Restarting a DNS (Domain Name System) server can vary slightly depending on the operating system and the DNS server software you are using. Below are step-by-step instructions for restarting DNS servers on various platforms.
On Windows Server
-
Using Services Management Console:
- Press
Windows + Rto open the Run dialog. - Type
services.mscand hitEnter. - In the Services window, locate
DNS Server. - Right-click on
DNS Serverand selectRestart.
- Press
-
Using Command Prompt:
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type the following command:
net stop dns - Then start the service again with:
net start dns
-
Using PowerShell:
- Open PowerShell as an administrator.
- To restart the DNS service, use:
Restart-Service -Name dns
On Linux (BIND)
-
Using Systemd (on modern Linux distributions):
- Open a terminal.
- Use the following command:
sudo systemctl restart named - You can check the status of the service with:
sudo systemctl status named
-
Using Service Command (older distributions):
- Open a terminal.
- Type the command:
sudo service bind9 restart - For some distributions, it might be:
sudo service named restart
-
For Other DNS Server Software (like dnsmasq):
- Use this command:
sudo systemctl restart dnsmasq
- Use this command:
On macOS
- Using Terminal:
- Open the Terminal application.
- You can restart the DNS service using the following command:
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder - This command will restart the mDNSResponder service, which handles DNS on macOS.
Notes:
- Backup Configuration: Before restarting, especially in production environments, ensure that you back up your DNS configuration files.
- Check Logs: After restarting the DNS server, check the logs for any errors or warnings to ensure that the server started correctly.
- Impact on Clients: Be aware that restarting a DNS server may temporarily affect clients that rely on it for name resolution.
These methods should help you successfully restart your DNS server based on the operating system and DNS software you are using. If you encounter issues, refer to the documentation specific to your DNS server software for troubleshooting.
This question has been answered using artificial intelligence. If there is any problem please contact us.

DNS servers translate names to DNS servers.
Domain Name Servers (DNS) translate domain names to IP addresses. When you create a DNS server on a Windows machine, DNS runs as a service on the computer. You can restart the DNS server to troubleshoot issues or restart the service after it stops running. The DNS service can be restarted using the Windows command line.
Step 1
Click the Windows «Start» button and select «Run.» Enter «cmd» into the text box and press «Enter.» This starts your Windows command prompt.
Step 2
Type «net stop dnscache» to stop the service. It may take a few seconds for the service to stop.
Step 3
Type «net start dnscache» into the command prompt and press «Enter.» This restarts the DNS service on the machine. The DNS service restarts. You can test the restart by opening a Web browser and entering a domain into the navigation text box. If the domain displays successfully, your DNS is working properly.
Windows
- Navigate to the desktop. …
- Right-click the Start button (the Windows logo in the lower-left).
- Choose Command Prompt (Admin).
- When asked whether to allow Command Prompt to make changes to your computer, select Yes. …
- Type «ipconfig /flushdns» and press Enter.
- Type «ipconfig /registerdns» and press Enter.
How do I start and stop DNS service?
Starting or stopping Domain Name System servers
To use the character-based interface to start all DNS server instances at once, type STRTCPSVR SERVER(*DNS) DNSSVR(*ALL) at the command line. To stop all DNS servers at once, type ENDTCPSVR SERVER(*DNS) DNSSVR(*ALL) at the command line.
Why is my DNS not connecting?
The “DNS server not responding” error message means that the DNS of the domain you want to reach is unavailable or your browser cannot connect to the internet. Possible fixes include restarting your router or modem, checking for network issues, and updating your browser.
How do I fix my DNS problem?
8 Strategies for Troubleshooting a DNS Failure
- Restart Your Software or Device. Sometimes simply exiting the browser completely for a few minutes will solve the problem. …
- Restart the Modem or Router. …
- Switch Browsers. …
- Pause Your Firewall. …
- Clear Your Cache. …
- Disable Extra Connections. …
- Keep Everything Updated. …
- Check DNS Settings.
How do I restart DNS services in Windows Server?
To restart the DNS Server service:
- On the DNS server, start Server Manager. To start Server Manager, click Start , and then click Server Manager .
- In the console tree, double-click Roles , double-click DNS Server , and then double-click DNS .
- Right-click the DNS server, click All Tasks , and then click Restart .
