The `scp` command, which stands for secure copy protocol, is used in Windows Command Prompt to securely transfer files between a local and a remote host over SSH.
Here’s an example of the syntax for using `scp` to copy a file from your local machine to a remote server:
scp C:\path\to\local\file.txt username@remote_host:/path/to/remote/directory/
Setting Up SCP on Windows
Prerequisites
Installing OpenSSH on Windows
To use SCP in Windows CMD, you need to have OpenSSH installed. Follow these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Navigate to Apps > Optional features.
- Click on Add a feature.
- Search for OpenSSH Client and click on Install.
- Confirm the installation and wait for it to finish. Once installed, you’re ready to use SCP.
Ensuring SSH Client is Enabled
To confirm that the SSH Client is enabled:
- Open Control Panel.
- Go to Programs > Turn Windows features on or off.
- Check whether OpenSSH Client is listed and ticked. If not, check it and click OK to enable it.
Utilizing Windows CMD
Opening Command Prompt
To execute SCP commands, you need to access the Windows Command Prompt:
- Press `Win + X` to open the quick access menu.
- Select Windows Terminal (Admin) or Command Prompt (Admin) to ensure you have the necessary permissions for file transfers.

Mastering SSH in Windows Cmd: A Quick How-To Guide
Understanding SCP Syntax
Basic Syntax Structure
The SCP command format is crucial for understanding how to use it effectively. The general syntax follows this structure:
scp [options] [source] [destination]
In this format:
- [options]: Additional flags to modify behavior.
- [source]: The file or directory you want to copy.
- [destination]: Where you want to copy the file or directory to.
Breaking Down the Components
Options
Common options include:
- `-r`: Use this flag to copy directories recursively.
- `-P`: Specify a port when connecting to SSH.
Source
The source can be a local file (on your machine) or a remote file (on another machine) following the pattern `user@host:/path/to/file`.
Destination
Similar to the source, the destination can be a local path or a remote path, adapting the same user and host format.

Mastering Pwd in Windows Cmd: Your Quick Reference Guide
Executing SCP Commands
Copying Files from Local to Remote
To transfer a file from your local machine to a remote host, you can use the following command:
scp C:\path\to\file.txt user@remote_host:/remote/path/
In this command:
- `C:\path\to\file.txt` is your source file.
- `user@remote_host:/remote/path/` specifies the user and host you’re transferring the file to.
Copying Files from Remote to Local
To copy a file from a remote server to your local machine, the command is slightly adjusted:
scp user@remote_host:/remote/path/file.txt C:\path\to\
Here:
- The source is now the remote file, and the destination is your local path.
Copying Directories Recursively
If you need to transfer a directory and all its contents, include the `-r` option:
scp -r C:\path\to\folder user@remote_host:/remote/path/
This command ensures that not just the folder, but all its nested files and directories are copied.
Port Specification
If the SSH server is running on a non-standard port (not 22), you can specify this with the `-P` option:
scp -P port_number C:\path\to\file.txt user@remote_host:/remote/path/
Replace `port_number` with the actual port when connecting to the server.

Repair Windows Cmd: Quick Fixes and Tips
Advanced SCP Usage
Using Identity Files
For added security, you may want to use SSH keys for authentication. If you have a private key, the command looks like this:
scp -i C:\path\to\key_file user@remote_host:/file/path /local/destination
This ensures that your key is used for connection without needing to input a password.
Batch Transfers
To copy multiple files matching a certain pattern, you can utilize wildcards:
scp C:\path\to\*.txt user@remote_host:/remote/path/
This command transfers all `.txt` files from your specified directory to the remote location.
Using Verbose Mode
If you encounter issues or want to see more information during the transfer, use the `-v` option:
scp -v C:\path\to\file.txt user@remote_host:/remote/path/
The verbose output will provide insights into the connection process and potential issues you may face.

Sleep Windows Cmd: Mastering Sleep Commands in Cmd
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Authentication Errors
One of the most common problems is authentication errors. These typically occur due to incorrect username/password combinations or SSH key setups. Ensure that your credentials are accurate, and if using a key, ensure it is correctly referenced.
