Сетевой протокол SMB (Server Message Block) используется для предоставления совместного удаленного доступа к файлам, принтерам и другим устройствам через порт TCP 445. В этой статье мы рассмотрим: какие версии (диалекты) протокола SMB доступны в различных версиях Windows (и как они соотносятся с версиями samba в Linux); как определить версию SMB на вашем компьютере; и как включить/отключить клиент и сервер SMBv1, SMBv2 и SMBv3.
Содержание:
- Версии протокола SMB в Windows
- Как проверить поддерживаемые версии SMB в Windows?
- Вывести используемые версии SMB с помощью Get-SMBConnection
- Об опасности использования SMBv1
- Включение и отключение SMBv1, SMBv2 и SMBv3 в Windows
Версии протокола SMB в Windows
Есть несколько версии протокола SMB (диалектов), которые последовательно появлялись в новых версиях Windows:
Для реализации протокола SMB в Linux/Unix системах используется samba. В скобках мы указали в каких версиях samba поддерживается каждый диалект SMB.
- CIFS — Windows NT 4.0;
- SMB 1.0 — Windows 2000;
- SMB 2.0 — Windows Server 2008 и Windows Vista SP1 (поддерживается в Samba 3.6);
- SMB 2.1 — Windows Server 2008 R2 и Windows 7 (поддерживается в Samba 4.0);
- SMB 3.0 — Windows Server 2012 и Windows 8 (поддерживается в Samba 4.2);
- SMB 3.02 — Windows Server 2012 R2 и Windows 8. 1 (не поддерживается в Samba);
- SMB 3.1.1 – Windows Server 2016 и Windows 10 (не поддерживается в Samba).
Начиная с версии Samba 4.14, по умолчанию используется SMB2.1.
При сетевом взаимодействии по протоколу SMB между клиентом и сервером используется максимальная версия протокола, поддерживаемая одновременно и клиентом, и сервером.
Ниже представлена сводная таблица, по которой можно определить версию протокола SMB, которая выбирается при взаимодействии разных версий Windows:
| Операционная система | Win 10, Server 2016 | Windows 8.1, Server 2012 R2 |
Windows 8, Server 2012 |
Windows 7, Server 2008 R2 |
Windows Vista, Server 2008 |
Windows XP, Server 2003 и ниже |
| Windows 10 ,
Windows Server 2016 |
SMB 3.1.1 | SMB 3.02 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows 8.1 , Server 2012 R2 |
SMB 3.02 | SMB 3.02 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows 8 , Server 2012 |
SMB 3.0 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows 7, Server 2008 R2 |
SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows Vista, Server 2008 |
SMB 2.0 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows XP, 2003 и ниже | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 |
К примеру, при подключении клиентского компьютера с Windows 8.1 к файловому серверу с Windows Server 2016 будет использоваться протокол SMB 3.0.2.
Согласно таблице Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 для доступа к общим файлам и папкам на сервере могут использовать только SMB 1.0, который в новых версиях Windows Server (2012 R2 / 2016) может быть отключен. Таким образом, если в вашей инфраструктуре одновременно используются компьютеры с Windows XP (снятой с поддержки), Windows Server 2003/R2 и сервера с Windows Server 2012 R2/2016/2019, устаревшие клиенты не смогут получить доступ к файлам и папкам на файловом сервере с новой ОС.
Если Windows Server 2016/2012 R2 с отключенным SMB v1.0 используется в качестве контроллера домена, значить клиенты на Windows XP/Server 2003 не смогут получить доступ к каталогам SYSVOL и NETLOGON на контроллерах домена и авторизоваться в AD.
На старых клиентах при попытке подключиться к ресурсу на файловом сервере с отключенным SMB v1 появляется ошибка:
The specified network name is no longer available
Как проверить поддерживаемые версии SMB в Windows?
Рассмотрим, как определить, какие версии протокола SMB поддерживаются на вашем компьютере Windows.
