Вы можете установить SMTP сервер с помощью встроенных средств во всех версиях Windows Server. Такой SMTP сервер внутри организации может работать в качестве почтового релея, который должен принимать и пересылать через себя SMTP сообщения от различных устройств (к примеру, сендеров, сканеров, устройств СКД и пр.) и приложений (веб приложения, SQL Reporting Services, SharePoint), которым необходимо иметь возможность отправлять почту через SMTP сервер. Такой релей может пересылать сообщения на полноценные Exchange сервер или на публичные почтовые сервисы в Интернет типа Gmail, Mail.ru, Office 365 и т.д (ведь не всегда целесообразно разворачивать полноценную внутреннюю почтовую инфраструктуру на базе Microsoft Exchange Server или других почтовых служб).
В этой статье мы покажем, как установить, настроить и протестировать работу SMTP сервера на Windows Server 2012 R2, 2016 и 2019, который будет функционировать в качестве mail релея. Такой SMTP сервер не хранит почтовые сообщения и на нем отсутствуют почтовые ящики, он сможет только отправлять или пересылать почту.
Содержание:
- Установка службы SMTP на Windows Server 2016/2012 R2
- Настройка SMTP сервера на Windows Server
- Автозапуск службы SMTPSVC
- Проверка работы SMTP сервера на Windows Server
Установка службы SMTP на Windows Server 2016/2012 R2
SMTP сервер – это один из компонентов Windows Server, который можно установить через Server Manager. Для этого откройте консоль Server Manager Dashboard (servermanager.exe), перейдите в режим Add roles and features и на этапе выбора функций отметьте чекбокс у пункта SMTP Server. Для управления службой SMTP нужно установить консоли управления, которые входят в комплект роли Web Server IIS (вам будет предложено установить IIS Management Tools).
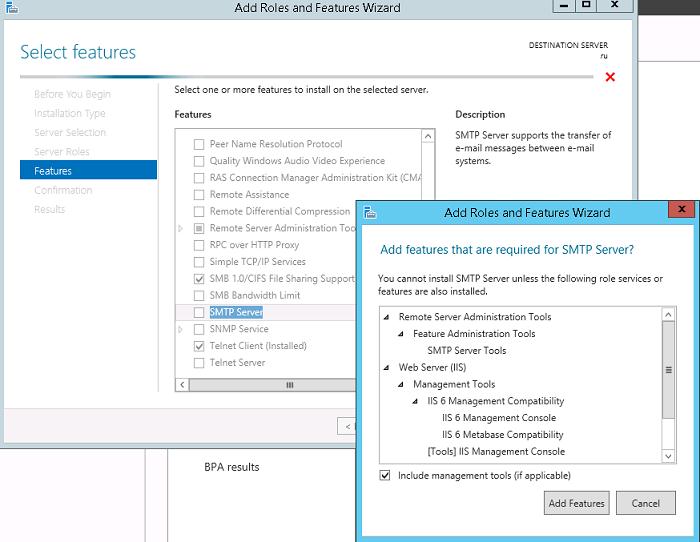
Оставьте все предлагаемые опции роли Web Server (IIS) и запустите установку.
Также вы можете установить компонент SMTP сервера с помощью одной команды PowerShell:
Install-WindowsFeature smtp-server
После окончания установки компонентов может потребоваться перезагрузка системы.
Настройка SMTP сервера на Windows Server
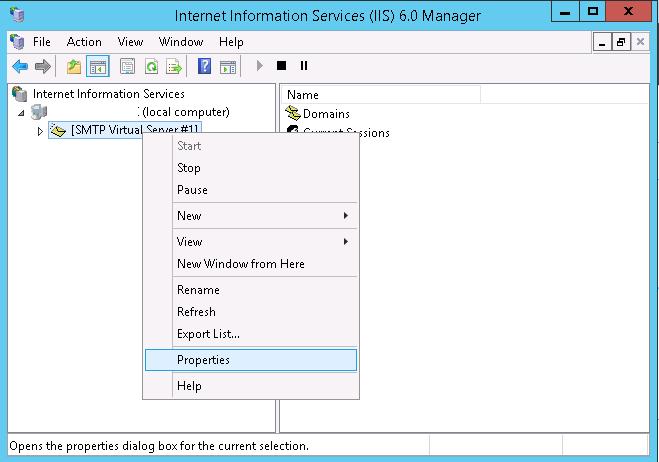
Управляется SMTP сервер консоль управления Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager 6. Открыть эту консоль можно через Server Manager: Tools-> Internet Information Services (IIS) 6.0 Manager или командой inetmgr6.exe.
В консоли IIS 6 Manager разверните ветку с именем сервера, щёлкните ПКМ по SMTP Virtual Server и откройте его свойства.
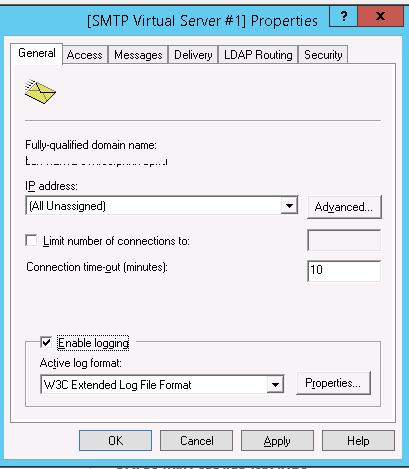
На вкладке General, если необходимо, выберите IP адрес, на котором должен отвечать SMTP сервер (если у сервера несколько IP адресов), и включите ведение логов Enable logging (чтобы сохранялась информация обо всех полученных письмах).
Затем перейдите на вкладку Access.
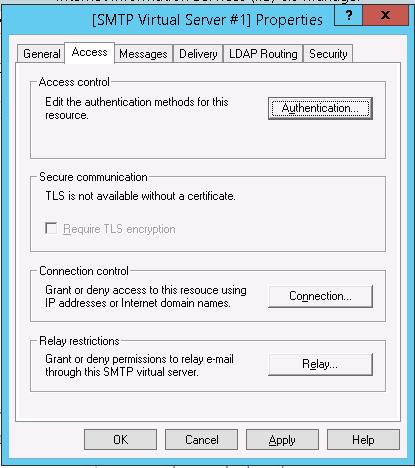
Здесь нажмите на кнопку Authentication и убедитесь, что разрешен анонимный доступ (Anonymous access).
Вернитесь на вкладку Access и нажмите кнопку Connection. Здесь вы можете указать IP адреса устройств, которым разрешено отправлять почту через наш SMTP релей. Нужно выбрать опцию Only the list below и указать список IP адресов, не забыв самого себя (127.0.0.1).
Аналогичным образом настройте список разрешенных IP в настройках Relay (нажмите соответствующую кнопку). В этой секции указано каким IP адресам (или подсетям) можно пересылать почту через ваш SMTP сервер.
Примечание. Как правило, обязательно стоит включать эту опцию, как минимум ограничив список обслуживаемых устройств диапазоном IP адресов. В противном случае ваш SMTP сервер может использоваться спамерами и другими злоумышленниками как открытый релей для массовых почтовых рассылок.
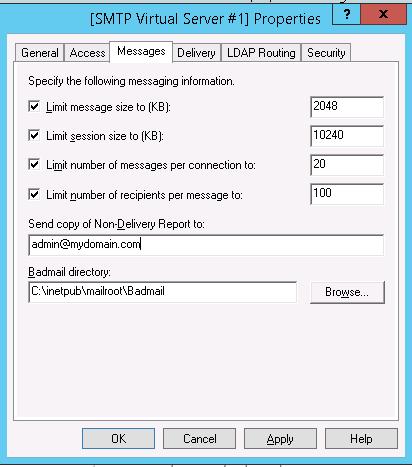
Перейдите на вкладку Messages. Здесь указывается email, на который будут отправляться копии всех NDR отчетов (Send copy of Non-Delivery Report to:). Также здесь можно указать ограничения на максимальный размер писем (Limit message size KB) и количество получателей (Limit number of recepients per message).
Перейдите на вкладку Delivery:
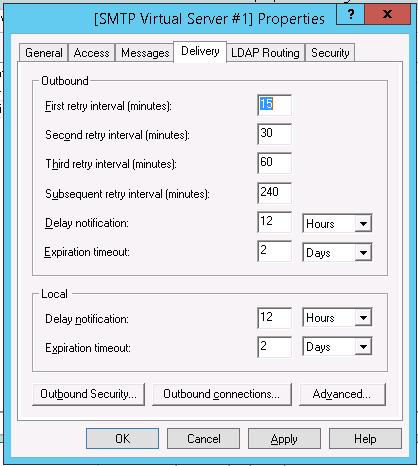
Затем нажмите на кнопку Outbound Security. Здесь указывается, как нужно авторизоваться на почтовом сервере, на который ваш SMTP-сервере будет пересылать (relay) всю почту. К примеру, если вся почта будет отправляться на почтовый сервер Gmail и уже с него пересылаться адресатам, вам нужно выбрать тип аутентификации Basic authentication, указав в качестве пользователя и пароля данные для доступа к почтовому ящику на сервисе Gmail (в настройках аккаунта Google нужно разрешить отправку через smtp сервера gmail).
Затем нажмите на кнопку Advanced.
Здесь указывается FQDN имя вашего SMTP сервера. Нажмите кнопку Check DNS, чтобы проверить корректность записи в DNS.
Если сервер должен пересылать почту внешнему smtp серверу, нужно указать его имя в поле Smart host (к примеру smtp.gmail.com или smtp.office365.com).
Некоторые внешние почтовые сервера принимает почту только при использовании защищенного SMTP соединения с помощью TLS Encryption (используется порт TCP 587). Это настраивается в разделе Delivery-> Outbound Security и Outbound Connections. Ознакомитесь с документацией вашего почтового провайдера.
Сохраните настройки SMTP сервера и перезапустите ваш виртуальный SMTP сервер для применения изменений.
Примечание.
- Настройки DNS критичны с точки зрения работоспособности почтовой системы. Если ваш SMTP сервер не может корректно разрешить DNS имена доменов, на которые он пытается отправить письма, доставка не удастся.