Connectivity Problems
If you experience connectivity issues, check your network connection. You can also use the `ping` command to verify the connectivity with the remote host.
Permissions Problems
Permission denied errors are common when your user does not have write access to the destination folder. Ensure you have the right permissions on the remote server to avoid this issue.

Lock Windows Cmd: A Quick Guide to Securing Your Commands
Conclusion
SCP in Windows CMD is a robust and versatile tool for transferring files securely between machines. With the proper setup and understanding of commands, it opens many possibilities for efficient file management across networks. By mastering these commands, you can enjoy streamlined file transfers while maintaining strong security protocols. With practice, you’ll find SCP is a vital addition to your toolkit for remote work.
Make File in Windows Cmd: A Quick Guide
Additional Resources
For those looking to deepen their understanding, consider browsing the official OpenSSH documentation or searching for tutorial videos that can guide you through various use-case scenarios.
Протокол SSH (Secure Shell) — это сетевой протокол для удаленного управления операционной системой через командную строку, который можно назвать стандартом для удаленного доступа к *nix-машинам. Позволяет производить защищенный вход на сервер, удаленно выполнять команды, управлять файлами (создавать, удалять, копировать и т.д.) и многое другое. Большинство облачных и хостинг-провайдеров требуют наличие SSH для доступа к своим сервисам. В этой статье рассмотрим копирование файлов по SSH в Windows и Linux-системах.
SSH способен передавать любые данные (звук, видео, данные прикладных протоколов) через безопасный канал связи. В отличие от устаревших и небезопасных протоколов telnet и rlogin, в SSH обеспечивается конфиденциальность передаваемых данных и подлинность взаимодействующих сторон — необходимые условия для сетевого взаимодействия в Интернете.
Рассмотрим алгоритм установки зашифрованного соединения между клиентом и сервером:
- Установка TCP-соединения. По умолчанию сервер слушает 22-й порт. В работе протокола используется набор алгоритмов (сжатие, шифрование, обмен ключами), поэтому стороны обмениваются списком поддерживаемых алгоритмов и договариваются, какие из них будут использовать.
- Чтобы третья сторона не смогла выдать себя за сервер или клиент, стороны должны удостоверится в подлинности друг друга (аутентификация). Для этого используются асимметричные алгоритмы шифрования и пара открытый-закрытый ключ. Вначале проверяется аутентичность сервера. Если соединение происходит впервые, пользователь увидит предупреждение и информацию о сервере. Список доверенных серверов и их ключей записывается в файл по адресу /home/<username>/.ssh/known_hosts.
- Как только клиент убедился в достоверности сервера, стороны генерируют симметричный ключ, с помощью которого происходит шифрования всех обмениваемых данных. Таким образом при перехвате данных, никто, кроме сторон не сможет узнать содержимое сообщений.
- Далее происходит аутентификация пользовательского сеанса. Для этого используется либо пароль, либо присланный клиентом публичный ключ, сохраняемый в файле /home/<username>/.ssh/authorized_keys на сервере.
Самая популярная реализация на Линукс, OpenSSH, предустанавливается практически на всех дистрибутивах: Ubuntu, Debian, RHEL-based и других. На Windows в качестве клиентов можно использовать программы PuTTY, MobaXterm. Начиная с WIndows 10 и Windows Server 2019 инструменты OpenSSH доступны и на Windows.
Подробнее об SSH и работе с ним мы писали в статье «Как пользоваться SSH».
VDS
Копирование файлов
Копирование файлов в Linux по SSH осуществляется с помощью двух основных программ: scp и sftp. Обе утилиты поставляются вместе с пакетом OpenSSH. Существуют две основные версии протокола SSH: 1 и 2. Оболочка OpenSSH поддерживает обе версии, однако первая применяется редко.
Настройка автодополнений
При работе с scp крайне удобно использовать tab для автодополнения путей на удаленной машине. Для этого нужно настроить аутентификацию пользователя по публичному ключу.
Для начала сгенерируем открытый и закрытый ключ:
ssh-keygenВывод:
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/home/user/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/home/user/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /home/user/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /home/user/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:wJQ/XBZq69qXGHxseTuccUEpzWYHhsVVHcDXE3MrTHQ user@hostВ конце вывода будет графическое представление ключа (key’s randomart image), которое легче запомнить, чем хэш ключа.
