В этой публикации, друзья, рассмотрим, как узнать все сетевые подключения Windows. Т.е. как узнать, какие есть на компьютере активные и неактивные сетевые подключения — проводные Ethernet, беспроводные Wi-Fi или мобильные, через USB-модем, подключения только к локальной сети без Интернета, виртуальные и различные другие подключения. Это необходимо для проверки этих сетевых подключений, диагностики и устранения проблем с ними, получения информации в различных целях. Узнать сетевые подключения Windows можно её штатными средствами и сторонними программами.
Узнать активные сетевые подключения Windows можно в современном штатном приложении «Параметры». В корне раздела «Сеть и Интернет» будем видеть все активные подключения. Здесь можно оперативно получить информацию о текущих подключениях и их статусе.
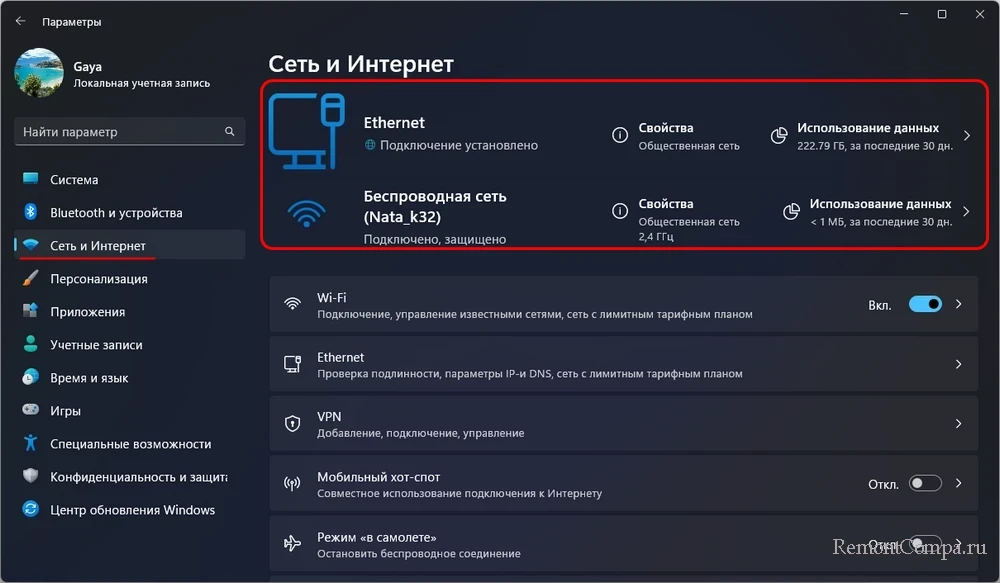
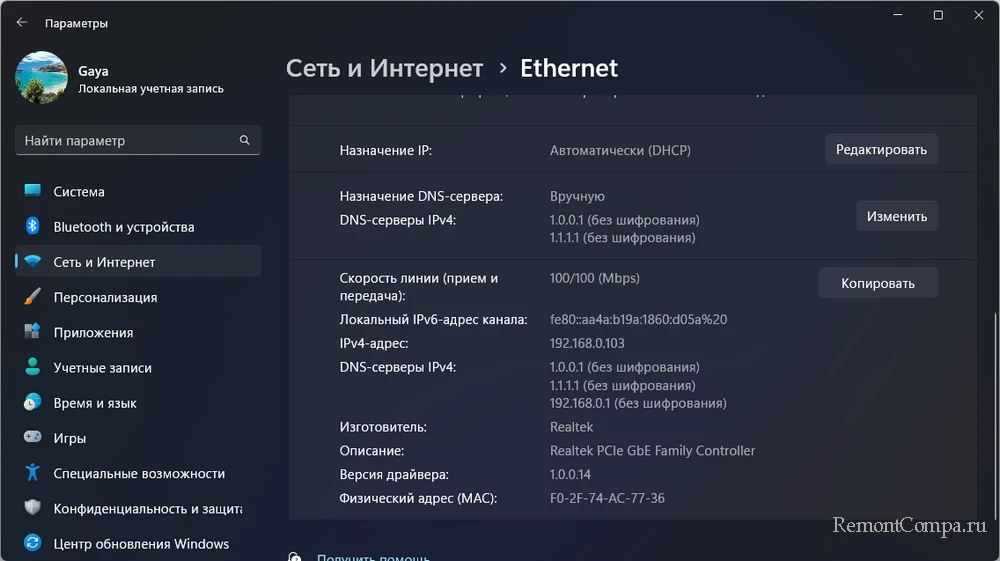
Клик по надписи «Свойства» для каждого подключения откроет детализацию о сетевом подключении.
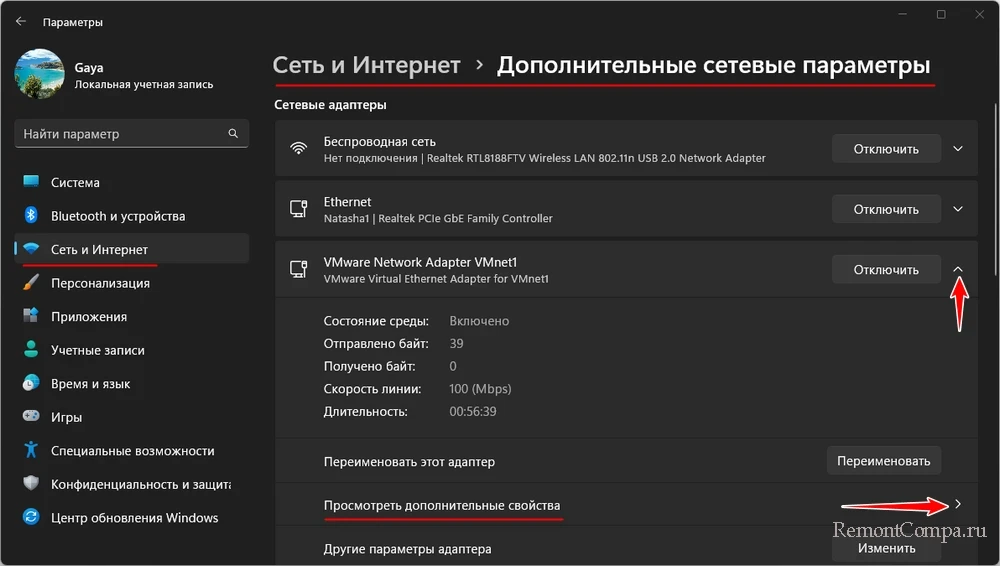
По пути «Сеть и Интернет → Дополнительные сетевые параметры» будем видеть все подключения — и активные, и неактивные, как реальные, так и виртуальные, привязанные к сетевому адаптеру. Можем раскрыть блок интересующего сетевого адаптера и кликнуть «Просмотреть дополнительные свойства».
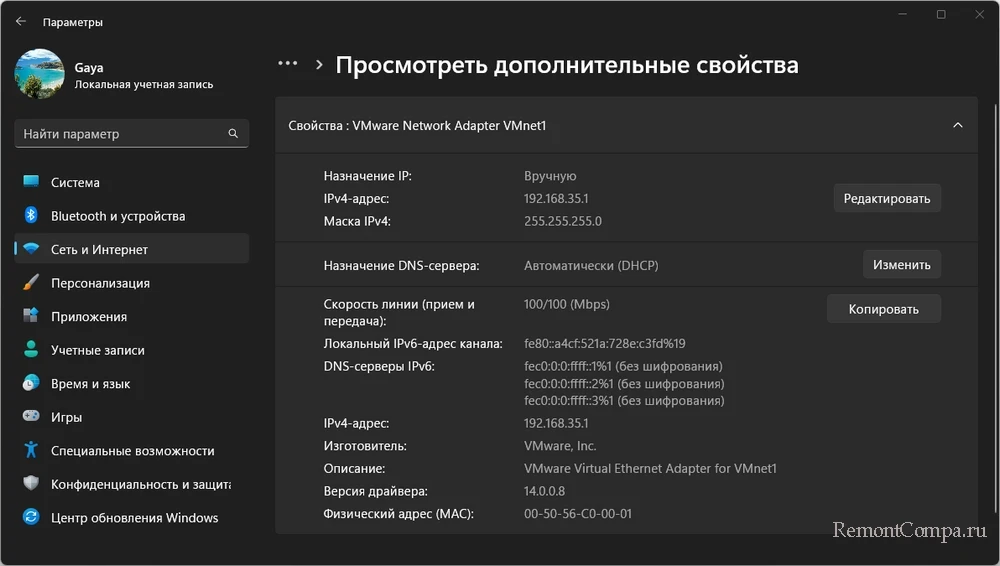
И посмотреть некоторые данные сетевого адаптера.
В любой версии Windows узнать её активные сетевые подключения можно в настройках классической панели управления. Клавишами Win+R запускаем командлет «Выполнить», вводим:
control.exe /name Microsoft.NetworkandSharingCenterОткроются основные сведения о сети, где в блоке активных сетей будем видеть все активные подключения.
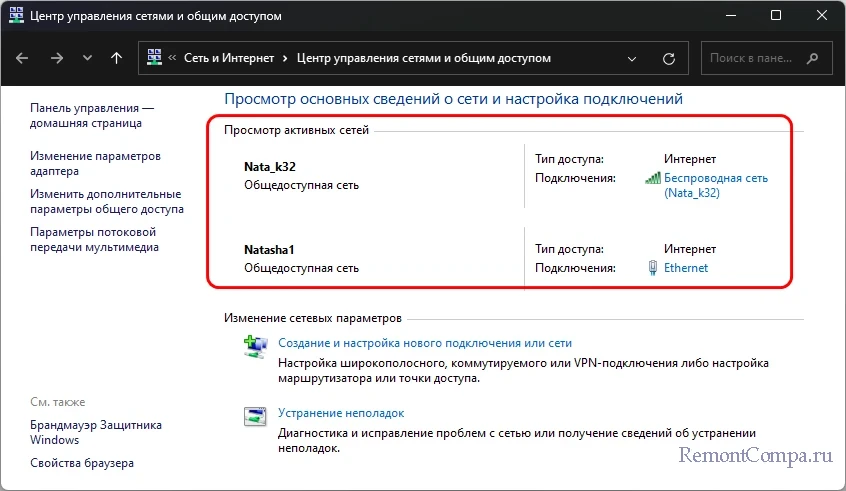
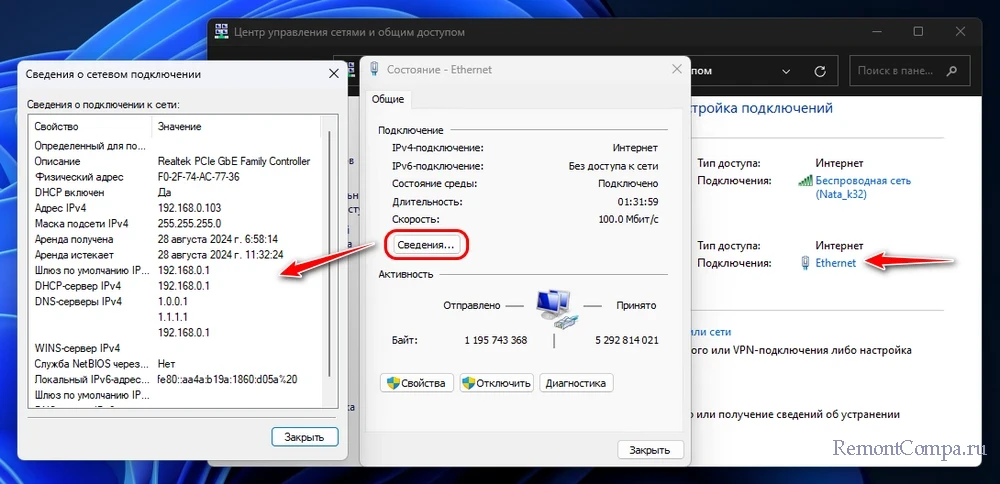
Клик по активной ссылке подключения откроет окошко его состояния, где, нажав кнопку «Сведения», можем получить в новом окошке детальные сведения о подключении.
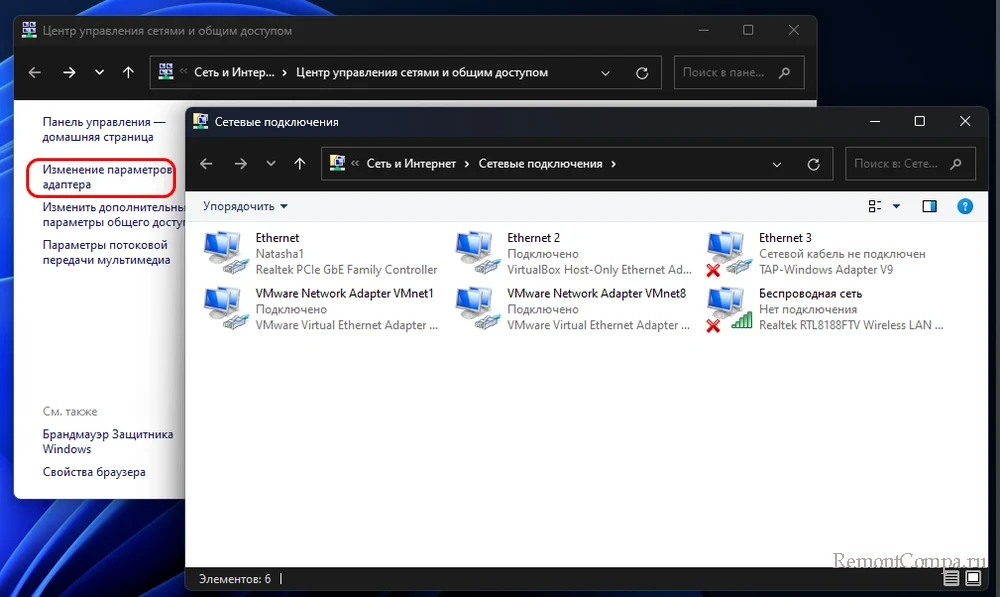
Для получения информации обо всех сетевых подключениях, включая неактивные, на боковой панели основных сведений о сети жмём «Изменение параметров адаптера». Выбираем адаптер нужного подключения.
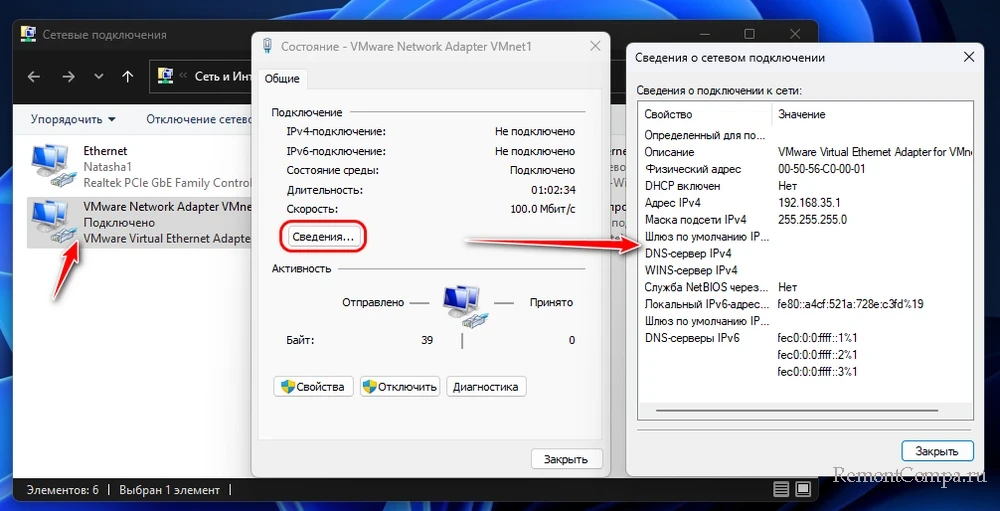
Двойным кликом открываем его окошко состояния. Жмём кнопку «Сведения» и получаем в новом окошке детальные сведения о сетевом подключении.
Различную информацию о сетевых подключениях Windows можно получить с помощью консольных команд в командной строке или PowerShell.
Команда:
ipconfig /allОтображает все сетевые адаптеры и некоторую информацию об их подключениях.
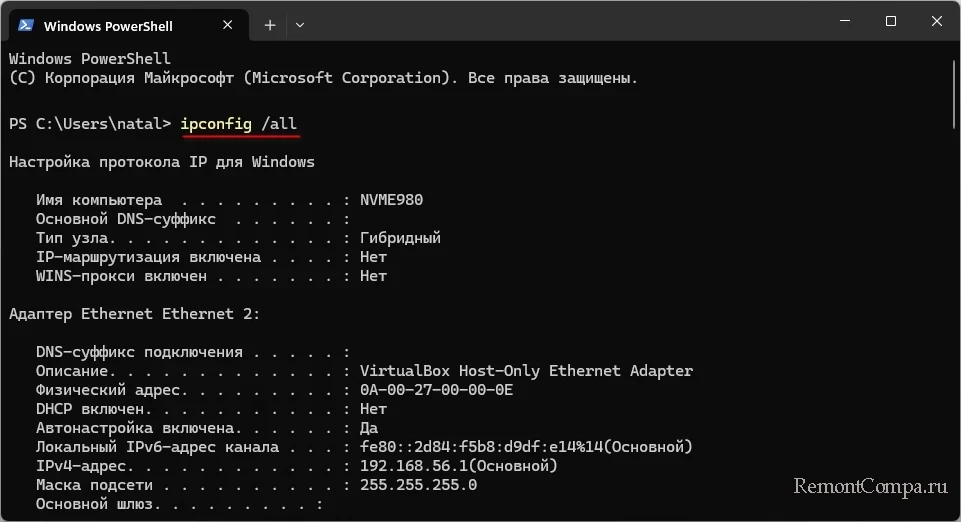
Команда:
netstat -anОтображает список активных соединений и прослушивающих портов на компьютере, этот список включает локальные и удалённые IP-адреса, порты и состояния соединений.
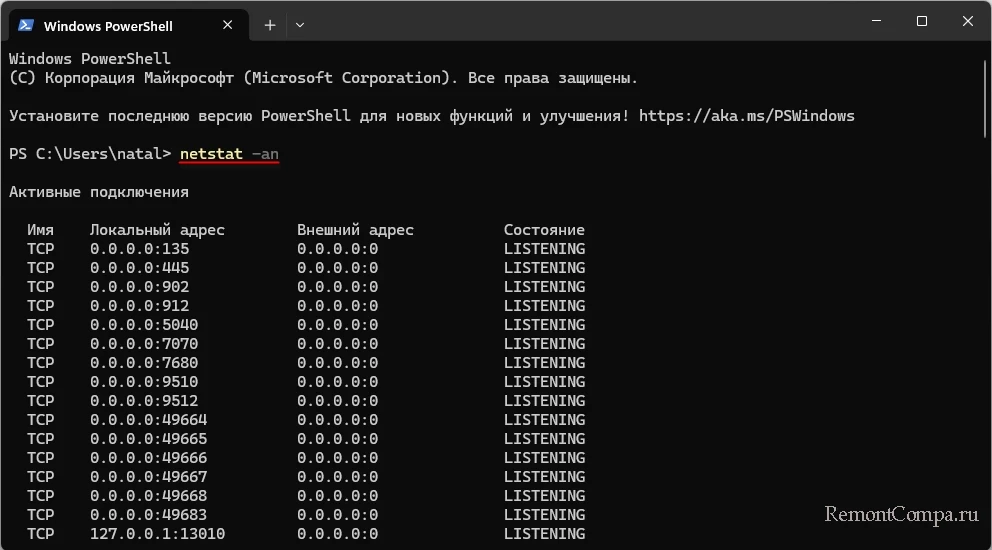
Команда:
Get-NetAdapter | Format-ListОтображает состояние и некоторые параметры сетевых адаптеров.
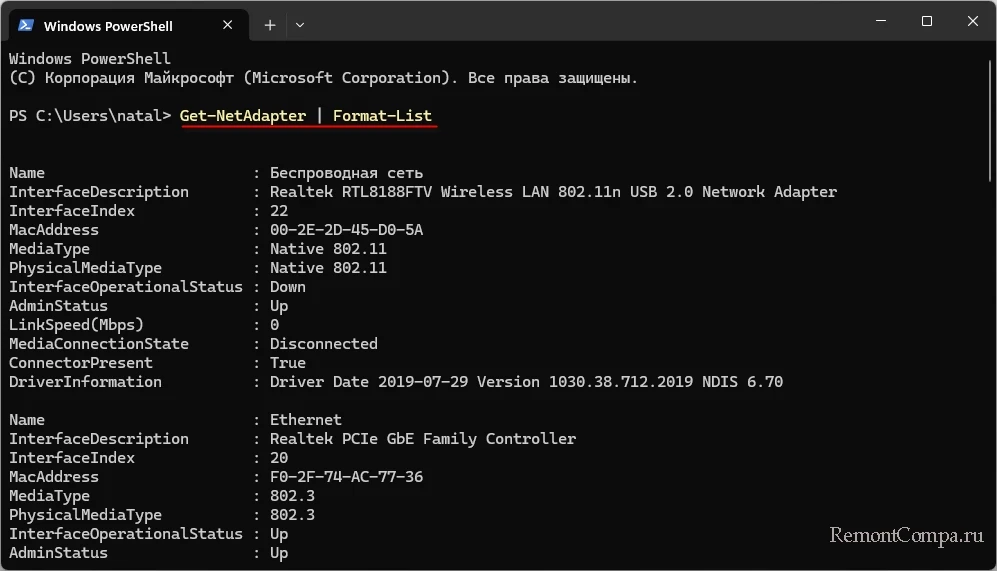
Дополнительные консольные команды для получения разной информации о сети в Windows:
|
Основная команда для получения информации о сетевых адаптерах и их IP-адресах. |
|
Команда для отображения активных соединений и статистики сетевых интерфейсов. |
|
Показывает таблицу соответствия IP-адресов и MAC-адресов. |
|
Отображает таблицу маршрутизации IP. |
|
Только PowerShell. Команда для отображения IP-адресов всех интерфейсов. |
|
Только PowerShell. Команда для отображения таблицы маршрутизации. |
|
Только PowerShell. Отображает информацию о профилях сетевых подключений (тип сети, состояние подключения и пр.). |
|
Только PowerShell. Показ статистики по каждому активному сетевому адаптеру, включая количество отправленных и полученных пакетов. |
Узнать активные сетевые подключения Windows можно с помощью бесплатных портативных программ от NirSoft.
NetConnectChoose позволяет просматривать активные сетевые подключения на компьютере.
