Если компьютер до сих пор не предложил установить новую версию
Установить Windows 11 оказалось не так просто, потому что Microsoft добавила к системным требованиям технологии TPM 2.0 и Secure Boot. Они есть в большинстве компьютеров с 2015 года, но часто отключены по умолчанию.
Даем подробную инструкцию, как проверить совместимость компьютера с Windows 11 и что нужно сделать, чтобы подготовиться к обновлению.
Проверьте совместимость компьютера с Windows 11
Минимальные системные требования:
- Процессор: от 2 ядер, тактовая частота выше 1 ГГц. Проверьте, есть ли ваш процессор в списке совместимых моделей Intel и AMD.
- Оперативная память: от 4 ГБ.
- Накопитель: от 64 ГБ.
- Монитор: разрешение 720p или выше.
- Дополнительно: TPM 2.0 и UEFI с Secure Boot.
Если компьютер подходит под требования Windows 11, скорее всего, в настройках он уже предлагает установить обновление. Чтобы это проверить, зайдите в «Параметры» → «Обновления и безопасность». В этом меню должно появиться уведомление о готовности установить новую Windows — нажмите «Скачать и установить».
Если компьютер еще не предлагает обновить систему, проверьте совместимость компьютера с Windows 11. Для этого установите и запустите официальную программу PC Health Check от Microsoft. В приложении нажмите на синюю кнопку «Проверить сейчас».
После проверки программа покажет результат — готов ваш компьютер к Windows 11 или нет.
Проверка показала, что наш компьютер не подходит по двум требованиям: нет TPM 2.0 и безопасной загрузки (Secure Boot). Чаще всего именно из-за них компьютеры не могут обновиться до Windows 11. Проблемы с системными требованиями к процессору и памяти компьютера встречаются реже — они не сильно ужесточились по сравнению с Windows 10.
Иногда бывает, что Windows не предлагает обновиться, даже если программа проверки совместимости пишет «На этом компьютере можно запустить Windows 11». В таком случае установите помощник для обновления с сайта Microsoft — программа начнет принудительную установку Windows 11.
Как включить TPM 2.0 и Secure Boot
Сначала нужно зайти в UEFI. Это операционная система, которая отвечает за диагностику всех компонентов компьютера и загрузку Windows. UEFI стала современной заменой BIOS с более понятным графическим интерфейсом. В большинстве ноутбуков она также называется BIOS.
Чтобы запустить UEFI в Windows, есть два способа:
Способ 1. Откройте «Параметры» → «Обновление и безопасность» → «Восстановление» → «Перезагрузить сейчас». Компьютер автоматически перезагрузится и запустит меню восстановления системы.
В меню восстановления системы откройте «Поиск и устранение неисправностей» → «Дополнительные параметры» → «Параметры загрузки» → «Параметры встроенного ПО UEFI», в появившемся меню нажмите «Перезагрузить». После этого компьютер автоматически запустит UEFI.
Способ 2. Выключите и включите компьютер, как только на экране появится логотип бренда вашего ноутбука или материнской платы (если обновляете стационарный ПК), зажмите клавишу для запуска UEFI, на разных компьютерах это может быть Delete, F1, F2, F10, F11 или F12. Обычно в нижней части загрузочного экрана есть подсказки с нужными кнопками для запуска UEFI. Если подсказок нет, посмотрите в руководстве пользователя к своему ноутбуку или материнской плате компьютера.
Запустили UEFI — осталось только найти меню для включения TPM 2.0 или Secure Boot.
Как включить TPM 2.0. Обычно модуль безопасности TPM 2.0 в настройках UEFI находится в разделе «Безопасность» или Security.
В зависимости от бренда материнской платы компьютера или ноутбука эта настройка может находиться в разных местах и называться по-разному: fTPM — для компьютеров с процессором AMD, Platform Trust Technology — для Intel. Другие варианты названий: Trusted Computing, TPM Device Selection или просто TPM.
Пункт для включения TPM 2.0 в UEFI на материнской плате AORUS
Когда найдете этот пункт, нажмите на него и выберите значение Enabled, «Разрешено» или PTT. После этого сохраните настройки UEFI и перезагрузите компьютер.