В Windows 10, 8.1 и Windows Server 2019/2016/2012R2 вы можете проверить состояние различных диалектов SMB протокола с помощью PowerShell:
Get-SmbServerConfiguration | select EnableSMB1Protocol,EnableSMB2Protocol
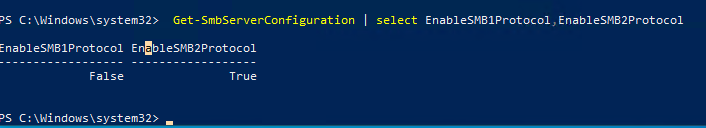
Данная команда вернула, что протокол SMB1 отключен (
EnableSMB1Protocol=False
), а протоколы SMB2 и SMB3 включены (
EnableSMB1Protocol=True
).
Обратите внимание, что протоколы SMBv3 и SMBv2 тесно связаны между собой. Нельзя отключить или включить отдельно SMBv3 или SMBv2. Они всегда включаются/отключаются только совместно, т.к. используют один стек.
В Windows 7, Vista, Windows Server 2008 R2/2008:
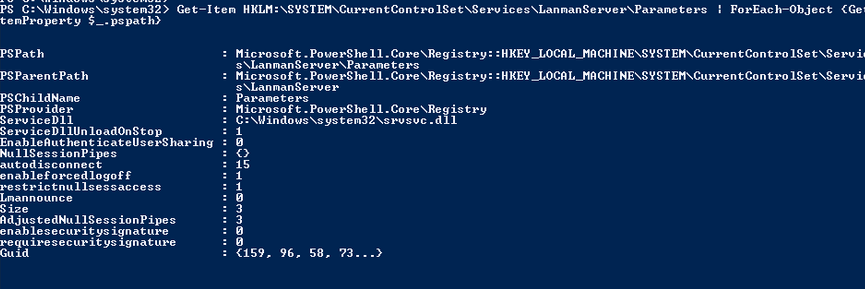
Get-Item HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters | ForEach-Object {Get-ItemProperty $_.pspath}
Если в данной ветке реестра нет параметров с именами SMB1 или SMB2, значить протоколы SMB1 и SMB2 по умолчанию включены.
Также в этих версиях Windows вы можете проверить, какие диалекты SMB разрешено использовать в качестве клиентов с помощью команд:
sc.exe query mrxsmb10
SERVICE_NAME: mrxsmb10 TYPE : 2 FILE_SYSTEM_DRIVER STATE : 4 RUNNING (STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, IGNORES_SHUTDOWN) WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) CHECKPOINT : 0x0 WAIT_HINT : 0x0
sc.exe query mrxsmb20
SERVICE_NAME: mrxsmb20 TYPE : 2 FILE_SYSTEM_DRIVER STATE : 4 RUNNING (STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, IGNORES_SHUTDOWN) WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) CHECKPOINT : 0x0 WAIT_HINT : 0x0
В обоих случаях службы запущены (
STATE=4 Running
). Значит Windows может подключаться как к SMBv1, так и к SMBv2 серверам.
Вывести используемые версии SMB с помощью Get-SMBConnection
Как мы говорили раньше, компьютеры при взаимодействии по протоколу SMB используют максимальную версию, поддерживаемую как клиентом, так и сервером. Для определения версии SMB, используемой для доступа к удаленному компьютеру можно использовать командлет PowerShell
Get-SMBConnection
:
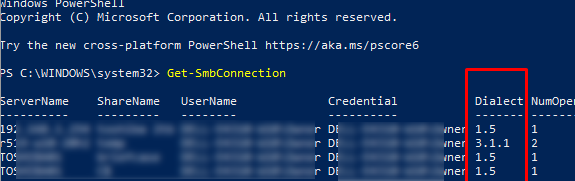
Версия SMB, используемая для подключения к удаленному серверу (ServerName) указана в столбце Dialect.
