Provide feedback
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
Sign up
Appearance settings
Learn how to easily install and use the Redis extension locally in XAMPP to communicate with Redis Servers.
I’m sure you may have already heard about Redis, the in-memory data structure store, used as a database and cache. Sooner or later, if you ever work with a project built with PHP that handles a significant amount of traffic and may require horizontal scaling, you will have to work with Redis. Of course in a local environment, it would be great to work as well with Redis, so you don’t have to create huge conditionals to check if it’s available in the current environment and run some logic if it isn’t. It would be simpler to have Redis available locally as well, just to make the whole project work as usual in your workstation.
In this article, I will explain how to easily install the Redis extension for PHP in your XAMPP installation in Windows.
Pre-installation notes
You need to know the following information about the PHP distribution that you are currently using in XAMPP:
| Name | Default value |
| Architecture (PHP) | x64 |
| Thread Safety |
Enabled TS: Stands for Thread Safety Enabled NTS: Stands for Thread Safety Disabled |
You can get those values with the function phpinfo() of PHP within an empty script:
<?php
phpinfo();Once you know these values, you should be able to follow the rest of the tutorial.
1. Download Redis DLL
The first thing you need is the dynamic link library of Redis, which fortunately for us is already compiled and available in the PECL repository of PHP on this website. You may select the version that fits your needs, in my case, I will use the latest stable version as I’m using PHP 8, click on the DLL link with the windows icon:
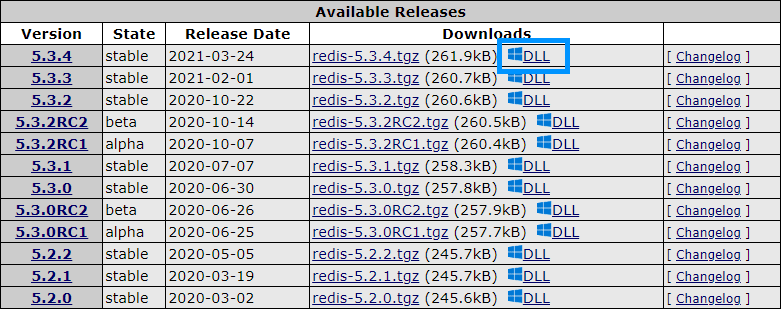
Then a new window will load, in this page scroll to DLL List and click on the right version for your PHP version with correct architecture (of XAMPP, not your operative system) and the Thread Safe in case that it’s enabled in your distribution). In my case, I’m using the latest version of XAMPP with PHP 8.0 of 64 bits with Thread Safety Enabled, so in my case, I will download the following one:
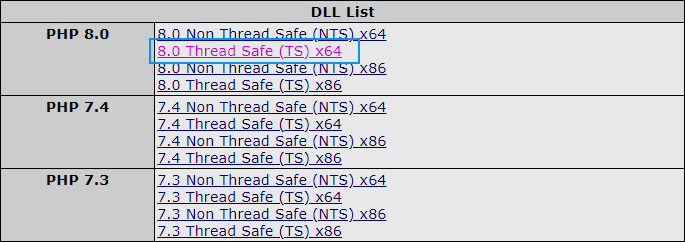
This will start the download of a ZIP file. Of our interest, is the php_redis.dll file that is included in it, so keep it at hand as you will need the file in the next step.
2. Store DLL in ext directory and enable the extension in php.ini
Now, from the downloaded zip, move the php_redis.dll file to the ext directory of PHP in your XAMPP directory (C:\xampp\php\ext):
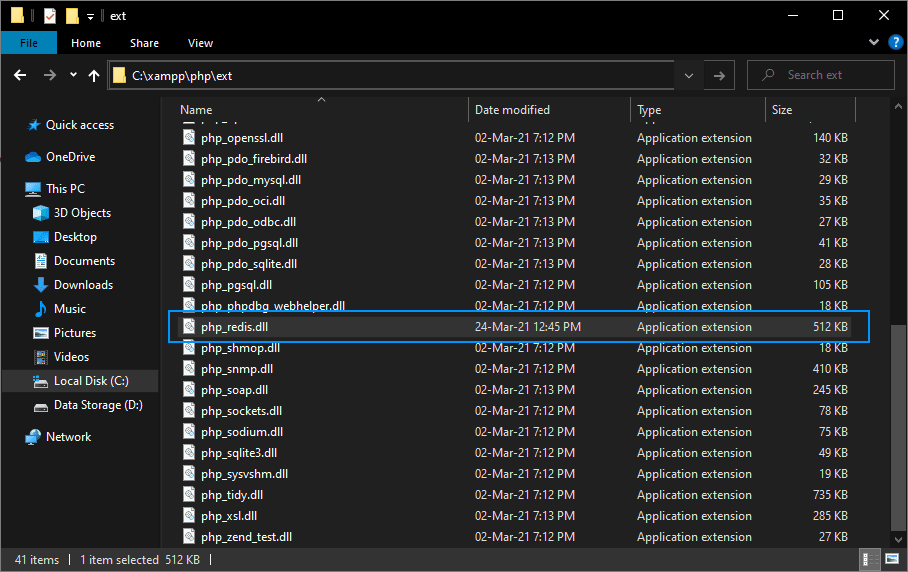
This will allow us to use the extension in PHP, however, we need to enable it as well. Open the php.ini (C:\xampp\php\php.ini) file and enable the extension adding the following new line under the extensions area:
extension=redisYou won’t find the mentioned line in the configuration file, so that’s why you need to write it by yourself. Save the changes of the ini file and restart Apache, so the changes will apply once it starts again.
3. Testing if the extension is enabled
And that’s it! After restarting apache and enabling the extension in the php.ini, you should be able to use Redis with PHP. You can easily verify if the extension is enabled either by checking in your phpinfo():
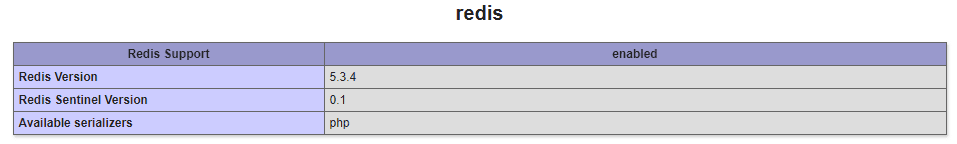
Or alternatively, run some code that uses Redis in case that you have a server running Redis through docker locally or a real Redis server, for example, the following code should succeed and print the username «sdkcarlos»:
try {
// Create a Redis Instance
$redis = new \Redis();
// Try to connect to a redis server
// In this case within the host machine and the default port of redis
$redis->connect('127.0.0.1', 6379);
// Define some Key
$redis->set('user', 'sdkcarlos');
// Obtain value
$user = $redis->get('user');
// Should Output: sdkcarlos
print($user);
} catch (Exception $ex) {
echo $ex->getMessage();
}Happy coding ❤️!
Install Redis & Configure it with WinSW
1. Install PHP 8.2 Redis Extension
Click Here to download PHP 8.2 NTS x64 zip file.