Если не смогли найти, как включить TPM 2.0 в UEFI, поищите инструкцию на сайте производителя вашего ноутбука или материнской платы. Ссылки на официальные инструкции брендов: ASUS, Dell, HP, Lenovo, MSI.
Как включить Secure Boot. В UEFI эта настройка тоже обычно находится в разделе «Безопасность» или Security. Она так и называется — Secure Boot.
Включение Secure Boot в UEFI на ноутбуке ASUS
Для настройки Secure Boot выберите значение «Включено», «Разрешено» или Enabled. Сохраните настройки UEFI и перезагрузите компьютер.
Если не можете найти пункт Secure Boot в UEFI, поищите информацию на сайте производителя вашего компьютера. Инструкции для материнских плат и ноутбуков разных брендов: ASUS, MSI, Lenovo, HP, Dell.
Когда включите обе настройки, TPM 2.0 и Secure Boot, перезагрузите компьютер и вернитесь в Windows. Система должна сама предложить обновиться до Windows 11. Для этого зайдите в «Параметры» → «Обновление и безопасность» или запустите помощник обновления от Microsoft.
Как установить Windows 11 без TPM 2.0 или Secure Boot
Если ваш компьютер не поддерживает TPM 2.0 или Secure Boot или вы не смогли включить эти настройки, установить Windows 11 все равно можно. Главное, чтобы процессор и память соответствовали системным требованиям обновления.
Зайдите на официальный сайт Microsoft и скачайте ISO-образ Windows 11.
Прокрутите страницу до пункта «Загрузка образ диска Windows 11 (ISO)»
Сайт предложит выбрать язык установщика — в выпадающем меню найдите русский.
Сайт создаст ссылку на скачивание образа с Windows 11. Нажмите на кнопку «Скачать».
Два раза кликните на ISO-файл с Windows 11, и система автоматически запустит его как новый диск. Откройте «Мой компьютер», найдите диск в списке и скопируйте из него все файлы в любую папку на компьютере.
Диск с образом Windows 11 называется CCCOMA_X64FRE_RU-RU_DV9
Откройте папку с файлами Windows 11 и найдите папку Sources. В этой папке удалите два файла: appraiserres.dll и appraiser.sdb. Будьте внимательны, есть много файлов с похожими названиями.
Вернитесь в первую папку с файлами Windows 11 и запустите setup.exe.
Откроется установщик Windows 11, но не торопитесь сразу переходить к загрузке обновления. Сначала нажмите на строку «Настройка скачивания обновлений программой установки».
В появившемся меню выберите «Не сейчас» и нажмите «Далее».
Осталось принять лицензионное соглашение и пройти повторную проверку совместимости компьютера — в этот раз программа не сообщит об ошибке.
Дальше установка Windows 11 пройдет автоматически. Она займет от 20 до 60 минут в зависимости от скорости вашего накопителя.
Secure Boot is an important security feature designed to prevent malicious software from loading when your PC starts up (boots). Most modern PCs are capable of Secure Boot, but in some instances, there may be settings that cause the PC to appear to not be capable of Secure Boot. These settings can be changed in the PC firmware. Firmware, often called BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), is the software that starts up before Windows when you first turn on your PC.
Note: This article is intended for users who are not able to upgrade to Windows 11 because their PC is not currently Secure Boot capable. If you are unfamiliar with this level of technical detail, we recommend that you consult your PC manufacturer’s support information for more instructions specific to your device.
How to enable Secure Boot on my PC
To access these settings, you can consult your PC manufacturer’s documentation or follow these instructions:
-
Go to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery and select Restart now under Advanced startup.
-
On the next screen, select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > UEFI Firmware Settings > Restart to make changes.
To change these settings, you will need to switch the PC boot mode from one enabled as “Legacy” BIOS (also known as “CSM” Mode) to UEFI/BIOS (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface). In some cases, there are options to enable both UEFI and Legacy/CSM. If so, you will need to choose for UEFI to be the first or only option. If you are unsure how to make any necessary changes to enable the UEFI/BIOS, we recommend that you check your PC manufacturer’s support information on their website. Here are a few links to information from some PC manufacturers to help get you started:
Dell | Lenovo | HP
While the requirement to upgrade a Windows 10 device to Windows 11 is only that the PC be Secure Boot capable by having UEFI/BIOS enabled, you may also consider enabling or turning Secure Boot on for better security.
