA;
- Размер ключа: 2048 бит;
- Допустимые варианты использования ключа: Client Authentication и Server Authentication;
- Сертификат может использоваться для: Digital Signature, Key Encipherment ;
- Срок действия сертификата: 1 год.
- Криптопровадер: Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider
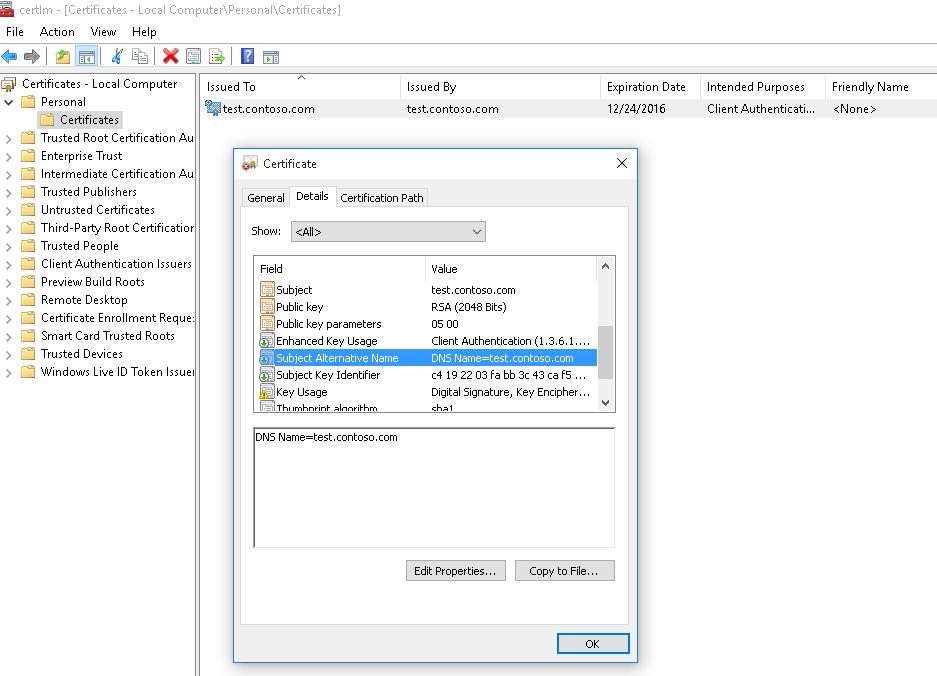
Данная команда создаст новый сертификат и импортирует его в персональное хранилище компьютера. Откройте оснастку certlm.msc и проверьте, что в разделе Personal хранилища сертификатов компьютера появился новый сертификат.
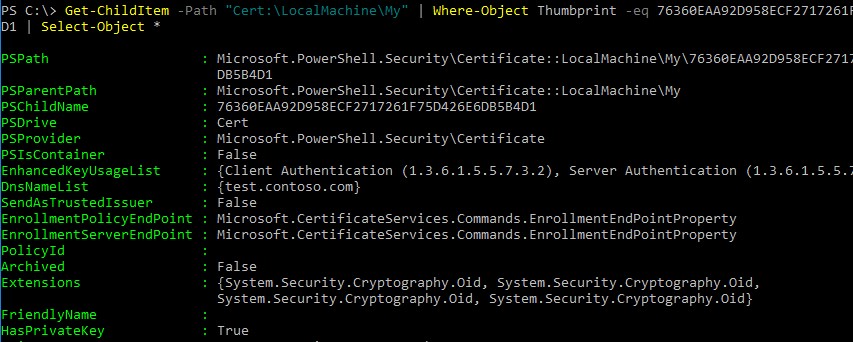
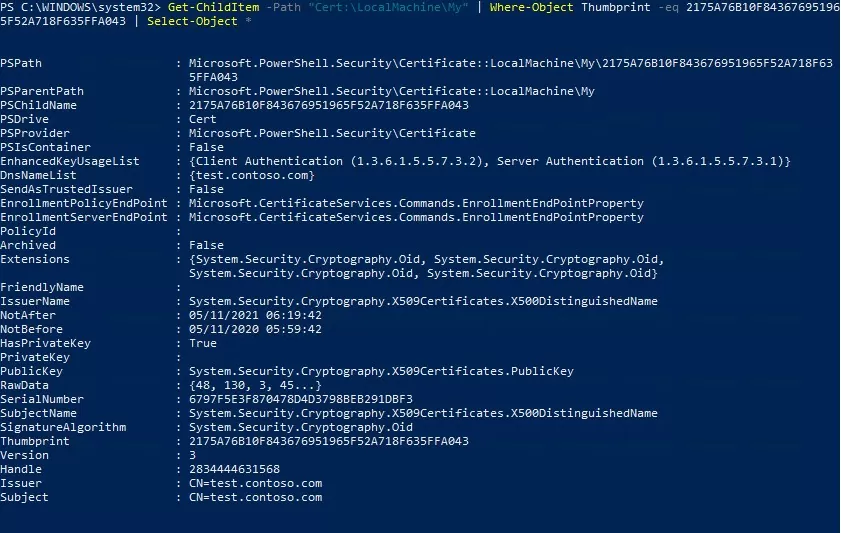
С помощью командлета Get-ChildItem можно вывести все параметры созданного сертификата по его отпечатку (Thumbprint):
Get-ChildItem -Path "Cert:\LocalMachine\My" | Where-Object Thumbprint -eq 76360EAA92D958ECF2717261F75D426E6DB5B4D1 | Select-Object *
PSPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Security\Certificate::LocalMachine\My\76360EAA92D958ECF2717261F75D426E6
DB5B4D1
PSParentPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Security\Certificate::LocalMachine\My
PSChildName : 76360EAA92D958ECF2717261F75D426E6DB5B4D1
PSDrive : Cert
PSProvider : Microsoft.PowerShell.Security\Certificate
PSIsContainer : False
EnhancedKeyUsageList : {Client Authentication (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2), Server Authentication (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1)}
DnsNameList : {test.contoso.com}
SendAsTrustedIssuer : False
EnrollmentPolicyEndPoint : Microsoft.CertificateServices.Commands.EnrollmentEndPointProperty
EnrollmentServerEndPoint : Microsoft.CertificateServices.Commands.EnrollmentEndPointProperty
PolicyId :
Archived : False
Extensions : {System.Security.Cryptography.Oid, System.Security.Cryptography.Oid,
System.Security.Cryptography.Oid, System.Security.Cryptography.Oid}
FriendlyName :
HasPrivateKey : True
PrivateKey : System.Security.Cryptography.RSACng
IssuerName : System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X500DistinguishedName
NotAfter : 12/2/2023 3:41:18 PM
NotBefore : 12/2/2022 3:21:18 PM
PublicKey : System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.PublicKey
RawData : {48, 130, 3, 45…}
SerialNumber : 24682351DA9C59874573BA2B5BB39874
SignatureAlgorithm : System.Security.Cryptography.Oid
SubjectName : System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X500DistinguishedName
Thumbprint : 76360EAA92D958ECF2717261F75D426E6DB5B4D1
Version : 3
Handle : 2007435579936
Issuer : CN=test.contoso.com
Subject : CN=test.contoso.com
Примечание. Срок действия такого самоподписанного сертификата истекает через 1 год с момента его создания. Можно задать другой срок действия сертификата с помощью атрибута —NotAfter.Чтобы выпустить сертификат на 3 года, выполните следующие команды:
$todaydate = Get-Date
$add3year = $todaydate.AddYears(3)
New-SelfSignedCertificate -dnsname test.contoso.com -notafter $add3year -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My
Можно создать цепочку сертификатов. Сначала создается корневой сертификат (CA), а на основании него генерируется SSL сертификат сервера:
$rootCert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -Subject "CN=TestRootCA,O=TestRootCA,OU=TestRootCA" -KeyExportPolicy Exportable -KeyUsage CertSign,CRLSign,DigitalSignature -KeyLength 2048 -KeyUsageProperty All -KeyAlgorithm 'RSA' -HashAlgorithm 'SHA256' -Provider "Microsoft Enhanced RSA and AES Cryptographic Provider"
New-SelfSignedCertificate -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My -DnsName "test2.contoso.com" -Signer $rootCert -KeyUsage KeyEncipherment,DigitalSignature
Чтобы изменить длину ключа сертификата и алгоритм шифрования, нужно использовать параметры
–KeyAlgorithm
,
–KeyLength
и
–HashAlgorithm
. Например:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -KeyAlgorithm RSA -KeyLength 2048 -HashAlgorithm "SHA256"
Если на компьютере доступен модуль TPM 2.0, можно использовать его для защиты ключа:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -Type Custom -Provider "Microsoft Platform Crypto Provider" ...
