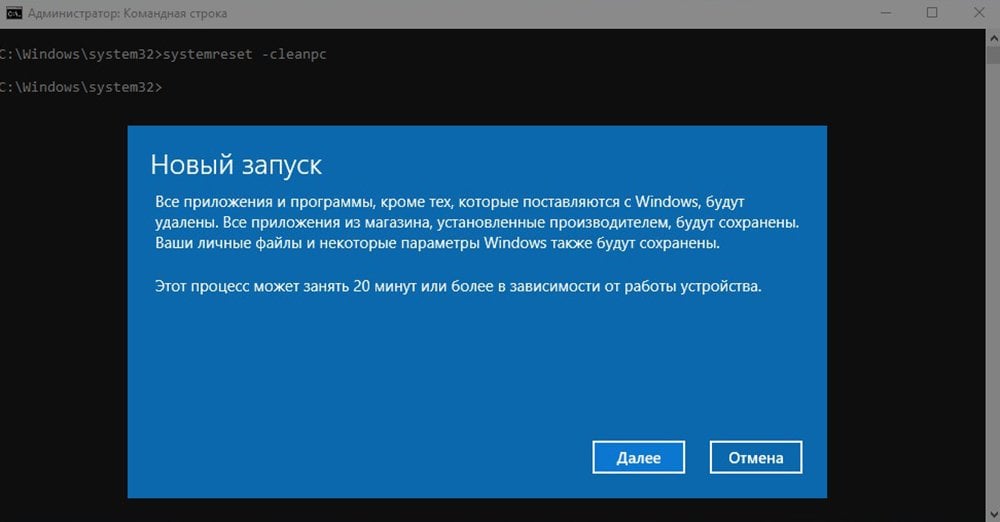
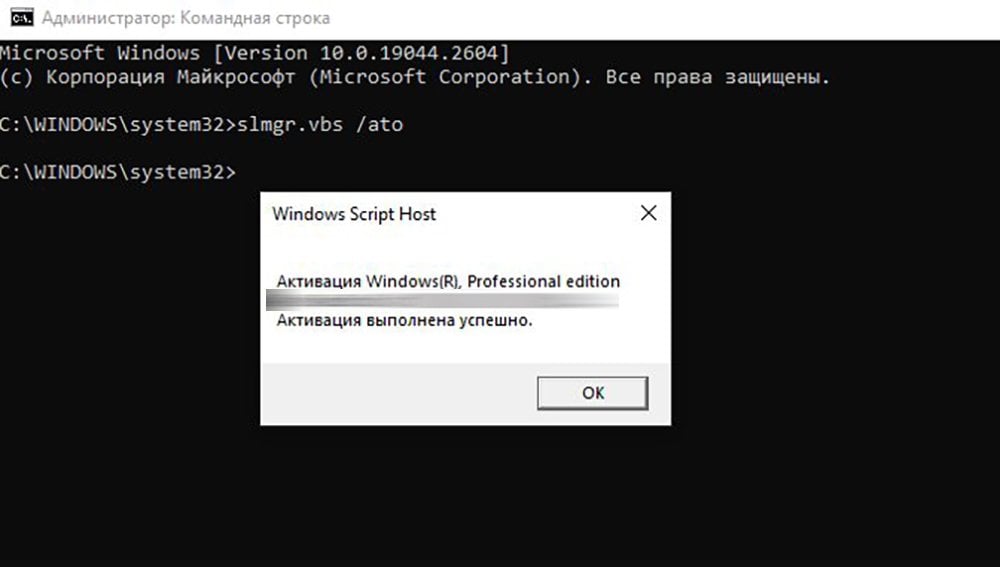
The Windows Command Prompt (CMD) is a powerful tool that allows users to interact with their operating system through text-based commands. Whether you’re a beginner exploring CMD for the first time, an expert troubleshooting advanced issues, or just looking for utility-focused tasks, this guide has you covered.
In this guide, we will provide you with some of the most useful commands for the following:
- CMD Commands for Beginners
- CMD Commands for Experts
- CMD Commands for Utility
- CMD Commands for Troubleshooting
- CMD Commands for Students
- CMD Commands for Programmers
CMD Commands for Beginners
These commands are essential for users who are new to CMD and provide basic functionalities to help them navigate and perform simple tasks.
1. View Directory ‘dir‘
- Function: Displays the contents of the current directory.
- How to use: Type
dirand press Enter. Usedir /sto include subdirectories. - Use case: Quickly view files and folders in your current location.
Syntax: dir
2. Change Directories ‘cd’
- Function: Lets you navigate between folders.
- How to use: Type
cd [folder_name]to move into a directory. Usecd ..to go up one level. - Use case: Navigate to specific directories to manage files or execute commands
Syntax: cd [folder name]
3. Create a New Directory ‘mkdir’ or ‘md’
- Function: Allows you to create a new directory
- How to use: Type mkdir [file_name]— Here the new directory name is GFG
- Use case: When you need a new directory for any separate work, you may create a new directory
Syntax: mkdir [GFG]
4. Rename a File ‘ren’
- Function: Helps in renaming any file or directory.
- How to use: Type
renorrename [old_name] [new_name]and press Enter. - Use case: Discover new method of renaming file or any directory.
Syntax: ren xyz.txt newxyz.txt
5. Delete a File ‘del’
- Function: Lets you to remove one or more files
- How to use: Type del [file_name]— This will erase the provided file name
- Use case: This function allows you to erase any file if you’re unable to fetch
Syntax: del[file_name]
6. Close ‘exit’
- Function: Closes the Command Prompt window.
- How to use: Type
exitand press Enter. - Use case: Ends your session with CMD.
Syntax: exit
7. Clear Screen ‘cls’
- Function: Clears all text from the CMD window.
- How to use: Type
clsand press Enter. - Use case: Removes clutter after multiple commands
Syntax: cls
8. View Available Command ‘help’
- Function: Lists all available commands and their descriptions.
- How to use: Type
helpand press Enter. - Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: help
9. Display or Set the System time ‘time’
- Function: Lets you set the system time or display the current time.
- How to use: Type
time [new_time] and press Enter. - Use case: Allows the user to set their system’s time without additional navigation
Syntax: time [new_time]
10. Copy Files ‘copy’
- Function: Lists all available commands and their descriptions.
- How to use: Type
copy [source1] [destination2] and press Enter. - Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: copy file.txt Backup\
| Command | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
dir |
View the contents of a directory | dir |
dir C:\Users\Documents |
cd |
Change the current working directory | cd [directory_name] |
cd Downloads |
mkdir |
Create a new directory | mkdir [directory_name] |
mkdir NewProject |
ren |
Rename a file | ren [old_name] [new_name] |
ren draft.txt final.txt |
del |
Delete a file | del [file_name] |
del unwanted.txt |
exit |
Close the Command Prompt | exit |
exit |
cls |
Clear the Command Prompt screen | cls |
cls |
help |
View available CMD commands and their descriptions | help |
help |
time |
Display or set the system time | time |
time 14:30:00 |
copy |
Copy files from one location to another | copy [source] [destination] |
copy report.docx D:\Backup\ |
CMD Commands for Experts
These commands are more advanced and suitable for users comfortable with troubleshooting and system management tasks.
1. System File Checker ‘sfc’
- Function: Scans and repairs corrupted system files.
- How to use: Type
sfc /scannowin CMD (run as administrator). - Use case: Fix system errors related to missing or corrupted files.
Syntax: sfc /scannow
2. Disk Error ‘chkdsk’
- Function: Scans the hard drive for bad sectors and file system errors.
- How to use: Type
chkdsk [drive letter]: /f(e.g.,chkdsk C: /f) in CMD. - Use case: Identify and fix disk issues.
Syntax: chkdsk C: /f
3. View Running Processor ‘tasklist’
- Function: Displays all running processes and their details.
- How to use: Type
tasklistto list processes. Usetasklist /fi "imagename eq [process name]"to filter. - Use case: Identify resource-heavy or unresponsive processes.
Syntax: tasklist /fi "imagename eq [process name]
4. Restart ‘shutdown’
- Function: Allows you to shut down or restart the computer via CMD.
- How to use:
- Shutdown:
shutdown /s /f /t [seconds]. - Restart:
shutdown /r /f /t [seconds].
- Shutdown:
- Use case: Automate shutdown or restart tasks
Syntax:
Shutdown: shutdown /s /f /t [seconds].
Restart: shutdown /r /f /t [seconds].
5. Network Statistics ‘netstat’
- Function: Displays active connections and listening ports.
- How to use: Type
netstatto view all active connections. - Use case: Diagnose network-related issues or monitor network activity.
Syntax: netstat
6. Kill a Running Process ‘taskkill’
- Function: Lets you terminate a process using its process ID (PID)
- How to use: Type
taskkill /[PID] /F to terminate - Use case: Can be helpful for terminating any dedicated PID.
Example (PID: 1124)
Syntax: taskkill /PID 11234 /F
7. View Saved Passwords ‘netsh wlan show profiles’
- Function: Retrieve the password of a saved Wi-Fi network.
