Сегодня мы разберемся, как установить и настроить клиент NFS (Network File System) в Windows Server 2012 R2 / Windows 8. Итак, чтобы подключить каталог (шару) с NFS сервера в Windows Server 2012 R2 / Win 8, нужно, как и в предыдущих версиях Windows, установить отдельный компонент — клиент NFS (Client for NFS). Дополнительно, для возможности управления настройками NFS подключения, можно установить компонент служб NFS (Services for Network File System).
Клиент NFS входит в состав ОС Microsoft, начиная с Windows 7. В Windows 2012 / 8 клиент NFS получил небольшие изменения. Теперь NFS клиент поддерживает аутентификацию по протоколу Krb5p — Kerberos версии 5 (в дополнение к Krb5 и Krb5i, поддержка которых появилась еще в Windows 7), поддерживаются большие NFS пакеты – до 1024KB (в Win 7 максимальный размер пакета 32KB)
Клиент NFS можно установить через GUI или с помощью Powershell. Для установки в графическом режиме, откройте консоль Server Manager и выберите компонент (Features) под названием Client for NFS.
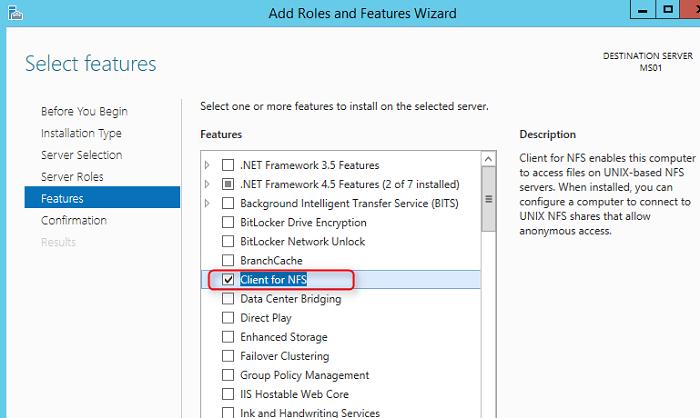
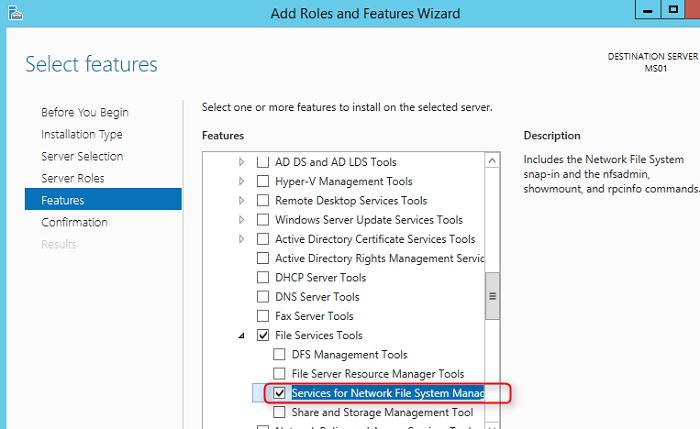
По умолчанию вместе с этим компонентом не устанавливается графическая консоль управления NFS, чтобы исправить это, установим опцию Services for Network File System Management Tools в разделе Remote Server Administration Tools -> Role Administration Tools -> File Services Tools.
Для установки NFS-клиента в Windows 8 нужно активировать компонент Services for NFS ->Client for NFS, через установку/удаление компонентов (Turn Windows features on or off) в Панели управления (Control Panel -> Programs -> Programs and Features).
Примечание. В отличии от Windows 7, в которой NFS клиент присутствовал в редакциях Enterprise и Ultimate, в Windows 8 клиент Network File System поддерживается только в старшой версии — Windows 8 Enterprise.
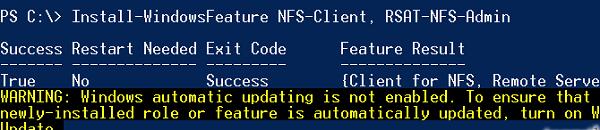
Все перечисленные выше компоненты системы можно установить всего одной командой Powershell:
Install-WindowsFeature NFS-Client, RSAT-NFS-Admin
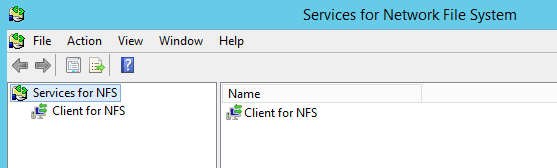
После окончания установки, запустите консоль Services for Network File System Managemen и откройте окно свойств NFS клиента (Client for NFS).
