Все способы:
- Способ 1: Изменение конфигурации системы
- Способ 2: Снятие ограничений через «Командную строку»
- Способ 3: Управление виртуальной памятью
- Способ 4: Проверка оперативной памяти на наличие ошибок
- Способ 5: Проверка параметров BIOS
- Способ 6: Уменьшение размера буфера интегрированной графики
- Способ 7: Внесение изменений в реестр
- Способ 8: Проверка работоспособности ОЗУ
- Вопросы и ответы: 0
Если у вас возникли подозрения, что операционная система Windows использует или отображает не всю оперативную память, для начала рекомендуем проверить, отображаются ли все подключенные планки, и как сторонние программы показывают доступный лимит памяти. В некоторых случаях отсутствие информации сразу указывает на физические проблемы комплектующих, поэтому программную часть можно будет пропустить и в первую очередь проверить подключение и состояние ОЗУ.
Подробнее: Просмотр оперативной памяти в Windows 11
Способ 1: Изменение конфигурации системы
Распространенная причина проблемы с использованием всей оперативной памяти в Windows 11 — неправильная настройка конфигурации системы. В ОС есть параметры, позволяющие вручную ограничить количество потребляемых системных ресурсов или же отключить подобное слежение. Поэтому вам понадобится самостоятельно проверить настройки, и при необходимости изменить их под себя.
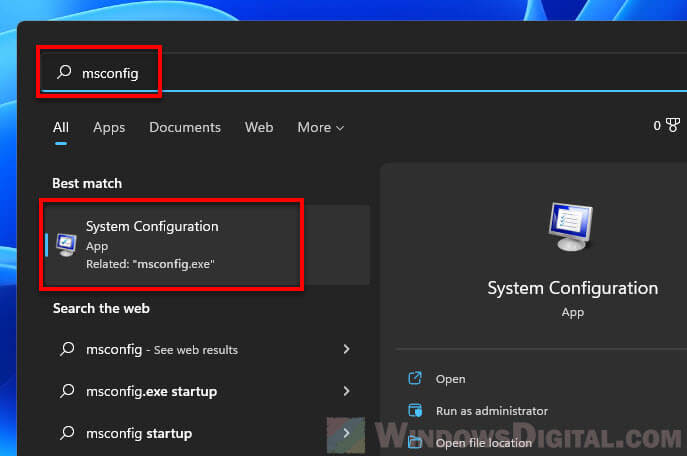
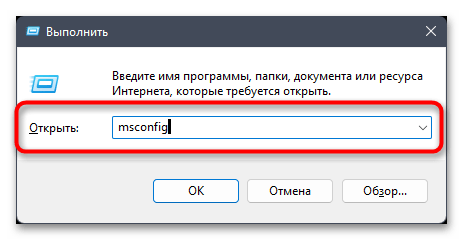
- Откройте утилиту «Выполнить», используя для этого сочетание клавиш Win + R. Введите в строке команду
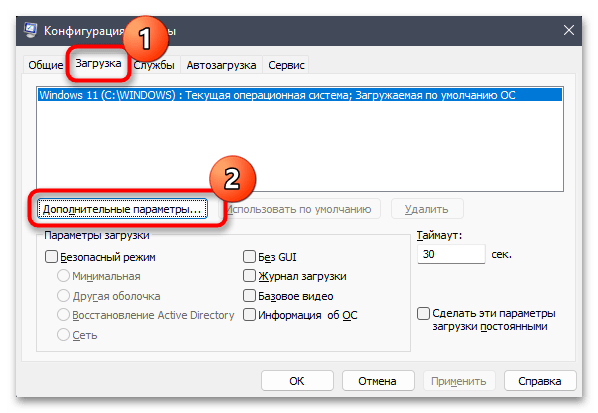
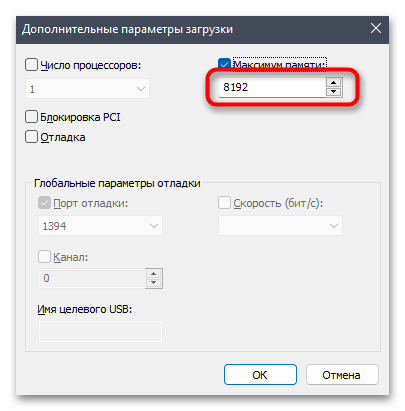
msconfigи нажмите Enter для ее применения. - В новом окне перейдите на вкладку «Загрузка» и нажмите по «Дополнительные параметры», чтобы открыть окно с требуемыми настройками.
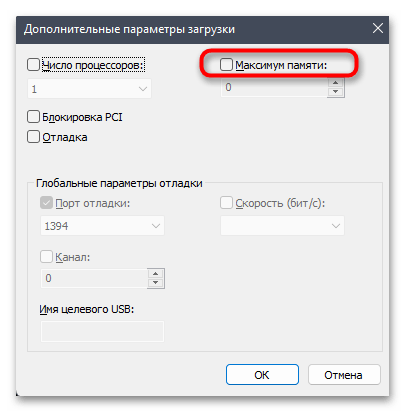
- Следующие действия зависят от того, установлена ли в параметрах загрузки галочка «Максимум оперативной памяти». Если да и выбрано количество мегабайт, рекомендуем отключить данный параметр.
- Если сейчас он и так отключен, поставьте галочку и укажите число в мегабайтах, соответствующее объему вашей оперативной памяти, после чего нажмите «ОК», чтобы выйти из данного окна.
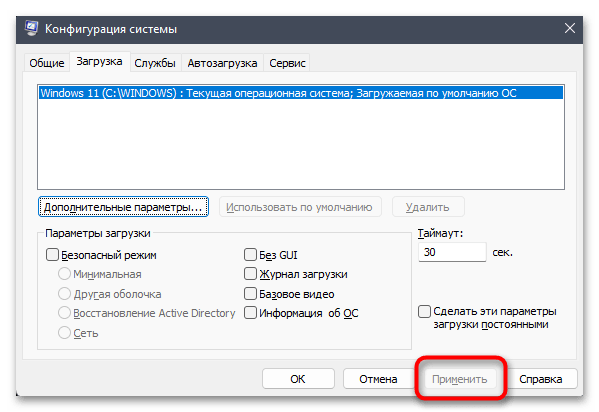
- В «Конфигурации системы» кликните по «Применить» и подтвердите отправку ПК на перезагрузку, чтобы изменения вступили в силу. При следующем входе в Windows можете приступать к проверке количества доступной оперативной памяти.
Способ 2: Снятие ограничений через «Командную строку»
Следующий метод по своему действию похож на предыдущий, но является более эффективным и иногда единственным рабочим, если установлено системное ограничение на количество доступной оперативной памяти. Суть способа заключается в использовании специальных консольных утилит, при помощи которых редактируется конфигурация загрузки ОС и убираются любые лимиты на использование ОЗУ.
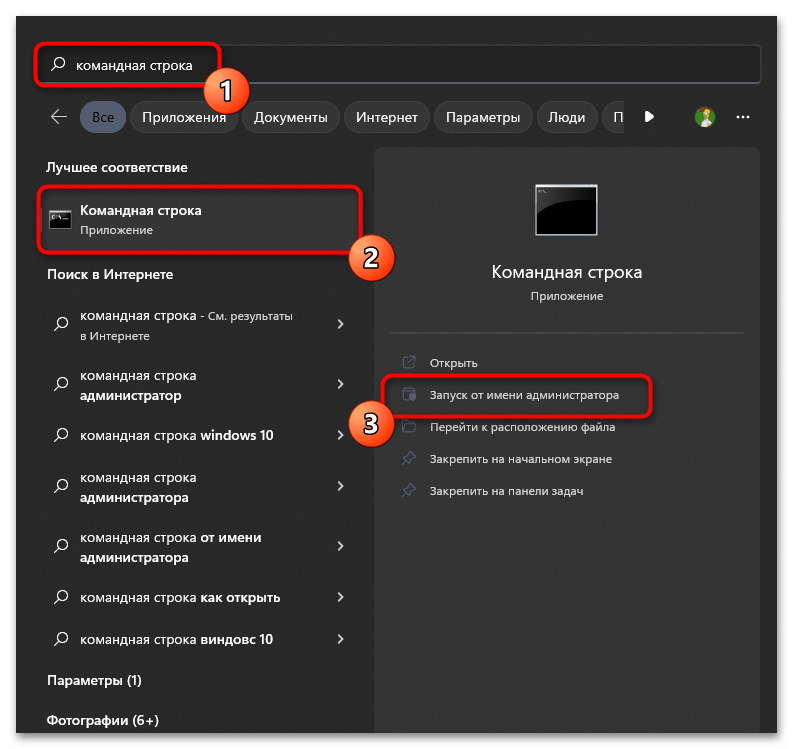
- Откройте «Пуск», отыщите «Командную строку» и обязательно запустите данное приложение от имени администратора.
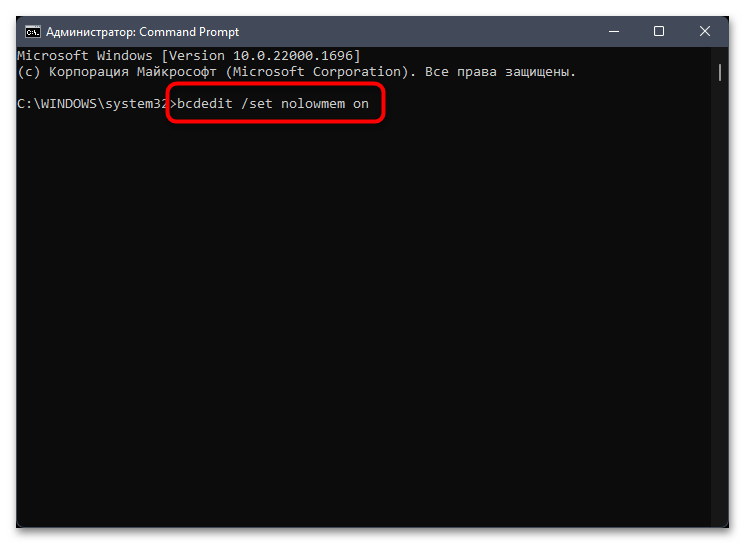
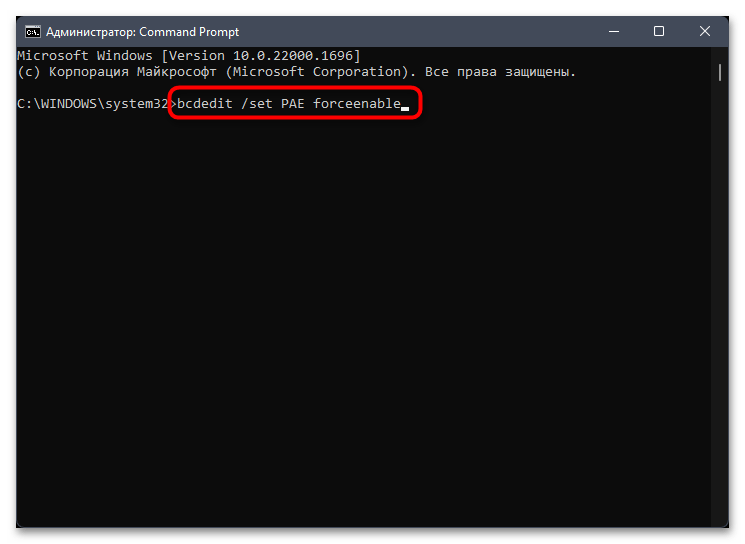
- Введите первую команду
bcdedit /set nolowmem onи подтвердите ее активацию, нажав по клавише Enter. - После появления информации об успешном применении напишите еще одну команду
bcdedit /set PAE forceenableи точно так же ее подтвердите. Остается только перезагрузить компьютер, чтобы проверить, помогли ли данные действия исправить ситуацию.