- How to use: Type netsh wlan show profile name=»WiFi-Name» key=clear
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Example: netsh wlan show profile name="MyHomeWiFi" key=clear
| Command | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
sfc |
System File Checker — Scans and repairs system files | sfc /scannow |
sfc /scannow |
chkdsk |
Check Disk — Scans and fixes disk errors | chkdsk [drive]: /f /r |
chkdsk C: /f /r |
tasklist |
View running processes | tasklist |
tasklist |
shutdown |
Shutdown or restart the system | shutdown /r /t [seconds] |
shutdown /r /t 10 (Restart in 10 seconds) |
netstat |
View network statistics and active connections | netstat -a |
netstat -an (Show all connections numerically) |
taskkill |
Kill a running process using its process ID (PID) | taskkill /PID [PID] /F |
taskkill /PID 4567 /F (Kill process with ID 4567) |
netsh wlan show profiles |
View saved Wi-Fi network names | netsh wlan show profiles |
netsh wlan show profiles |
CMD Commands for Utility
These commands are focused on specific tasks and utilities to enhance productivity and system performance.
1. Network Configuration ‘ipconfig’
- Function: Displays IP address, subnet mask, and gateway information.
- How to use:
- Basic: Type
ipconfig. - Detailed: Type
ipconfig /all.
- Basic: Type
- Use case: Troubleshoot internet connectivity issues.
Syntax: ipconfig
2. Network Connectivity ‘ping’
- Function: Sends packets to test communication with another device or website.
- How to use: Type
ping[destination] - Use case: Check if a device or website is reachable.
Syntax: ping geeksforgeeks.org
3. System Information ‘systeminfo’
- Function: Displays detailed information about your computer.
- How to use: Type
systeminfo. - Use case: Quickly access system specifications for troubleshooting or reporting.
Syntax: systeminfo
4. Trace Route ‘tracert’
- Function: Shows the path packets take to reach a specific destination.
- How to use: Type
tracert[destination] - Use case: Identify network bottlenecks or connectivity issues.
Syntax: tracert geeksforgeeks.org
5. Manage Drives ‘diskpart’
- Function: Opens a command-line utility for managing disk partitions.
- How to use: Type
diskpartto enter the disk management interface. - Use case: Create, delete, or modify partitions on your drives.
Syntax: diskpart
6. Delete a Directory ‘rmdir’
- Function: Removes directory from the origin
- How to use: Type rmdir [directory_name] and press Enter.
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Example: GFG — Directory name
Syntax: rmdir GFG
7. View ‘rmdir’
- Function: Removes directory from the origin
- How to use: Type rmdir [directory_name] and press Enter.
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Example: GFG - Directory name
8. Manage User Account ‘net user’
- Function: To list all the user accounts
- How to use: Type net user and press Enter.
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: net user username password /add
9. View Startup Programs ‘wmic startup get caption,command’
- Function: To check what programs launch on startup.
- How to use: Type wmic startup get caption,command, and press Enter.
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: wmic startup get caption,command
| Command | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
ipconfig |
View network configuration, including IP address, subnet mask, and gateway | ipconfig |
ipconfig /all (Displays detailed network info) |
ping |
Test network connectivity by sending packets to a host | ping [host or IP] |
ping google.com (Check connection to Google) |
systeminfo |
Display detailed system information, including OS version, installed memory, and processor | systeminfo |
systeminfo |
tracert |
Trace the route packets take to a network destination | tracert [hostname or IP] |
tracert google.com (View network path to Google) |
diskpart |
Manage disk partitions, including creating, formatting, and deleting partitions | diskpart |
diskpart → list disk → select disk 1 → create partition primary |
rmdir |
Delete a directory (folder) | rmdir [directory_name] |
rmdir /s /q OldFolder (Delete a folder and its contents without confirmation) |
dir |
View contents of a directory | dir |
dir C:\Users\Documents (List files in a specific directory) |
net user |
Manage user accounts, including adding, modifying, or deleting users | net user |
net user John password123 /add (Create a new user account) |
wmic startup get caption,command |
View startup programs and their commands | wmic startup get caption,command |
wmic startup get caption,command |
CMD Commands for Troubleshooting
1. File Comparison ‘fc’
- Function: Compares two files and highlights differences.
- How to use: Type
fc [file1] [file2]to compare files. - Use case: Detect changes or errors in files
Syntax: fc 1 2
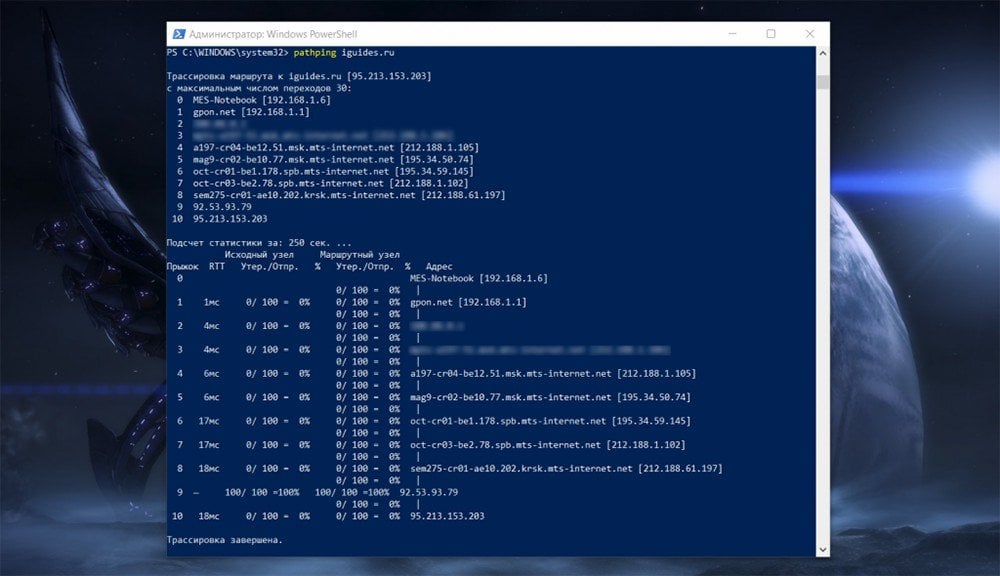
2. Advanced Network Diagnostics ‘pathping’
- Function: Combines
pingandtracertfunctionalities to provide detailed network path diagnostics. - How to use: Type
pathping[destination] - Use case: Troubleshoot complex network issues.
Syntax: pathping geeksforgeeks.org
3. Registry Editor ‘regedit’
- Function: Launches the Windows Registry Editor.
- How to use: Type
regeditto open the registry. - Use case: Modify registry keys for advanced configuration or troubleshooting.
Syntax: regedit
4. View MAC ‘getmac’
- Function: Displays the MAC address of your network adapter.
- How to use: Type
getmacto view the MAC address. - Use case: Identify your device’s hardware address for network configurations
Syntax: getmac
5. Power Configuration ‘powercfg’
- Function: Displays and manages power settings.
- How to use: Type
powercfg/[option] - Use case: Optimize power usage and troubleshoot battery issues.
Syntax: powercfg /energy for a detailed power usage report
6. Enable Boot Manager ‘bcdedit’
- Function: Used to modify boot configuration settings
- How to use: Type
bcdedit/ set current - Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: bcdedit /set {current} bootmenupolicy standard
7. Format a Drive ‘format’
- Function: To erase any specific drive.
- How to use: Type format [drive]: /FS:NTFS and press Enter.
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: format D: /FS:NTFS
| Command | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
fc |
Compare two files and highlight differences | fc [file1] [file2] |
fc file1.txt file2.txt (Compare two text files) |
pathping |
Perform advanced network diagnostics with packet loss details | pathping [destination] |
pathping google.com (Analyze network route to Google) |
regedit |
Open the Windows Registry Editor (GUI) | regedit |
regedit (Opens the registry editor – use with caution!) |
getmac |
Display the MAC (Media Access Control) address of your network adapters | getmac |
getmac /v /fo list (View MAC addresses in detailed format) |
powercfg |
Manage and analyze power configurations | powercfg /[option] |
powercfg /batteryreport (Generate a battery usage report) |
bcdedit |
Enable, disable, or modify Windows Boot Configuration | bcdedit /set {current} [option] |
bcdedit /set {current} bootmenupolicy standard (Enable boot menu in Windows 10/11) |
format |
Format a drive (erase all data) | format [drive]: /FS:[filesystem] |
format D: /FS:NTFS (Format drive D: with NTFS file system) |
CMD Commands for Students
Students can use these commands to manage files, perform simple calculations, and even help with tasks like coding and studying.
1. Calculator ‘calc’
- Function: Opens the Windows Calculator application.
- How to use: Type
calcand press Enter. - Use case: Quickly open the calculator for
Syntax: calc
CMD Commands for Programmers
Programmers often use CMD to automate tasks, compile code, and test network functionality. These commands can be especially useful for developers working in command-line environments.
1. Compile Java Code ‘javac’
- Function: Compiles Java source files into bytecode.
- How to use: Type
javac [file name].javato compile Java code. - Use case: Compile and test Java programs directly from the command line.