- Если ваш сервер сам будет отправлять почту в другие домены, важно, чтобы для вашего адреса была сформирована правильная PTR запись для разрешения обратных DNS запросов. PTR запись для белого IP адреса должна указывать на FQDN имя. В противном случае большинство внешних smtp серверов не будут принимать от вас почту, считая ваш сервер спамерским.
Автозапуск службы SMTPSVC
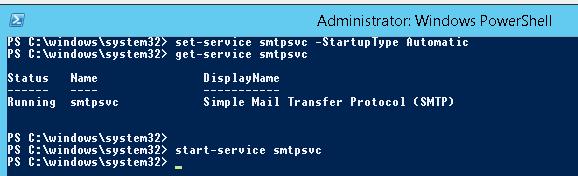
Осталось настроить автозапуск службы SMTP сервера. Быстрее всего это сделать из командной строки PowerShell:
set-service smtpsvc -StartupType Automatic
Запустим службу:
start-service smtpsvc
Проверим, что запущена служба SMTPSVC :
get-service smtpsvc
Status Name DisplayName
—— —- ————
Running smtpsvc Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
Проверка работы SMTP сервера на Windows Server
Ну и последнее, что осталось сделать, проверить работу созданного SMTP сервера. Проще всего это сделать, создав на рабочем столе текстовый файл smtp-test-email.txt и скопировав в него следующий текст, заменив имя отправителя и получателя на ваши.
From: [email protected]
To: [email protected]
Subject: Email test
This is the test email
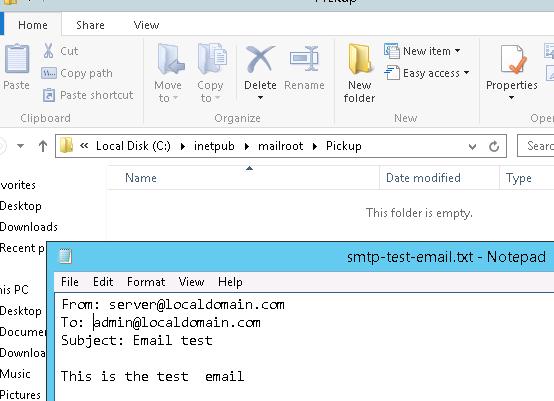
Скопируйте файл smtp-test-email.txt в каталог C:\inetpub\mailroot\Pickup. SMTP сервер следит за появлением файлов в этой каталоге и при обнаружении файла прочтет его содержимое и попытается отправить письмо с данной темой и текстом адресату, указанному в разделе To:.
Проверьте ящик получателя, в него должно прийти такое письмо.
Совет. Протестировать работу SMTP сервера можно и из командой строки telnet, скрипта vbs или PowerShell:
Send-MailMessage -SMTPServer localhost -To [email protected] -From [email protected] -Subject "Email test" -Body "This is the test email sent via PowerShell"
Если вы хотите, чтобы вы включили Basic Authentication (Обычная проверка подлинности) для авторизации всех ваших SMTP клиентов (вместо анонимной аутентификации), вы можете отправить письмо с smtp-аутентификацией через telnet следующим образом.
Также убедитесь, что на вашем SMTP сервере не блокируется порт TCP 25 при удаленном подключении (локальным файерволом, антивирусом или межсетевым экраном). Проще всего это сделать с компьютера Windows, IP адрес которого добавлен в разрешенные. Проверку доступности порта можно выполнить с помощью командлета Test-NetConnection:
Test-NetConnection smtpsrv1.name.local –port 25
Если 25 порт блокируется, проверьте настройки Windows Firewall, антивируса и аппаратных межсетевых экранов.
Итак, вы настроили собственный почтовый SMTP релей на Windows Server 2016/2012 R2 и протестировали отправку писем через него.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is a service that enables email exchange on the Internet and within a local network. To achieve that, SMTP interacts with the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) and ensures the messages reach the intended recipients.
Mail servers and other message transfer agents usually use SMTP to send and receive email messages.
In this tutorial, you will learn to install and configure the SMTP server on Windows.

Prerequisites
- A Windows Server operating system.
- A user account with administrator privileges.
Note: Client operating systems like Windows 11, Windows 10, and Windows 8, do not have SMTP Server capabilities. Windows Server operating systems provide an SMTP server as part of the Internet Information Services (IIS). The client operating systems only provide the SMTP email client, which is not an SMTP server.
Install SMTP on Windows
SMTP installation is a straightforward process on Windows Server operating systems. Use the Server Manager management console and follow the steps below to install SMTP.
Step 1: Add Roles and Features in Server Manager Dashboard
Open the Server Manager management console and select Dashboard in the left pane.
From the Dashboard, select the Add roles and features option to start the wizard and install the SMTP server.
The Before You Begin screen appears, stating that the prerequisites for adding a role are:
- Having a strong password on the Administrator account.
- Configured network settings on the server.
- That you have installed the latest security updates.
If all the prerequisites are met, click Next to continue the installation.
Step 2: Select Installation Type
In the Installation type window, select Role-based or feature-based installation. Click Next to continue.
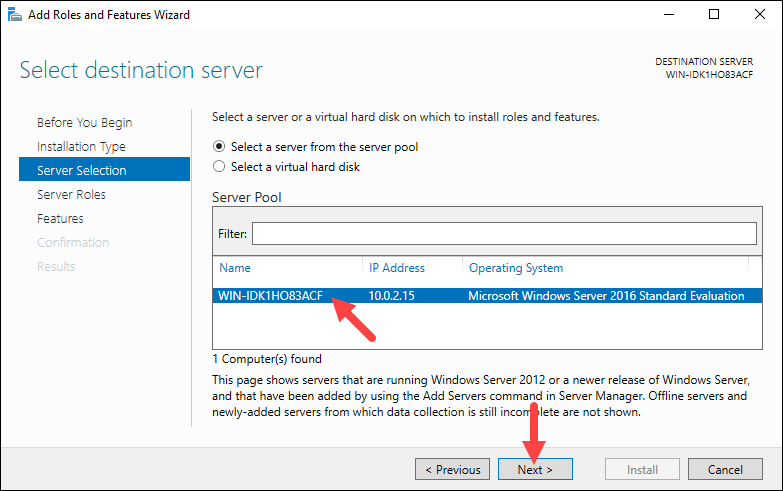
Step 3: Select Destination Server
Choose the Select a server from the server pool option and pick the desired server from the Server Pool to set the destination server. The Server Pool lists the servers you have added using the Add Server option in Server Manager. By default, the local server is selected.
Click Next to move on to the next step.
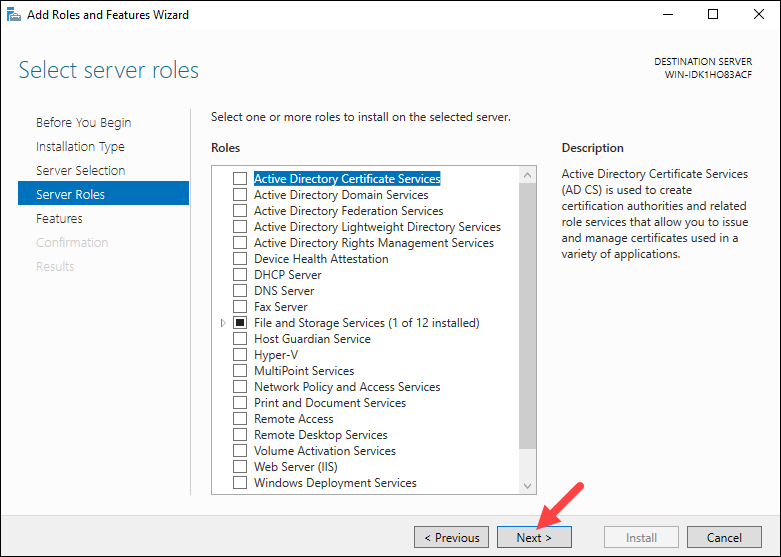
Step 4: Select Server Role
The Select server roles screen allows you to select which features and roles to install. Keep the default selection and click Next.
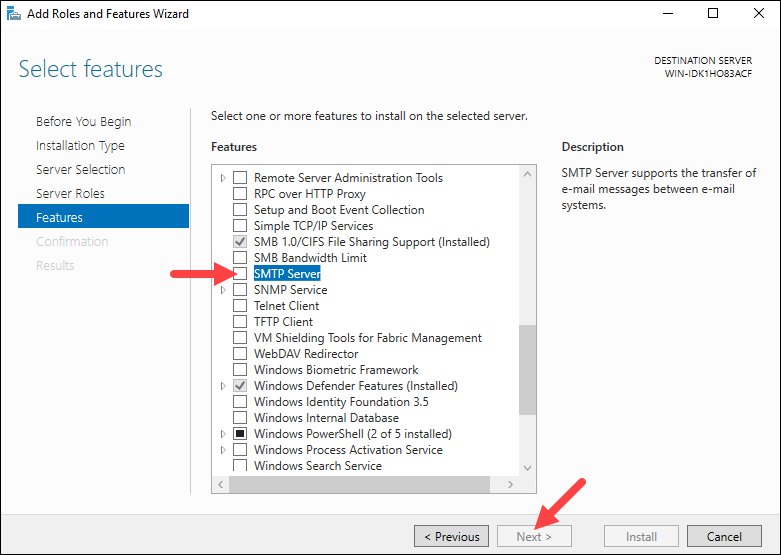
Step 5: Select Features
The next step is to select which features to install. Scroll through the list to find and select SMTP Server. Click Next to proceed.