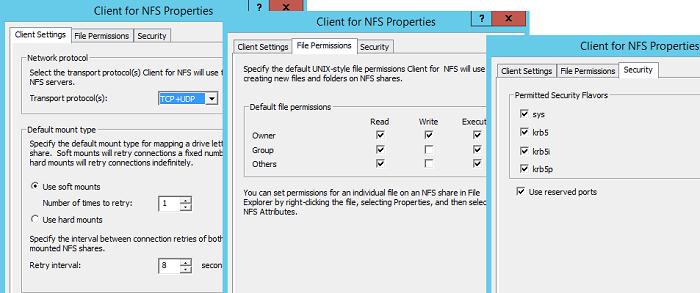
В настройках NFS клиента можно задать:
- Используемый транспортный протокол (Transport protocols) – по умолчанию TCP+UDP
- Тип монтирования NFS шар: hard или soft
- На вкладке File Permissions указываются дефолтные права для создаваемых папок и файлов на NFS шарах
- На вкладке Security указываются протоколы аутентификации, с помощью которых можно аутентифицироваться на NFS сервере
После настройки установки, администраторы смогут смонтировать NFS каталог с помощью команды mount:
Mount \\lx01.abc.lab\nfs z:
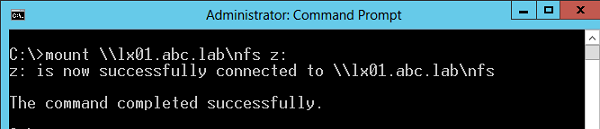
В этом примере мы смонтировали под буквой Z: каталог NFS, расположенный на сервере lx01.abc.lab.
После монтирования, подключенный таким образом каталог на NFS сервере доступен в системе как отдельный диск с буквой Z:\ .
Смонтировать NFS шару можно и с помощью Powershell:
New-PSdrive -PSProvider FileSystem -Name Z -Root \\lx01.abc.lab\nfs
Примечание. Подключенный таким образом nfs каталог будет доступен только внутри сессии Powershell, в которой была выполнена команда монтирования. Чтобы смонтировать NFS каталог в системе на постоянной основе, в конце Powershell команды нужно добавить ключ –Persist.
Отключить смонтированный каталог можно так:
Remove-PSdrive -Name Y
Overview
Out of the box, a Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8 cannot connect to NFS-based shares from your Linux environment by default. Although, they both include a feature that when enable does allow them to.
Microsoft likes to trumpet that 90% of servers deployed in enterprise environments run Windows Server. But that still means there are a lot of Linux\Unix servers out there. When you include startups and mid-sized companies, the number of Linux servers grows substantially.
With the growth of Linux adoption, especially at the small-to-medium sized business, odds you may eventually need to connect a Windows server or a Windows desktop to an NFS share.
Install NFS Client Feature
The NFS client is now an installable feature in Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 and higher.
- Launch Server Manager
- On the top-left side of the console, click Manage.
- Click Add Roles and Features.
- On the Before you begin screen, click Next.
- On the Select installation type screen, select Role-based or feature-based installation, and then click Next.
- On the Select destination server screen, if you are installing to the local server, click Next. Otherwise, select a server from the Server Pool list.
- On the Select server roles screen, click Next.
- On the Select features screen, scroll down the list of available features until you see Client for NFS. Click its checkbox to select it for installation, and then click Next.
- On the Confirm installation selections screen, review your selections and then click Install.
- After the installation completes, review the results and then click Close.
Mount NFS Share
To mount an NFS share into Windows we need to use the mount command. There is no GUI interface to perform this task. The command is very simple to use and relatively similar to the same command found in Linux.
The examples below will connect to a host named LNXSRV01. The local user account on LNXSRV01 that will be used to mount the share will be Sam.
- Open a command-prompt.
- Mount an NFS share called /exports/dept to the Z:.
mount -user:Sam -p:MyPassword \\LNXSRV01\exports\dept Z:
Instead of typing the password into the command-line, we can use ‘*’ to force a password prompt when mounting.
mount -user:Sam -p:* \\LNXSRV01\exports\dept Z:
To mount the share into any available drive letter on the Windows server we can replace Z: with ‘*’.
mount -user:Sam -p:* \\LNXSRV01\exports\dept *
Set whether the mount type is hard or soft using the mtype option.
mount -o mtype=hard -user:Same -p:* \\LNXSRV01\exports\dept *
Persistent Mounts
There is no method of creating a persistent mount of an NFS share on a Windows server. The only option to mount an NFS share at system boot or logon is to use a batch script. This, however, is not recommended.