Способ 3: Управление виртуальной памятью
Виртуальная память, она же еще называется файлом подкачки, никак не связана с физическим объемом установленной в компьютере оперативной памяти, поскольку потребляет свободное место с жесткого диска или SSD. Однако иногда неправильные настройки виртуальной памяти или системные сбои влияют на визуальное отображение или доступность максимального количества RAM, которое отличается от фактического. Поэтому мы рекомендуем проверить виртуальную память, отключив ее или выбрав режим автоматического назначения.
- Откройте «Пуск» и найдите элемент «Панели управления» с названием «Настройка представления и производительности системы». Нажмите по нему левой кнопкой мыши, чтобы перейти к соответствующему окну.
- В нем выберите вкладку «Дополнительно» и в блоке «Виртуальная память» кликните по «Изменить».
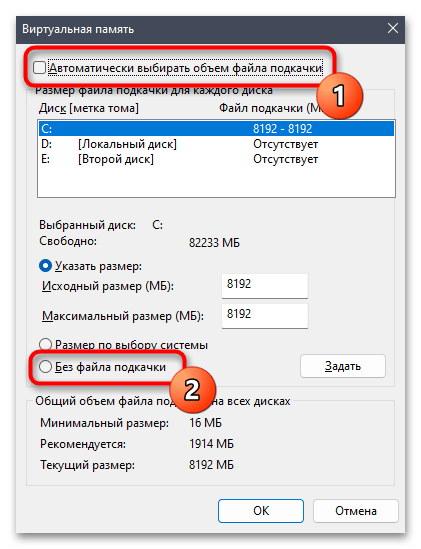
- Проверьте, какой режим использования файла подкачки сейчас установлен. Если он и так автоматический, попробуйте отключить файл подкачки, установив маркер возле соответствующего пункта. При ручном выборе размера пока что лучше переключиться на автоматически, чтобы проверить, повлияет ли это на решение рассматриваемой проблемы. Обязательно примените изменения и перезагрузите компьютер, чтобы они вступили в силу.
Способ 4: Проверка оперативной памяти на наличие ошибок
Существует вероятность, что проблемы с доступным количеством оперативной памяти вызваны программными сбоями в ее работе. Это может отражаться и на быстродействии операционной системы и появлении различных зависаний в программах или играх. Существуют разные методы программной проверки памяти, которые часто оказываются эффективными и исправляют различные сбои, налаживая корректное функционирование ОЗУ. О таких методах читайте в материале по следующей ссылке.
Подробнее: Поиск ошибок оперативной памяти на компьютере с Windows 11
Способ 5: Проверка параметров BIOS
Микропрограммное обеспечение BIOS влияет на настройки материнской платы и всех комплектующих. В нем есть множество разных параметров, предназначенных для работы функций, установки различных ограничений и изменения общей конфигурации системы. В случае с оперативной памятью в БИОС понадобится найти параметр, отвечающий за назначение ОЗУ в сборках, где ее объем превышает 4 ГБ. Сама функция должна быть обязательно активированной, чтобы пользователь мог использовать всю доступную память.
- В первую очередь щелкните по ссылке ниже и выберите подходящий для вас метод входа в BIOS, если собираетесь делать это впервые.
Подробнее: Как попасть в BIOS на компьютере
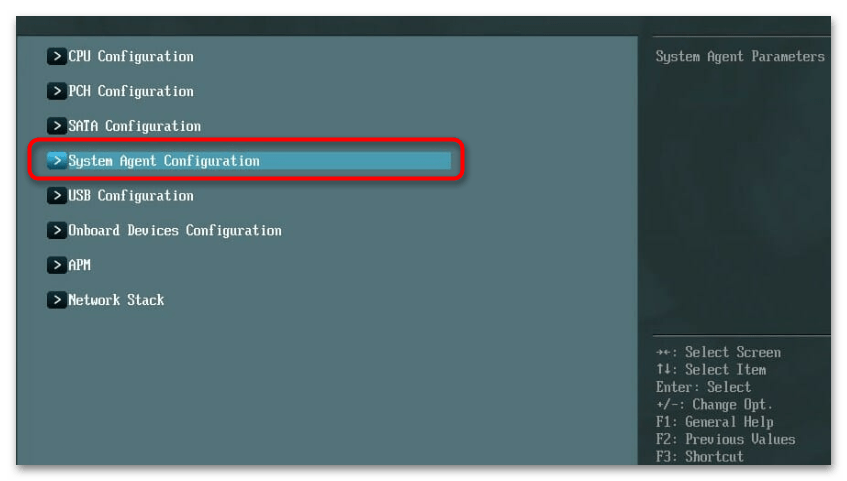
- Далее в BIOS или UEFI (зависит от ревизии и модели материнской платы) откройте раздел с дополнительными настройками. Он может называться «Advanced», «Advanced Options» или «System Agent Configuration».
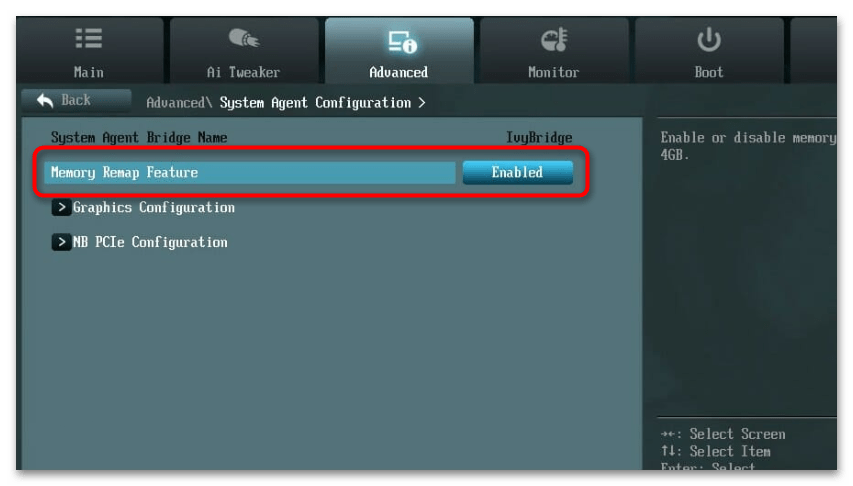
- В таком разделе понадобится найти функцию с названием «Memory Remap Feature». Реже могут встречаться следующие названия: «Memory Remapping», «DRAM Over 4G Remapping», «H/W DRAM Over 4GB Remapping», «Hardware Memory Hole», «Memory Hole Remapping». Все они относятся к одной и той же функции и отвечают за одинаковое действие — разблокировку ОЗУ, объем которой превышает 4 ГБ. Обязательно установите значение для данного параметра «Enabled». При выходе из BIOS сохраните настройки, затем запустите Windows 11 и проверьте изменения.
Способ 6: Уменьшение размера буфера интегрированной графики
Данный метод актуален только для пользователей с ПК или ноутбуком, в которых есть интегрированный в процессор видеочип. У интегрированной видеокарты память берется с оперативной, а сам буфер доступного размера формируется через BIOS по умолчанию в автоматическом режиме. Как раз потребление или блокировка RAM интегрированной графикой и может стать причиной того, что в Windows вы видите не всю оперативную память в операционной системе.
Читайте также: Что значит интегрированная видеокарта
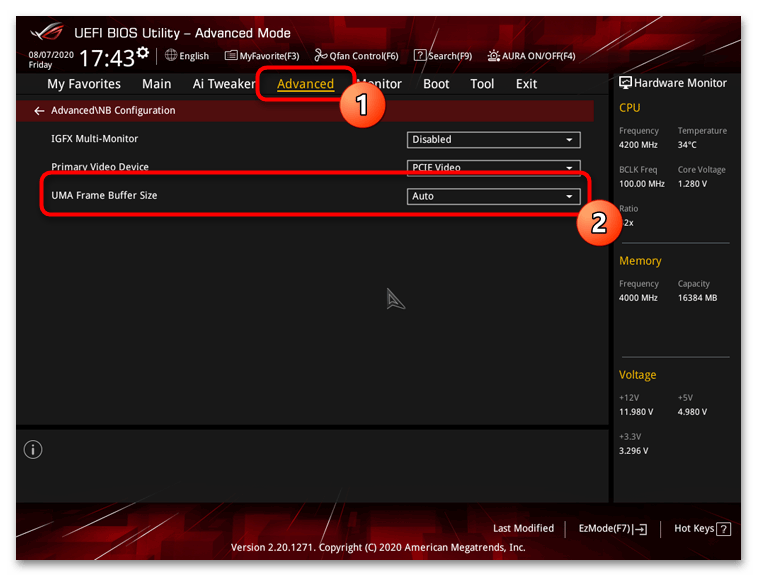
Для решения этой ситуации вам необходимо в BIOS выбрать раздел «Advanced» и найти «Video Memory» или «UMA Frame Buffer Size», чтобы поменять автоматическое назначение на любое удобное для вас количество выделяемой памяти. Если интегрированной графикой вы в принципе не пользуетесь, блокировку ОЗУ можно отключить, тогда ее объем точно будет полностью доступен в Windows 11.
Способ 7: Внесение изменений в реестр
Рекомендация по внесению изменений в системный реестр больше рассчитана на устранение системных сбоев, когда файл подкачки автоматически не очищается при выключении ПК, что влечет за собой появление нарушений как в визуальном отображении доступного ОЗУ, так и в физическом, когда в играх или программах память задействована не вся. Отредактировать нужно всего один параметр, а осуществляется это так:
- Откройте «Пуск», через поиск отыщите «Редактор реестра» и запустите данное классическое приложение.
- Вставьте в адресную строку путь
Компьютер\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Managementи перейдите по нему, нажав клавишу Enter. - Найдите параметр с названием «ClearPageFileAtShutdown» и кликните по нему дважды для открытия «Свойств».
- Поменяйте значение на «1», сохраните изменения и перезагрузите компьютер, поскольку новые настройки реестра активируются только в новом сеансе ОС.