Можно вывести информацию о версиях SMB, используемых для доступа к конкретному серверу:
Get-SmbConnection -ServerName servername
Если нужно отобразить, используется ли SMB шифрование (появилось в SMB 3.0), выполните:
Get-SmbConnection | ft ServerName,ShareName,Dialect,Encrypted,UserName
В Linux вывести список SMB подключения и используемые диалекты в samba можно командой:
$ sudo smbstatus
Чтобы на стороне сервера вывести список используемых клиентами версий протокола SMB и количество клиентов, используемых ту или иную версию протокола SMB, выполните команду:
Get-SmbSession | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Dialect | Sort-Object -Unique
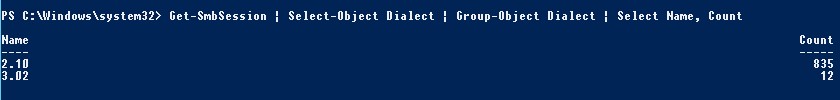
В нашем примере имеется 825 клиентов, подключенных к серверу с помощью SMB 2.1 (Windows 7/Windows Server 2008 R2) и 12 клиентов SMB 3.02.
С помощью PowerShell можно включить аудит версий SMB, используемых для подключения:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration –AuditSmb1Access $true
События подключения затем можно извлечь из журналов Event Viewer с помощью PowerShell:
Get-WinEvent -LogName Microsoft-Windows-SMBServer/Audit
Об опасности использования SMBv1
Последние несколько лет Microsoft из соображений безопасности планомерно отключает устаревший протокол SMB 1.0. Связано это с большим количеством критических уязвимостей в этом протоколе (вспомните историю с эпидемиями вирусов-шифровальщиков wannacrypt и petya, которые использовали уязвимость именно в протоколе SMBv1). Microsoft и другие IT компании настоятельно рекомендуют отказаться от его использования.
Однако отключение SMBv1 может вызвать проблемы с доступом к общий файлам и папкам на новых версиях Windows 10 (Windows Server 2016/2019) с устаревших версий клиентов (Windows XP, Server 2003), сторонних ОС (Mac OSX 10.8 Mountain Lion, Snow Leopard, Mavericks, старые версии Linux), различных старых NAS устройствах.
Если в вашей сети не осталось legacy устройств с поддержкой только SMBv1, обязательно отключайте эту версию диалекта в Windows.
В том случае, если в вашей сети остались клиенты с Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 или другие устройства, которые поддерживают только SMBv1, их нужно как можно скорее обновить или тщательно изолировать.
Включение и отключение SMBv1, SMBv2 и SMBv3 в Windows
Рассмотрим способы включения, отключения различных версий SMB в Windows. Мы рассматриваем отдельно включение клиента и сервера SMB (это разные компоненты).
Windows 10, 8.1, Windows Server 2019/2016/2012R2:
Отключить клиент и сервер SMBv1:
Disable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName smb1protocol
Отключить только SMBv1 сервер:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $false
Включить клиент и сервер SMBv1:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName smb1protocol
Включить только SMBv1 сервер:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $true
Отключить сервер SMBv2 и SMBv3:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $false
Включить сервер SMBv2 и SMBv3:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $true
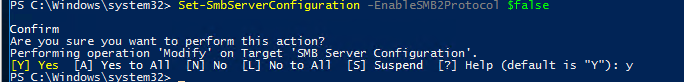
Windows 7, Vista, Windows Server 2008 R2/2008:
Отключить SMBv1 сервер:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB1 -Type DWORD -Value 0 –Force

Включить SMBv1 сервер:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB1 -Type DWORD -Value 1 –Force
Отключить SMBv1 клиент:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb20/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb10 start= disabled
Включить SMBv1 клиент:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/mrxsmb20/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb10 start= auto
Отключить SMBv2 сервер:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB2 -Type DWORD -Value 0 -Force
Включить SMBv2 сервер
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB2 -Type DWORD -Value 1 –Force
Отключить SMBv2 клиент:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb20 start= disabled
Включить SMBv2 клиент:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/mrxsmb20/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb20 start= auto
Для отключения сервера SMBv1 на всех компьютерах независимо от версии Windows можно распространить параметр реестра типа REG_DWORD с именем SMB1 и значением 0 (HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters)на через GPO.
