Last Updated :
24 Apr, 2025
The «fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory» error is a common issue encountered when compiling C/C++ code that interacts with Python. This error occurs when the C/C++ compiler is unable to locate the Python.h header file, which is part of the Python development package required for compiling code that interacts with Python.In this article, we will discuss in detail how to fix the «fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory» error, providing step-by-step instructions and guidelines to successfully compile C/C++ code that interacts with Python.
Problem Statement :
When attempting to compile C/C++ code that interacts with Python, developers often encounter the error message «fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory». This error occurs when the C/C++ compiler is unable to locate the Python.h header file, which is essential for compiling code that interacts with Python.
This error can pose a significant hurdle in building and running C/C++ programs that depend on Python, preventing developers from successfully integrating Python functionalities into their code. It can be caused by various factors, such as the Python development package not being installed, incorrect header file location, improper compiler settings, or missing environment variables related to Python.
Problem Screenshot:
The error message «fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory» typically occurs when the C/C++ compiler is unable to find the Python.h header file, which is part of the Python development package required for compiling C/C++ code that interacts with Python.
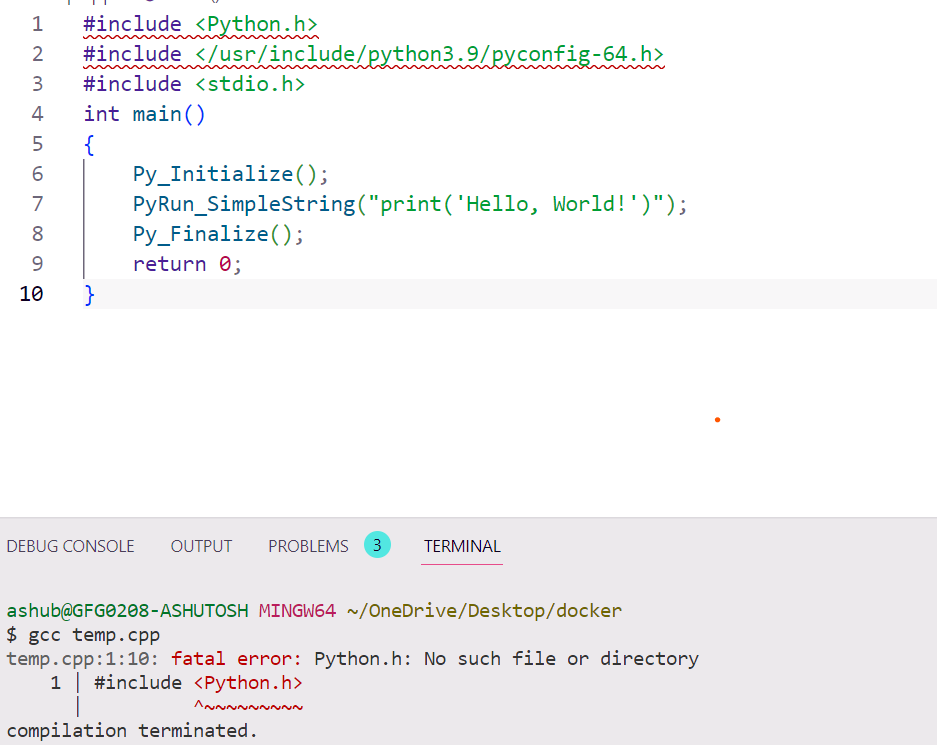
Steps required to solve the problem :
Step 1: Install the Python development package.
Installing the Python development package is an essential step when working with Python, especially when compiling C/C++ code that interacts with Python. The development package provides the header files and libraries necessary for compiling Python extension modules or embedding Python in other applications. In this article, we will guide you through the installation process for different Linux-based systems.
For Ubuntu/Debian-based systems:
Ubuntu and Debian-based systems, such as Ubuntu, Debian, and Linux Mint, use the apt-get package manager. To install the Python development package, open a terminal window and run the following command with administrative privileges:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install python-dev
For Fedora/RHEL-based systems:
Fedora and Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) use the yum package manager. To install the Python development package, open a terminal window and run the following command with administrative privileges:
sudo yum install python-devel
For Arch Linux:
Arch Linux uses the pacman package manager. To install the Python development package, open a terminal window and run the following command with administrative privileges:
sudo pacman -S python
Step 2 : Set up in the include path.
Including Python.h is typically required when embedding Python in other applications, such as creating Python extension modules, embedding Python interpreter in a C/C++ program, or calling Python functions from C/C++ code. This header file defines the Python C API, which is a set of C functions and macros that allow C/C++ code to interact with the Python interpreter and Python objects.
C++
#include <Python.h>
Including the pyconfig-64.h header file is a crucial step when compiling C/C++ code that interacts with Python x.y. It provides platform-specific configuration settings and macros that are necessary for correctly building Python extension modules or embedding Python in other applications. It’s important to verify the correct path of the pyconfig-64.h header file on your system and ensure that the Python development headers are installed and configured correctly to avoid compilation errors.
C++
#include </usr/include/python3.9/pyconfig-64.h>
Step 3 : Complie and runAfter setting the inclusion path and installing the Python development package, you should be able to successfully build and run your application.
For Example :
Py_Initialize(): This function initializes the Python interpreter in the C/C++ program. It must be called before any Python code can be executed.
PyRun_SimpleString(«print(‘Hello, World!’)»): This function runs a simple Python code string within the C/C++ program. In this case, it prints the string «Hello, World!» to the standard output using the Python interpreter embedded within the C/C++ program.
Py_Finalize(): This function finalizes the Python interpreter in the C/C++ program. It must be called after all Python code has been executed.
C++
#include <Python.h> #include </usr/include/python3.9/pyconfig-64.h> #include <stdio.h> int main() { Py_Initialize(); PyRun_SimpleString("print('Hello, World!')"); Py_Finalize(); return 0; }
.png)
To create a output file we need to run the command
gcc -I/usr/include/python3.9 test.c -o test -l/usr/lib -lpython3.9
Let’s break down the command and understand its components:
- gcc: This is the command to invoke the GCC compiler.
- -I/usr/include/python3.9: This option specifies the directory where the Python 3.9 header files are located (/usr/include/python3.9). The -I option is used to add the directory to the compiler’s include path, allowing it to find the necessary header files during compilation.