По умолчанию ключи (id_rsa.pub — открытый, id_rsa — закрытый) сохранятся в домашнем каталоге пользователя в директории .ssh. Также во время генерации программа попросит ввести пароль, которым будут защищены ключи. Если не хотите дополнительной защиты, нажмите два раза Enter.
Теперь копируем публичный ключ на удаленную машину:
ssh-copy-id [имя пользователя]@[ip-адрес]Здесь [имя пользователя] — учетная запись пользователя, под которой будем логиниться на удаленной машине, [ip-адрес] — адрес удаленной машины (можно использовать доменное имя, если они локально резолвится). Далее вводим пароль пользователя. Если все прошло корректно, то в выводе будет команда для удаленного подключения:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh '<имя пользователя>@<ip-адрес>'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.Secure copy (SCP)
Для копирования небольших объемов информации (например, конфиги сервисов) лучше всего подойдет утилита scp.
Синтаксис команды для копирования с локальной машины на удаленный сервер:
scp [путь к файлу] [путь к файлу] [имя пользователя]@[ip-адрес]:[путь к файлу]Попробуем скопировать файл на сервер:
scp test.txt user@192.168.1.29:/home/user/Вывод:
test.txt 100% 12 20.6KB/s 00:00Можно передать несколько файлов за раз. Для этого указываем пути, разделенные пробелами:
scp test1.txt test2.txt user@192.168.1.29:/home/user/Для копирования с удаленного сервера на локальную машину нужно поменять источник и место назначения местами:
scp user@192.168.1.29:/home/user/test.txt ~/Для передачи директории используйте ключ -r:
scp -r testdir user@192.168.1.29:/home/user/Также имеется возможность передачи с одного удаленного сервера на другой:
scp gendo@192.168.1.25:/home/gendo/test.txt user@192.168.1.29:/home/user/Secure FTP (SFTP)
Еще одной утилитой для передачи файлов, поставляемых в OpenSSH, является sftp. C релизом OpenSSH 9.0 утилита scp переведена по умолчанию на использование SFTP вместо устаревшего протокола SCP/RCP. Sftp работает практически также, как и классический ftp, за исключением того, что в sftp данные передаются не в виде обычного текста, а по зашифрованному туннелю (туннелирование — это процесс упаковки и передачи одного сетевого подключения с помощью другого). Также для работы sftp не нужен отдельный FTP-сервер.
Пример простого скачивания через sftp:
gendo@melhior:~$ sftp misato@192.168.1.29
Connected to 192.168.1.29.
sftp> ls
file.txt file1.txt file2.txt test.txt
sftp> lcd testdir/
sftp> get test.txt
Fetching /home/misato/test.txt to test.txt
test.txt 100% 12 4.8KB/s 00:00
sftp> byeСам по себе sftp применяется редко: вместо этого его используют файловые менеджеры, например Midnight Commander и Nautilus:
Использование sftp в файловом менеджере Nautilus. Удаленная машина отображается в виде папки с именем пользователя и IP-адресом.
Копирование файлов по SSH в Windows
Скачать файл с сервера или на сервер в Windows можно с помощью консольной программы pscp, поставляемой вместе с PuTTY. Синтаксис очень похож на обычный scp:
pscp [путь к файлу] [имя пользователя]@[имя сервера/ip-адрес]:[путь к файлу]Для SSH-копирования файлов на сервер, используйте следующую команду:
pscp C:\server\test.txt misato@192.168.1.29:/home/misato/Скачивание файла с сервера на компьютер:
pscp misato@192.168.1.29:/home/misato/test.txt C:\file.txtУвидеть список файлов на сервере можно при помощи опции -ls:
pscp -ls [имя пользователя]@[ip-адрес]:[путь]Если в пути или в названии файла есть пробелы, используйте кавычки:
pscp "C:\dir\bad file name" misato@192.168.1.29:/home/misatoДля получения помощи по команде введите pscp без аргументов.