Syntax: javac
2. Version Control ‘git’
- Function: Interacts with Git repositories from the command line.
- How to use: Type
git [command] - Use case: Manage version control, clone repositories, or push commits from the command line.
Syntax: git clone [repository URL]
3. Execute Python Script ‘python’
- Function: Runs Python scripts in the command prompt.
- How to use: Type
python [script.py]to execute a Python program. - Use case: Test and run Python code directly in the command line.
Syntax: python [script.py]
4. Run Node.js Scripts ‘node’
- Function: Executes Node.js scripts.
- How to use: Type
node [script.js]to run a JavaScript file using Node.js. - Use case: Run backend scripts and test JavaScript programs in the command line.
Syntax: node [script.js]
5. Node Package Manager ‘npm’
- Function: Installs and manages JavaScript packages.
- How to use: Type
npm install [package]to install a package. - Use case: Manage dependencies and libraries in Node.js applications.
Syntax: npm install [package]
| Command | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
javac |
Compile Java source code into bytecode (.class files) | javac [filename].java |
javac HelloWorld.java (Compile a Java file) |
git |
Version control system for tracking changes in files | git [command] |
git clone https://github.com/user/repo.git (Clone a repository) |
python |
Execute a Python script or enter interactive mode | python [script.py] |
python script.py (Run a Python script) |
node |
Execute JavaScript code using Node.js | node [script.js] |
node app.js (Run a Node.js script) |
npm |
Manage Node.js packages and dependencies | npm [command] |
npm install express (Install the Express.js package) |
Bonus: CMD Tricks and Tips
To make CMD usage even more efficient, here are some bonus tips:
1. Save CMD Output to a File
Use the > operator to save the output of a command to a text file.
2. Open CMD in a Specific Directory
Instead of navigating manually, you can directly open CMD in a folder by typing cmd in the File Explorer’s address bar.
3. Use && for Multiple Commands
You can run multiple commands sequentially:
ipconfig && ping google.com
Conclusion
Mastering the most useful CMD commands in Windows can empower you to perform tasks more efficiently, troubleshoot problems, and gain deeper control over your system. By familiarizing yourself with these essential CMD commands, you’ll be better equipped to handle a variety of situations, from simple file management to advanced system configurations. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, these commands are invaluable tools to have at your disposal.
Command prompt (CMD) is a tool designed especially for the Windows Operating System which gives you a direct approach to complete tasks, which otherwise, needs a lot of effort and time. It’s so useful that even today we apply it to fix multiple errors and to enable/disable various Windows user settings. The tool works with certain commands.
As we can’t remember each one of them individually, we have come here with a list of 30 Best Commands (cmd.exe) in Windows 10 that you simply can’t ignore working with.
So just buckle up and enjoy the ride.
Compilation of 30 Best Commands (cmd.exe) in Windows 10
1: ipconfig: To find your IP Address within Seconds
If you waste a lot of time figuring out the “IP” (Internet Protocol) then this is one of the best commands meant for you. It permits easily trace out system’s IP address details. Moreover, the tool also displays info about the gateway as well as Router’s pre-specified web interface. After the execution of this command, you view a list of all the networks your system is connected to. The command looks like:
ipconfig /all command
2: shutdown: To create Shutdown shortcuts
This command lets restart or turn off PC within seconds which makes it very effective. The “shutdown” command line is a relief to all the latest versions where it’s very hard to search and execute the shutting down functionality. Using this, you can easily create shortcuts and can effectively place them wherever want, say at the desktop, taskbar or at the Start menu-list. In the advanced versions, you are able to use “cmd.exe” like a switch to turn your PC on/off taking into consideration many advanced options for the startup. For this, just type:
a) shutdown /r /o: To start the PC into various advanced options.
b) shutdown /s /t 0: To perform a regular power off
c) shutdown /r/t 0: To Restart your PC
3: ping: To test if there is no packet loss
You can run this command as: “ping howto-connect.com”. Here, “howto-connect.com” is the name of the server that we want to test. After hitting the Enter key, Windows will start sending packets to the address fed to the input (here, howto-connect.com). IP address will also work for the same in this utility. The server in return would inform that it has received those tiny data packets. This way you check if any of the data packets were not received by the server or if the server is saturated (can no longer hold the data packets).
4: ipconfig /flushdns: To Flush the DNS Resolver Cache
When you change DNS settings, they don’t just take place immediately. Instead, they take time for a complete setup. Meanwhile, if you’ll try to visit a particular site (changed DNS server settings for) time and again, the Windows in return will use the “cache” which retains the record for all the previous responses from that specific address. So this cache ensures that the Windows is fetching Data from the new DNS server by running “ipconfig /flushdns” command even after changing the DNS settings. It looks like:
ipconfig /flushdns
5: sfc /scannow: Scans your System files to fix Errors
Do you know that Windows 10 has an (SFC) System file checking tool as well following its predecessors? Yes, it does. This tool scans all system files and finds out errors in them moreover, replaces if any file is corrupt automatically. To use this “tool” via command prompt, just open up and type:
sfc /scannow
then, press Enter.
6: telnet: Connects you to the Telnet servers
Windows versions also carry a Telnet client approved by the Microsoft itself and this comes uninstalled. So you have to install manually from the Control Panel first. After installing this, use the telnet command to connect to the various telnet servers without needing to practice a 3rd-party software.
It is primarily advised to avoid using the telnet client but certain programs require this in the first place, to set up. This is where you’ll need Telnet. The syntax follows as:
telnet
7: cipher: To Overwrite or to permanently delete a Directory
Cipher has a lot of functions to perform. It is primarily used to manage encryption and write data to a drive and to clear instantly as well. When you run cipher command no deleted data can be restored. So The command allows to directly wipe a drive’s data without seeking for any permissions prior to the execution. This command is:
cipher /w:D:\ (assuming that D is the drive that you want to wipe here).
8: nslookup: To find the IP address of a Domain
Nslookup tells the IP address of the desired server. The same thing takes place when you type a domain name into your browser’s address bar as doing this tracks the IP address of the server first and accordingly, takes to the destination. This is a very passive process. But with “nslookup”, you can directly obtain this IP from your Command prompt within seconds. Furthermore, it can also tell you the server name if you type in the IP address. The syntax is as follows:
nslookup howto-connect.com
here, the server name is “howto-connect.com”.
9: netstat –an: Lists all your Network Connections and Ports
Netstat command allows you see a list of all the network connections along with the name and the details of the port they are operational with. This also informs you about the foreign IPs connected to these ports. The syntax is:
netstat -an
10: fc: To compare two files
You can exercise “fc” to compare certain parameters between 2 given files. It is very useful for those who face a hard time in finding out the differences in the text of two files. But not now, as this command does all within a matter of time. Straightway type ‘fc’ followed by the directory path and the file name to compare them real quick. Type:
fc /l “C:\Program Files (x86) \ABC1.doc” “C:\Program Files (x86) \ABC2.doc”
Here, ABC1 and ABC2 are the files names respectively. C is the drive which contains these files. The above command juxtaposes ASCII (text) in these two documents/files.
Note: Use, ‘/b’ to compare binary output and ‘/c’ for the case of text in the two specified documents.
11: sigverif: To Verify the File Signature
This command works to check if all the system files are digitally signed or not. Windows 10 and all other versions carry the tool popular as File Signature Verification tool. It uses a GUI interface and tells you accordingly that which system files are signed and which remain unsigned. The command performing to launch this signature verification tool is as follows:
sigverif
12: driverquery: Displays all the Installed Drivers
Windows 10 gives you Driver Query as a complementary tool to test your drivers. This tool works to identify the drivers that are being used with an entire list showcasing the installed drivers. If you need some additional information for these drivers, you can modify this command as follows:
driverquery -v (to know details regarding each driver)
driverquery -si (displays the signature information about each driver)
13: repair-bde: To recover the Encrypted data
Now retrieve data from your drive using “repair -bde”command. This is very handy when your drive is protected by the BitLocker. To run this command, you’ll need to have a destination drive, recovery key or the password for BitLocker. The basic format/syntax for this command is:
repair-bde -rk | rp
Here, you’ll need to specify the source and the destination drive along with the key/password followed by the path leading to the key/password. Here are some examples to run this command:
repair-bde c: d: -rk e:\recovery.bek
repair-bde c: d: -rp 111111-111111-111111-111111-111111-111111
14: tasklist: To list all the running tasks on a system
Tasklist, as the name suggests, provides a list of entire tasks active on your PC. This command is also compatible with multiple switches like –m and –svc. The –m switch displays all the DLL modules related to a task while -svc switch lists the services that support each task listed in the prompt. It looks like:
a) tasklist
b) tasklist –m
c) tasklist –svc
15: taskkill: to terminate a task
Taskkill performs the termination of the desired task taking help from its process identification code or the Image name. The syntax of the command includes taskkill followed by –pid or –im, of the task which you want to kill. Here is how this command looks like:
taskkill –pid 4104
taskkill –im iexplore.exe
16: Attrib: To change attributes of a file
Attrib command works to identify attributes of a file within the directory that you are executing the command from. You can use switches like: +a, -a, +h, -h, +I, -I, +r, -r, +s, -s, +v, -v, +x and, -x with this command. When apply with these switches, the command performs different functions as operated.
