All recent versions of Windows include the Windows Firewall utility. A firewall includes options for opening and closing ports, as well as allowing and disabling specific programs and services.
Computer resources can be protected from unauthorized access by firewalls on networks and servers. Incoming or even outgoing traffic is checked for by the firewall systems and in accordance with the rules configured, decisions are made about them.
Windows Firewall cannot access the port if it isn’t explicitly allowed. TCP/IP ports are reserved for applications whenever they want to access the network, which means anyone else cannot use them.

Also Read: How to Change RDP Port in Windows Server?
In Windows Server 2008/2012 R2/2016 and Windows Server 2019, there are three ways to open ports.
- MMC
- The command line (netsh)
- PowerShell commands (For 2012R2 and 2016 only)
So, you can open ports on Windows Server by following the instructions in the following article.
Open Ports via MMC
- Here first of all you have to log in using an admin account.
- Then you have to click on:
Start > Administrative Tools > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
- Now you have to click on the Inbound Rules on the left of the MMC.
- Then click on the New Rule on the Right of the MMC.
- Now here you will get five steps to open a port and accept incoming connections:-
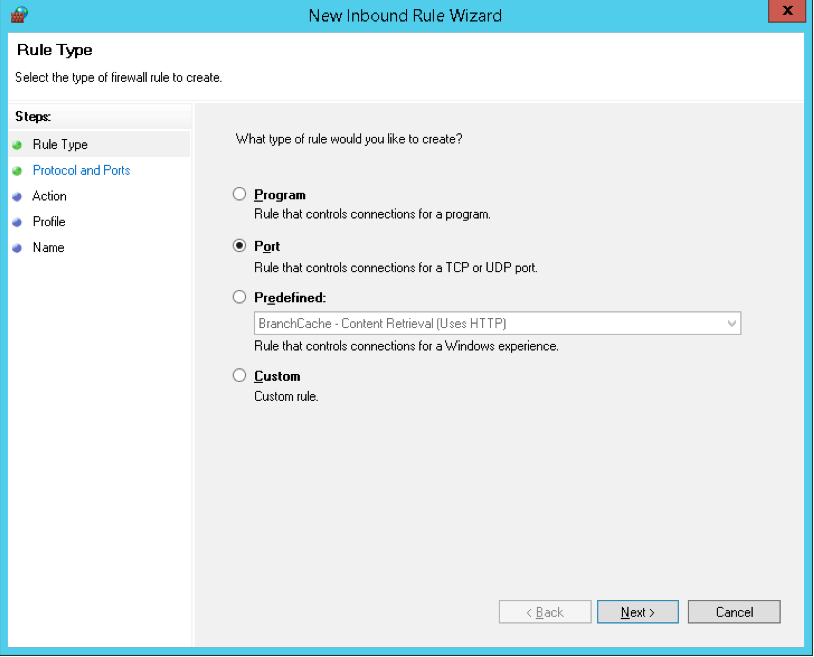
- Rule Type
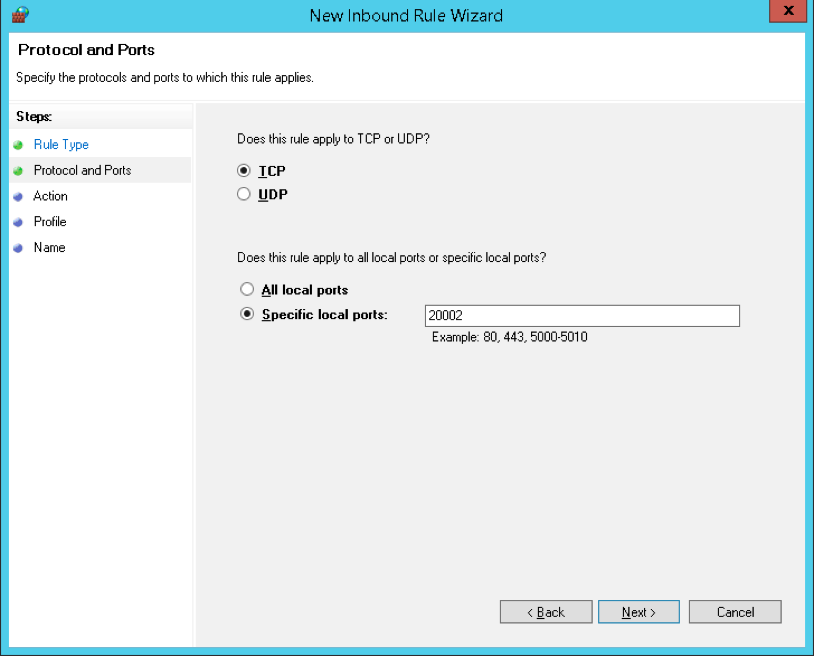
- Protocol and Ports
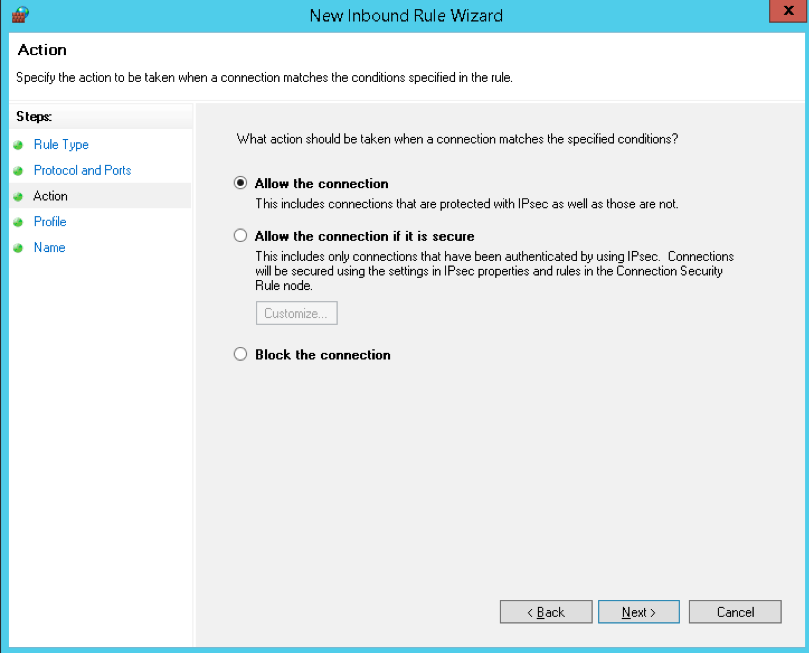
- Action
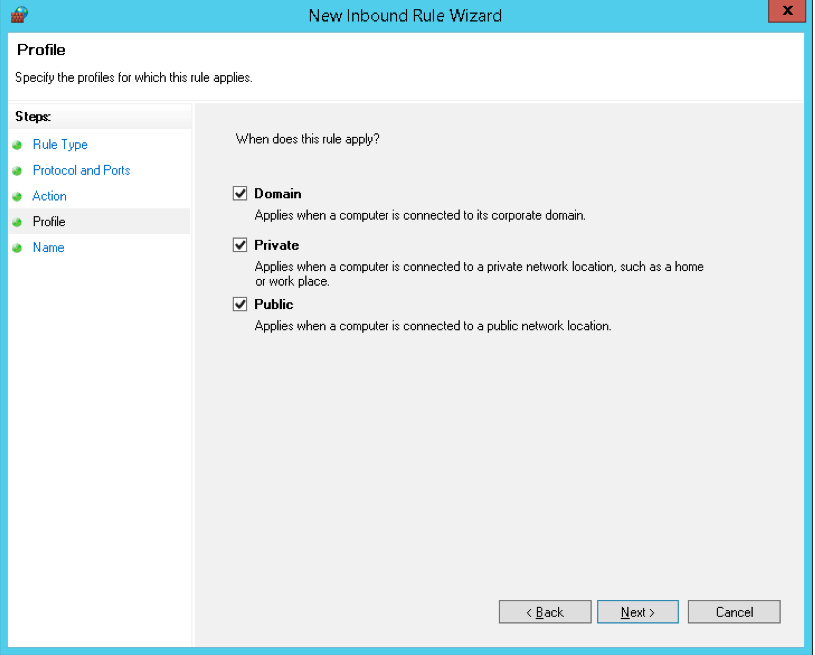
- Profile
- Name
- Suppose for example the servers with Parallels RAS Publishing Agents will need to open TCP port 20002.