Заключение
Мы рассмотрели, как копировать файлы на сервер и с сервера с помощью безопасного сетевого протокола SSH. Если вы используете облачные серверы, важно уметь работать с SSH, так как он является стандартом для удаленного доступа к *nix-машинам и будет необходим вам в повседневной работе.
Кстати, в официальном канале Timeweb Cloud собрали комьюнити из специалистов, которые говорят про IT-тренды, делятся полезными инструкциями и даже приглашают к себе работать.
pscp / scp is the keyword when wanting to copy files from Windows to Linux and vice versa.
How to use
example
Linux to Windows
scp /home/ubuntu/myfile.txt username@IP_of_windows_machine:/C:/Users/Admin/Desktop
Windows to Linux
scp C:\Users\Admin\Desktop\myfile.txt username@IP_of_linux_machine:/home/ubuntu
Instead of ip the hostname can be used as well
PSCP
PSCP usually comes with the popular ssh client Putty and is used to copy files via the command line interface from one machine to another.
Quick example
Windows to Linux
pscp C:\Users\Name\Downloads\myfile.txt username_linux_machine@ip_of_linux_machine:/home/ubuntu
Linux to Windows
pscp username_linux_machine@ip_of_linux_machine:/home/ubuntu/myfile.txt C:\Users\Name\Downloads
Set up
1. Download pscp.exe [1]
2. copy pscp.exe executable to system32 folder
copy the pscp.exe executable to the system32 directory of your windows machine. This folder normally exists in C:\Windows\System32 path.
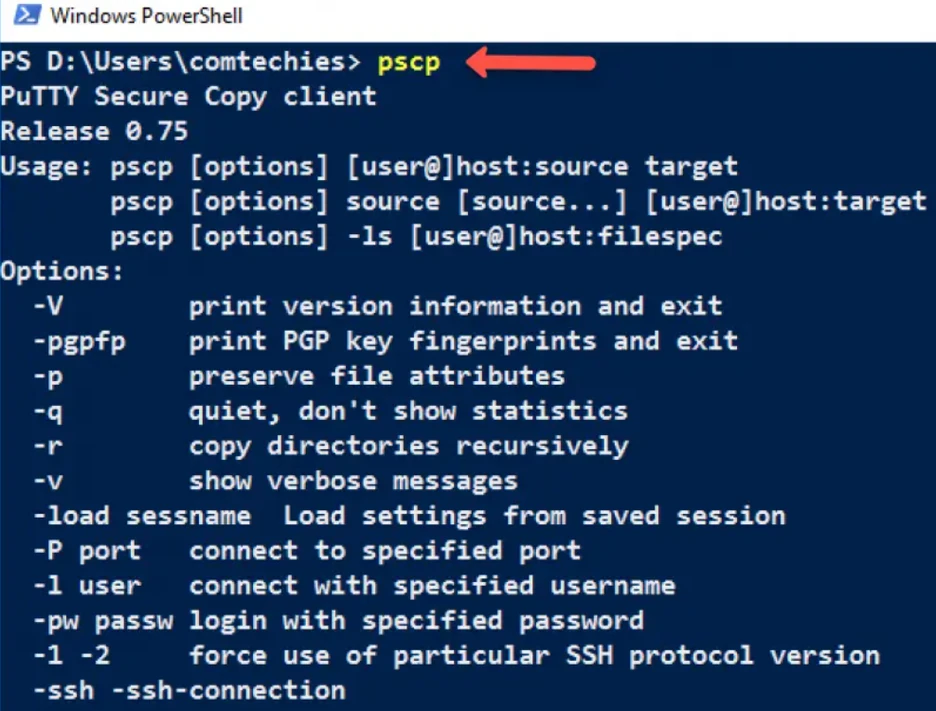
3. Verify with PowerShell
Open Windows PowerShell and use the following command to verify if pscp is accessible from the path.
You should see the following output.
4. Copy file
From Windows to Linux
Use the following format to copy the single file from Windows to the Linux box.
pscp -pw password C:\Users\Admin\Desktop\test.txt \user@192.168.33.10:/home/JohnDoe
From Linux to Windows
pscp -pw password user@192.168.33.10:/path/to/file \C:\Users\Admin\Desktop\
Explanation of the command:
-pwfor the password.- Replace
passwordwith the Linux user password. C:\Users\Admin\Desktop\test.txtrepresents the path of the file that has to be copied to the Linux system.192.168.33.10is the IP of the Linux server./home/vagrantis the user-accessible path in the Linux system to copy the file.