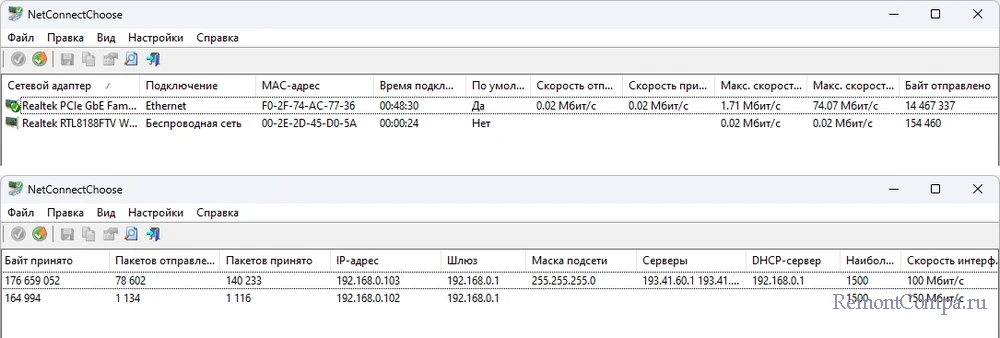
Предоставляет подробнейшую информацию о каждом подключении — тип, состояние, используемые IP-адреса и многое другое.
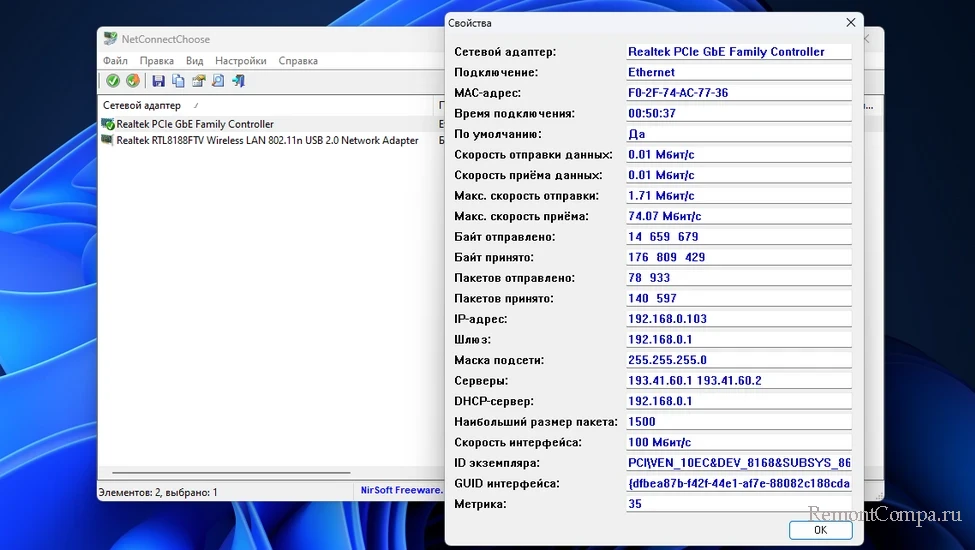
Позволяет сбрасывать счётчики пакетов, что может пригодиться для мониторинга сетевой активности с нуля.
AdapterWatch отображает значимые сведения о сетевых адаптерах, общую статистику TCP, IP, UDP, ICMP.
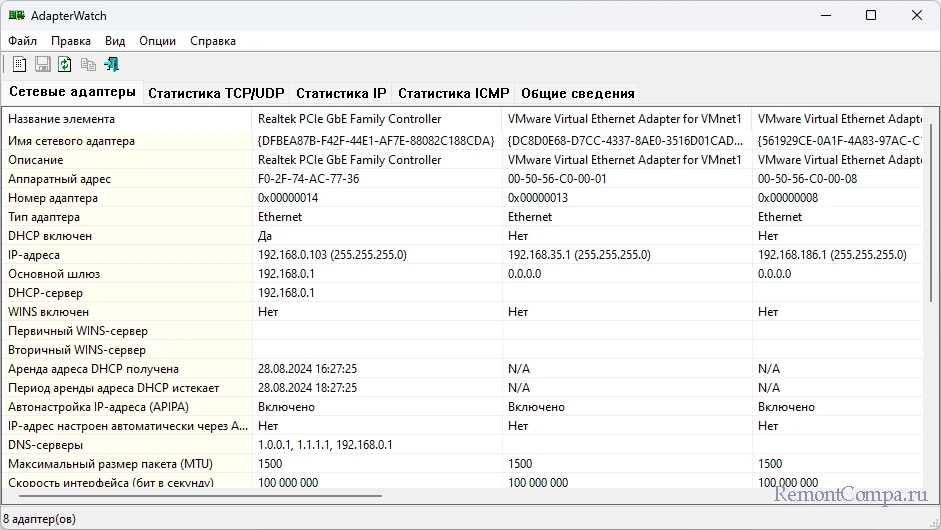
Друзья, виновником возникновения проблем с сетью (медленная скорость, прерывания соединения и т.п.) может быть какая-то из работающих программ на компьютере. В таких случаях анализ сетевых подключений мало чем поможет в решении проблемы. Нужно смотреть, какие программы устанавливают большое количество соединений и потребляют слишком много ресурсов сети, замедляя её работу. Детально об этом – в статье «Какие программы используют Интернет».
Download Article
Get a full list of your computer’s network connections
Download Article
- Checking Internet Connectivity Fast
- Using Windows 11
- Using Windows 10
- Using the Command Prompt
- Video
- Q&A
- Tips
|
|
|
|
|
|
On Windows 10 and 11, you can see your network connections in the Settings app, or by clicking the Wi-Fi or network icon on the taskbar. We’ll cover this in-depth and also show you how to use the netstat command to view information about active network connections so you can figure out if you have an internet connection or server problem.
Viewing Network Connections
- In Windows 11, type “settings” into the search bar, click «Settings,» and then click «Network & Internet.»
- In Windows 10 and earlier, open Settings from the Start menu, then open the «Network & Sharing Center» to view your connections.
- You can also check your network connections and traffic by typing “netstat -a” in the command prompt.
-
On every version of Windows, the network connectivity is displayed on the taskbar. Click the little radio signal logo (WiFi) or globe (ethernet).
- This will not show you all of the network connections on your computer, but it will show you if you have an active internet network connection.
-
Windows will display the name of the network, the strength of the connection, whether the internet is active, and whether you’re on a secured network or not.
- Below your network, there may be a list of more networks if you’re looking for a specific connection.
Advertisement
-
Press the Start menu and click on the little gear icon in the bottom left to open the settings.[1]
- If you don’t see a gear icon, you can also just type “settings” into the search bar and click it when it pops up in the results.
-
You can now see the status of your network connection and the name of any internet networks you’re connected to.
Advertisement
-
If the Settings are pinned to your start menu, click it. Otherwise, type “settings” into the menu’s search bar and click Settings.
-
-
The Network and Sharing Center is a feature of Windows 10 where you can find the status of your network, the type of connection you have, if you can connect to other computers other than your own, and if you are connected to your network or the internet.[2]
-
This should correspond to your connection type. For example, «Ethernet» will be paired with an ethernet cable «plug» and a wireless network connection will be paired with five bars.[3]
-
This will prompt a window to display the details of your network connection.
Advertisement
-
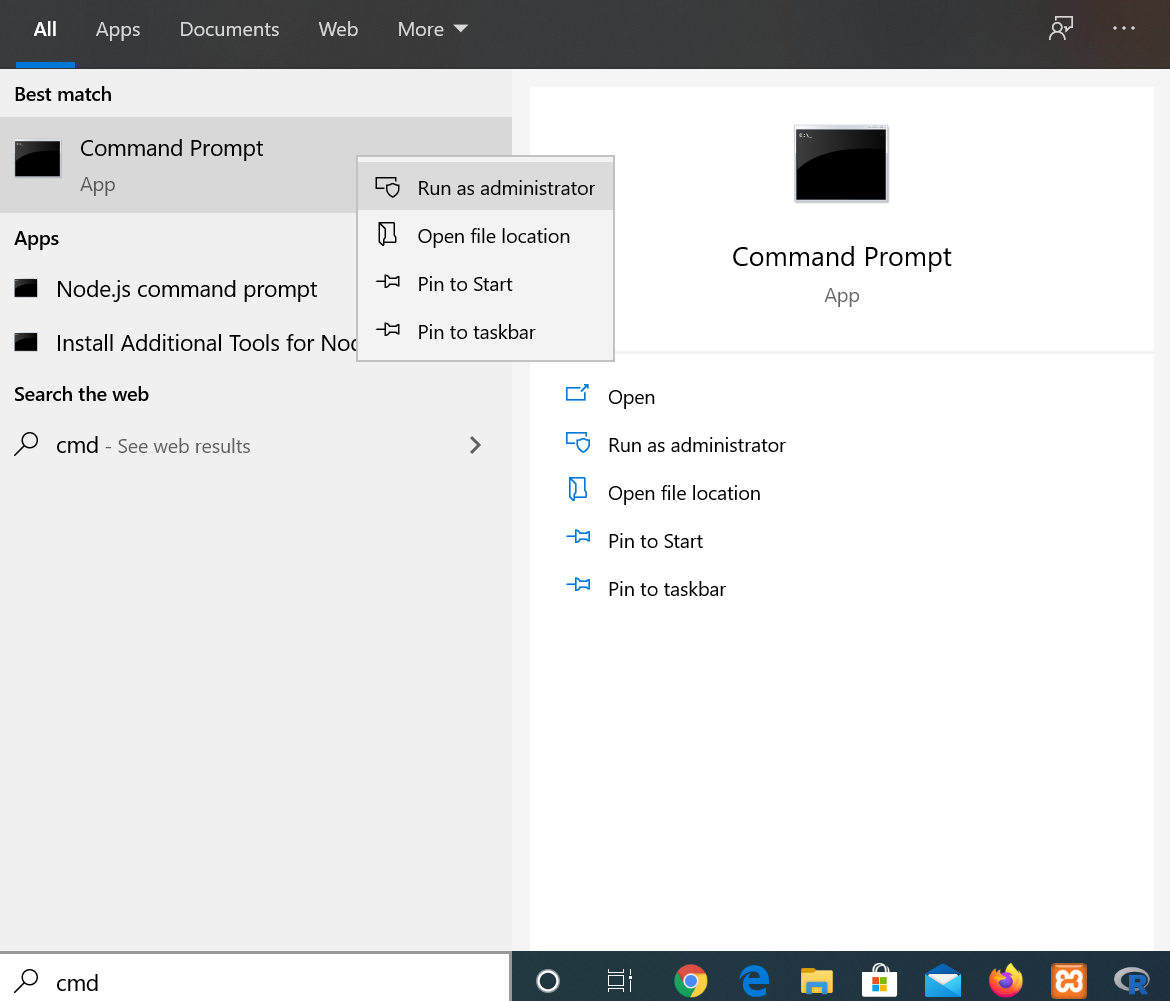
You can use the netstat command on any version of Windows (including older versions like Windows 7 and 8.1) to view your network connections, network status, connected hosts, and other helpful details. You’ll need to use an administrator-level command prompt to use the command effectively. To open the command prompt as an administrator:
- Press the Windows key (or click the Start menu) and type cmd.
- Right-click «Command Prompt» and select Run as administrator.
- Click Yes when prompted.
-
This command will show you a list of your current TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) connections and ports, physical computer names listed for local addresses, and hostnames for remote addresses. It will also tell you the state of the port (waiting, established, etc.)[4]
-
This command will show you the same list as netstat -a, but it will also show you which programs are using the connections/ports.[5]
-
This command will show you the same list of connections and ports but with numerical IP addresses instead of hostnames.[6]
-
to see the different netstat command. This command will provide you with additional options for using netstat.[7]
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
Why isn’t my computer shown in the network group?
Your computer is probably not set to work with the networking group then. You need to re-configure that correctly.
-
Question
How do I get access on other websites using my active network connections?
If you have the proper credentials, use an ssh-connection, if this port is open on the website you would like to access.
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
-
Experiment — many UNIX commands are available (i.e., «netstat» mentioned above) in Windows. Use your favorite search engine to look them up.
-
On Linux, use «ip –s,» «ss,» or «ip route» instead of the netstat command.
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
References
About This Article
Article SummaryX
To see your active network connections in Windows, start by selecting Settings in your Start menu and going to Ethernet. Then, click on the Network and Sharing Center before choosing the icon that’s next to Connections. On the next page, click on Details to display information about your network connection. Alternatively, if you’re using Windows 7, open the Start menu and type NCPA.CPL into the search box. After the Network Connections folder opens, right click on the connection you want and choose Status from the dropdown menu. After the Network Status page loads, go to Details to find out more about the connection. For tips on how to get network connection details on Windows Vista or XP, keep reading!
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 1,034,994 times.
Reader Success Stories
-
«Needed to find how to connect a DVR to my computer. Could not find network connections and was afraid of pressing…» more
Is this article up to date?
Содержание статьи:
- Сетевые подключения
- Как открыть данную вкладку
- Как посмотреть свойства адаптера, изменить ряд параметров
- Пару слов о сетевых параметрах Windows 10/11
- Вопросы и ответы: 0
Всех приветствую!
В современных Windows 10/11 почему-то «скрыли от глаз» классическую панель управления, а вместе с ней и вкладку «Сетевые подключения» (которая бывает ой как нужна при различных настройках ОС). Забавная коллизия… 🙂
Между тем, эта вкладка помогает просмотреть все ранее созданные подключения (те же PPPoE), работающие сетевые адаптеры Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Ethernet, их свойства, установленные параметры, и прочее.
В рамках этой заметки приведу неск. способов, как открыть «Сетевые подключения», а также посмотреть свойства того или иного адаптера (в общем-то, базовые моменты, которые часто требуются при настройке сети).
Итак, ближе к теме…
*
Сетевые подключения
Как открыть данную вкладку
📌 Способ 1 (универсальный)
- нажать сочетание клавиш Win+R (должно появиться окно «Выполнить»);
- в строку «Открыть» ввести команду ncpa.cpl и нажать Enter.
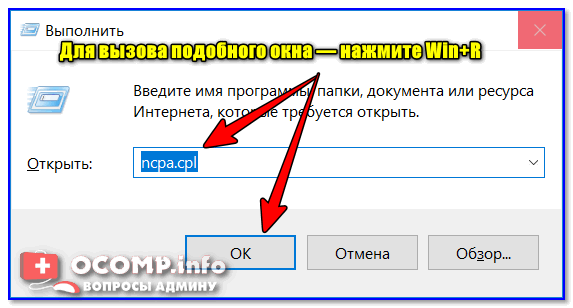
ncpa.cpl — просмотр всех сетевых подключений
*
📌 Способ 2 (проверен в Windows 10 и 11)
Если у вас в трее (рядом с часами) есть сетевой значок — нажмите по нему правой кнопкой мыши и в меню выберите «Параметры сети и Интернета».
Далее нужно перейти во вкладку «Дополнительные сетевые параметры / Доп. параметры сетевого адаптера». Скрин см. ниже. 👇
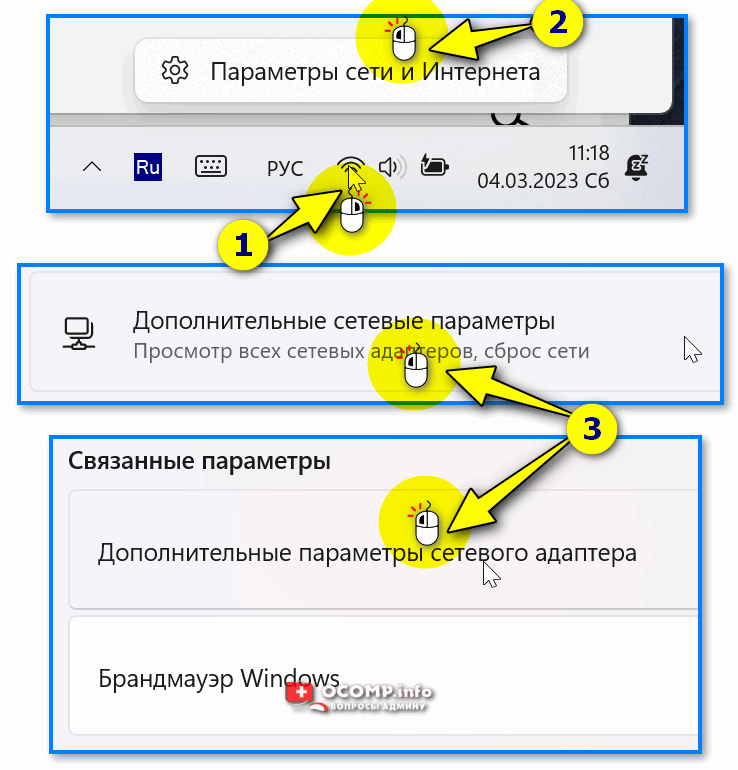
Доп. параметры сетевого адаптера — значок сети в трее Windows
*
📌 Способ 3
- открыть контрольную панель управления;
- далее перейти во вкладку «Сеть и интернет / центр управления сетями…»;
- затем в боковом меню перейти по ссылке «Изменение параметров адаптера».
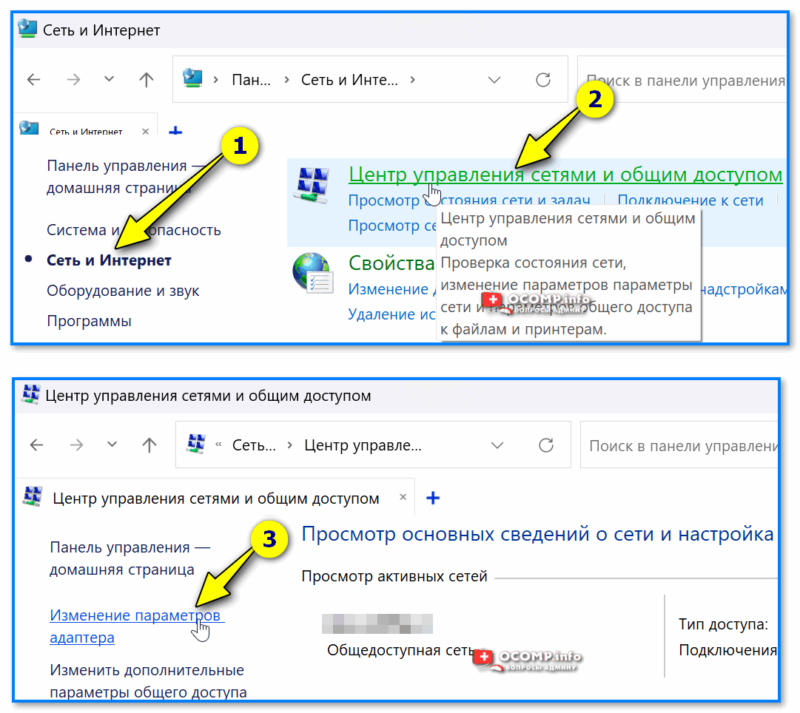
Центр управления сетями — контрольная панель
*
📌 Способ 4
Если вкладка сетевых подкл. не открывается — информацию можно посмотреть и другим образом — с помощью командной строки. Как это делается:
- запускаем командную строку;
- вводим команду netsh interface show interface и нажимаем Enter;
- получаем список адаптеров, и видим, какие из них подключены, а какие нет.
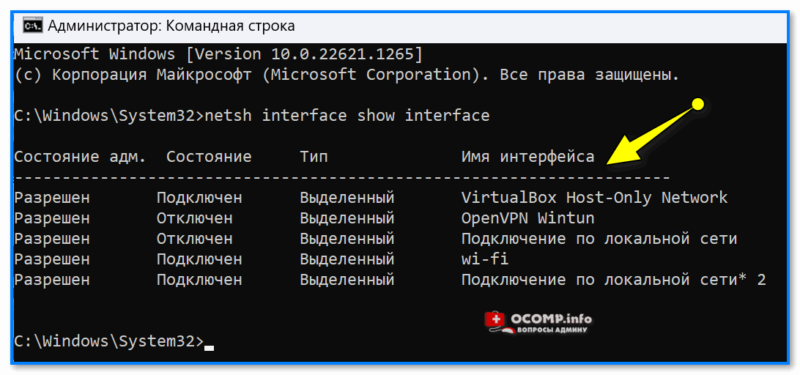
netsh interface show interface
*
Как посмотреть свойства адаптера, изменить ряд параметров
Для неискушенных пользователей: обратите внимание на цвет значков в этой вкладке («Сетевых подкл.»):
- если значок серый (бесцветный) — значит этот адаптер выключен (т.е. не работает). В моем примере ниже таких 2; 👇
- если значок цветной, но рядом с ним горит красный крестик — значит, что сам адаптер работает, но ничего к нему не подключено (в моем примере Bluetooth адаптер именно такой 👇);
- если значок цветной и рядом с ним нет никаких крестиков — адаптер работает, подключение активно.