- Now under the Rule Type section, you have to select “Port” and then click on the “Next” button.
- Then under the Protocol and Ports section, you have to select the “TCP” as the type of protocol.
- After that, you have to type “20002” in the “Specific local ports” input field.
- Next, you have to head to the Action section in which you have to select “Allow the Connection“ and then you have to click on the “Next” button.
- Now under the Profile section, you have to select all three options and click on the “Next” button.
(NOTE: Here at this point if you wish to limit the connection to a particular profile then you can simply select the profiles that are appropriate to your setup.)
- After that, now you have to enter a “Name” for this rule under the Name section, and then click on the “Finish” button when you are done.
- That’s it, now you are done.
Open Ports through command line (netsh)
- First of all, using an administrator account you have to login to the server.
- Then you have to open and run the Command Prompt as Administrator.
- For the Publishing Agents role on the servers, open the TCP port 20002 with the following command.
- That’s it, now you are done.
Open Ports through PowerShell commands
- First of all, using an admin account you have to Log in.
- Then you have to run the Windows PowerShell as Administrator.
- You need to open the TCP port 20002 on the publishing agents server using the following command.
- That’s it, now you are done.
Once all is done, now immediately after creating this rule, the firewall rule will allow traffic to (or from) your server. While if you want to open a port for both sending and receiving, you need to repeat the process as an Outbound rule.
Ports play a very important role in any computer system. In computer networks, ports are used to connect computers and other devices to one another. When you open a port, you are allowing specific types of information to go in and out of your computer.
For example, if you want to host a website, you need to open port 80 to allow web traffic to go in and out. This blog is all about how to open ports on a Windows server and we hope that you liked it.
FAQs
What is a firewall and how does it work?
A firewall is a security system that is used to protect computer resources from unauthorized access. It checks incoming and outgoing traffic on a network or server, and according to the configured rules, decides whether to allow or block traffic.
How do I open ports on Windows Server?
There are three ways to open ports on Windows Server 2008/2012 R2/2016 and Windows Server 2019: using MMC, command line (netsh), or PowerShell commands. To open a port using MMC, you need to log in as an admin, click on Start > Administrative Tools > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security, click on Inbound Rules, then click on New Rule, and follow the five steps to open a port and accept incoming connections.
What is a TCP/IP port and why do applications need them?
TCP/IP ports are reserved for applications when they want to access the network, which means that no one else can use them. Ports are used to connect computers and other devices to one another. When you open a port, you are allowing specific types of information to go in and out of your computer.
What is the difference between Inbound and Outbound rules when opening a port?
Inbound rules control traffic coming into the server, while outbound rules control traffic going out of the server. If you want to open a port for both sending and receiving, you need to repeat the process as an outbound rule.
Why is it important to open ports on a Windows server?
Opening ports on a Windows server is important because it allows specific types of information to go in and out of your computer. For example, if you want to host a website, you need to open port 80 to allow web traffic to go in and out. By opening ports, you can ensure that the applications and services you want to use can communicate properly.
What you will read?
- 1 Opening and Closing Ports in Windows Server
- 2 Remote Management and Port Configuration
- 3 Monitoring Port Activity on Windows Server
- 4 Troubleshooting Port Issues in Windows Server
- 5 Security Best Practices for Port Management
Managing ports on Windows Server is crucial for controlling network traffic and ensuring that communication between servers, clients, and external systems is secure and functional. Ports are logical endpoints used for communication over networks, and they are vital for applications and services to operate. On Windows Server, ports are managed primarily through the Windows Firewall, which allows administrators to configure inbound and outbound rules to control access to these ports.
By understanding port management, server administrators can protect their systems from unauthorized access while ensuring that necessary services, such as HTTP (port 80), FTP (port 21), and RDP (port 3389), are properly enabled and accessible. In the next section, we’ll explore how to open and close specific ports using both graphical interfaces and command-line tools like PowerShell.
Opening and Closing Ports in Windows Server
Managing ports in Windows Server is an essential task for controlling network traffic. The process involves configuring the Windows Defender firewall to either allow or block specific ports. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to open and close ports.