Related articles
Windows 11 System Requirements
Ways to install Windows 11
Windows help & learning
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Если установщик Windows 11, а возможно и какая-то программа или игра (такое тоже возможно) сообщает о том, что его не устраивает состояние безопасной загрузки и её необходимо включить — сделать это сравнительно легко, но возможны нюансы.
В этой инструкции подробно о способах включить безопасную загрузку на вашем компьютере или ноутбуке, при условии, что это возможно. Обратите внимание, если задача — установка Windows 11, существуют возможности запуска установки и без включенной безопасной загрузки (Secure Boot), например — создание загрузочной флешки в Rufus с отключением проверки совместимости при чистой установке, или обновление с обходом требований для установки.
Проверка состояния безопасной загрузки, особенности работы после включения
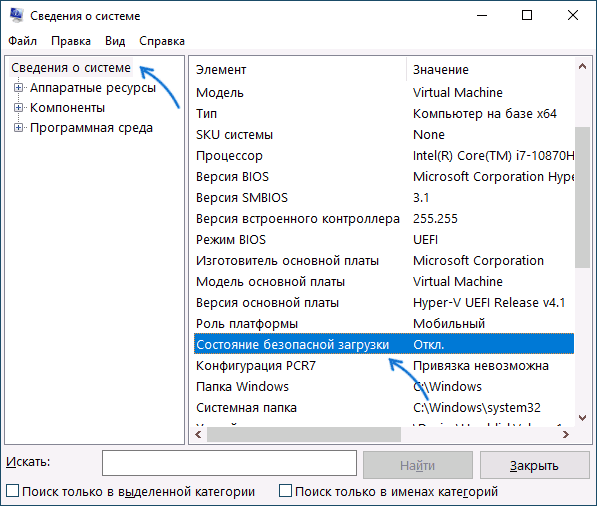
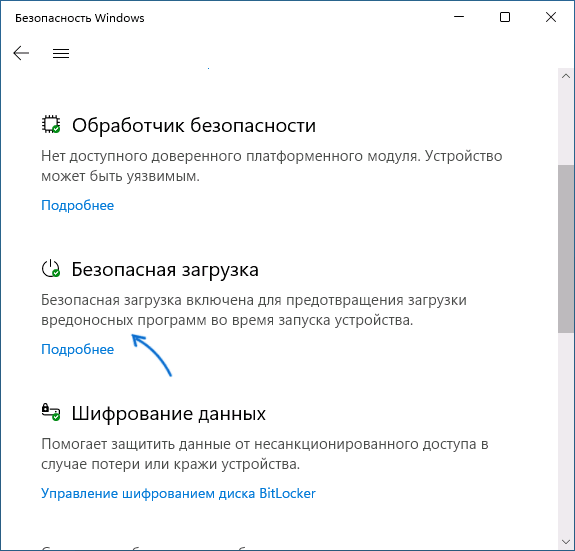
Прежде чем начать, о том, где вы можете проверить текущее состояние безопасной загрузки в Windows 11 или Windows 10:
- Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по кнопке «Пуск», выберите пункт «Выполнить», введите msinfo32 и нажмите Enter. В разделе «Сведения о системе» вы увидите пункт «Состояние безопасной загрузки» с её текущим статусом.
- Можно зайти в окно «Безопасность Windows», например, с помощью значка в области уведомлений и открыть раздел «Безопасность устройства». Если вы наблюдаете там пункт «Безопасная загрузка» с зеленой отметкой, она включена. Иначе — нет.
Ещё один важный момент: загрузка с включенной безопасной загрузкой возможна только для систем, установленных в UEFI-режиме на GPT диск.
Если, к примеру, у вас Windows 10 и установлена в Legacy-режиме на диск MBR, после включения Secure Boot она перестанет загружаться. Возможные варианты действий: конвертировать диск в GPT с помощью mbr2gpt.exe и включить UEFI-загрузку, либо использовать вариант с чистой установкой с флешки и обходом требований Windows 11, как было указано в начале статьи.