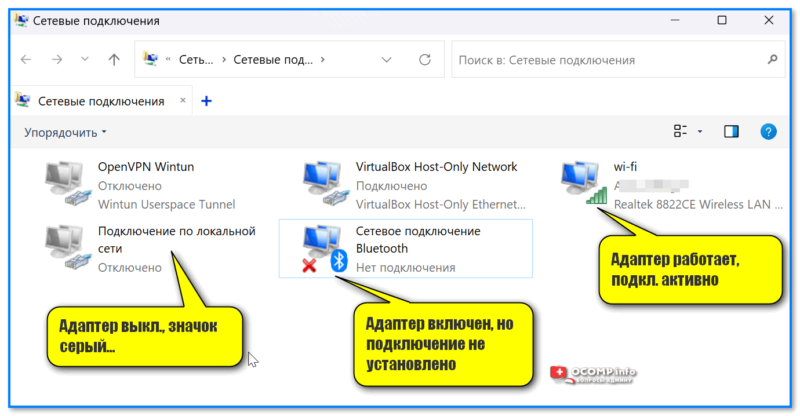
Какой адаптер вкл., какой выключен
Кстати, чтобы включить адаптер — кликните по нему правой кнопкой мыши и в меню выберите «Подключить». (Прим.: по умолчанию все адаптеры должны быть вкл., однако, в некоторых случаях их откл. вручную…)
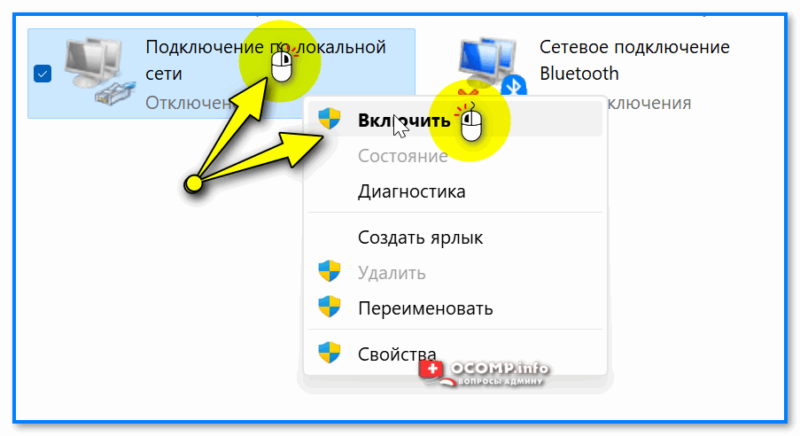
Вкл. адаптера — ПКМ по значку адаптера
Чтобы открыть свойства конкретного адаптера — сделайте по нему ПКМ и в контекстном меню выберите соотв. пункт. Как в примере ниже. 👇
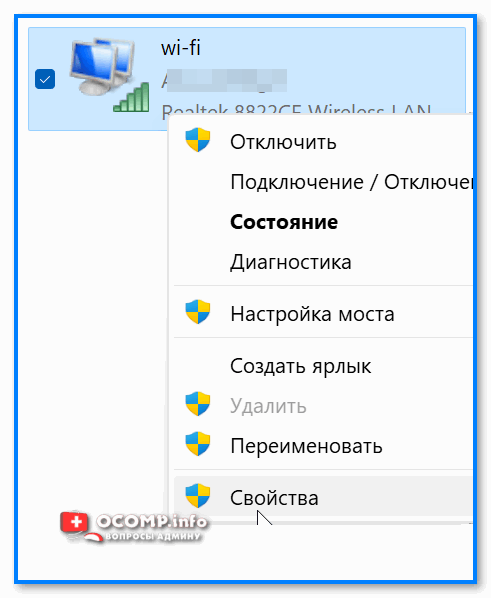
Свойства адаптера
Далее появится окно свойств: в нем можно будет настроить некоторые параметры более точечно. Например, довольно часто требуется поменять IP или DNS — для этого выберите строку «IP версии 4» и откройте ее свойства. 👇
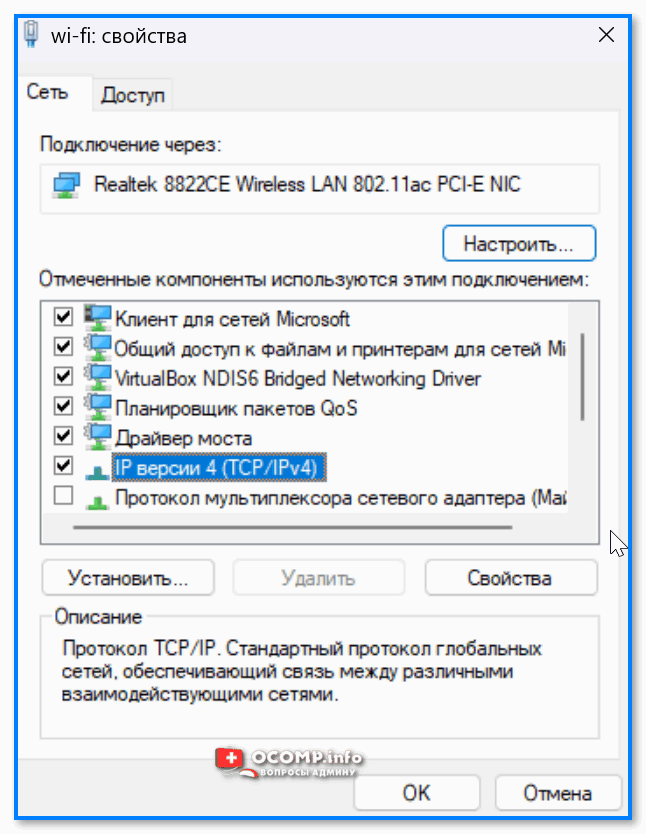
IP версии 4 — свойства
Далее можно задать требуемые 📌DNS (IP, маску…). 👇
📌 В помощь!
Как сменить DNS в Windows, и как выбрать наиболее быстрый публичный DNS-сервер — https://ocomp.info/kak-vyibrat-public-dns.html
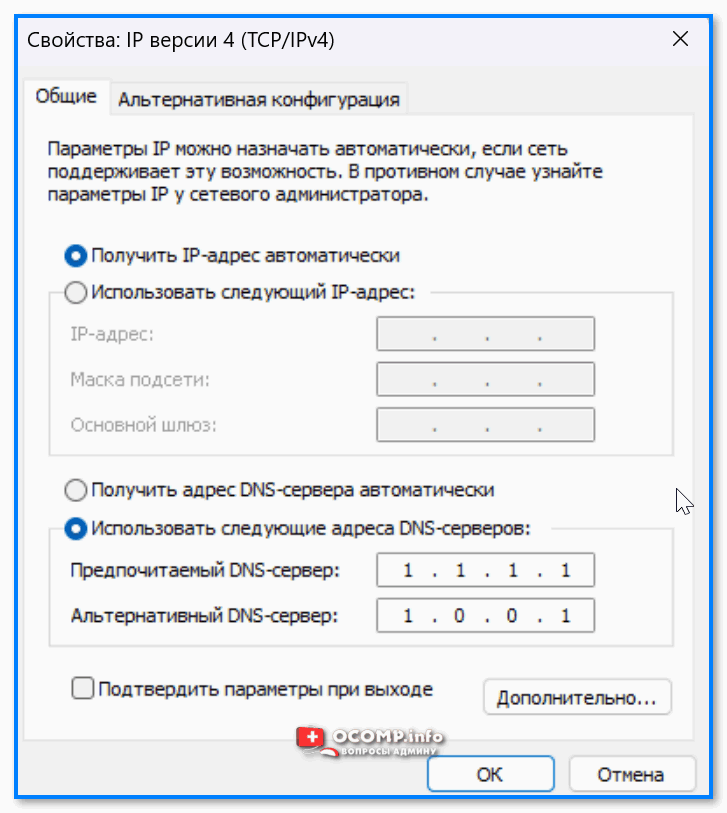
Использовать следующие DNS и IP
*
Пару слов о сетевых параметрах Windows 10/11
Кстати, в современных Windows 10/11, если нажать ПКМ по меню ПУСК, — то в меню можно заметить возможность открыть вкладку с сетевыми подкл. Однако, на деле откроется раздел «Сеть и Интернет» в 📌параметрах ОС (см. пару скриншотов ниже 👇).
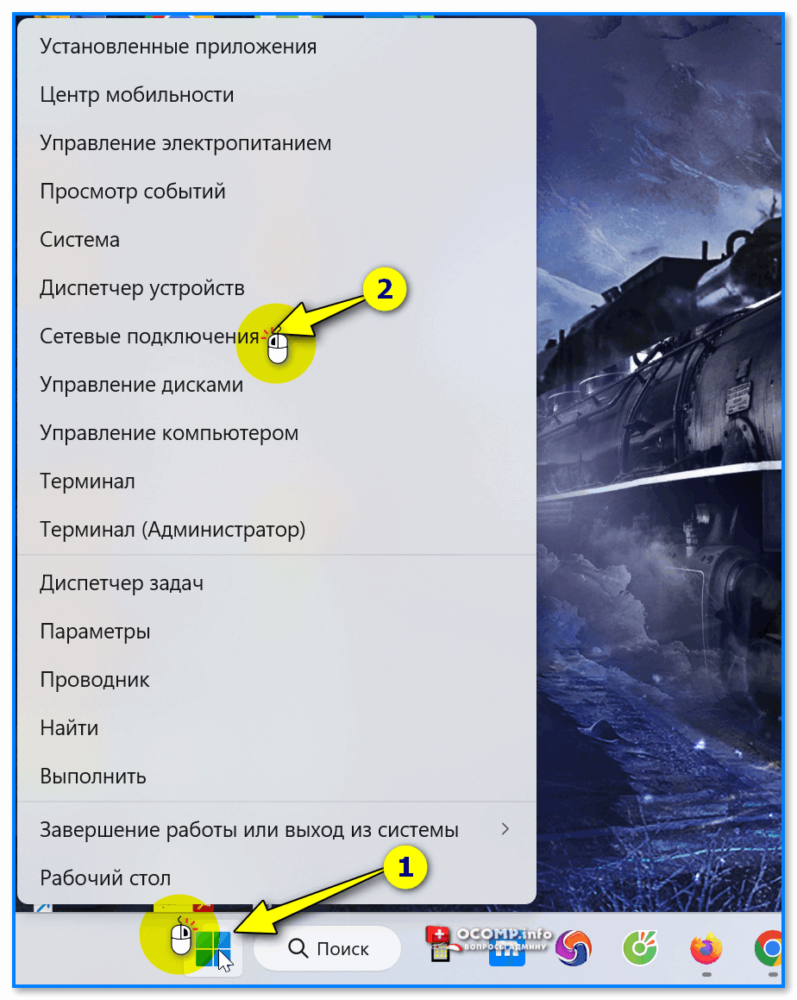
Сетевые подключения — параметры в Windows 10-11
Раздел этот достаточно «большой» и относительно удобный — есть все основные разделы: VPN, Wi-Fi, исп. данных, прокси и др. Однако, решить он помогает не все вопросы… и иногда вкладка сетевых подкл. просто необходима…
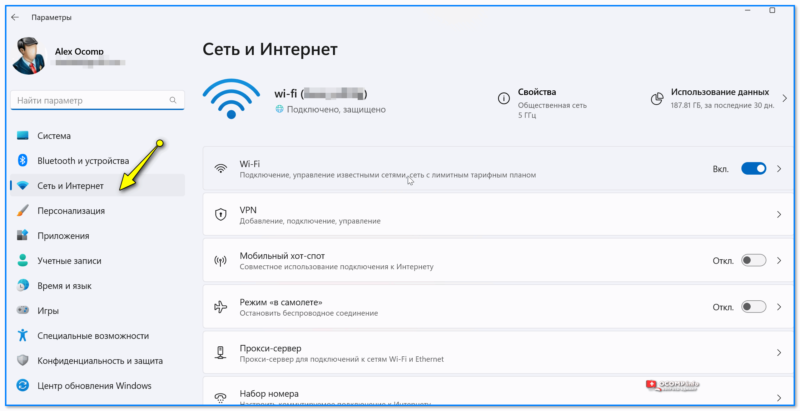
Сеть и Интернет — параметры Windows 11
📌 Кстати, если у вас не работает какой-нибудь адаптер, или вы никак не можете открыть «Сетевые подкл.» — можно попробовать сбросить все сетевые настройки Windows. В этом случае будут использоваться настройки по умолчанию, и скорее всего вопрос разрешится…
О том, как это сделать, расскажет моя предыдущая заметка, ссылочка на нее ниже. 👇
https://ocomp.info/kak-sbrosit-nastroyki-seti.html
*
За сим откланяюсь, успехов!
🙂
Last Updated :
17 May, 2020
There could be instances where we need to check our current network connectivity or sometimes troubleshoot a particular connection. We can follow a few simple steps to check the active connections. We also have some predefined commands that when entered in command prompt give a detailed explanation about the connection including the IP address, port numbers, and connection status. In this article lets look at the ways to check the active network connections on Windows.
Network Connections
There are two methods to check network connections:
Method 1: Using control panel
Step 1: In the search tab, search for the control panel and click on view network status and tasks below the Network and Internet. (This displays the current network the system is connected to.)
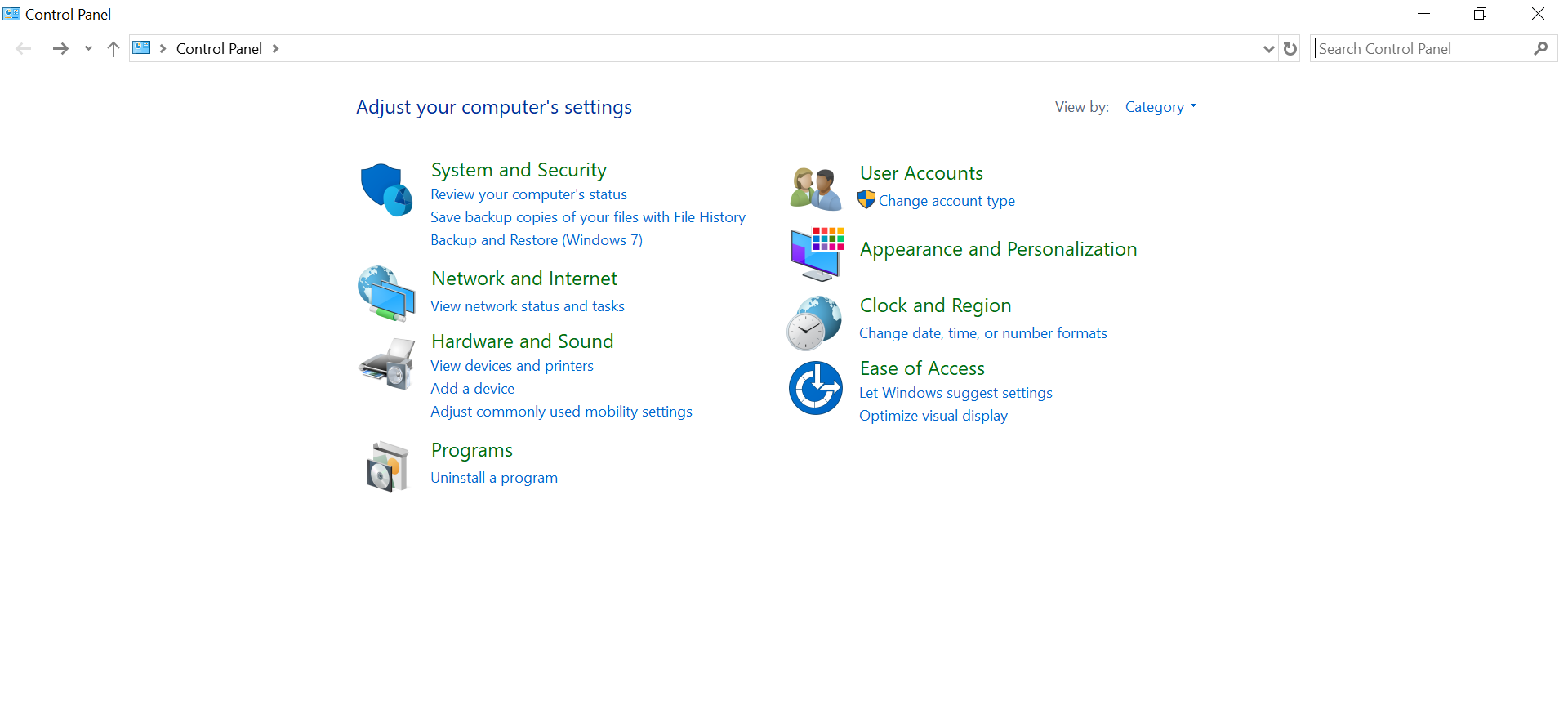
Step 2: You can click on connections to check the network status
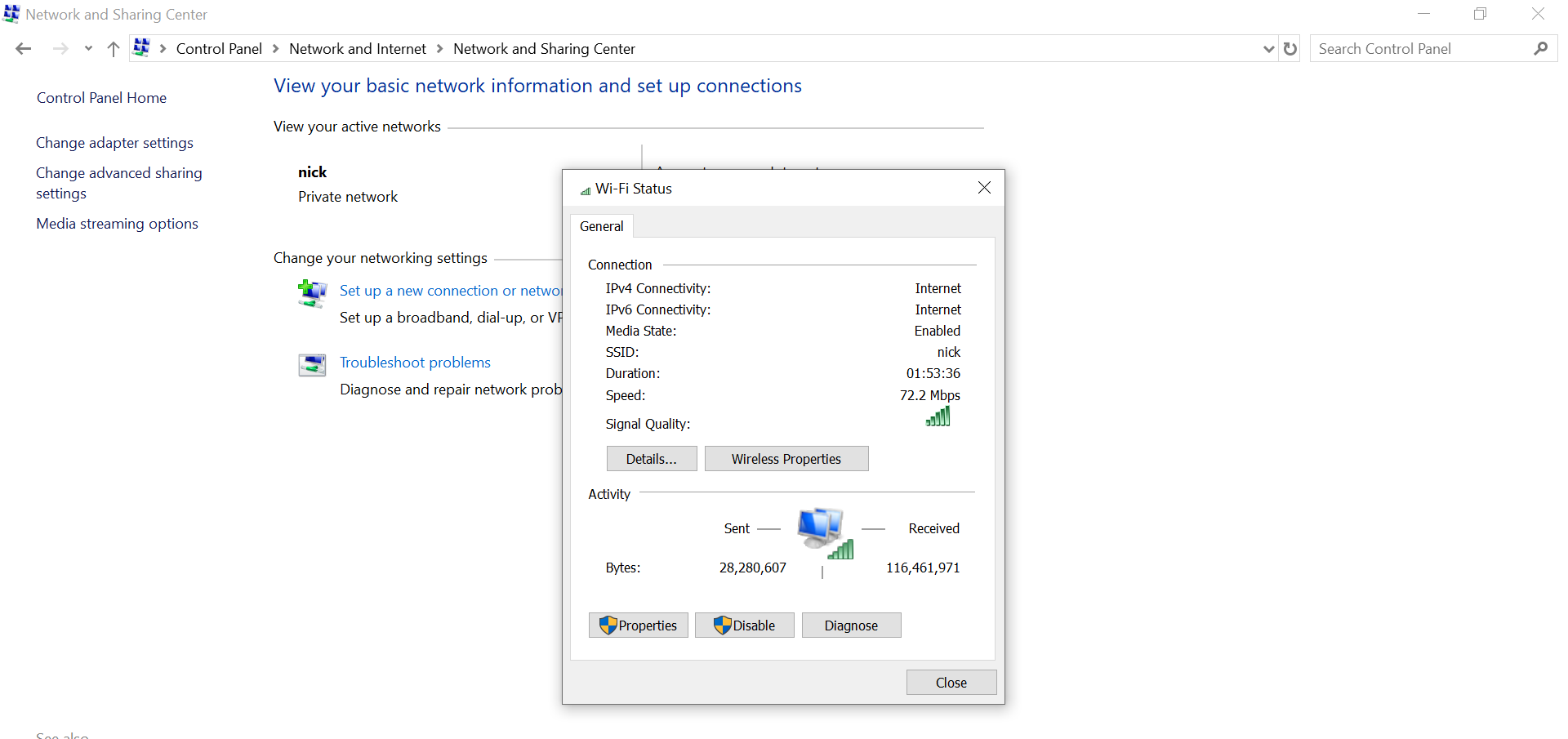
Step 3: Click on Details for more information about the network connection like IPv6 address, subnet mask, etc.