- test.c: This is the name of the C file that you want to compile.
- -o test: This option specifies the name of the output file that will be generated after successful compilation. In this case, the output file will be named test.
- -L/usr/lib: This option specifies the directory where the Python 3.9 library files are located (/usr/lib). The -L option is used to add the directory to the compiler’s library search path, allowing it to find the necessary Python library during linking.
- -lpython3.9: This option specifies the name of the Python 3.9 library that should be linked with the compiled code. The -l option is used to specify a library to be linked, and the library name follows the -l option without the lib prefix or file extension. In this case, it specifies the python3.9 library.
Once the compilation command is executed successfully without any errors, it should generate an executable file named test (or the name specified with the -o option), which can be executed to run your program that interacts with Python 3.9.
./test
Output :
Hello World
.png)
-
Causes of
'Python.h': No such file or directoryError in C++ -
Python Installation That Allows Embedding Its Code in C++
-
Steps to Add Python Path to IDE’s
Includeand Linker -
Add Python Path to
Includeand Linker -
Write Python Codes in C++ and Compile Them
-
Conclusion
This article will explain how to solve the error 'Python.h': No such file or directory. This usually happens when we try to embed Python code in C++, but the compiler cannot find a reference to Python inside the system.
Causes of 'Python.h': No such file or directory Error in C++
Below is a C++ program that uses Python codes.
#include <Python.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
PyObject* pInt;
Py_Initialize();
PyRun_SimpleString("print('Hello World from Embedded Python!!!')");
Py_Finalize();
printf("\nPress any key to exit...\n");
if (!_getch()) _getch();
return 0;
}
When this program is compiled, it gives the error 'Python.h': No such file or directory.
Build started...
1>------ Build started: Project: Python into Cpp, Configuration: Debug x64 ------
1>1.cpp
1>C:\Users\Win 10\source\repos\Python into Cpp\1.cpp(3,10): fatal error C1083: Cannot open include file: 'Python.h': No such file or directory
1>Done building project "Python into Cpp.vcxproj" -- FAILED.
========== Build: 0 succeeded, 1 failed, 0 up-to-date, 0 skipped ==========
Various reasons cause the 'Python.h': No such file or directory issue.
-
Python is not installed inside the system.
Python is third-party enterprise software that does not come with standard Windows and C++ compilers installation. It must be installed with correct settings and linked to the C++ compiler.
-
C++ compiler cannot find Python.
If the compiler is run through an IDE or mingw4, it can only detect that standard C++ includes packages that come with a standard installation.
Third-party libraries are needed to be added to the IDE
includeand linker files.Three steps need to be executed to solve the above issues.
- Custom installing Python that allows it to be embedded in IDEs.
- Adding Python path to IDE
includeand linker paths. - Writing Python codes inside C++ codes and compiling them.
Python Installation That Allows Embedding Its Code in C++
If there is no Python inside the system, or if it is installed and linked but still the error 'Python.h': No such file or directory occurs, it’s because the Python installation did not download the debug binaries with it.
It is recommended that Python be uninstalled and then reinstalled correctly to solve the error 'Python.h': No such file or directory.
Head to the Python website and download the latest Python version. If a certain version is required, head to the All Releases download section.
This article demonstrates the steps in Windows OS, so the suitable option is to go with the Windows installer(64bit or 32bit). It is recommended to use the 64-bit version if a modern PC is used.
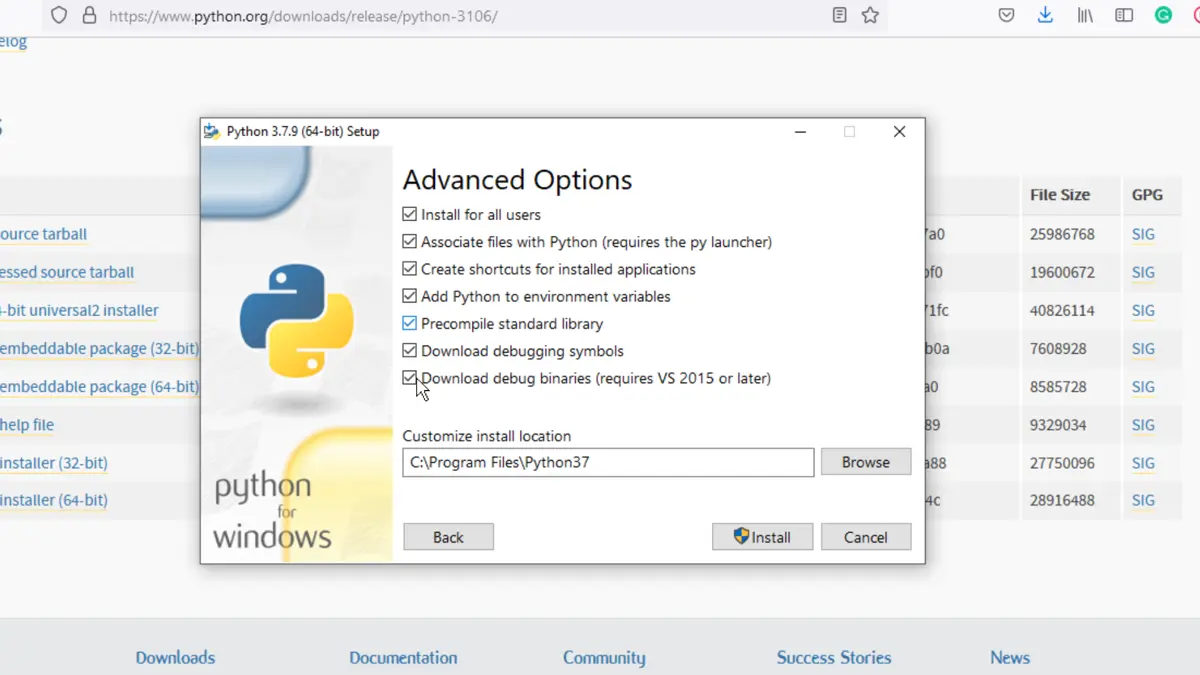
After the download is complete, run the installer, and choose Customize Installation. The Install now option will install Python with default settings but leave the debug binaries out that allows embedding it into IDEs.