The syntax is as follows:
attrib [the switch: as listed above] [drive:][path][filename] [/s][/d][/l][/?]
For Example:
attrib +r c:\windows\system\secretfolder
17: bcdboot: To copy boot files
“Bcdboot” can definitely help if you are experiencing problems with the Windows boot-up functionality. This command lets you rebuild BCD inventory (for data) and also repair the existing one. The syntax is like:
bcdboot [/l][/s][/v][/m]
18: XCOPY: To copy files between drives
Now copy your files between drives using the “XCOPY” command. The command-line to copy photos from drive C to the drive F will be:
XCOPY c:\photos f:\photos /s /e
19: CD: To quickly switch between directories
CD command lets quickly access the directory of choice. For example, let’s just say that you are way too far from the C drive and quickly want to reach there. Then the syntax would follow:
cd c:\
This will take you to the C drive.
20: DIR: To see the contents of a directory
Navigating through the Windows Explorer to check data on your directories is very hectic. CMD gives you a power to quickly go through the contents of a directory with just 3 simple alphabets i.e “dir”. The syntax goes like:
dir
21: Assoc: Displays file name extensions
The Assoc command displays all the relevant file extensions and program associations on the system. You are capable of even extending this command to change file parameters like its associations and so on. For e.g. “assoc .txt=” will change the text files to whatever format you enter after the “=” sign in the command line. The syntax to change text files to pdf would be:
assoc .txt=.pdf
22: pathping: Advanced version of Ping
Pathping command is useful if you have a no.of router installed between a system and the device and want to test. This is a Post-established version of the “ping” command. It displays a little information about the routes which the packets take while traveling between multiple nodes. The syntax looks like:
pathping
23: powercfg: To manage your systems power consumption
You can run this command to track PC’s power consumption resources.To manage hibernation type:
powercfg /hibernate on
powercfg /hibernate off
and,
“powercfg /a” (to check power saving states)
Similarly, “powercfg /lastwake” will tell the programs/processes that woke the system from sleep. You, therefore, execute this command to troubleshoot a system if it wakes from sleep too often.
24: recimg.exe
The recimg.exe is the best command helps to design a custom recovery image for Windows 10 operating system. This image contains all the installed apps and Windows system files in their current state. It does not contain documents, user profiles, personal settings, etc. and is a highly sophisticated program. Simply type:
recimg.exe
and it will form a custom recovery image for your Windows version.
25: tracert: To track path of the transmitted packets
The Tracert command traces the path through with the packets are transferred to a known server. It’ll show the information about how each node packet interacts while moving to the destination. So if you are having any issues with the server, simply run this command line:
tracert howto-connect.com
(“howto-connect.com” is the name of the server here)
26: Tree: to obtain a tree structure of a Directory
This is among the best commands and represents the components of a directory/sub-directory into a Tree structure format. Simply open the Command Prompt and type “tree” followed by the drive or any sub-directory you want to see. This will showcase your entire user profile within that directory/path name. The syntax for checking constituents of the C drive (assume) will be:
tree c:/
Note: To zoom in, right-click the top bar of the prompt and go to Properties > Layout tab and change the default height parameter from 300 to something bigger, like 500 or so.
27: netsh interface: To check WiFi Connections
You can also catch the real culprit (in Windows 10) if your system is connected to a wifi network or not using this very effective command line. To know this, type in the following command into the command prompt:
netsh interface show interface | findstr /C: ”Wireless” /C: ”Name”
Executing this command will show the things like Admin State, State, Type moreover the Interface Name.
28: Move: To move files and directories to another location
This is one of the best commands lets change locations of a file. Just type in the simple command in CMD and that’s it. The file will successfully move to the desired location. The syntax for this command goes like:
move <filename> <destination folder>
For example, to move a file named “howto-connect.docx” to the folder “d:\backup\folder”; the command would be:
move howto-connect.docx d:\backup\folder
29: /?: To find the usage of a command
A few commands are very hard to understand, in this case, you will simply type the doubtful one, followed by this argument i.e. “/?”. For example, to see what “shutdown” does through CMD, simply type:
shutdown /?
And, this will show the list of all the switches that could be used with the “shutdown” command to perform numerous functions.
30: net share: To disable administrative shares
Windows shares automatically share some specific folders once it connects to a network. You can easily disable this, or can even eliminate this using a special command line. It is also one of the Best Commands in Windows 10. First of all, to view these shared folders and their locations, type:
net share
Now run the command to disable these shares. Type:
a) net share C$ /delete
b) net share IPC$ /delete
c) net share ADMIN$ /delete
and all other folders who you don’t want to display shares from.
Final Words
Command lines make it very easy to execute really hectic tasks within seconds. These, obviously, are hard to remember but you can easily learn a few of these to impress those tech-geeks and freaks around you. Commands mentioned above are no doubt very effective and functional. So just hold on to these Best Commands (cmd.exe) in Windows 10 and you’ll never ever be going through those very bulky procedures of executing functions within Windows OS.
Feel free to share more commands, which you feel could be important for Windows 10 users. Till then, share this article to lend a helping hand to others.
В наших статьях про работу Windows 10 и других версий часто можно встретить упоминание командной строки. Все дело в том, что это удобный системный инструмент, который позволяет настраивать ОС под себя и управлять разными ее частями с помощью простых текстовых команд. Например, мгновенно запускать разные приложения или проводить проверку и сканирование файлов.
Для командной строки существует огромное количество различных кодов, которые мы можете использовать для того, чтобы упростить себе работу с системой и использовать ее функции по максимуму. Ниже разберемся, как открывается командная строка и какие команды можно в нее вводить.
Виды командной строки
Утилита для выполнения команд в Windows разделена на два интерфейса: непосредственно командную строку и оболочку PowerShell. Каждая из них — это консоль, которая напрямую соединяет вас с компонентами ОС или конкретными приложениями на вашем ПК.
Первой появилась командная строка. Ее встроили в систему для того, чтобы оптимизировать стандартные задачи, например, работу с учетными записями на ПК или создание резервных копий по ночам. Вы можете запускать и куда более сложные сценарии. Скрипты командной строки помогают вам облегчить и ускорить работу.
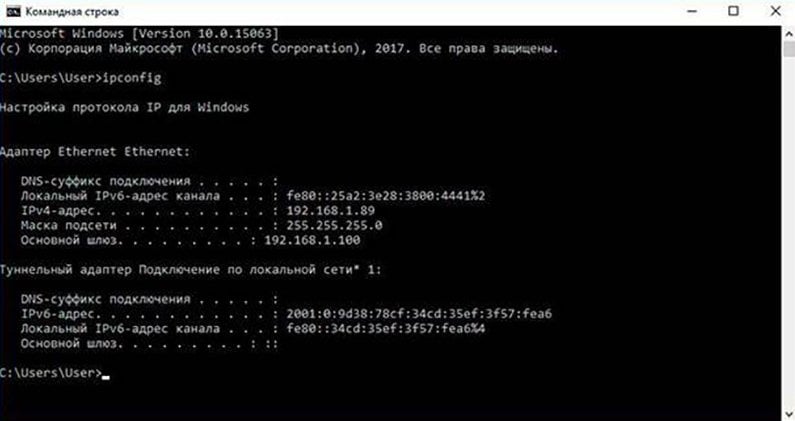
командная строка виндовс 10
PowerShell же создан как расширенная версия прошлой утилиты и использует собственные скрипты — командлеты. Они представляют собой язык сценариев, который можно расширять. По сути, вы можете использовать ту утилиту, которая удобнее вам, но помните, что командная строка не может использовать командлеты для PowerShell.
командная строка виндовс 10
Открываем командную строку
Проще всего запустить командную строку через системную утилиту «Выполнить». Ее можно вызвать с помощью комбинации клавиш Windows + R. В открывшемся окне введите cmd и подтвердите выполнение запроса.
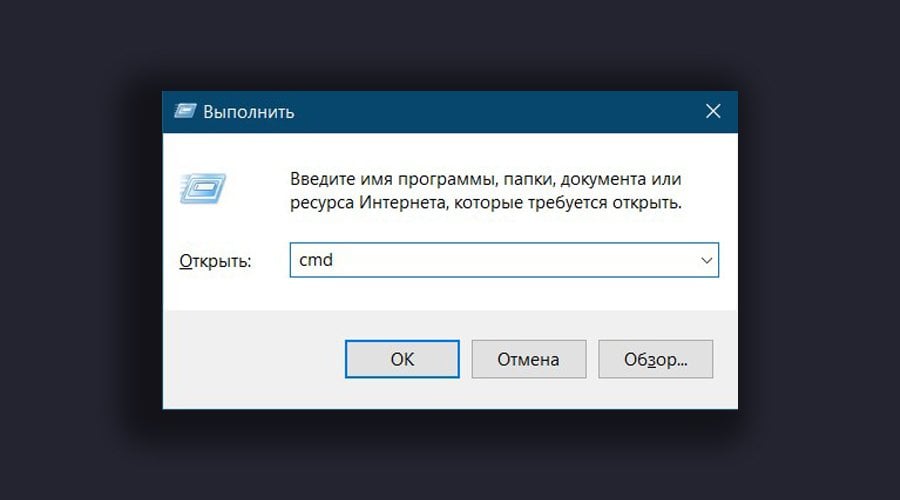
командная строка виндовс 10
Еще один вариант — запуск через меню «Пуск». Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по иконке меню и выберите «Командная строка» или «Windows PowerShell». Также вы таким образом можете запустить командную строку от имени администратора и получить максимальный ее функционал. Но помните, что этот способ сработает только если у вас не стоит модификации на меню «Пуск». В ином случае у вас откроется другое всплывающее окно.