Alternatively:
Step 1: Go to settings and click on Network & Internet
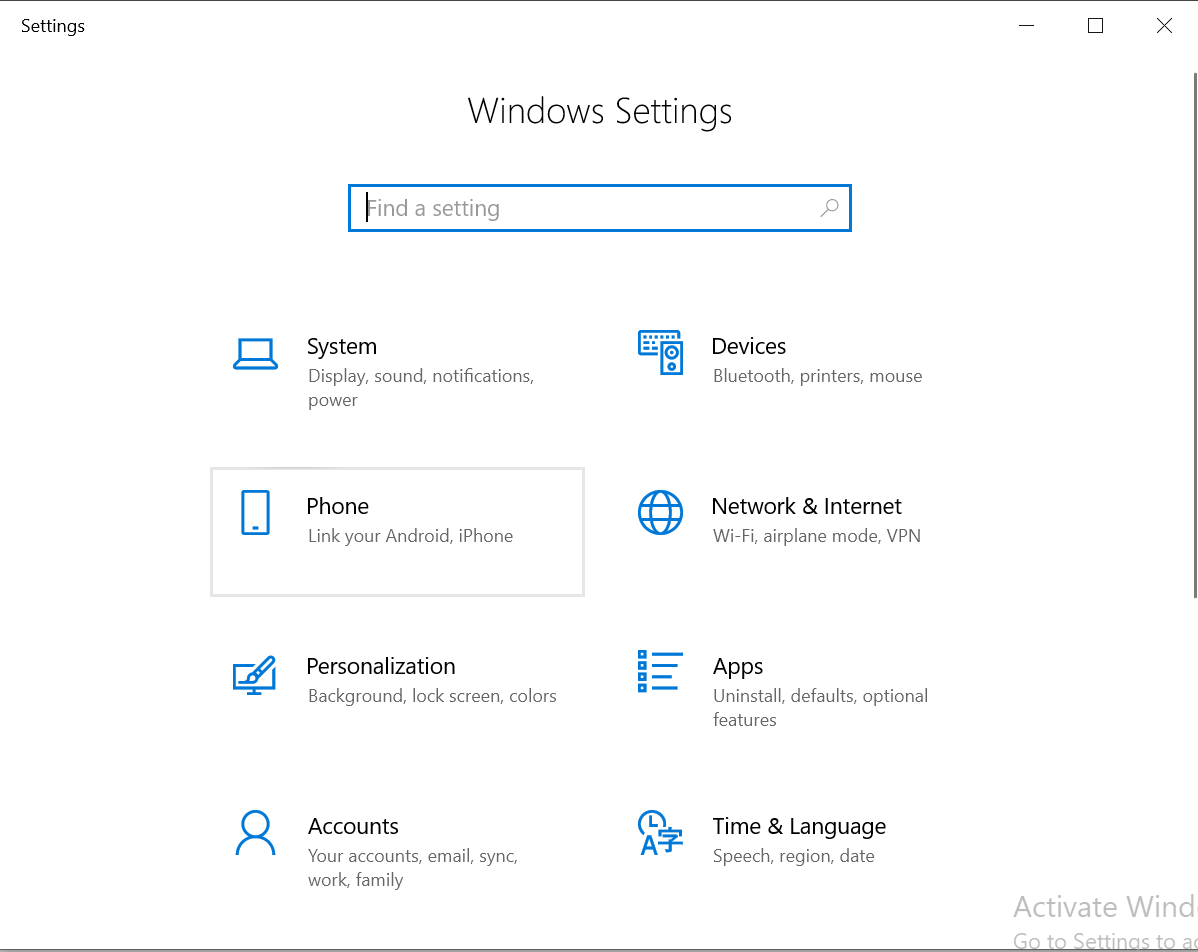
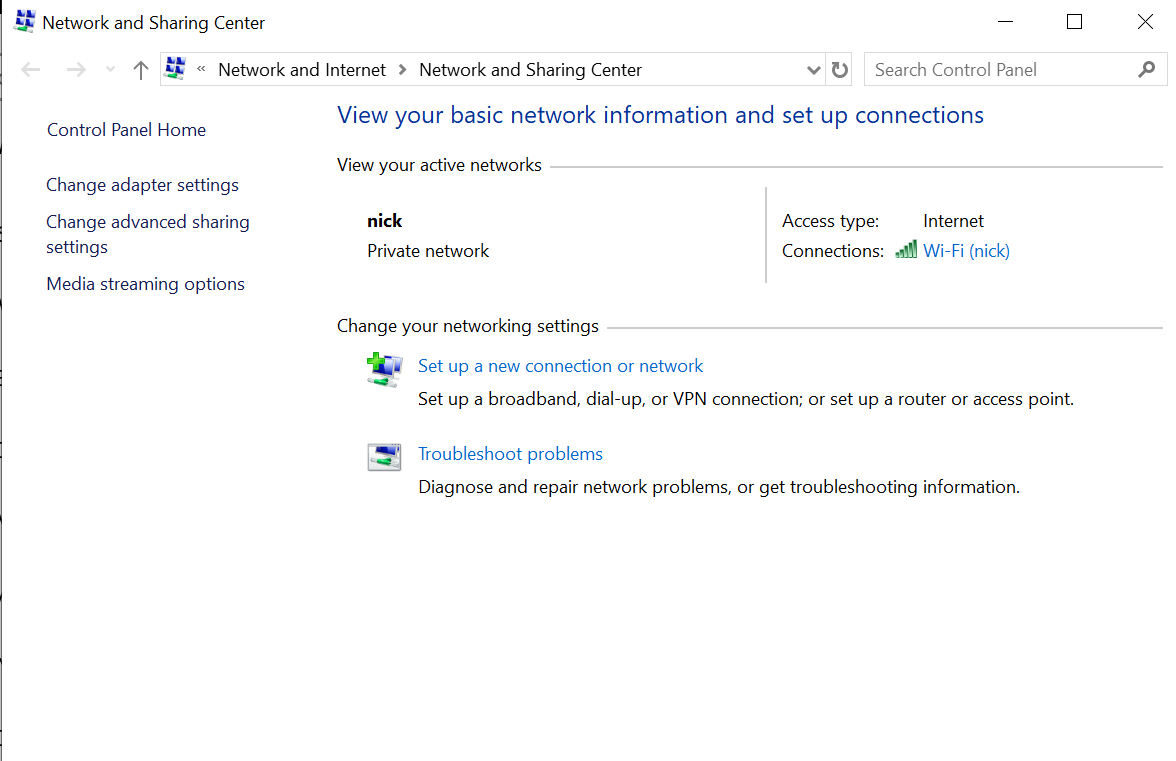
Step 2: Select Ethernet and then click on Network and Sharing Center that would navigate to the same page where the current network is shown
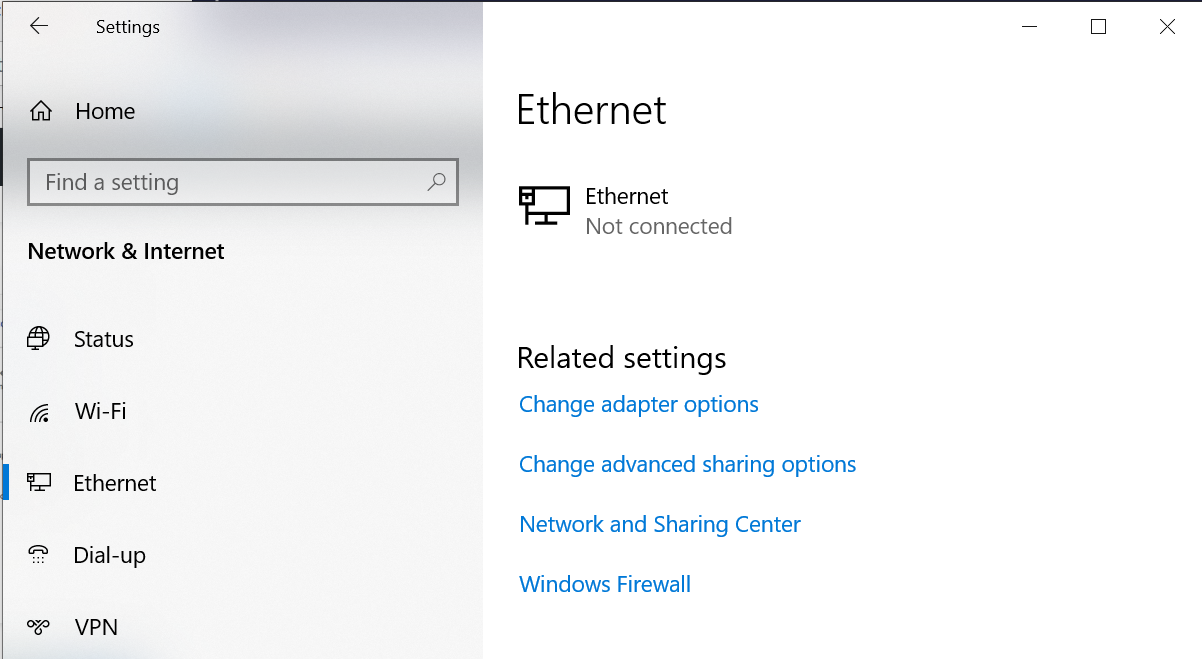
Method 2: Using Network connections folder
Step 1: In the search bar type: “ncpa.cpl” and press enter
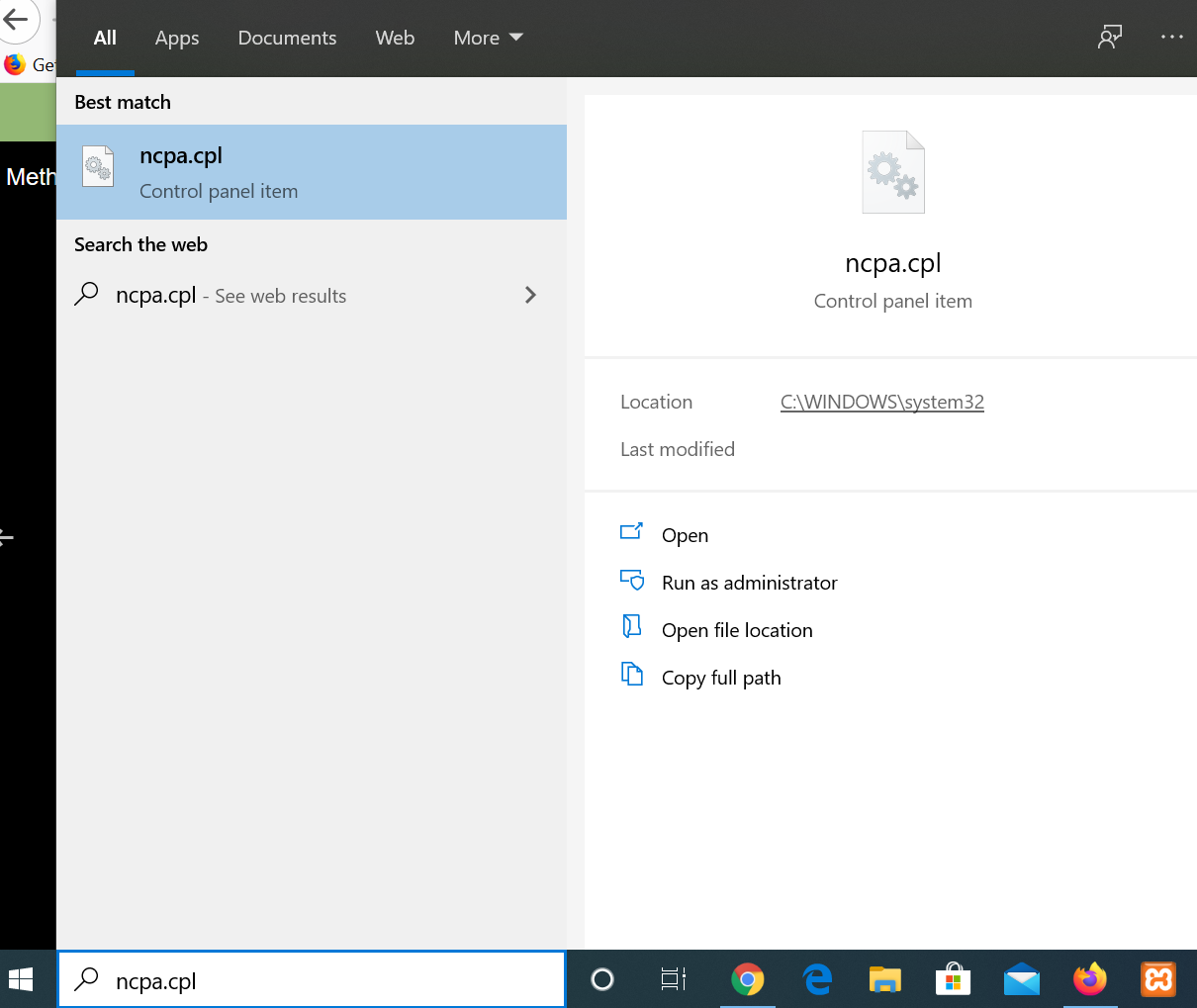
This would show all the connections but we can identify the active connection using the green icon
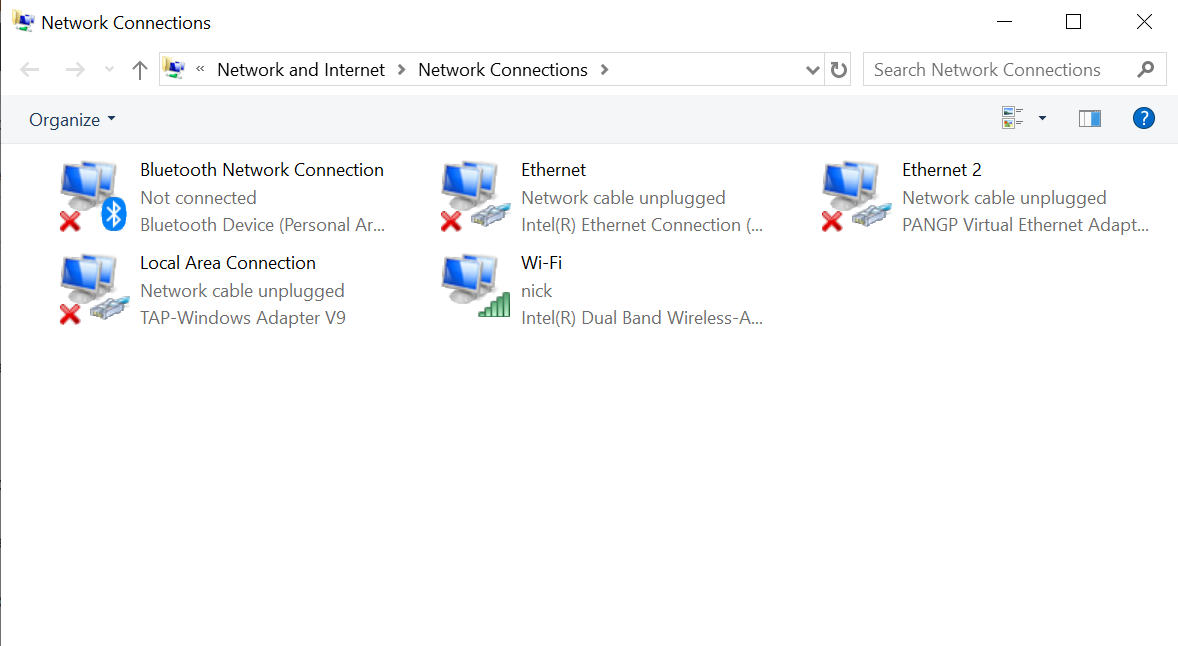
Step 2: Right-click on the active connection and click on the status to see the status page.
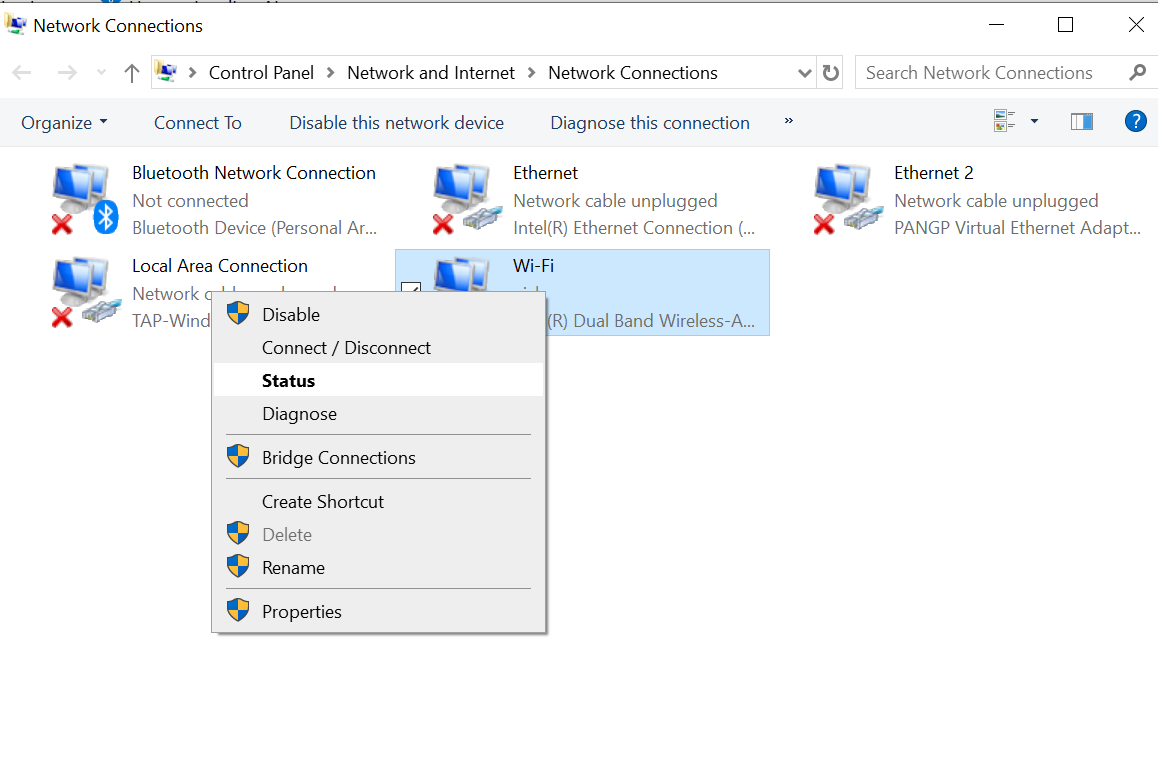
Now, you can click on details for more information just like we did in the earlier steps
Checking All active connections
Other than the internet connections which we have seen till now, there are many more active connections in order for the system to function. To look at such connections follow the steps below:
Step 1: In the search bar type “cmd” (Command Prompt) and press enter.
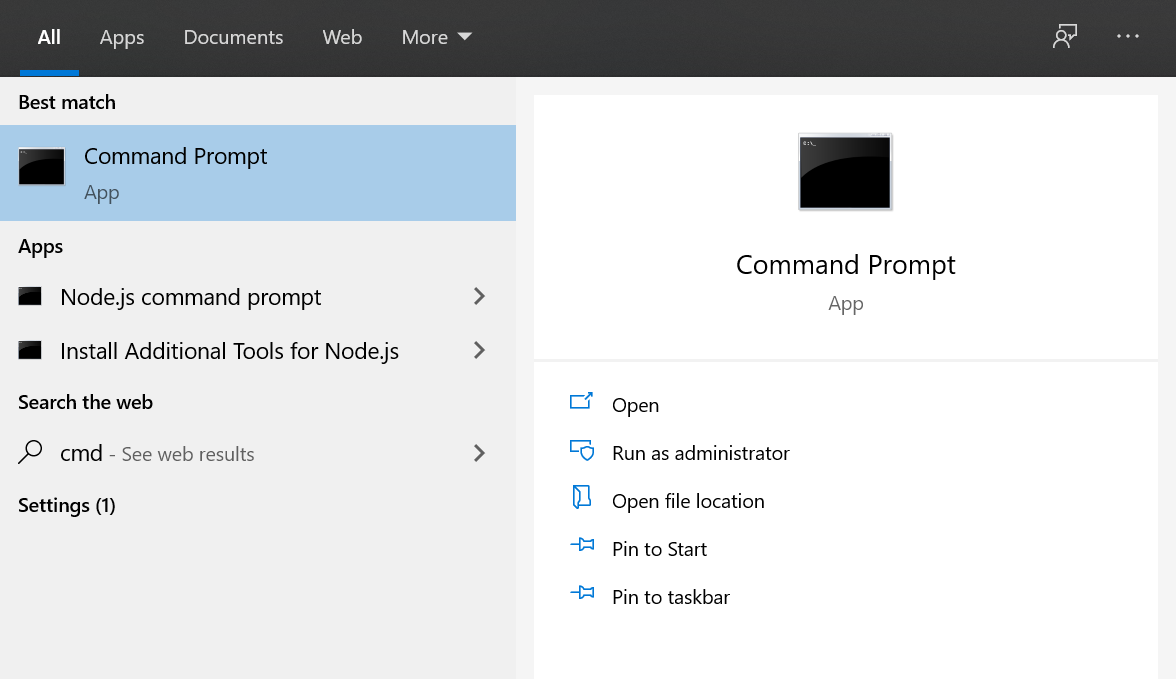
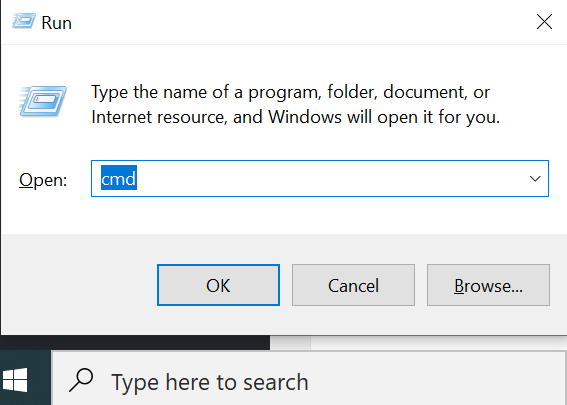
Alternatively, press “ + R” on the keyboard. In the open text box type “cmd” and click on OK
This would open the command prompt window.
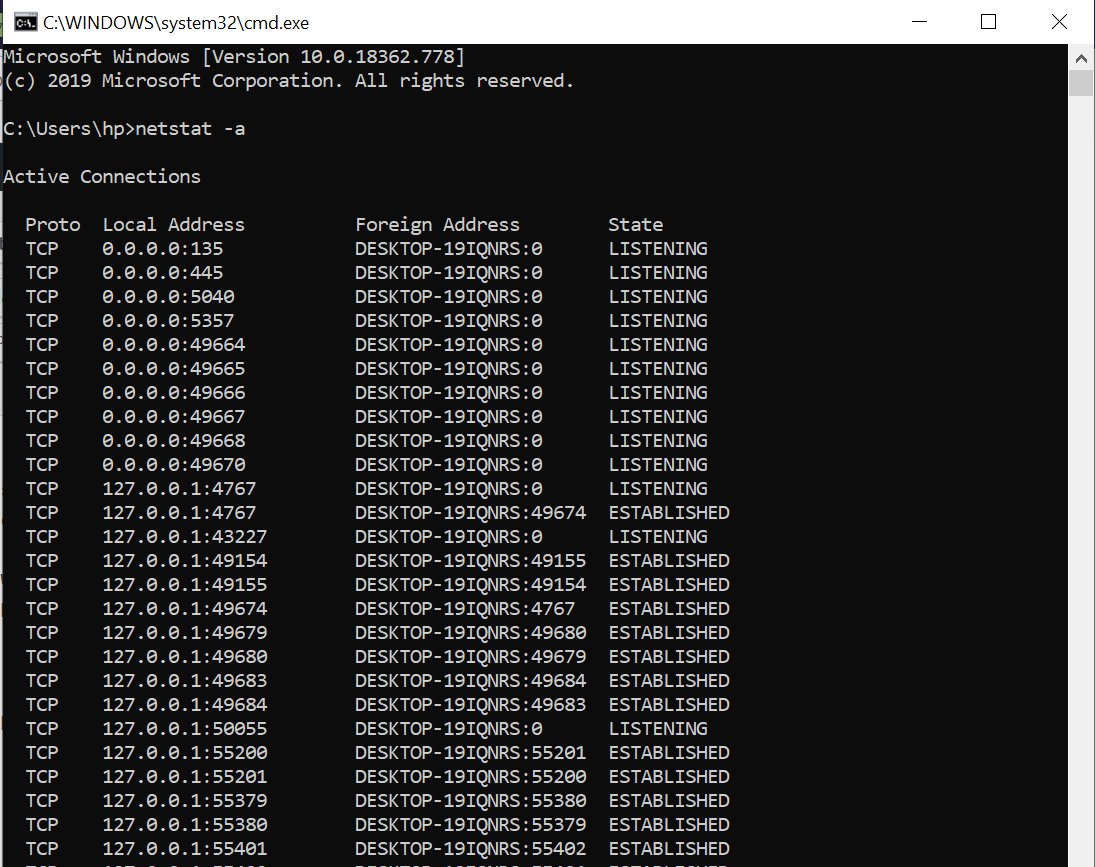
Step 2: We can now enter the netstat commands to look at all current active connections
“netstat -a” shows all the currently active connections and the output display the protocol, source, and destination addresses along with the port numbers and the state of the connection.