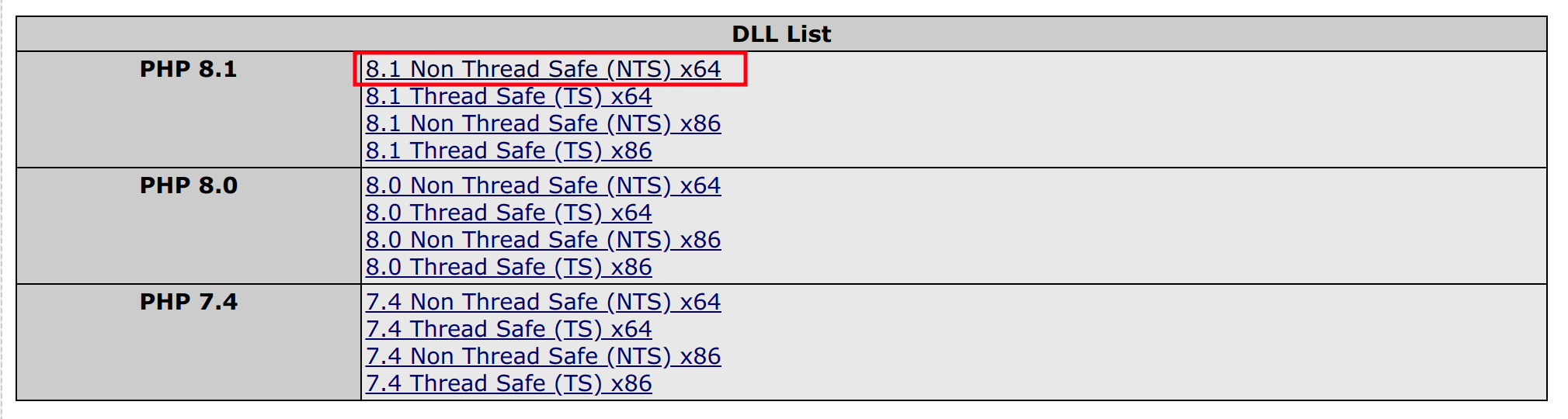
- Unzip the php-redis zip file, a folder will be created, go inside the folder, copy the php_redis.dll file and paste it in C:\php8.2\ext. (C:\php\ext incase of Apache WebServer).
- Now enable php redis extension in php.ini configuration located in C:\php8.2. (C:\php incase of Apache WebServer).
- Now go to Server Manager, open IIS Server and restart it. (or restart Apache incase of Apache WebServer)
2. Install Redis
Click Here to download last recent release of Redis.

Execute the installer to perform the required installation steps
- Accept the terms in the License agreement.
- Add the Redis installation folder to the PATH environment variable.

- Set the Max Memory Limit from 300-500 MB.
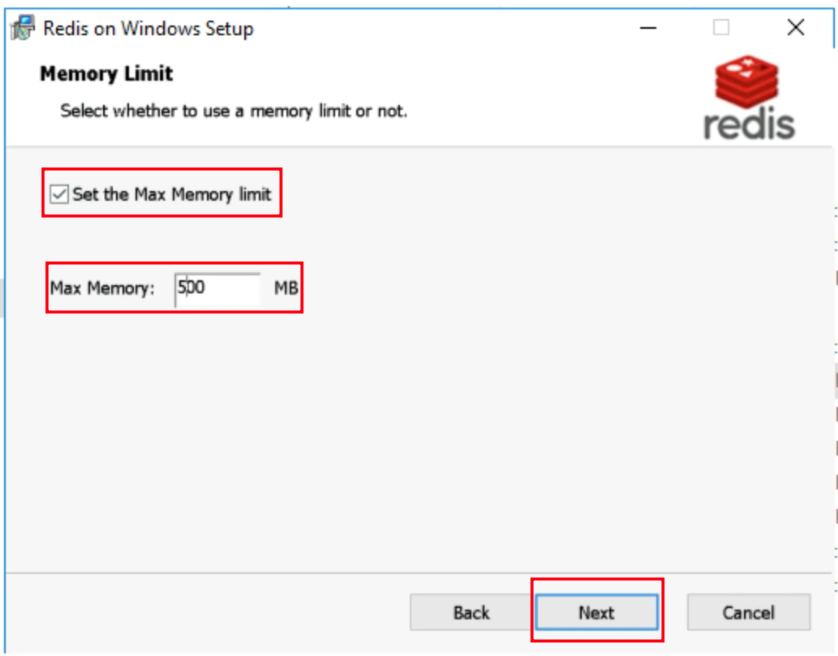
The Redis installation is finished.
- Now go to windows menu > Run > Services, This can be done by following shortcut win+R, type services.msc & click OK, it will open a new Services tab.
- Find Redis right click on it & go to Properties > Recovery a new tab will open.
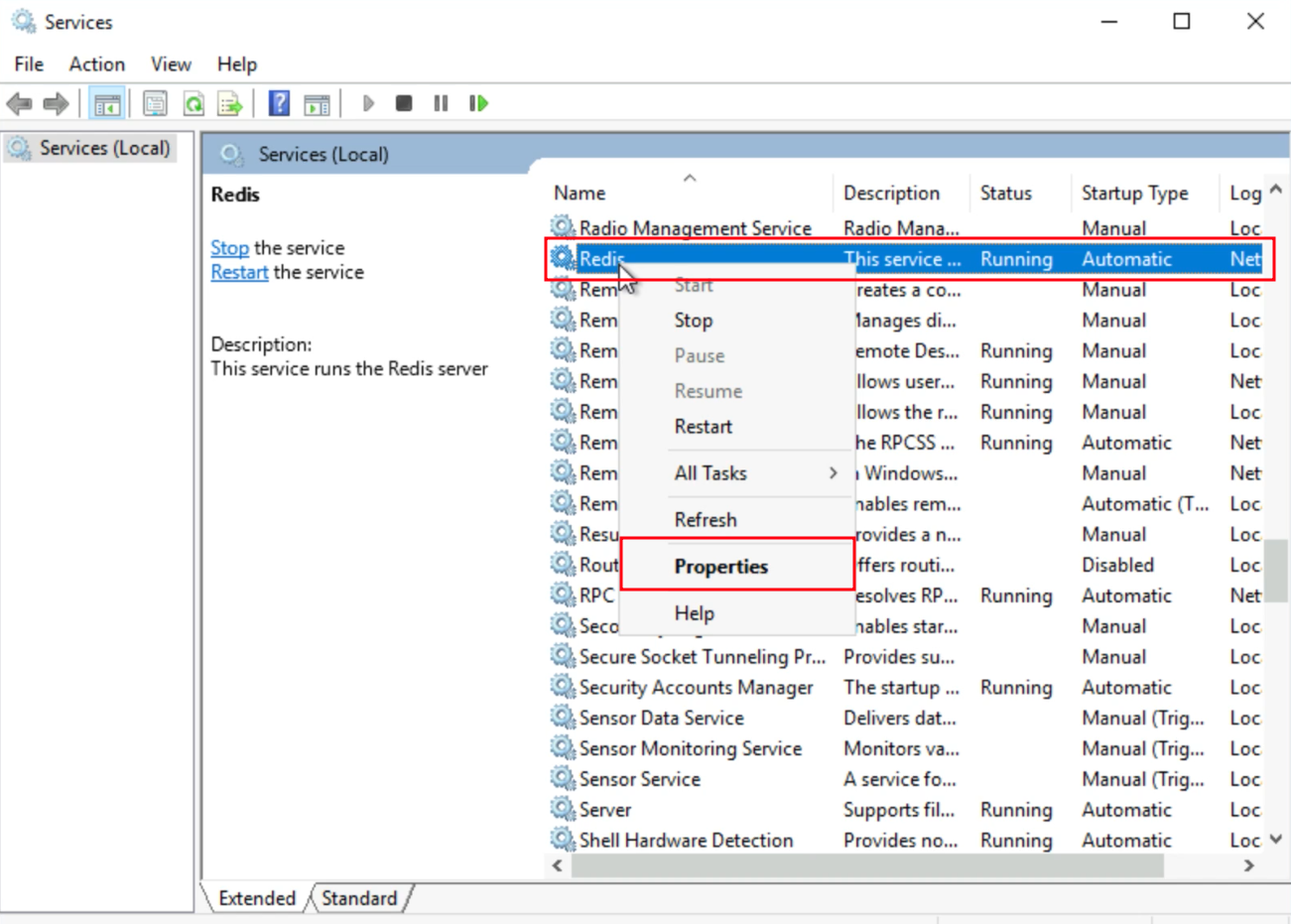
- Change first failure, second failure & subsequent failure from Take No Action to Restart the Service & click OK.