Tick the box that asks to Add Python X.X(version) to PATH and then click on Customize Installation.
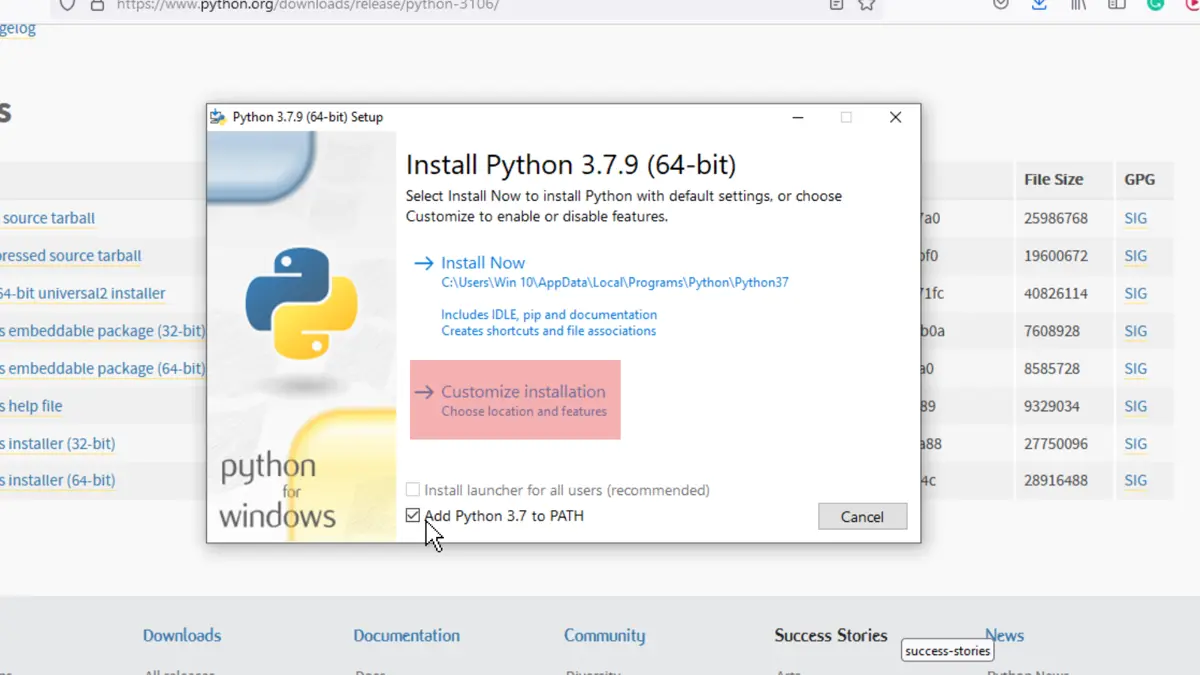
On the next page, mark all the boxes and then click next.
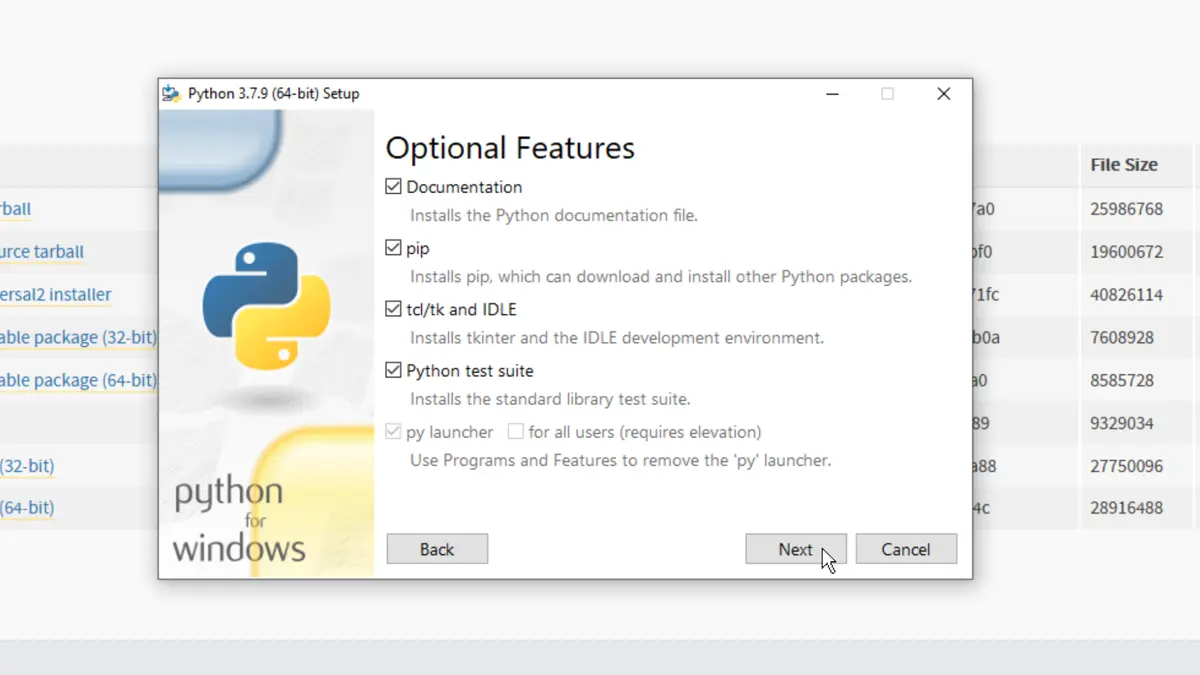
In the third menu, tick the box Download debug binaries and click on Install. Python will be installed inside the selected directory.
Steps to Add Python Path to IDE’s Include and Linker
Any third-party library that does not come with C++ in its standard installation must be referenced to the IDE. IDEs cannot automatically search and detect third-party libraries inside the system.
This is the reason that causes the error 'Python.h': No such file or directory.
Though IDE can search for files when the package library is stored in the same directory where the C++ script is located, its path should be mentioned inside the program’s #include<> header.
But storing dependencies this way is a bad practice.
What needs to be done is that the path of the library should be linked to the IDE so that it can be included the way standard header files are included, removing the need to provide a file path with the source code.
