In this article i will describe how to create custom Winforms window, which can be resized, dragged, and snapped, providing the same experience as standard Windows window.
What motivates developer to create custom Winforms window is, in most cases, an application window design. Standard windows window is configurable to some extend, however not all features are supported or easy to implement. For instance, in my recent project I designed a window with title bar and navigation buttons placed inside the kind of centered “notch”.
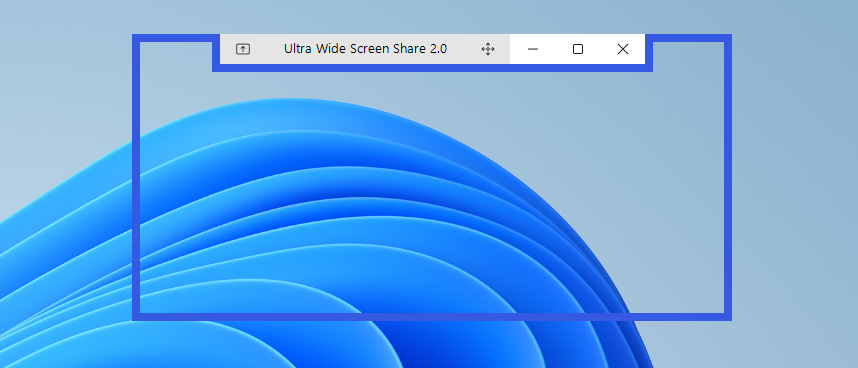
I decided to create this article, since I didn’t find any comprehensive material covering the topic.
Table of contents
- Removing default window tittle bar and borders
- Window dragging
- ReleaseCapture
- SendMessage
- Window resizing
- Window snapping to the screen edges
Removing default window tittle bar and borders
In order to design custom window we need get rid of default windows tittle bar and border. It can be done by setting Form’s FormBorderStyle property.
FormBorderStyle = FormBorderStyle.None;
FormBorderStyle.None hides the widow tittle bar and borders. Afterwards, custom tittle bar and border can be implemented and styled inside the window client area using Winforms controls.
Unfortunately, once FormBorderStyle.None is set, window loses resizing, dragging and snapping functionalities.
Let’s add it back!
Window dragging
Window dragging can be normally achieved by pressing left mouse button a on a window tittle bar, and moving the window around, as long as the button is pressed.
Default window tittle bar was removed by setting FormBorderStyle property. Now, let’s create a custom tittle bar, by placing a Panel control at top of the Form.
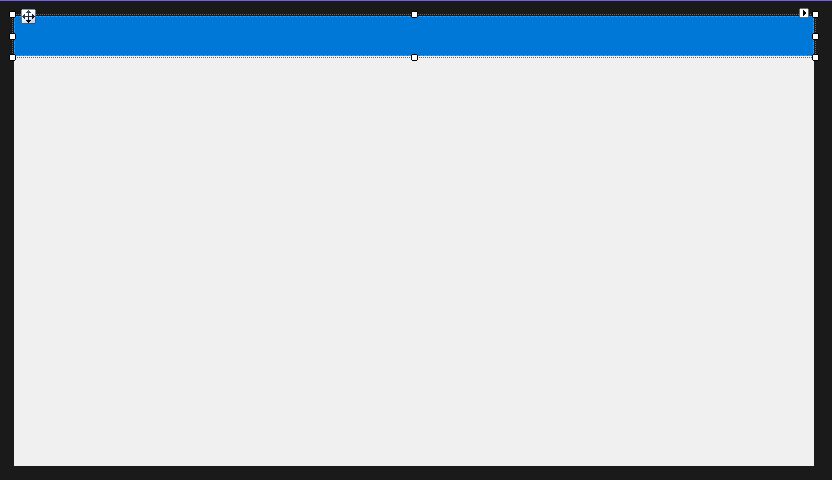
In order to detect when user left mouse button is pressed in the panel area, and start dragging the window, panel’s MouseDown event needs to be handled
const uint WM_NCLBUTTONDOWN = 0xA1;
const uint HT_CAPTION = 0x2;
private void menuPanel_MouseDown(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Button == MouseButtons.Left)
{
PInvoke.ReleaseCapture();
PInvoke.SendMessage(new HWND(Handle), WM_NCLBUTTONDOWN, new WPARAM(HT_CAPTION), new LPARAM());
}
}
Above implementation requires a comment. ReleaseCapture and SendMessage functions are implemented in Windows native user32.dll. In order to invoke user32.dll methods in C# code, marshalling is needed.
You can use DllImport attribute to specify these functions signatures, or, as I did, make use of the Microsoft.Windows.CsWin32 nuget package, which does the marshalling for you.
ReleaseCapture
Normally the the mouse is captured by the control, after user presses mouse button over it, and released after uses releases the button. ReleaseCapture function does not wait for mouse up event, but releases the capture instantly. It is a preparation for the next step.
SendMessage
SendMessage function with WM_NCLBUTTONDOWN and HT_CAPTION arguments, is used to inform the system that mouse button was pressed over the original window title bar. Thanks to this trick, windows starts dragging action. Since the mouse button is already pressed, dragging continues as usual, until it is released by the user.
Window resizing
After applying FormBorderStyle.None style, window lost borders and the ability to use them to for resizing.
In order to bring back resizing functionality, we will try to capture WM_NCHITTEST message.WM_NCHITTEST message is sent by the system to Winforms form, whenever cursor moves or mouse button is clicked. System sends this message to the Winforms form, expecting window to respond. Winforms form response contains an information about the window element which is currently pointed by the cursor.