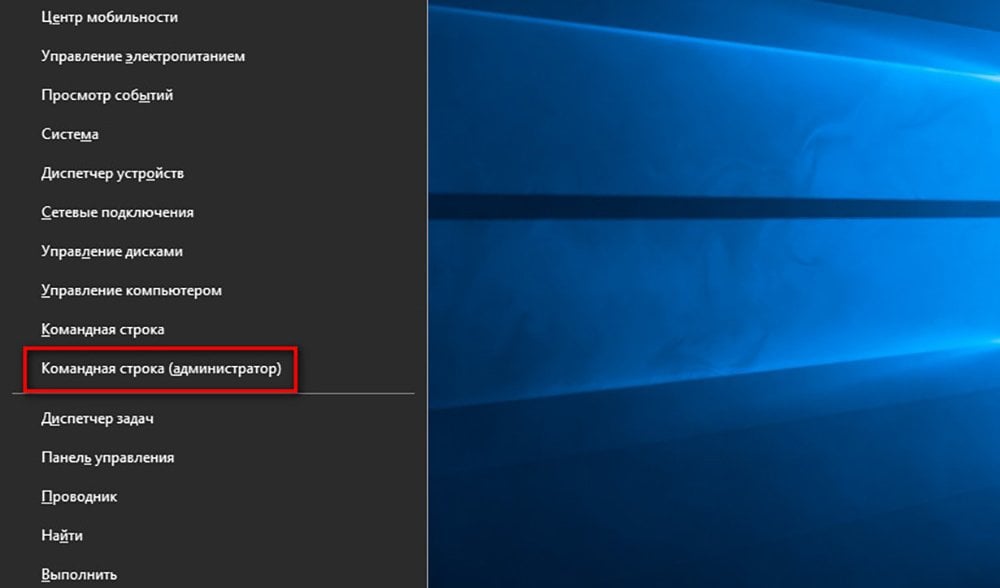
командная строка виндовс 10
Какой бы способ вы не выбрали — итог будет одинаковым. В результате откроется окно командной строки, в которое вы сразу же можете вводить нужные вам команды для системы и прочих файлов.
Список команд
Как мы уже отметили ранее, в командной строке есть очень много различных команд, но большинство из них настолько специфичны, что нужны только в редких случаях. В статье мы постарались собрать только основные команды, которые могут помочь вам быстро открывать системные утилиты и работать с папками на вашем ПК.
командная строка виндовс 10
Помните об осторожности при работе с системными файлами и инструментами, и не забывайте делать бэкапы файлов, если вам нужно что-то серьезно изменить.
Программы и утилиты
Эти команды позволят вам моментально запускать программы и открывать разные системные утилиты. С их помощью вы можете быстро перемещаться по разным компонентам системы, без необходимости делать несколько шагов в меню пуск. А еще это позволяет запускать важные утилиты, для доступа к которым нужно лезть вглубь ПК.
- appwiz.cpl — программы и компоненты;
- certmgr.msc — меню управление системными сертификатами
- control — панель управления;
- control printers — меню управления подключенными устройствами и принтерами;
- control userpasswords2 — учетные записи на ПК;
- compmgmt.msc — управление параметрами ПК;
- devmgmt.msc — диспетчер устройств;
- dfrgui — меню оптимизации дискового пространства;
- diskmgmt.msc — управление дисками и пространством;
- dxdiag — средство диагностики DirectX.
командная строка виндовс 10
- hdwwiz.cpl — диспетчер устройств (другая команда);
- firewall.cpl — брандмауэр Защитника Windows;
- gpedit.msc — редактор локальной групповой политики;
- lusrmgr.msc — локальные пользователи и группы на вашем ПК;
- mblctr — центр мобильности;
- mmc — консоль управления системными оснастками;
- msconfig — системная конфигурация;
- odbcad32 — панель администрирования источника данных ODBC;
- perfmon.msc — системный монитор (можно смотреть изменения в производительности ПК и системы);
- presentationsettings — режим презентации;
- powershell — PowerShell (расширенная версия командной строки);
- powershell_ise — интегрированная среда сценариев для PowerShell;
- regedit — редактор реестра.
командная строка виндовс 10
- resmon — монитор ресурсов;
- rsop.msc — результирующая политика Windows;
- shrpubw — мастер создания общих ресурсов;
- secpol.msc — локальная политика безопасности;
- services.msc — средство управления службами операционной системы;
- taskmgr — диспетчер задач;
- taskschd.msc — планировщик заданий.
Приложения
Команд для работы с приложениями довольно мало. Они направлены в основном на уже открытые программы, которые выполняют определенные процессы на ПК.
- schtasks – отложенный запуск приложения через планировщик задач;
- shutdown – выключить или перезагрузить ПК;
- tasklist – список выполняемых задач на ПК;
- taskkill – остановить выполнение задачи и закрыть процесс (нужен PID, его вы можете узнать из прошлой команды);
- reg – редактор реестра;
- runas – запустить задачу от имени другого пользователя.
командная строка виндовс 10
Управление системой
С этим пунктом нужно обращаться осторожнее, ведь команды в нем связаны непосредственно с работой вашей системы. Конечно, если вы просто запустите утилиты с помощью этих запросов, и ничего не будете менять, все будет нормально. Но если вам нужно что-то изменить в системе — будьте крайне осторожны.
- computerdefaults — параметры программ по умолчанию;
- control admintools — папка со средствами администрирования;
- date — управление датой на ПК;
- displayswitch — управление подключенными экранами;
- dpiscaling — параметры дисплея;
- eventvwr.msc — журнал событий;
- fsmgmt.msc — средство работы с общими папками;
- fsquirt — работа с файлами по Bluetooth;
- intl.cpl — региональные настройки;
- joy.cpl — внешние игровые устройства;
- logoff — выход из системы.
командная строка виндовс 10
- lpksetup — управлениее языками интерфейса;
- mobsync — центр синхронизации Windows;
- msdt — средство диагностики службы поддержки Microsoft;
- msra — удаленный помощник Windows;
- msinfo32 — сведения о системе;
- mstsc — удаленный рабочий стол;
- napclcfg.msc — конфигурация операционной системы;
- netplwiz — управление учетными записями пользователей;
- optionalfeatures — управление стандартными компонентами операционной системы;
- shutdown — завершение работы компьютера;
- sigverif — средство проверки подлинности файлов;
- sndvol — запуск микшера громкости;
- slui — активация лицензии Windows;
- sysdm.cpl — свойства системы;
- systempropertiesperformance — параметры быстродействия;
- systempropertiesdataexecutionprevention — запуск службы DEP параметров быстродействия.
командная строка виндовс 10
- timedate.cpl — дата и время ПК;
- tpm.msc — управление доверенным платформенным модулем TPM на локальном компьютере;
- useraccountcontrolsettings — параметры управления учетными записями пользователей;
- utilman — специальные возможности;
- ver — сведения о текущей версии Windows;
- wf.msc — режим повышенной безопасности брандмауэра;
- winver —общие сведения о Windows;
- WMIwscui.cpl — центр поддержки Windows;
- wscript — параметры сервера сценария;
- wusa — автономный установщик обновлений Windows.
Сеть и интернет
С помощью этих команды вы можете проверить работоспособность вашего интернета и изменить настройки. Также вам будет доступна информация о сетевых устройствах и интерфейсах.
- control netconnections — просмотр и настройка сетевых подключений;
- inetcpl.cpl — свойства интернета;
- NAPncpa.cpl — аналог первой команды;
- telephon.cpl — настройка модемного подключения к интернету;
- ipconfig – информация о сетевых интерфейсах;
- ping – отправляет ICMP-запросы на целевой хост, проверяет его доступность.
командная строка виндовс 10
- tracert – путь пакетов в сети;
- nslookup – поиск IP-адреса по имени ресурса;
- route – таблицы сетевых маршрутов;
- arp – таблицу с IP-адресами, преобразованными в физические адреса;
- netsh – программа управления сетевыми настройками;
- getmac – MAC-адрес сетевого адаптера;
- tftp – запускает TFTP-клиент в консоли.
Периферия
Команды для управления оборудованием, подключенным к вашему ПК тоже есть. Их немного и они вызывают в основном окна настройки разных устройств, от мышки для принтера и графического планшета.