Для отключения SMBv2 нужно в этой же ветке установить параметр SMB2=0.
Для отключения SMBv1 клиента нужно распространить такой параметр реестра:
- Key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\mrxsmb10
- Name: Start
- Type: REG_DWORD
- Value: 4
При отключении SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support в Windows вы можете столкнуться с ошибкой “0x80070035, не найден сетевой путь”, ошибкой при доступе к общим папкам, и проблемами обнаружения компьютеров в сетевом окружении. В этом случае вместо служба обозревателя компьютеров (Computer Browser) нужно использовать службы обнаружения (линк).
At a Glance
#
Default Ports
- SMB over NBT (NetBIOS over TCP/IP): 139
- SMB over TCP/IP: 445
SMB is a network communication protocol for providing shared access to files, printers, and serial ports between nodes on a network. It also provides an authenticated IPC (inter-process communication) mechanism.1
Windows SMB Ports and Protocols
#
Originally,
in Windows NT,
SMB ran on top of NBT (NetBIOS over TCP/IP),
which uses ports UDP 137 and 138,
and TCP 139.
With Windows 2000,
was introduced what Microsoft calls “direct hosting”,
the option to run “NetBIOS-less” SMB,
directly over TCP/445.
Older versions of Windows
(with NBT enabled)
will try to connect to both port 139
and 445 simultaneously,
while in newer versions,
port 139 is a fall-back port,
as clients will try to connect to port 445
by default.2
SMB Host Discovery
#
Refer to host discovert with nbtscan.
Server Version
#
Metasploit SMB Auxiliary Module 3
#
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/smb/smb_version
msf> set rhost 10.0.0.3
msf> run
Common Login Credentials
#
Backup and Management software requires dedicated user accounts on the server or local machine to function, and are often set with a weak password. 4
| Usernmae | Password |
|---|---|
| (blank) | (blank) |
Administrator admin guest |
(blank) admin password |
arcserve |
arcserve backup |
tivoli |
tivoli |
backupexec |
backupexec backup |
test |
test |
Enumeration
#
enum4linux 5
#
With credentials:
enum4linux -a -u "<username>" -p "<passwd>" 10.0.0.3
Parameters
-a: Do all simple enumeration (-U -S -G -P -r -o -n -i).-u <user>: specify username to use.-p <pass>: specify password to use.
NSE Scripts
#
nmap --script "safe or smb-enum-*" -p 139,445 10.0.0.3
Note:
NSE SMB enumeration scripts:
smb-enum-domainssmb-enum-groupssmb-enum-processessmb-enum-servicessmb-enum-sessionssmb-enum-sharessmb-enum-users
smbclient 6
#
List available shares.
smbclient -N -L //10.0.0.3
Connect to a share.
smbclient -N //10.0.0.3/Share
Parameters
-N: remove the password prompt from the client to the user.-L: list services available on the server.
RPC Enumeration
#
Null Session
#
Windows Administrative Shares
#
Administrative shares are hidden shares that provide administrators the ability to remotely manage hosts. They are automatically created and enabled by default.
Note:
It is worth clarifying these shares are not hidden but removed from views just by appending a dollar sign ($) to the share name. Ultimately, the share will be part of the result if listing from a Unix-based system or by using: net share and net view /all.
Various shares are exposed to clients via SMB, as follows:
C$: C Drive on the remote machine.Admin$: Windows installation directory.IPC$: The inter-process communication or IPC share.SYSVOLandNETLOGON: domain controller shares.PRINT$andFAX$: printer and fax shares.