The plan for implementation is quite simple. Fist WM_NCHITTEST message needs to be captured. To do so, we override the WndProc method in the code-behind. Next, we check if cursor is pointing at the specific widow edge (left, right, top, bottom or corner). If that is a case, we generate the response, containing corresponding window border identifier. Thanks to this trick, windows start to behave like the original window border (which is hidden by FormBorderStyle.None) is clicked on hovered.
Following code-behind shows how to implement resizing feature for the right window edge.
const int WM_NCHITTEST = 0x0084;
const int HTRIGHT = 11;
const int BorderSize = 4;
protected override void WndProc(ref Message m)
{
base.WndProc(ref m);
if (m.Msg == WM_NCHITTEST)
{
//cursor position
var cursorPosition = PointToClient(Cursor.Position);
//border area
Rectangle rightBorderRectangle = new Rectangle(ClientSize.Width - BorderSize, 0, BorderSize, ClientSize.Height);
if (rightBorderRectangle.Contains(cursorPosition))
m.Result = (IntPtr)HTRIGHT;
}
}
Implementation can be extended for other edges and corners, by using corresponding return values defined at https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/inputdev/wm-nchittest
Note that
BorderSizecan be adjusted to your needs. It defines the width of the area, which will be considered as window border, given in px.
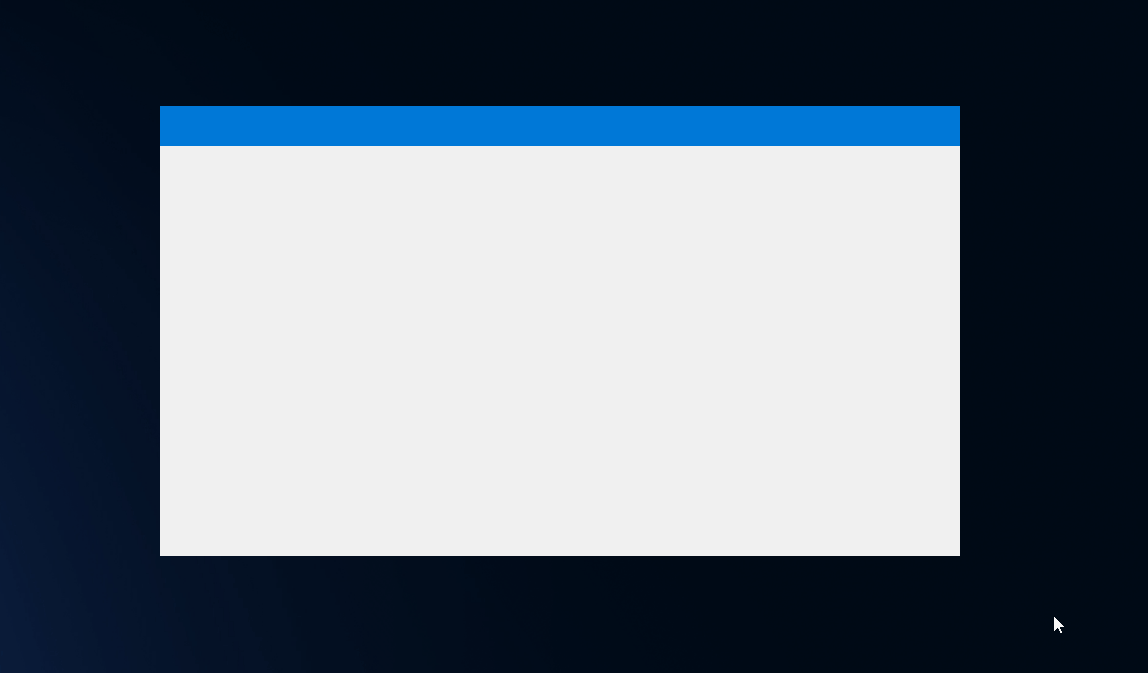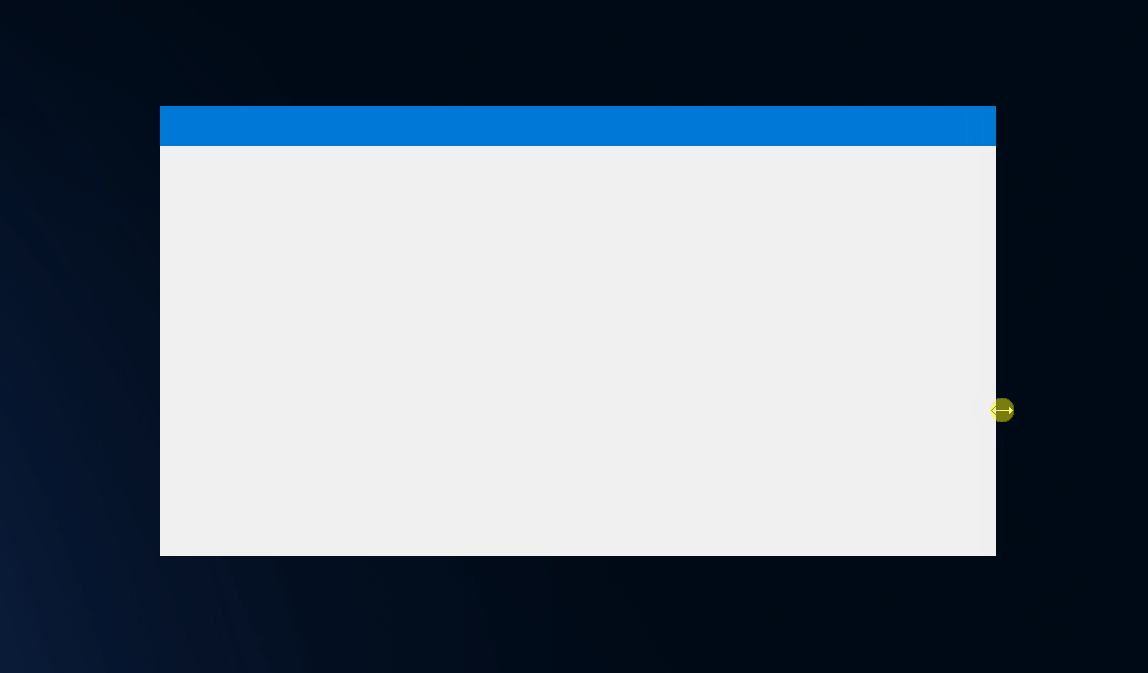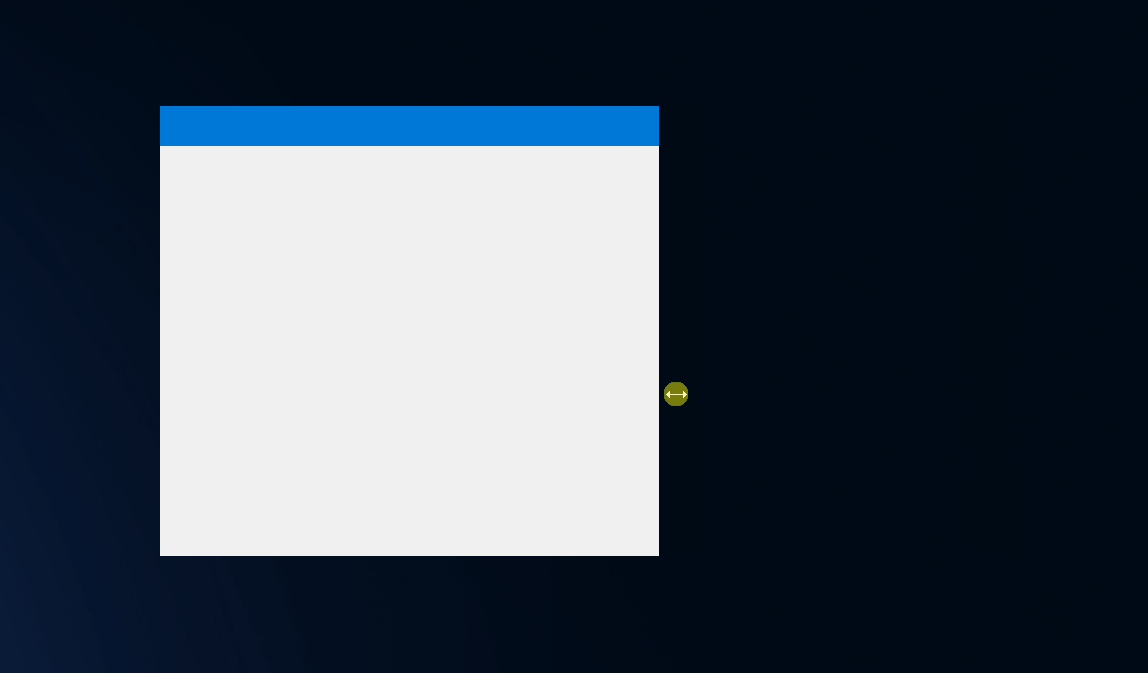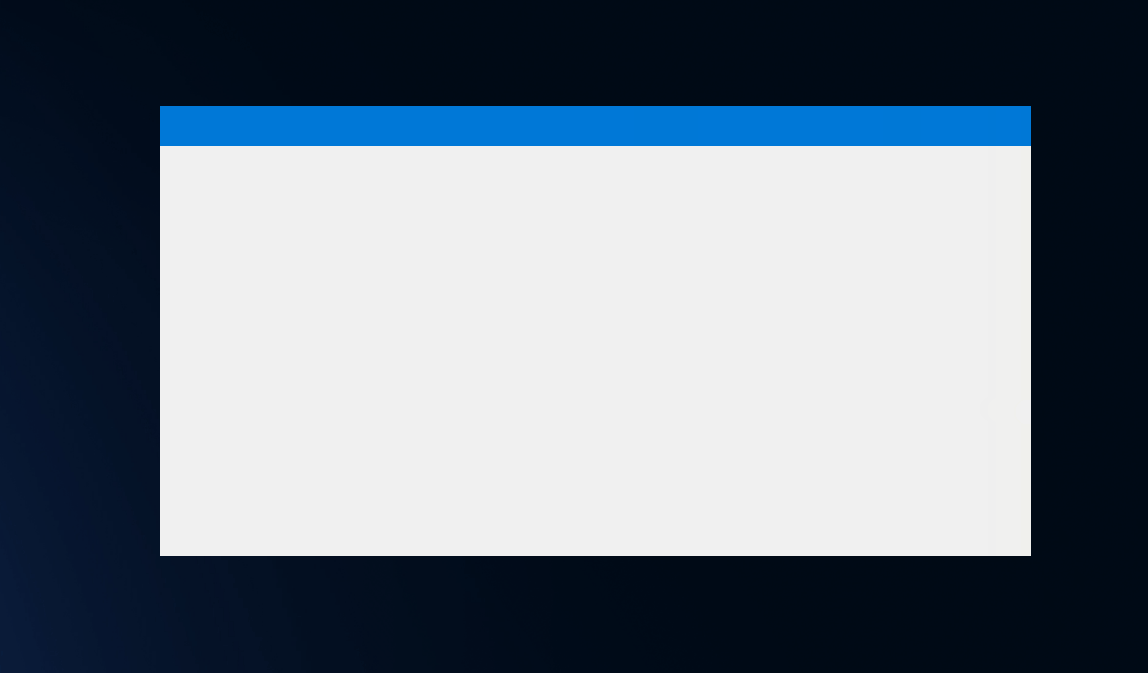
Window snapping to the screen edges
After applying FormBorderStyle.None style, window lost the ability to snap to screen edges.