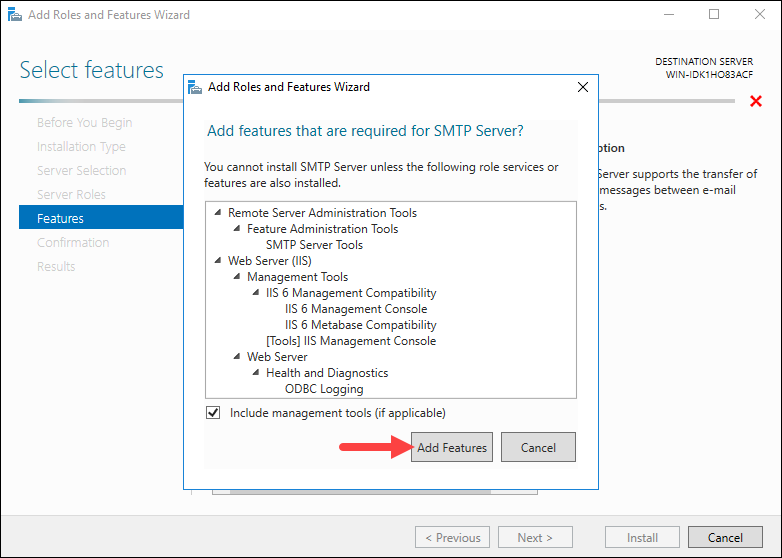
Step 6: Install Missing Features
If the Remote Server Administration Tools and Web Server roles have not been previously installed, the wizard prompts you to install them. Check the Include management tools option and click Add Features to install them:
Install Web Server Role
The wizard displays an information screen about the Web Server Role (IIS). Click Next to install the role.
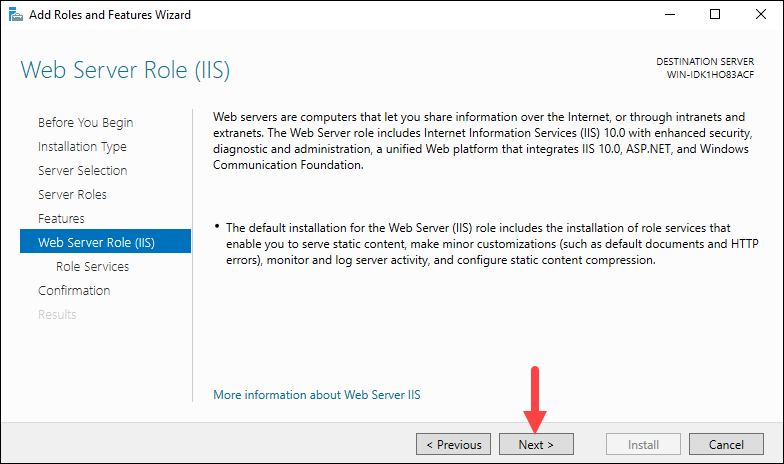
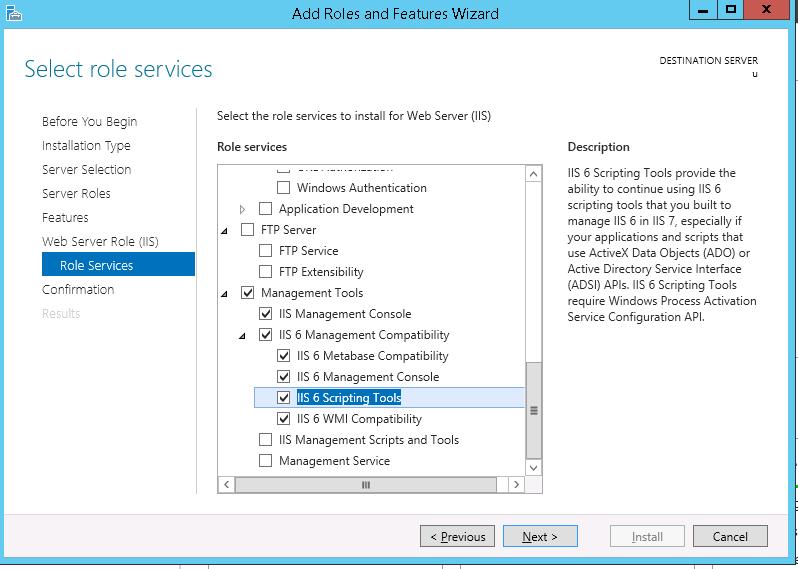
Install Role Services
Check all the services you want to install for the Web Server role. The default options are preselected.
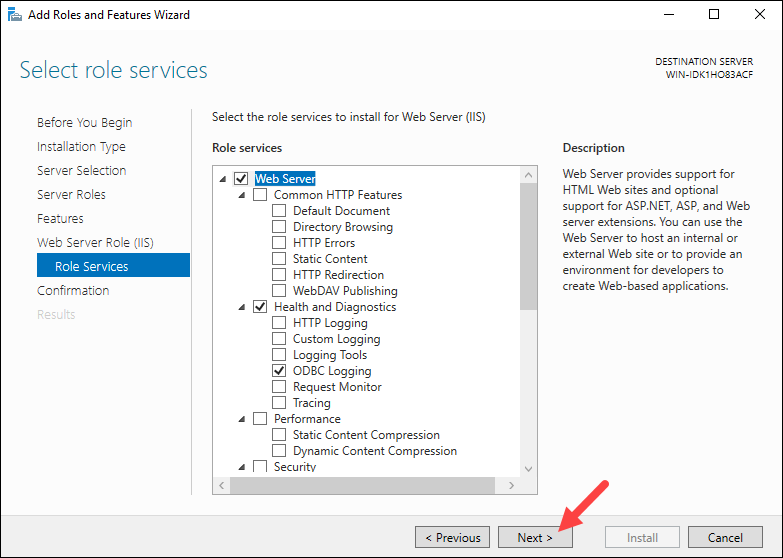
Click Next to proceed to the final step when you finish selecting the services.
Step 7: Confirm Installation
The wizard displays a confirmation window with a summary of all the roles, services, and features about to be installed. Make sure that the Restart the destination server automatically if required option is checked and click Install to finish the installation.
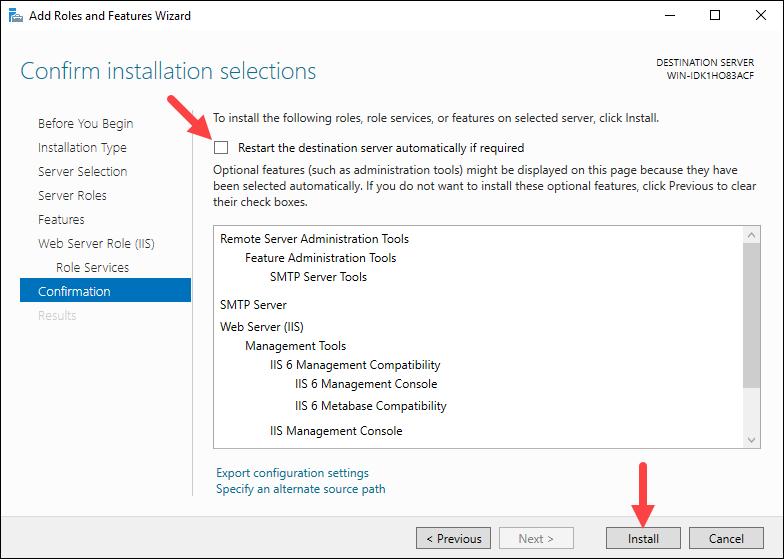
When the installation completes, click Close to exit the installation wizard.
Configure SMTP on Windows
Configure the SMTP server using the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager 6.0. Follow the steps in the chapters below.
Step 1: Open IIS 6.0
Open the IIS Manager 6.0 from the Server Manager dashboard.
Select the Tools option, and locate Internet Information Services (IIS) 6.0 Manager from the dropdown menu:
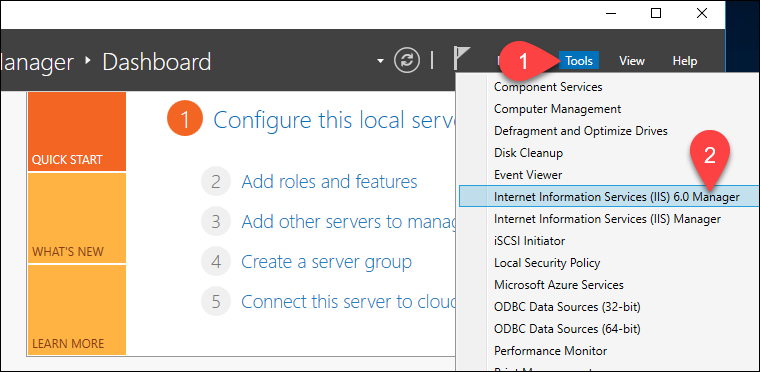
Step 2: Configure SMTP Virtual Server
In IIS Manager 6.0, expand the computer name and right-click [SMTP Virtual Server #1].
Select Properties from the dropdown menu.
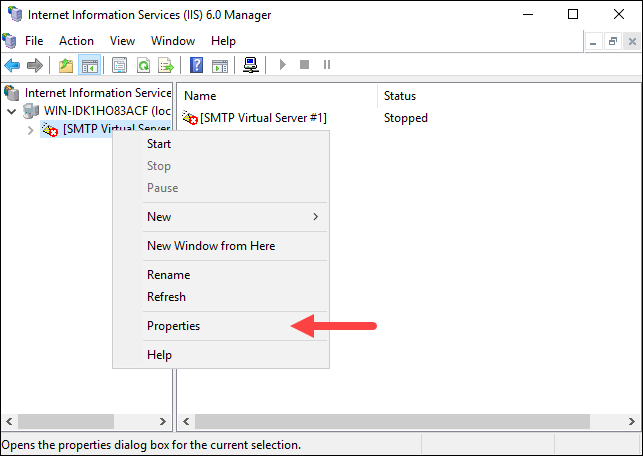
Step 3: Configure Relay
The relay options allow you to relay emails through the SMTP virtual server.