Copy all files of a folder:
If you want to copy all the files in a directory to Linux, you need to add a star (*) to the folder. eg. folder\*
pscp -pw password C:\Users\Admin\Desktop\folder\* \user@192.168.33.10:/home/JohnDoe
When you are working on the multiple servers, copying files between two servers is a common task for any system administrator. In this case, the SCP utility is the best choice for any system administrator.
SCP stands for “Secure Copy Protocol” is a Linux command-line tool used to transfer files and directories securely between two servers.
By default, GUI mode is not installed in Linux servers. SCP utility makes it easier for Linux system administrator to manage the multiple servers from the command-line.
SCP utility is based on the SSH, as so you will need a username and password of the source and target system to transfer the files.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to transfer files and directories between two systems using SCP file transfers!
Basic Syntax
The basic syntax of the scp command is shown below:
scp [OPTION] local-file-or-directory user@remote-ip:/directory/
You can use the above command to transfer files and directories from a local system to remote system.
scp [OPTION] user@remote-ip:/remote-file /local-directory
You can use the above command to transfer files and directories from a remote system to local system.
scp [OPTION] user@remote-ip:/directory/ user@remote-ip:/directory/
You can use the above command to transfer files and directories from one remote system to another remote system.
A brief explanation of each option in SCP command are shown below:
*Note: all these options are Case sensitive!
- -r
This option will copy files and directories recursively. - -v
This option will display verbose output during the copying process. - -P
This option is used to specify the ssh port number of the target host when the target host using the different SSH port. - -l
This option is used to limit the bandwidth while copying the files and directories. - -q
This option skips the SSH warning message. - -p
This option will preserve permissions, modes and access time of files while copying. - -i
This option is used to specify the SSH private key.
Transfer Files and Directories with SCP in Linux
The SCP utility allows you to transfer files between, local to remote, remote to local and remote to remote systems.
In this section we will show you how to transfer files and directories between them.
Local to Remote System Transfers:
Local to Remote File Transfers:
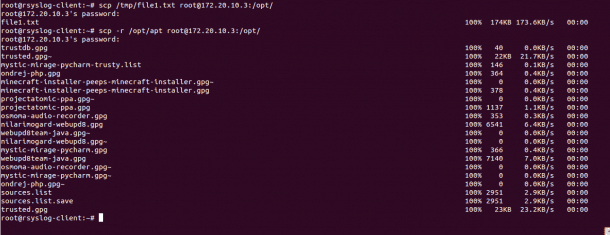
To transfer a file named file1.txt located inside /tmp directory from a local system to the remote system directory /opt use the following command:
scp /tmp/file1.txt root@172.20.10.3:/opt/
You will be asked to provide remote system’s root user password to transfer the file as shown below:
root@172.20.10.3's password:
file1.txt 100% 174KB 173.6KB/s 00:00
You can use the option -v with SCP to see the verbose output during the file transfer:
scp -v /tmp/file1.txt root@172.20.10.3:/opt/
Local to Remote Directories/Folders Transfers:
To transfer a directory named apt located inside /opt from a local system to the remote system directory /opt recursively use the following command:
scp -r /opt/apt root@172.20.10.3:/opt/
Provide remote system’s root user password to transfer the directory as shown below:
trustdb.gpg 100% 40 0.0KB/s 00:00
trusted.gpg~ 100% 22KB 21.7KB/s 00:00
mystic-mirage-pycharm-trusty.list 100% 146 0.1KB/s 00:00
ondrej-php.gpg 100% 364 0.4KB/s 00:00
minecraft-installer-peeps-minecraft-installer.gpg~ 100% 0 0.0KB/s 00:00
minecraft-installer-peeps-minecraft-installer.gpg 100% 378 0.4KB/s 00:00
projectatomic-ppa.gpg~ 100% 0 0.0KB/s 00:00
projectatomic-ppa.gpg 100% 1137 1.1KB/s 00:00
osmoma-audio-recorder.gpg 100% 353 0.3KB/s 00:00
nilarimogard-webupd8.gpg 100% 6541 6.4KB/s 00:00
webupd8team-java.gpg~ 100% 0 0.0KB/s 00:00
nilarimogard-webupd8.gpg~ 100% 0 0.0KB/s 00:00
mystic-mirage-pycharm.gpg 100% 366 0.4KB/s 00:00
webupd8team-java.gpg 100% 7140 7.0KB/s 00:00
osmoma-audio-recorder.gpg~ 100% 0 0.0KB/s 00:00
mystic-mirage-pycharm.gpg~ 100% 0 0.0KB/s 00:00
ondrej-php.gpg~ 100% 0 0.0KB/s 00:00
sources.list 100% 2951 2.9KB/s 00:00
sources.list.save 100% 2951 2.9KB/s 00:00
trusted.gpg 100% 23KB 23.2KB/s 00:00
Example:
Remote to Local Transferring:
Remote to Local File Transfers:
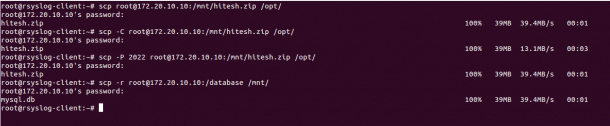
To transfer a file named hitesh.zip located inside /mnt directory of the remote to the local system’s directory /opt use the following command:
scp root@172.20.10.10:/mnt/hitesh.zip /opt/
You can increase the transfer speed by enabling the compression using the option -C with SCP as shown below:
scp -C root@172.20.10.10:/mnt/hitesh.zip /opt/
If your remote server uses SSH port 2022, then you can use -P option to specify the remote SSH port as shown below:
scp -P 2022 root@172.20.10.10:/mnt/hitesh.zip /opt/
Remote to Local Directory/Folders Transfers:
To transfer a directory named /etc from the remote system to local system’s directory /mnt recursively use the following command:
scp -r root@172.20.10.10:/database /mnt/
Example:
Remote to Remote System Transfers:
Remote to Remote File Transfers:
In order to transfer files and directories between two remote servers. You will need to configure SSH key-based authentication between both remote servers.
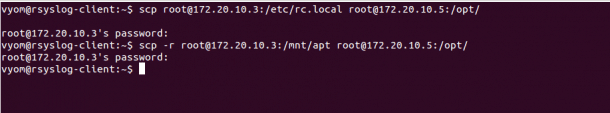
To transfer a file named /etc/rc.local from the one remote system (172.20.10.3) to another remote system’s (172.20.10.5) directory /opt use the following command:
scp root@172.20.10.3:/etc/rc.local root@172.20.10.5:/opt/
To transfer a directory named /mnt/apt from the one remote system (172.20.10.3) to another remote system’s (172.20.10.5) directory /opt use the following command:
scp -r root@172.20.10.3:/mnt/apt root@172.20.10.5:/opt/
Transfer Files and Directories with SCP in Windows (7, 8, 10, and Server)
If you are working on the Windows system and want to transfer files and directories from Windows to Linux and Linux to Windows system. Then, you can achieve this using WinSCP utility.
WinSCP is a free and open-source SCP and SFTP client for Windows based operating systems.
Transfer files between Windows and Linux system follow the below steps:
1. On the windows system, launch the WinSCP utility as shown below:
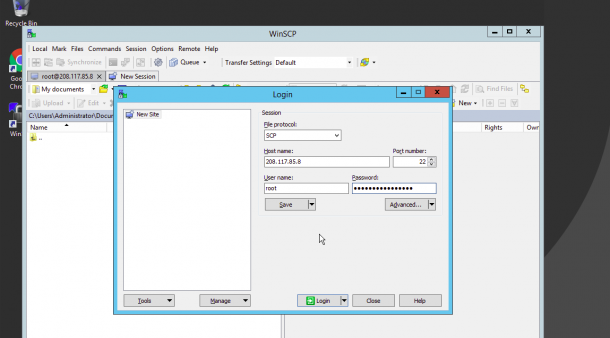
Now provide the following information:
- File Protocol : Select SCP as file transfer protocol.
- Host name : Provide your Linux server IP address.