Включение безопасной загрузки Secure Boot в БИОС/UEFI
Само включение безопасной загрузки или Secure Boot выполняется не в Windows 11/10, а в БИОС/UEFI вашего компьютера или ноутбука. Для того, чтобы включить её, необходимо:
- Зайти в БИОС при включении/перезагрузке устройства. На ноутбуках для этого обычно используется клавиша F2 (или сочетание Fn+F2), которую необходимо ритмично нажимать сразу после появления заставки производителя (но бывают и другие варианты клавиши), на ПК как правило используется клавиша Delete. Более подробно: Как зайти в БИОС/UEFI на компьютере или ноутбуке.
- Найти раздел БИОС, на котором доступна опция включения (установка в Enabled) функции Secure Boot. Учитывайте, что на очень старых компьютерах такой настройки может и не быть. Как правило, она располагается где-то в разделе Security, Boot, System Configuration, иногда — Advanced Settings. Несколько примеров расположения будут приведены далее.
- Сменить состояние Secure Boot на Enabled (если ранее выполнялась очистка ключей Secure Boot, восстановить их), сохранить настройки БИОС/UEFI (обычно выполняется клавишей F10 или на вкладке Exit) и перезагрузиться обратно в систему.
Примеры расположения опции для включения безопасной загрузки (Secure Boot)
Ниже — несколько примеров, где можно найти опцию включения безопасной загрузки на разных материнских платах и ноутбуках. У вас может отличаться, но логика везде одна и та же.
Ещё раз отмечу: включить безопасную загрузку можно только в случае, если у вас включен режим загрузки UEFI, а режим Legacy/CSM отключен, иначе опция будет недоступна. В некоторых вариантах БИОС переключение в режим загрузки UEFI выполняется путем выбора типа операционной системы (OS Type) между Windows 11/10/8 и «Other OS» (нужно выбрать Windows).
ASUS
На разных версиях материнских плат и ноутбуков включение Secure Boot реализовано слегка по-разному. Обычно пункт «Secure Boot» можно найти на вкладке «Boot» или «Security». При этом для OS Type может потребоваться выставить Windows UEFI Mode (параметр может и отсутствовать).
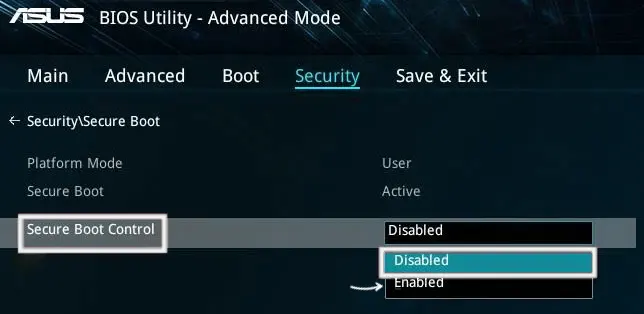
Также, для доступности пункта настройки безопасной загрузки в БИОС может потребоваться перейти в Advanced Mode, обычно — по клавише F7.
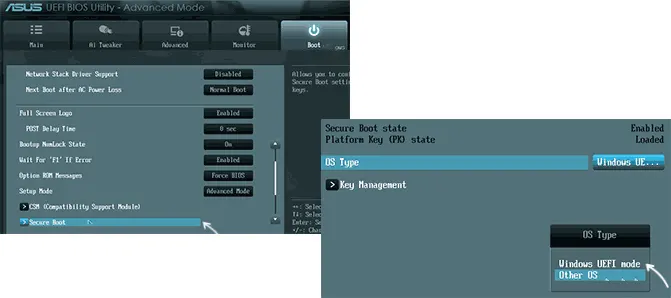
В некоторых случаях может потребоваться восстановление ключей безопасной загрузки, обычно выполняется следующим образом: в Advanced Mode в BIOS на вкладке Boot или в Secure Boot — Key Management выбираем Load Default PK и подтверждаем загрузку ключей по умолчанию.