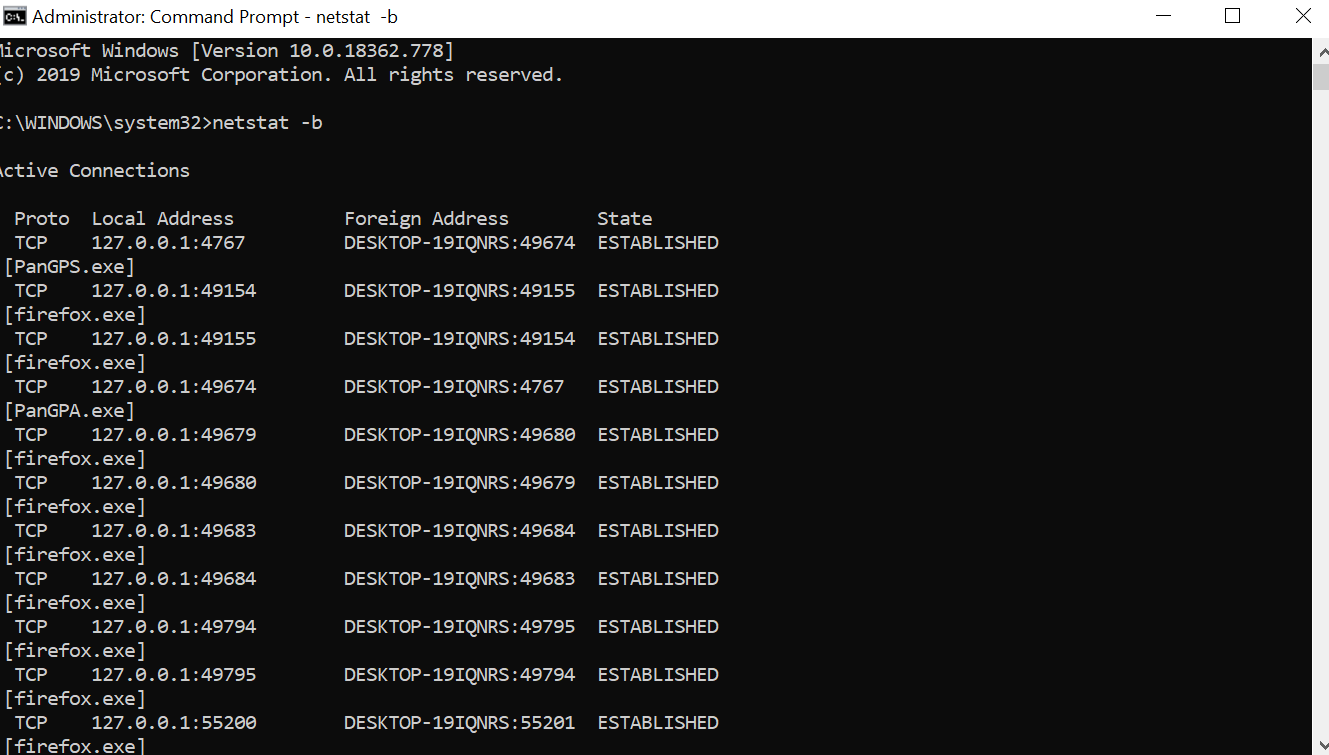
“netstat -b” shows the executable involved in creating each connection or listening port
Please note that we need extra privileges to execute this output. We might see the following error.
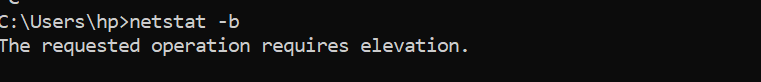
In such cases, open the command prompt and run it as administrator.
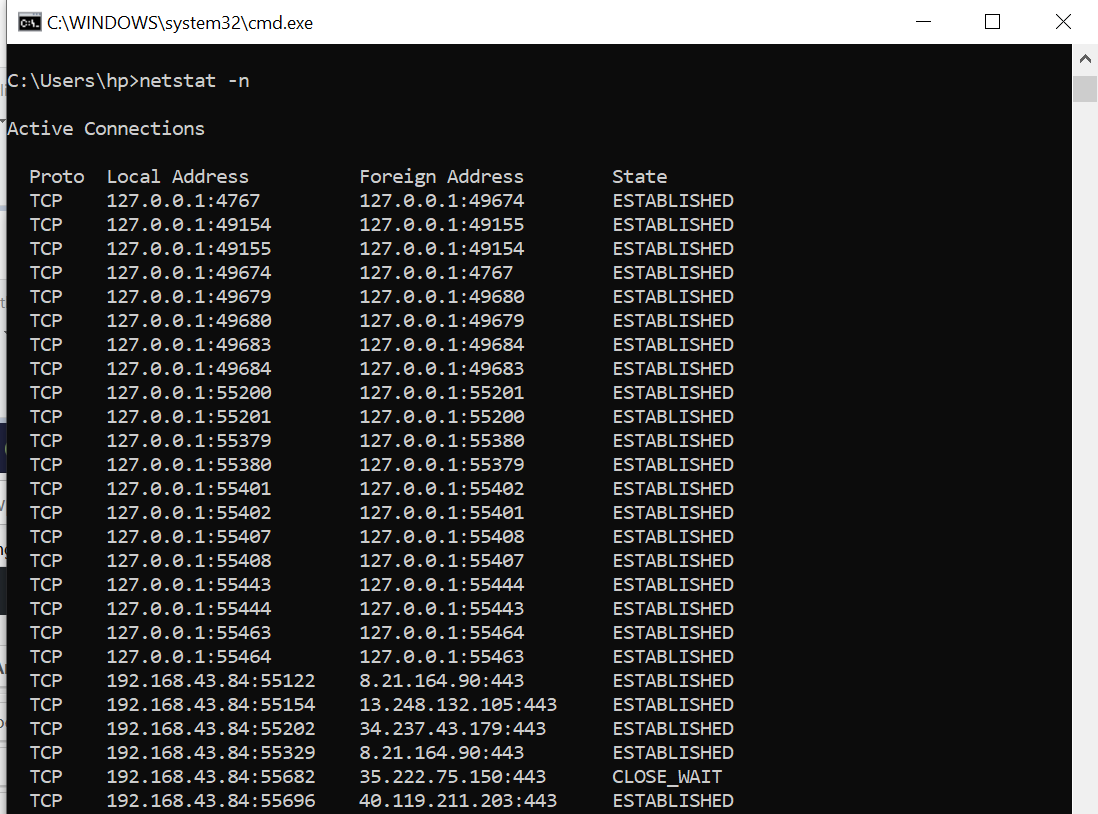
“netstat -n” shows similar outputs with IP addresses rather than names of system or services
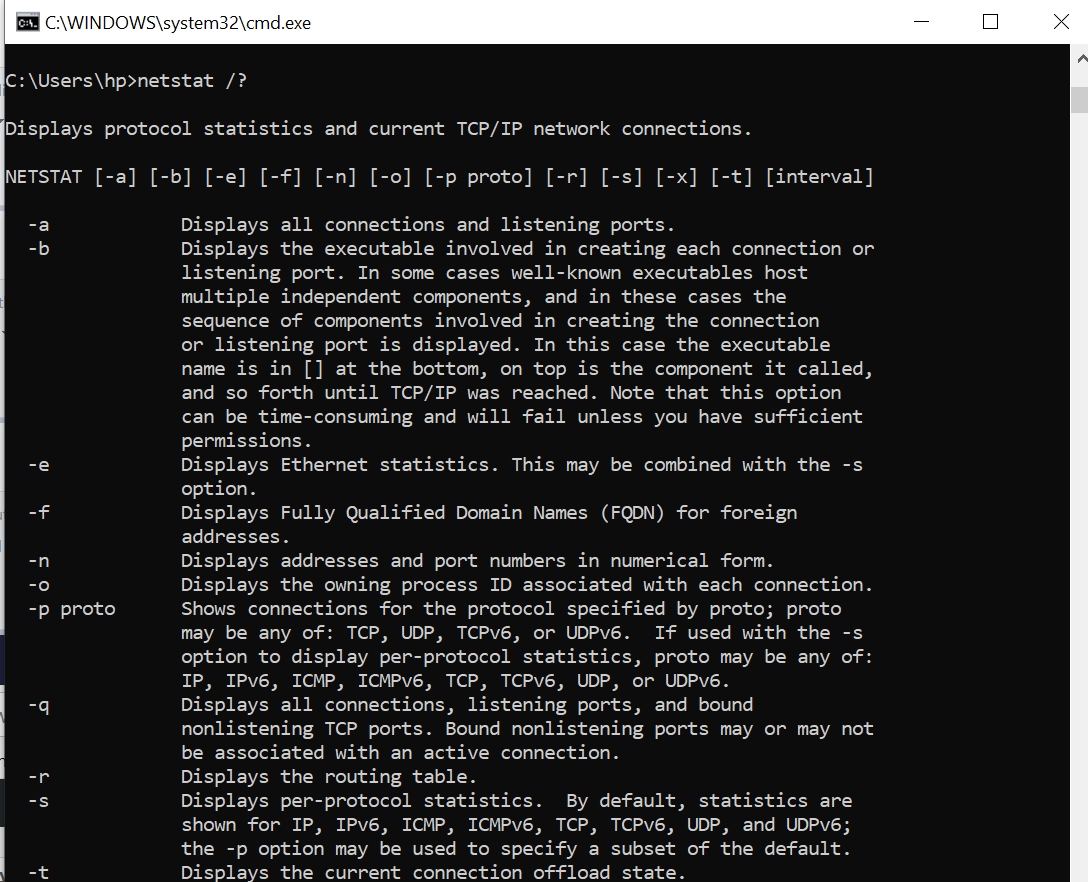
“netstat /?” shows all the options available with the command
(Image credit: Future)
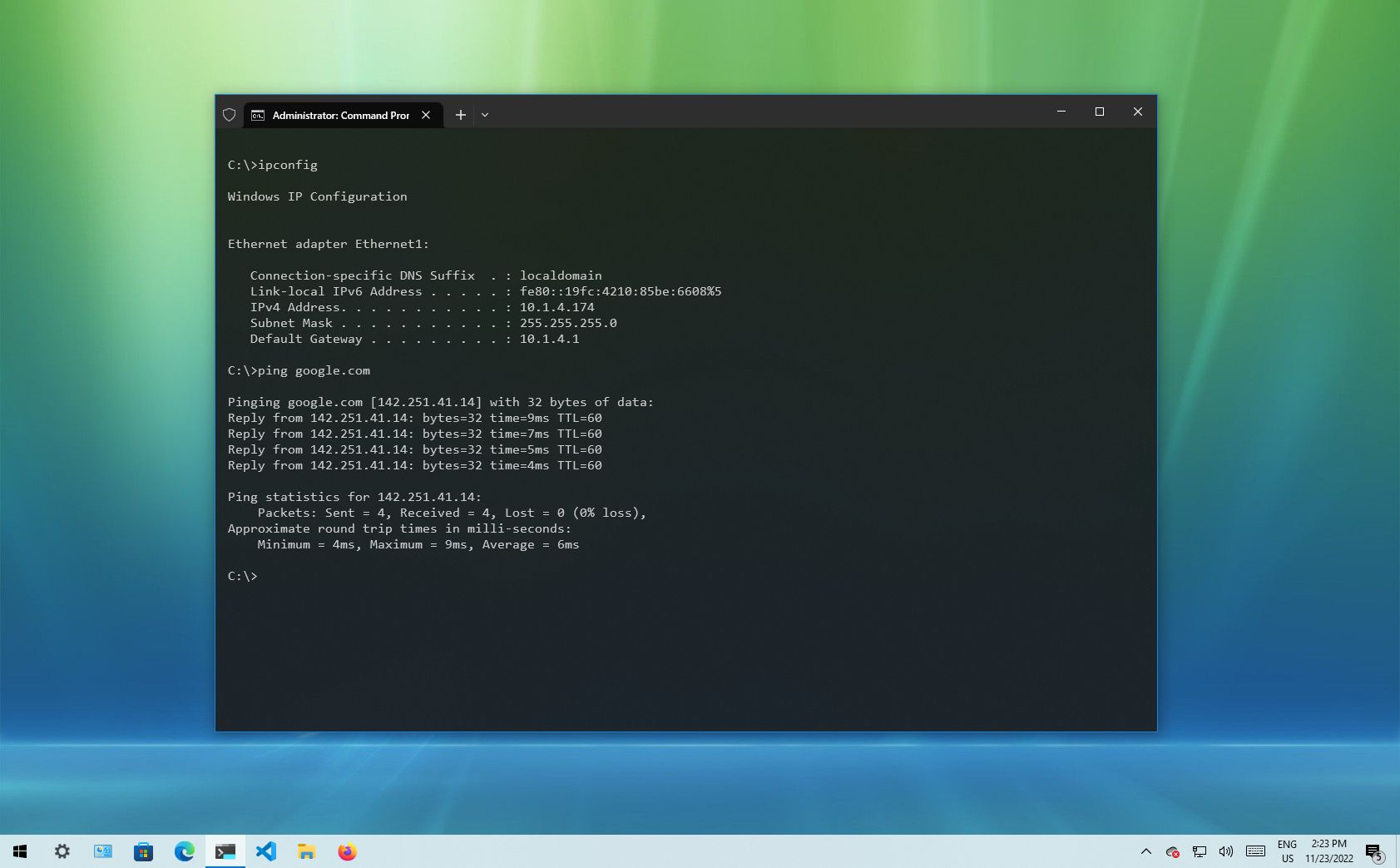
Windows 10 makes it easy to connect to a network and the internet using a wired or wireless connection. However, sometimes, you may still need to manually manage settings or troubleshoot connectivity problems, which is when the built-in command-line tools can come in handy.
Regardless of the issue, Windows 10 will likely have a Command Prompt tool to help you resolve the most common problems. For instance, ipconfig and ping are among the most important tools for viewing network settings and troubleshooting connectivity issues. If you are dealing with a routing problem, the route command can display the current routing table to examine and determine related problems, and with the nslookup tool, you can diagnose DNS problems.
You also have tools like arp to troubleshoot switching problems and determine the MAC address from an IP address. The netstat command-line tool allows you to view statistics for all the connections. And you can use the netsh tool to display and change many aspects of the network configuration, such as checking the current configuration, resetting settings, managing Wi-Fi and Ethernet settings, enabling or disabling the firewall, and a lot more.
This guide highlights eight Command Prompt tools that should help you manage and troubleshoot networking problems on your device and across the network.
1. IPConfig
On Windows 10, ipconfig (Internet Protocol configuration) is among the most common networking tools that allow you to query and show current TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) network configuration. The command also includes options to perform different actions, such as refreshing Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) settings.
Display network configuration
To get started with ipconfig on Windows 10, use these steps:
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
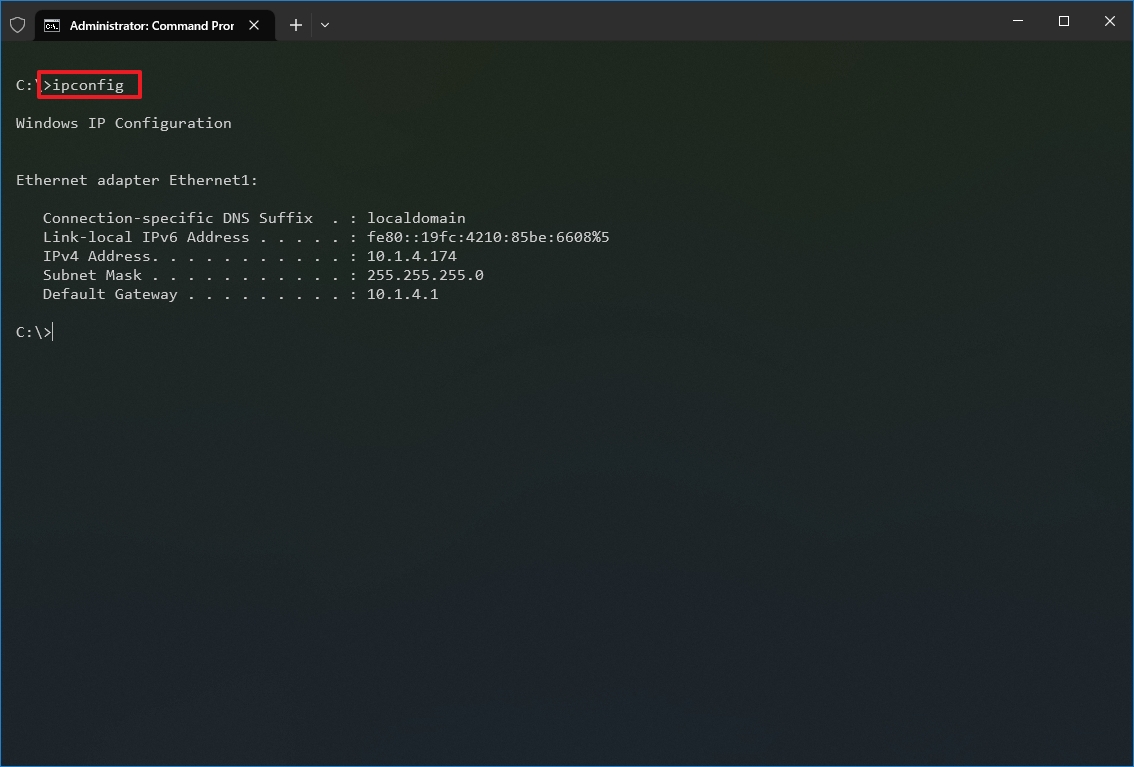
- Type the following command to view a summary of the TCP/IP network configuration and press Enter: ipconfig
- Quick tip: In Command Prompt, you can use the CLS command to clear the screen after you no longer need the information to continue running commands without clutter.
- Type the following command to view the complete TCP/IP network configuration and press Enter: ipconfig /all
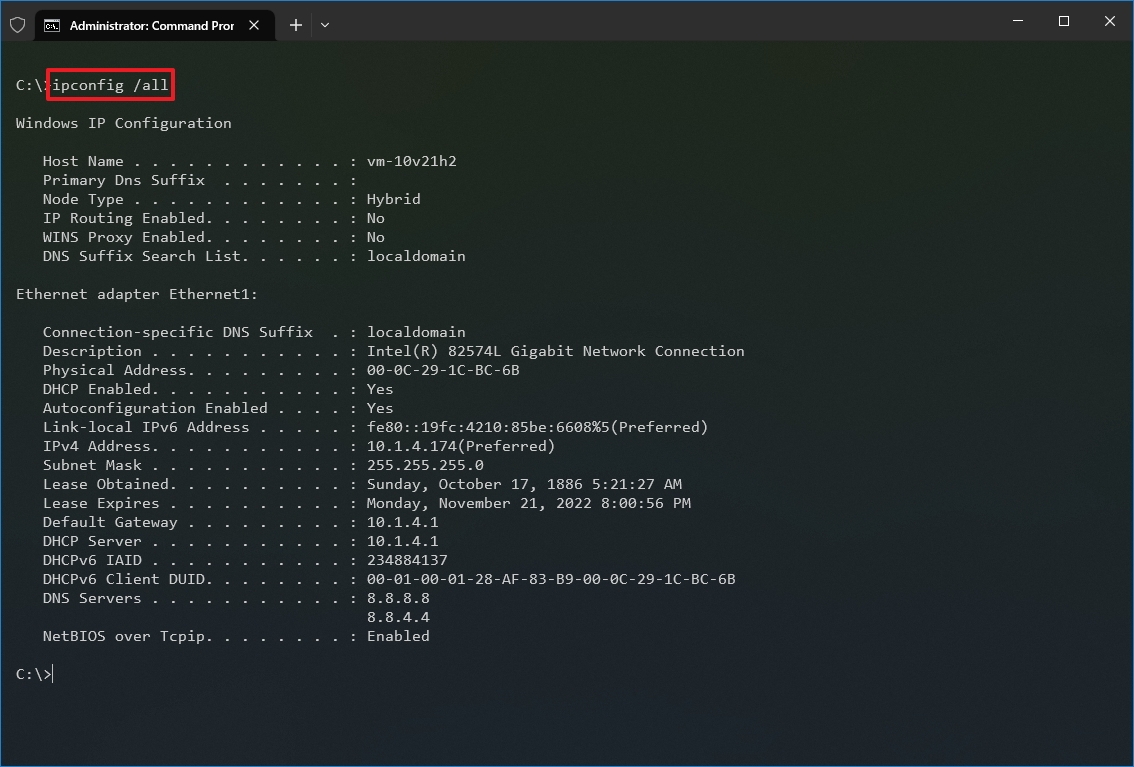
Once you complete the steps, you will have an overview of the PC’s entire TCP/IP configuration.
Refresh network settings
To release and renew the network configuration with Command Prompt, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to remove the current network configuration and press Enter: ipconfig /release
- Type the following command to reconfigure the network configuration and press Enter: ipconfig /renew
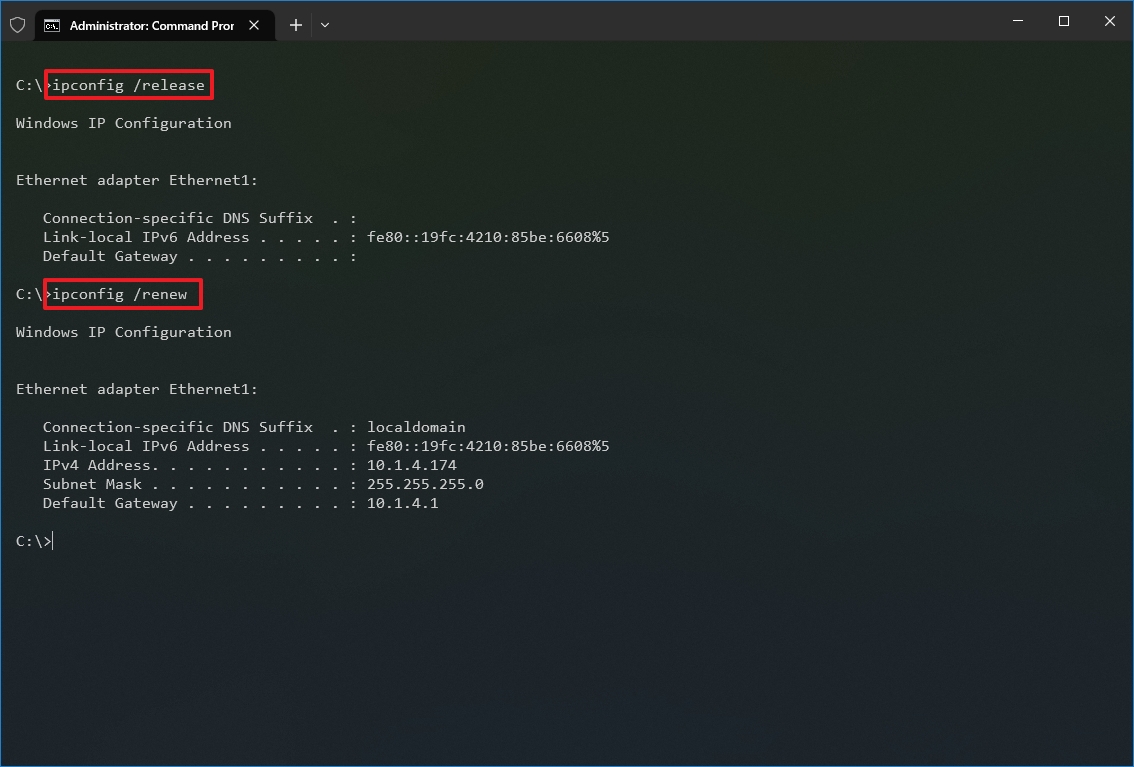
After you complete the steps, the first command will clear the current configuration, and the second command will fetch new settings from the DHCP server to resolve connectivity issues. If the dynamically assigned settings have not expired in the server, it is common to see the same IP address reconfigured on the device.