Провайдер Microsoft Platform Crypto Provider использует Trusted Platform Module чип устройства для создания ассиметричного ключа.
$Params = @{
"DnsName" = "mylocalhostname"
"CertStoreLocation" = "Cert:\\CurrentUser\\My"
"KeyUsage" = "KeyEncipherment","DataEncipherment","KeyAgreement"
"Type" = "DocumentEncryptionCert"
}
New-SelfSignedCertificate @Params
Как сгенерировать SAN (SubjectAltName) сертификат с помощью PowerShell?
Командлет New-SelfSignedCertificate позволяет создать сертификат с несколькими различными именами Subject Alternative Names (SAN).
Примечание. Утилита Makecert.exe, в отличии от командлета New-SelfSignedCertificate, не умеет создавать сертификаты с SAN.
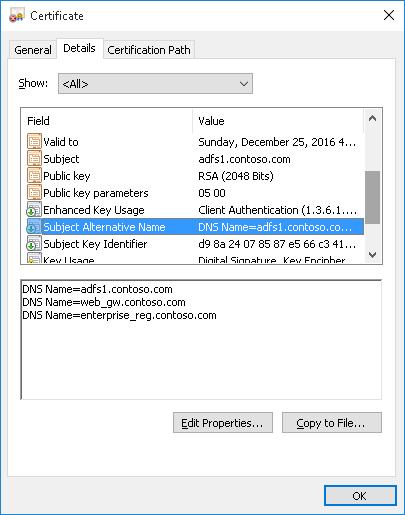
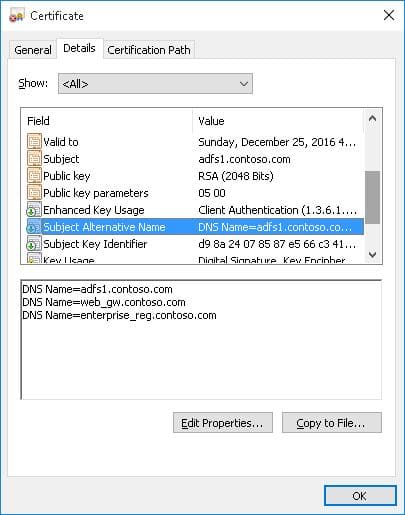
Если создается сертификат с несколькими именами, первое имя в параметре DnsName будет использоваться в качестве CN (Common Name) сертификата. К примеру, создадим сертификат, у которого указаны следующие имена:
- Subject Name (CN): adfs1.contoso.com
- Subject Alternative Name (DNS): web-gw.contoso.com
- Subject Alternative Name (DNS): enterprise-reg.contoso.com
Команда создания сертификата будет такой:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName adfs1.contoso.com,web_gw.contoso.com,enterprise_reg.contoso.com -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My
Также можно сгенерировать wildcard сертификат для всего пространства имен домена, для этого в качестве имени сервера указывается *.contoso.com.
New-SelfSignedCertificate -certstorelocation cert:\localmachine\my -dnsname *.contoso.com
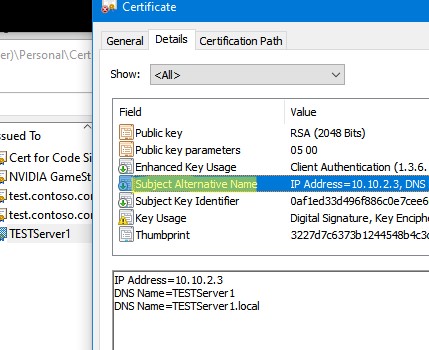
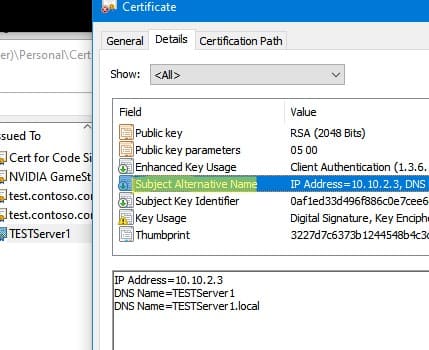
Вы можете привязать сертификат не только к DNS имени, но и к IP адресу. Для этого вместе параметр -DnsName нужно использовать -TextExtension. Например:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -TextExtension @("2.5.29.17={text}IPAddress=10.10.2.3&DNS=TESTServer1&DNS=TESTServer1.local")
Как вы видите, в поле Subject Alternative Name теперь содержится IP адрес.
Экспорт самоподписаного сертификата в Windows
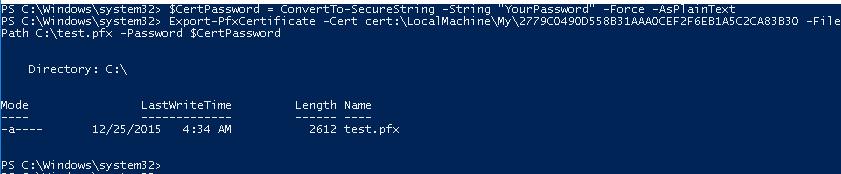
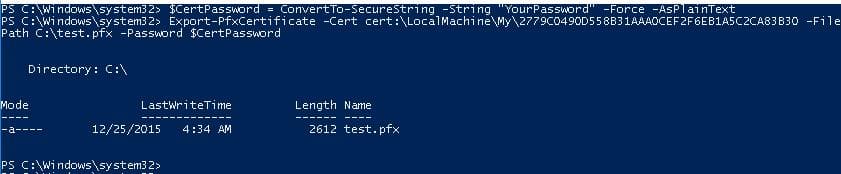
Для экспорта полученного сертификата c закрытым ключом в pfx файл, защищенный паролем, нужно получить его отпечаток (Thumbprint). Сначала нужно указать пароль защиты сертификата и преобразовать его в формат SecureString. Значение Thumbprint нужно скопировать из результатов выполнения команды New-SelfSignedCertificate.
$CertPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString -String “YourPassword” -Force –AsPlainText
Export-PfxCertificate -Cert cert:\LocalMachine\My\2779C0490D558B31AAA0CEF2F6EB1A5C2CA83B30 -FilePath C:\test.pfx -Password $CertPassword
Можно экспортировать открытый ключ сертификата:
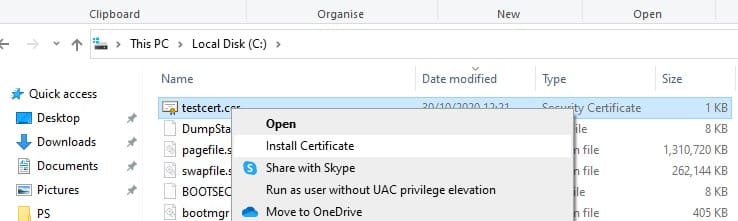
Export-Certificate -Cert Cert:\LocalMachine\My\2779C0490D558B31AAA0CEF2F6EB1A5C2CA83B30 -FilePath C:\testcert.cer
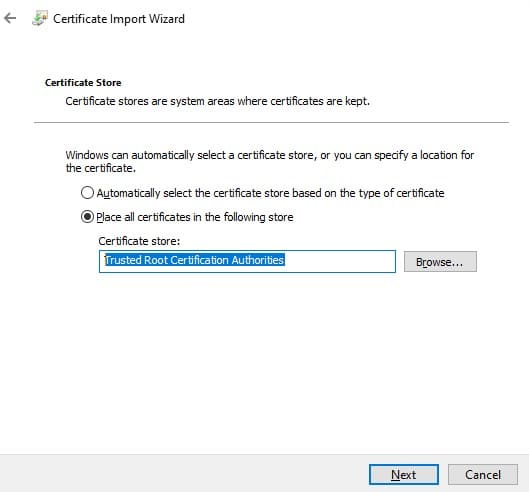
Проверьте, что в указанном каталоге появился CER (PFX) файл сертификата. Если щелкнуть по нему правой клавишей и выбрать пункт меню Install Certificate, можно с помощью мастера импорта сертификатов добавить сертификат в корневые доверенные сертификаты компьютера.
Выберите Store location -> Local Machine, Place all certificates in the following store -> Trusted Root Certification Authorities.
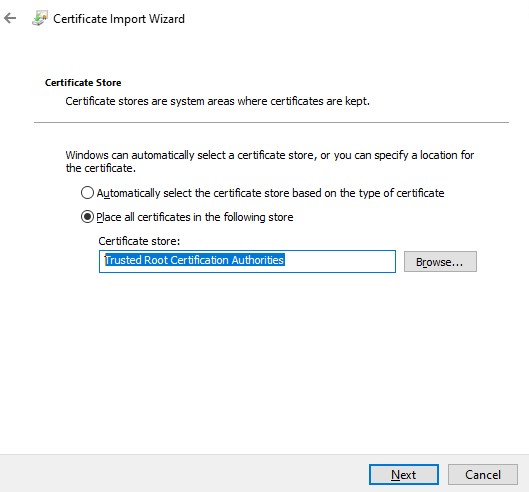
Можно создать сертификат и сразу импортировать его в доверенные корневые сертификаты компьютера командами:
$cert=New-SelfSignedCertificate …..
$certFile = Export-Certificate -Cert $cert -FilePath C:\certname.cer
Import-Certificate -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\AuthRoot -FilePath $certFile.FullName
Полученный открытый ключ или сам файл сертификата можно распространить на все компьютеры и сервера в домене с помощью GPO (пример установки сертификата на компьютеры с помощью групповых политик).
Сгенерировать сертификат для подписи кода типа Code Signing
В PoweShell 3.0 командлет New-SelfSifgnedCertificate позволял генерировать только SSL сертификаты, которые нельзя было использоваться для подписывания кода драйверов и приложений (в отличии сертификатов, генерируемых утилитой MakeCert).
В версии PowerShell 5 командлет New-SelfSifgnedCertificate теперь можно использовать чтобы выпустить сертификат типа Code Signing.
Вы можете обновить версию PowerShell согласно инструкции.
Для создания самоподписанного сертфиката для подписывания кода приложений, выполните команду:
$cert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -Subject "Cert for Code Signing” -Type CodeSigningCert -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My
Теперь можно подписать ваш PowerShell скрипт эти сертификатом:
Set-AuthenticodeSignature -FilePath C:\PS\test_script.ps1 -Certificate $cert
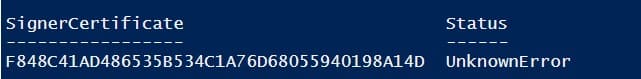
Если при выполнении команды появится предупреждение UnknownError, значит этот сертификат недоверенный, т.к. находится в персональном хранилище сертификатов пользователя.
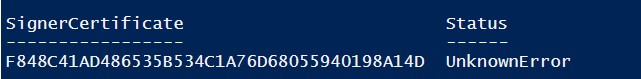
Нужно переместить его в корневые сертификаты (не забывайте периодически проверять хранилище сертификатов Windows на наличие недоверенных сертфикатов и обновлять списки корневых сертификатов):
Move-Item -Path $cert.PSPath -Destination "Cert:\CurrentUser\Root"
Теперь вы можете использовать этот самоподписанный сертификат для подписи PowerShell скриптов, драйверов или приложений.
Создать самоподписанный SSL сертификат SHA-256 для IIS
Обратите внимание, что при создании самоподписанный сертификат для IIS через консоль Internet Information Manager (пункт меню Create Self-Signed Certificate), создается сертификат с использованием алгоритма шифрования SHA-1. Такие сертификаты многими браузерами считаются недоверенными, поэтому они могут выдавать предупреждение о небезопасном подключении. Командлет New-SelfSignedCertificate позволяет создать более популярный тип сертификата с помощью алгоритма шифрования SHA-256.
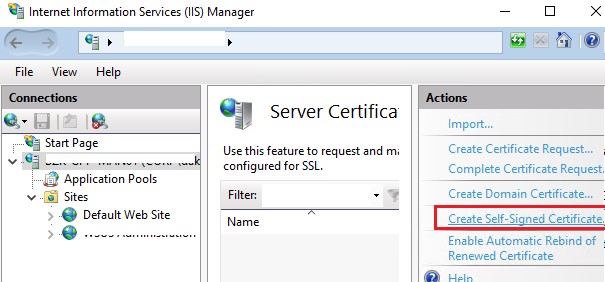
Вы можете привязать самоподписанный сертификат SHA-256, созданный в PowerShell, к сайту IIS. Если вы с помощью PowerShell создали SSL сертификат и поместили его в хранилище сертификатов компьютера, он будет автоматически доступен для сайтов IIS.
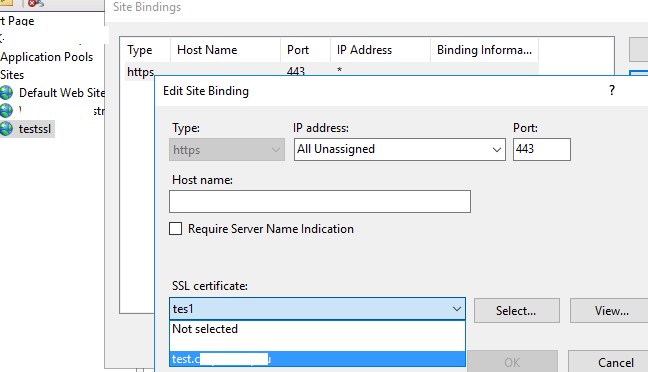
Запустите консоль IIS Manager, выберите ваш сайт, затем в настройке Site Binding, выберите созданный вами сертификат и сохраните изменения.
Также можно привязать SSL сертификат к сайту IIS по его отпечатку:
New-IISSiteBinding -Name "Default Web Site" -BindingInformation "*:443:" -CertificateThumbPrint $yourCert.Thumbprint -CertStoreLocation "Cert:\LocalMachine\My" -Protocol https
В этой статье мы расскажем, как создать самоподписанный SSL сертификат в Windows с помощью PowerShell, а также рассмотрим различные способы его использования.