36 related questions found
How do I run DNS services?
Android
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Advanced > Private DNS.
- Select Private DNS provider hostname.
- Enter dns.google as the hostname of the DNS provider.
- Click Save.
How do I fix my DNS on Windows?
To change your DNS server on a Windows 10 computer, go to Settings > Network & Internet > Change Adapter Settings. Then right-click a connection and select Properties > IPv4 > Properties. Finally,select Use the following DNS server address.
How do I check DNS settings?
Check DNS Settings in Windows
- Open the Control Panel by clicking on the Windows button, then click Control Panel.
- Type «Network and Sharing» in the upper right hand corner and click on Network and Sharing Center.
- Click Change Adapter Settings.
How do I find my DNS server?
Open your Command Prompt from the Start menu (or type “Cmd” into the search in your Windows task bar). Next, type ipconfig/all into your command prompt and press Enter. Look for the field labeled “DNS Servers.” The first address is the primary DNS server, and the next address is the secondary DNS server.
How do I clear my DNS cache?
Android (version 12)
In the URL bar type in chrome://net-internals/#dns: In the left pane select DNS. In the right pane tap the Clear host cache button.
What happens when DNS fail?
If DNS isn’t working properly, you won’t be able to use web-connected services, such as your browser or email, despite your computer or router showing a working internet connection. The webpage may timeout, give you an error message, or even bring up a specific «DNS error» message.
Do I need a DNS service?
It’s one of the cornerstones of how the internet operates. Without it, we’d be stuck memorizing long lists of numbers (IP addresses) to access the content we want. If a DNS cannot translate the domain name with the right IP address, you won’t be able to access the website you’re looking for.
What is a DNS server for Wi-Fi?
The Domain Name System (DNS) Server is a server that is specifically used for matching website hostnames (like example.com)to their corresponding Internet Protocol or IP addresses. The DNS server contains a database of public IP addresses and their corresponding domain names.
What is a DNS for Wi-Fi?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical naming system that allows communication across devices on a network. Most commonly, it translates human-readable domain names (like bluecatnetworks.com) to computer-friendly Internet Protocol (IP) addresses (like 104.239. 197.100).
How do I find a DNS IP address?
To do a DNS lookup in a Windows computer, go to Start, then Run, and type command to open the command prompt. Type nslookup and hit Enter. Your search will bring back information about your local DNS default server and IP address.
How do I know if my DNS is active?
Here’s how to check DNS settings in Windows and see if your DNS is working: Open the Command Prompt. Type ipconfig /all and press Enter. Look for the DNS Servers entry to check your DNS settings and verify that they are correct.
How do I know if my DNS is enabled?
How to check your DNS settings
- Click on Start, select Control Panel then double click on Network Connections.
- Right-click on the network connection in use and select Properties.
- Double click on Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
- Make sure “Obtain an IP address automatically” is selected.
How can I tell if DNS is running?
Run ipconfig /all at a command prompt, and verify the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway. Check whether the DNS server is authoritative for the name that is being looked up. If so, see Checking for problems with authoritative data.
What is a DNS service?
DNS, or the Domain Name System, translates human readable domain names (for example, www.amazon.com) to machine readable IP addresses (for example, 192.0.2.44).
Do you need DNS for WIFI?
The DNS system provides a domain name to IP address mapping for devices connected to the Internet, and it is crucial to the working of the Internet. Usually you don’t need to worry about it as your are automatically assigned the address of the DNS server by your ISP and Home router.
Can DNS affect WIFI?
How can DNS affect your Internet speed? Although DNS is not directly related to your Internet speed, it can influence how fast an individual webpage appears on your computer. Once a connection has been established though, it should not affect download speeds.
How do I change my WIFI DNS settings?
This is how you change DNS servers on Android:
- Open the Wi-Fi settings on your device. …
- Now, open the network options for your Wi-Fi network. …
- In the network details, scroll to the bottom, and tap on IP Settings. …
- Change this to static.
- Change DNS1 and DNS2 to the settings you want — for example, Google DNS is 8.8.
How to configure a DNS server?
In Local Area Connection Properties, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties. Click Use the following DNS server addresses, and in Preferred DNS server and Alternate DNS server, type the IP addresses of the preferred and alternate DNS servers. To add more DNS servers, click the Advanced button.