Refresh DNS settings
To flush and rebuild the current DNS cache entries on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to clear the DNS system cache on the device and press Enter: ipconfig /flushdns
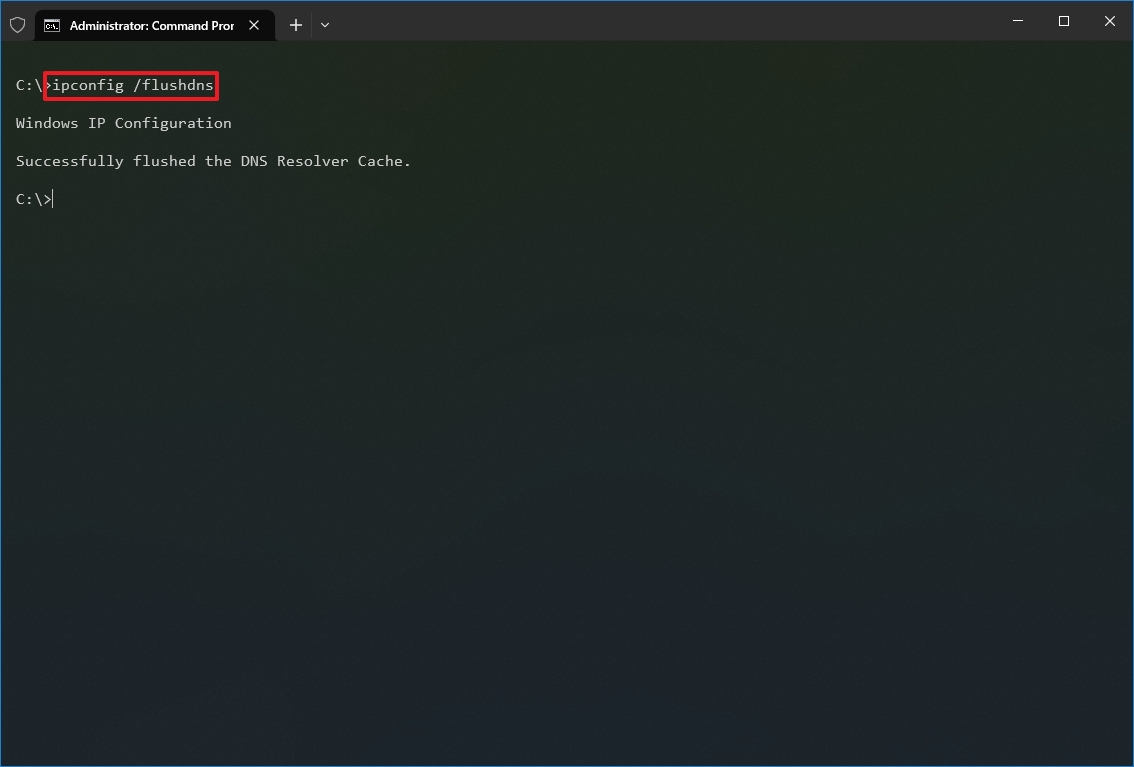
Once you complete the steps, the entries stored in the DNS cache of Windows 10 will be deleted and refreshed. Usually, this command will come in handy when you cannot connect to another computer or website using the host or domain name due to outdated information in the local cache.
2. Ping
Ping is another essential networking tool because it allows you to send ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) echo request messages to test the IP connectivity with other devices, whether it is another computer in the network or internet service.
Test device connectivity
To test the network connectivity with the ping command on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to send ICMP echo requests to test connectivity and press Enter: ping IP-OR-DOMAIN
In the command, replace IP-OR-DOMAIN with the actual IP address or domain name of the computer or service you want to test. For example, this command tests the communication between the local device and router: ping 10.1.4.1
- Quick tip: If you use the -a option (for example, ping -a 10.1.4.1), the command will also resolve the address to a hostname.
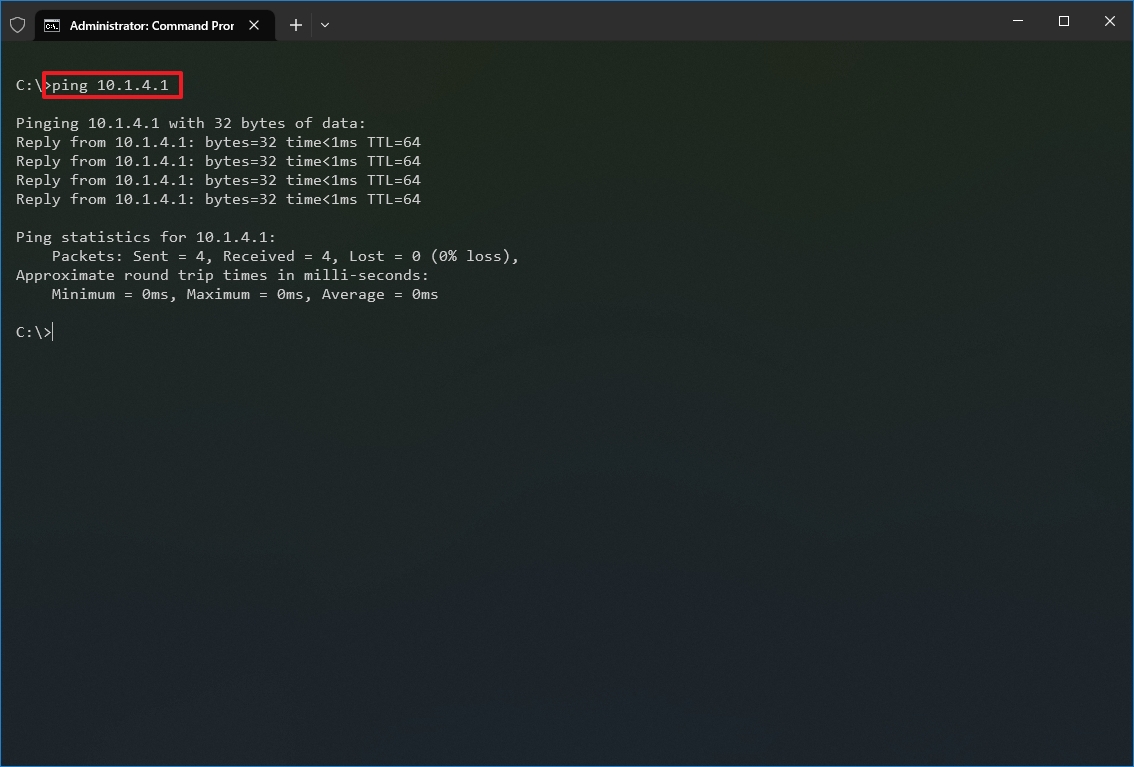
- (Optional) Type the following command to test the local computer networking stack and press Enter: ping 127.0.0.1 or ping loopback
- Quick note: The 127.0.0.1 is a well-known address, and it is referred to as the loopback address. When you run the command, if you get a reply, it means that the networking stack on Windows 10 is up and running. This is the same as pinging the device using its own network address.
Once you complete the steps, receiving four successful echo replies from the destination means the device can talk with the remote host. If the request times out, there is a problem between the host and the remote device.
If you are dealing with connectivity problems, start pinning the local computer to ensure the network stack is working. Then test the router’s connection to ensure the issue is not in the local network. Then try to ping a website to find out whether there is a problem with the internet connection or the remote host.
You should also know that the ping command will always time out if the remote device or service blocks the ICMP protocol.
Diagnose packet loss activity
The ping command includes many options that you can access with the «ping /?» command, and one of these options is the ability to set the time you want to run the tool, which can come in handy to examine packets lost when you are troubleshooting connectivity problems.
To run the ping command for a specific period, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to continue pinging until stopped and press Enter: ping IP-OR-DOMAIN -t
In the command, replace IP-OR-DOMAIN with the actual IP address or domain name of the computer or service you want to test. For example, this command tests the communication between the local device and router: ping 10.1.4.1 -t
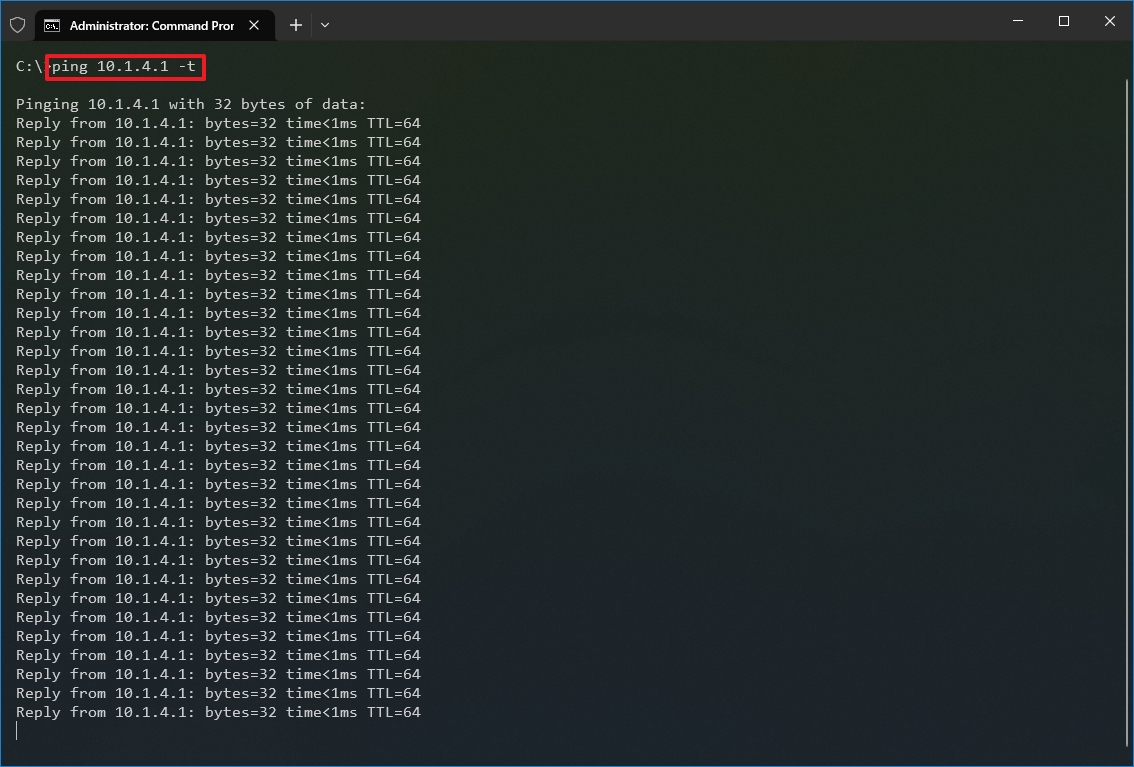
- Use the «Control + C» keyboard shortcut to stop the ping.
After you complete the steps, you will be able to see the successful and lost requests that can give you a clue on how to continue troubleshooting and resolving the connectivity problem. Administrators usually use the ping command in a local network to find out when a service goes down quickly. Also, the tool can be used as a quick way to know when the server is up and running again when restarting a server remotely.
3. Tracert
Windows 10 also includes tracert (Trace Route), a diagnostic tool to determine the network path to a destination using a series of ICMP echo requests. However, unlike the ping command, each request includes a TTL (Time to Live) value that increases by one each time, allowing to display of a list of the route the requests have taken and their duration.
To trace the route to a destination with Command Prompt on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to understand the path taken to the destination and press Enter: tracert IP-OR-DOMAIN
In the command, replace IP-OR-DOMAIN with the actual IP address or domain name for the destination you want to troubleshoot. For example, this command allows you to view the path the packets are taking to reach Google.com: tracert google.com
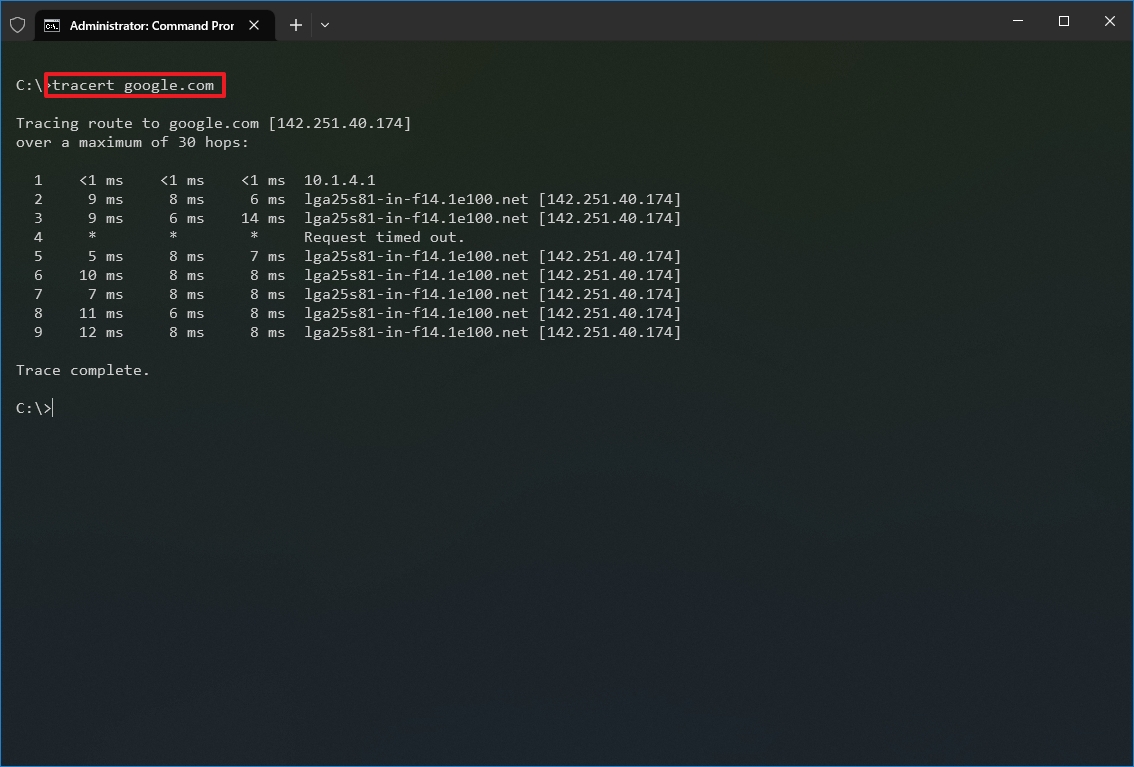
- (Optional) Type the following command to adjust the hop counts to the destination and press Enter: tracert -h HOP-COUNT IP-OR-DOMAIN
In the command, replace IP-OR-DOMAIN with the actual IP address or domain name for the destination you want to troubleshoot and HOP-COUNT for the number of hops you want to trace. For example, this command puts the limit of 5 hops (nodes) to the destination: tracert -h 5 google.com
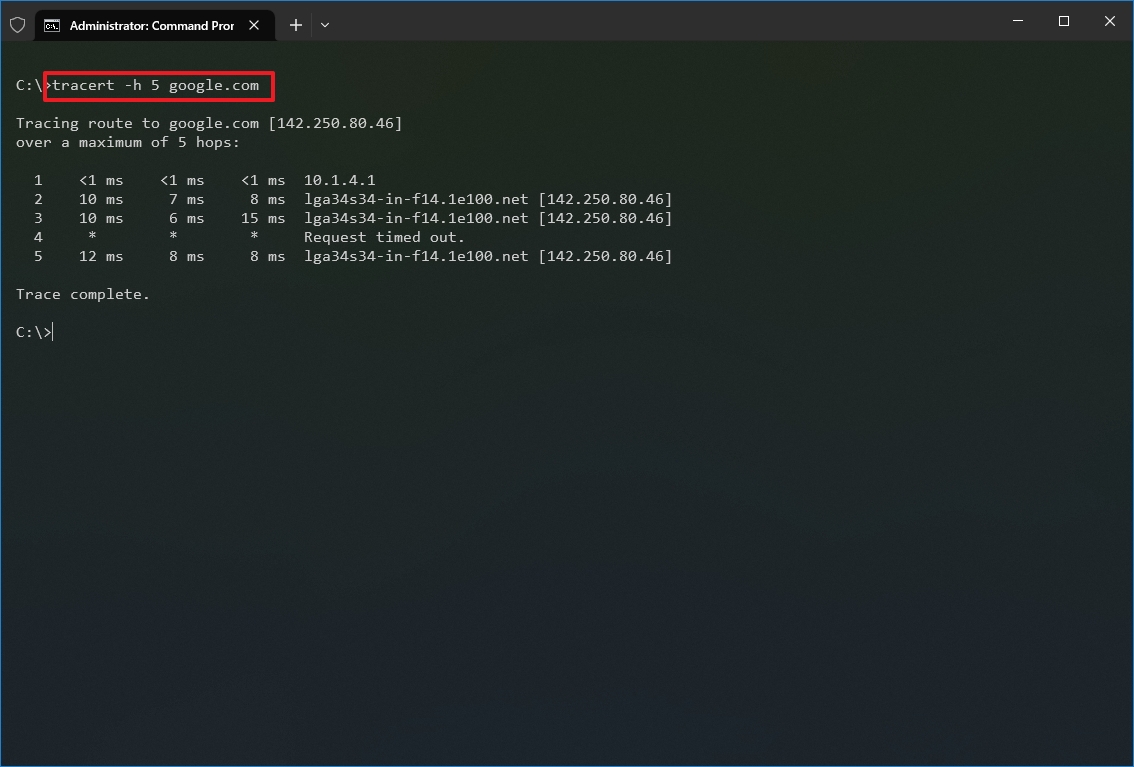
Once you complete the steps, you will know if the destination is reachable or if there is a networking problem along the way.
Similar to the ping tool, tracert includes several options, which you can view with the «tracert /?» command.
4. NSLookup
The nslookup (Name Server Lookup) tool can show valuable details to troubleshoot and resolve DNS-related issues. The tool includes an interactive and non-interactive modes. However, you will be using the non-interactive mode more often than not, which means you will type the full command to obtain the necessary information.
You can use this command to display the default DNS name and address of the local device and determine the domain name of an IP address or the name servers for a specific node.
To get started with nslookup on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to look up the local DNS name and address and press Enter: nslookup
- Quick note: This command also happens to open the nslookup interactive mode.
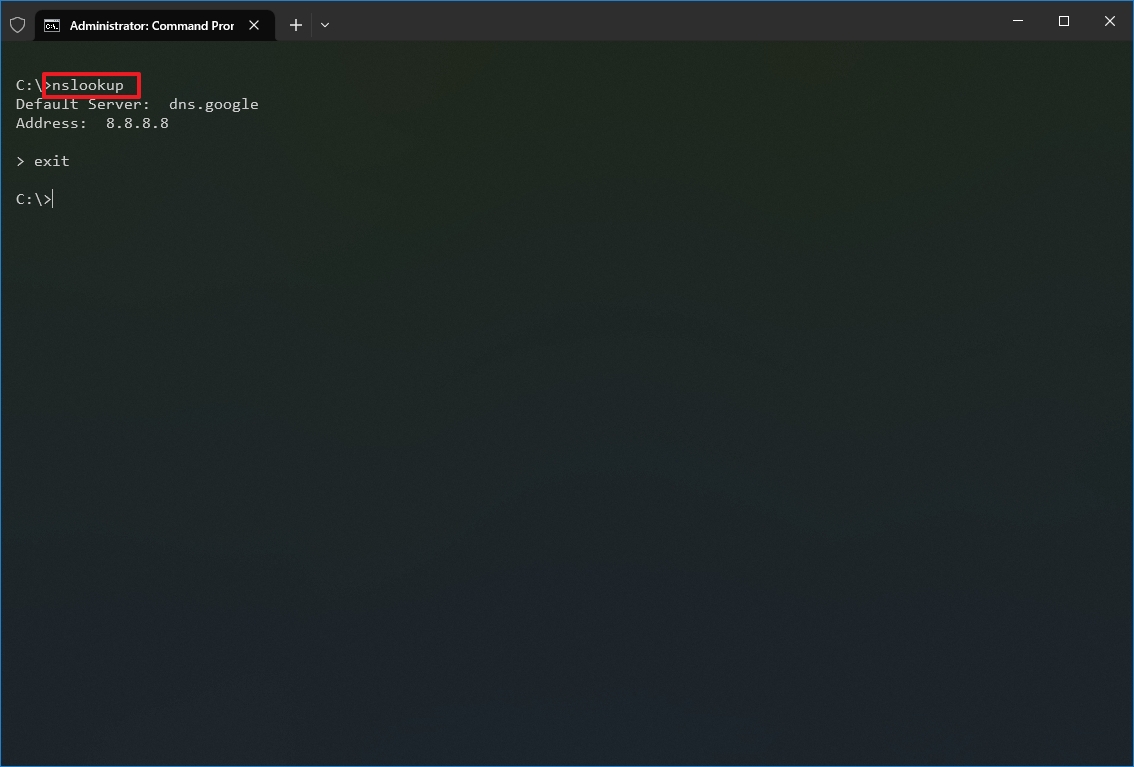
- Confirm the current DNS information.