Any third-party library that does not come with C++ in its standard installation must be referenced to the IDE. IDEs cannot automatically search and detect third-party libraries inside the system.
This is the reason that causes the error 'Python.h': No such file or directory.
At first, an IDE is needed. It is recommended to go with Visual Studio (2017 or later), and this article will cover the same.
Any other IDE can also be used, the steps are identical in most of them, but Visual Studio makes it simple.
Install Visual Studio in the System
The installer of Visual Studio can be downloaded from here. After downloading the 64-bit Community version, install the software, including the C++ development option.
After installation is completed, create a new project.
The window can look intimidating for readers who have never used Visual Studio before, but there’s no need to worry. Most of the features that will be needed are in front, and this article will guide the rest.
Create a project, and give it a name like ‘Python in cpp’. After the project is created, the main window would look something like this:
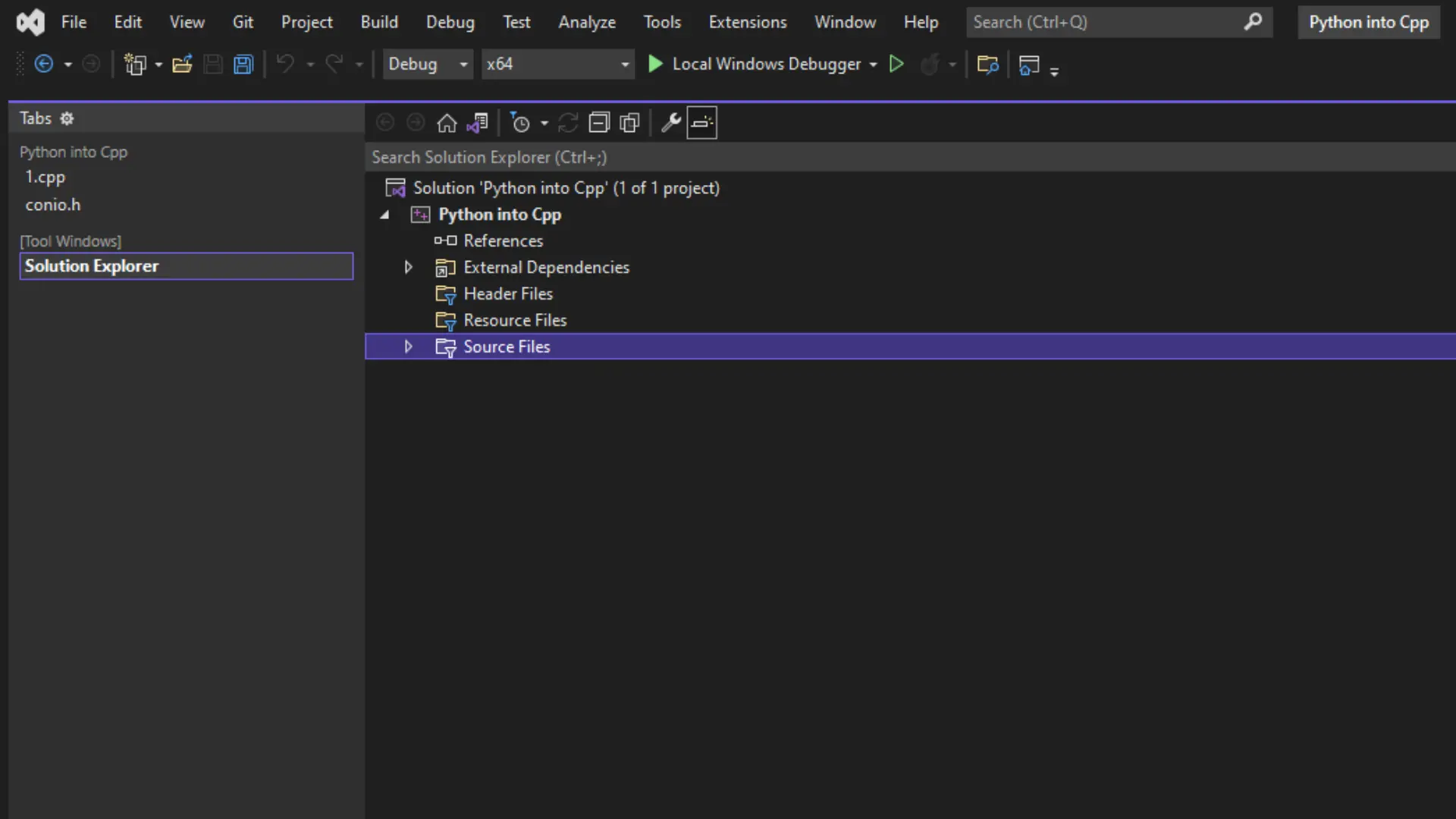
If there is just a black screen, press Ctrl+Alt+l, and the solution explorer will open. The solution explorer shows all the files and dependencies available for the project.
Add Python Path to Include and Linker
In this step, the Python path will be included and linked to Visual Studio so that the IDE knows where to look when #include <python.h> is written.
A prerequisite for this step is to know the directory where Python is installed and keep it open in another window. Now head down to Debug > Project Name > Properties (Instead of Project name, it will display the project’s name).