IPC$ is a special share
used to facilitate inter-process communication (IPC).
It does not allow access to files or directories,
but it allows to communicate
with processes running on the remote system.
Specifically, IPC$, exposes named pipes,
which can be written or read
to communicate with remote processes.
These named pipes
are opened by the application
and registered with SMB
so that it can be exposed by the IPC$ share.
They are usually used
to perform specific functions on the remote system,
also known as RPC or remote procedure calls.
Some versions of Windows
allow you to authenticate
and mount the IPC$ share
without providing a username and password.
Such a connection is often called a NULL session,
which,
despite its limited privileges,
could be used to make multiple RPC calls
and obtain useful information
about the remote system.7
Note:
RPC endpoints exposed via IPC$
include the Server service,
Task Scheduler,
Local Security Authority (LSA),
and Service Control Manager (SCM).
Upon authenticating,
you can use these
to enumerate user and system details,
access the registry,
and execute commands
In Linux
enum4linux utility
can be used to dump data
from these service
Refer to MSRPC for more about RPC.
mount -t cifs -o username=user,password=password //10.0.0.3/Share /mnt/share
Download Files
#
Create a tar file of the files beneath users/docs. 6
smbclient //10.0.0.3/Share "" -N -Tc backup.tar users/docs
Parameters
-N: remove the password prompt from the client to the user.-T: TAR options.c: Create a tar backup archive on the local system.
Brute Forcing
#
Refer to SMB Brute Forcing
SMB Exploits Search
#
Refer to Exploits Search
-
Contributors to Wikimedia projects. “Server Message Block — Wikipedia.” Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia, Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., 26 Oct. 2003, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Server_Message_Block. ↩︎
-
“The Use of TCP Ports 139 and 445 in Windows.” Vidstrom Labs, https://vidstromlabs.com/blog/the-use-of-tcp-ports-139-and-445-in-windows/. ↩︎
-
“Scanner SMB Auxiliary Modules — Metasploit Unleashed.” Infosec Training and Penetration Testing | Offensive Security, https://www.offensive-security.com/metasploit-unleashed/scanner-smb-auxiliary-modules/. ↩︎
-
McNab, Chris. Network Security Assessment. “O’Reilly Media, Inc.,” 2007, p. 281. ↩︎
-
“Enum4linux.” Enum4linux | Portcullis Labs, Portcullis Computer Security Ltd & Portcullis Inc., 16 Sept. 2008, https://labs.portcullis.co.uk/tools/enum4linux/. ↩︎
-
“Smbclient.” Samba — Opening Windows to a Wider World, https://www.samba.org/samba/docs/current/man-html/smbclient.1.html. ↩︎
-
“A New Look at Null Sessions and User Enumeration.” SensePost, https://sensepost.com/blog/2018/a-new-look-at-null-sessions-and-user-enumeration/. ↩︎
-
“Mounting Samba Shares from a Unix Client.” SambaWiki, https://wiki.samba.org/index.php/Mounting_samba_shares_from_a_unix_client. ↩︎
If you are using Windows Server 2019 and need to enable SMB1 for compatibility reasons, follow these steps to enable it safely and securely.
What is SMB1?
SMB1 (Server Message Block version 1) is an older version of the file sharing protocol used by Windows operating systems. While SMB1 is considered outdated and less secure than newer versions like SMB2 and SMB3, some legacy systems may still rely on it for file sharing.
Enabling SMB1 on Windows Server 2019
- Open the ‘Server Manager’ on your Windows Server 2019.
- Click on ‘Manage’ from the top menu and select ‘Add Roles and Features’.
- Click ‘Next’ until you reach the ‘Features’ section.
- Scroll down and locate ‘SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support’.
- Check the box next to ‘SMB 1.0/CIFS Client’ and ‘SMB 1.0/CIFS Server’.