AsRock
Настройка для включения безопасной загрузки на материнских платах AsRock обычно находится в разделе «Security».

Зайдя в раздел необходимо будет установить значение Secure Boot в Enabled, а если выбор недоступен, включить стандартный Secure Boot Mode и установить ключи по умолчанию (Install default Secure Boot keys).

Acer
Как правило, опция включения Secure Boot на ноутбуках Acer находится либо в разделе Advanced — System Configuration, либо в Boot или Authentication.
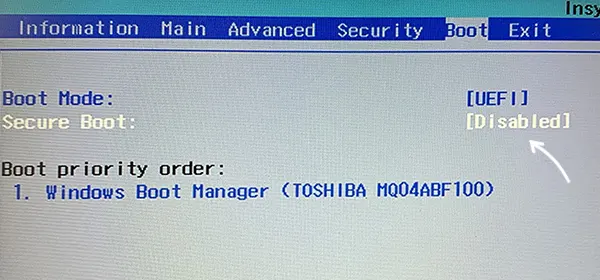
Также помните, о том, что должен быть включен режим загрузки UEFI, а не Legacy/CSM для возможности изменения состояния безопасной загрузки на Enabled.
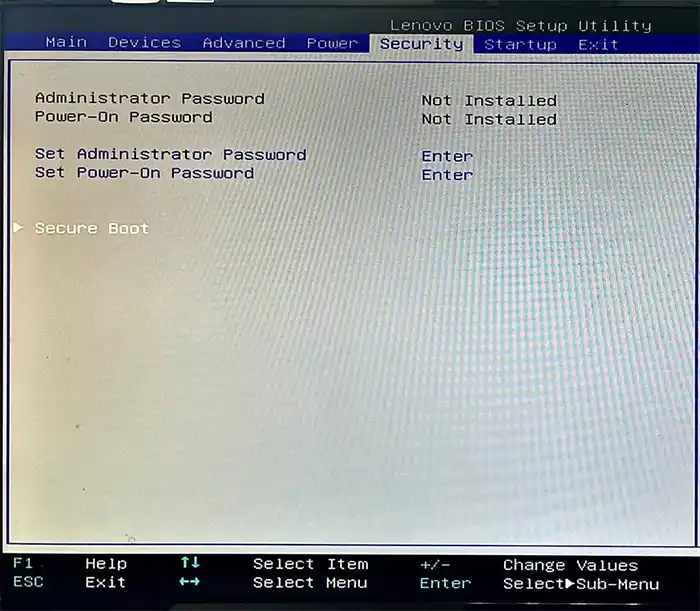
Lenovo
ПК и ноутбуки Lenovo имеют разные варианты интерфейса БИОС, но обычно нужная опция находится на вкладке Security, как на фото ниже:

Ещё один пример с ноутбука Lenovo:
Gigabyte
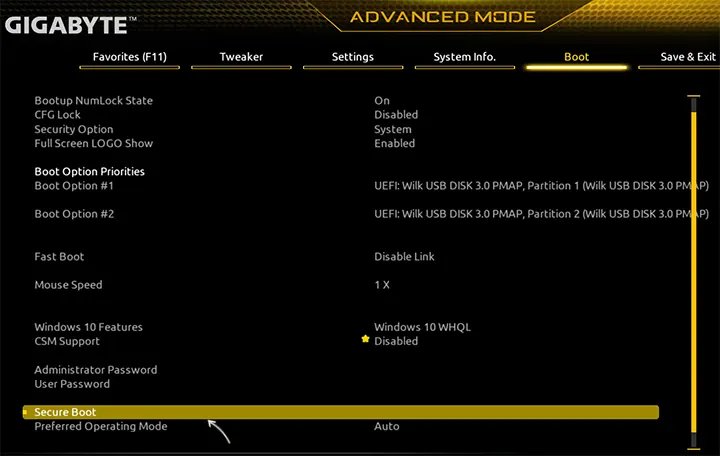
Варианты отключения Secure Boot на материнских платах и ноутбуках Gigabyte могут отличаться, обычно порядок действий следующий:
- На вкладке Boot или BIOS отключить CSM Support, и выбрать тип операционной системы или установить пункт Windows 8/10 Features в, соответственно, Windows 8/10, а не Other OS.