- main.cpl — панель настройки мыши;
- mmsys.cpl — панель настройки звука;
- printui — пользовательский интерфейс принтера;
- printbrmui — средство переноса принтера, с возможностью экспорта и импорта программ и драйверов;
- printmanagement.msc — управление параметрами печати.
командная строка виндовс 10
- sysedit — редактирование системных файлов с расширениями .ini и .sys;
- tabcal — средство калибровки дигитайзера;
- tabletpc.cpl — свойства планшета и пера;
- verifier — диспетчер проверки драйверов;
- wfs — факсы и сканирование;
- wmimgmt.msc — элемента управления WMI стандартной консоли.
Файлы и диски
Здесь мы рассмотрим команды для работы с дисками, папками и хранящимися в них файлами. Некоторые из них будут работать только если вы уже вызвали какую-то утилиту или запустили программу. А если вы запутаетесь, то всегда можно воспользоваться командой help, чтобы получить справку по командной строке.
- assoc — связь между расширениями имени и типа пакетного файла;
- attrib — редактирование атрибутов файла или папки;
- bcdboot — создание/восстановление системного раздела;
- cd — смена диска или просмотр выбранного;
- chdir — просмотр папки или переход к другой;
- chkdisk — проверка дисков и внешних накопителей;
- cleanmgr — очистка диска.
командная строка виндовс 10
- convert — смена файловой системы тома;
- copy — копирование файлов (с выбором конечного каталога);
- del — удаление выделенных файлов;
- dir — просмотр файлов и папок по выбранному пути;
- diskcopm — сравнить содержимое двух дисков;
- dickcopy — скопировать содержимое одного диска на любой другой;
- diskpart — утилита для работы с дисками (открывается в отдельном окне командной строки);
- erase — удаление одного или нескольких файлов;
- fc — сравнение файлов и поиск различий;
- format — форматирование дисков Windows;
- label — изменение меток тома для дисков;
- md — новая папка;
- mdsched — проверка оперативной памяти;
- move — перемещение файлов по указанному пути.
командная строка виндовс 10
- ntmsmgr.msc — средство работы с внешними накопителями;
- recdisc — создание диска восстановления операционной системы (только оптические накопители);
- recover — восстановление данных;
- rekeywiz — шифрующая файловая система (EFS);
- RSoPrstrui — восстановление системы;
- sdclt — резервное копирование и восстановление;
- sfc /scannow — проверка целостности системных файлов;
- tree — графическое отображение структуры каталогов;
- verify — анализ правильности записи файлов на диск;
- vol — метка и серийный номер тома диска.
Настройка командной строки
Командную строку также можно кастомизировать под себя. Изменить ее цвет, установить приветствие, очистить содержимое, если кода стало слишком много. Словом, всячески управлять ей.
- cls — очистить экран командной строки;
- color — изменить цвет фона (нужен идентификатор цвета);
- exit — закрыть утилиту;
- help — полный список команд;
- prompt — изменяет слева название.
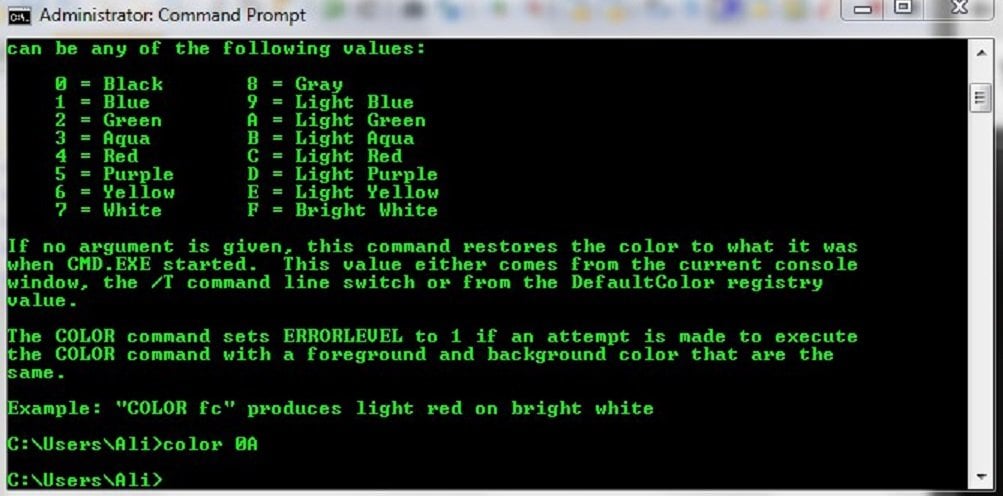
командная строка виндовс 10
В статье мы собрали самые полезные команды для командной строки. Пользуйтесь ими при необходимости, но не забывайте об осторожности. Все действия с системными файлами и утилитами вы выполняете на свой страх и риск.
Заглавное изображение: wall.alphacoders.com
Командная строка Windows (CMD) — мощный инструмент, который предоставляет доступ к широкому набору команд для выполнения различных задач, от работы с файлами до настройки сети и автоматизации процессов. В статье рассмотрим 100 популярных команд CMD, которые пригодятся как новичкам, так и опытным пользователям. Для удобства они разделены по категориям.

Разделы
- Общие команды CMD
- Сетевые команды CMD
- Команды для управления процессами
- Команды для управления файловой системой
- Команды для управления пользователями
- Команды для управления безопасностью
- Команды для диагностики и устранения неполадок
- Команды для скриптинга и автоматизации
- Команды для управления сетевыми подключениями
- Команды для управления печатью
- Дополнительные команды в Windows
Общие команды командной строки (CMD) позволяют пользователям управлять ОС Windows через интерфейс командной строки. Они нацелены на различные задачи – от получения справочной информации до управления процессами.
- hel — выводит список всех доступных команд и их краткое описание, что полезно для получения информации о базовых командах.
- cls — очищает экран командной строки. Если в окне CMD много текста, этой командой можно убрать весь вывод и начать работу «с чистого листа».
- exit — завершает текущую сессию командной строки и закрывает окно CMD.
- echo — выводит сообщения в консоль или включает/выключает отображение команд в пакетных файлах – echo Hello, World! выведет Hello, World! на экран.
- ver — отображает версию операционной системы Windows.
- title — изменяет заголовок окна командной строки. Например, title Моя Командная Строка изменит заголовок на «Моя Командная Строка».
- pause — временно приостанавливает выполнение скрипта, но при нажатии любой клавиши можно продолжить работу.
- date — позволяет узнать или изменить текущую дату в системе.
- time — отображает или изменяет текущее время в системе.
- tasklist — выводит список всех запущенных процессов с их PID (идентификатором процесса).
- powercfg — управляет настройками энергопотребления и профилями питания.
- fc — сравнивает два файла и отображает их различия.
Сетевые команды CMD
В разделе собраны основные сетевые команды CMD, которые помогут управлять подключениями, диагностировать сетевые проблемы и выполнять разнообразные операции с сетью. Они незаменимы для системных администраторов и пользователей, нуждающихся в решении сетевых задач.
- ping — проверяет связь с удаленным узлом, отправляя ему пакеты данных. Например, ping google.com проверит доступность сервера Google.
- ipconfig — отображает конфигурацию сетевых интерфейсов системы (IP-адреса, маску подсети и шлюзы).
- netstat — выводит информацию о сетевых соединениях и открытых портах
- netstat -an — показывает все активные соединения.
- tracert — отслеживает маршрут пакета до целевого узла – tracert yandex.ru покажет все узлы, через которые проходит запрос.
- nslookup — используется для проверки информации о DNS-серверах.
- nslookup example.com — отображает IP-адрес сайта example.com.
- arp — выводит или изменяет записи ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) –: arp -a покажет текущие записи ARP.
- route — управляет таблицей маршрутизации сети – route print выведет все существующие маршруты в системе.
- net use — подключает сетевые диски. Например, net use Z: \\server\folder подключит сетевой ресурс как диск Z:.
- netsh — позволяет настраивать различные параметры сети через командную строку.
- netsh wlan show profiles — отображает сохраненные профили Wi-Fi.
Команды для управления процессами
Команды ниже позволяют эффективно управлять процессами и службами на вашем ПК: помогают запускать службы, планировать задачи, управлять активными процессами, а также выключать или перезагружать систему. С их помощью можно автоматизировать выполнение задач, получать информацию о состоянии системы и контролировать её работоспособность.
- sc — управляет службами Windows. Пример: sc start servicename запустит службу с именем servicename.
- schtasks — управляет планировщиком задач. Так, schtasks /create /tn «Моя Задача» /tr notepad.exe /sc once /st 12:00 создаст задачу для запуска.
- start — запускает программу или команду в новом окне. Например, start notepad откроет блокнот.
- wmic — взаимодействует с системой через Windows Management Instrumentation – wmic process list brief покажет список процессов.
- shutdown — выключает, перезагружает или завершает работу системы. Так, shutdown /s /f /t 0 немедленно выключит компьютер.
- systeminfo — выводит информацию о системе, включая версию Windows, параметры оборудования и установленные обновления.