Многие администраторы Windows, знакомые с инфраструктурой PKI, знают утилиту MakeCert.exe, с помощью которой можно выпускать самоподписанные сертификаты. Эта утилита входит в состав Microsoft .NET Framework SDK и Microsoft Windows SDK. В современных версиях Windows (11/10/8.1) и Windows Server (2022/2019/2016/2012R2) вы можете использовать встроенные командлеты PowerShell для создания самоподписанных сертификатов, не прибегая к сторонним утилитам.
Приобрести оригинальные ключи активации Windows всегда можно у нас в каталоге от 1099 ₽
Как создать самоподписанный SSL сертификат в PowerShell
Для создания самоподписанного сертификата в PowerShell используется командлет New-SelfSignedCertificate, который входит в модуль PKI (Public Key Infrastructure).
Чтобы получить список всех доступных командлетов модуля PKI, выполните команду:
Get-Command -Module PKI
Самоподписанные SSL сертификаты обычно используются для тестирования или для обеспечения безопасности внутренних интранет-служб (IIS, Exchange, Web Application Proxy, LDAPS, ADRMS, DirectAccess и т.п.), когда покупка сертификата у внешнего провайдера или разворачивание собственной PKI инфраструктуры не представляется возможным.
Совет: Вы также можете использовать бесплатные SSL сертификаты от Let’s Encrypt, которые подходят для использования на IIS и других веб-серверах.
Для создания сертификата необходимо указать параметры -DnsName (DNS имя сервера, которое может быть произвольным и отличаться от localhost) и -CertStoreLocation (раздел локального хранилища сертификатов, в который будет помещён созданный сертификат).
Для создания нового SSL сертификата с DNS именем test.contoso.com (полное доменное имя) и добавления его в личное хранилище сертификатов компьютера, выполните следующую команду:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName test.contoso.com -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My
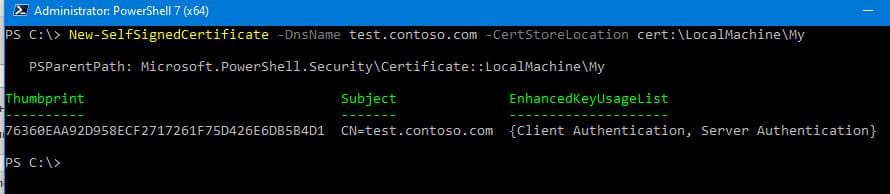
Команда вернёт отпечаток сертификата (Thumbprint), Subject и EnhancedKeyUsageList. По умолчанию такой сертификат можно использовать для аутентификации клиента (Client Authentication (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2)) или сервера (Server Authentication (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1)).
Если команда выполняется без административных прав, может возникнуть ошибка:
New-SelfSignedCertificate : CertEnroll::CX509Enrollment::_CreateRequest: Access denied. 0x80090010 (-2146893808 NTE_PERM)
При использовании нестандартного криптографического провайдера CSP (например, параметров -KeyAlgorithm «ECDSA_secP256r1» -Provider ‘Microsoft Smart Card Key Storage Provider’), убедитесь, что он установлен на вашем компьютере. В противном случае появится ошибка:
New-SelfSignedCertificate: CertEnroll::CX509Enrollment::_CreateRequest: Provider type not defined. 0x80090017 (-2146893801 NTE_PROV_TYPE_NOT_DEF)
Самоподписанный сертификат создаётся по умолчанию со следующими параметрами:
— Криптографический алгоритм: RSA;
— Размер ключа: 2048 бит;
— Использование ключа: Client Authentication и Server Authentication;
— Сертификат может использоваться для: Digital Signature, Key Encipherment;
— Срок действия сертификата: 1 год;
— Криптопровайдер: Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider.
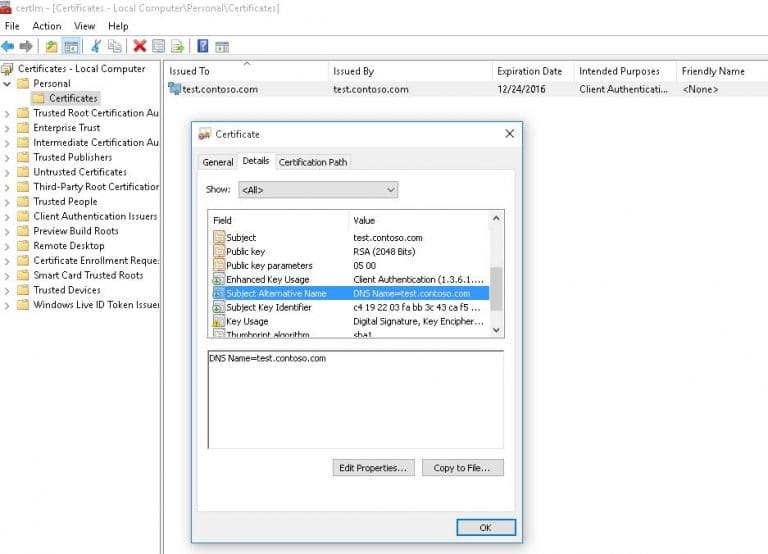
Эта команда создаёт новый сертификат и импортирует его в личное хранилище компьютера. Чтобы убедиться в его успешном добавлении, откройте оснастку certlm.msc и проверьте наличие сертификата в разделе Personal (Личный).
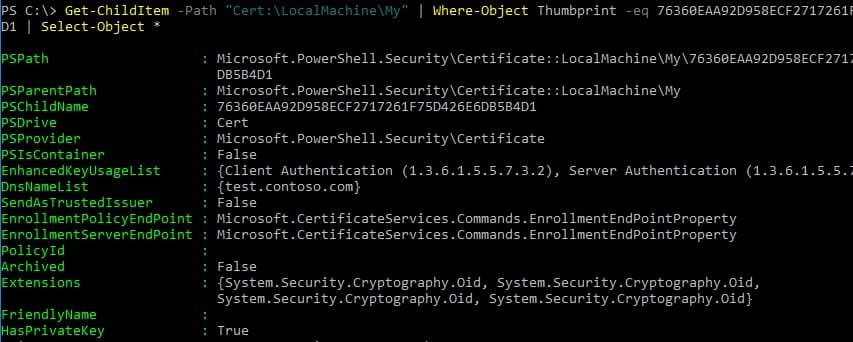
Чтобы вывести все параметры созданного сертификата по его отпечатку (Thumbprint), используйте командлет Get-ChildItem:
Get-ChildItem -Path "Cert:\LocalMachine\My" | Where-Object Thumbprint -eq 76360EAA92D958ECF2717261F75D426E6DB5B4D1 | Select-Object *
Примечание: Срок действия самоподписанного сертификата составляет 1 год с момента его создания. Чтобы задать другой срок действия, используйте параметр -NotAfter. Например, для создания сертификата с трехлетним сроком действия выполните следующие команды:
$todaydate = Get-Date
$add3year = $todaydate.AddYears(3)
New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName test.contoso.com -NotAfter $add3year -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My
Создание цепочки сертификатов
Вы можете создать цепочку сертификатов, сначала выпустив корневой сертификат (CA), а затем на его основе сгенерировать SSL сертификат сервера:
$rootCert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -Subject "CN=TestRootCA,O=TestRootCA,OU=TestRootCA" -KeyExportPolicy Exportable -KeyUsage CertSign,CRLSign,DigitalSignature -KeyLength 2048 -KeyUsageProperty All -KeyAlgorithm 'RSA' -HashAlgorithm 'SHA256' -Provider "Microsoft Enhanced RSA and AES Cryptographic Provider"
New-SelfSignedCertificate -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My -DnsName "test2.contoso.com" -Signer $rootCert -KeyUsage KeyEncipherment,DigitalSignature
Для изменения длины ключа и алгоритма шифрования, используйте параметры -KeyAlgorithm, -KeyLength и -HashAlgorithm:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -KeyAlgorithm RSA -KeyLength 2048 -HashAlgorithm "SHA256"
Если на компьютере установлен модуль TPM 2.0, его можно использовать для защиты ключа:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -Type Custom -Provider "Microsoft Platform Crypto Provider"
Создание SAN (SubjectAltName) сертификата с помощью PowerShell
С помощью командлета New-SelfSignedCertificate можно создать сертификат с несколькими именами Subject Alternative Names (SAN).