- После этого должен появиться пункт Secure Boot, в который необходимо зайти, чтобы включить безопасную загрузку.
Несколько дополнительных мест расположения опции включения Secure Boot (устанавливаем в Enabled) на старых Dell, Gigabyte, HP:

Также, если в вашем интерфейсе БИОС предусмотрен поиск, можно использовать его:

В случае, если вы не нашли способа включить безопасную загрузку на вашей материнской плате, либо её не удается перевести в Enabled, укажите её марку и модель в комментариях, я постараюсь подсказать, где именно требуется включать этот параметр. Кстати, часто достаточно просто сбросить настройки БИОС (Load Defaults на вкладке Exit), чтобы включить безопасную загрузку, так как на большинстве современных материнских плат она по умолчанию включена.

Secure boot is a computer security tool that only allows validated programs to run upon computer start up. This protocol ensures that unauthorized programs, specifically malicious rootkits, do not run at computer start up to bypass anti-virus software detection. This feature is mandatory to install the latest operating systems, Windows 11, as it is a part of the UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) or BIOS prerequisite for Windows 11 installation. It is not a requirement for older versions of Windows, like Windows 10 IoT 2021 LTSC, but is necessary for industrial enterprise applications.
How does Secure Boot Work?
Since Secure Boot is a protocol within the UEFI BIOS, it operates on each computer start up. This works hand-in-hand with the TPM (Trusted Platform Module) that is also a prerequisite for Windows 11 installation. In summary, TPM 2.0 is a hardware-based security tool that provides additional data protection where software-based security does not have the capabilities to. This process prevents a computer boot up if hardware has been tampered with and if unauthorized programs, like malicious software, are executed. Secure boot is another layer of data security and protection that ensures only digitally signed and certified programs are launched. There are three main databases that we are going to look at, and they are the signature database (DB), the revoked signature database (DBX), and the key enrollment database (KEK).
-
Signature Database (DB) – The signature database contains the public keys and certificates of trusted firmware components, operating system bootloaders, such as the Microsoft operating system loader, UEFI applications, and UEFI drivers.
-
Revoked Signature Database (DBX) – The revoked signature database contains hashes of malicious and vulnerable components, compromised keys, and compromised certificates, blocking them from being executed to protect your system.
-
Platform Key (PK) – The platform key establishes a trust relationship between the system owner and the firmware in the BIOS, controlling access to the KEK Database.
- Key Exchange Key (KEK)– The key-exchange key is a database that establishes a relationship of trust between the operating system and the firmware. The KEK contains a list of public keys that can be checked when modifying the whitelist database or revoked signature database. A single platform can have multiple KEKs.
Why is it useful for Industrial Edge Applications?
With the world seeing an uprise in cyberattacks, it is crucial that enterprises take every precaution possible to deter and prevent their valuable data from being tampered with. Tier-one companies such as Microsoft, AMD, and Intel have developed their own methods to enhance protection against malware. Microsoft launched Windows 11 with TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot requirements, and the leading semiconductor giants, Intel and AMD, have developed their versions of firmware TPM (fTPM). TPM is considered a legacy component that was primarily utilized by enterprises that operated with sensitive data. Nowadays, TPM 2.0 is included and almost mandatory for industrial edge computers due to this increase in cyberattacks.
What is the difference between Secure Boot and TPM 2.0?
Secure boot is a simple premeasure feature that is enabled through UEFI BIOS. The role of secure boot is to only allow validated and digitally signed software to launch. For example, the matching operating system and other start up applications like anti-malware programs. TPM 2.0, however, acts as a vault that stores and encrypts the data sensitive digital keys and certificates that is needed to boot the system. If the TPM detects a new hard drive or the incorrect operating system license, then it will not allow the computer to boot further. With Secure Boot, it acts as a security checkpoint where it will only give access to validated start up programs.
What are some disadvantages/downsides of Secure Boot?