Configure Server Access
1. In [SMTP Virtual Server #1] properties, click the Access tab and select the Relay button:
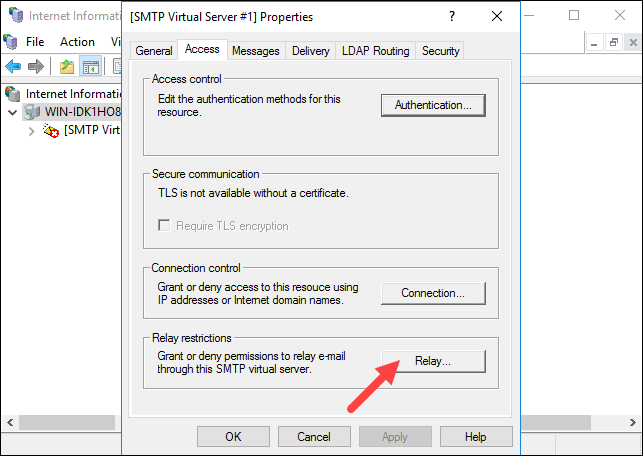
2. Select the Add… option to set which computer is allowed to relay emails through the SMTP server.
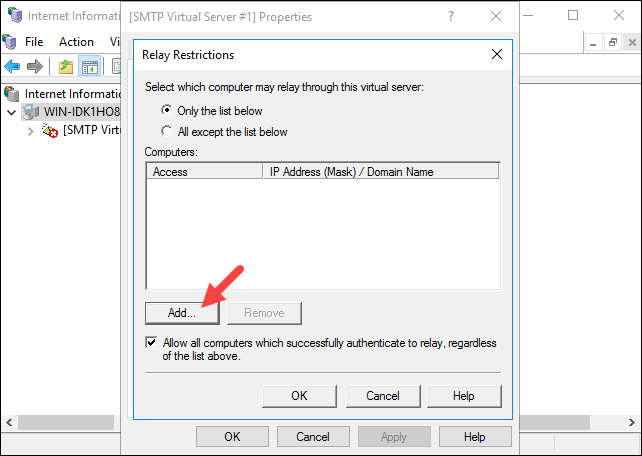
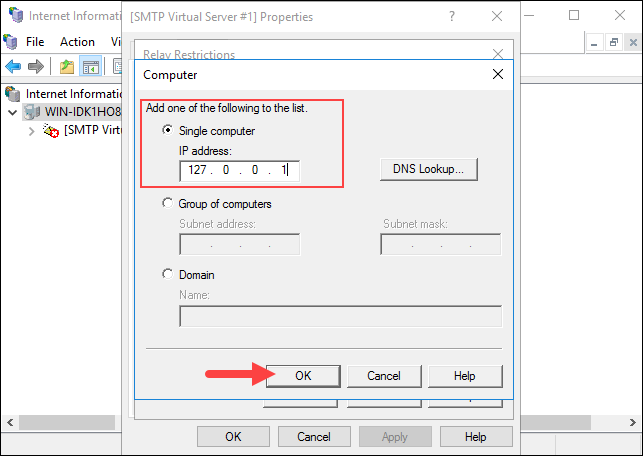
Select the Single Computer option and enter 127.0.0.1 to allow the localhost to relay emails through the SMTP server. You can also specify a group of computers using the Group of computers option.
Click OK to confirm the changes.
Step 4: Configure Security Options
The Delivery tab of [SMTP Virtual Server #1] properties contains different settings related to the intervals of retrying to send outbound emails after a failed delivery, and different security options.
To configure the security options, click Outbound Security.
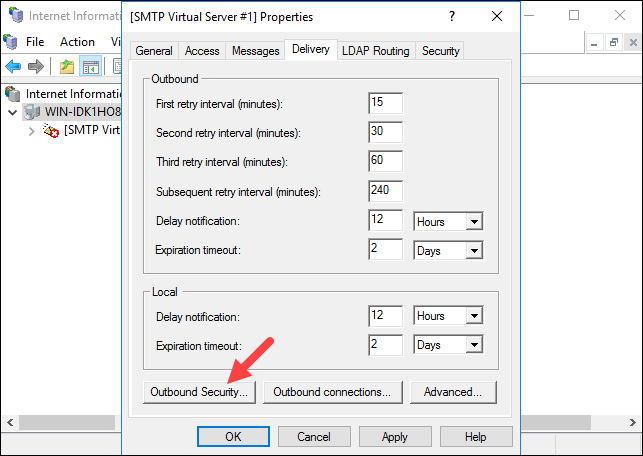
The pop-up window allows you to choose one of four options for securing your SMTP server:
- Anonymous access. Disables SMTP server authentication since it doesn’t require an account name or password.
- Basic authentication. Used when sending emails to a personal or exchange account. This option passes the account name and password as clear text, so make sure to use TLS encryption if you select this option.
- Integrated Windows Authentication. Uses the Windows domain account name and password for authentication.
- TLS encryption. Use TLS to secure the connection. This option requires you to install a valid SSL certificate on the server.
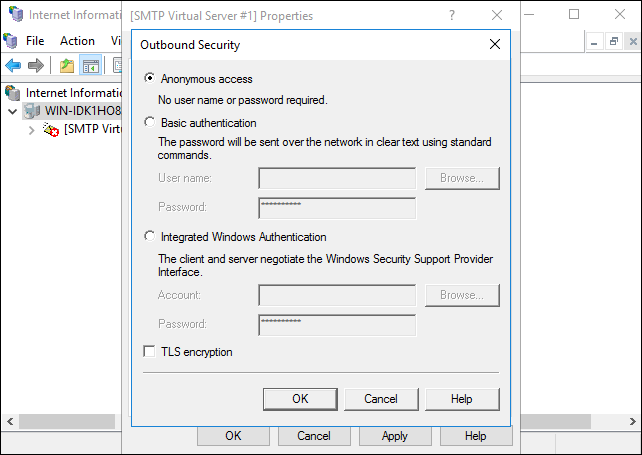
Note: Test core SMTP functionality with a personal e-mail or Exchange account by selecting Anonymous access. SMTP uses the AUTH command with Basic authentication, which can cause some e-mail providers to fail.
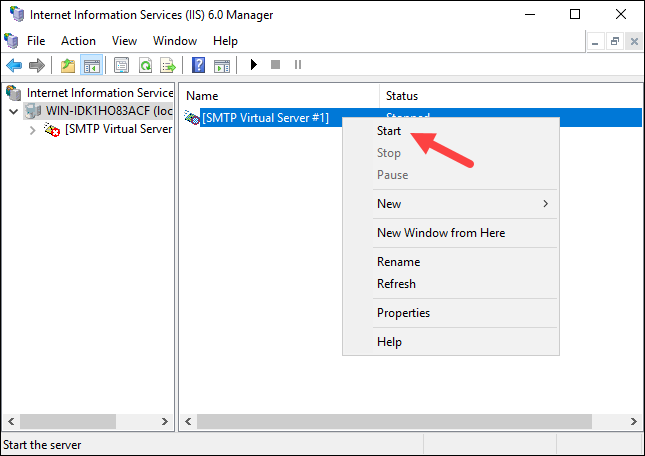
Step 5: Restart SMTP Server
Restart the SMTP Server to apply the changes. Right-click [SMTP Virtual Server #1], select Stop, and then select Start.
Test SMTP Server
Test the SMTP server configuration by sending an email message using the SMTP server. One of the ways to do that is to use telnet. Follow the steps below:
1. Press the Windows key and search for PowerShell.
2. Run the PowerShell app as Administrator.
3. Run the following command:
telnet localhost 254. Start the communication with the server by running:
EHLO server5. Enter the email address you will use to send the email. The syntax is:
MAIL FROM: [[email protected]]6. Enter the recipient email address. The syntax is:
RCPT TO: [[email protected]]7. Inform the SMTP Server you are ready to send the message by entering:
DATA8. Enter the email subject:
Subject: Test Message9. Press Enter twice to move on to the email body. Type in the message body and press Enter to finish.
10. Send the email by entering a period (.) and pressing Enter.
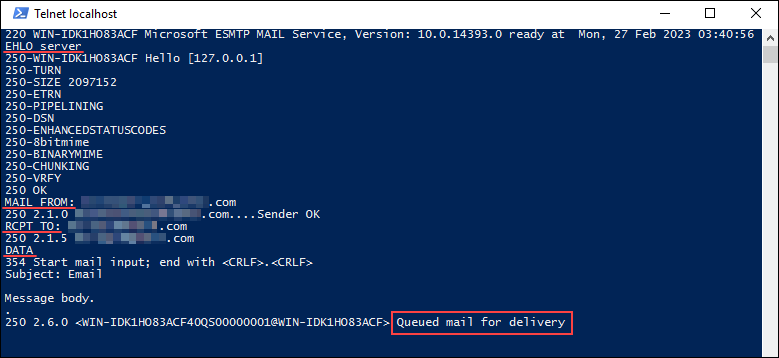
Check the recipient’s inbox to see if the email was delivered. If not, the message may still be in the SMTP Queue directory (C:\inetpub\mailroot\Queue).
Conclusion
This tutorial showed how to install and configure the SMTP server on Windows Server operating systems. An SMTP server allows you to exchange emails using the MTA, making it a great solution when you want to set up your own mail server.
Next, learn how to set up Postfix to use an external SMTP server, or learn to use the mail command in Linux.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
-
Star
(83)
You must be signed in to star a gist -
Fork
(18)
You must be signed in to fork a gist
-
Clone this repository at <script src="https://gist.github.com/raelgc/6031306.js"></script>
- Save raelgc/6031306 to your computer and use it in GitHub Desktop.
Clone this repository at <script src="https://gist.github.com/raelgc/6031306.js"></script>
Setup a Local Only Email Server (Windows Only)
1 — Install hMailServer
Download hMailServer from here: http://www.hmailserver.com/index.php?page=background_download_file&downloadid=207.
- In setup, select internal db engine.
- Now you have a service called hMailServer and an administration program on the Windows start menu (hMailServer Administrator).
2 — Create a domain
- Open hMailServer Administrator program.
- Click on «Domains» and then «add domain».
- At «domain name» put a fake domain to test. Use «localhost.com» (without the quotes): hMailServer requires a fully qualified domain, so, we cannot use @localhost.
- Make sure to add your domain (localhost.com) to hosts file: C:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts
3 — Change server name
- Expand Settings > Protocols > SMTP -> Delivery of e-mail
- At «Host name» put «localhost» (without the quotes).
- Check if TCP Port is 25.
4 — Create an account
- Go to «Domains», click on the created domain, and then click on «accounts», then «add account».
- At «address», create your account name, here I use «rael» (without the quotes), and put a password.
- Change «Administration level» to «Server».
5 — Configure «catch-all» address
- Enabling this, you can use any email address ending with you fake domain. Example: here, my unique account is rael@localhost.com. But while testing systems, I can use any address like joe@localhost.com, foo@localhost.com, etc, because all will be redirected to rael@localhost.com
- Open «Domains», click on your domain, open Advanced tab, fill field «catch-all address» with account created on previous step.