Redis has been successfully installed, this can be confirmed in Command Prompt by typing redis-cli, a loopback address will be shown in the Command Prompt.
Install WinSW Service
Download WinSW Config File.
- IIS
- Apache
Unzip the WinSW-{version}.zip file.
Go inside the folder & copy the WinSW folder & paste it in C:\ .
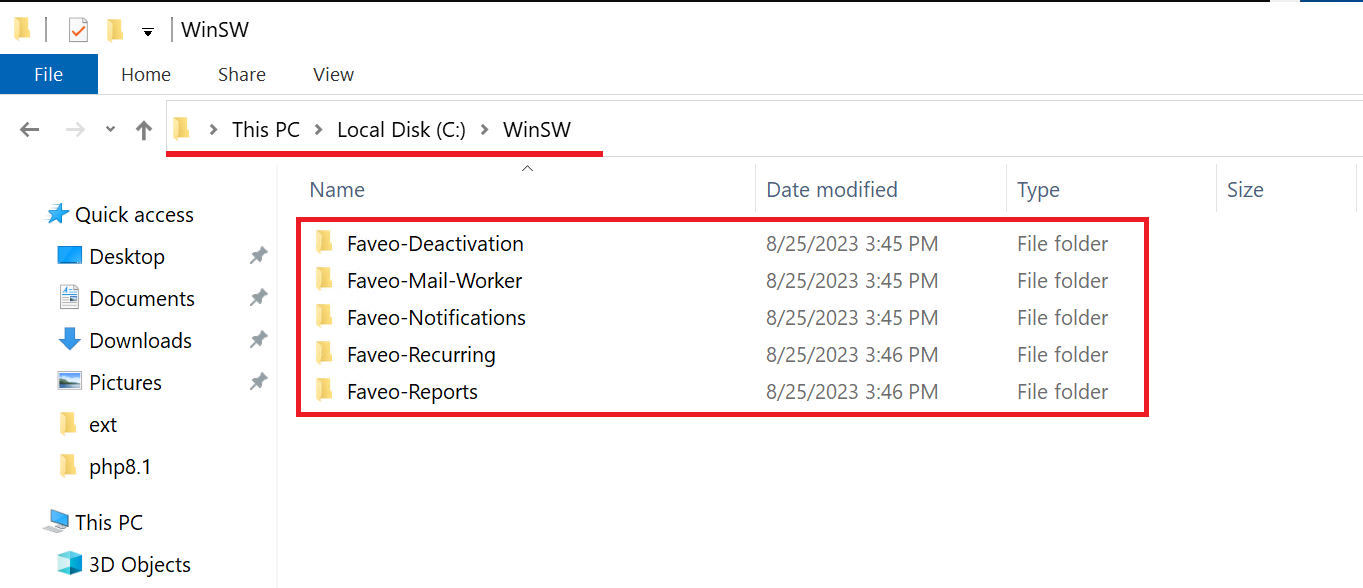
4. General Instructions to Create WinSW Services
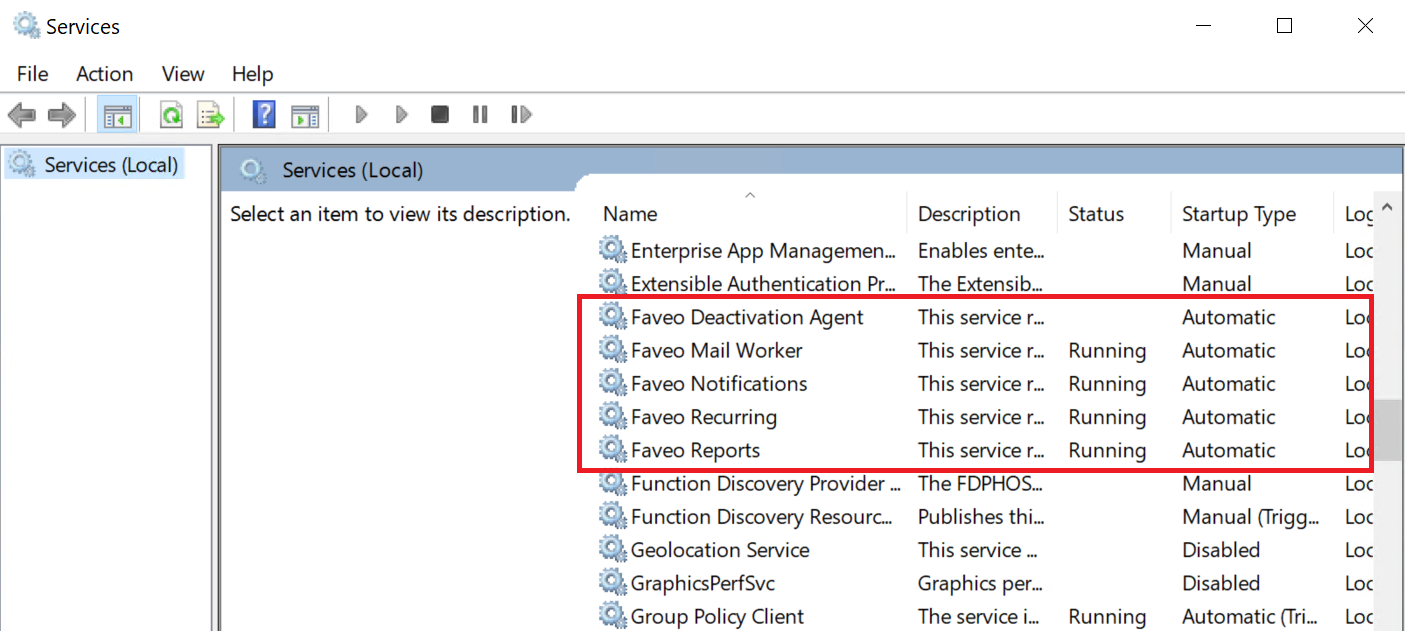
NOTE: These are the General Instructions to create WinSW Services for Faveo. The actual ones are listed below as Faveo-Mail-Worker, Faveo-Recurring, Faveo-Reports, Faveo-Notifications & Faveo Deactivation.