Команды для управления файловой системой
Команды для управления файловой системой в CMD позволяют работать с файлами и папками: просматривать содержимое директорий, перемещаться между папками, создавать и удалять файлы и каталоги, копировать данные с использованием различных опций.
- dir — отображает список файлов и каталогов в указанной директории. Пример: dir C:\Windows выведет содержимое папки Windows.
- cd — меняет текущий каталог. Так, cd C:\Users перейдет в папку пользователей.
- md NewFolder — создает новую папку.
- rd — удаляет пустую папку. Пример: rd NewFolder удалит папку NewFolder.
- copy — копирует файлы из одного места в другое.
- move — перемещает файлы или папки.
- del — удаляет файлы. Например, del file.txt удалит файл file.txt.
- xcopy — копирует файлы и директории, включая их структуру. Так, xcopy C:\Source D:\Destination /s /e скопирует все файлы и папки из Source в Destination.
- robocopy — более продвинутая версия xcopy, используется для надежного копирования данных. Например, robocopy C:\Source D:\Destination /mir синхронизирует две папки.
Команды для управления пользователями
Команды для управления пользователями предоставляют средства для администрирования учетных записей, настройки групповых прав и управления политиками безопасности. А также позволяют администраторам эффективно управлять пользователями в системе, добавлять новых пользователей, изменять их права и настраивать параметры учетных записей.
- net user — управляет учетными записями пользователей.
- net user UserName /add — добавляет нового пользователя с именем UserName.
- net localgroup — управляет локальными группами пользователей.
- net localgroup Administrators UserName /add — добавляет пользователя в группу администраторов.
- whoami — выводит имя текущего пользователя и информацию о его правах.
- runas — позволяет запускать программы от имени другого пользователя. Так, runas /user:administrator cmd запустит CMD с правами администратора.
- net accounts — управляет параметрами учетных записей, например, минимальной длиной пароля и периодом его действия.
- gpupdate — обновляет групповые политики на локальном компьютере, что полезно для администраторов, управляемых сетей.
- taskview — открывает таймлайн Windows, показывая историю активности пользователя, полезно для управления и поиска ранее использованных файлов и приложений.
- msg — отправляет сообщение пользователям, подключенным к системе. Пример: msg «Система будет перезагружена через 5 минут» отправит сообщение всем пользователям.
Команды для управления безопасностью
Команды для управления безопасностью предназначены для обеспечения защиты данных и управления доступом к файлам и системным ресурсам, что позволяет шифровать файлы, проверять целостность системных файлов и управлять правами доступа.
- cipher — управляет шифрованием файлов на дисках NTFS.
- cipher/e — зашифровывает файлы в указанной директории.
- sfc — проверяет целостность системных файлов и автоматически восстанавливает их при обнаружении повреждений.
- sfc /verifyonly — проверяет системные файлы на наличие повреждений, но не исправляет их автоматически.
- sfc /scannow — выполняет полную проверку системы.
- cacls — изменяет права доступа к файлам. Пример: cacls file.txt /g UserName:F даст пользователю полный доступ к файлу.
- icacls — расширяет возможности команды cacls и предоставляет дополнительные параметры для управления правами доступа.
- takeown — позволяет взять владение файлом или директорией. Так, takeown /f file.txt предоставит доступ к файлам.
- attrib — изменяет атрибуты файлов и папок. Например, attrib +r file.txt сделает файл доступным только для чтения.
Команды для диагностики и устранения неполадок
Команды из раздела помогают находить и устранять неполадки в системе, восстанавливать загрузочные параметры и проверять целостность данных на диске, а также они позволяют решать проблемы, связанные с запуском операционной системы или со сбоями на уровне файловой системы.
- chkdsk — проверяет диск на наличие ошибок и исправляет их. Так, chkdsk C: /f выполнит проверку диска C.
- bootrec — восстанавливает загрузочный сектор.
- bcdedit — управляет параметрами загрузки системы.
- bcdedit /set {current} safeboot minimal — включает безопасный режим.
Команды для скриптинга и автоматизации
Команды, приведенные ниже, предназначены для создания сложных сценариев выполнения команд, что позволяет автоматизировать повседневные задачи и более эффективно управлять процессами.
- for — создает цикл для выполнения команд. Например, for %i in (1 2 3) do echo %i выведет числа 1, 2, 3.
- if — выполняет условное выполнение команд.
- goto — перенаправляет выполнение скрипта к определенной метке.
- call — вызывает другую команду или скрипт.
Команды для управления сетевыми подключениями
Команды для управления сетевыми подключениями предоставляют возможности для настройки, диагностики и оптимизации сетевых параметров и соединений, позволяя управлять IP-адресами, подключаться и отключаться от сетей.
- ipconfig /release — освобождает текущий IP-адрес, назначенный DHCP сервером, что позволяет при необходимости сбросить сетевое подключение.
- ipconfig /renew — обновляет IP-адрес, полученный от DHCP сервера. Часто используется после команды ipconfig /release для восстановления подключения.
- ipconfig /flushdns — очищает кэш DNS, если изменился DNS-сервер или необходимо устранить проблемы с доступом к сайтам.
- ipconfig /displaydns — выводит содержимое кэша DNS, часто используется для диагностики проблем с DNS.
- netsh interface ip set address — используется для назначения статического IP-адреса сетевому интерфейсу. Пример: netsh interface ip set address Ethernet static 192.168.1.100 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1.
- netsh wlan show drivers — выводит информацию о драйверах беспроводной сети, что полезно при настройке Wi-Fi подключения.
- netsh wlan show interfaces — отображает текущие активные беспроводные подключения и их параметры, например, мощность сигнала.
- netsh wlan connect — подключает к указанной Wi-Fi сети. Для этого нужно ввести: netsh wlan connect name=MyWiFi.
- netsh wlan disconnect — отключает текущее беспроводное подключение.
- netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state — управляет состоянием брандмауэра Windows – netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state off отключает брандмауэр для всех профилей.
- netsh int ip reset — сбрасывает настройки IP стека (TCP/IP) к значениям по умолчанию, помогая при сетевых неполадках.
- route add — добавляет маршрут в таблицу маршрутизации. Например, route add 192.168.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 добавит маршрут для подсети 192.168.2.0 через шлюз 192.168.1.1.
- route delete — удаляет указанный маршрут из таблицы маршрутизации.
- netsh interface show interface — выводит список всех сетевых интерфейсов в системе, включая их состояние и тип.
- net view — отображает список компьютеров в локальной сети – net view \\server покажет общие ресурсы на указанном сервере.
- net use /delete — удаляет существующее подключение к сетевому ресурсу. Так, net use Z: /delete отключает сетевой диск Z:.
- ftp — открывает FTP-клиент для передачи файлов между локальной и удаленной системами. Например, по команде ftp ftp.example.com ПК подключится к FTP-серверу.
- telnet — используется для подключения к удаленным системам через Telnet-протокол. Так, telnet example.com 23 подключит ПК к серверу на порту 23.
- getmac — выводит MAC-адреса всех сетевых интерфейсов компьютера.
Команды для управления печатью
В этом разделе команды для управления печатью позволяют эффективно управлять процессом печати (включая очередью на печать), настройками принтеров и заданиями на печать.
- print — отправляет файл на печать. Например, print C:\Documents\file.txt отправит текстовый файл на принтер по умолчанию.
- rundll32 printui.dll,PrintUIEntry — открывает диалоговое окно для установки или управления принтерами – rundll32 printui.dll,PrintUIEntry /in /n\\server\printer установит сетевой принтер.
- net print — отображает список заданий на печать – net print \\server\printer покажет очередь печати на указанном принтере.
- net stop spooler — останавливает службу диспетчера очереди печати (spooler), особенно когда требуется устранить зависшие задания печати.
- net start spooler — запускает службу диспетчера очереди печати после её остановки.
- wmic printer list brief — выводит список установленных принтеров с краткой информацией о каждом из них.
- wmic printer where default=true get name — выводит имя принтера, установленного по умолчанию.
- wmic printer where name=’PrinterName’ delete — удаляет указанный принтер из системы.
- wmic printerconfig — отображает информацию о конфигурации принтера, включая его настройки и параметры печати.
- cscript prnjobs.vbs — используется для управления заданиями печати через скрипт prnjobs.vbs, который можно использовать для удаления, приостановки или возобновления заданий.
Дополнительные команды в Windows
В дополнение к основным инструментам для управления системой, командная строка Windows предоставляет ряд дополнительных команд, которые расширяют возможности администрирования и диагностики.
- wevtutil — управляет журналами событий Windows. Например, wevtutil qe System выведет события из системного журнала.
- tzutil — управляет настройками часовых поясов. tzutil /s Pacific Standard Time установит часовой пояс на Тихоокеанское стандартное время.
- taskkill — завершает процесс по его PID или имени. Так, taskkill /F /PID 1234 завершит процесс с PID 1234.
- powercfg /hibernate off — отключает режим гибернации.
- powercfg /energy — создает отчет об использовании энергии системой.
Windows’ celebrated CLI (Command-Line Interpreter) is a treasure trove of hidden features, tools, and settings.
Command Prompt lets you tap into every area of your Operating System, from creating new folders to formatting internal and external storage.