Способ 8: Проверка работоспособности ОЗУ
Если ничего из перечисленного выше не помогло сделать всю оперативную память доступной в Windows 11, скорее всего, дело не в программных ошибках, а физических. В первую очередь стоит запустить средства проверки оперативной памяти на работоспособность или переподключить планки к другим разъемам на материнской плате. Иногда единственным выходом будет замена ОЗУ или обращение в сервисный центр, но сначала все-таки попробуйте выполнить проверку вручную так, как это описано в материале далее.
Подробнее: Как проверить оперативную память на работоспособность
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
Readers help support Windows Report. We may get a commission if you buy through our links.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Windows 11 not using all RAM can have a serious impact on performance. You need this memory to tempoarily store your in-progress files and if you don’t have enough, you’ll run into errors and possibly lose progress.
To help you prevent that, we’ll explain how to use all RAM in Windows and give you a glimpse into the most common causes of it.
Let’s get started.
How to use all RAM in Windows
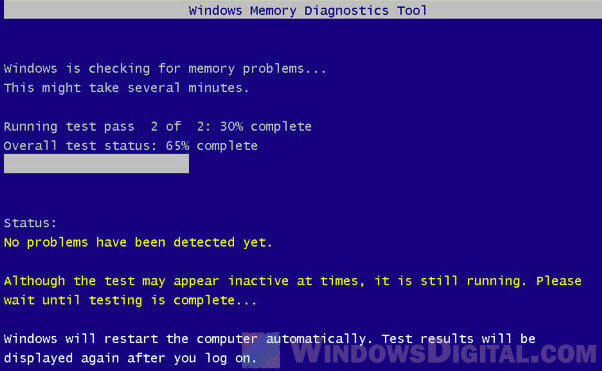
1. Run the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool
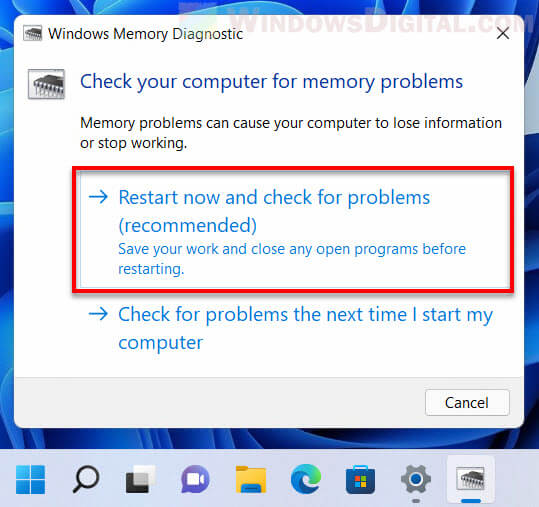
- Press Windows + S to launch the Search menu, enter Windows Memory Diagnostic tool in the text field at the top, and then click on the relevant search result that appears.
- Now, select Restart now and check for problems (recommended) from the two options listed here.
Windows Memory Diagnostic identifies problems with the RAM and automatically eliminates them. Before you run it, save any open files to avoid data loss, because your computer will restart.
2. Check page file
- Press Windows + S to launch the Search menu, enter View advanced system settings in the text field at the top, and click on the relevant search result that appears.
- Click on Settings under Performance in the Advanced tab.
- Navigate to the Advanced tab in the Performance Options window.
- Click on Change under Virtual memory.
- Untick the checkbox for Automatically manage paging file size for all drives.
- Select the drive, check the No paging file option and then click on the Set button.
- Click Yes on the warning box that appears.
- Repeat the process for all drives if they have a page file, and then click on OK at the bottom to save the changes.
- Finally, restart the computer for the changes to come into effect.
The page file is a set space on your storage drive that is used to store data temporarily when the RAM (memory) starts to fill up. If there are problems with it, you may notice that Windows 11 is not using all the RAM.
If disabling the page file doesn’t fix the problem, revert the changes you made earlier, and continue with the next fix.
3. Modify the usable RAM
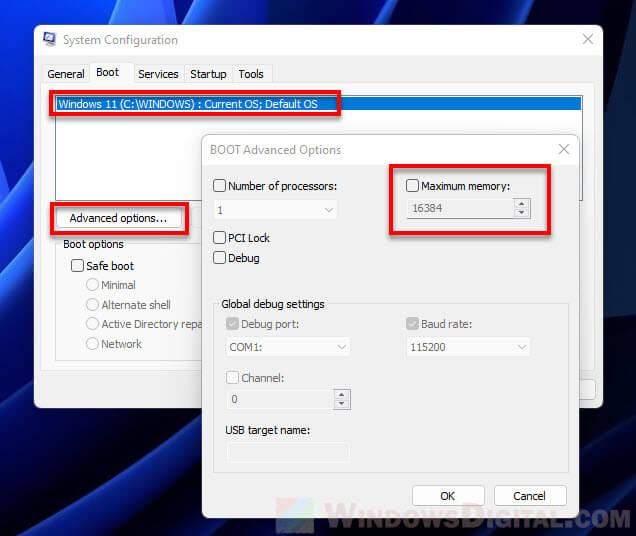
- Press Windows + S to launch the Search menu, enter System configuration in the text field at the top, and click on the relevant search result that appears.
- Now, go the Boot tab and click on Advanced options.
- Tick the checkbox for Maximum memory, enter the installed RAM on your system in the text field underneath, and then click on OK at the bottom.
- Again, click on OK to save the changes and close the System Configuration window.
- Restart the computer, if prompted.
- In case it doesn’t work, uncheck the Maximum memory checkbox in BOOT Advanced Options window, and save the changes.
To calculate the value in the text field earlier, check the installed RAM in your system, and multiply it by 1024 to find the value in MB (Megabyte). For instance, your computer has 16 GB RAM, so the value to be entered becomes 16 x 1024 = 16384 MB.
4. Modify the registry
- Press Windows + R to launch the Run command, enter regedit in the text field, and either click on OK or hit Enter to launch the Registry Editor.
- Click Yes on the UAC (User Account Control) prompt that pops up.
- Now, enter the following path in the address bar at the top and then hit Enter. Alternatively, you can navigate the path using the pane on the left:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management - Locate and double-click on the ClearPageFileAtShutdown DWORD to modify its value data.
- Enter 1 under Value data and click on OK to save the changes.
- Close the registry, and restart the computer.
5. Enable memory remapping in BIOS
NOTE
The method to enter the BIOS and its interface are different for every manufacturer. Therefore, we recommend that you check the FAQ or Support section of your OEM’s website for the exact steps. The steps listed below you should give you an idea though.
- Restart the computer, hit the F12 key as soon as the diplay lights up to enter the BIOS, navigate to the Advanced tab, and then select the System Agent Configuration option.
- Now, select the Memory Remap Feature and Enable it.
Enabling memory remapping is known to increase the available RAM to Windows on the system. But, the feature is not available on all devices, so do check if you have it before proceeding with the method.
Once done, check if Windows 11 now uses all the available RAM.
6. Rearrange the RAM modules
If you have multiple slots available, rearranging the RAM modules could help. To do that, turn off the computer, open the back panel, remove the memory modules and change their slots.
Check if that fixes the issue.
Also, some systems require you to arrange the RAM in a certain order when all the slots are not being used. For instance, if you have four slots available but are using only two memory modules, you may be required to use the first and third slots.
7. Take your PC to a repair center
If you have reached this part of the article after executing the methods listed above and the issue persists, it’s likely an issue with the hardware itself.
It could be broken or malfunctioning slots, issues with the connections, or other similar problems.
In such cases, we would recommend taking your PC to a repair center since the components we are dealing with here are fragile and the connections intricate. Any lapse on your part can severely damage the system.
Why isn’t Windows 11 using all RAM on my PC?
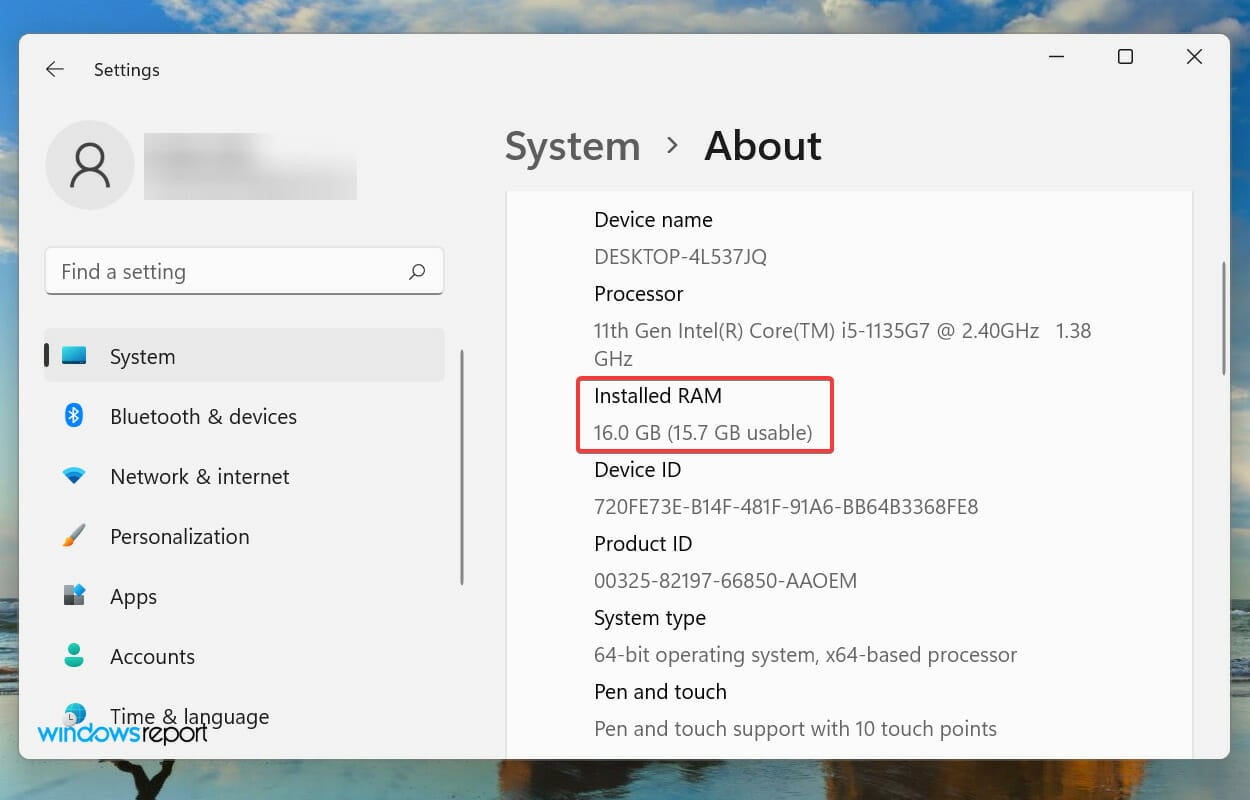
First of all, your computer would never use all the available memory or RAM. For instance, the Dell Inspiron laptop that is being used to write this article has 16 GB of installed RAM while only 15.7 GB of it is usable.