Secure Boot can be a minute hassle when trying to boot unauthorized software such a different operating system, or dual-booting. In order to proceed with a dual-boot, Secure Boot must be disabled, but rest assured, Ubuntu supports Secure Boot with dual-boot processes. If you need to disable secure boot for a dual-boot setup, reinstall Ubuntu and Secure Boot can be reenabled. This minimal downside should not be an influential factor to disable the benefits and security of Secure Boot.

How to enable Secure Boot for Windows 11?
First, let us check if secure boot is already enabled. Search ‘msinfo32’ in the Windows search menu, then look for the item ‘Secure Boot State’. If it says ON, then secure boot is already enabled. If it is labeled OFF, then it can be enabled in the UEFI BIOS. Refer to your motherboard manual to navigate through the UEFI BIOS to enable Secure Boot. Once again, check if secure boot is enabled. If Secure Boot is needed to be disabled, simply enter the UEFI BIOS and disable Secure Boot. It is highly encouraged that Secure Boot is left enabled as it has little to no effect on performance or compatiblility, but disabling Secure Boot is not mandatory. If the end user does not download a rootkit virus or any malicious programs, Secure Boot is not needed for computer usage.
- Share
Microsoft just revealed the next iteration of Windows OS. Officially called Windows 11, Microsoft claims that they have completely redesigned the entire user experience with fresh new design elements like animations, icons, fonts, and much more from the ground up.
But all of that excitement slowly started turning into a disappointment, and in some cases, even frustration. Why, you wonder? It’s because when Microsoft released the system requirements for their shiny new version of Windows, they mentioned two key specs that were a must-have for running the upcoming release. They were Secure Boot and TPM 2.0, which couldn’t be found on even some of the latest products either from Microsoft themselves.
Related: Enable TPM 2.0 | Bypass TPM 2.0 requirement
Up until now, Windows versions starting from 8 till 10 could all be run without Secure Boot even if the feature was listed as a requirement. We wish the same could be said for Microsoft’s latest Windows 11.
Some of the many early users of the first Windows 11 Insider Preview build are reporting that they’re unable to install the build and are outright shown a message that their PC can’t run Windows 11. The exact message can be seen in the image below.
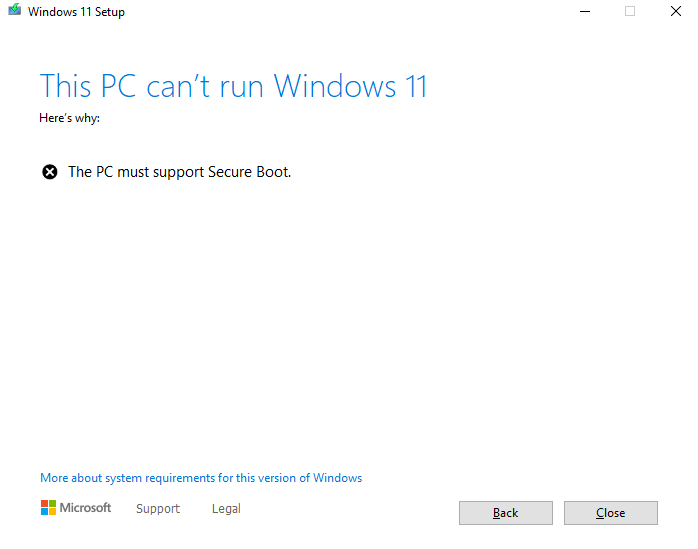
Let’s take a step back and find out what Secure Boot really is.
What is Secure Boot?
Secure Boot falls under UEFI, short for Unified Extensible Firmware Interface. You can think of UEFI as a software interface that sits between your operating system, firmware, and hardware. UEFI plans to replace BIOS (the interface that we had during the Windows 7 era and before) and it is what comes installed in every modern PC you can purchase right now.
In reality, Secure Boot is a protocol under UEFI 2.3.1 that exists to secure the system boot process by not loading any unsigned UEFI drivers or unsigned operating system boot loaders.
Its only role is to essentially block any piece of code (drivers, bootloaders, or applications) that aren’t signed by the OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) Platform Key.
If the UEFI driver, application, or OS bootloader does have the signed Platform Keys, only then is it permitted to run.
For you and me, it’s just a simple toggle in the UEFI menu that should always be enabled for maximum protection.