In order bring this functionality back, the window style needs be adjusted, to get the original border back.
Forms’s CreateParams getter needs to be overrode, to properly style the window. WS_SIZEBOX style applies back window sizing border .
const int WS_SIZEBOX = 0x40000;
protected override CreateParams CreateParams
{
get
{
var @params = base.CreateParams;
@params.Style |= WS_SIZEBOX;
return @params;
}
}
More about window styles can be found at https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/winmsg/window-styles
Next, by handling specific windows messages, we can prevent from drawing the original border.
The main goal of this trick is to utilize snapping functionality, which is implemented by the original window sizing boarder, but prevent from displaying the original border.
Let’s take a look at the code-behind implementation
const int WM_NCCALCSIZE = 0x0083;
const int WM_NCACTIVATE = 0x0086;
protected override void WndProc(ref Message m)
{
if (m.Msg == WM_NCCALCSIZE)
return;
if (m.Msg == WM_NCACTIVATE)
m.LParam = new IntPtr(-1);
base.WndProc(ref m)
}
By handling WM_NCCALCSIZE and WM_NCACTIVATE messages, we can prevent from drawing the window sizing border.
WM_NCCALCSIZEmessage is sent by the system, to notify the Winforms form, that window size or position has changed. By default in Winforms application,WM_NCCALCSIZEmessage is handled byPresentationFramework. Default handler implementation checks, if widow style assumes any borders. If that is a case, window size is increased, in each direction by the value of border size, to ensure window is large enough display both client area and window border. In proposed implementation this behavior is bypassed.WM_NCACTIVATEmessage is sent by the system, to notify the Winforms form, that window has been activated or deactivated. (For instance when window lost or gets focus.) To reflect new window state, defaultWM_NCACTIVATEmessage handler tries to repaint the window tittle bar. It needs to be prevented. As per documetation. If this [lParam] parameter is set to -1, DefWindowProc does not repaint the nonclient area to reflect the state change.
Now the snapping functionality is in place.

using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ruponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form1_Activated(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Activated");
}
private void Form1_AutoSizeChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Autosizechanged");
}
private void Form1_AutoValidateChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("AutoValidateChanged");
}
private void Form1_BackColorChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("BackColorChanged");
}
private void Form1_BackgroundImageChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("BackgroundImageChanged");
}
private void Form1_BackgroundImageLayoutChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("BackgroundImageLayoutChanged");
}
private void Form1_BindingContextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("BindingContextChanged");
}
private void Form1_CausesValidationChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("CausesValidationChanged");
}
private void Form1_ChangeUICues(object sender, UICuesEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("ChangeUICues");
}
private void Form1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Click");
}
private void Form1_ContextMenuStripChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("ContextMenuStripChanged");
}
private void Form1_ControlAdded(object sender, ControlEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("ControlAdded");
}
private void Form1_ControlRemoved(object sender, ControlEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("ControlRemoved");
}
private void Form1_CursorChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("CursorChanged");
}
private void Form1_Deactivate(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Deactivate");
}
private void Form1_DockChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("DockChanged");
}
private void Form1_DoubleClick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("DoubleClick");
}
private void Form1_DragDrop(object sender, DragEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("DragDrop");
}
private void Form1_DragEnter(object sender, DragEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("DragEnter");
}
private void Form1_DragLeave(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("DragLeave");
}
private void Form1_DragOver(object sender, DragEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("DragOver");
}
private void Form1_EnabledChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("EnabledChanged");
}
private void Form1_Enter(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Enter");
}
private void Form1_FontChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("FontChanged");
}
private void Form1_ForeColorChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("ForeColorChanged");
}
private void Form1_FormClosed(object sender, FormClosedEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("FormClosed");
}
private void Form1_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("FormClosing");
}
private void Form1_GiveFeedback(object sender, GiveFeedbackEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("GiveFeedback");
}
private void Form1_HelpButtonClicked(object sender, CancelEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("HelpButtonClicked");
}
private void Form1_HelpRequested(object sender, HelpEventArgs hlpevent)
{
Console.WriteLine("HelpRequested");
}
private void Form1_ImeModeChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("ImeModeChanged");
}
private void Form1_InputLanguageChanged(object sender, InputLanguageChangedEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("InputLanguageChanged");
}
private void Form1_InputLanguageChanging(object sender, InputLanguageChangingEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("InputLanguageChanging");
}
private void Form1_KeyDown(object sender, KeyEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("KeyDown");
}
private void Form1_KeyPress(object sender, KeyPressEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("KeyPress");
}
private void Form1_KeyUp(object sender, KeyEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("KeyUp");
}
private void Form1_Layout(object sender, LayoutEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Layout");
}
private void Form1_Leave(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Leave");
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Load");
}
private void Form1_LocationChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("LocationChanged");
}
private void Form1_MarginChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("MarginChanged");
}
private void Form1_MaximizedBoundsChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("MaximizedBoundsChanged");
}
private void Form1_MaximumSizeChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("MAximumSizeChanged");
}
private void Form1_MdiChildActivate(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("MdiChildActivate");
}
private void Form1_MenuComplete(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("MenuComplete");
}
private void Form1_MenuStart(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("MenuStart");
}
private void Form1_MinimumSizeChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("MinimumSizeChanged");
}
private void Form1_MouseCaptureChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("MouseCaptureChanged");
}
private void Form1_MouseClick(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("MouseClick");
}
private void Form1_MouseDoubleClick(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("MouseDoubleClick");
}
private void Form1_MouseDown(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("MouseDown");
}
private void Form1_MouseEnter(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("MouseEnter");
}
private void Form1_MouseHover(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("MouseHover");