Step-by-Step Guide to Opening Ports
1. Opening ports via Windows Defender firewall (graphical interface):
- Step 1: Open the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security. You can do this by typing
wf.mscin the Start menu search bar and pressing Enter. - Step 2: In the left pane, click on Inbound Rules (for incoming traffic) or Outbound Rules (for outgoing traffic).
- Step 3: In the right pane, click on New Rule.
- Step 4: Choose Port and click Next.
- Step 5: Select the protocol (either TCP or UDP) and enter the specific port number you want to open (e.g., TCP port 80 for HTTP).
- Step 6: Select Allow the connection, then specify when the rule applies (domain, private, or public).
- Step 7: Name the rule (e.g., “Allow HTTP Traffic”) and click Finish.
2. Opening ports using PowerShell:
- Step 1: Open PowerShell as Administrator.
- Step 2: Use the
New-NetFirewallRulecommand to open a specific port. For example, to open TCP port 80 (HTTP), enter the following command:
- Step 3: Press Enter to apply the rule.
Step-by-Step Guide to Closing Ports
1. Closing Ports via Windows Defender Firewall (Graphical Interface):
- Step 1: Open the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security again by typing
wf.mscin the Start menu search bar. - Step 2: In the left pane, click on Inbound Rules (for incoming traffic) or Outbound Rules (for outgoing traffic).
- Step 3: Locate the rule that allows the port you want to close.
- Step 4: Right-click the rule and select Disable Rule to block the traffic for that port.
2. Closing ports using PowerShell:
- Step 1: Open PowerShell as Administrator.
- Step 2: Use the
Remove-NetFirewallRulecommand to remove the rule associated with the open port. For example, to remove the rule allowing port 80 (HTTP), use the following command: - Step 3: Press Enter to remove the rule and close the port.
Remote Management and Port Configuration
Remote management of Windows Server involves controlling the server from another computer over the network, typically through Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) or PowerShell remoting. Port configuration plays a critical role in enabling or restricting remote access. For RDP, the default port is TCP 3389, and for PowerShell remote, it uses TCP 5985 (HTTP) or TCP 5986 (HTTPS). To configure ports for remote management:
- Enable Remote Desktop: Ensure port 3389 is open on the firewall to allow RDP connections.
- Use PowerShell Remoting: Run
Enable-PSRemoting -Forceto configure the server to accept remote PowerShell commands. Open the necessary ports (TCP 5985 for HTTP or TCP 5986 for HTTPS) on the firewall. - Firewall Rule Configuration: For security, create specific rules that allow connections only from trusted IP addresses.
Remote management tools help administer servers without requiring physical access, but ensuring the appropriate ports are open while maintaining strict firewall rules is essential to minimize security risks.
Monitoring Port Activity on Windows Server
Monitoring port activity helps ensure that only authorized traffic is flowing through open ports and helps identify potential security threats. Tools like Netstat, PowerShell, and Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security allow administrators to track port usage.
- Netstat: Use the
netstatcommand to view a list of open ports and active connections:This shows all listening ports and active connections. - PowerShell Commands: Use
Get-NetTCPConnectionorGet-NetUDPEndpointto list active ports and their states. - Windows Firewall Logs: Enable logging in Windows Defender Firewall to track which ports are being accessed and to monitor unusual activity.
Regular monitoring helps detect unauthorized access or unexpected services running on open ports, allowing administrators to take proactive measures.
Troubleshooting Port Issues in Windows Server
When ports fail to function as expected, administrators must troubleshoot the issue systematically. The first step is to check the firewall settings to ensure that no conflicting rules are blocking the desired traffic. If the firewall rules are correct, it’s important to verify network connectivity using tools like ping or tracert to determine if the server can reach other devices or if there’s an issue with the network. Tools such as Telnet and PowerShell’s Test-NetConnection cmdlet can help diagnose port connectivity issues by checking if a specific port is open and accessible. Additionally, examining logs—both Windows Event Logs and firewall logs—can provide insights into any errors or denied connections that may be impacting the port’s functionality. Troubleshooting these issues in a methodical manner ensures that the server remains accessible while minimizing security risks.