Apr 3, 2016
Introduction
Let’s face it, we support mixed environments and sometimes we need to access information on Linux systems on our Windows systems. With that said say you have a Windows server that needs to get to NFS exports on a Linux systems. Well that is completely doable on Windows Server 2012 R2 using Client for NFS. Note: You can also mount NFS if you are running Windows 7 Enterprise or Ultimate versions.
Using Client for NFS
First we will need to install the Client for NFS feature on our systems needing to access the FS exports. Using Server Manager click on Manage > Add Roles and Features. Click Next until you reach the features selection and then select Client for NFS. Click Next then install. Now the client is installed. There are a few new commands installed with the client that we will cover in this post.
nfsadmin.exe
nfsclnt.exe
mount.exe
umount.exe
showmount.exe
To start Client for NFS from the Windows interface
After installation this service should start by default, if not. Open Services for Network File System: click Start, point to Programs or All Programs, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Services.
Right-click Client for NFS, and then click Start Service.
To start Client for NFS from the command line
Open an elevated privilege command prompt.
At the command prompt, type:
nfsadmin client [ComputerName] start
Mounting and NFS Share
To mount an NFS shared resource to a drive letter using the command line
Open a command prompt (this does not need to be an elevated command prompt).
At the command prompt, type the following:
mount [-o options] [-u:username] [-p:<password | *>] <\\computername\sharename> <devicename | *>
Here are a few of the options when mounting and NFS share on Windows.
| Option | Description |
| -0 rsize= n | The read buffer size, in kilobytes. Acceptable values are 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32. The default is 32 KB. |
| -o wsize= n | The write buffer size, in kilobytes. Acceptable values are 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32. The default is 32 KB. |
| -o timeout= n | The time-out for a remote procedure call (RPC), in seconds. Acceptable values are 0.8, 0.9, and any integer in the range 1-60. The default is 0.8. |
| -o retry= n | The number of retries for a soft mount. Acceptable values are integers in the range 1-10. The default is 1. |
| –o mtype={soft | hard} | Soft or hard mount. Regardless of the mount type, the mount will return if it cannot immediately mount the shared resource. However, once the shared resource has been successfully mounted, if the mount type is a hard mount and the Network File System (NFS) server becomes unavailable, Client for NFS will retry accessing the shared resource until the NFS server is once again available. As a result, Windows applications that are trying to access the shared resource will appear to stop responding. |
| -0 anon | Mounts as anonymous user. |
| -o nolock | Disables locking. This option might improve performance if you only need to read files. |
| -o lang= n | To specify the encoding used for file and directory names. euc-jp|euc-tw|euc-kr|shift-jis|big5|ksc5601|gb2312-80|ansi |
| -o fileaccess= mode | Specifies the default permission mode of new files that are created on the NFS shared resource. The permission mode is written as a three-digit number in the form ogw, where o, g, and w represent the access granted to the file (o)wner, (g)roup, and the (w)orld. Each digit must be in the range 0–7, with the values corresponding to the following access levels:
|
| -o casesensitive | Forces case-sensitive file lookup (similar to that of UNIX-based NFS clients). |
| -o sec= sys | |krb5|krb5i|krb5p (Kerberos Security) |
| ComputerName | The name of the server with the shared resource to mount.The name of the shared directory to mount. |
| ShareName | The name of the shared directory to mount. |
| DeviceName | * | The drive letter to assign to the mounted shared resource. The asterisk (*) means to use the next available letter. |
Notes:
To view the complete syntax for this command, at a command prompt, type: mount /?
When mounting an NFS shared resource to a drive letter, we recommend the format ComputerName:/ ShareName.
You can also use the net use command to mount an NFS shared resource to a drive letter.
Examples:
To mount and NFS Export to drive no user credentials G:
mount \\192.168.1.110\export G:
Mount an NFS export in read write mode with username and password
mount -o fileaccess= 7 -u: homey -p: homestead 192.168.1.110/export g:
To view NFS exports on a server
showmount -e 192.168.1.110
To unmount an NFS shared resource from a drive letter using the command line
Open a command prompt (this does not need to be an elevated command prompt).
At the command prompt, type:
umount [–f] {–a | Drive}
umount options:
-f = Force unmount
-a = Unmount all NFS drives
umount -f G:
Conclusion
As you can see, we can now access NFS exports from our Windows Server 2012 R2 systems using the Client for NFS feature. At this point we can start exploring PowerShell NFS cmdlets and their usage https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj603081(v=wps.630).aspx.
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
To connect NFS shares on Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2, administrators can install «Client for NFS» on these operating systems and then perform «mount» command to connect it. After that, administrators also can install «Services for Network File System» to manage «Client Settings«, «File Permissions» and «Security» of «Client for NFS«.