Is it good to clear DNS cache?
It’s important to flush a DNS cache for a few reasons. The first is the cache may contain outdated information. You might experience this as difficulty accessing websites or applications. If the domain name in the cache points to an old or incorrect IP address, the website won’t return the correct information.
Does restarting flush DNS cache?
A DNS Server’s cache is cleared at reboot. Other than that you can manually clear the cache at any time by using the DNS Admin console. If you leave the cache alone, the individual records are removed from the DNS cache as the TTL (time-to-live) expires.
You can’t uninstall / reinstall DNS from a Domain Controller so if your DNS server has insurmountable problems, make sure that you have a second DC with a working DNS then dcpromo (demote) the problematic DC, make sure DNS has been removed, then repromote that server to be a DC.
Beyond that the next thing to do is restart the DNS Service which you can do through the DNS MMC console or through SERVICES.MMC .
If you have a DNS server that is not working well or has errors indicating partial corruption there are a few ways to kick the server using simple commands:
- Open PowerShell as an Administrator
- Type:
DNSCMD /Config /BootMethod 2
- Press the ENTER key
- Restart the DNS service, or just reboot the whole server if want
I found that it took about 20 minutes for the errors and problems I was seeing to go away and for DNS to start functioning properly.
You can also try to view the DNS servers basic configuration to look for anomalies:
- Open PowerShell as an Administrator
- Type:
DNSCMD /Info
- Press the ENTER key
- Look for oddities

DNSCMD BACKGROUND:
According to THIS Microsoft article there are four different sources for DNS start up information:
0 – Clears the source of configuration information.
1 – Loads from the BIND file that is located in the DNS directory, which is %systemroot%\System32\DNS by default.
2 – Loads from the registry.
3 – Loads from AD DS and the registry. This is the default setting
If there is a problem with this command you can place the setting directly in the registry manually:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\DNS\Parameters\BootMethod
and set it to the number 2.
Here is a complete list of DNSCMD options:
Usage: DnsCmd <ServerName> <Command> [<Command Parameters>]
<ServerName>:
IP address or host name — remote or local DNS server
. — DNS server on local machine
<Command>:
/Info — Get server information
/Config — Reset server or zone configuration
/EnumZones — Enumerate zones
/Statistics — Query/clear server statistics data
/ClearCache — Clear DNS server cache
/WriteBackFiles — Write back all zone or root-hint datafile(s)
/StartScavenging — Initiates server scavenging
/IpValidate — Validate remote DNS servers
/EnumKSPs — Enumerate available key storage providers
/ResetListenAddresses — Set server IP address(es) to serve DNS requests
/ResetForwarders — Set DNS servers to forward recursive queries to
/ZoneInfo — View zone information
/ZoneAdd — Create a new zone on the DNS server
/ZoneDelete — Delete a zone from DNS server or DS
/ZonePause — Pause a zone
/ZoneResume — Resume a zone
/ZoneReload — Reload zone from its database (file or DS)
/ZoneWriteBack — Write back zone to file
/ZoneRefresh — Force refresh of secondary zone from master
/ZoneUpdateFromDs — Update a DS integrated zone by data from DS
/ZonePrint — Display all records in the zone
/ZoneResetType — Change zone type
/ZoneResetSecondaries — Reset secondary\notify information for a zone
/ZoneResetScavengeServers — Reset scavenging servers for a zone
/ZoneResetMasters — Reset secondary zone’s master servers
/ZoneExport — Export a zone to file
/ZoneChangeDirectoryPartition — Move a zone to another directory partition
/ZoneSeizeKeymasterRole — Seize the key master role for a zone
/ZoneTransferKeymasterRole — Transfer the key master role for a zone
/ZoneEnumSKDs — Enumerate the signing key descriptors for a zone
/ZoneAddSKD — Create a new signing key descriptor for a zone
/ZoneDeleteSKD — Delete a signing key descriptor for a zone
/ZoneModifySKD — Modify a signing key descriptor for a zone
/ZoneValidateSigningParameters — Validate DNSSEC online signing parameters for a zone