But if you notice that the OS isn’t able to utilize even the available RAM, it could be due to misconfigured settings, problems with the slot, or the RAM itself.
Apart from that, certain devices, say the graphic card, are also known to reserve a certain amount of RAM/memory.
By now, you are fairly acquainted with the concept and in a far better position to troubleshoot the problem. Let’s now walk you through the most effective fixes to eliminate the Windows 11 not using all the RAM issue.
If the installed RAM is low or you are using too many too programs at once, there’s a chance that the RAM usage becomes high, which will likely be evident through the poor system performance. The programs may lag or freeze, or the system may crash altogether.
That’s all there’s to eliminating issues preventing Windows 11 from using all available RAM. Once you are done executing these, the system performance will most likely be a lot better.
In case you are facing the same problem on the previous iteration, check what you should do if Windows 10 is not using all the available RAM.
Tell us which fix worked for you in the comments section below.
Kazim Ali Alvi
Windows Hardware Expert
Kazim has always been fond of technology, be it scrolling through the settings on his iPhone, Android device, or Windows PC. He’s specialized in hardware devices, always ready to remove a screw or two to find out the real cause of a problem.
Long-time Windows user, Kazim is ready to provide a solution for your every software & hardware error on Windows 11, Windows 10 and any previous iteration. He’s also one of our experts in Networking & Security.
Unlike 32-bit system which supports only up to 4GB of RAM, since Windows 11 is all 64-bit by default, you can use literally any amount of RAM (theoretically with a limit of 16 exabytes of RAM) on your Windows 11 PC.
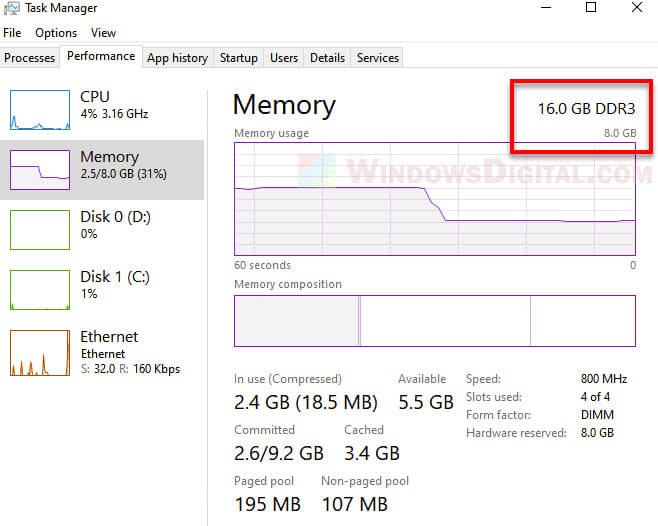
If you are seeing your PC is capped at certain amount of RAM but you know you have more than just that, e.g. you have 16 GB of RAM installed but only 8 GB is usable in Windows 11, try using the following suggested solutions to troubleshoot the problem.
Also see: How to Clear RAM Cache in Windows 11
Why is only 8GB of 16GB RAM usable?
Check the Maximum Memory setting
In Windows 11, there is an option that allow users to set how much RAM the system can use. However, this option (checkbox) should always be left unchecked to allow Windows to automatically use all available RAM.
Check the maximum memory setting to see if the option is enabled accidentally or a wrong amount of memory was set. To check the maximum memory setting in Windows 11, follow the steps below.
- Search for “msconfig” via Start menu and select “System Configuration“.
- Select the Boot tab.
- Select the operating system which you want to manage the options for. In our case, it would be the Windows 11 OS.
- Click Advanced Options.
- Make sure the Maximum memory checkbox is unchecked (disabled) so that Windows can utilize all available RAM on your computer.
It is not recommended to manually set the maximum memory if you do not know the exact amount of memory you have. Doing so may risk causing your OS to fail to boot.
Related: Why is My Memory Usage So High When Nothing is Running?
Check the BIOS settings
Check your BIOS to see if there are any settings that could limit the memory your computer can use, configurations that could enable or disable certain memory module slots or channels, RAM overclock settings that may cause the RAM to overvolting and ultimately failing to work, etc.
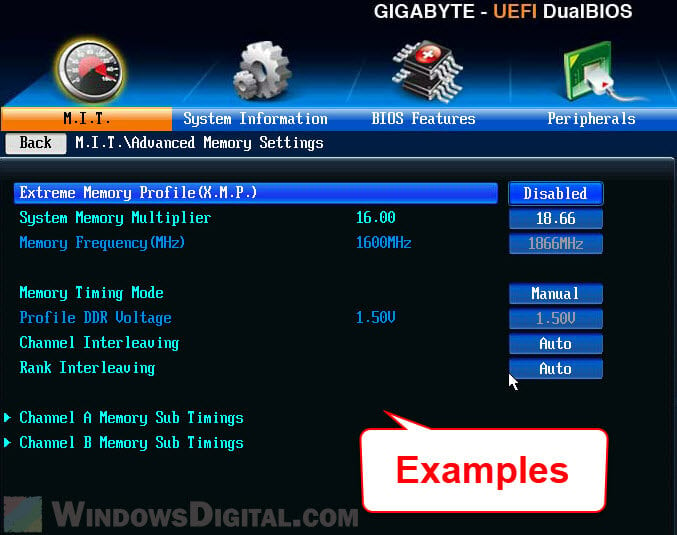
Find in the BIOS and see if there is any setting called “Memory Remap” feature. Enabling the feature will allow the installed but previously unusable RAM to be utilized to its full potential.
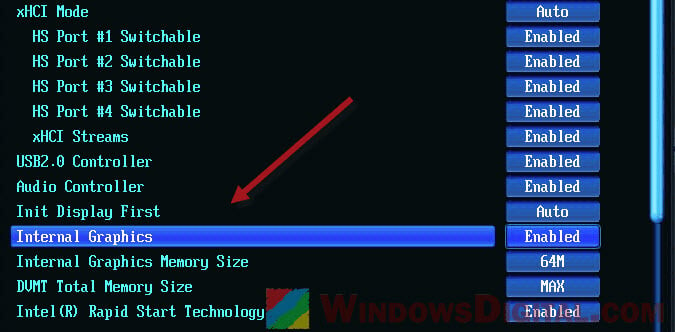
In addition, try disabling the integrated graphics (only if you are already using a dedicated GPU) via the BIOS. This is because some systems may reserve an amount of memory for the integrated graphics.
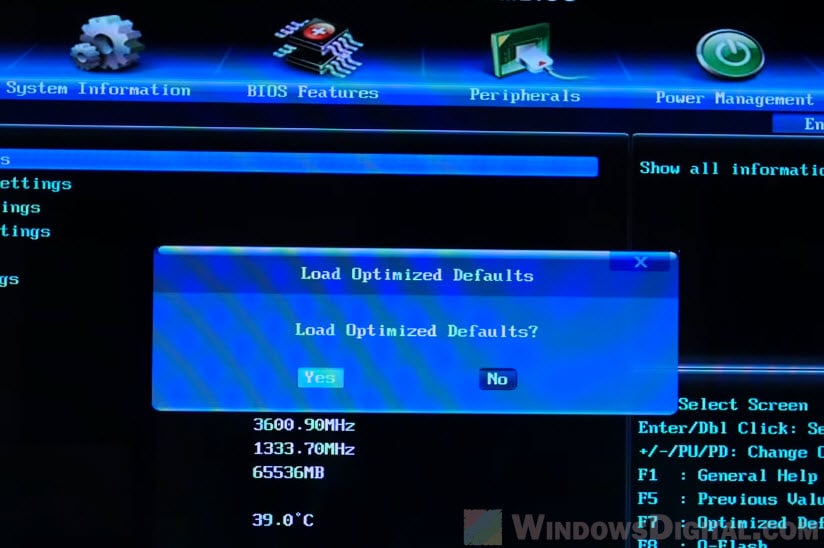
If you doubt that you may have accidentally changed the BIOS settings incorrectly, you can try to reset the BIOS settings to its optimal defaults.
Reseat the RAM sticks
The issue is often due to either the RAM stick or the DIMM slot (the place where your RAM goes) on your motherboard. Try reseating all your RAM sticks and see if the problem can be resolved. Turn off your computer and carefully remove the RAM from the memory module slot and put it back in.
Also, try inserting the RAM sticks onto different slots and memory channel. For example, if you are previously using slot 1 and 3 for two 8GB RAM sticks (16GB in total), try using slot 2 and 4 instead.
Be sure to also check your motherboard’s manual for information on how to correctly install the RAM on the DIMM slots. Different motherboards may have varying rules and limitations about RAM installation. Read the motherboard’s manual and install the RAM as per the manual.
In addition, note that if you are using two RAM sticks of different brands, models, sizes and/or clock speeds, things like this may happen. It is always recommended to use identical RAM sticks to ensure they work well together. Learn more: How to Check RAM Brand, Model and Specs in Windows 11.
Run memory diagnostic
Try running the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool to diagnose your RAM and check if there are any memory problems. To run memory diagnostic in Windows 11, follow the steps below.
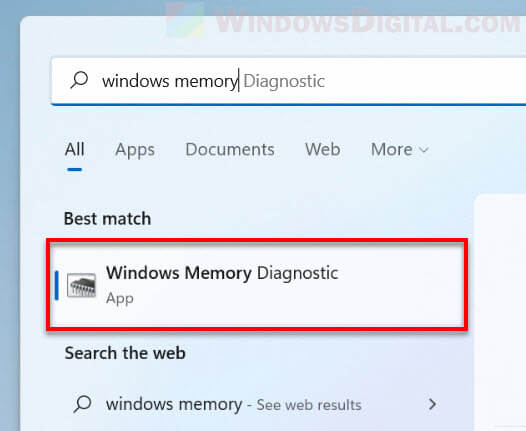
- Go to Start menu. Search for and open “Windows Memory Diagnostic“.
- You will be prompted to restart your computer so that the diagnostic tool can run on next startup. You can choose to restart now or later.
- Once restarted, your computer will automatically boot into the Windows Memory Diagnostics Tool. It will then begin the diagnostic automatically and display the result after you log on on next restart.
Faulty RAM or DIMM slot
Test the RAM on another computer and see if that computer can detect and use it. If it doesn’t work on the other computer either, this may indicate that the RAM stick has failed.
Additionally, if you have another spare working RAM stick, try putting it in the DIMM slot that failed to detect your existing RAM and see if your motherboard and Windows can detect the new one. If the result is the same even when you use the other RAM stick, this may indicate a problem with the DIMM slot on the motherboard.
Side note: DIMM (dual in-line memory module) slots are the place on your motherboard where you insert the RAM sticks.
Quick Tips
- Running the System Maintenance Troubleshooter and Check Disk scan can help resolve memory-related issues on Windows.
- If your PC has 8GB of RAM or less, utilize the virtual memory feature in Windows to supplement the shortage.
- Consider running Windows Memory Diagnostic if low memory errors persist.