Если сертификат содержит несколько имен, первое имя из параметра DnsName используется в качестве CN (Common Name). Например, для создания сертификата с несколькими именами используйте следующую команду:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName adfs1.contoso.com,web_gw.contoso.com,enterprise_reg.contoso.com -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My
Также можно создать wildcard сертификат для всего домена, указав имя сервера как *.contoso.com:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My -DnsName *.contoso.com
Вы можете привязать сертификат не только к DNS имени, но и к IP адресу. Для этого используйте параметр -TextExtension вместо -DnsName:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -TextExtension @("2.5.29.17={text}IPAddress=10.10.2.3&DNS=TESTServer1&DNS=TESTServer1.local")
Как вы видите, в поле Subject Alternative Name теперь содержится IP адрес.
Экспорт самоподписанного сертификата в Windows
Для экспорта сертификата с закрытым ключом в pfx файл, защищенный паролем, нужно получить его отпечаток (Thumbprint). Сначала задайте пароль и преобразуйте его в формат SecureString. Значение Thumbprint можно скопировать из вывода команды New-SelfSignedCertificate:
$CertPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString -String "YourPassword" -Force -AsPlainText
Export-PfxCertificate -Cert cert:\LocalMachine\My\2779C0490D558B31AAA0CEF2F6EB1A5C2CA83B30 -FilePath C:\test.pfx -Password $CertPassword
Чтобы экспортировать открытый ключ сертификата, выполните команду:
Export-Certificate -Cert Cert:\LocalMachine\My\2779C0490D558B31AAA0CEF2F6EB1A5C2CA83B30 -FilePath C:\testcert.cer
Проверьте, что в указанном каталоге появился CER (PFX) файл сертификата. Если щелкнуть по нему правой клавишей и выбрать пункт меню Install Certificate, можно с помощью мастера импорта сертификатов добавить сертификат в корневые доверенные сертификаты компьютера.
Выберите Store location -> Local Machine, Place all certificates in the following store -> Trusted Root Certification Authorities.
Создание сертификата для подписи кода (Code Signing)
Начиная с PowerShell 5, командлет New-SelfSignedCertificate можно использовать для создания сертификатов типа Code Signing:
$cert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -Subject "Cert for Code Signing" -Type CodeSigningCert -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My
Для подписи вашего PowerShell скрипта этим сертификатом используйте следующую команду:
Set-AuthenticodeSignature -FilePath C:\PS\test_script.ps1 -Certificate $cert
Если при выполнении команды появится предупреждение UnknownError, значит этот сертификат недоверенный, т.к. находится в персональном хранилище сертификатов пользователя.
Нужно переместить его в корневые сертификаты (не забывайте периодически проверять хранилище сертификатов Windows на наличие недоверенных сертфикатов и обновлять списки корневых сертификатов):
Move-Item -Path $cert.PSPath -Destination "Cert:\CurrentUser\Root"
Теперь вы можете использовать этот самоподписанный сертификат для подписи PowerShell скриптов, драйверов или приложений.
Создание самоподписанного SSL сертификата SHA-256 для IIS
При создании самоподписанного сертификата для IIS через консоль Internet Information Manager (пункт меню Create Self-Signed Certificate) создаётся сертификат с использованием алгоритма SHA-1, который многими браузерами считается небезопасным. Чтобы создать сертификат с использованием алгоритма SHA-256, используйте командлет New-SelfSignedCertificate.
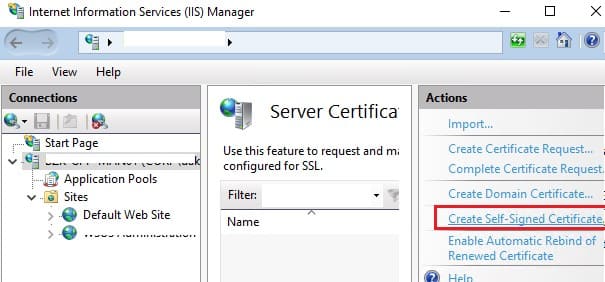
Вы можете привязать самоподписанный сертификат SHA-256, созданный в PowerShell, к веб-сайту в IIS. Сертификат, помещённый в хранилище сертификатов компьютера, автоматически становится доступен для сайтов в IIS.
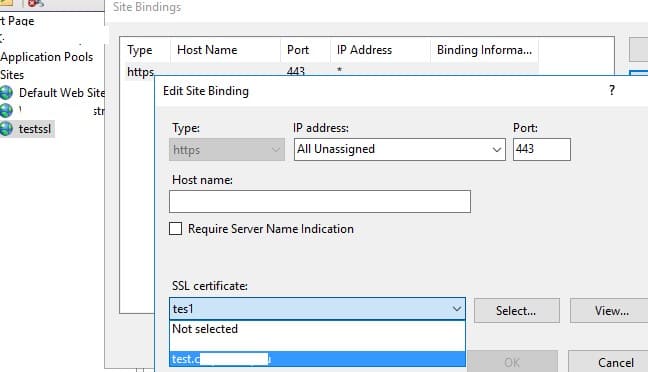
Откройте консоль IIS Manager, выберите сайт и в настройках Site Binding укажите созданный вами сертификат, затем сохраните изменения.
Для привязки SSL сертификата к сайту по его отпечатку используйте команду:
New-IISSiteBinding -Name "Default Web Site" -BindingInformation "*:443:" -CertificateThumbPrint $yourCert.Thumbprint -CertStoreLocation "Cert:\LocalMachine\My" -Protocol https

We need to a create self-signed certificate for local development so that the local development server behaves similar to a live production server. Additionally the certificate must not generate warnings in the browser (Chromium based browsers only) that the certificate is self-signed and can’t be trusted.
Developing locally with plain http is just fine. But sometimes we need to mimic development with production so that TLS encryption via https is available also on our development machines. We also don’t want to see ugly security warnings from browsers. The following article shows how to create self-signed certificates on Windows that doesn’t generate browser warnings on Chrome and other Chromium based browsers.
The article is a bit long but please grab a coffee and follow along. The result is worth the effort as you only need to generate the certificate once in a very long time. I set the expiry date 10 years in the future for the domains I create for local development.
Goal: Create an imaginary domain pdb.oak.san with a self-signed certificate that works on major browsers (except Firefox) without generating a warning. Works great on Chromium based browsers like Chrome, Canary, Microsoft Edge and Opera, IE.