Security Best Practices for Port Management
Port management is a critical component of server security, and following best practices ensures that only necessary services are accessible while minimizing the risk of unauthorized access. It is important to follow the principle of least privilege by opening only the ports that are required for specific services and closing any unused or unnecessary ports. Firewalls should be configured to allow traffic only from trusted IP addresses, especially for sensitive services like RDP or administrative ports. Regular audits of open ports should be performed to ensure that security policies are adhered to and that any outdated or unused ports are closed. Additionally, it is essential to implement encrypted communication protocols, such as HTTPS and SSH, for services exposed to external networks, ensuring that sensitive data transmitted over these ports remains secure. By following these security best practices, administrators can significantly reduce the attack surface and protect their servers from potential threats.
Effective port management in Windows Server is essential for both operational functionality and server security. It requires a proactive approach to opening, closing, and monitoring ports based on the specific needs of the server and its services. Administrators should focus on minimizing open ports, regularly auditing their firewall settings, and applying strict access controls to protect against unauthorized access. Employing remote management tools like RDP and PowerShell securely, monitoring network traffic, and troubleshooting port issues as they arise help maintain a stable and secure server environment. By adhering to these best practices, organizations can ensure their servers are both functional and protected from external threats, balancing accessibility with robust security measures.
Huda Henry
Modified on: Mon, 29 Jan, 2024 at 1:44 PM
For those of you Windows server users if you want to open a port on your server, you can follow the following guide. We strongly recommend that your server firewall is always turned on.
- Login to your windows server.
- Launch Powershell or cmd then type wf.msc the firewall settings will open
- Click inbound rules on the left
- Then click New Rule on the right side
- Select the Port option and then Next
- Select TCP then in Specific Local Port fill in the port you want to open, then Next
- Select Allow The Connection, then Next
- Set the rules on the desired profile settings. Usually just check everything, then Next
- Set the profile name that will be applied (letters only) Next
- Finish
Публичное облако на базе VMware с управлением через vCloud Director
Чтобы разрешить тот или иной порт в брандмауэре Windows Server:
- В меню «Пуск» выберите «Служебные — Windows» — «Панель управления»
- Далее выберите «Система и безопасность» — «Брандмауэр защитника Windows».
- В меню слева выберите пункт «Дополнительные параметры».
- В меню слева кликните «Правила для входящих подключений» и в блоке «Действия» справа кликните «Создать правило…».
- Выберите «Для порта» и кликните «Далее».