6 — Configure an Email client
- At Windows, you can use Windows Live Email (http://explore.live.com/windows-live-essentials-other-programs?T1=t2).
- Of course, you can use any email client.
- While configuring
- Incoming Server is POP3, and the username is the full email address (like rael@localhost.com), and the password is raw text (no encrypt).
- POP3 and SMTP server are «localhost» (without the quotes).
- Outgoing server do not require authentication.
- Don’t use the email client and the hMailServer Administration application at the same time!
Почтовый сервер – это устройство, при помощи которого происходит доставка электронных сообщений от отправителя к получателю. Собственно, это и следует из его названия. В данной статье рассмотрим, как происходит установка и базовая настройка почтового сервера на VPS с операционной системой семейства Windows Server, а также на виртуальном сервере, работающем на Ubuntu 20.04.
Установка сервера SMTP на Windows Server
На серверах, работающих под управлением операционных систем Windows, для передачи почтовых сообщений часто используется протокол SMTP. В Windows Server служба SMTP является одним из компонентов операционной системы.
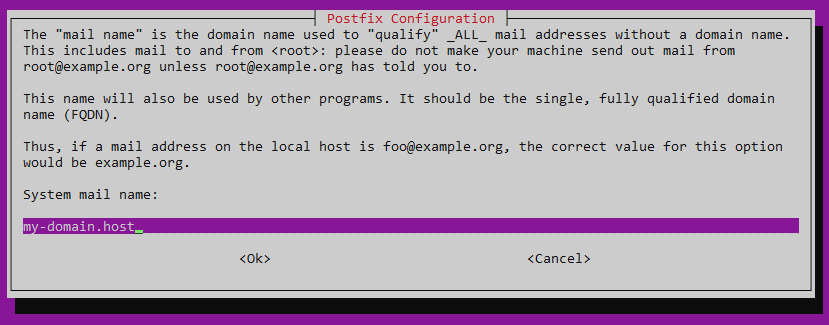
Для корректной отправки почтового сообщения от имени домена, к которому будет привязан сервер SMTP, нам необходимо иметь доменное имя. При этом в настройках домена должна быть указана A-запись, содержащая IP-адрес VPS. В нашем примере мы будем использовать имя домена my-domain.host.
Установку почтового сервера нужно будет начать именно с добавления необходимых компонентов. Для этого запустите Server Manager, перейдите Manage → Add Roles and Features.
В открывшемся окне нажмите Next.
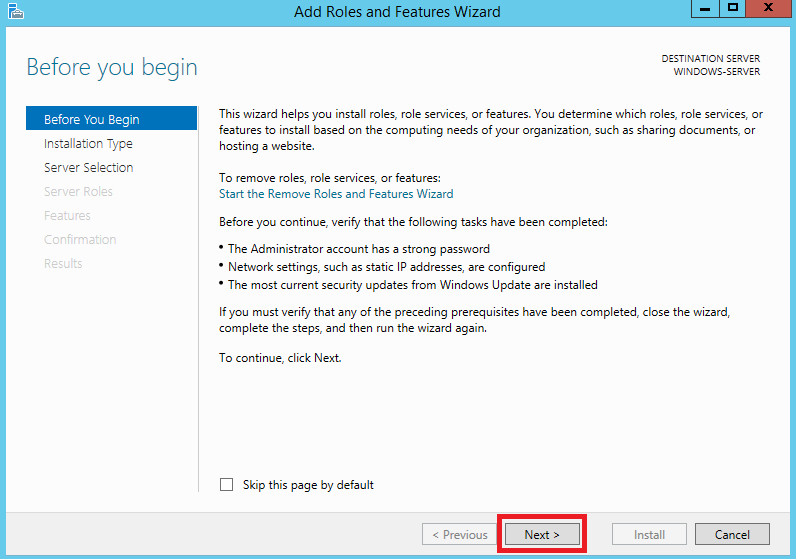
Далее выберите опцию Role-based or feature-based installation, после чего нажмите Next.
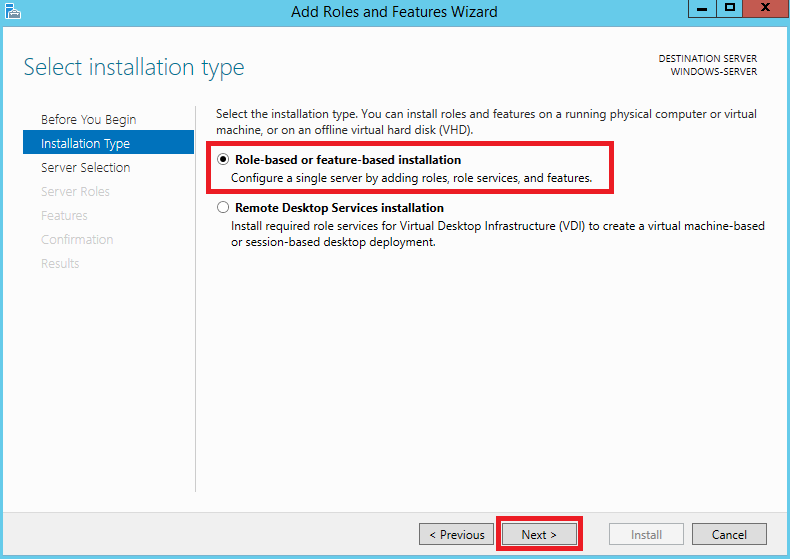
В следующем окне укажите сервер, на который будет производиться установка новых компонентов, либо просто нажмите Next, если в вашем пуле серверов одна-единственная запись.
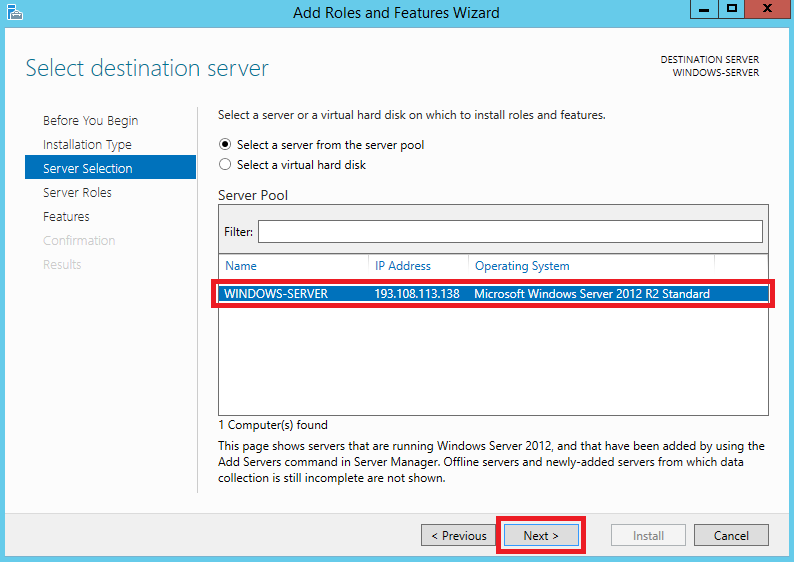
На следующем шаге активируйте строку Web Server (IIS), после чего нажмите Add Features.
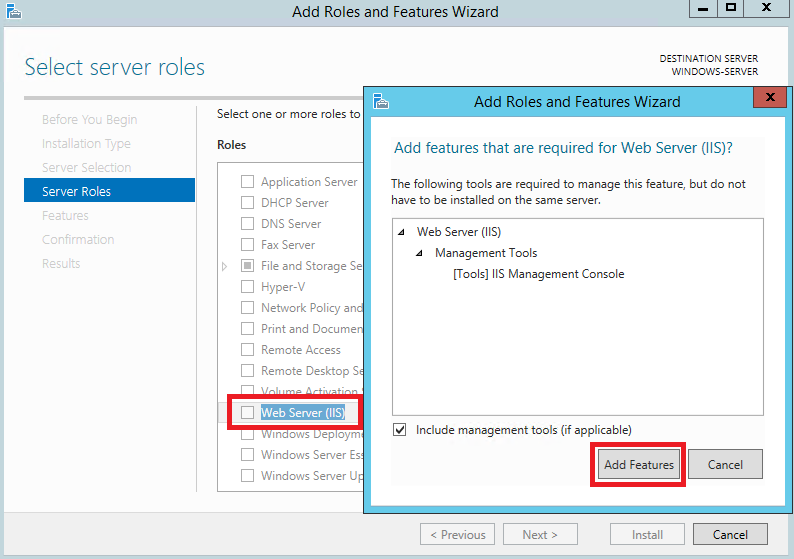
Далее нажмите Next.
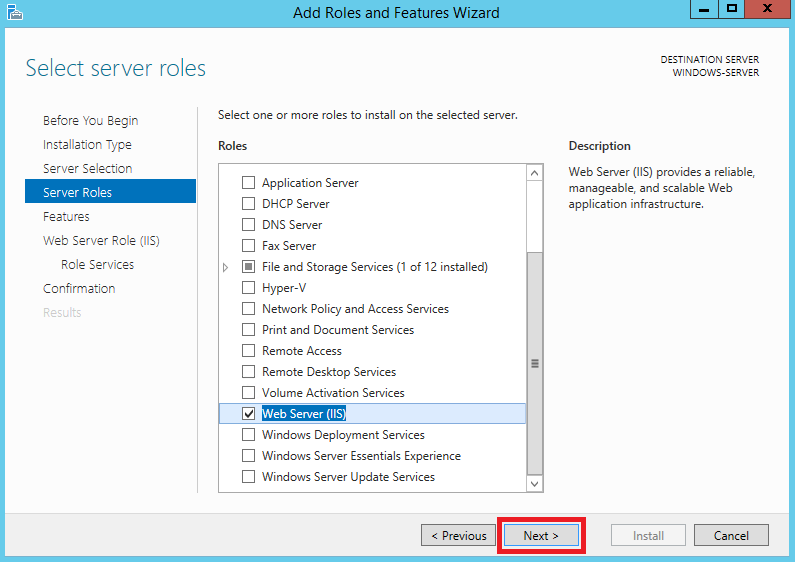
После чего отметьте строку SMTP Server и нажмите Add Features.