}
private void Form1_MouseLeave(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("MouseLeave");
}
private void Form1_MouseMove(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("MouseMove");
}
private void Form1_MouseUp(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("MouseUp");
}
private void Form1_Move(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Move");
}
private void Form1_PaddingChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("PaddingChanged");
}
private void Form1_Paint(object sender, PaintEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Paint");
}
private void Form1_ParentChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("ParentChanged");
}
private void Form1_QueryAccessibilityHelp(object sender, QueryAccessibilityHelpEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("QueryAccessibilityHelp");
}
private void Form1_QueryContinueDrag(object sender, QueryContinueDragEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("QueryContinueDrag");
}
private void Form1_RegionChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("RegionChanged");
}
private void Form1_Resize(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Resize");
}
private void Form1_ResizeBegin(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("ResizeBegin");
}
private void Form1_ResizeEnd(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("ResizeEnd");
}
private void Form1_RightToLeftChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("RightToLeftChanged");
}
private void Form1_RightToLeftLayoutChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("RightToLeftLayoutChanged");
}
private void Form1_Scroll(object sender, ScrollEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Scroll");
}
private void Form1_Shown(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Shown");
}
private void Form1_SizeChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("SizeChanged");
}
private void Form1_StyleChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("StyleChanged");
}
private void Form1_SystemColorsChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("SystemColorsChanged");
}
private void Form1_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("TextChanged");
}
private void Form1_Validated(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Validated");
}
private void Form1_Validating(object sender, CancelEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Validating");
}
private void Form1_VisibleChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("VisibleChanged");
}
}
partial class Form1
{
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.button1 = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
this.SuspendLayout();
//
// button1
//
this.button1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(87, 79);
this.button1.Name = "button1";
this.button1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(75, 23);
this.button1.TabIndex = 0;
this.button1.Text = "button1";
//
// Form1
//
this.AutoScaleDimensions = new System.Drawing.SizeF(6F, 13F);
this.AutoScaleMode = System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode.Font;
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(292, 266);
this.Controls.Add(this.button1);
this.Name = "Form1";
this.Text = "Form1";
this.CursorChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_CursorChanged);
this.RightToLeftLayoutChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_RightToLeftLayoutChanged);
this.QueryContinueDrag += new System.Windows.Forms.QueryContinueDragEventHandler(this.Form1_QueryContinueDrag);
this.Deactivate += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_Deactivate);
this.Load += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_Load);
this.BackgroundImageLayoutChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_BackgroundImageLayoutChanged);
this.RightToLeftChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_RightToLeftChanged);
this.DragLeave += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_DragLeave);
this.InputLanguageChanged += new System.Windows.Forms.InputLanguageChangedEventHandler(this.Form1_InputLanguageChanged);
this.Validating += new System.ruponentModel.CancelEventHandler(this.Form1_Validating);
this.BackgroundImageChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_BackgroundImageChanged);
this.MouseDoubleClick += new System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventHandler(this.Form1_MouseDoubleClick);
this.DragEnter += new System.Windows.Forms.DragEventHandler(this.Form1_DragEnter);
this.ControlAdded += new System.Windows.Forms.ControlEventHandler(this.Form1_ControlAdded);
this.FontChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_FontChanged);
this.MaximizedBoundsChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_MaximizedBoundsChanged);
this.AutoSizeChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_AutoSizeChanged);
this.Paint += new System.Windows.Forms.PaintEventHandler(this.Form1_Paint);
this.VisibleChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_VisibleChanged);
this.BindingContextChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_BindingContextChanged);
this.HelpButtonClicked += new System.ruponentModel.CancelEventHandler(this.Form1_HelpButtonClicked);
this.EnabledChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_EnabledChanged);
this.MouseDown += new System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventHandler(this.Form1_MouseDown);
this.ContextMenuStripChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_ContextMenuStripChanged);
this.Scroll += new System.Windows.Forms.ScrollEventHandler(this.Form1_Scroll);
this.MouseLeave += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_MouseLeave);
this.MouseClick += new System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventHandler(this.Form1_MouseClick);
this.Validated += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_Validated);
this.ParentChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_ParentChanged);
this.Resize += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_Resize);
this.ControlRemoved += new System.Windows.Forms.ControlEventHandler(this.Form1_ControlRemoved);
this.Shown += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_Shown);
this.AutoValidateChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_AutoValidateChanged);
this.SizeChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_SizeChanged);
this.DoubleClick += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_DoubleClick);
this.Activated += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_Activated);
this.Enter += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_Enter);
this.Layout += new System.Windows.Forms.LayoutEventHandler(this.Form1_Layout);
this.MouseUp += new System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventHandler(this.Form1_MouseUp);
this.StyleChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_StyleChanged);
this.ForeColorChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_ForeColorChanged);
this.DragDrop += new System.Windows.Forms.DragEventHandler(this.Form1_DragDrop);
this.MouseEnter += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_MouseEnter);
this.MdiChildActivate += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_MdiChildActivate);
this.Leave += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_Leave);
this.MouseMove += new System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventHandler(this.Form1_MouseMove);
this.MinimumSizeChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_MinimumSizeChanged);
this.Move += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_Move);
this.MouseCaptureChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_MouseCaptureChanged);
this.FormClosed += new System.Windows.Forms.FormClosedEventHandler(this.Form1_FormClosed);
this.PaddingChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_PaddingChanged);
this.KeyPress += new System.Windows.Forms.KeyPressEventHandler(this.Form1_KeyPress);
this.ChangeUICues += new System.Windows.Forms.UICuesEventHandler(this.Form1_ChangeUICues);