/ZoneSetSKDState — Set Active and/or Standby keys for a signing key descriptor for a zone
/ZoneGetSKDState — Retrieve dynamic state for a signing key descriptor for a zone
/ZonePerformKeyRollover — Trigger a key rollover in a signing key descriptor for a zone
/ZonePokeKeyRollover — Trigger a key rollover in a signing key descriptor for a zone
/ZoneSign — Signs the zone using DNSSEC online signing parameters
/ZoneUnsign — Removes DNSSEC signatures from a signed zone
/ZoneResign — Regenerate DNSSEC signatures in a signed zone
/EnumRecords — Enumerate records at a name
/RecordAdd — Create a record in zone or RootHints
/RecordDelete — Delete a record from zone, RootHints or cache
/NodeDelete — Delete all records at a name
/AgeAllRecords — Force aging on node(s) in zone
/TrustAnchorAdd — Create a new trust anchor zone on the DNS server
/TrustAnchorDelete — Delete a trust anchor zone from DNS server or DS
/EnumTrustAnchors — Display status information for trust anchors
/TrustAnchorsResetType — Change zone type for a trust anchor zone
/EnumDirectoryPartitions — Enumerate directory partitions
/DirectoryPartitionInfo — Get info on a directory partition
/CreateDirectoryPartition — Create a directory partition
/DeleteDirectoryPartition — Delete a directory partition
/EnlistDirectoryPartition — Add DNS server to partition replication scope
/UnenlistDirectoryPartition — Remove DNS server from replication scope
/CreateBuiltinDirectoryPartitions — Create built-in partitions
/ExportSettings — Output settings to DnsSettings.txt in the DNS server database directory
/OfflineSign — Offline signing zone files, including key generation/deletion
/EnumTrustPoints — Display active refresh information for all trust points
/ActiveRefreshAllTrustPoints — Perform an active refresh on all trust points now
/RetrieveRootTrustAnchors — Retrieve root trust anchors via HTTPS<Command Parameters>:
DnsCmd <CommandName> /? — For help info on specific CommandIn future versions of Windows, Microsoft might remove dnscmd.exe.
If you currently use dnscmd.exe to configure and manage the DNS server, Microsoft recommends that you transition to Windows PowerShell.
To view a list of commands for DNS server management, type “Get-Command -Module DnsServer” at the Windows PowerShell prompt. Additional information about Windows PowerShell commands for DNS is available at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=217627 .
Here is a list of the DNSCMD /COMMAND options:
PS C:\Windows\system32> DNSCMD /Config /?
Usage: DnsCmd <ServerName> /Config <ZoneName> <Property> <Value>
Server <Property>:
/RpcProtocol
/LogLevel
/LogFilePath <Log file name>
/LogIPFilterList <IP list>
/LogFileMaxSize
/EventlogLevel
/NoRecursion
/BootMethod
/ForwardDelegations
/ForwardingTimeout
/EnableGlobalQueryBlockList
/EnableGlobalNamesSupport
/GlobalQueryBlockList
/GlobalNamesQueryOrder
/GlobalNamesBlockUpdates
/IsSlave
/SecureResponses
/RecursionRetry
/RecursionTimeout
/MaxCacheTtl
/MaxCacheSize
/MaxNegativeCacheTtl
/RoundRobin
/LocalNetPriority
/AddressAnswerLimit
/BindSecondaries
/WriteAuthorityNs
/NameCheckFlag
/StrictFileParsing
/UpdateOptions
/DisableAutoReverseZones
/SendPort
/XfrConnectTimeout
/DsPollingInterval
/DsTombstoneInterval
/ScavengingInterval
/DefaultAgingState
/DefaultNoRefreshInterval
/DefaultRefreshInterval
/EnableDnsSec
/EnableEDnsProbes
/EDnsCacheTimeout
/DisableNSRecordsAutoCreation
/CacheLockingPercent
/SocketPoolExcludedPortRanges
/EnableForwarderReordering
/RootTrustAnchorsURL
Zone <Property>:
/SecureSecondaries
/AllowUpdate <Value>
<Value> — 0: no updates; 1: unsecure updates; 2: secure updates only
/Aging
/RefreshInterval <Value>
/NoRefreshInterval <Value>
/ForwarderTimeout <Value>
/ForwarderSlave <Value>
/AllowNSRecordsAutoCreation <IP List>
/AllowUpdate
/DsIntegrated
/Aging
/RefreshInterval
/NoRefreshInterval
/SignWithNSEC3
/NSEC3HashAlgorithm
/NSEC3Iterations
/NSEC3RandomSaltLength
/NSEC3UserSalt
/NSEC3OptOut
/MaintainTrustAnchor
/SignatureInceptionOffset
/DNSKEYRecordSetTTL
/DSRecordSetTTL
/SecureDelegationPollingPeriod
/DsRecordAlgorithms
/RFC5011KeyRollovers
/SigningKeyDescriptors
/PropagationTime
<Value>: New property value. Use 0x prefix to indicate hex value.