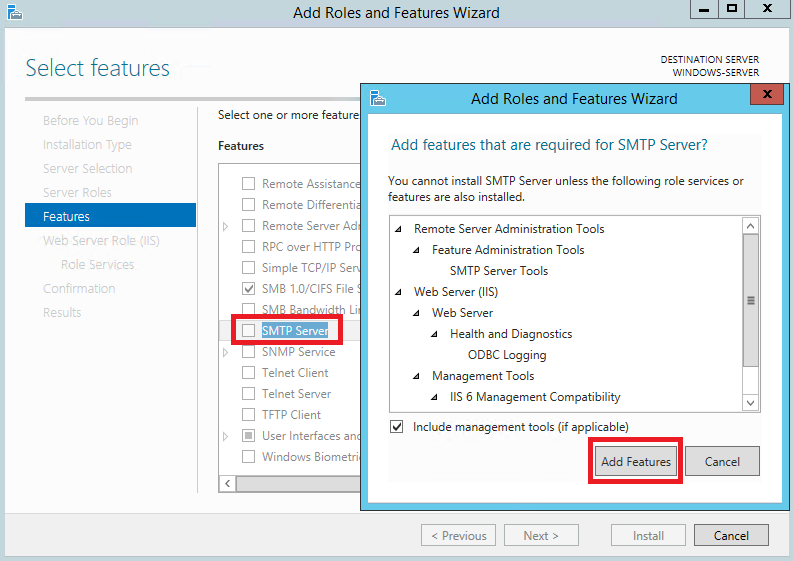
И нажмите Next.
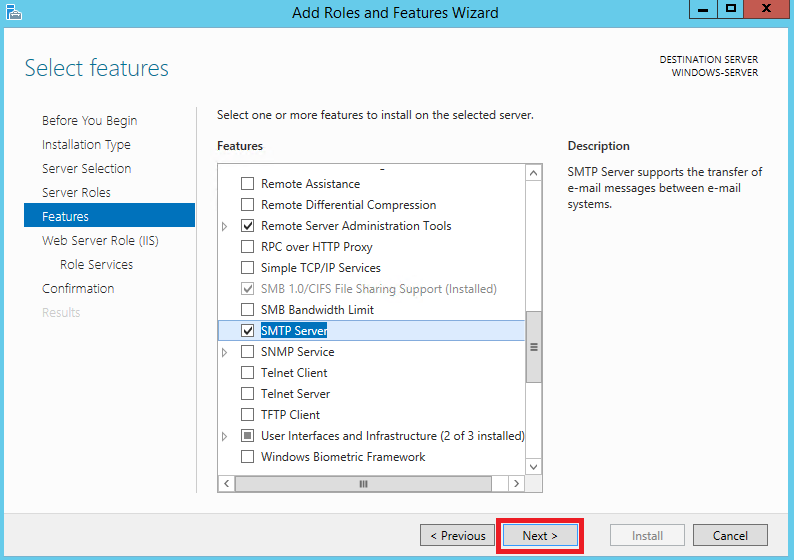
Далее ещё раз нажмите Next.
В следующем окне снова нажмите Next.
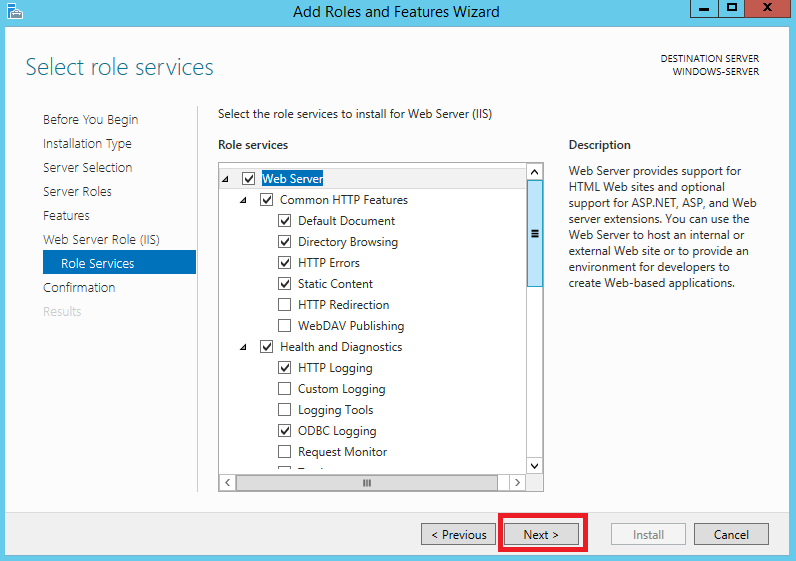
Для запуска установки выбранных компонентов нажмите Install.
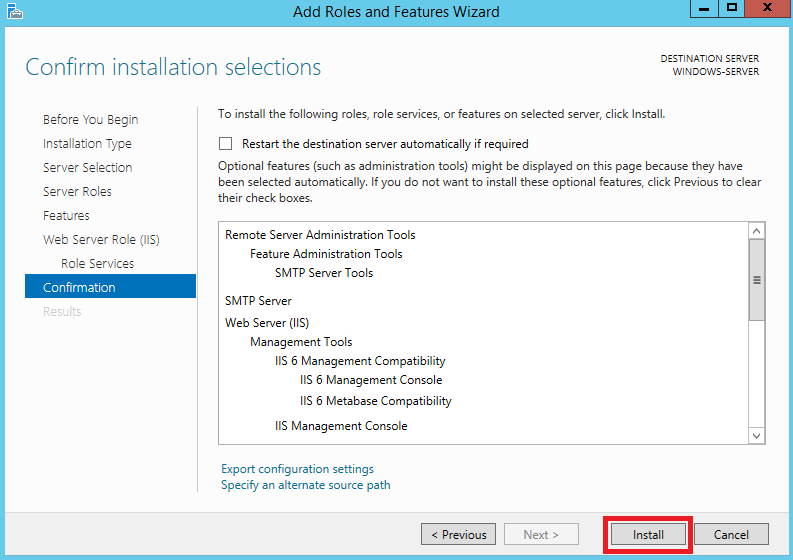
Настройка сервера SMTP
На следующем этапе необходимо будет настроить сервер SMTP. Для чего в Server Manager перейдите Tools → Internet Information Services (IIS) 6.0 Manager.
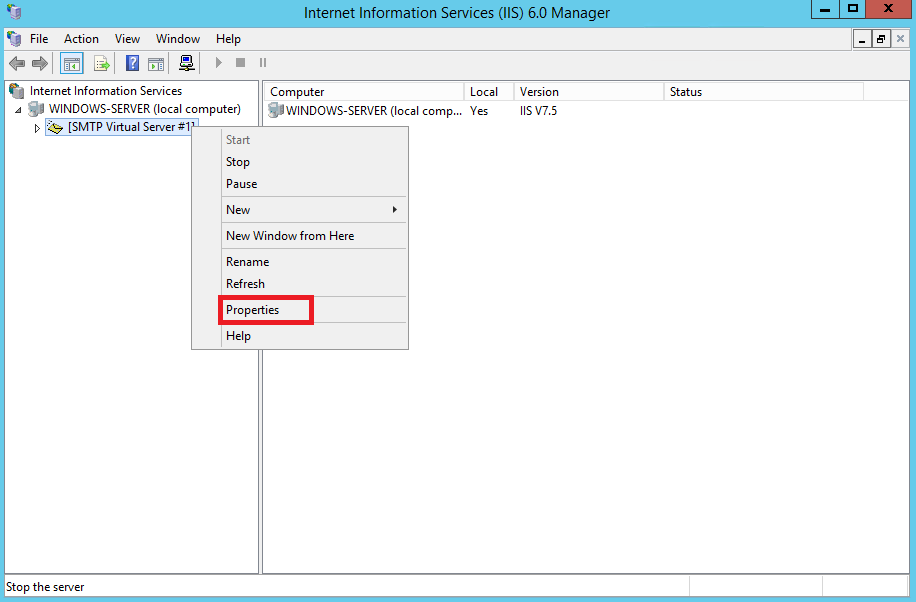
В открывшемся окне менеджера IIS раскройте ветку вашего сервера и на строке SMTP Virtual Server нажмите правую кнопку мыши, после чего перейдите в Properties.
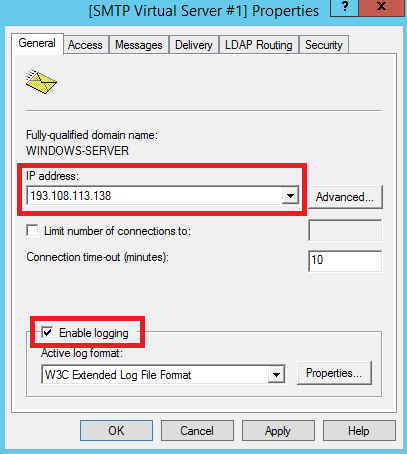
Далее в строке IP address: необходимо выбрать IP-адрес вашего сервера и активировать опцию Enable logging.
Во вкладке Access нажмите кнопку Authentication...
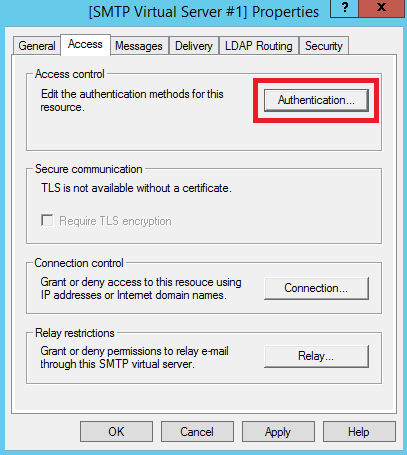
В открывшемся окне активируйте опцию Anonymous access. Активация данной опции нужна, чтобы пользователи и приложения смогли бы использовать сервер SMTP анонимно. Позже можно будет настроить более безопасную аутентификацию, пока же нажмите OK.
Далее в разделе Connection control нажмите кнопку Connection...