- Type the following command to exit the interactive mode and press Enter: exit
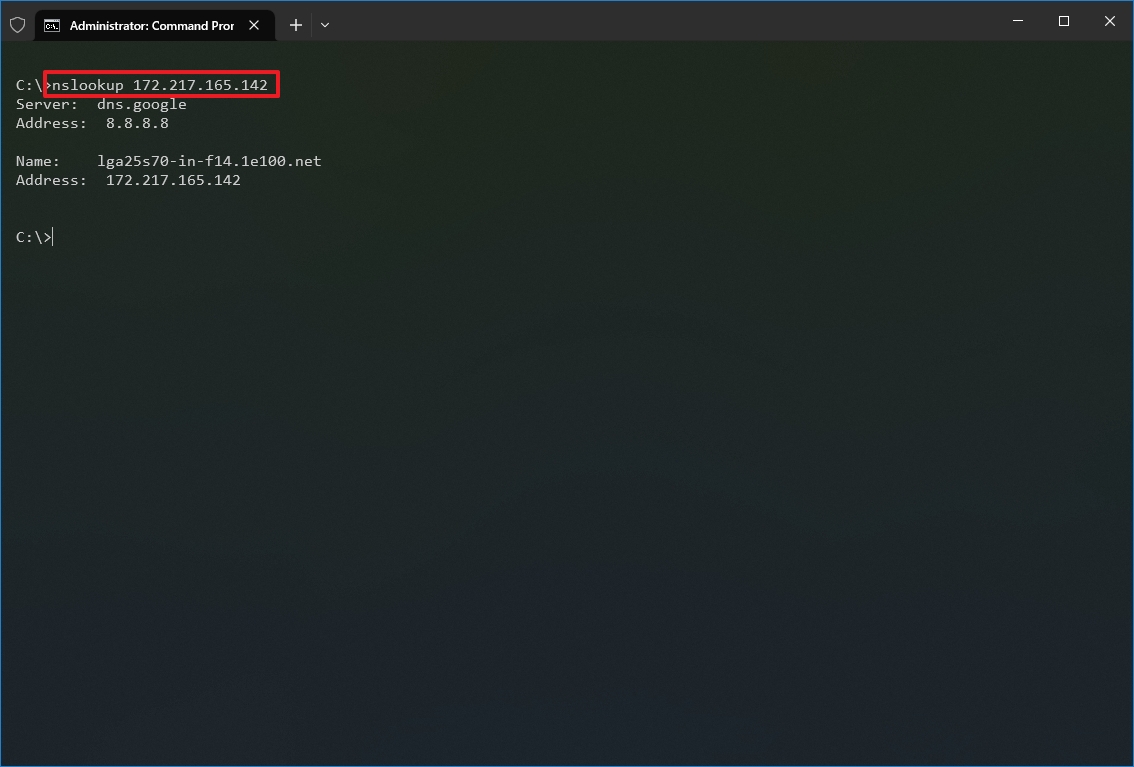
- Type the following command to determine the name and address of a specific server and press Enter: nslookup IP-ADDRESS
In the command, replace the IP-ADDRESS with the address of the remote device. For example, this command looks up the IP address 172.217.165.142 address: nslookup 172.217.165.142
- Type the following command to determine the address of a specific server and press Enter: nslookup DOMAIN-NAME
In the command, replace the DOMAIN-NAME with the address of the remote device. For example, this command looks up the IP address Google.com address: nslookup google.com
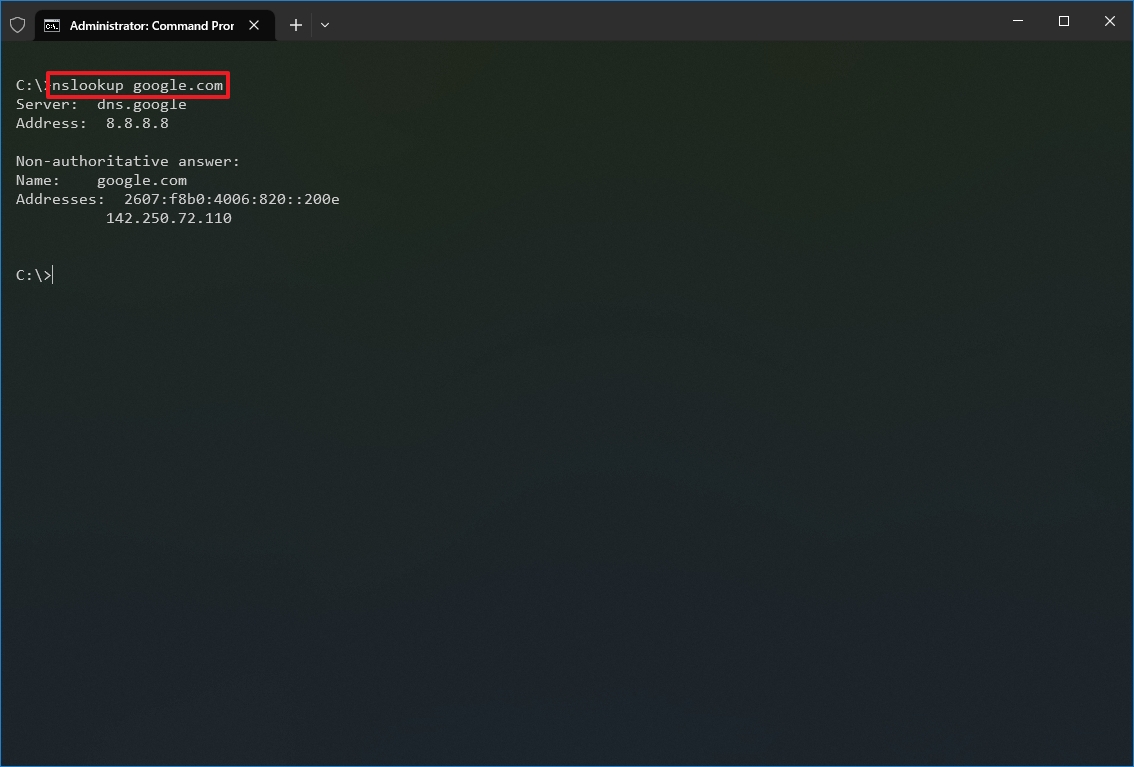
After you complete the steps, depending on the command, you will know whether the device has a DNS resolver and the IP address or domain and vice versa of the remote host.
5. NetStat
The netstat (Network Statistics) tool displays statistics for all network connections. It allows you to understand open and connected ports to monitor and troubleshoot networking problems for Windows 10 and apps.
When using the netstat tool, you can list active network connections and listening ports. You can view network adapter and protocol statistics. You can even display the current routing table and much more.
To get started with netstat, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
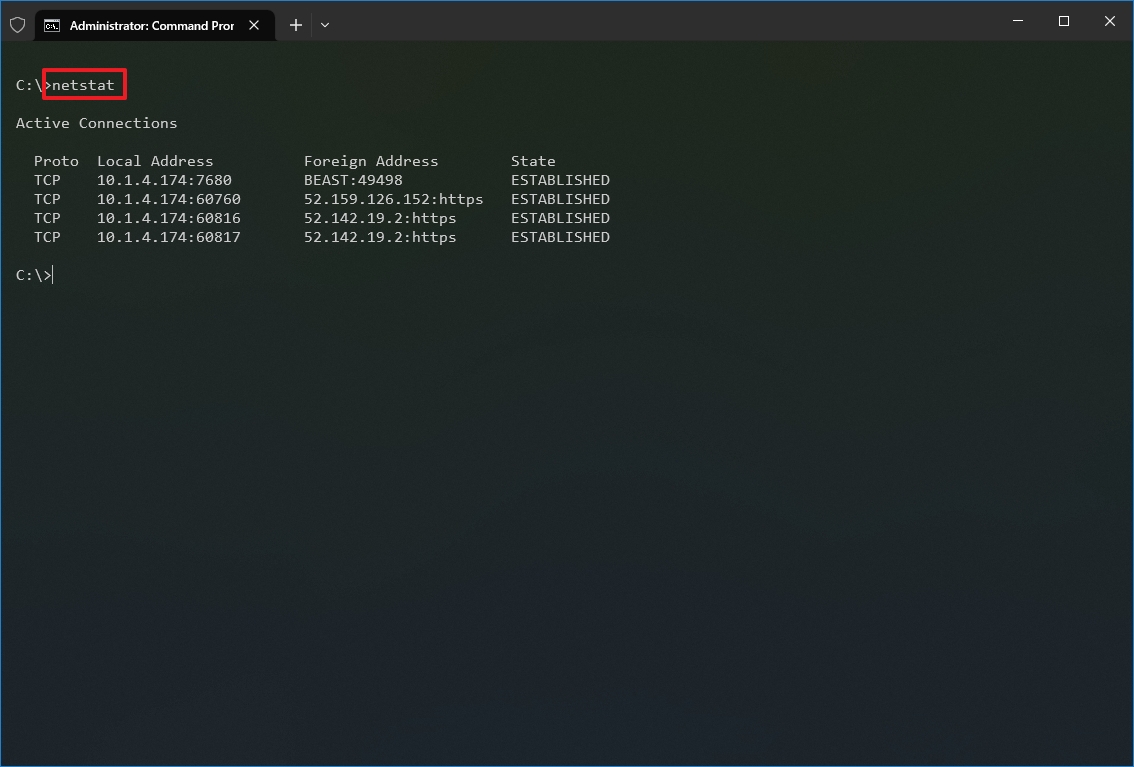
- Type the following command to show all active TCP connections and press Enter: netstat
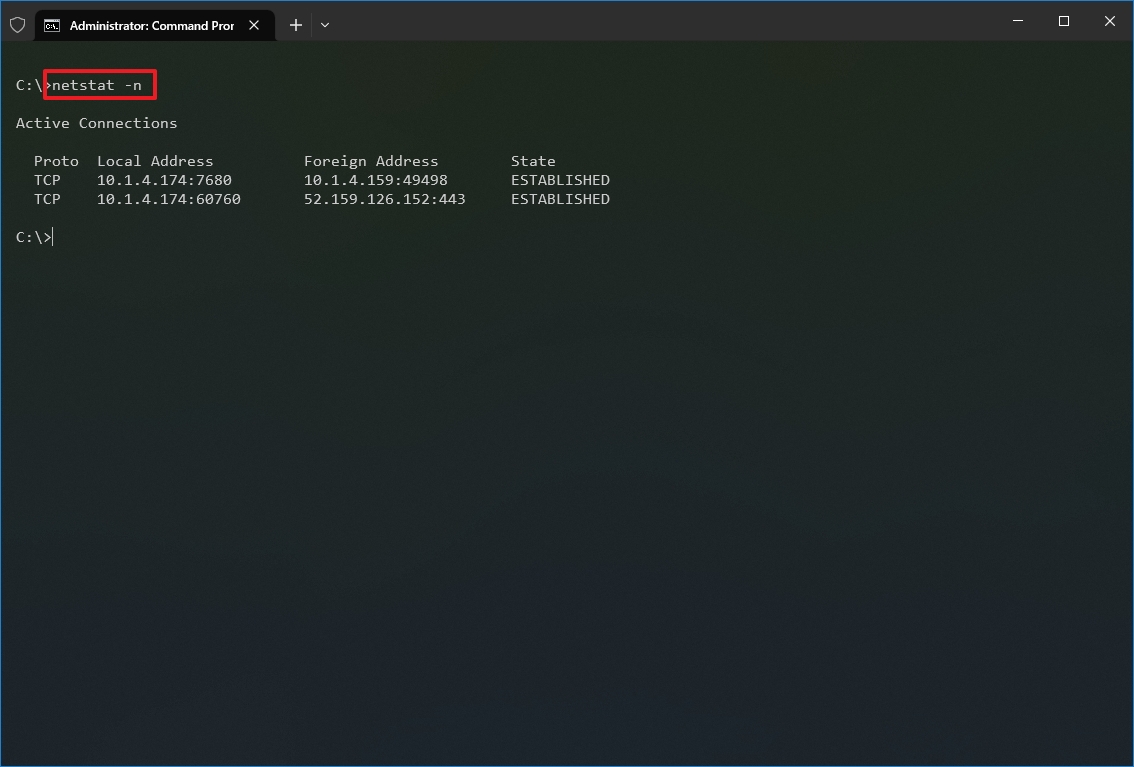
- (Optional) Type the following command to display active connections showing numeric IP address and port number instead of trying to determine the names and press Enter: netstat -n
- (Optional) Type the following command to refresh the information at a specific interval and press Enter: netstat -n INTERVAL
In the command, make sure to replace INTERVAL for the number (in seconds) you want to redisplay the information. This example refreshes the command in question every five seconds: netstat -n 5
- Quick note: When using the interval parameter, you can terminate the command using the «Ctrl + C» keyboard shortcut in the console.
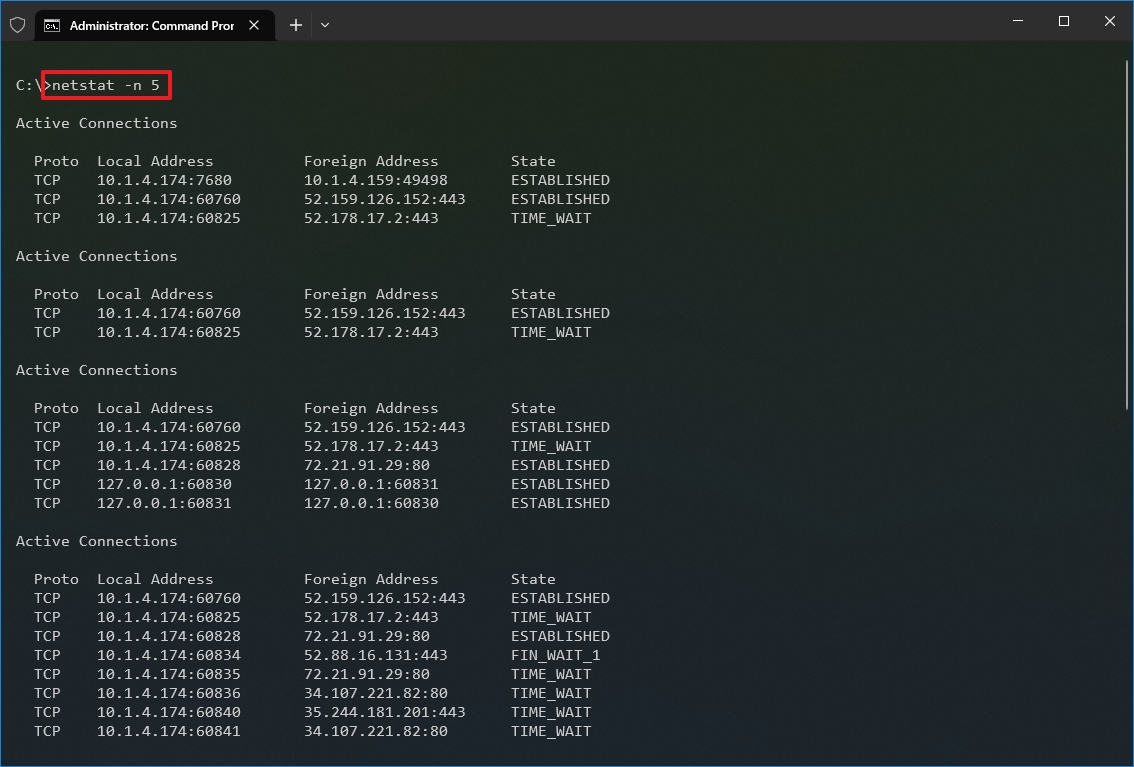
Once you run the command, it will return a list of all active connections in four columns, including:
- Proto: Displays the connection protocol, including TCP or UDP.
- Local Address: Displays the device’s IP address followed by a semicolon with a port number of the connection. The double-semicolon inside brackets indicates the local IPv6 address. The «0.0.0.0» address also refers to the local address.
- Foreign Address: Shows the remote computer’s IP (or FQDN) address with the port number after the semicolon port name (for instance, https, http, microsoft-ds, wsd).
- State: Shows whether the connection is active (established), if the port has been closed (time_wait) and if the program has not closed the port (close_wait). Other statuses available include closed, fin_wait_1, fin_wait_2, last_ack, listen, syn_received, syn_send, and timed_wait.
6. ARP
Windows 10 maintains an arp (Address Resolution Protocol) table, which stores IP to Media Access Control (MAC) entries that the system has resolved. The arp tool lets you view the entire table, modify the entries, and use it to determine a remote computer’s MAC address.
Usually, you do not need to worry about MAC addresses, but there are scenarios when this information may come in handy. For example, when troubleshooting network problems at the data link layer (switching) or when restricting access or filtering content through the network for specific devices.
To get started with arp on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to view the current arp table cache on Windows 10 and press Enter: arp -a
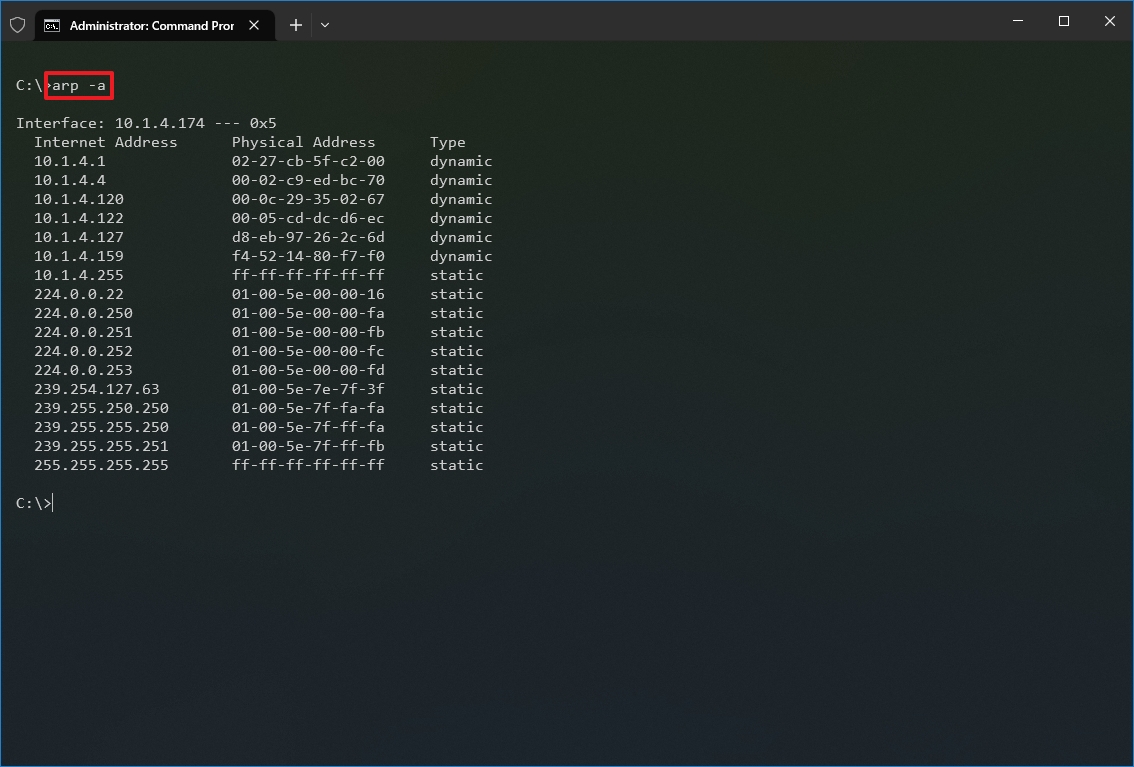
- Type the following command to determine the MAC address of a remote device and press Enter: arp -a IP
In the command, make sure to replace IP with the address of the destination. For example, this command reveals the physical address of the 10.1.4.120 destination: arp -a 10.1.4.120

- Confirm the MAC (physical) address for the remote device.
After you complete the steps, you will be able to view the entire arp table and MAC address of a specific IP address.
If you want to know all the available options, use the «arp /?» command to list the available options with their corresponding descriptions.
7. Route
The route tool displays the routing table that allows Windows 10 to understand the network and communicate with other devices and services. The tool also offers some options to modify and clear the table as needed.
Like the arp tool, you typically do not have to worry about the routing table, but the command-line tool will come in handy when troubleshooting related problems.
To view or flush the routing table available on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to view the routing table known to Windows 10 and press Enter: route print
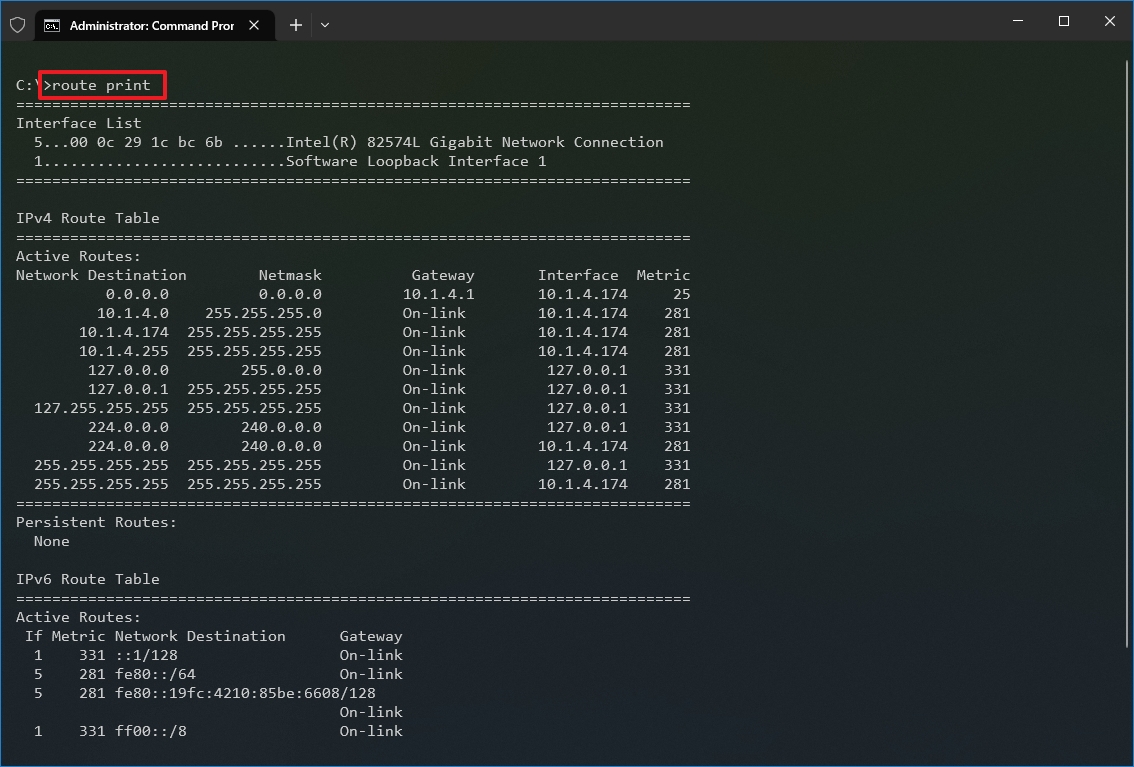
- Confirm the routing table information.
- (Optional) Type the following command to clear the routing table and press Enter: route -f
- Quick note: When running this command, the device will lose network connectivity since the system no longer understands the network topology. After running the command, restart the machine to allow the networking stack to rebuild the routing table. Usually, you should not have to clear the table unless you modify some of the entries and you need to reset the table.
Once you complete the steps, you will understand the routing table and how to clear the information.