To help you navigate cmd.exe like a pro, we’ve prepared a compressive list of cool CMD commands to make you feel like a hacker.
Getting Started with Command Prompt
Unsure about using cmd.exe? Not a problem; just follow this step-by-step guide to get started.
First of all, you’ll need to fire up the Command Prompt Window by hitting Windows Key + R and typing in cmd in the Run window. Hit Enter and CMD will momentarily pop up on your screen.
There’s more than one way to prompt command.
For the second method, hit the Windows key to bring up the Start Menu. After that, type in cmd or command prompt in the search bar and left-click on the icon.
To sum up…
Method 1: Windows key + R -> type cmd -> press Enter
Method 2: Windows key -> type cmd or command prompt -> left-click on the CMD icon.
Now that Command Prompt is up and running, it’s time to have some fun. We’re going to start with a couple of basic commands and then move on to the more advanced stuff.
Basic Windows CMD Commands
Ver– displays operating system version on the screen (e.g., Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.19045.2486])Date– displays the current date on the screen. Can also be used to change the date.Shutdown– shuts down your machine.Taskkill– allows you to terminate a process or a running app. To use this, type intaskkillfollowed by ‘/f’, ‘/im’, and the name of the process or app you want to terminate (e.g. winword.exe). So, if we want to kill all instances of MS Word, we would need to type intaskkill /f /im winword.exe. Hit Enter to confirm.Color– changes the color of the foreground and background. For instance, typing in ‘color fc’ will make the background bright white and the foreground (i.e., writing) light red.Getmac– displays your machine’s MAC address.Ipconfig– displays your IP address.Ping– sends data packets to a specific IP address or network (e.g.,ping google.com). Very useful in troubleshooting Internet connectivity issues.Pathping– maps the connection to a specific IP address. Can also be used to troubleshoot connectivity issues.Nslookup– displays the DNS record or IP address of a specific domain (e.g.,nslookup facebook.com).Chkdks– performs a routine check on a specified disk and corrects errors.Gpupdate– updates group policies. Usually used in conjunction with the force (/f) argument.Mkdir– creates a new directory.Tasklist– displays a list of all live processes and applications.Timeout– very useful when working with batch files. This command allows you to delay execution for a specified number of seconds. When appended the -1 value, process execution will be delayed indefinitely. The computer will wait for a keystroke to continue.Type– this command allows you to view text files (.txt) in your cmd window.Vol– displays disk volume information such as serial numbers or labels.Systeminfo– displays useful sys info such as Host Name, OS version, processor, BIOS version, time zone, applied hotfixes, and more.Netstat– displays info about active TCP connections.Help– outputs a list of commonly used commands.
Advanced Windows CMD Commands
And now it’s time to lose the kid gloves and talk about some more advanced (and cool) CMD commands.
Telnet– allows you to establish a remote, Telnet-type connection.Before attempting to ‘dial’, ensure that both machines support Telnet communication and that the client software is installed.To initiate this type of remote session, you must specify the IP address of the server or the main computer followed by 13531 (e.g. telnet 60.227.102.16 13531). The number at the far end of the command represents the communication port used by the Sage 50 Connection Manager.If the setup’s done right, your CMD cursor should become blank. Otherwise, it will return the message “telnet is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program, or batch file”. This error message appears when Telnet’s not enabled on the machine.To switch it on, click on the Start button and head to Control Panel. Under Programs and Features, select Turn Windows Features on or off.Scroll down until you see Telnet Client and Telnet Server. Enable both features and click the Ok button to confirm. Restart your machine. Open a new CMD window and retry the connection.Klist– this command allows you to visualize cached Kerberos tickets and retrieve useful information such as encryption type, server, start time, renew time, session key type, cached flags, and more.FC– changes made to files may not always be obvious.To see if a file has been modified, use the File Compare (FC) command in CMD. You can perform two kinds of file comparisons: ASCII or binary.For instance, you may want to use an ASCII-type comparison when working with a text file. On the other hand, for media (e.g. pictures, clips, etc.) a binary comparison would be the proper approach.Powercfg– this is a great diagnostic tool for laptop users.Ever wondered why your battery’s running out so fast, leaving you high and dry, possibly in the middle of an (important) e-meeting? Well, you can quickly find out by running this Power Configuration utility in CMD. Powercfg usually works best with the ‘-energy’ argument.So, after running the combo ‘powercfg -energy’, your machine will begin a 60-second power test. It will generate a power efficiency diagnostic report. If any errors are found, they will be highlighted in the second section of the report, along with recommendations.Cacls– this nifty command allows you to display or modify ACLs (i.e. Access Control Lists) of various files.Some of its more popular uses include granting specific access rights to users (i.e. Read, Write, Change, or Full Control), revoking permissions, denying specific users, or replacing the user’s access rights. Here’s a quick example of how to use the Cacls command.
Step 1. Create a text document on your desktop area. Name it ‘test.txt’
Step 2. Open CMD.
Step 3. Navigate to the Desktop directory by typing in ‘cd desktop’
Step 4. Type in ‘cacls test.txt’. This will display users and permissions.
Step 5. In this example, we will update (replace) the default rights of user BUILTIN\Administrators from F (i.e. Full Control) to R (i.e. Read only) using the /P argument.
Step 6. Type in ‘cacls test.txt /P BUILTIN\Administrators: R
Step 7. Type ‘Y’ and press Enter to confirm changes.
6. ARP – display or commit changes to the ARP cache.
To view the contents of the cache, type in ARP -a and press ENTER. If you want to make changes to the ARP cache such as adding a static entry use ARP-a, followed by the Internet address (i.e. IP) and the physical address (i.e. MAC).
For instance, if we have a new host and want to associate its IP to its physical address, we will need to type in the following line: ARP-a [IP_address] [Physical_Adress].
7. Chgport – use this command to display or remap COM ports.
8. Cipher – check the encryption status of your files or folders (i.e., NTFS partitions only).
9. Cmdkey – displays and allows you to make modifications to all host-stored passwords and usernames.
10 Dispdiag – allows you to diagnose display-related issues. Can create log dump files when used together with the [-d] argument.
11. Driverquery – displays a list of all the drivers installed on the machine.
12. Fondue – install optional MS Windows updates from CMD.
13. Hwrcomp – this command allows you to install or update existing handwriting recognition dictionaries.
14. Makecab – used to compress files and folders.
15. Mrinfo – displays router interface info.
16. Pentnt – this command allows to user to detect so-called floating-point division errors in Pentium processors.
17. Reagentc – use this command to configure the Windows Recovery Environment.
18. Recover – retrieve data from a bad disk.
19. Repair-bde – useful in decrypting/repairing a damaged drive that’s been encrypted with BitLocker.
20. Runas – execute an application with another user’s credentials.
21. Chgusr – modify the install mode for your terminal server.
22. Cmstp – used to install or uninstall a service profile for the Connection Manager.
23. Ctty – modify the default input or output devices.
24. Forfiles – Selects and executes a command on a file or set of files.
25. Format – Prepares a disk for use with Windows, by formatting it.
26. Fsutil – Performs tasks related to file allocation table (FAT) and NTFS file system, such as managing reparse points or sparse files.
27. Ftp – Transfers files to and from a remote network site using the File Transfer Protocol.
28. Getmac – Displays the Media Access Control (MAC) address for network adapters.
29. Goto – Directs the Command Prompt to a labeled line in a batch program.
30. Gpresult – Displays Group Policy information for a machine or user.
31. Gpupdate – Refreshes local and Active Directory-based Group Policy settings, including security settings.
32. Graftabl – Enables the ability to display an extended character set in graphics mode.
33. Hostname – Displays the host name portion of the full computer name of the computer.
34. Icacls – Displays or modifies discretionary access control lists (DACLs) on specified files.
35. If – Performs conditional processing in batch programs.
36. Ipconfig – Displays all current TCP/IP network configuration values and refreshes Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) settings.
37. Iscsicli – Starts the Microsoft iSCSI Initiator, used to manage iSCSI.
38. Klist – Displays or deletes Kerberos tickets.
39. Ktmutil – Starts Kernel Transaction Manager Utility.
40. Label – Creates, changes, or deletes the volume label of a disk.
41. Lodctr – Updates registry values related to performance counters.
42. Logman – Manages and schedules performance counter and event trace log collections on local and remote systems.
Did you get the cool CMD commands you wanted?
I’m always open to getting feedback. If you enjoyed the article or feel we’re missing anything, let me know by reaching out to us on social media. It’s a relatively short list of CMD commands but enough to show you what’s possible.
Don’t forget to stay safe.
If you liked this article, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, YouTube, and Instagram for more cybersecurity news and topics.
Newsletter
If you liked this post, you will enjoy our newsletter.
Get cybersecurity updates you’ll actually want to read directly in
your inbox.
Senior PR & Communications Officer
Experienced blogger with a strong focus on technology, currently advancing towards a career in IT Security Analysis. I possess a keen interest in exploring and understanding the intricacies of malware, Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), and various cybersecurity challenges. My dedication to continuous learning fuels my passion for delving into the complexities of the cyber world.