this.DockChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_DockChanged);
this.GiveFeedback += new System.Windows.Forms.GiveFeedbackEventHandler(this.Form1_GiveFeedback);
this.ImeModeChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_ImeModeChanged);
this.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_Click);
this.SystemColorsChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_SystemColorsChanged);
this.QueryAccessibilityHelp += new System.Windows.Forms.QueryAccessibilityHelpEventHandler(this.Form1_QueryAccessibilityHelp);
this.FormClosing += new System.Windows.Forms.FormClosingEventHandler(this.Form1_FormClosing);
this.RegionChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_RegionChanged);
this.KeyUp += new System.Windows.Forms.KeyEventHandler(this.Form1_KeyUp);
this.MarginChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_MarginChanged);
this.TextChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_TextChanged);
this.ResizeBegin += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_ResizeBegin);
this.HelpRequested += new System.Windows.Forms.HelpEventHandler(this.Form1_HelpRequested);
this.LocationChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_LocationChanged);
this.KeyDown += new System.Windows.Forms.KeyEventHandler(this.Form1_KeyDown);
this.BackColorChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_BackColorChanged);
this.InputLanguageChanging += new System.Windows.Forms.InputLanguageChangingEventHandler(this.Form1_InputLanguageChanging);
this.MenuStart += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_MenuStart);
this.MouseHover += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_MouseHover);
this.ResizeEnd += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_ResizeEnd);
this.DragOver += new System.Windows.Forms.DragEventHandler(this.Form1_DragOver);
this.CausesValidationChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_CausesValidationChanged);
this.MenuComplete += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_MenuComplete);
this.MaximumSizeChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_MaximumSizeChanged);
this.ResumeLayout(false);
}
private System.Windows.Forms.Button button1;
}
public class FormEventAll
{
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.Run(new Form1());
MessageBox.Show("Click OK to finish");
}
}
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Collections;
using System.ruponentModel;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data;
public class FormClosingEventCancle : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
private System.ruponentModel.Container components = null;
public FormClosingEventCancle()
{
InitializeComponent();
this.Closing += new System.ruponentModel.CancelEventHandler(this.FormClosingEventCancle_Closing);
}
protected override void Dispose( bool disposing )
{
if( disposing )
{
if (components != null)
{
components.Dispose();
}
}
base.Dispose( disposing );
}
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.AutoScaleBaseSize = new System.Drawing.Size(5, 13);
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(280, 177);
}
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new FormClosingEventCancle());
}
private void FormClosingEventCancle_Closing(object sender, System.ruponentModel.CancelEventArgs e)
{
DialogResult dr = MessageBox.Show("Do you REALLY want to close this app?",
"Closing event!", MessageBoxButtons.YesNo);
if(dr == DialogResult.No)
e.Cancel = true;
else
e.Cancel = false;
}
}
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Collections;
using System.ruponentModel;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data;
public class FormMouseKeyEvent : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
private System.ruponentModel.Container components = null;
public FormMouseKeyEvent()
{
this.KeyUp += new KeyEventHandler(OnKeyUp);
InitializeComponent();
CenterToScreen();
}
protected override void Dispose( bool disposing )
{
if( disposing )
{
if (components != null)
{
components.Dispose();
}
}
base.Dispose( disposing );
}
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.ruponents = new System.ruponentModel.Container();
this.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(300,300);
this.Text = "Form1";
}
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new FormMouseKeyEvent());
}
public void OnKeyUp(object sender, KeyEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show(e.KeyCode.ToString(), "Key Pressed!");
}
}
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Collections;
using System.ruponentModel;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data;
public class FormLifeTimeEvent : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
private System.ruponentModel.Container components = null;
public FormLifeTimeEvent()
{
InitializeComponent();
this.Closing += new System.ruponentModel.CancelEventHandler(this.FormLifeTimeEvent_Closing);
this.Load += new System.EventHandler(this.FormLifeTimeEvent_Load);
this.Closed += new System.EventHandler(this.FormLifeTimeEvent_Closed);
this.Activated += new System.EventHandler(this.FormLifeTimeEvent_Activated);
this.Deactivate += new System.EventHandler(this.FormLifeTimeEvent_Deactivate);
}
protected override void Dispose( bool disposing )
{
if( disposing )
{
if (components != null)
{
components.Dispose();
}
}
base.Dispose( disposing );
}
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.AutoScaleBaseSize = new System.Drawing.Size(5, 13);
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(280, 177);
}
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new FormLifeTimeEvent());
}
private void FormLifeTimeEvent_Closing(object sender, System.ruponentModel.CancelEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Closing event");
}
private void FormLifeTimeEvent_Load(object sender, System.EventArgs e) {
Console.WriteLine("Load event");
}
private void FormLifeTimeEvent_Activated(object sender, System.EventArgs e) {
Console.WriteLine("Activate event");
}
private void FormLifeTimeEvent_Deactivate(object sender, System.EventArgs e) {
Console.WriteLine("Deactivate event");
}
private void FormLifeTimeEvent_Closed(object sender, System.EventArgs e) {
Console.WriteLine("Closed event");
}
}
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Collections;
using System.ruponentModel;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data;
public class FormMouseMoveEvent : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
private System.ruponentModel.Container components = null;
public FormMouseMoveEvent()
{
this.MouseMove += new MouseEventHandler(OnMouseMove);
InitializeComponent();
}
protected override void Dispose( bool disposing )
{
if( disposing )
{
if (components != null)
{
components.Dispose();
}
}
base.Dispose( disposing );
}
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.ruponents = new System.ruponentModel.Container();
this.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(300,300);
this.Text = "Form1";
}
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new FormMouseMoveEvent());
}
protected void OnMouseMove(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
this.Text = "Current Pos: (" + e.X + ", " + e.Y + ")";
}
}
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Collections;
using System.ruponentModel;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data;
public class FormMouseUpEvent : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
private System.ruponentModel.Container components = null;
public FormMouseUpEvent()
{
this.MouseUp += new MouseEventHandler(OnMouseUp);
InitializeComponent();
}
protected override void Dispose( bool disposing )
{
if( disposing )
{
if (components != null)
{
components.Dispose();
}
}
base.Dispose( disposing );
}
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.ruponents = new System.ruponentModel.Container();
this.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(300,300);
this.Text = "Form1";
}
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new FormMouseUpEvent());
}
protected void OnMouseUp(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
// Which mouse button was clicked?