Go to Command Prompt and configure WinSW-SERVICE by typing the following commands. (Faveo-Mail-Worker, Faveo-Recurring, Faveo-Reports, Faveo-Notifications & Faveo-Deactivation are to be configured in actual).
- Install your application as a service using the following command:
This will register your application as a Windows service.
Verifying the Installation
After installing the service, you can use standard service management commands to control it. For example:
- Start the service:
- Checks the status of the service.
- Stop the service:
- Restart the service:
Uninstalling a Service
If you need to remove the service:
Uninstall the service using the following command:
Follow the below steps to create WinSW Services for Faveo-Mail-Worker, Faveo-Recurring, Faveo-Reports, Faveo-Notifications & Faveo Deactivation.
- FAVEO WORKER
Open a Command Prompt window with administrator privileges.
Navigate to the directory containing the WinSW executable and your application files using the cd command.
cd C:\WinSW\Faveo-Mail-Worker
Install your application as a service using the following command:
Start the service:
- FAVEO RECURRING
Open a Command Prompt window with administrator privileges.
Navigate to the directory containing the WinSW executable and your application files using the cd command.
cd C:\WinSW\Faveo-Recurring
Install your application as a service using the following command:
Start the service:
- FAVEO REPORTS
Open a Command Prompt window with administrator privileges.
Navigate to the directory containing the WinSW executable and your application files using the cd command.
cd C:\WinSW\Faveo-Reports
Install your application as a service using the following command:
Start the service:
- FAVEO NOTIFICATIONS
Open a Command Prompt window with administrator privileges.
Navigate to the directory containing the WinSW executable and your application files using the cd command.
cd C:\WinSW\Faveo-Notifications
Install your application as a service using the following command:
Start the service:
- FAVEO DEACTIVATYE AGENTS
Open a Command Prompt window with administrator privileges.
Navigate to the directory containing the WinSW executable and your application files using the cd command.
cd C:\WinSW\Faveo-Deactivation
Install your application as a service using the following command:
Start the service:
Open service manager and check status of all the services configured by WinSW.
Redis is no longer supported in Windows, but the version
3.2.1is still available to use (ref), so that’s why laragon contain version3.*only. If you want to taste the latest redis version, using Docker through Laradock would be an alternative.
Installing PHP Redis Extension
If you right-click on the dashboard & check on PHP > Extensions, you will not find redis extension because it doesn’t come up with Laragon by default. So you have to add it manually, but yet it so easy.
Downloading The PHP Redis Extension DLL File
Go to https://pecl.php.net/package/redis and find the right match your current PHP version but also use the latest stable available. In my case, it was version 5.3.4 at the moment and it supports PHP 8.0, 7.4, 7.3.

Click the Windows icon DLL link to get the available distribution for the version. Download the archive that match with your PHP version. You might be confuse which one between Non-Thread-Safe (NTS) and Thread-Safe (TS) should you pick to download. To find out, just check on your Laragon dashboard and see the php version along with NTS or TS indication.

Adding the DLL File to the PHP Extension Folder
On the downloaded archive, you should find the php_redis.dll file.

copy or move the file to the C:\laragon\bin\php\php-7.4.19-Win32-vc15-x64\ext (change to your own path), and then add the line extension=php_redis.dll to the C:\laragon\bin\php\php-7.4.19-Win32-vc15-x64\php.ini file.
the
php.ini filewas generated after a version of php in laragon was run for the first time.
you should see that Redis extension is available now.

Starting The Redis Server
If you installed the full laragon, redis is availabe in this path C:\laragon\bin\redis\redis-x64-3.2.100 (change to your own path). To run the redis server, you can use Command Prompt to execute the redis-server.exe.

And you can also stop it later using Ctrl + C.
The phpRedisAdmin
The phpRedisAdmin also available in the full laragon installation and can be accessed at http://localhost/redis

Redis is a data store that stores data primarily in memory. It’s faster than traditional databases, and has grown quite popular.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn the basics of how Redis works, when to use it, how to install it on your device, and how to use it as a caching system in a PHP web application.
What Is Redis?
Redis is a data store – like a database, but one that stores data primarily in-memory. This makes it much faster than traditional databases where data is stored in disks. Because of this speed, Redis is often used as a caching tool.
Redis can store data in any data type, as it uses a key-value pair system to store data. This is also unlike traditional databases that use documents or rows.
You can think of a Redis database as a big JSON object, where everything in the database is a key-value pair. This means it might not be the best place to store structured data.
You can also use Redis as a database, as it has the ability to write data to disk for persistence. You can configure Redis to persist data either periodically or after every command you issue. When Redis isn’t configured to persist data, it is very volatile, and a system crash would result in a loss of data.
Redis is popular in production level applications and it’s used by large companies like Twitter, Github, SnapChat and StackOverFlow.
- For One Time Passwords (OTPs): These are usually generated to be used once, and have short lifespans. With Redis’ ability to set an expiry date for data, you can safely store the OTP without worrying about deleting them after a certain period.
- For frequently accessed resources: For data that doesn’t change too frequently but is accessed a lot, you can use Redis to save time that would have been spent querying the database or making a call to some external service.
- For heavy duty queries: For database queries that take time, and also won’t change too often, use Redis to reduce this time by storing the results for as long as you like.
How to Install Redis
You can install Redis on any operating system. Here are the instructions for macOS, Windows Subsystem for Linux, and Linux.
macOS
To install Redis on macOS, run:
brew install redis
Then, run this command to start Redis:
redis-server
Windows Subsystem for Linux and Linux
Redis doesn’t exactly support the Windows operating system yet, so you can install WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) on windows to have a Linux environment.
To install Redis on Linux, run:
curl -fsSL https://packages.redis.io/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/redis-archive-keyring.gpg
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/redis-archive-keyring.gpg] https://packages.redis.io/deb $(lsb_release -cs) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/redis.list
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install redis
Then, run this command to start Redis:
sudo service redis-server start
Now that Redis is installed, you can test it by running redis-cli ping. This will output «PONG». Like this:

Testing Redis Installation
Redis Basics
To use Redis as a REPL or as a standalone application, run redis-cli. It will open the REPL environment.