- Port number : Provide your Linux server SSH port.
- User name : Provide the user name of your Linux server.
- Password : Provide your user’s password.
2. Now click on the Login button. You should see the following page:
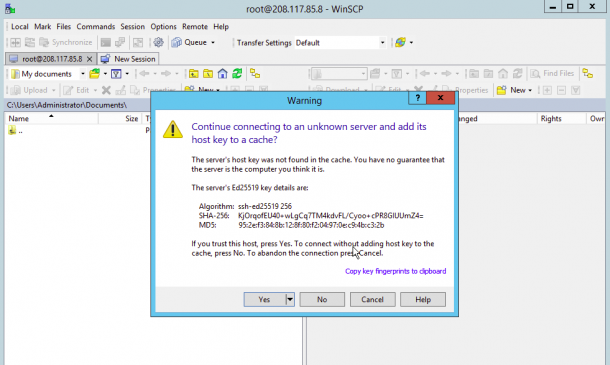
Click on the Yes button to verify the host. Once you are connected to the Linux server, you should see the following page:
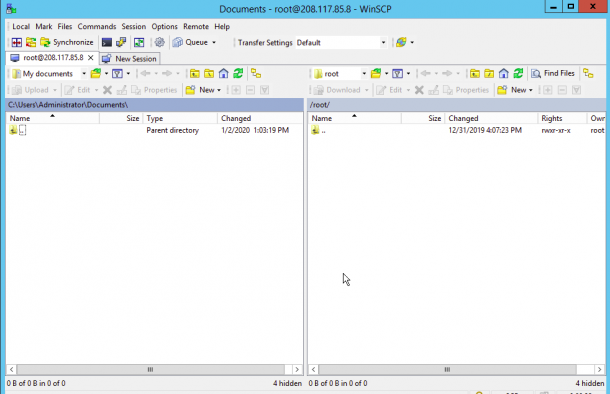
On the left pane, right-click on the file you want to upload on the Linux server and click on the Upload button as shown below:
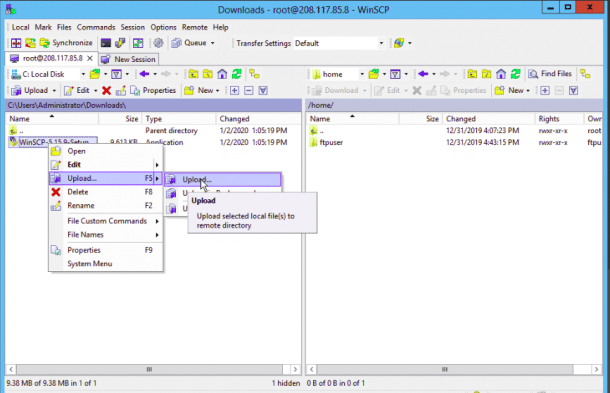
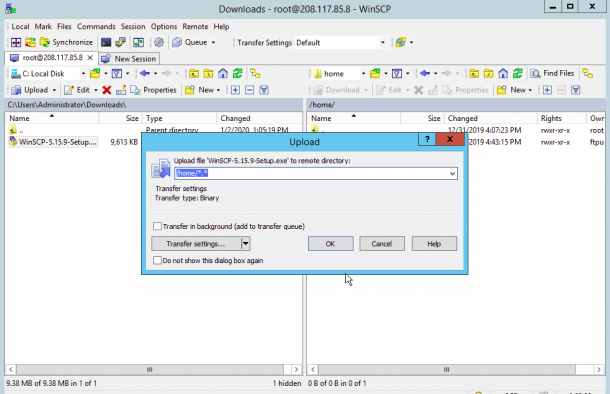
Now, provide the path of the Linux server’s directory and click on the OK button. Once the file has been uploaded, you should see the following page:
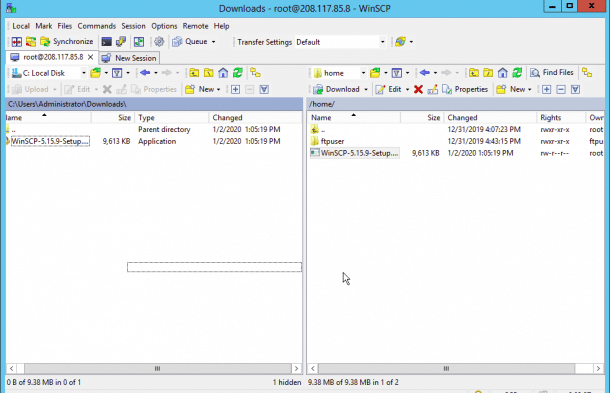
3. On the right pane, right-click on the directory you want to download from the Linux server to the Windows system and click on the Download button as shown below:
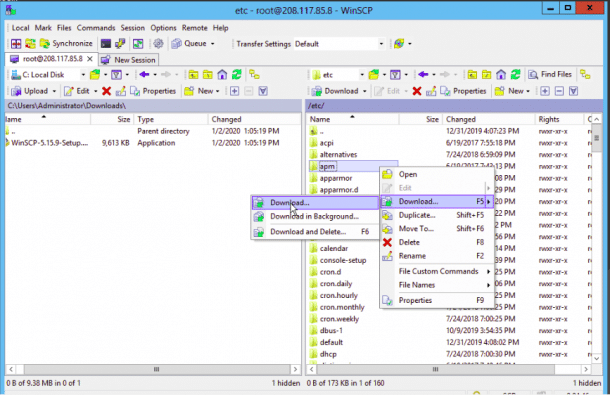
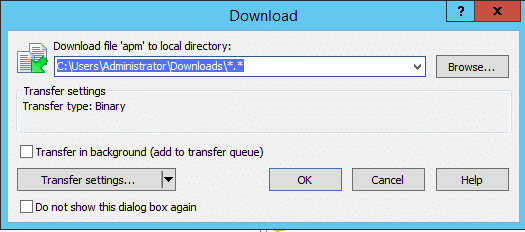
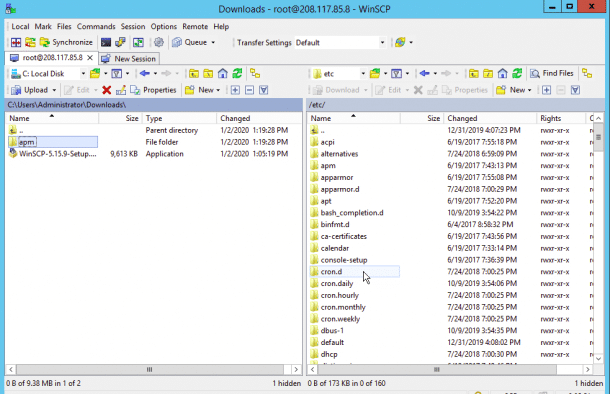
Now, provide the path of the Windows system directory and click on the OK button. Once the file has been uploaded, you should see the following page.
Conclusion
In the above tutorial, we’ve learned how to transfer files and directories from Linux to Linux, Windows to Linux and Linux to Windows. Feel free to ask questions below in the comments section if you have any!
Secure Copy Files Between Windows and Linux Servers
SCP (Secure Copy Protocol) is a secure way to transfer files between your Windows machine and a Linux server. This article explains how to use WinSCP, a popular and user-friendly tool for Windows users, to copy files to and from a Linux server.
Step 1: Enable SSH on the Linux Server
Before transferring files, ensure the SSH service is installed and running on your Linux server. Use the following command on the Linux server:
Step 2: Install and Set Up WinSCP on Windows
-
Download WinSCP from winscp.net.
-
Install WinSCP by following the on-screen instructions.
-
Launch WinSCP after installation.
Step 3: Connect to the Linux Server
-
In WinSCP, create a new connection:
-
File Protocol: Choose
SCP. -
Hostname: Enter the IP address or domain name of your Linux server.
-
Port Number: Default is
22. -
Username: Enter the username for your Linux account.
-
Password: Provide your password or configure a private key.
-
-
Click Login to connect to your server.
Step 4: Transfer Files
Once connected, use the graphical interface to:
-
Drag and drop files from your Windows machine to the Linux server.
-
Drag files from the Linux server to your local Windows machine.
WinSCP provides a simple interface to manage your files securely.