if(e.Button == MouseButtons.Left)
MessageBox.Show("Left click!");
if(e.Button == MouseButtons.Right)
MessageBox.Show("Right click!");
if(e.Button == MouseButtons.Middle)
MessageBox.Show("Middle click!");
}
}
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public class ControlDynamicSizeLocation : Form
{
private Button btnShow = new Button();
private Label lbl = new Label();
int xButtonSize, yButtonSize;
public ControlDynamicSizeLocation()
{
btnShow.Parent = this;
btnShow.Text = "Show Button Properties";
Size = new Size(400,400);
xButtonSize = (int)(Font.Height * .75) * btnShow.Text.Length;
yButtonSize = Font.Height * 2;
btnShow.Size = new Size(xButtonSize, yButtonSize);
btnShow.Click += new System.EventHandler(btnShow_Click);
lbl.Text = "Control Size and Location - Dynamic";
lbl.AutoSize = true;
lbl.Parent = this;
OnResize(EventArgs.Empty);
}
protected override void OnResize(EventArgs e)
{
base.OnResize(e);
int xPosition = (int)(this.ClientSize.Width / 2) - (int)(xButtonSize / 2);
int yPosition = (int)(this.ClientSize.Height / 2) - (int)(yButtonSize / 2);
btnShow.Location = new Point(xPosition, yPosition);
}
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new ControlDynamicSizeLocation());
}
private void btnShow_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Button Bottom:" + btnShow.Bottom.ToString());
Console.WriteLine("Button Top:" + btnShow.Top.ToString() );
Console.WriteLine("Button Left:" + btnShow.Left.ToString() );
Console.WriteLine("Button Right:" + btnShow.Right.ToString() );
Console.WriteLine("Button Location:" + btnShow.Location.ToString() );
Console.WriteLine("Button Width:" + btnShow.Width.ToString() );
Console.WriteLine("Button Height:" + btnShow.Height.ToString() );
Console.WriteLine("Button Size:" + btnShow.Size.ToString() );
Console.WriteLine("Button ClientSize:" + btnShow.ClientSize.ToString() );
Console.WriteLine("Font:" + btnShow.Font.ToString());
}
}
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Collections;
using System.ruponentModel;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data;
public class PaintForm : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
private System.ruponentModel.Container components;
public PaintForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
protected override void Dispose( bool disposing )
{
if( disposing )
{
if (components != null)
{
components.Dispose();
}
}
base.Dispose( disposing );
}
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.AutoScaleBaseSize = new System.Drawing.Size(5, 13);
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(292, 273);
this.Text = "DataGridExample";
this.Resize += new System.EventHandler(this.PaintForm_Resize);
this.Paint += new System.Windows.Forms.PaintEventHandler(this.PaintForm_Paint);
}
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new PaintForm());
}
private void PaintForm_Resize(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Invalidate();
Console.WriteLine("Resize");
}
private void PaintForm_Paint(object sender, System.Windows.Forms.PaintEventArgs e)
{
Graphics g = e.Graphics;
g.DrawString("Text",
new Font("Times New Roman", 20),
new SolidBrush(Color.Black),
this.DisplayRectangle);
}
}
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
class TwoPaintHandlers
{
public static void Main()
{
Form form = new Form();
form.Text = "Two Paint Handlers";
form.BackColor = Color.White;
form.Paint += new PaintEventHandler(PaintHandler1);
form.Paint += new PaintEventHandler(PaintHandler2);
Application.Run(form);
}
static void PaintHandler1(object objSender, PaintEventArgs pea)
{
Form form = (Form)objSender;
Graphics graphics = pea.Graphics;
graphics.DrawString("First Paint Event Handler", form.Font,
Brushes.Black, 0, 0);
}
static void PaintHandler2(object objSender, PaintEventArgs pea)
{
Form form = (Form)objSender;
Graphics graphics = pea.Graphics;
graphics.DrawString("Second Paint Event Handler", form.Font,
Brushes.Black, 0, 100);
}
}
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
class PaintTwoForms
{
static Form form1, form2;
public static void Main()
{
form1 = new Form();
form2 = new Form();
form1.Text = "First Form";
form1.BackColor = Color.White;
form1.Paint += new PaintEventHandler(MyPaintHandler);
form2.Text = "Second Form";
form2.BackColor = Color.White;
form2.Paint += new PaintEventHandler(MyPaintHandler);
form2.Show();
Application.Run(form1);
}
static void MyPaintHandler(object objSender, PaintEventArgs pea)
{
Form form = (Form)objSender;
Graphics graphics = pea.Graphics;
string str;
if(form == form1)
str = "Hello from the first form";
else
str = "Hello from the second form";
graphics.DrawString(str, form.Font, Brushes.Black, 0, 0);
}
}
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Collections;
using System.ruponentModel;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data;
public class ResizeForm : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
private System.ruponentModel.Container components;
public ResizeForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
protected override void Dispose( bool disposing )
{
if( disposing )
{
if (components != null)
{
components.Dispose();
}
}
base.Dispose( disposing );
}
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.AutoScaleBaseSize = new System.Drawing.Size(5, 13);
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(292, 273);
this.Resize += new System.EventHandler(this.ResizeForm_Resize);
}
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new ResizeForm());
}
private void ResizeForm_Resize(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Invalidate();
Console.WriteLine("Resize");
}
}
You could try using a custom EventHandler for the resize event and checking if the window has been redrawn since the last resize. If it has, you can either set the current size to (0, 0) or reset the display mode so that any future resize events will update only parts of the screen instead of redrawing the entire form.