How to Set Data
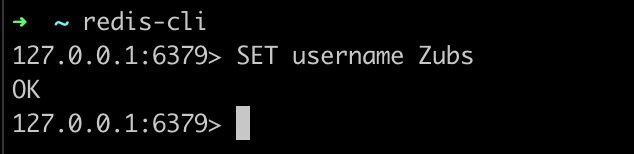
Use the SET keyword to set a key value pair in Redis. To set a username key to the value Zubs , run this:
SET username Zubs
Setting a key-value pair
How to Get Data
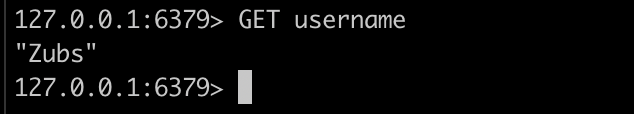
To get the recently saved username key, use the GET keyword like this:
GET username
Getting a value by key
How to Delete Data
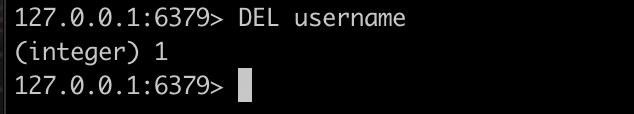
You can also delete a previously stored key using the DEL keyword like this:
DEL username
Deleting a value by key
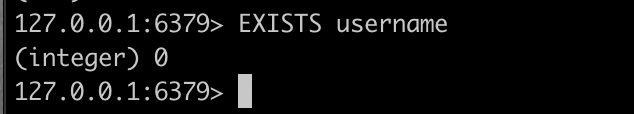
How to Check if a Value Exists
You can check for the existence of a key by using the EXISTS keyword. It returns 0 when the key doesn’t exist, and 1 if it does. You can test by checking if the recently deleted username key exists. Like this:
How to Set a Time to Live for Keys
Redis lets you specify how long some key should exist for when creating it. This is one really great feature of Redis. To do this, use the SETEX keyword like this:
SETEX key seconds value
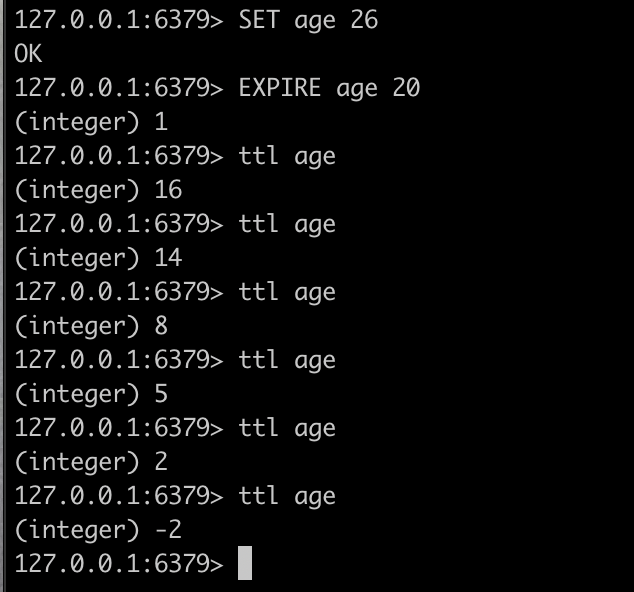
You can check the time to live for a specific key using the TTL keyword. This returns -1 if the key has no set expiration, meaning it will be stored indefinitely. It returns -2 if the key doesn’t exist. And it returns the time in seconds if the key exists.
You can set an expiration time in seconds for a key previously created without an expiration time using the EXPIRE keyword. For example, create a key to store a variable age with a value of 26.
SET age 26
Then, set an expiration time of 10 seconds for it.
EXPIRE age 20
Check the time left to live repeatedly a couple of times to see how it actually reduces and eventually doesn’t exist again.
How to Build a Simple Application with Redis
To help you understand how Redis works, we’ll now build a basic web application that uses Redis to cache data to load responses faster. You’ll be building a simple application that fetches images data from JSONPlaceholder and returns them.
Create a New PHP Project Using Composer
Create a new folder for the project, change directory into the newly created folder, and run the following compound to create a new composer project:
composer init -q
This will create a new composer.json file that should look like this:
{
"require": {}
}
Next, create a public folder to house your public facing code files. Then create a new index.php file in the folder.
Put in some boilerplate content in the PHP file for now and start a server.
<?php
echo "Hello World!";
php -S localhost:8080
Install a Simple Router and Handle Requests
To complete the project, install a simple PHP router, Altorouter, and a web client, Guzzlehttp.
composer require altorouter/altorouter guzzlehttp/guzzle
Update the index.php to contain this code:
<?php
// Import composer autoload file
require_once __DIR__ . '/../vendor/autoload.php';
// Import GuzzleHttp Client
use GuzzleHttp\Client;
// Instantiate router and web client
$router = new AltoRouter();
$client = new Client();
// Register Sample route
$router->map('GET', '/', function () {
// Set response Content-Type
header('Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8');
// Return basic response
echo json_encode(['data' => 'Hello World']);
});
/**
* Route to get all photos
*/
$router->map('GET', '/photos', function () use ($client) {
// Make request to JSONPlaceholder
$response = $client->request('GET', 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/photos');
header('Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8');
echo json_encode([
'data' => json_decode($response->getBody()->getContents())
]);
});
/**
* Route to get single photo by id
*/
$router->map('GET', '/photos/[i:id]', function (int $id) use ($client) {
$response = $client->request('GET', 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/photos/' . $id);
header('Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8');
echo json_encode([
'data' => json_decode($response->getBody()->getContents())
]);
});
$match = $router->match();
if( is_array($match) && is_callable( $match['target'] ) ) {
call_user_func_array( $match['target'], $match['params'] );
} else {
// no route was matched
header( $_SERVER["SERVER_PROTOCOL"] . ' 404 Not Found');
}
The code is pretty self explanatory. But, here’s a breakdown for clarity. From lines 1-11, the required classes GuzzleHttp and AltoRouter are imported and instantiated.
From lines 14-20, the first route is registered, with a simple closure that returns «Hello World!». Lines 25-45 register two more routes, one to fetch all photos, /photos and another to fetch a single photo, /photos/id.
The final lines are required based on documentation of the router package to actually execute the closures set in the routes declaration.
You can test these routes using Postman.