Step 1: Setup hostname
- Open Notepad in Administrator mode: Click Windows Start icon in task bar and start typing Notepad, right click the Notepad icon and click Run as administrator
- Inside Notepad, open the file:
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts - We want to create an imaginary domain:
pdb.oak.san, add the following line to the hosts file:
- Save the file and close
Step 2: Create a client-side self-signed certificate
- Open PowerShell in Administrator mode: Click Windows Start icon in task bar and start typing PowerShell, right click the PowerShell icon and click Run as administrator
- Type the following to generate a self-signed certificate for domain
pdb.oak.sanwith friendly namepdb.oak.santhat expires after 10 years:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\My -DnsName "pdb.oak.san" -FriendlyName "pdb.oak.san" -NotAfter (Get-Date).AddYears(10)
- You should get the following output

Step 3: Copy the certificate created in Step 2 to Trusted Root Certification Authorities, then export it
- Open Management Console for Certificates: Click Windows Start icon and start typing certificates, click Manage computer certificates
- On the left panel, click Personal -> Certificates, you should see the client-side certificate for pdb.oak.san created above in Step 2

- On the left panel, open the tree for (but don’t left click the folder) Certification Authorities -> Certificates
- With the right mouse button, drag and drop the certificate to the location opened in the previous step

- Now export the certificate: right-click the certificate, All Tasks -> Export…

- Welcome screen appears, click Next
- Select Yes, export the private key, click Next
- Keep the default values for .PFX, click Next
- Type a password for the private key, click Next
- Browse for a location and give the certificate a name (cert.pfx), click Next
- Finally click Finish
- You will get a notice that the export was successful
Step 4: Create the server-side certificate and key
- Pre-requisite: you need to have OpenSSL https://www.openssl.org/ installed. Since you are a developer and on Windows, it’s highly likely you already have https://git-scm.com/ installed, so you should also have OpenSSL installed. Otherwise we recommend installing Git for Windows with Git Bash support – this will automatically also install OpenSSL.
- Open Command Prompt and change directory to the location where you exported the certificate with .PFX extension cert.pfx in Step 3 above.
- Type the following commands in the Command Prompt one by one. When prompted for password, type the password you used in Step 3 above when exporting the .PFX certificate.
$ openssl pkcs12 -in cert.pfx -nocerts -out key.pem -nodes $ openssl pkcs12 -in cert.pfx -nokeys -out cert.pem $ openssl rsa -in key.pem -out server.key

- You should now have the following files in the folder, we will be using the cert.pem and server.key files. You can delete the other files if you want to.
cert.pem --> KEEP server.key --> KEEP cert.pfx key.pem
Step 5: Test
- You can use Apache or Nginx to test the https connection for the pdb.oak.san domain. We will create a simple Go server as it can be created really fast with a few lines of code. Create a file called main.go and type the code below. Make sure cert.pem and server.key is in the same folder as the main.go file.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
func handleHome(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
_, _ = fmt.Fprintln(w, "Home page to test the TLS cert and secure https connection")
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/", handleHome)
s:=http.Server{}
_ = s.ListenAndServeTLS("cert.pem", "server.key")
}
- Build and run the Go server:
go build main.go, then run the resulting executable programmain.exe - Now if we visit https://pdb.oak.san/ in a browser, we can see the home page with the following content: “Home page to test the TLS cert and secure https connection”

- We can also check the certificate by clicking on the lock icon in the browser address bar:
For Nginx Users
To test on Nginx instead of writing Go code, you can use the configuration below.
- Make sure to copy your cert.pem and server.key to the locations for ssl_certificate and ssl_certificate_key.
- Folder paths like
C:\Users\sanji\pdn\pdb.oak.san\wwwshould of course match the locations in your own computer.
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name pdb.oak.san;
root C:\Users\sanji\pdn\pdb.oak.san\www;
access_log C:\Users\sanji\pdn\pdb.oak.san\logs\access.log;
error_log C:\Users\sanji\pdn\pdb.oak.san\logs\error.log;
index index.html;
ssl_certificate C:\Users\sanji\pdn\pdb.oak.san\ssl\cert.pem;
ssl_certificate_key C:\Users\sanji\pdn\pdb.oak.san\ssl\server.key;
}
The video below shows the steps I took to setup SSL on an imaginary domain on my local machine. The video is 20 minutes; maybe I could have been done the video in 10 minutes or less. But here I am showing the actual problems I am running into and the steps I am taking to solve them.
Setting up domains, servers and certificates in real-life is not without problems. This is not a scripted video. It shows the problems I face and how I resolve them.
This a scenario where you have created personal certificates and digitally signed them on your own and now you want them available and trusted on another machine.
Most Windows administrators, who are familiar with PKI, know about the MakeCert.exetool, which allows to create self-signed certificates. This tool is part of the Microsoft .NET Framework SDK and Microsoft Windows SDK. You can create a self-signed certificate using the built-in PowerShell cmdlet New-SelfSignedCertificate without using additional tools.
Contents:
- New-SelfSignedCertificate: Creating a Self-Signed Certificate with PowerShell
- Create a Certificate with the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) Using PowerShell
- How to Export a Self-Signed Certificate on Windows?
- Generating a Self-Signed Certificate for Code Signing on Windows
- Creating SHA-256 Self-Signed SSL Certificate in IIS on Windows Server
New-SelfSignedCertificate: Creating a Self-Signed Certificate with PowerShell
To create a self-signed certificate with PowerShell, you can use the built-in New-SelfSignedCertificate cmdlet, which is a part of the PowerShell PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) module:
To list all available cmdlets in the PKI module, run the command:
Get-Command -Module PKI
It is recommended to use self-signed certificates for testing/developing tasks or to provide certificates for internal Intranet services (IIS, Exchange, Web Application Proxy, LDAPS, ADRMS, DirectAccess, etc.) if you cannot deploy PKI/CA infrastructure or purchase a trusted certificate from an external provider.
To create a certificate, you have to specify the values of –DnsName (name of a server, the name may be arbitrary and even different from the current hostname) and -CertStoreLocation (a local certificate store in which the generated certificate will be placed).
To create a new SSL certificate (with the default SSLServerAuthentication type) for the DNS name test.contoso.com (use an FQDN name) and place it to the personal certificates on a computer, run the following command:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName test.contoso.com -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My
The command will return the Thumbprint, Subject, and EnhancedKeyUsageList of the new certificate. By default, such a certificate can be used for Client Authentication (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2) or Server Authentication (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1).
If you run this command in a non-elevated PowerShell prompt (without local admin permissions), an error will appear:
New-SelfSignedCertificate : CertEnroll::CX509Enrollment::_CreateRequest: Access denied. 0x80090010 (-2146893808 NTE_PERM)
If you have specified a non-standard cryptographic provider (CSP) ( for example, using the -KeyAlgorithm "ECDSA_secP256r1" -Provider "Microsoft Smart Card Key Storage Provider"parameters), make sure it is installed on your computer (the default is Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider). Otherwise, an error will appear:
New-SelfSignedCertificate: CertEnroll::CX509Enrollment::_CreateRequest: Provider type not defined. 0x80090017 (-2146893801 NTE_PROV_TYPE_NOT_DEF).
By default, a self-signed certificate is generated with the following settings:
- Cryptographic algorithm: RSA;
- Key length: 2048 bit;
- Acceptable key usage: Client Authentication and Server Authentication;
- The certificate can be used for: Digital Signature, Key Encipherment;
- Certificate validity period: 1 year;
- Crypto provider: Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider.
This command creates a new certificate and imports it into the computer’s personal certificate store. Open the certlm.msc MMC snap-in and make sure that a new certificate appears in the Personal section of the computer’s certificate store.