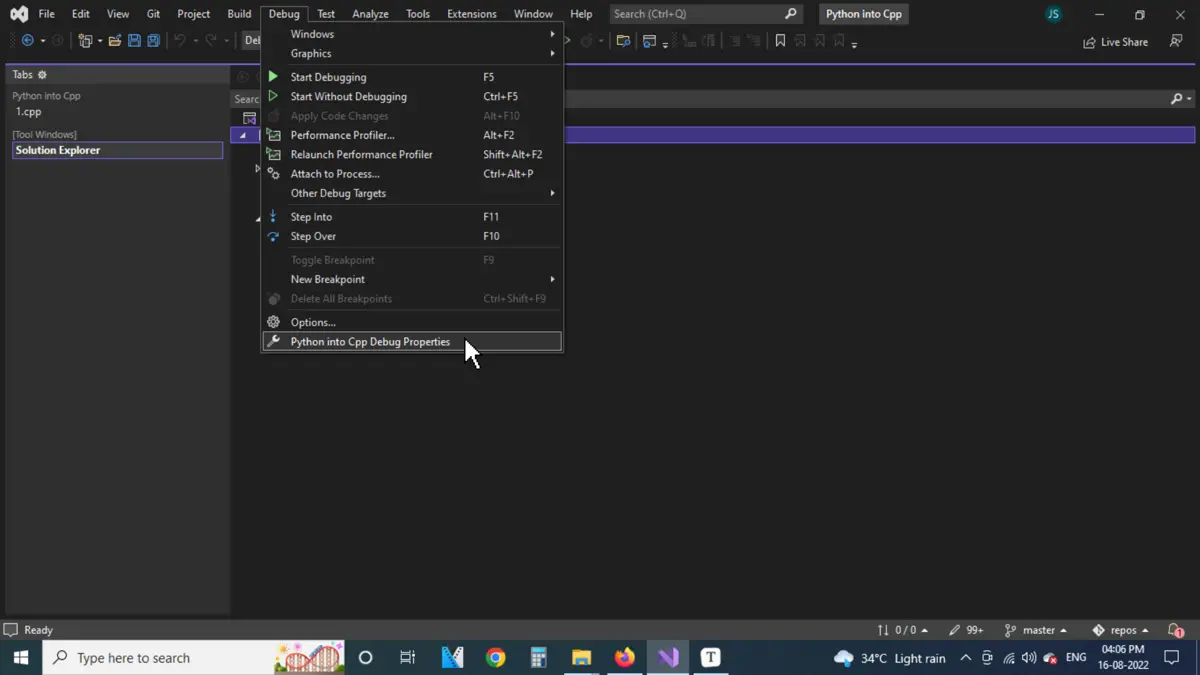
Inside the project properties window, go to C/C++ > General > Additional Include Directories, click on the tiny drop button on the extreme right, and then click on <Edit...>.
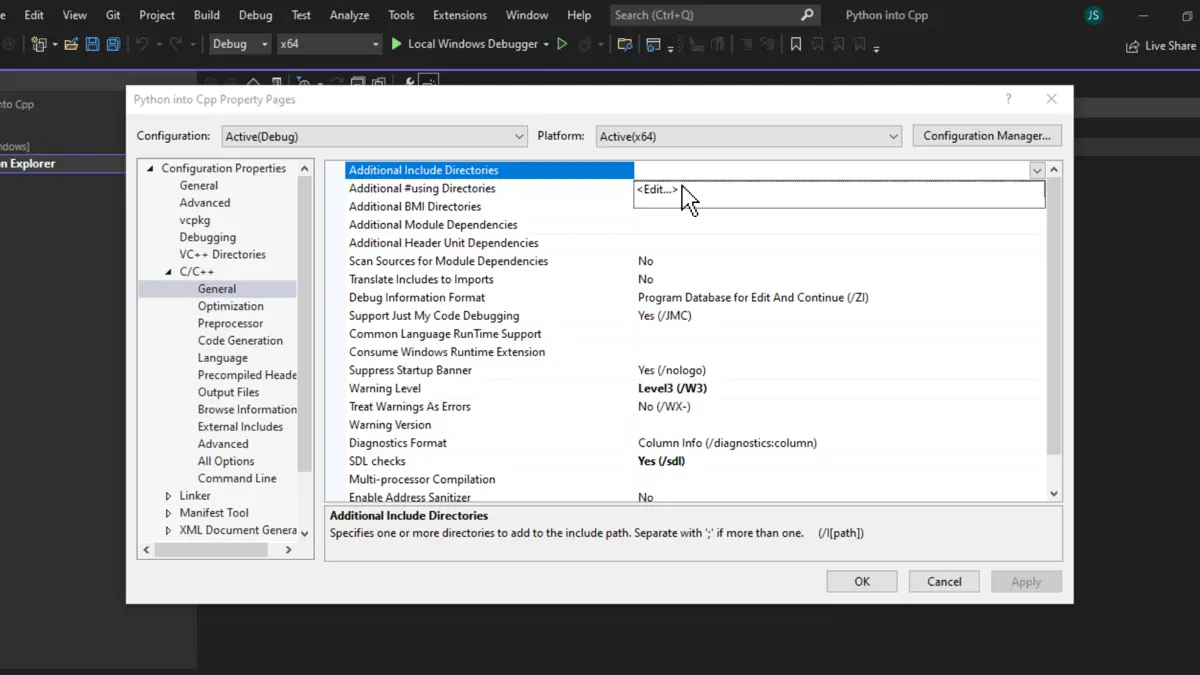
The Additional Include Directories dialog box will open. Here, double-click on the first blank space and paste the path of the include folder from the directory where Python is installed inside the system, then click OK.
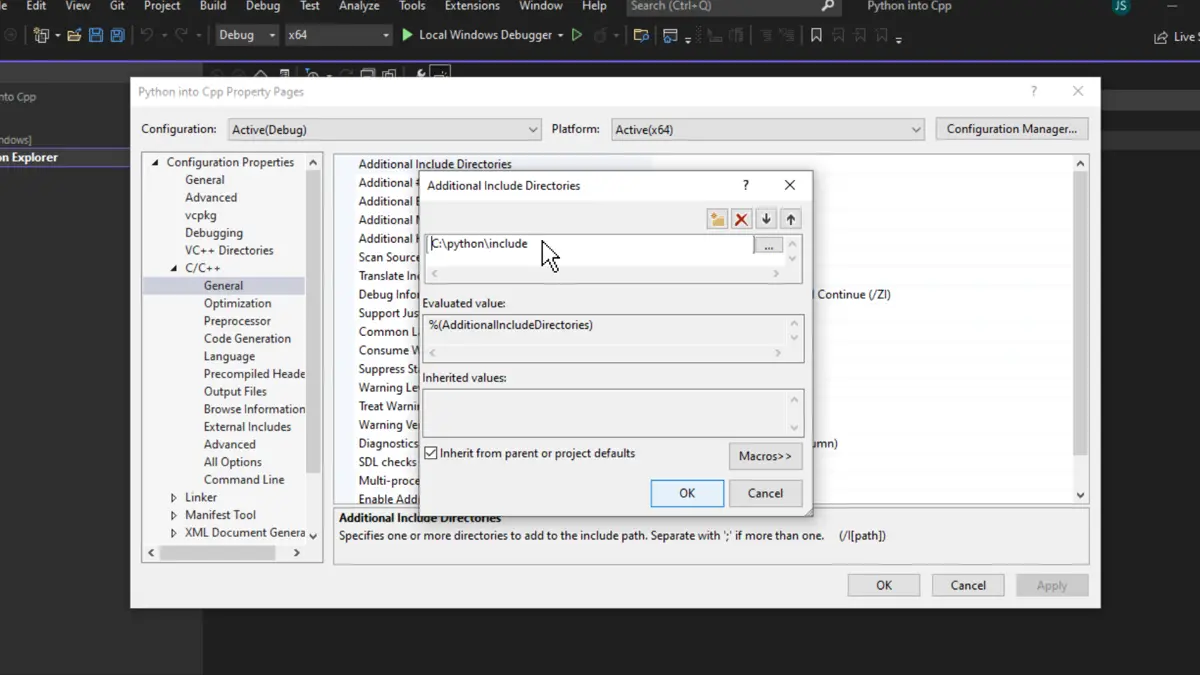
After the path of include directory is added, head down to Linker > General > Additional Library Directories. Like the previous step, click on <Edit...>.