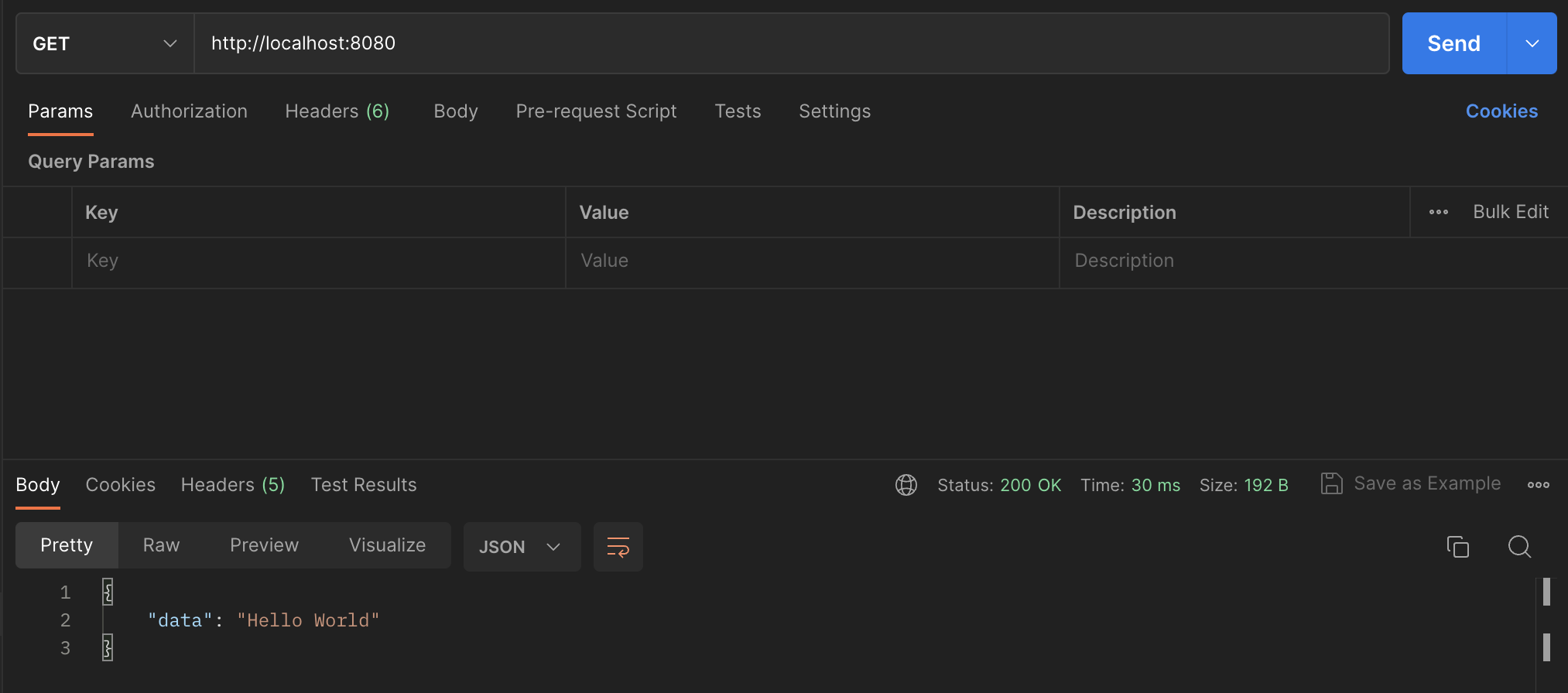
Hello World route
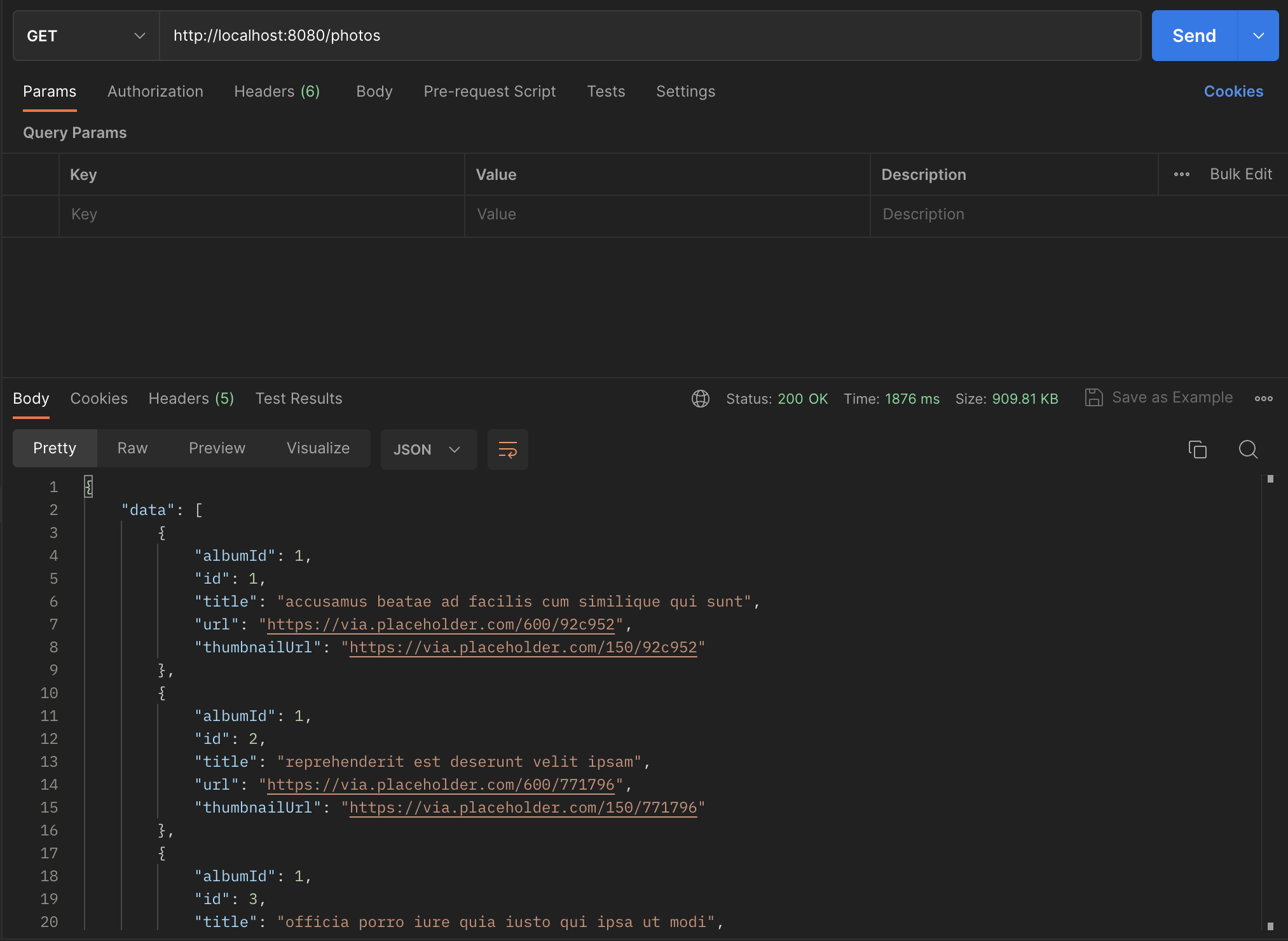
Get All Photos route
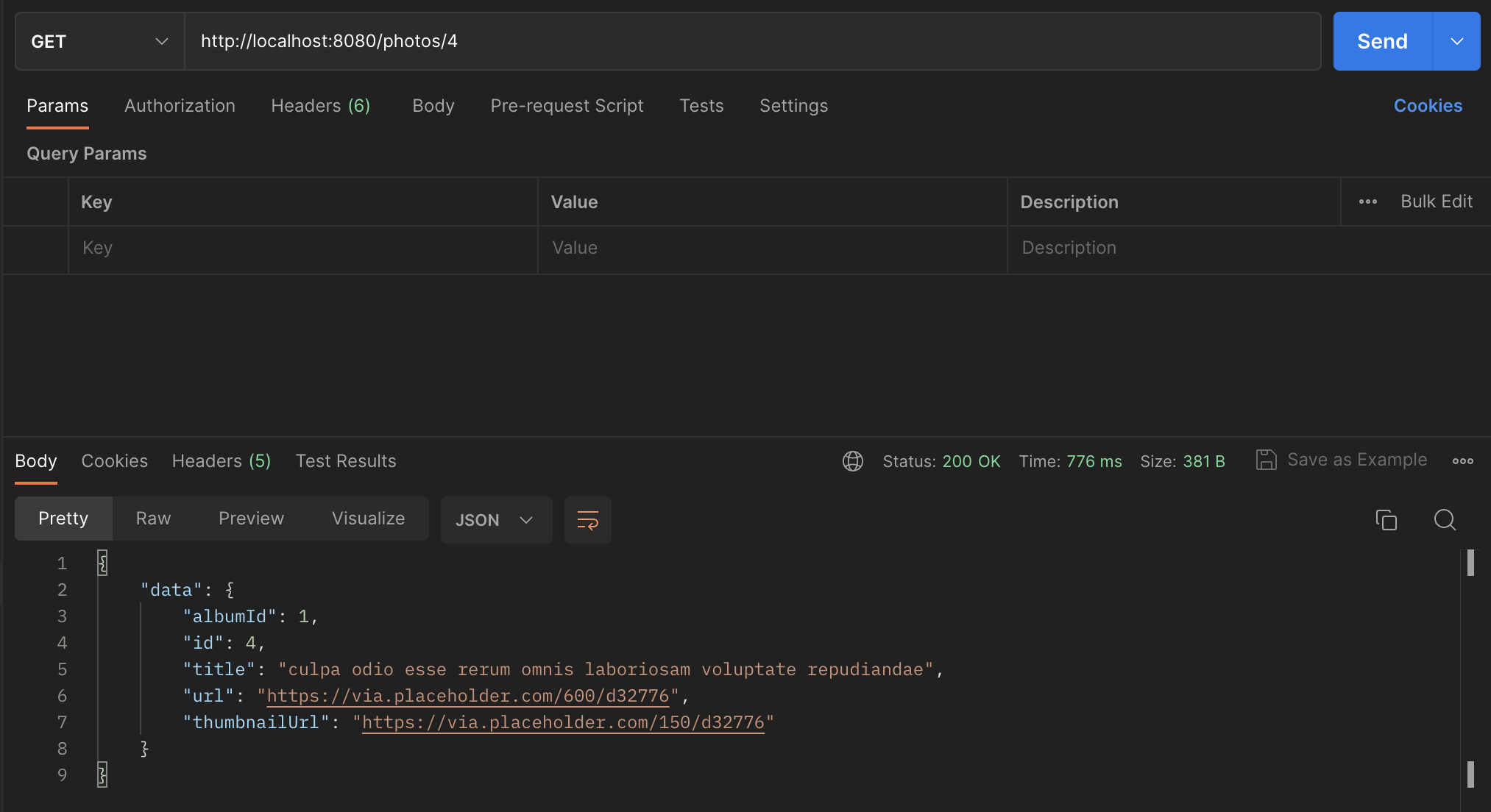