Using the Get-ChildItem cmdlet, you can display all the parameters of the created certificate by its Thumbprint:
Get-ChildItem -Path "Cert:\LocalMachine\My" | Where-Object Thumbprint -eq 2175A76B10F843676951965F52A718F635FFA043 | Select-Object *
PSPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Security\Certificate::LocalMachine\My\2175A76B10F843676951965F52A718F635FFA043
PSParentPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Security\Certificate::LocalMachine\My
PSChildName : 2175A76B10F843676951965F52A718F635FFA043
PSDrive : Cert
PSProvider : Microsoft.PowerShell.Security\Certificate
PSIsContainer : False
EnhancedKeyUsageList : {Client Authentication (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2), Server Authentication (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1)}
DnsNameList : {test.contoso.com}
SendAsTrustedIssuer : False
EnrollmentPolicyEndPoint : Microsoft.CertificateServices.Commands.EnrollmentEndPointProperty
EnrollmentServerEndPoint : Microsoft.CertificateServices.Commands.EnrollmentEndPointProperty
PolicyId :
Archived : False
Extensions : {System.Security.Cryptography.Oid, System.Security.Cryptography.Oid,
System.Security.Cryptography.Oid, System.Security.Cryptography.Oid}
FriendlyName :
IssuerName : System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X500DistinguishedName
NotAfter : 12/4/2023 5:35:15 PM
NotBefore : 12/4/2022 5:15:15 PM
HasPrivateKey : True
PrivateKey :
PublicKey : System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.PublicKey
RawData : {48, 130, 3, 45...}
SerialNumber : 6797F5E3F870478D4D3798BEB291DBF3
SubjectName : System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X500DistinguishedName
SignatureAlgorithm : System.Security.Cryptography.Oid
Thumbprint : 2175A76B10F843676951965F52A718F635FFA043
Version : 3
Handle : 2834444631568
Issuer : CN=test.contoso.com
Subject : CN=test.contoso.com
Note. This self-signed certificate will expire 1 year after it was created. You can set a different certificate validity period using the –NotAfter option. For example, you can issue an SSL/TLS certificate with a three-year validity period with the following commands:
$todaydt = Get-Date
$3years = $todaydt.AddYears(3)
New-SelfSignedCertificate -dnsname test.contoso.com -notafter $3years -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My
You can create a certificate chain. First, a root certificate (CA) is created. Then based on it, an SSL server certificate is generated:
$rootCert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -Subject 'CN=TestRootCA,O=TestRootCA,OU=TestRootCA' -KeyExportPolicy Exportable -KeyUsage CertSign,CRLSign,DigitalSignature -KeyLength 2048 -KeyUsageProperty All -KeyAlgorithm 'RSA' -HashAlgorithm 'SHA256' -Provider 'Microsoft Enhanced RSA and AES Cryptographic Provider'
New-SelfSignedCertificate -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My -DnsName "test2.contoso.com" -Signer $rootCert -KeyUsage KeyEncipherment,DigitalSignature
To change the certificate key length and encryption algorithm, you need to use the -KeyAlgorithm, -KeyLength, and -HashAlgorithm options. For example:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -KeyAlgorithm RSA -KeyLength 2048 -HashAlgorithm "SHA256" …
The Microsoft Platform Crypto Provider allows you to use the device’s Trusted Platform Module chip (TPM 2.0) to protect the key.
New-SelfSignedCertificate -Type Custom -Provider "Microsoft Platform Crypto Provider" ...
You can generate a document encryption certificate to protect your document and email. Use the DocumentEncryptionCert type when creating a cert:
$Params = @{
"DnsName" = "myhostname"
"CertStoreLocation" = "Cert:\\CurrentUser\\My"
"KeyUsage" = "KeyEncipherment","DataEncipherment","KeyAgreement"
"Type" = "DocumentEncryptionCert"
}
$doccert=New-SelfSignedCertificate @Params
Check the certificate EnhancedKeyUsageList value:
$doccert|select EnhancedKeyUsageList
{Document Encryption (1.3.6.1.4.1.311.80.1)}
Create a Certificate with the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) Using PowerShell
The New-SelfSignedCertificate cmdlet allows you to create a certificate with several different Subject Alternative Names (SANs).
Note. The Makecert.exetool, unlike the New-SelfSignedCertificate cmdlet, cannot create SAN and Wildcard certificates.[/alert]
If you want to create a certificate with multiple names, the first name of the DnsName parameter will be used as the CN (Common Name) of the certificate. For example, let’s create a self-signed SAN certificate with the following names:
- Subject Name (CN):
adfs1.contoso.com - Subject Alternative Name (DNS):
web_gw.contoso.com - Subject Alternative Name (DNS):
enterprise_reg.contoso.com
You can the following command to generate a certificate with different common names (or even for multiple domains):
New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName adfs1.contoso.com,web_gw.contoso.com,enterprise_reg.contoso.com -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My
Also, you can generate a wildcard certificate for the entire domain namespace by specifying *.contoso.com as the server name.
New-SelfSignedCertificate -certstorelocation cert:\localmachine\my -dnsname *.contoso.com
You can generate a self-signed certificate not only for a DNS hostname but also for an IP address. To do this, you need to use -TextExtension instead of the -DnsName parameter. For example:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -TextExtension @("2.5.29.17={text}IPAddress=10.1.2.3&DNS=TESTServer1&DNS=TESTServer1.local")
As you can see, the Subject Alternative Name field now contains the IP address of the host and its DNS names.
How to Export a Self-Signed Certificate on Windows?
To export the generated certificate with a private key to a password-protected PFX file, you need to specify its Thumbprint. It can be copied from the results of the New-SelfSignedCertificate command. You also need to specify the certificate’s security password and convert it to a SecureString format:
$CertPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString -String “YourPassword” -Force –AsPlainText
Export-PfxCertificate -Cert cert:\LocalMachine\My\2779C7928D055B21AAA0Cfe2F6BE1A5C2CA83B30 -FilePath C:\test.pfx -Password $CertPassword
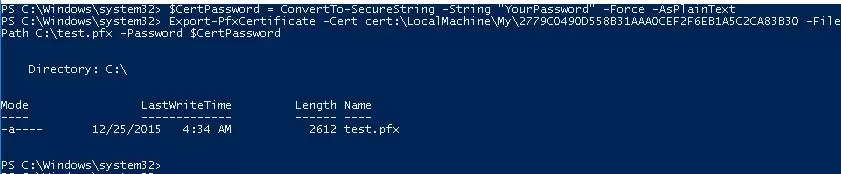
You can export the certificate public key as follows (the private key is not included in the export):
Export-Certificate -Cert Cert:\LocalMachine\My\2779C7928D055B21AAA0Cfe2F6BE1A5C2CA83B30 -FilePath C:\tstcert.cer
Make sure the *.CER (PFX) certificate file appears in the specified directory. If you right-click it and select the “Install Certificate” menu item, you can use the Certificate Import Wizard to add the certificate to the trusted root certificates on your computer.
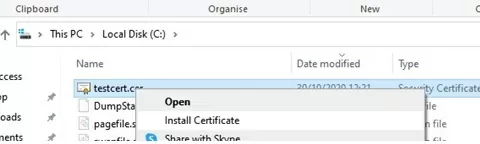
Select Cert Store location -> Local Machine, Place all certificates in the following store -> Trusted Root Certification Authorities.
[alert]You can create a certificate and immediately import it into the Trusted Root Certificate store of the computer using the commands:
$SelfSignCert=New-SelfSignedCertificate …..
$certFile = Export-Certificate -Cert $SelfSignCert -FilePath C:\ps\export-certname.cer
Import-Certificate -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\AuthRoot -FilePath $certFile.FullName
You can deploy this public key or the certificate file itself on all user computers and servers in the Active Directory domain using GPO (How to deploy certificates to users with GPO?).
Generating a Self-Signed Certificate for Code Signing on Windows
In PowerShell 3.0, the New-SelfSifgnedCertificate cmdlet only generates SSL certificates which cannot be used to sign the driver code, application, or script (unlike the certificates generated by the MakeCert utility).
You can use the New-SelfSifgnedCertificate cmdlet to issue Code Signing certificates in PowerShell version 5.0 and newer.
To create a self-signed certificate for sign application code, run the command:
$cert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -Subject "My Code Signing Certificate” -Type CodeSigningCert -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My
Now you can sign your PowerShell script file with a self-signed certificate:
Set-AuthenticodeSignature -FilePath C:\PS\my_posh_script.ps1 -Certificate $cert
If you are receiving an UnknownError warning when executing the command, this means that the certificate is not trusted, because it is located in the user’s personal certificates store.