Note some server and zone DWORD properties must be reset as part of a more complex operation.In future versions of Windows, Microsoft might remove dnscmd.exe.
If you currently use dnscmd.exe to configure and manage the DNS server, Microsoft recommends that you transition to Windows PowerShell.
To view a list of commands for DNS server management, type “Get-Command -Module DnsServer” at the Windows PowerShell prompt. Additional information about Windows PowerShell commands for DNS is available at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=217627.
PS C:\Windows\system32> DNSCMD /Config /?
Readers help support Windows Report. We may get a commission if you buy through our links.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
The DNS server, short for Domain Name Server, is where the management, maintenance, and processing of Internet domain names occur. Or in simple terms, a DNS server assigns an IP address to your PC so that you are easily recognizable on the world wide web. And it does so by translating the domain names to IP addresses.
However, often the server might stop running altogether or have other issues like web pages not getting loaded correctly.
That could be due to some error cropping up, though, in such a scenario, one easy and sure-shot method of getting things back on track is to restart the DNS Server, which is exactly what we discuss in this article.
How can I fix DNS client restart issues?
1. Via command line interface

Start command prompt: You can do this either by clicking on Start followed by selecting Run or by simply pressing the Windows and R button simultaneously. When the Run dialog box appears, type cmd and press Enter to start the Windows command prompt.
Alternatively, you can simply type cmd in the Cortana search box, right click on the Command prompt app that shows and select Run as administrator.
Type the command net stop dnscache and press enter. This will stop the service. However, it might take a few seconds for the command to take effect.
You will be shown the following messages:
- The DNS Server service is stopping.
- The DNS Server service was stopped successfully.
Next, type the command net start dnscache and press Enter. This will restart the DNS server though again there might be a few seconds’ delay for that to happen. DNS Server runs as a service in your PC and the above command restarts the service.
The following message should confirm the above.