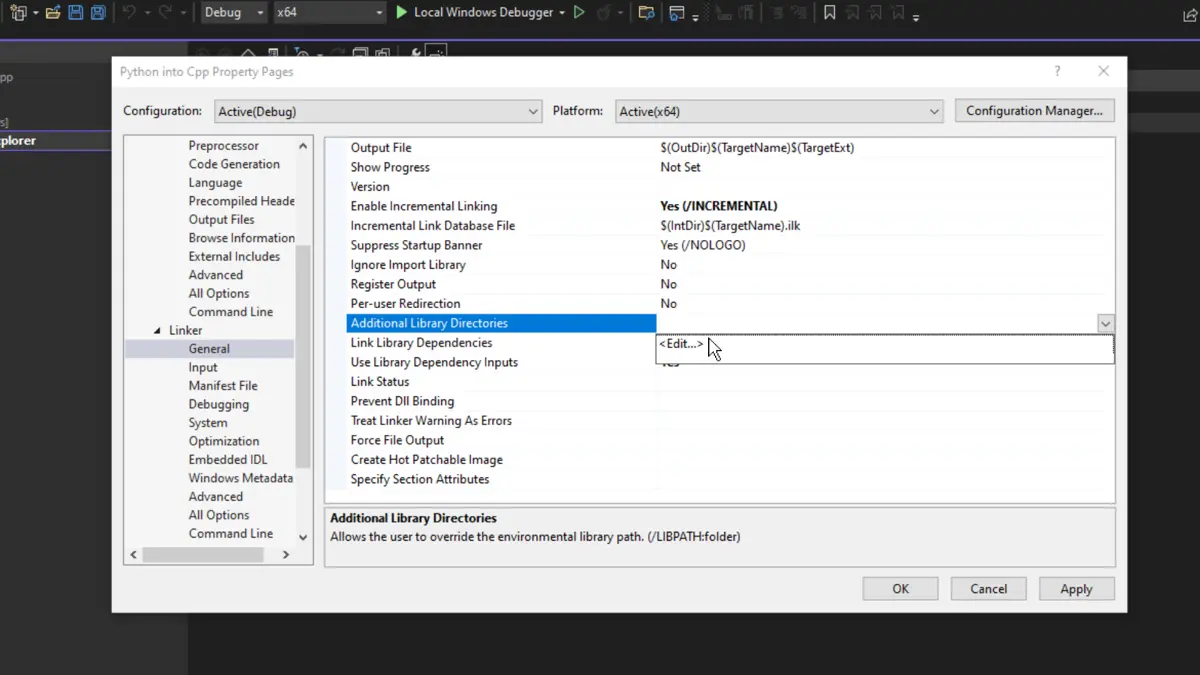
Now, the libs folder should be added to the linker. This folder is also found inside the Python directory, where the include folder is located.
After it is added, click on OK and then click on Apply.
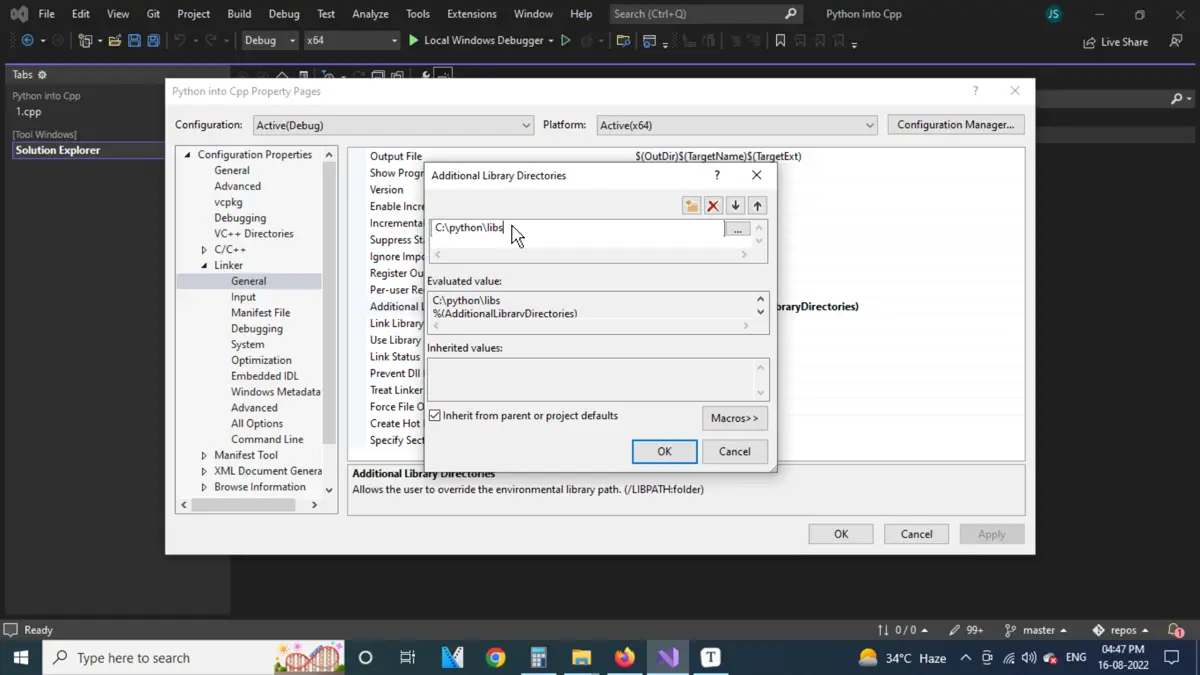
Write Python Codes in C++ and Compile Them
Once the include and linker paths are added, a sample program must be compiled to check whether the above steps have been executed correctly, and the 'Python.h': No such file or directory error is not encountered again.