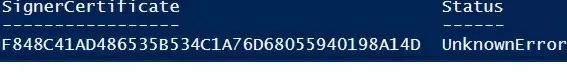
You need to move it to the Trusted Root Certificate store (don’t forget to periodically scan the Windows certificate root store for untrusted and suspicious certificates and update the lists of trusted root certificates).
Move-Item -Path $cert.PSPath -Destination "Cert:\CurrentUser\Root"
Now you can use this self-signed certificate to sign your PowerShell scripts, drivers, or applications.
Creating SHA-256 Self-Signed SSL Certificate in IIS on Windows Server
Please note that when creating a self-signed certificate for IIS through the Internet Information Manager console (using Create Self-Signed Certificate action menu item), an SSL certificate is created using the SHA-1 encryption algorithm. Such certificates are considered untrusted by many browsers and cannot be used to establish a secure connection (or you may see other SSL warnings and errors). The New-SelfSignedCertificate cmdlet allows you to create a more popular type of certificate using the SHA-256 encryption algorithm.
You can bind a self-signed SHA-256 certificate generated with PowerShell to an IIS site on Windows Server. If you create an SSL certificate using PowerShell and place it in the computer’s certificate store, it will automatically be available to IIS sites.
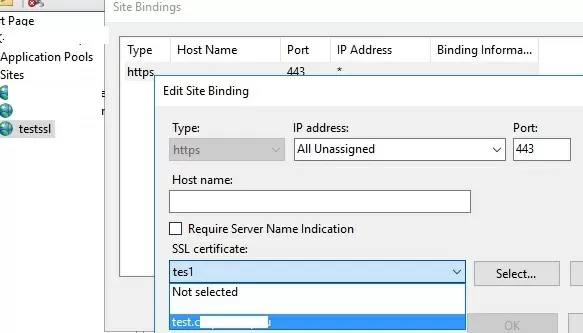
Open the IIS Manager console (inetmgr.exe), select your site, and then select the certificate you created in the Site Binding options. Save your changes.
You can also bind an SSL certificate by its thumbprint to an IIS site:
New-IISSiteBinding -Name "Default Web Site" -BindingInformation "*:443:" -CertificateThumbPrint $yourCert.Thumbprint -CertStoreLocation "Cert:\LocalMachine\My" -Protocol https
A Step-by-Step Guide for Creating Self-Signed SSL in Windows 10
A self-signed certificate is a certificate that is signed by its own creator rather than by a certificate authority (CA). Self-signed certificates can be useful for testing purposes or internal uses but are not recommended for public-facing production websites as they will generate browser warnings. In this guide, we will cover steps on how to create self-signed certificate in Windows 10.
Overview of Self-Signed Certificates
Create a Self-Signed Certificate Using the Certificates Snap-in
Here are the steps to create a self-signed certificate using the Certificates console in Windows 10:
Export the Self-Signed Certificate
To use the new self-signed certificate, it needs to be exported to a file. Here’s how to export the cert:
The exported .cer file can then be imported or installed on servers or devices to utilize the self-signed certificate for encryption and identification purposes.
Create a Self-Signed Certificate in PowerShell
Self-signed certificates can also be generated using PowerShell on Windows 10. Here are the steps:
$certificate = New-SelfSignedCertificate `
-Subject "CN=SelfSignedCert" `
-CertStoreLocation "Cert:\CurrentUser\My" `
-KeyExportPolicy Exportable `
-KeySpec Signature `
-KeyLength 2048 `
-KeyAlgorithm RSA `
-HashAlgorithm SHA256 `
-Provider "Microsoft Enhanced RSA and AES Cryptographic Provider" `
-NotAfter (Get-Date).AddYears(5) -Verbose
$certificatePath = "C:\Users\username\Desktop\self-signed.cer"
Export-Certificate -Cert $certificate -FilePath $certificatePath
cd C:\Users\username\Desktop
.\Create-Self-SignedCertificate.ps1
The exported .cer file contains the new self-signed certificate and can be installed or distributed as needed.
Install the Self-Signed Certificate
To use a self-signed certificate for server encryption like HTTPS or application authentication, it needs to be installed after export:
Install on Windows Server
Import-Certificate -FilePath C:\path\to\cert.cer -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\My
netsh http add sslcert ipport=0.0.0.0:443 certhash=XXXXXXXXXX appid="{00112233-4455-6677-8899-AABBCCDDEEFF}"
Use the certificate thumbprint for the certhash value.
Install on Windows Client
The self-signed certificate is now trusted at the system level and can be used for client authentication purposes.
Remove or Delete a Self-Signed Certificate
If a self-signed certificate is no longer needed, it can be deleted:
Remove in Certificates Console
Remove in PowerShell
Identify the certificate thumbprint, then run:
Remove-Item Cert:\LocalMachine\My\THUMBPRINT -Force
This will permanently delete the self-signed certificate.
Conclusion
In summary, self-signed certificates are not issued by a certificate authority so they enable encryption without verified trust. While useful for testing and development purposes, self-signed certificates will generate errors on public production websites. On Windows 10, creating your own self-signed certificate is straightforward using either the Certificates console or PowerShell commands. Be sure to export the certificate and install it as a trusted root on systems that need to trust the self-signed cert. Follow the guidelines covered in this article to properly generate, distribute, manage, and delete self-signed certificates on your Windows devices and servers. Used appropriately, self-signed certificates provide a quick way to test and deploy transport layer security.
Why are self-signed certificates considered untrusted?
Self-signed certificates are not issued by a trusted certificate authority that validates the requester’s identity. Anyone can generate a self-signed cert, so they are inherently untrusted until explicitly installed as trusted on a system or device.
Can I use a self-signed certificate for a public production website?
Self-signed certificates are not recommended for public-facing production websites because visitors will receive browser errors about the certificate being untrusted. Public sites should use certificates signed by a trusted certificate authority.
What are some typical uses for a self-signed certificate?
Self-signed certificates are commonly used for testing, development environments, intranets, IoT communications, and anywhere untrusted/insecure connections are acceptable. They are not suitable for public production websites.
What key size should I make a self-signed certificate?
For modern encryption strength, self-signed certificates should be generated with a 2048-bit or higher RSA key size. 1024-bit keys are considered insecure and should not be used.
How do I resolve trust warnings for a self-signed certificate?
Install the self-signed certificate as a trusted root certificate on any device that needs to trust it. On Windows, this means installing it in the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store. On Macs, add it as a trusted root in Keychain Access. On Linux, add it to the appropriate trusted certificates directory. Mobile devices also provide certificate installation options to trust specific self-signed certs.
What is the maximum validity period for a self-signed certificate?
When generating a self-signed certificate in Windows, the maximum validity period is 10 years. However, limitations may vary on other platforms. For better security, most recommendations suggest using shorter validity periods like 1-2 years for self-signed certs.
Can I sign a self-signed certificate with my own intermediates?
No, self-signed certificates are not issued by a root CA, so they cannot be chained to intermediate certificates. A self-signed cert can only ever have a single tier validity coming from its own self-generated private key signature.
Is there a size limit for self-signed certificates?
There is generally no inherent size limit. However, there may be restrictions imposed by the application or system that will be consuming the certificate. Most certificates are well under 5KB. Larger certificates may impact performance.
What characters can I use in the subject name for a self-signed certificate?
RFC5280 recommends using only English upper and lowercase letters, digits, and the hyphen for maximum compatibility in X.509 certificate subjects. Other symbols and special characters can produce issues unless specifically required.