Try Basic Fixes
- Close unwanted apps and programs: Start by closing any unwanted apps and programs on your computer, especially the ones consuming a major chunk of your PC’s memory. You can use the Task Manager on Windows to identify such apps and programs.
- Check for malware: Malware or viruses can also trigger such low-memory errors on your PC. You can run a system scan with the Windows Security app or a third-party antivirus program to check for this possibility.
Fix 1: Run System Maintenance Troubleshooter
Running the System Maintenance troubleshooter allows Windows to clean up unused files, shortcuts and perform various maintenance tasks. You can also use this tool to fix abnormal memory usage on your PC. Here’s how.
Step 1: Click the search icon on the taskbar, type in control panel, and press Enter.
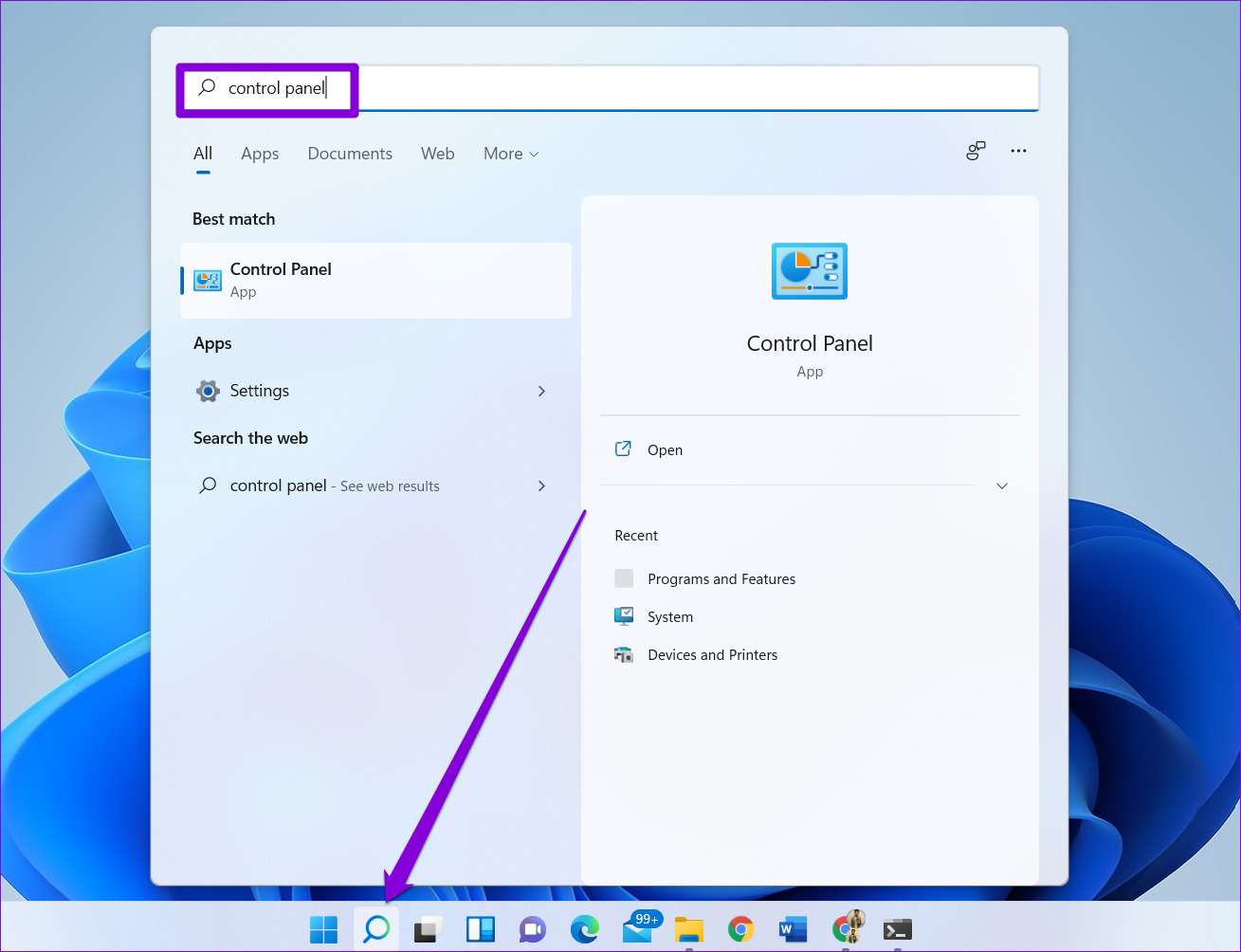
Step 2: In the Control Panel window, change the view type to Large icons and go to Troubleshooting.
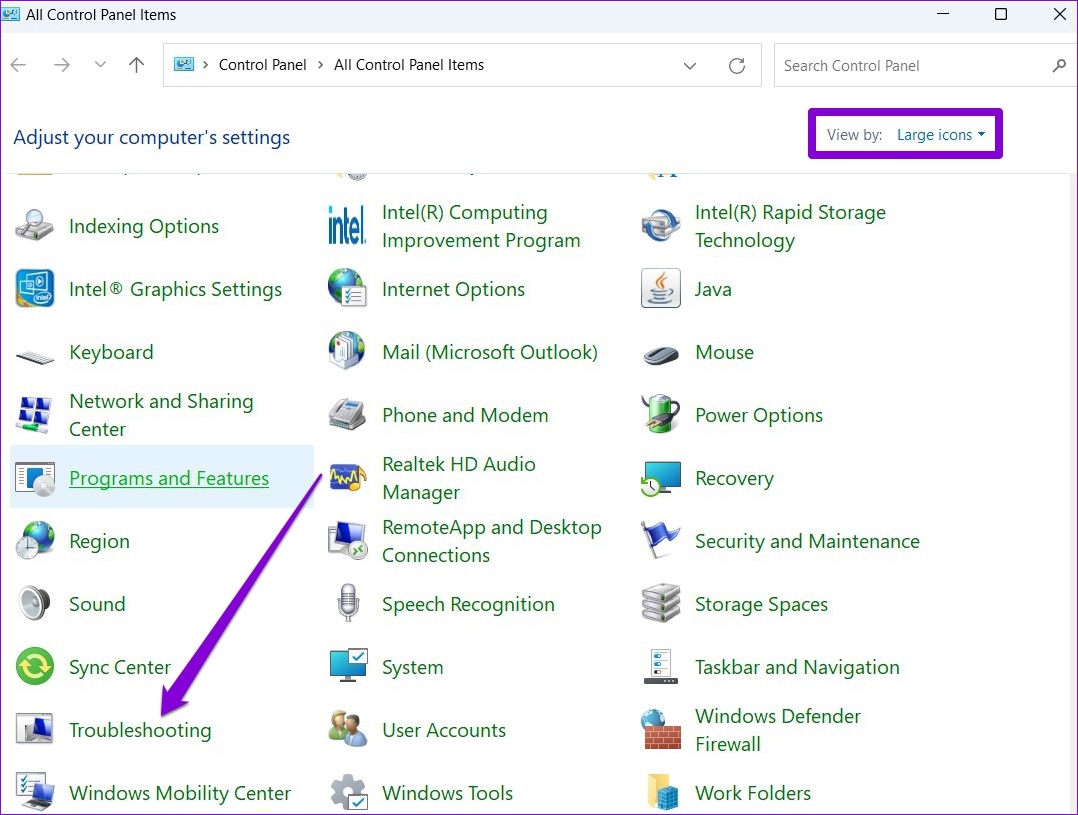
Step 3: Under System and Security, click the Run maintenance tasks option.
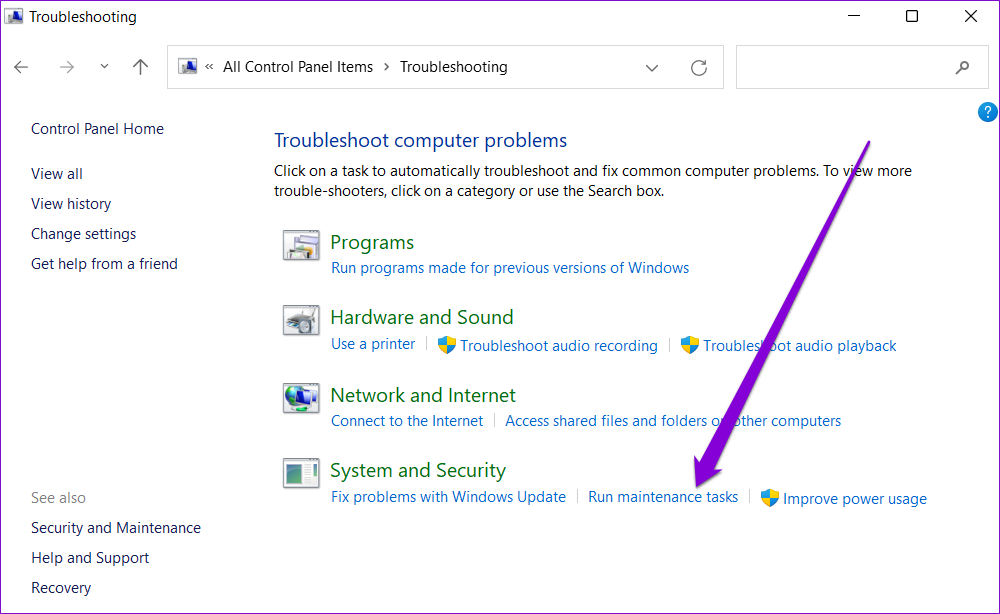
Follow the on-screen instructions to run the troubleshooter and restart your PC. After that, the error should no longer appear.
Fix 2: Increase Virtual Memory
Virtual memory is a nifty feature that allows Windows to temporarily store information on your hard drive that it normally stores in RAM. You can increase the virtual memory size to compensate for the physical memory shortage.
Step 1: Press the Windows key + S to open the search menu, type in view advanced system settings and press Enter.