- Click ‘Install’ to enable SMB1 support on your server.
- Restart the server for the changes to take effect.
Security Risks of SMB1
It’s important to note that SMB1 is highly vulnerable to security risks such as Ransomware attacks and EternalBlue exploits. Microsoft recommends disabling SMB1 whenever possible and using newer, more secure versions of the protocol.
Hashtags
#WindowsServer2019#SMB1#FileSharing
The estimated reading time 1 minutes
Windows Server 2019 Core activate SMB-in rule via PowerShell
Today I deployed a brand new Windows Server 2019 Datacenter Core for installing the new Exchange Server 2019. I wrote a little PowerShell Script for joining domain and do IP configuration so on..
After enabling remote management, my windows admin center was able to manage the complete core server. Really nice, but what to do if you don’t have an windows admin center and you only want to activate SMB-in rule on the local firewall of this core server. (of course there are dozen way to do this, but this short article shows a really quick method)
To achieve this goal you have to change firewall settings directly on the core server. First step is to open powershell in the cmd console. Easy! Only type “powershell.exe” . Here we go

Have a look at the firewall rules with cmdlet
Get-NetFirewallRule | ft
To find the “ping allow” rule:
Get-NetFirewallRule *icmp4* | ft Name,DisplayName,Enabled
also see the “smb-in” rule:
Get-NetFirewallRule *smb-in* | ft Name,DisplayName,Enabled

To enable these rules just write these two lines:
Set-NetFirewallRule FPS-SMB-In-TCP -Enabled True Set-NetFirewallRule FPS-ICMP4-ERQ-In -Enabled True


It is of course possible to disable, these rules for security reasons:
Set-NetFirewallRule FPS-ICMP4-ERQ-In -Enabled False Set-NetFirewallRule FPS-SMB-In-TCP -Enabled False
If you liked this article, please click on “helpful” at the bottom of this page. Have fun with Windows Core Server.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
Organizations are increasing their use of various solutions to address communication needs across their infrastructure. As file systems are an integral part of collaboration, this article will dive into one of the most widely used protocols necessary for many systems. We will learn more about the SMB protocol, Port 139, Port 445, how it works, the risks associated with it, and remediation steps to provide a more secure communication channel.
What is SMB Port?
The SMB (Server Message Block) port is a network port primarily utilized for file and resource sharing across a computer network. SMB operates over TCP port 445 and enables shared access to files, printers, and serial ports among devices on a network.
Moreover, its core function of resource sharing, enables SMB to be utilized for following use cases:
- Involving mail slots (inter-process communication mechanisms)
- Named pipes (a method for processes to communicate either on the same machine or over a network).
What are Port 139 and Port 445?
For the SMB protocol to function correctly, network ports are required to communicate with other systems. SMB requires either port 139 or port 445 to be an open port.
Port 139
Originally, SMB ran on port 139 as an application layer protocol for Windows computers to communicate with each other on the same network. It was run on NetBIOS over TCP/IP and is being passed over by port 445 in modern environments.
Port 445
Port 445 port is used by newer versions of SMB as Windows 2000 adopted it for use for direct TCP/IP communication. Generally favored over port 139, it also allows for communication across different networks for things like internet-based file sharing.
How does SMB Protocol work?
Client-Server Communication
SMB is known as a response-request protocol. It uses the approach of a client-server relationship, where the client makes any specific request, and the server responds as requested. Some examples of practical use today are situations where file resources are requested or printers need to be shared. SMB is also used for other uses, such as mail slots and named pipe situations.
Historical Development
Historically, SMB originated with IBM and was designed in 1983 for DOS file access over networks. It wasn’t until 1990 that Microsoft merged the SMB protocol with its LAN Manager product. From there, continual maturation of the SMB protocol appeared in instances such as the introduction of CIFS, as well as milestone improvements in efficiency, performance, and security, as described through the aforementioned upgrades of SMB 2 and SMB 3.