- The DNS Server service is starting.
- The DNS Server service was started successfully.
2. Via graphical user interface
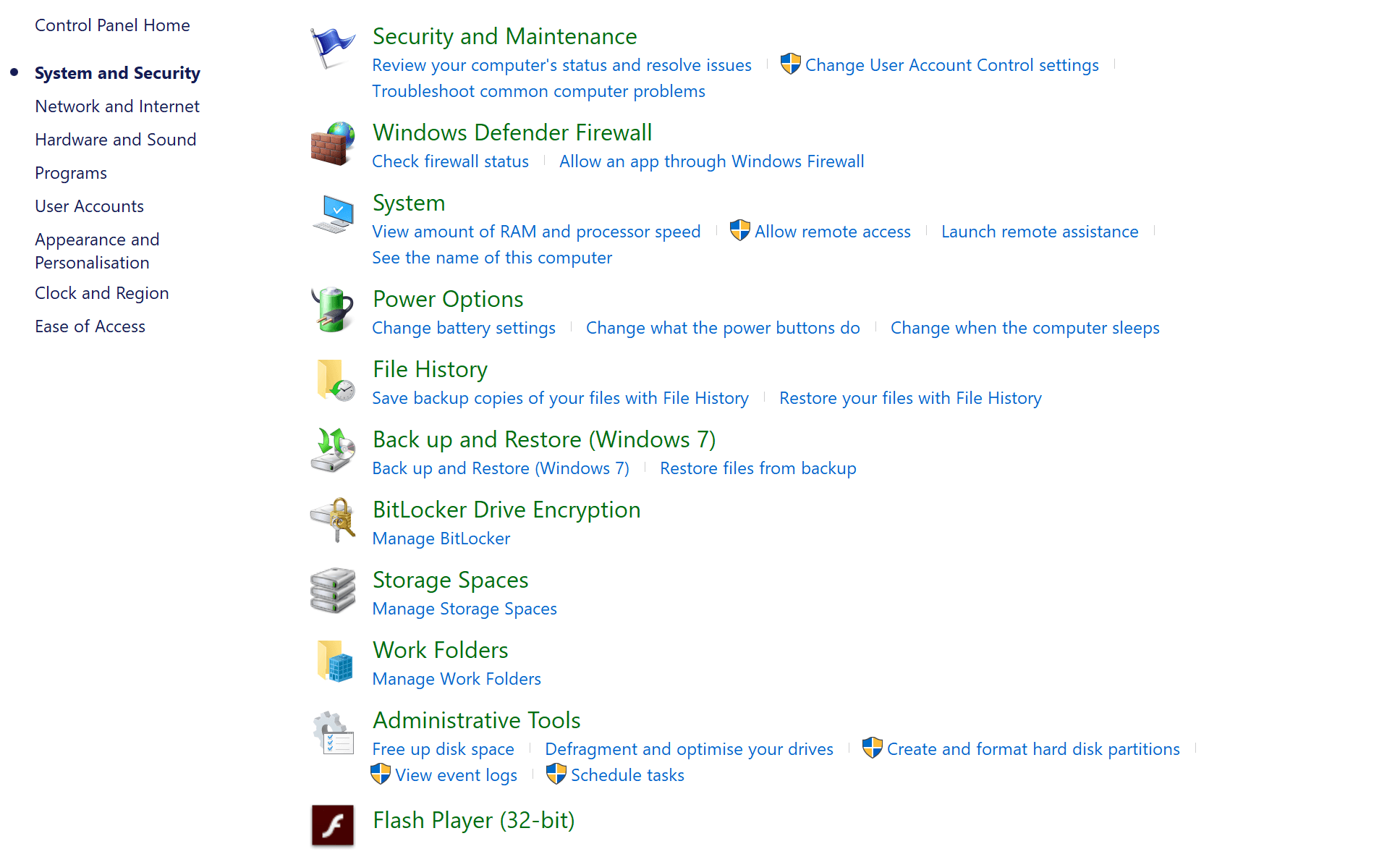
Launch Control Panel: You can do this by clicking on Start > Windows Systems > Control Panel. Alternately, you can also type Control Panel in the Cortana search box and selecting accordingly from the search results shown. You can also right click on the Start menu and select Control Menu.
Under Control Panel, click on System and Security > Administrative Tools and open DNS snap-in.
From the list of options on the left, locate server, right-click on it and select All Tasks. Here, there are Start and Stop options for starting and stopping the service, respectively.
- Fix: An Error Occurred While Loading a Higher Quality Version of This Video
- iTunesMobileDevice.dll is Missing From Your Computer [Solved]
- SYNSOACC.DLL Could Not Be Located: How to Fix in Cubase
- Fix: Omen Gaming Hub Undervolting Not Working
3. Restart DNS Server on a remote server
This is done with the help of the utility named sc, which gets installed together with the OS so far as Windows Server 2003 is concerned. To perform the start and stop DNS operations, here is what needs to be done.
To Stop DNS.
C:> sc \matrix stop dns
SERVICE_NAME: dns
TYPE : 10 WIN32_OWN_PROCESS
STATE : 3 STOP_PENDING
(STOPPABLE, PAUSABLE, ACCEPTS_SHUTDOWN)
WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
CHECKPOINT : 0x1
WAIT_HINT : 0x7530
To Start DNS.
C:> sc \matrix start dns
SERVICE_NAME: dns
TYPE : 10 WIN32_OWN_PROCESS
STATE : 2 START_PENDING
(NOT_STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, IGNORES_SHUTDOWN))
WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
CHECKPOINT : 0x0
WAIT_HINT : 0x7d0
PID : 504
FLAGS :
This is all you need to do.
You can check if things have been resolved by launching any internet browser and entering a domain name in the address bar. If the page launches successfully, you know you have your issue resolved.
Meanwhile, here are some additional resources worth having a look at.
Ivan Jenic
Windows Hardware Expert
Passionate about all elements related to Windows and combined with his innate curiosity, Ivan has delved deep into understanding this operating system, with a specialization in drivers and driver troubleshooting.
When he’s not tackling diverse driver-related problems, Ivan enjoys watching good movies and spending time hiking with his family and friends.