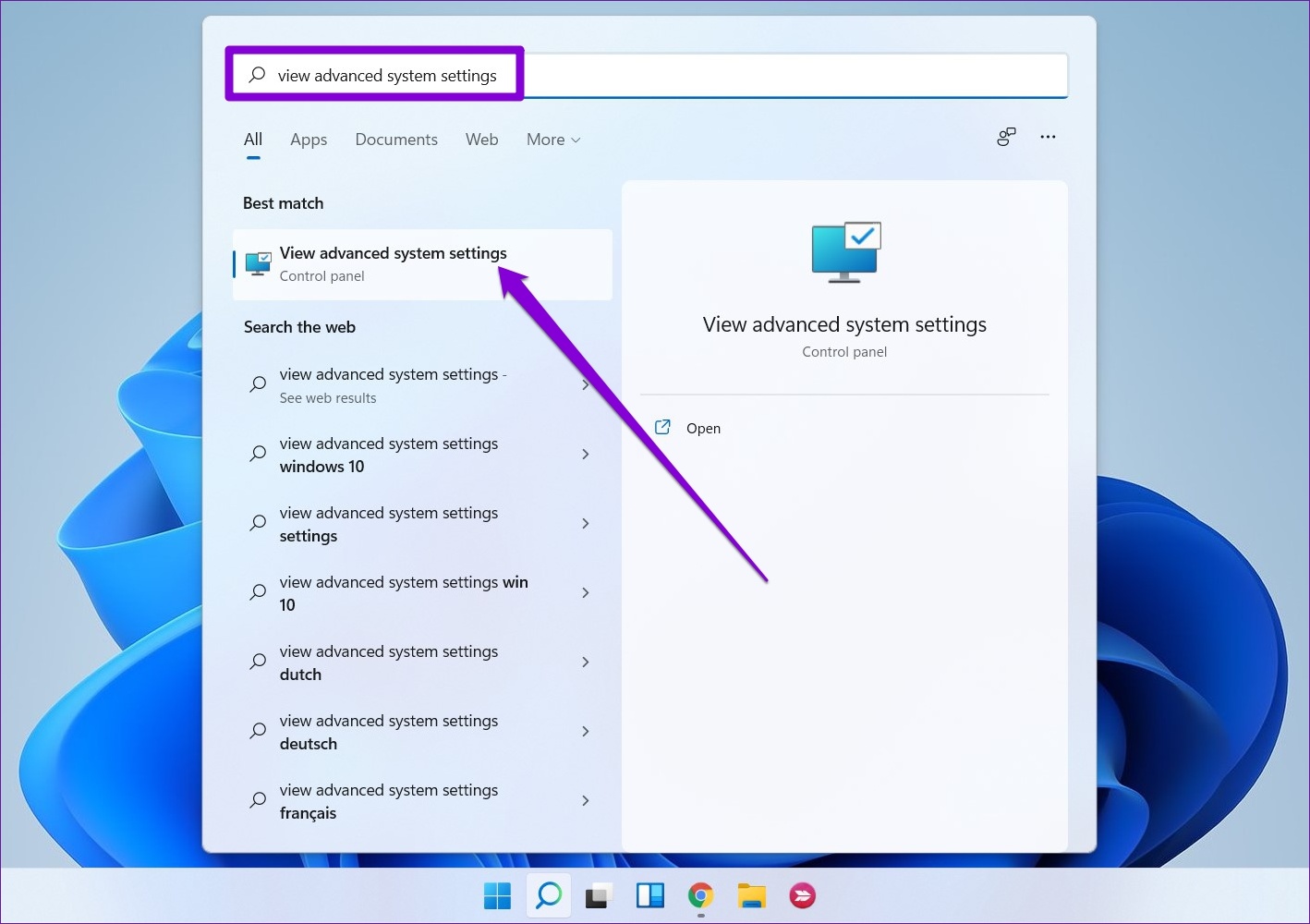
Step 2: Under the Advanced tab, click the Settings button under Performance.
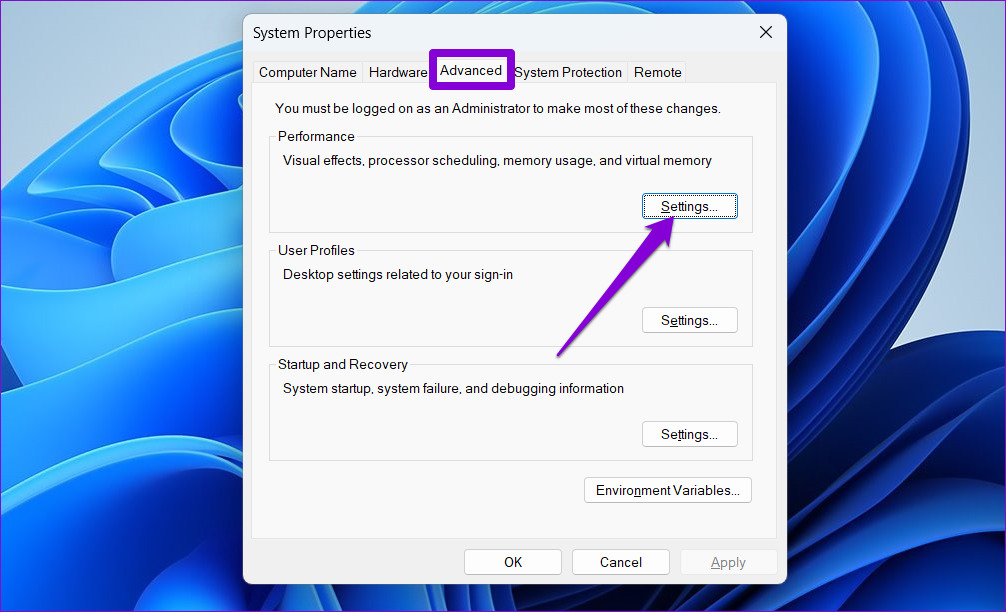
Step 3: In the Performance Options window, switch to the Advanced tab and click the Change button.
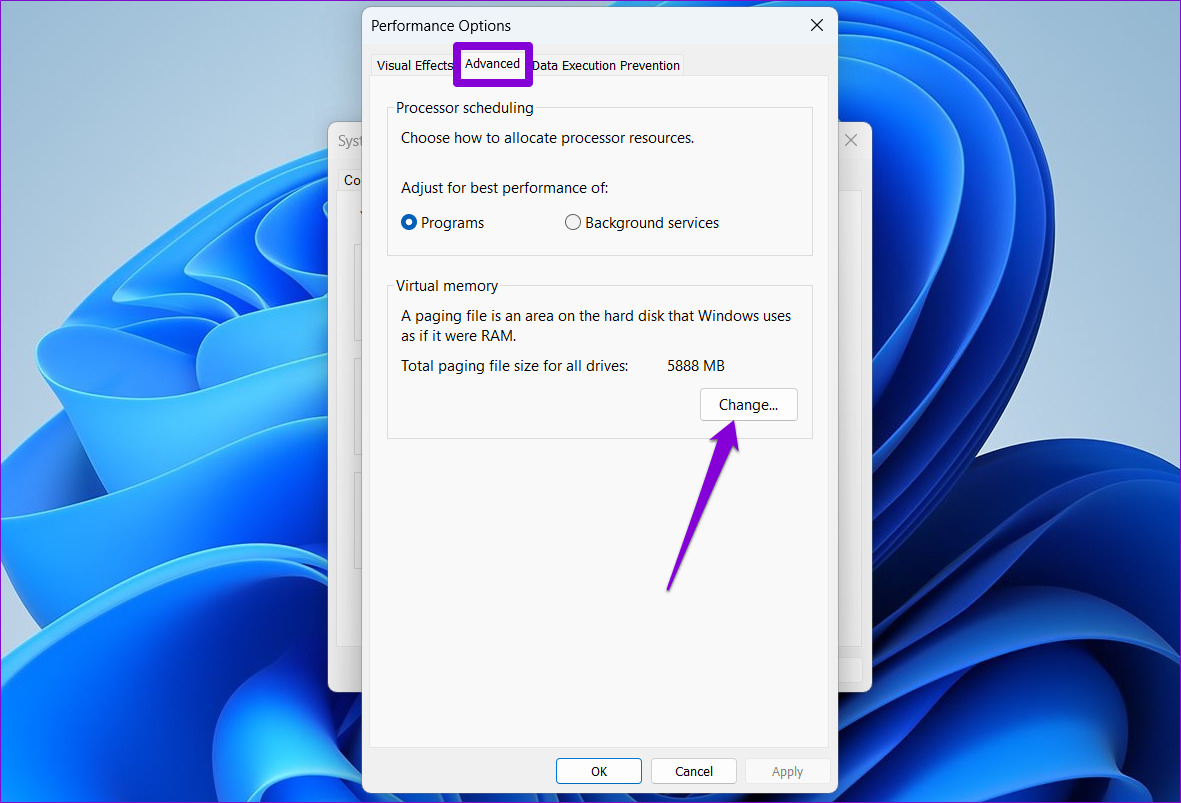
Step 4: Uncheck the Automatically manage paging files size for all drives option.
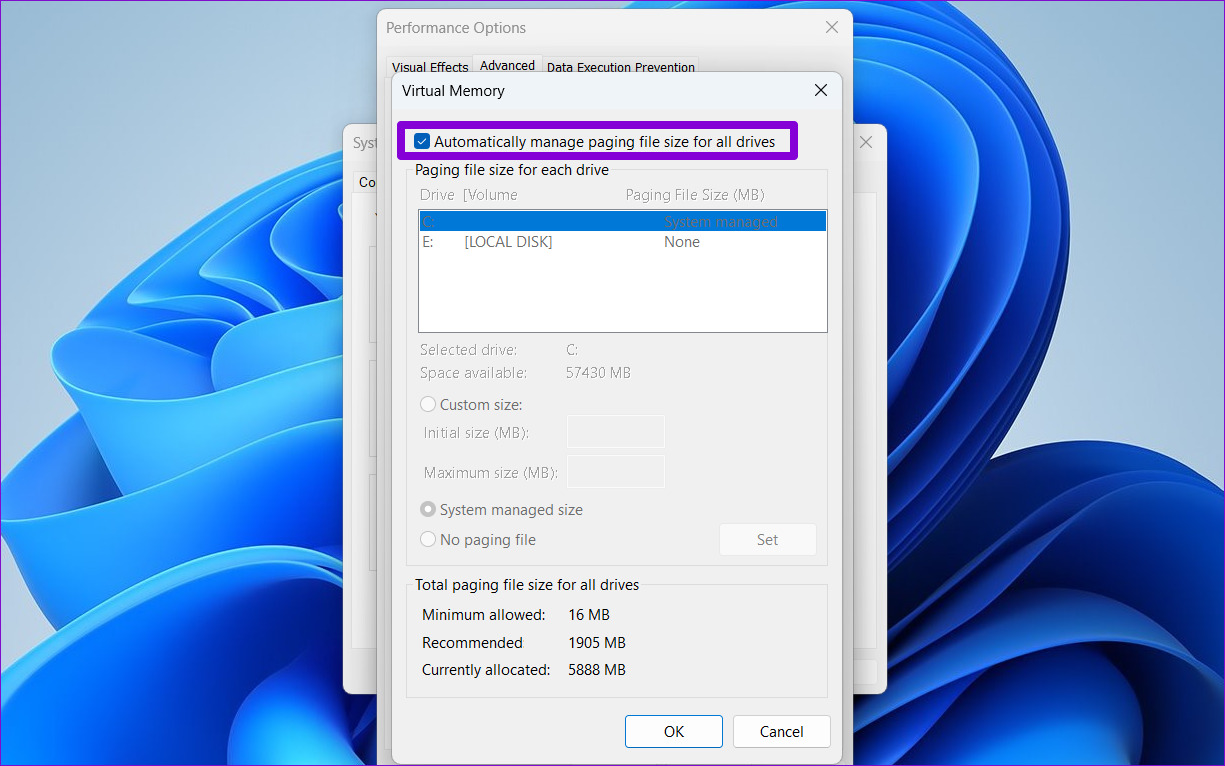
Step 5: Select Custom size and enter the initial and maximum size for the paging file in MB. The initial size should be 1.5 times the size of your RAM, and the maximum size can be up to 3 times the size of your RAM. So, if your PC has 4GB of RAM (1GB = 1024MB), the initial size should be 6,144MB, and the maximum size allowed is 12,288MB.