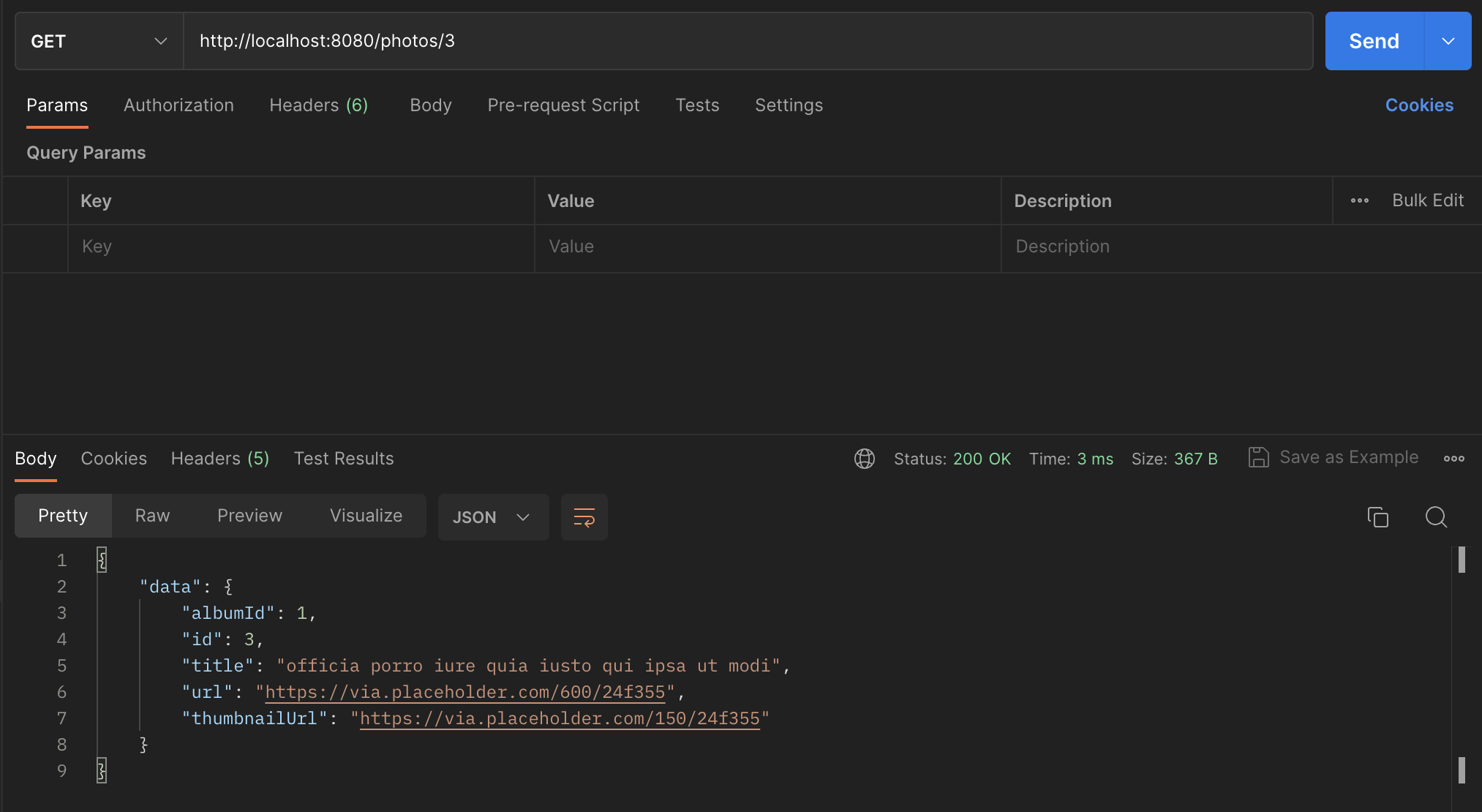
Get a Single Photo route
The /photos route takes an average of 1400ms per request. The /photos/id takes an average of 900ms per request.