You can also use the «route /?» command to view a list of available options, including options to change networking metrics, specify a gateway, add a new route, and much more. However, modifying these settings is usually not recommended unless you understand how the network works.
8. Netsh
On Windows 10, netsh (Network Shell) is a legacy command-line tool that allows you to display and change virtually any network configuration. For instance, you can use the tool to view the current network configurations, manage wireless connections, reset the network stack to fix most common problems, enable or disable the firewall, and a lot more.
To get started with the netsh command-line tool, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to view a list of the available commands (contexts) and press Enter: netsh /?
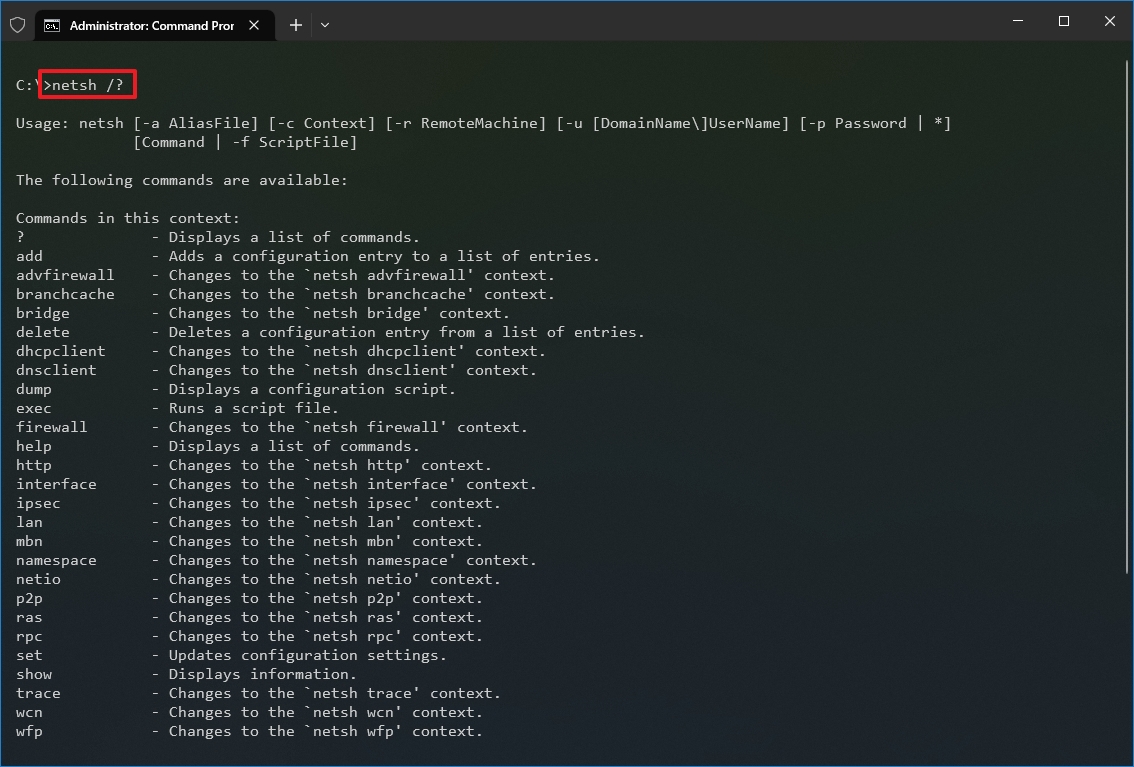
- Type the following command to view the list of available subcommands (subcontexts) for a specific option and press Enter: netsh CONTEXT-COMMAND
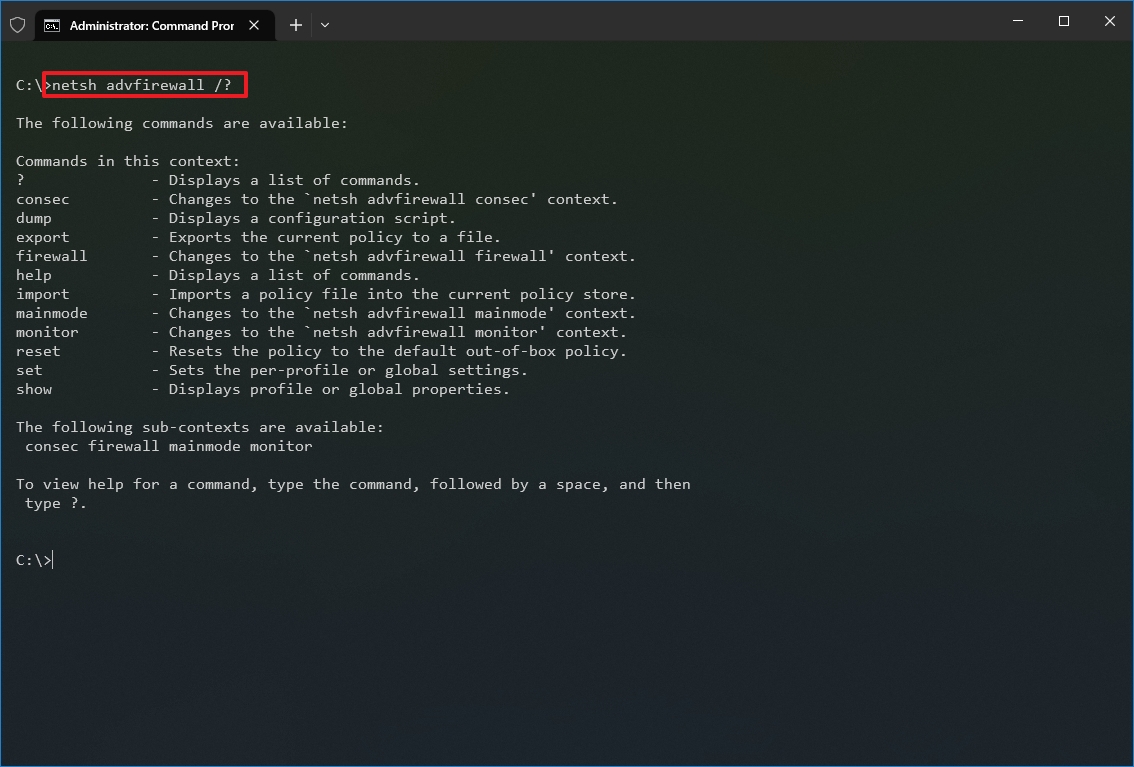
In the command, change the CONTEXT-COMMAND for the command that includes additional options. For example, this command shows the commands available to manage the firewall with netsh: netsh advfirewall /?
Once you complete the steps, you will know how to navigate the netsh contexts and subcontexts command to manage networking settings.
Reset system network stack
To reset the network stack to resolve common connectivity problems, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to reset the winsock stack and press Enter: netsh winsock reset
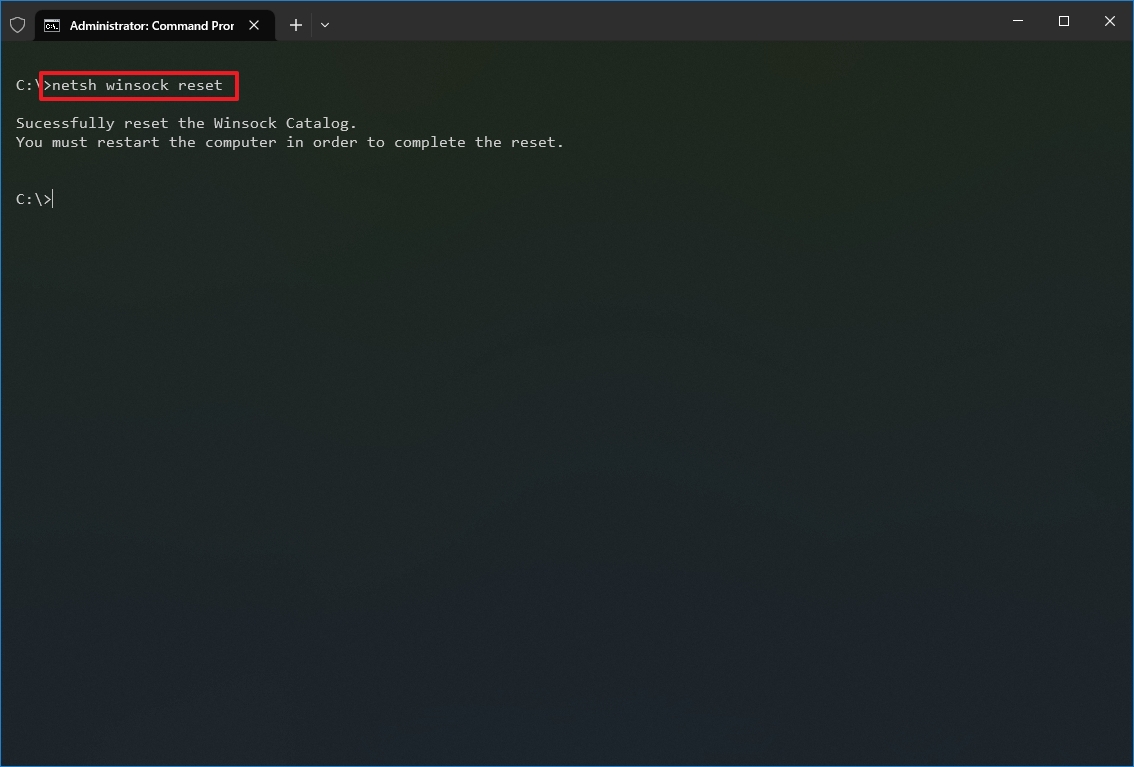
- Restart your computer.
After you complete the steps, the winsock configuration will reset, hopefully fixing the problems connecting to a network and the internet.
Export and import network configuration
To export the network configuration with netsh on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to export the current configuration for all the network adapters and press Enter: netsh -c interface dump>PATH\TO\EXPORTED.txt
In the command, replace the PATH\TO\EXPORTED.txt with the path and name of the file to store the configuration. For example, the following command exports the settings to the netshconfig.txt file: netsh -c interface dump>c:\netshconfig.txt
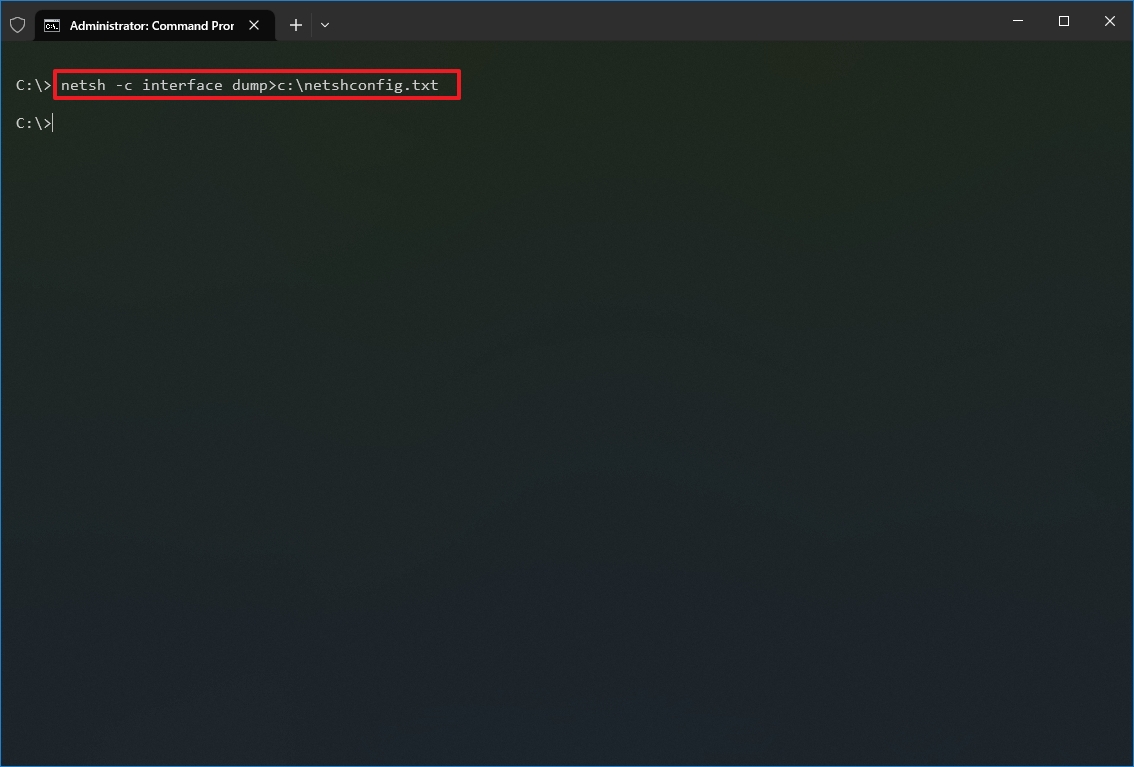
Once you complete the steps, you can open the file with any text editor to view the exported configuration.
Import network configuration
To import the network configuration settings with netsh, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to import the network configuration and press Enter: netsh -c interface dump>PATH\TO\IMPORTED.txt
In the command, replace the PATH\TO\EXPORTED.txt with the path and name of the file you want with the exported configuration. For example, the following command imports the settings from the netshconfig.txt file: netsh -f c:\netshconfig.txt
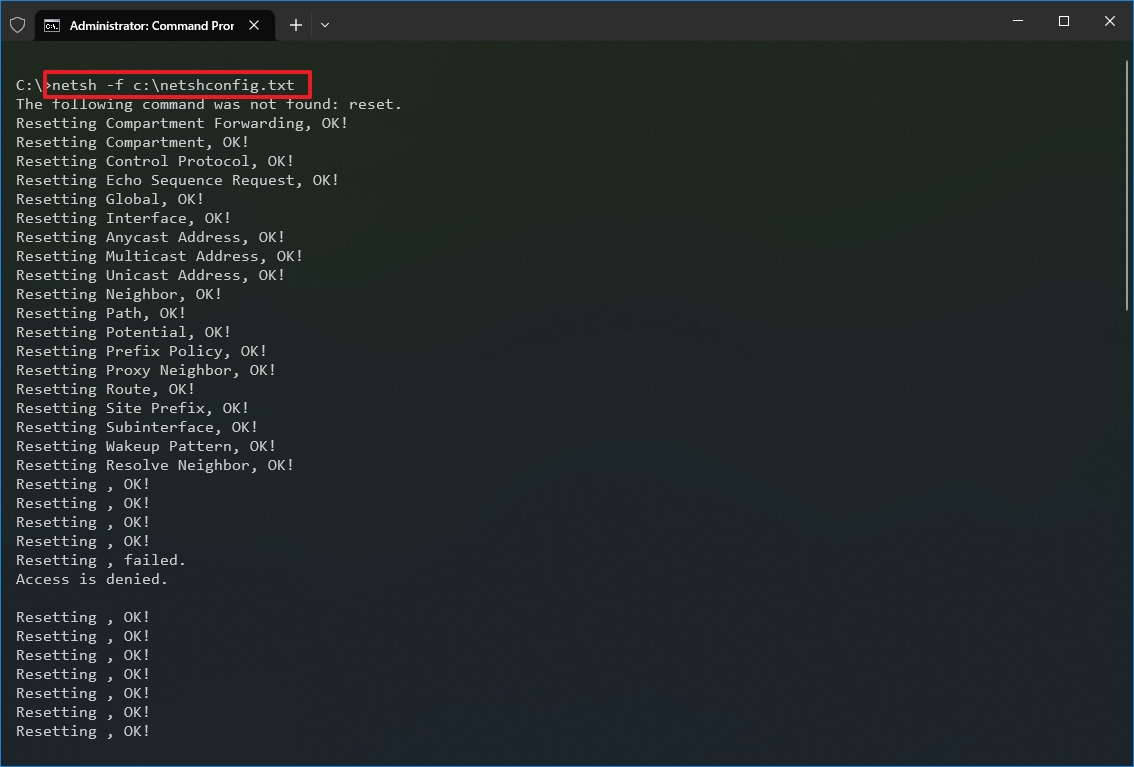
After you complete the steps, the new networking configuration will be imported and applied to Windows 10.
Enable and disable firewall
To enable the Windows 10 firewall with netsh, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to enable the default firewall and press Enter: netsh advfirewall set currentprofile state on
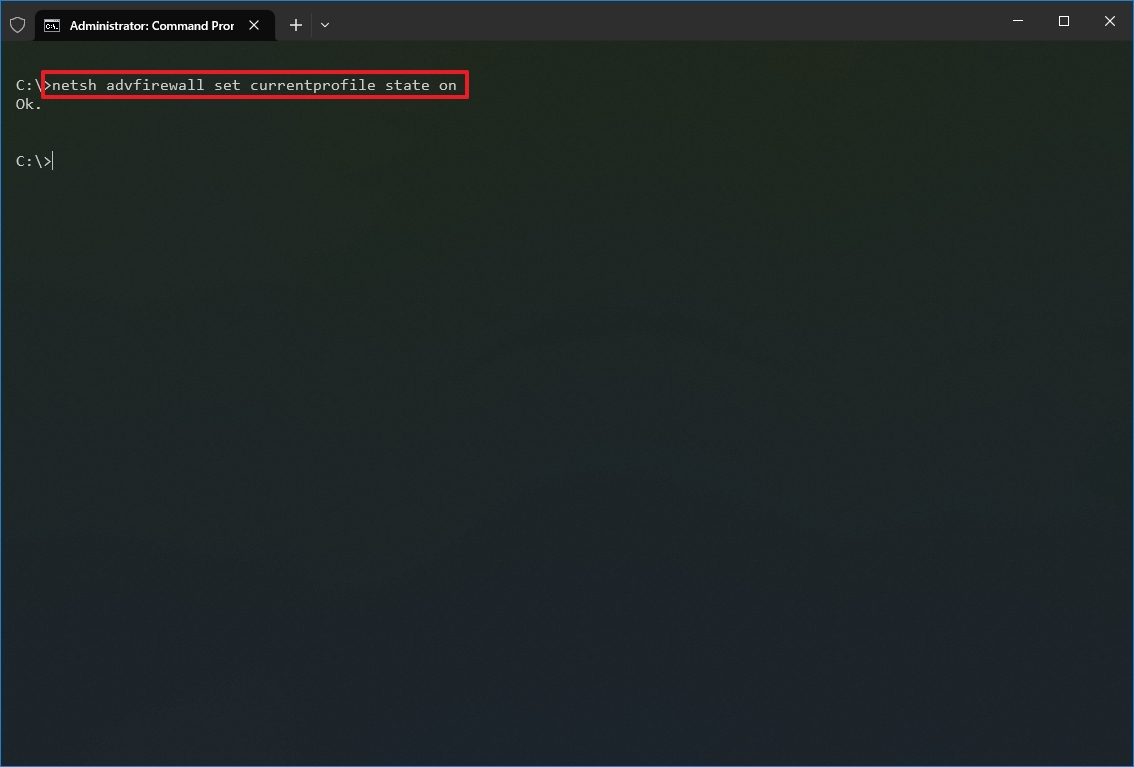
Once you complete the steps, the Windows Defender Firewall will enable on the device.
Disable firewall
To disable the Windows 10 firewall with netsh, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to disable the default firewall and press Enter: netsh advfirewall set currentprofile state off
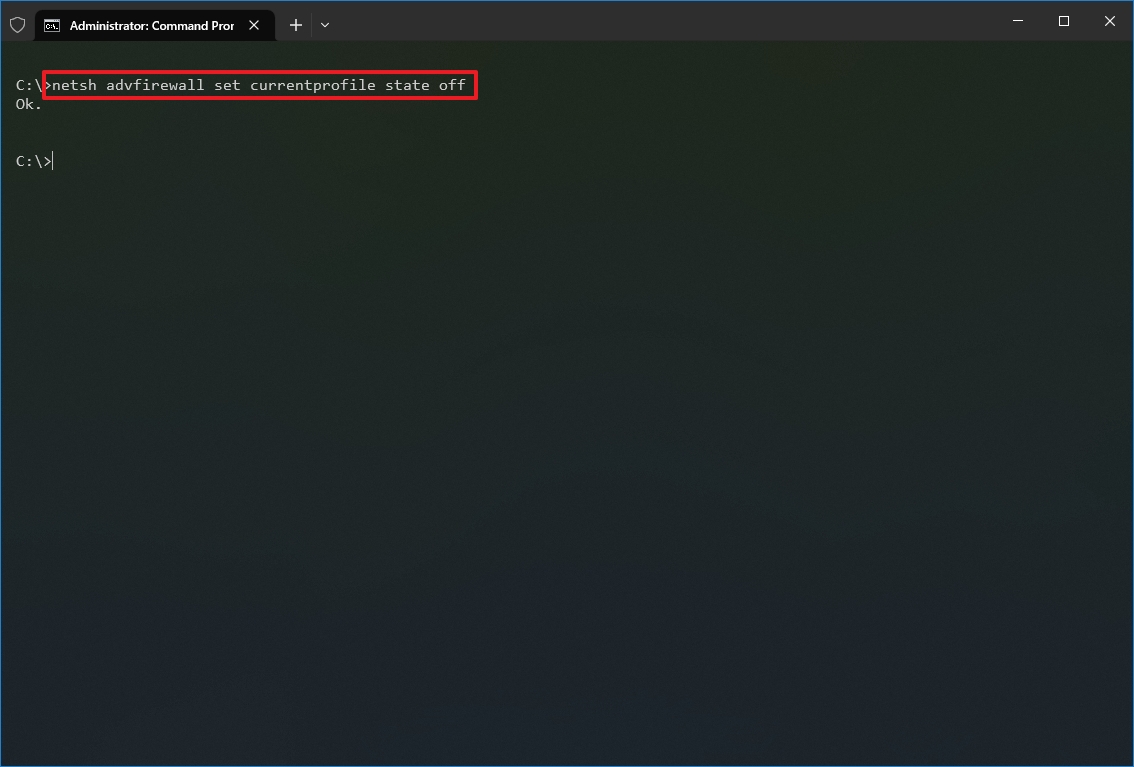
Once you complete the steps, the Windows Defender Firewall will be disabled on the device.
On Windows 10, there are many tools you can use to change settings and troubleshoot networking issues using Command Prompt, PowerShell, and graphical applications. However, in this guide, we only focus on getting you started with some of the most common tools available in Command Prompt.
More resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 and Windows 11, visit the following resources:
- Windows 11 on Windows Central — All you need to know
- Windows 10 on Windows Central — All you need to know
Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 15 years of experience writing comprehensive guides. He also has an IT background and has achieved different professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA. He has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.