But Why is Windows 11 so dead set on requiring Secure Boot?
Windows has been trying to enforce Secure Boot ever since the release of Windows 8, and it seems like they won’t take no for an answer as the pros far outweigh the cons.
Microsoft claims that they have built Windows 11 around three key principles: Security, Reliability, and Compatibility. Looking at the additional requirement of Secure Boot and TPM 2.0, it seems that Security has taken the limelight.
According to Microsoft, these hardware requirements are critical to implementing stronger security for your PC, including for the features like Windows Hello, Device Encryption, Virtualization-Based Security (VBS), and HyperVisor-protected Code Integrity (HVCI).
Together, they can help keep your PC safe by reducing malware attacks by 60%.
Still too complex? Let’s make it even simpler.
Think of a scenario where you’ve just downloaded an executable file, say, an installer for a photo editing application. Little did you know that the program you just downloaded, and installed contained a harmful block of code that’s designed to execute on the next system boot.
You finish your task, shut down the PC, and go to bed. You turn back your PC the next day and everything goes haywire.
Your screen gets bombarded with alerts saying “Your car insurance has expired! Click here to renew.” Whatever you do, nothing seems to work. And the result? A completely unusable PC.
Thankfully, modern PCs (think 2017 and later) come with UEFI out-of-the-box, which means that by default Secure Boot is enabled on them.
Now, let’s re-run the same scenario we just mentioned and see what would’ve happened if the PC had Secure Boot enabled.
When you pressed the power button the next morning and unknowingly triggered the malicious code block to execute, Secure Boot takes total control of the boot process, thoroughly checking each and every application, driver, and bootloader that was queued up in the boot queue.
It found out that a harmful block of code exists in the boot queue without a valid Platform Key and hence completely denied its execution.
Yay! No more unwanted popups!
All in all, Secure Boot does a wonderful job of strengthening the security of your operating system while offering a couple of more powerful and advanced features than BIOS.
But there are a couple of downsides to Secure Boot. Some applications, even Linux distros require Secure Boot to be disabled.
How Do I Enable Secure Boot?
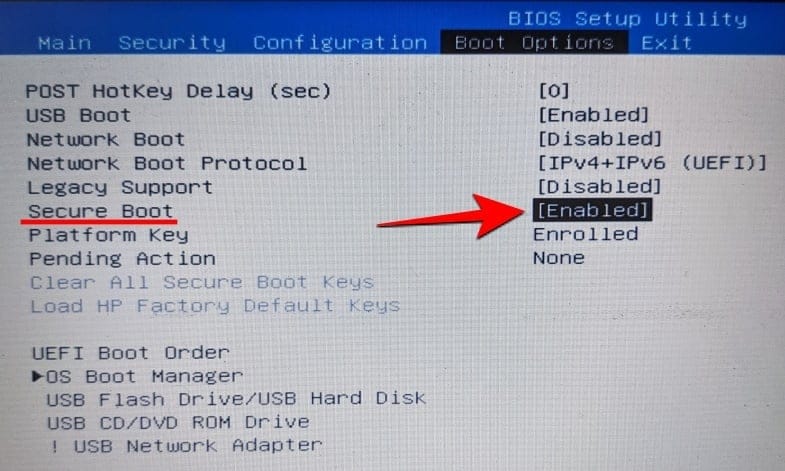
Enabling Secure Boot is a fairly straightforward process. One of our amazing writers has already gone over the process in great detail at the link below. Be sure to check it out.
- How To Secure Boot in BIOS for Windows 11
On some systems, you have to disable CSM to unlock the hidden Secure Boot option in your UEFI screen. If your PC is a recent buy, let’s say 2017 or later, then you should be able to enable Secure Boot. If you can’t, do share your PC’s motherboard’s model no. with us in the comments box below.
That’s all.
How to install Windows 11 yourself without the Microsoft Insider program:
- Step 1: Download Windows 11 Insider ISO
- Step 2: Create a Bootable Windows 11 USB Pen Drive with ISO
- Step 3: Install Windows 11 From USB
- Also see: How To Dual Boot Windows 11 with Windows 10