Go to the solution explorer and right-click on source files. Click on add > new item, give the file a name and click add.
This new file will contain the code that will be compiled.
Below is the C++ program used at the start of the article that threw errors.
#include <Python.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
PyObject* pInt;
Py_Initialize();
PyRun_SimpleString("print('Hello World from Embedded Python!!!')");
Py_Finalize();
printf("\nPress any key to exit...\n");
if (!_getch()) _getch();
return 0;
}
Now, when the file is compiled by clicking on the green play button on the top, we get the output:
Hello World from Embedded Python!!!
Press any key to exit...
Conclusion
This article explains the steps to solve the error 'Python.h': No such file or directory. After reading this article, the reader can install Python and Visual Studio and link them to the Python library.
Enjoying our tutorials? Subscribe to DelftStack on YouTube to support us in creating more high-quality video guides. Subscribe
Пройдите тест, узнайте какой профессии подходите
При работе с C-расширениями в Python возможно столкнуться с ошибкой компиляции, которая выглядит следующим образом: utilsmodule.c:1:20: fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory
При работе с C-расширениями в Python возможно столкнуться с ошибкой компиляции, которая выглядит следующим образом:
utilsmodule.c:1:20: fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory
compilation terminated.
Она сообщает о том, что компилятор не может найти заголовочный файл Python.h.
Этот заголовочный файл Python.h включается в исходный код C для обеспечения взаимодействия с интерпретатором Python и является частью Python Development Headers. Когда этот файл не найден, это означает, что Python Development Headers не установлены в системе.
Решение проблемы
Для решения этой проблемы необходимо установить Python Development Headers. Способ установки этого пакета зависит от используемой операционной системы.
Для Ubuntu или Debian:
В системах на базе Debian, таких как Ubuntu, можно использовать следующую команду для установки:
sudo apt-get install python-dev # для Python 2
sudo apt-get install python3-dev # для Python 3
Для Fedora:
В Fedora Python Development Headers можно установить с помощью команды:
sudo dnf install python-devel # для Python 2
sudo dnf install python3-devel # для Python 3
Для CentOS или RHEL:
В CentOS или RHEL используйте следующую команду:
sudo yum install python-devel # для Python 2
sudo yum install python3-devel # для Python 3
Для macOS:
В macOS Python Development Headers предоставляются вместе с Python, когда он устанавливается через Homebrew:
brew install python # для Python 2
brew install python3 # для Python 3
Для Windows:
В Windows Python Development Headers включены в стандартную установку Python. При установке Python убедитесь, что выбрана опция «Install development headers and libraries».
После установки Python Development Headers ошибка с отсутствием Python.h должна исчезнуть.
- Author
- Recent Posts
I started writing code around 20 years ago, and throughout the years, I have gained a lot of expertise from hands-on experience as well as learning from others. This website has also grown with me and is now something that I am proud of.
Python h no such file or directory error can occur when the Python.h library is not present in your code. Python.h is a header file that is required for specific Python modules and extensions to work correctly, especially when incorporating Python in C/C++ code.

Running this header file can be tricky, which often leads to this error. Fortunately, this article explores the causes of this error and provides you with a step-by-step guide to resolving it.
JUMP TO TOPIC
- Why Does the Python H No Such File or Directory Error Occurs?
- – Missing Development Libraries – Crucial Building Blocks
- – Incorrect Version of Python – Using the Wrong Version
- – Incorrect Path to Python.h – It’s Like Using the Wrong Map
- – Random Mistakes or Errors
- Proven Solutions To Fix Python H No Such File or Directory
- – Install the Development Libraries – Use the Right Command
- – Make Use of Compatible Python Version – Install Correct One
- – Setting the Correct Path to Python.h – The Header File
- Conclusion
Why Does the Python H No Such File or Directory Error Occurs?
The python h no such file or directory error occurs when you are attempting to create a shared library in another language, most likely C/C++, without installing the necessary Python development package. The Python development package includes header files, development tools, and a static library.
The fatal error Python.h: No such file or directory is a common error you may come across when building or compiling a C or C++ extension for Python on Linux or other UNIX-like systems.
This error occurs when the compiler is unable to find the Python.h header file, which is required for the extension to interact with the Python API. Well, there are several reasons why this might happen. Below is a quick dive into the most common causes.
– Missing Development Libraries – Crucial Building Blocks
One of the most common causes of the fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory error is the missing development libraries. The Python.h header file is part of the Python development libraries, which include header files, libraries, and other files that are needed to build Python extensions.

When these libraries are not installed on your system, the compiler will be unable to find the Python.h header file, which is required for the extension to interact with the Python API. As a result, the compiler will throw this error.
Example: Not Having the python.h Library in the Code
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
// some code here
Py_Initialize();
// some more code here
Py_Finalize();
return 0;
}
Here, the code is trying to include the Python.h library, which is needed to interact with Python code, but if this library is not installed in the system or not properly configured. As a result, the compiler will throw the python H no such file or directory error.
– Incorrect Version of Python – Using the Wrong Version
An incorrect version of Python can also cause the error we are talking about today. This can happen when the extension you are building uses a different version of Python than the one installed on your system.
For example, suppose you are building a C extension for Python 3.8, but the version of Python installed on your system is 3.7. The compiler will be unable to find the necessary header files and libraries for the 3.8 version of Python, which will result in this error.
In addition, if you have multiple versions of Python installed on your system, it is likely that your code is not using the correct version. This can happen if the environment variables such as PYTHONPATH and PYTHONHOME are not set correctly. Also, it can happen if you are invoking the wrong version of Python when running the code.