SMB Protocol Dialects
With an increasing presence of SMB implementations across the industry, network requirements evolved to have different demands of SMB. This led to the emergence of different SMB protocol dialects to cater to different environments. Depending on the need and use, different dialects could be implemented for a variety of purposes.
SMB Dialect Variations
Here’s a list of popular SMB dialects along with their uses:
- CIFS (Common Internet File System): was a Microsoft developed dialect debuting in Windows 95 that was designed for network connections over remote servers. This dialect (CIFS Port) enabled clients to connect to remote file and printer shares as if they were accessed locally.
- Samba: Samba is an open source dialect (Samba port) that enables Linux/Unix machines to communicate with Windows devices.
- NQ: was developed by Visuality Systems that brings the SMB protocol to non-Windows platforms. Especially prevalent in devices such as printers and home network devices.
- Tuxera SMB and MoSMB: Dialects were also created as proprietary methods using the SMB protocol for specific features, such as enterprise file sharing and advanced authentication.
Security Risks Associated with Open SMB Ports
Ports like the ones used with the SMB protocol are necessary to communicate from within and across different networks. While their use isn’t itself dangerous, open ports can be used and exploited for malicious purposes.
Having over exposed ports can lead to the following vulnerabilities, such as:
- A Wormable port
- Man-In-The-Middle attacks,
- NetBIOS spoofing,
Case Study: WannaCry Ransomware:
Once recent occurrence was the WannaCry ransomware attack that targeted Windows clients running an outdated version of SMB. A worm infection was installed on a target machine, encrypting the user’s files in exchange for ransom. In addition to that, the infected system would also start searching for other machines via the SMB v1 protocol, and if other systems were using those open ports, they would be susceptible to the ransomware self-install on that machine and continue its spread.
While WannaCry created havoc and pain for many companies and networks, its disastrous results could have been much less impactful had systems been patched with up-to-date security measures.
Best Practices to Secure SMB Ports 139 and 445
Since SMB ports can be targeted, here are some best practices to implement to protect against various attacks:
Enable Firewall and Endpoint Protection
Enabling these network security devices can protect these ports from threats as well provide blacklisting services against known malicious IP addresses.
Utilize VPNs
By utilizing VPNs, network traffic can be encrypted and protected against malicious actors.
Create VLANs
Creating Virtual LANs can be utilized to isolate internal traffic to limit attack surface.
Implement MAC Address Filtering:
These filters can keep unknown systems from accessing and infiltrating your internal network.
Implement System Configuration Changes
Following changes can be made to harden your security against SMB attacks:
Disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP
- Select Start, point to Settings, and then select Network and Dial-up Connection.
- Right-click Local Area Connection, and then select Properties.
- Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then select Properties.
- Select Advanced.
- Select the WINS tab, and then select Disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP.
Commands to monitor port status
To determine if NetBIOS is enabled on a Windows computer, run a net config redirector or net config server command to see if if any ‘NetBT_Tcpip’ device is bound to the network adapter.
Conclusion
The SMB protocol has proved to be a valuable and vital method of accessing different network resources. While it has enabled things like file sharing and connectivity, security measures should be taken to ensure authorized access within the network. Securing ports and keeping up to date with protocols are a couple of examples of how to heighten your security profile in modern-day networking.
In conjunction with network security, Netwrix can fulfill your security plan at the data layer. With Netwrix solutions, we can help your organization see who has access to your data and the activity that surrounds it. Monitoring is a critical part of detecting attacks and protecting against breaches.
Mark has over 20 years in the IT industry and has consulted in a wide array of industries including the automotive, insurance, medical, legal, and financial sectors. With his IT background, he joins Netwrix with his ability to empathize with the problems IT teams face today. In his role as Solutions Engineer, Mark will understand the needs your organization faces and provide solutions to help overcome those challenges.