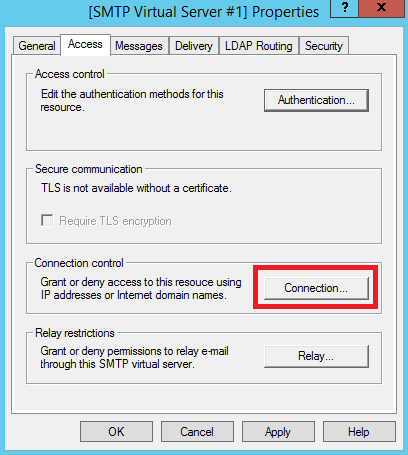
В окне Connection установите переключатель на Only the list below и при помощи кнопки Add... добавьте IP-адрес вашего VPS. После чего нажмите OK.
Точно такую же настройку необходимо проделать в разделе Relay restrictions. Для чего нажмите кнопку Relay... и добавьте IP-адрес вашего сервера установив переключатель в Only the list below.

После чего перейдите во вкладку Delivery и нажмите Advanced...
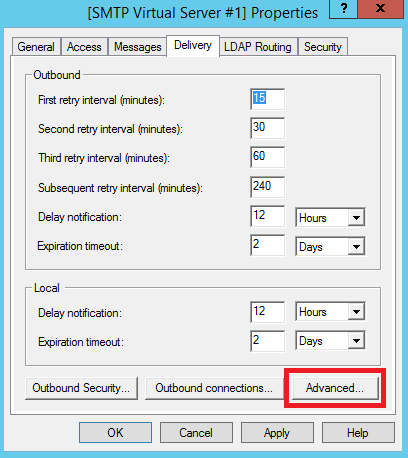
Здесь в строку Fully-qualified domain name: необходимо внести имя вашего домена, в нашем примере это – my-domain.host.
Для того, чтобы проверить корректность данной настройки, нажмите кнопку Check DNS.
Далее сохраните все внесённые в настройки изменения при помощи кнопки OK.
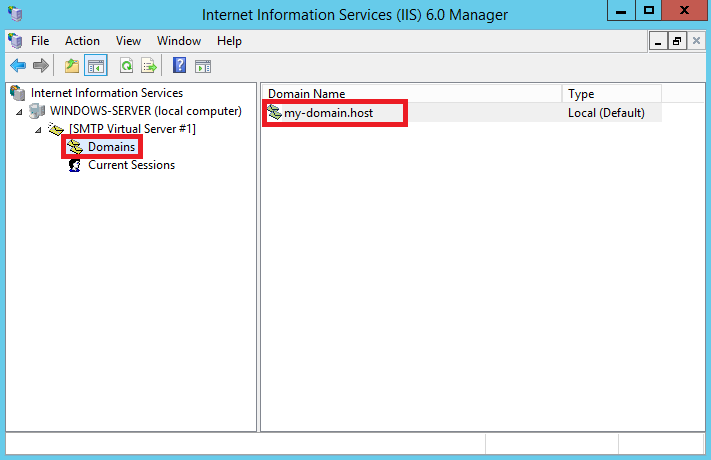
Также необходимо указать корректное имя домена в ветке Domains.
На следующем шаге нужно активировать функцию автоматического запуска сервера SMTP. Для этого запустите командную строку PowerShell и выполните следующие команды для запуска службы:
set-service smtpsvc -StartupType Automatic
start-service smtpsvcЧтобы убедиться, что служба запущена, необходимо выполнить ещё одну команду:
get-service smtpsvcВывод данной команды должен выглядеть примерно следующим образом:
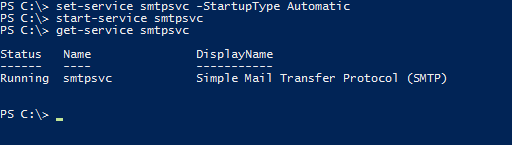
Теперь там же, в командной строке PowerShell, при помощи следующей команды отправьте сообщение на свою электронную почту:
Send-MailMessage -SmtpServer my-domain.host -To your@email.address -From mail@my-domain.host -Subject "Message Subject" -Body "Message Body"Здесь:
my-domain.host– имя домена, с которого будет производиться отправка сообщения;your@email.address– адрес электронной почты, на который будет отправлено сообщение;mail@my-domain.host– этот электронный адрес будет указан в сообщении как адрес отправителя;Message Subject– тема письма;Message Body– тело письма.
После чего проверьте свою почту, на которую должно прийти сообщение от вашего почтового сервера.
Установка и настройка Postfix на Ubuntu 20.04
Для операционной системы Ubuntu существует довольно популярный почтовый сервер – Postfix. Для установки Postfix мы будем использовать виртуальный сервер, работающий на Ubuntu 20.04. При этом на VPS должны быть произведены работы по первоначальной настройке, описанные в соответствующей статье нашего справочника.
Также, для работы Postfix нужен домен с привязанной A-записью, которой является IP-адрес вашего виртуального сервера.
Плюс ко всему, необходимо соотнести имя домена с именем сервера и его IP-адресом. Для этого запустите следующую команду:
$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname ubuntu-serverЗдесь, ubuntu-server – имя нашего сервера, вместо которого вы можете использовать своё.
Теперь при помощи текстового редактора откройте файл /etc/hosts:
$ sudo nano /etc/hostsВ данный файл добавьте строку:
XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX my-domain.host ubuntu-serverВ данном случае:
XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX– IP-адрес вашего сервера;my-domain.host– имя вашего домена;ubuntu-server– имя вашего сервера.
Теперь запустите установку Postfix и почтового пакета mailutils:
$ sudo apt install postfix mailutilsВ процессе установки система попросит вас выбрать тип конфигурации. Необходимо указать Internet Site:
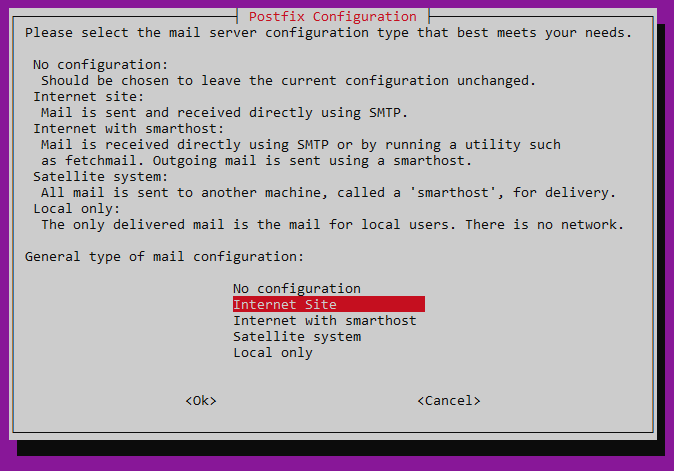
Также установщик попросит согласиться с именем домена, в отношении которого производится настройка почтового сервера. В нашем случае это будет my-domain.host.
По окончании установки можно попробовать с нашего почтового сервера отправить тестовое сообщение. Команда для отправки сообщения выглядит следующим образом:
$ echo "Message Body" | mail -s "Message Subject" your@email.addressВ данной команде:
Message Body– тело письма;Message Subject– тема письма;your@email.address– адрес электронной почты, на который будет отправлено сообщение.
Проверьте свой почтовый ящик (в нашем примере это – your@email.address), на который должно прийти отправленное из Postfix сообщение.
Setting up an SMTP server on a Windows 10 machine can transform how businesses handle email communication. Whether you’re running a small business, managing marketing campaigns, or working in enterprise IT, having a local SMTP server offers better control, enhanced security, and improved email deliverability.
This guide simplifies the process of installing and configuring an SMTP server on Windows 10. We’ll cover:
- Essential prerequisites.
- Step-by-step instructions to enable and configure the SMTP virtual server using Internet Information Services (IIS).
- Troubleshooting common issues.
By the end, you’ll be equipped to send emails securely, handle outbound email delivery, and manage your email infrastructure with confidence.
What Is an SMTP Server and Why Do You Need One?
An SMTP server is a type of email server used to send and relay emails over the internet. SMTP, short for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, is the standard for transferring email messages between servers and to recipients.
Why Businesses Rely on SMTP Servers
For small businesses, marketers, and enterprise teams, an SMTP server ensures reliable email delivery, which is essential for communication and marketing campaigns. Here’s why:
- Email Deliverability: A dedicated SMTP server reduces the chances of your messages being flagged as spam.
- Control: Unlike third-party email services, you can customize and manage your own server configuration.
- Cost Efficiency: It’s a cost-effective solution for handling large volumes of email without third-party fees.
How It Works
When you send an email, the SMTP server processes the message by identifying the recipient’s domain, establishing a connection, and transferring the email to the destination server automatically. It also manages authentication, ensuring only authorized users can send emails.
Benefits of Running an SMTP Server on Windows 10
Setting up a local SMTP server on a Windows 10 machine offers several advantages:
- It enables outbound email delivery within your local network or across the internet.
- Supports tools like IIS 6.0 Manager, which simplifies SMTP server configuration.
- Provides options for TLS encryption, which secures communication.
Prerequisites for Setting Up an SMTP Server on Windows 10
Before starting the process of installing and configuring an SMTP server on Windows 10, make sure you have the necessary tools and resources. Proper preparation ensures a smoother setup and avoids unnecessary troubleshooting later.
System and Hardware Requirements
- Windows 10 machine with administrative access.
- Stable internet connection for sending emails beyond the local network.
- Adequate system resources to run an SMTP service, such as sufficient RAM and disk space.
Software Requirements
- Internet Information Services (IIS): A built-in feature in Windows 10 that supports SMTP server configuration.
- Firewall Access: Ensure your firewall settings allow traffic on port 25 (default SMTP port) or another designated port.
- Email Client: Optional but recommended for testing email delivery. Examples include Outlook or Thunderbird.
Key Preparations
- Install IIS Components: The SMTP virtual server functionality is part of IIS 6.0 Manager, which may need to be added via the Server Manager.
- Obtain a Domain Name: If you plan to send emails over the internet, a registered domain name adds professionalism and improves deliverability.
- SSL Certificate (Optional): Secure communication with TLS encryption by installing a valid SSL certificate on the server.
Optional Tools
- Telnet: Useful for troubleshooting connection issues with the SMTP server.
- Testing Tools: Services like Mailtrap or Postman can verify if your SMTP server setup is working correctly.
How to Enable and Configure SMTP Server on Windows 10 (Step-by-Step)
Follow these steps to enable and configure the SMTP server on your Windows 10 machine. This process involves enabling necessary features, configuring settings, and testing the server to ensure it’s ready to send emails.