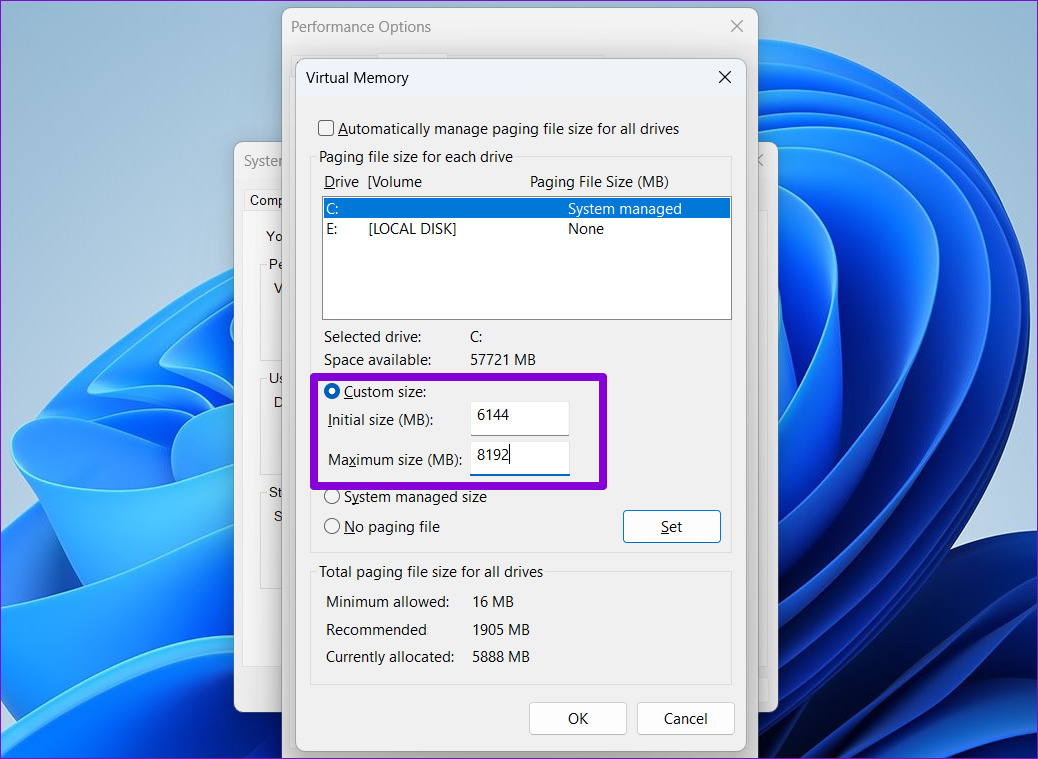
Step 6: Click Set followed by OK.
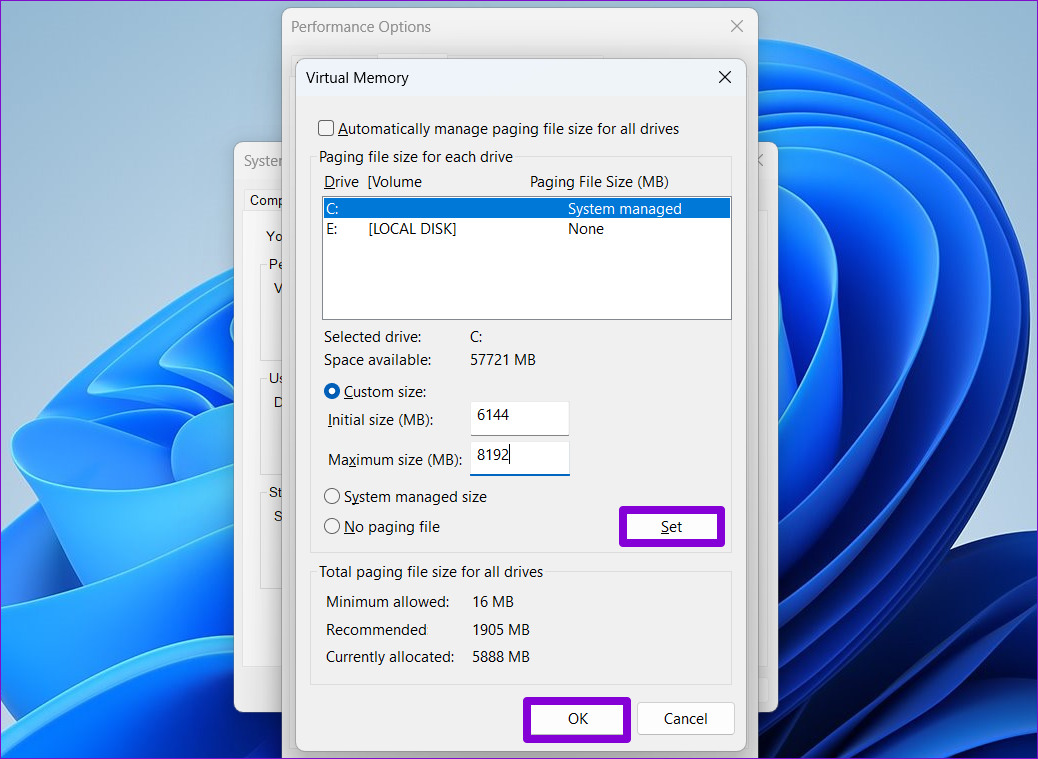
Fix 3: Run Check Disk Scan
Running the CHKDSK (short for check disk) scan allows Windows to scan and repair your drive for corrupted data and bad sectors. If the error message is caused by an issue with your hard drive, running the CHKDSK scan will help.
Step 1: Right-click the Start icon and select Terminal (Admin) from the list.
Step 2: In the console, paste the following command and press Enter.
chkdsk c: /f
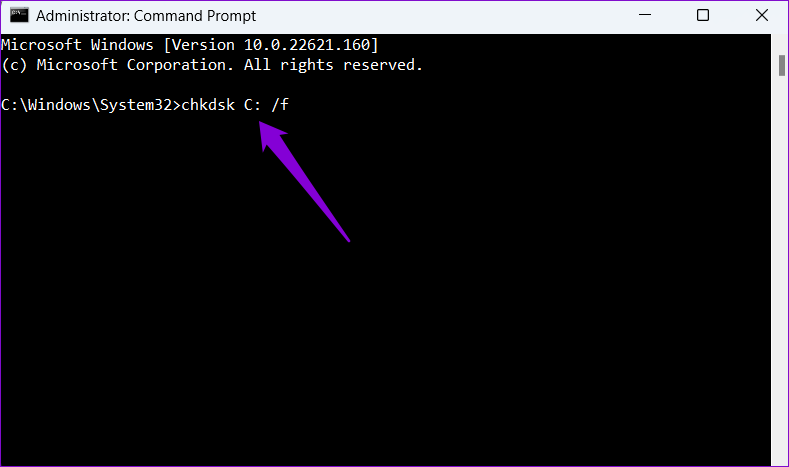
After running the command, restart your PC and check if the “Your computer is low on memory” error occurs again.
Fix 4: Delete Temporary Files
Old temporary files on your PC can also interfere with Windows processes and create problems. You can get rid of such temporary files by running the Disk Cleanup tool.
Step 1: Click on the search icon on the taskbar, type in disk cleanup, and press Enter.
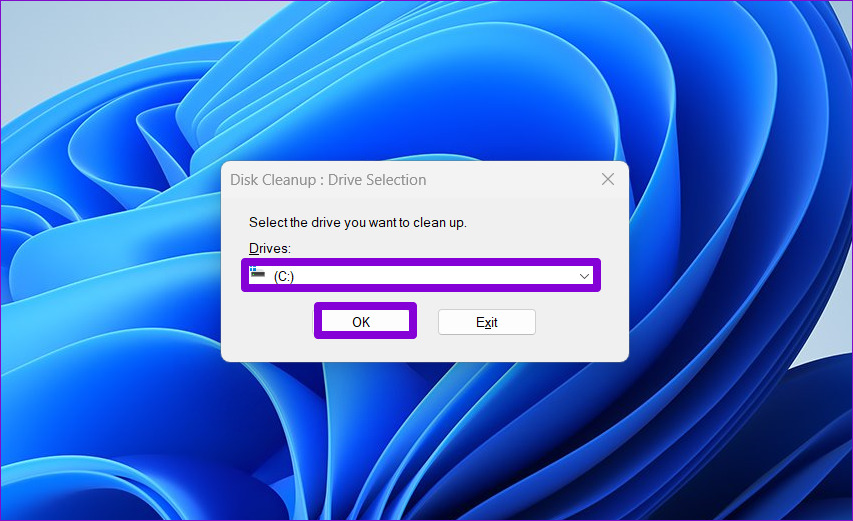
Step 2: Use the drop-down menu to select your primary drive and click OK.
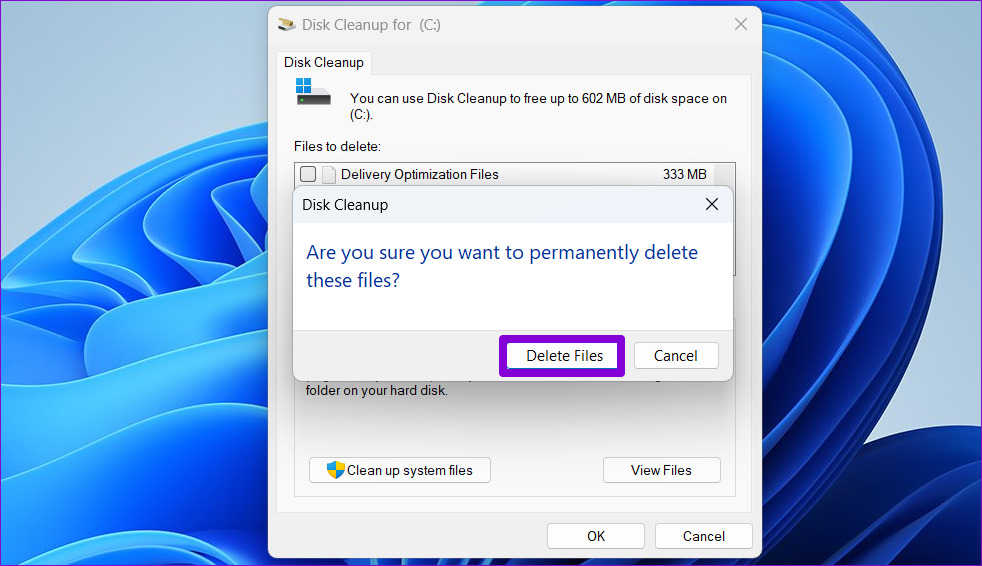
Step 3: Under Files to delete, use the checkboxes to select all the temporary files. Then, click OK.