- Укажите нужный протокол и порт (порты). Здесь можно ввести:
-
- один конкретный порт;
- несколько портов через запятую (1540,1541);
- диапазон портов через дефис (1560-1591);
- Нажмите «Далее», затем снова «Далее».
- Выберите, для каких профилей применять созданное правило, и снова нажмите «Далее».
- Введите имя и описание правила и кликните «Готово».
Была ли статья полезна?
Ваша оценка очень важна
Opening Ports on the Windows Firewall Using GUI
To open a port in the firewall using the GUI in Windows Server 2008/2012 R2 and Windows Server 2016, follow the below steps:
- Login using an administrator account.
- Click Start > Administrative Tools > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
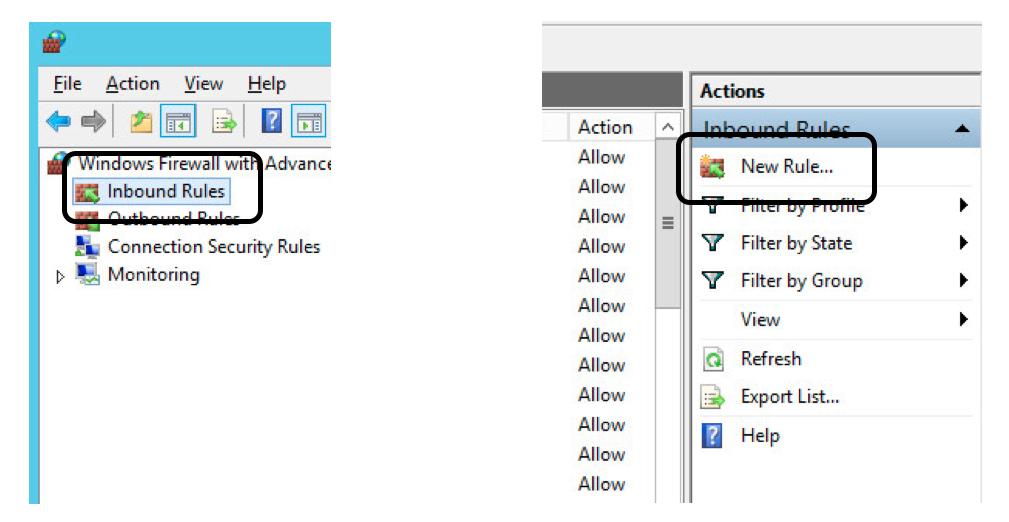
- Click on
Inbound Rules, and then onNew Rule
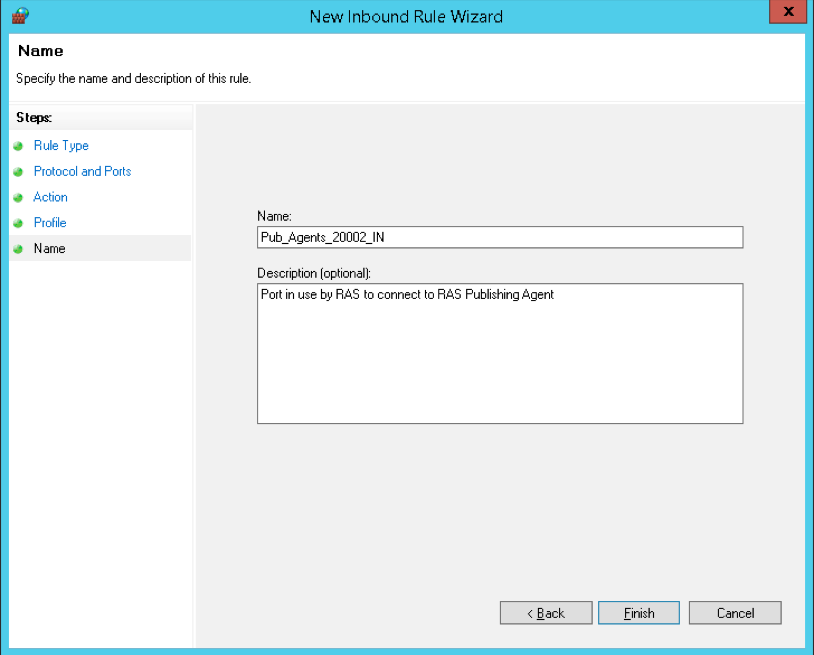
The wizard to open a port and accept incoming connections has five steps: Rule Type, Protocol and Ports, Action, Profile, and Name. For this example, we will open TCP port 20002 on servers that are running the Parallels RAS Publishing Agents role:
-
In the
Rule Typesection, selectPortand click Next: -
In the
ProtocolandPortssection, select TCP as the type of protocol and type 20002 in the Specific local ports input field: -
In the
Actionsection, selectAllow the Connectionand click Next. -
In the
Profilesection, select all three options and click Next. If you wish to limit the connection to a particular profile, you can do so by selecting only the profiles you think are appropriate to your setup. For this example, we will open the port on all profiles. -
In the
Namesection, enter a descriptive name for this rule. It is recommended to list the port number in the name, so the rule is easily recognizable. For example, name the new rule Pub_Agent_20002_IN. Click Finish when ready.
To open additional ports, repeat the above procedure for each additional port and/or protocol you’d like to open in each server.
Opening Ports on the Windows Firewall Using Command Line (netsh)
To open a port on the Windows Firewall using the netsh command line, follow the below procedure:
- Login to the server using an administrator account.
- Run the Command Prompt as Administrator.
- Execute the following command to open the TCP port 20002 on the servers running the Publishing Agents role:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="name" dir=in|out protocol=tcp|udp localport=20002 action=allowTo open additional ports, repeat the above procedure for each additional port and/or protocol you’d like to open in each server.
Opening Ports on the Windows Firewall Using PowerShell
To open a port in the Windows Firewall using PowerShell commands, follow the below procedure (applies only for 2012 R2 and 2016 Windows Server OS):
- Logon using an administrator account.
- Run the Windows PowerShell as Administrator.
- Execute the following command to open the TCP port 20,002 on the servers running the Publishing Agents role:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "Name" -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 2002