Goal
- Install «Client for NFS» by GUI and «PowerShell«
- Install «Services for Network File System» by GUI and «PowerShell«
Prerequisites
- 1 server is installed Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2 and named MS01
Lab
1. On MS01, log in as Local Administrator.
2. Launch «Server Manager«.
3. Click «Add roles and features«.
4. On «Before You Begin» window, click «Next«.
5. On «Installation Type» window, select «Role-based or feature-based installation«.
6. Click «Next«.
7. On «Server Selection» window, click «Next» twice.
8. On «Features» window, check «Client for NFS«.
By default, the «Services for Network File System» management console isn’t installed with «Client for NFS«. Administrators need to check it by themselves.
9. Check «Services for Network File System Management Tools» under «Remote Server Administration Tools > Role Administration Tools > File Services Tools«.
10. Click «Next«.
11. On «Confirmation» window, click «Install«.
12. On «Results» window, click «Close«.
As a result, «Client for Network File System» and «Client for NFS» have been installed.
Now, administrators can manage the settings of «Client of NFS«.
Administrators can perform «mount» command to connect the NFS share.
Administrators also can perform «Install-WindowsFeature NFS-Client, RSAT-NFS-Admin» in PowerShell console to install «Client for NFS» and «Client for Network File System«.
More information:
This posting is provided “AS IS” with no warranties, and confers no rights!
The Network File System (NFS) client is not installed by default on Windows Server 2022/2019/2016/2012R2 and Windows 11/10 desktop versions. To install it, open the Server Manager and select Add Roles and Features -> Client for NFS.

If you want to install graphical NFS management consoles (nfsmgmt.msc), select Services for Network File System Management Tools under Remote Server Administration Tools -> Role Administration Tools -> File Services Tools.

Or you can use PowerShell to install the NFS client and management snap-in:
Install-WindowsFeature NFS-Client, RSAT-NFS-AdminIf you are running Windows 10 or 11, run the following to install the NFS client:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -FeatureName ServicesForNFS-ClientOnly, ClientForNFS-Infrastructure -Online -NoRestartThe Windows NFS client supports NFSv2 and NFSv3 protocol verions.
Now you can mount the NFS share using PowerShell:
New-PSdrive -PSProvider FileSystem -Name M -Root \\192.168.0.211\mnt\hyperv -PersistPersist option allows to connect NFS shares automatically after a system reboot.
With CMD:
mount -o anon nolock \\192.168.0.211\mnt\hyperv M:You can also mount an NFS directory from the File Explorer GUI.
In order to disconnect NFS share, run:
Umount M:Or:
Remove-PSdrive -Name MAn error may occur when mounting NFS shares:
The remote device or resource won’t accept the connection.

To resolve the problem, start the Services for Network File System (NFS) console and check the permissions that you have to connect to the remote share.
If you want to connect to an NFS share as an anonymous user, there are two registry items that you will need to add:
New-ItemProperty HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\ClientForNFS\CurrentVersion\Default -Name AnonymousUID -Value 000001f4 -PropertyType "DWord"
New-ItemProperty HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\ClientForNFS\CurrentVersion\Default -Name AnonymousGID -Value 00000064 -PropertyType "DWord"If you always want to connect using the root account, change the AnonymousUID and AnonymousGID settings to 0.
When using NFS connections in an Active Directory environment, there’s an important caveat:
If UNIX attributes are not added to AD and user name mapping is not configured, an anonymous connection is used to connect to the NFS server from Windows. You need to make changes to the AD schema (attributes uidNumber and gidNumber) in order to use alternative credentials to connect to NFS folder.
On WS 2012R2 domain controllers, you can add the UNIX Attributes tab to the AD user properties in ADUC:
Dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:adminui /allHowever, this option is deprecated in Windows Server 2016, and it is suggested that user attributes be edited manually or using PowerShell:
Set-ADUser -identity user1 -add @{uidNumber="<user_unix_uid>";gidNumber="<user_unix_gid>"}An error may also occur when mounting an NFS directory:
You can't access this shared folder because your organization's security policies block unauthenticated guest access. These policies help protect your PC from unsafe or malicious devices on the network
In this case, you must create the AllowInsecureGuestAuth registry entry.
New-ItemProperty HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanWorkstation\Parameters -Name AllowInsecureGuestAuth -Value 00000001
New-ItemProperty HKLM:\ oftware\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\LanmanWorkstation -Name AllowInsecureGuestAuth -Value 00000001Then restart the NFS service from the nfsmgmt.msc snap-in.