Here is an example implementation:
private void UpdateWindowSize(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int x1 = (int)e.ClientWidth;
int y1 = (int)e.ClientHeight;
int width = Math.Max(x2 - x1 + 1, 0);
int height = Math.Max(y2 - y1 + 1, 0);
if (!UpdateDisplayMode)
SetCurrentSize((width, height));
}
private void UpdateWindowSize_Event(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Debug.Assert(UpdateDisplayMode == false); // assume this has been set to true for testing purposes
int x1 = (int)e.ClientWidth;
int y1 = (int)e.ClientHeight;
int width = Math.Max(x2 - x1 + 1, 0);
int height = Math.Max(y2 - y1 + 1, 0);
if ((width <= 50 || height <= 50) && UpdateDisplayMode)
UpdateDisplayMode = false;
Debug.Assert(UpdateDisplayMode == true); // make sure we're back to normal after updating display mode
}
private void SetCurrentSize(int width, int height)
{
// set the current size of the window according to the passed values
}
private void UpdateDisplayMode()
{
// update the display mode based on certain conditions
}
In this example, we have three event handlers. The UpdateWindowSize method handles both resize and resize events by checking if the window has been redrawn since the last resize. If it has, then we set the current size to (0, 0) or reset the display mode.
The UpdateDisplayMode_Event method is an event handler that is called when the user resizes the window while the display mode is enabled. It checks if the window size is within a certain range and updates the display mode accordingly.
Finally, the SetCurrentSize, UpdateDisplayMode, and UpdateWindowSize methods are custom events handlers that set the current size of the window, update the display mode, or handle both resize and resize events respectively.
This way, you can prevent your windows from redrawing their content every time they’re resized by using these custom event handlers to monitor for changes in the window’s size or position.
Разработка собственного фреймворка для тестирования в C#
UnmanagedCoder 04.05.2025
C# довольно богат готовыми решениями – NUnit, xUnit, MSTest уже давно стали своеобразными динозаврами индустрии. Однако, как и любой динозавр, они не всегда могут протиснуться в узкие коридоры. . .
Распределенная трассировка в Java с помощью OpenTelemetry
Javaican 04.05.2025
Микросервисная архитектура стала краеугольным камнем современной разработки, но вместе с ней пришла и головная боль, знакомая многим — отслеживание прохождения запросов через лабиринт взаимосвязанных. . .
Шаблоны обнаружения сервисов в Kubernetes
Mr. Docker 04.05.2025
Современные Kubernetes-инфраструктуры сталкиваются с серьёзными вызовами. Развертывание в нескольких регионах и облаках одновременно, необходимость обеспечения низкой задержки для глобально. . .
Создаем SPA на C# и Blazor
stackOverflow 04.05.2025
Мир веб-разработки за последние десять лет претерпел коллосальные изменения. Переход от традиционных многостраничных сайтов к одностраничным приложениям (Single Page Applications, SPA) — это. . .
Реализация шаблонов проектирования GoF на C++
NullReferenced 04.05.2025
«Банда четырёх» (Gang of Four или GoF) — Эрих Гамма, Ричард Хелм, Ральф Джонсон и Джон Влиссидес — в 1994 году сформировали канон шаблонов, который выдержал проверку временем. И хотя C++ претерпел. . .
C# и сети: Сокеты, gRPC и SignalR
UnmanagedCoder 04.05.2025
Сетевые технологии не стоят на месте, а вместе с ними эволюционируют и инструменты разработки. В . NET появилось множество решений — от низкоуровневых сокетов, позволяющих управлять каждым байтом. . .
Создание микросервисов с Domain-Driven Design
ArchitectMsa 04.05.2025
Архитектура микросервисов за последние годы превратилась в мощный архитектурный подход, который позволяет разрабатывать гибкие, масштабируемые и устойчивые системы. А если добавить сюда ещё и. . .
Многопоточность в C++: Современные техники C++26
bytestream 04.05.2025
C++ долго жил по принципу «один поток — одна задача» — как старательный солдатик, выполняющий команды одну за другой. В то время, когда процессоры уже обзавелись несколькими ядрами, этот подход стал. . .
Продвинутые List Comprehension в Python
py-thonny 04.05.2025
Когда я впервые столкнулся с list comprehension в Python, это было похоже на открытие тайной комнаты в знакомом доме. Вроде бы обычный цикл, но настолько элегантный, что заставляет переосмыслить. . .
Confluent Kafka Go и потоковые приложения в реальном времени на Golang
golander 03.05.2025
Мир обработки данных перевернулся, когда в 2011 году LinkedIn открыл исходный код Kafka – распределённой системы передачи сообщений, разработанной для внутренних нужд компании. Изначально Кафка. . .