– Incorrect Path to Python.h – It’s Like Using the Wrong Map
Another cause of this error is an incorrect path to the Python.h header file. This can happen when the compiler is looking for the Python.h header file in the wrong location.
For example, suppose you are building a C extension for Python on a Linux system using the command gcc -shared -o myextension.so myextension.c -I/usr/include/python3.9 but the actual location of the Python.h header file is in /usr/local/include/python3.9. In this case, the compiler will be unable to find the Python.h header file, resulting in this error.
– Random Mistakes or Errors
The python.h: no such file or directory error message can be triggered in various instances and platforms due to random errors. Here is a quick look at the various examples:
- h no such file or directory linux: This error message can pop up on Linux systems when building or compiling a C or C++ extension for Python.
- h: no such file or directory ubuntu: The error message can appear on Ubuntu systems when building or compiling a C or C++ extension for Python.
- h no such file or directory Windows: The error message is not common in windows systems. However, it is possible to encounter this error on windows if you are trying to build a C or C++ extension for python using a UNIX-like environment like Cygwin or MinGW.
- h no such file or directory centos: This error message can pop up on Centos systems when building a C or C++ extension for Python.
- ‘Python.h’ file not found mac: The error message is an issue you may face on Mac systems when building or compiling a C or C++ extension for Python.
- h: no such file or directory fedora: When building or compiling a C or C++ extension for Python on Fedora systems, you may come across this error.
Proven Solutions To Fix Python H No Such File or Directory
One of the proven solutions to python h no such file or directory error involves installing the Python-dev package. Additionally, using the appropriate and compatible Python version serves as a great solution to this error as well. Setting the correct path to the header file is also a viable option.
That said, there are several solutions to this issue, depending on the cause of the error. Here are some proven methods for resolving Python.h: No such file or directory error:
– Install the Development Libraries – Use the Right Command
If the cause of the error is missing development libraries, you can install them by running the correct command. By installing the Python dev package, you are making sure the compiler has access to the necessary header files and libraries, including the Python.h header file. This will allow the extension to interact with the Python API and resolve the error.

It is important to note that you need to install the development libraries for the specific version of Python that you are using. If you are using Python 3.8, you should install the development libraries for Python 3.8 and not for another version.
Examples of How To Install the Python-dev Package:
On Ubuntu and Debian-based systems, you can install the Python-dev package by running the following command in the terminal:
sudo apt-get install python3-dev
If you are using Red Hat-based systems such as Fedora and Centos, you can install the package by running the following command:
sudo yum install python3-devel
On macOS, you can use pip to install python-dev as follows:
By installing the Python-dev package, you are ensuring that the compiler has access to the necessary header files, libraries, and other files that are necessary to build Python extensions.
– Make Use of Compatible Python Version – Install Correct One
It is important to ensure that you build the extension against the correct version of Python. To make sure that you build the extension against the correct version of Python, you can use the following methods.
First, specify the correct version of Python when installing the development libraries. For example, instead of running sudo apt-get install python3-dev, you can run sudo apt-get install python3.9-dev to install the development libraries for Python 3.9.
Second, set the environment variables to point to the correct version of Python. You can accomplish this by setting the PYTHONPATH and PYTHONHOME environment variables to point to the correct version of Python.
Alternatively, you can also check which python version you are using by typing python –version or python3 –version if you have multiple python versions installed in your system. Moreover, you can also check the python version for which the python.h is present by searching it in the included path of your system.
By ensuring that the extension is built against the correct version of Python, the compiler will be able to find the necessary header files, including the Python.h header file, and you will resolve the error in question.
If the cause of the error is an incorrect path to the Python.h header file, you can ensure that the include path for your compiler is set correctly and points to the location of the Python.h file. By setting the correct path to the Python.h header file, the compiler will be able to find the header file, and you will resolve the error.
To set the correct path to the Python.h header file, you can use any of the following methods. First, you can modify the include path for your compiler.
Depending on the compiler you are using, you can modify the include path to include the directory where the Python.h header file is located. For example, in GCC you can use the -I flag to specify the include directory, like this: gcc -I/usr/include/python3.9
Second, you can use pkg-config: pkg-config, a tool that can be used to obtain information about installed libraries. You can use pkg-config to find the correct include path for the Python.h header file. On Ubuntu and Debian-based systems, you can use the following command: pkg-config –cflags python3
Lastly, you can find python.h in your system. You can search for python.h file in your system, in the include path of your system, and use that path to specify the include directory.
Conclusion
In this guide, you have learned that python h no such file or directory is an issue you may face when building or compiling a C or C++ extension for Python on Linux or other UNIX-like systems. Here is a summary of what you have learned:
- The error occurs when the compiler is unable to find the Python.h header file, which is necessary for your extension to interact with the Python API.
- Causes of this error include missing development libraries and using an incorrect version of Python.
- Also, you will trigger the error if you specify an incorrect path to the Python.h header file.
- Solutions to this error include installing the required development libraries and ensuring that the extension is built against the correct version of Python.
- As well, make sure you set the correct path to the Python.h header file and set the correct environment variables.
By understanding the causes of this error and the solutions available, you are now better positioned to troubleshoot and resolve the issue when it arises.
I am trying to use this header only library. And I get it down from github, and I put it into a folder. And in a test VS2017 C++ console project (in Windows 10), with a simple line:
#include "..\matplotlib-cpp\matplotlibcpp.h"
I’ve generated a nice error:
1>c:\project\matplotlib-cpp\matplotlibcpp.h(5): fatal error C1083: Cannot open include file: 'Python.h': No such file or directory
Yes, I know I should use libpython library (I guess), but until there I need to overcome this error: Cannot open include file: 'Python.h'
I have installed Python 3.9:
C:\Project>python --version
Python 3.9.6
Also, I already have installed matplotlib in Python: matplotlib 3.4.2
Can you lead me to solve this ? Thank you for any hint !!!
P.S. I have included in my test project the requested path: C:\Program Files\Python39\include
But now I got another missing files, which make me to think that I am not going in the right direction to solve this. How can I use this library in Visual Studio on Windows ?
P.S2. I have installed on my system matplotlib-cpp using vcpkg:

Even so, I still have the same error in my test app.