Step 1: Enable IIS and SMTP Components
To set up the SMTP virtual server, you need to enable the necessary components in Internet Information Services (IIS).
- Open Control Panel:
- Go to Control Panel > Programs > Programs and Features.
- Turn Windows Features On or Off:
- Click on Turn Windows features on or off from the left panel.
- Enable IIS and SMTP:
- Expand Internet Information Services and check the box for SMTP Server.
- Ensure related services like IIS Management Console and IIS 6.0 Manager are also selected.
- Install Features:
- Click OK and let Windows install the necessary components.
Step 2: Configure the SMTP Virtual Server
Once IIS and SMTP components are installed, you can configure the SMTP server.
- Open IIS Manager (6.0):
- Search for IIS 6.0 Manager in the Start menu and open it.
- Expand the Computer Name:
- In the left panel, expand your local server name to reveal the SMTP virtual server.
- Set Basic Authentication:
- Right-click on the SMTP virtual server and select Properties.
- Under the Access tab, configure authentication settings. Enable Integrated Windows Authentication if you’re using domain accounts.
- Specify IP Address and Port:
- Under the General tab, specify the IP address your SMTP server will bind to. Keep port 25 unless your ISP blocks it.
- Configure SMTP Relay Restrictions:
- Go to the Relay tab. Choose whether to allow specific IP addresses or a group of computers to relay emails.
Step 3: Configure Firewall for SMTP Traffic
Your SMTP server must communicate through the firewall for outbound email delivery.
- Open Windows Firewall Settings:
- Go to Control Panel > System and Security > Windows Defender Firewall.
- Create a New Rule:
- Click on Advanced Settings and add a new inbound rule for port 25 (or the port you configured).
- Allow the SMTP Service:
- Make sure the rule is applied to the SMTP service to allow incoming and outgoing traffic.
Step 4: Test Your SMTP Server
After configuring the SMTP server, test it to confirm it’s working properly.
- Send Test Emails:
- Use an email client to send a message through your server. Configure the client with your SMTP server’s IP address, port, and authentication credentials.
- Use Telnet for Troubleshooting:
- Open the Command Prompt and type
telnet [SMTP server IP] 25to check connectivity.
- Open the Command Prompt and type
Next Steps
You’ve now installed and configured the SMTP server on your Windows 10 machine. Make sure to restart the server and test different scenarios to ensure reliable email delivery. In the next section, we’ll discuss best practices for maintaining and optimizing your SMTP setup.
Best Practices for Using an SMTP Server
Proper maintenance and optimization are essential for ensuring your SMTP server performs reliably and securely. Here are some key practices to keep your server running smoothly and avoid issues like poor deliverability or security breaches.
1. Regular Monitoring and Maintenance
- Monitor Email Logs: Regularly review logs to detect failed deliveries, authentication errors, or spam activity.
- Update Server Software: Keep your Windows 10 and SMTP service components updated to fix bugs and improve performance.
- Restart the SMTP Server: Periodically restart the server to clear potential issues and ensure all updates are applied.
2. Secure Your SMTP Server
- Enable TLS Encryption: Always use TLS to secure the connection and protect emails during transmission.
- Install a Valid SSL Certificate: Enhance trust and secure the SMTP server with an SSL certificate.
- Authentication Settings: Require an account name and password for authentication to prevent unauthorized access.
- Restrict Anonymous Access: Configure your server to allow email relay only from trusted users or systems.
3. Improve Email Deliverability
- Avoid Blacklisting: Adhere to anti-spam regulations like CAN-SPAM. Use your domain name in email headers to boost credibility.
- SPF, DKIM, and DMARC: Set up these DNS records for your domain to verify emails sent through your SMTP server.
- Test Emails Using Tools: Use services like Mailtrap or Postman to simulate and test email delivery.
4. Manage Access and Traffic
- IP Restrictions: Limit email relays to a specified group of computers or IP ranges.
- Set Limits for Outbound Emails: Define quotas for the number of emails to be sent within a given time to prevent misuse.
- Throttling Settings: Configure throttling to ensure the server handles a large number of requests without crashing.
5. Troubleshoot Common Issues Proactively
- Connection Errors: Check firewall rules and ensure the SMTP service is running.
- Delivery Failures: Verify recipient addresses and inspect email headers for issues.
- Authentication Failures: Ensure users are using the correct account name or password.
Why Follow These Best Practices?
Adhering to these practices not only ensures smooth email operations but also protects your business’s reputation. By optimizing the SMTP server setup, you can reliably send outbound emails and build trust with your recipients.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting Tips
Even with proper setup, you might face challenges when running an SMTP server on Windows 10. Here’s a list of common problems and their solutions to keep your server functioning smoothly.
1. Connection Errors
Problem: Unable to connect to the SMTP server or port.
Solution:
- Check if port 25 (or the designated SMTP port) is open in your firewall settings.
- Use Telnet to test the connection: cssCopy code
telnet [SMTP server IP] 25If this fails, confirm the server’s IP address and port configuration.
2. Email Delivery Failures
Problem: Emails are not being sent or are stuck in the queue.
Solution:
- Verify that the recipient’s email address and domain name are correct.
- Check server logs for errors related to authentication or email routing.
- Ensure the server isn’t blacklisted by verifying its IP address on public spam lists.
3. Authentication Issues
Problem: Clients fail to authenticate with the server.
Solution:
- Confirm the account name and password are entered correctly.
- Ensure Integrated Windows Authentication is enabled in the SMTP virtual server settings.
- Update user credentials if passwords were recently changed.
4. Spam and Security Concerns
Problem: Emails sent through your server are flagged as spam.
Solution:
- Configure SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records for your domain to enhance email authentication.
- Avoid open relay setups that allow unauthorized users to send emails.
5. Firewall or Network Conflicts
Problem: Emails are blocked by the firewall or other network policies.
Solution:
- Verify that your firewall allows SMTP traffic. Add rules for the specific port used (default is 25).
- Test with a different network or temporarily disable antivirus software to rule out conflicts.
6. TLS Encryption Issues
Problem: Email clients cannot establish a secure connection.
Solution:
- Ensure you have a valid SSL certificate installed on the server.
- Configure the client to use TLS to secure communications.
7. High Email Queue Volume
Problem: Large numbers of emails are stuck in the queue due to server overload.
Solution:
- Implement throttling to manage the number of emails processed per second.
- Use a dedicated local SMTP server for bulk emails to reduce load on your main server.
Tools to Enhance Your SMTP Server Performance
Optimizing your SMTP server setup goes beyond basic configuration. Using the right tools can improve performance, ensure deliverability, and streamline troubleshooting. Here are some helpful tools and services to consider.
1. Email Testing Tools
Testing your SMTP server setup is crucial for verifying that emails are being sent correctly.
- Mailtrap: Simulates an SMTP server to test email delivery without sending emails to real recipients.
- Postman: Allows you to test and debug your email requests, ensuring proper configuration.
- Telnet: A command-line tool for verifying server connectivity and diagnosing port or IP address issues.
2. Monitoring Tools
Track your server’s performance and email delivery metrics to ensure everything runs smoothly.
- MxToolBox: Monitors the health of your SMTP server, including blacklist status and DNS settings.
- Nagios: Provides real-time monitoring of server resources and alerts for potential issues.
- GFI MailEssentials: Offers email security and performance monitoring for business servers.
3. Security Tools
Secure your SMTP server to protect against unauthorized access and ensure compliance with best practices.
- SSL Certificate Managers: Simplify the process of installing and managing SSL certificates for TLS encryption.
- SpamAssassin: Filters spam and prevents malicious emails from being relayed through your server.
4. Performance Optimization Tools
- Email Delivery Services: Use tools like Amazon SES or SendGrid alongside your server to improve bulk email performance.
- SMTP Load Testing Tools: Simulate high traffic to test how your server handles outbound emails under pressure.
5. Automation and Integration Tools
- PowerShell Scripts: Automate routine tasks like restarting the server, updating settings, or managing logs.
- Email Client Plugins: Ensure seamless integration with applications like Outlook or Thunderbird.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between an SMTP server and a regular email server?
An SMTP server focuses solely on sending emails using the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, while a regular email server handles both sending and receiving emails. For receiving emails, servers use protocols like POP3 or IMAP.
2. Can I use this setup for bulk email campaigns?
Yes, but it’s recommended to configure your server properly with anti-spam measures like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. Additionally, use throttling settings to manage email volumes and avoid server overload.
3. How do I secure my SMTP server?
To secure your server:
Enable TLS encryption and install an SSL certificate.
Require authentication with a valid account name and password.
Restrict anonymous access and relay permissions to trusted IPs.
4. What’s the difference between port 25 and port 587?
Port 25 is the standard port for email relay between servers but is often blocked by ISPs to reduce spam.
Port 587 is commonly used for sending emails from clients with authentication and encryption enabled.
5. What are some tools to troubleshoot SMTP server issues?
Telnet: Test server connectivity and port availability.
Mailtrap: Verify email delivery without sending real emails.
MxToolBox: Check server health, blacklist status, and DNS configurations.
6. How do I enable TLS encryption on my SMTP server?
To enable TLS:
Install a valid SSL certificate on your server.
Configure your SMTP settings to support encrypted connections.
Ensure your email clients are set to use TLS to secure the connection.
7. Why are my emails being flagged as spam?
This could happen if:
Your server’s IP is blacklisted.
Your emails lack proper SPF, DKIM, or DMARC authentication.
The content or email headers trigger spam filters.
Conclusion
Setting up an SMTP server on Windows 10 empowers businesses to take control of their email communication. With a properly configured SMTP virtual server using Internet Information Services (IIS), you can ensure reliable email delivery, enhance security with TLS encryption, and avoid the limitations of third-party services.
This guide walked you through:
- Understanding the importance of an SMTP server.
- Preparing your system with the right tools and software.
- A detailed step-by-step process for setup and configuration.
- Troubleshooting common issues and optimizing performance.
Whether you’re managing email campaigns, sending automated notifications, or improving your organization’s email infrastructure, having your own SMTP server can be a game-changer. Follow the best practices outlined here, and make the most of your setup.