Install and Instantiate Redis
These times can be reduced by caching the results of the original request to JSONPlaceholder, then returning a response from the cache instead of making a request every time.
To use Redis with PHP, install the PhpRedis extension. This extension provides an API for communicating with Redis. You can easily install it using the command:
pecl install redis
After installation, you can then use this class in your PHP project. Import the class and instantiate it at the top of your index.php file:
$redis = new Redis();
$redis->connect('127.0.0.1');
Having done this, you can now use Redis in your project.
How to Cache Data with Redis
Store the raw JSON response returned from JSONPlaceholder to Redis with an expiry time of 1 hour (3600 seconds).
$response = $client->request('GET', 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/photos');
$redis->setex(
'photos',
3600,
$response->getBody()->getContents()
);
Here, you create a new key called photos, give it an expiration time of 1 hour, then assign it the raw response gotten from JSONPlaceholder.
But at this point the API still takes a long time to respond. This is because you’re only storing this response, you’re not using Redis to return the response.
To fix this, when a new request comes in, check if you have some data previosuly stored in-memory. If yes, you return the data in-memory, else, you make a call to JSONPlaceholder.
Update the /photos block to this:
/**
* Route to get all photos
*/
$router->map('GET', '/photos', function () use ($client, $redis) {
// Check if Redis has the key
if (!$redis->exists('photos')) {
$response = $client->request('GET', 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/photos');
// Store the data for next use
$redis->setex(
'photos',
REDIS_STANDARD_EXPIRY,
$response->getBody()->getContents()
);
}
header('Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8');
echo json_encode([
'data' => json_decode($redis->get('photos'))
]);
});
Testing in Postman to see improvements, you see the average response time after the first call (the original call before it is cached) has dropped to an average of 20ms for the /photos route. This is an improvement of over 50x. Redis saves a lot of processing time and power.
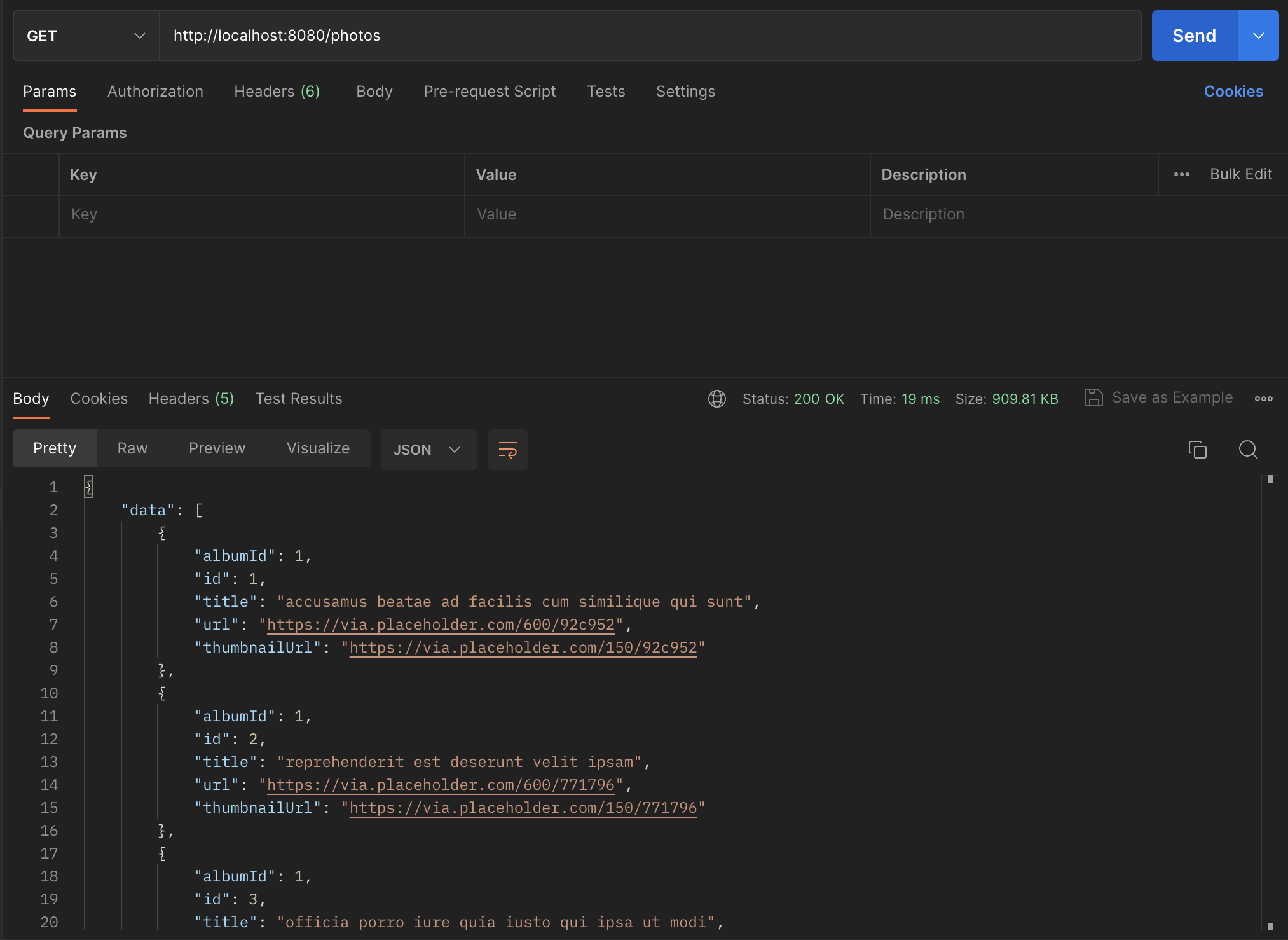
Update the /photos/id route to use Redis too:
$router->map('GET', '/photos/[i:id]', function (int $id) use ($client, $redis) {
if (!$redis->exists('photos:' . $id)) {
$response = $client->request('GET', 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/photos/' . $id);
$redis->setex(
'photos:' . $id,
REDIS_STANDARD_EXPIRY,
$response->getBody()->getContents()
);
}
header('Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8');
echo json_encode([
'data' => json_decode($redis->get('photos:' . $id))
]);
});
The /photos/id route is now also much faster as it takes less than 5ms to get a response, an improvement of over 45x.
Summary
I hope you now understand the what Redis is, its basics, and how you can use it to enhance the speed of your PHP web applications. You can find the code files used in this article on GitHub.
If you have any questions or relevant advice, please get in touch with me to share them.
To read more of my articles or follow my work, you can connect with me on LinkedIn, Twitter, and Github. It’s quick, it’s easy, and it’s free!
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