Step 4: Choose Delete Files when prompted.
Fix 5: Run Windows Memory Diagnostic
Windows Memory Diagnostic is a handy tool that can scan your PC for any memory problems and fix them. Running it requires you to restart your PC, so save all your work before that.
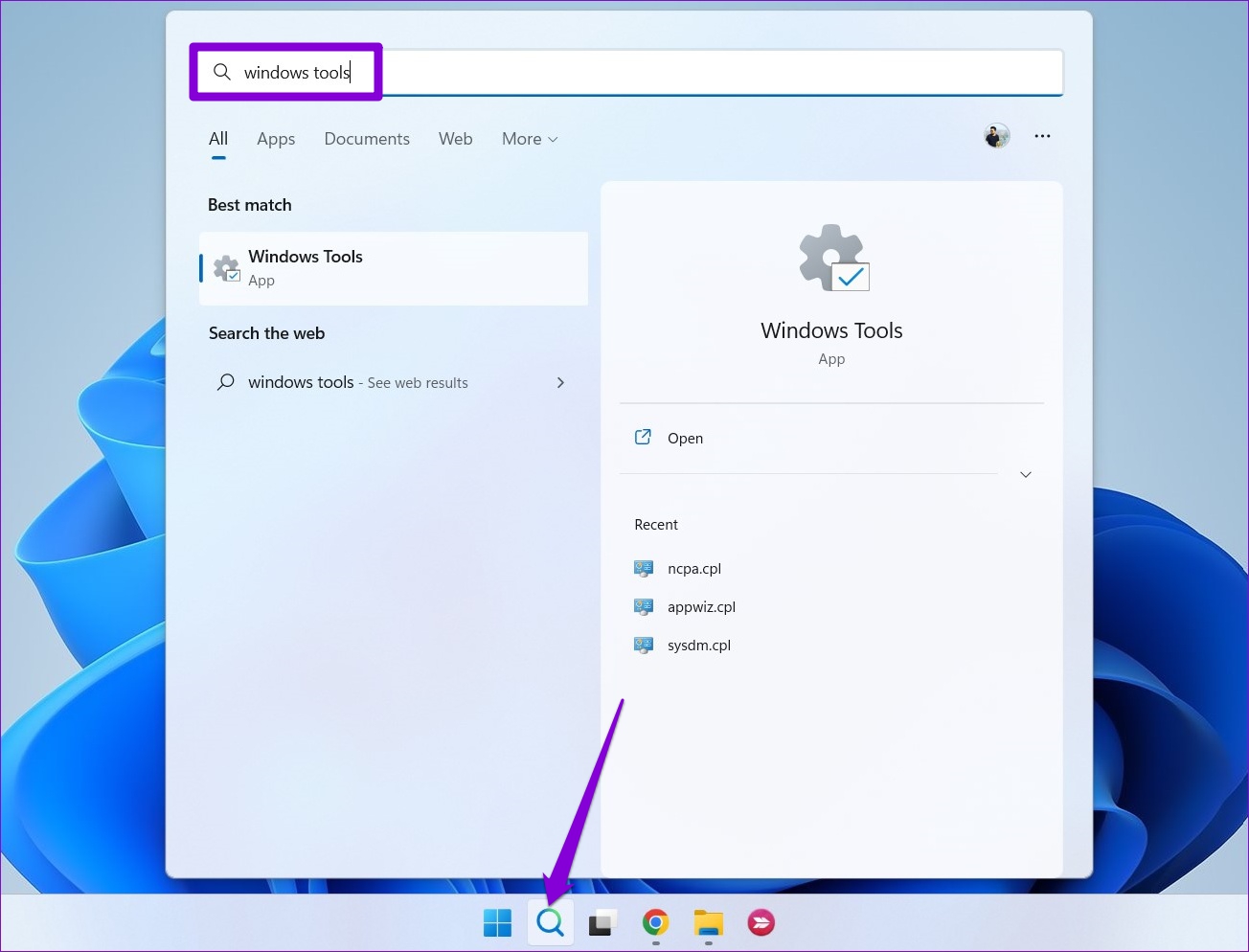
Step 1: Click on the search icon on the taskbar, type in windows tools and press Enter.
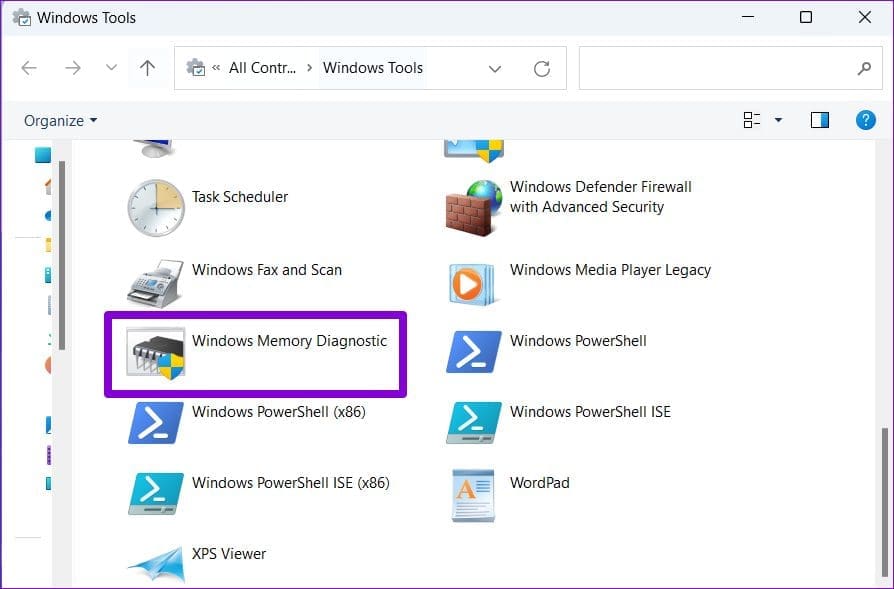
Step 2: Double-click the Windows Memory Diagnostic option.
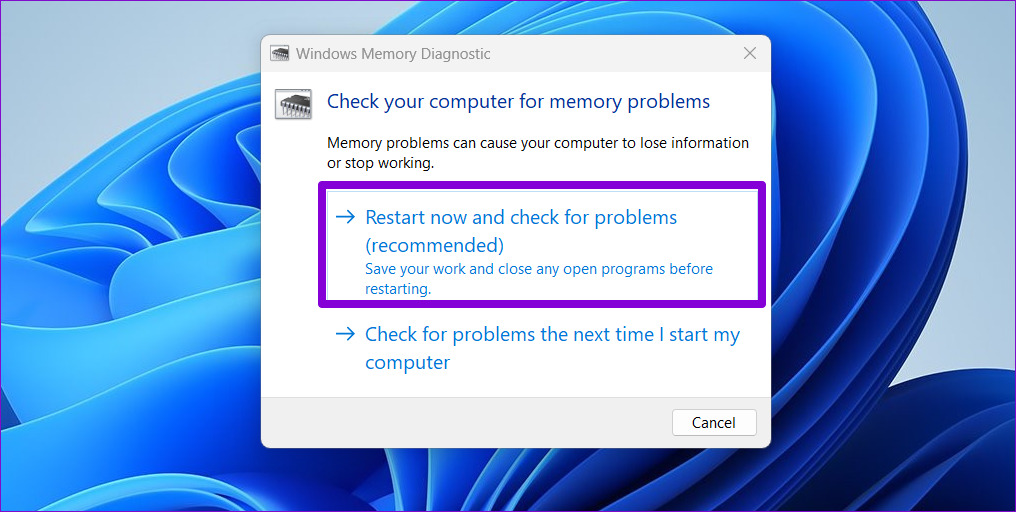
Step 3: Select Restart now and check for problems option.
Once the PC reboots, it will run the diagnostic tool and inspect for any RAM issues on your computer.
Was this helpful?
Thanks for your feedback!
The article above may contain affiliate links which help support Guiding Tech. The content remains unbiased and authentic and will never affect our editorial integrity.
Dmitry Roo, Нет, его объём равен 128 мегабайтам на всех дисках.
Sergey В., Позже попробую….дело только в том, что у меня это единственныё ПК с DDR4 памятью.
Владислав Лысков, Нет, на нём свободно 16 гигабайт.
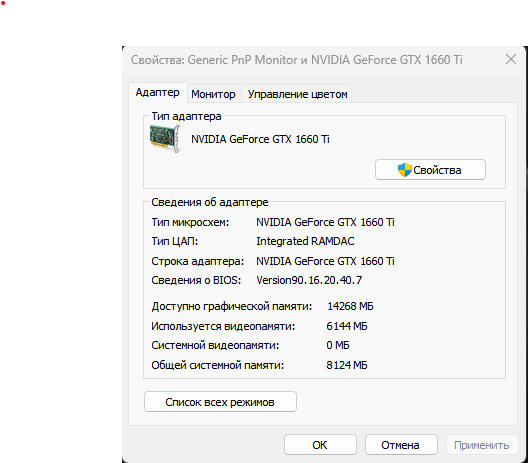
hint000, По памяти, Вы правы, доступный объём — 16248 МБ. Видео у меня дискретное.
Прикрепил скрин свойств видеоадаптера к которому подключен монитор.
Свойства PnP Monitor и nVIDIA GeForce 1660 Ti
AntHTML,
Полная конфигкрация ПК
Системная плата
Тип ЦП HexaCore Intel Core i5-10400F, 4100 MHz (41 x 100)
Системная плата Gigabyte Z590 Gaming X (2 PCI-E x1, 2 PCI-E x16, 3 M.2, 4 DDR4 DIMM, Audio, Video, 2.5GbE LAN)
Чипсет системной платы Intel Tiger Point Z590, Intel Comet Lake-S
Системная память 16248 МБ (DDR4 SDRAM)
DIMM2: GeIL CL16-18-18 D4-3200 8 ГБ DDR4-3200 DDR4 SDRAM (16-18-18-36 @ 1600 МГц)
DIMM4: GeIL CL16-18-18 D4-3200 8 ГБ DDR4-3200 DDR4 SDRAM (16-18-18-36 @ 1600 МГц)
Тип BIOS AMI (01/24/2022)
Коммуникационный порт Последовательный порт (COM1)
Дисплей
Видеоадаптер NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1660 Ti (6 ГБ)
Видеоадаптер NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1660 Ti (6 ГБ)
Видеоадаптер NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1660 Ti (6 ГБ)
Видеоадаптер NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1660 Ti (6 ГБ)
3D-акселератор nVIDIA GeForce GTX 1660 Ti
Монитор Asus VG248 [24″ TN LCD] (M4LMQS264196)
Мультимедиа
Звуковой адаптер nVIDIA TU116 HDMI/DP @ nVIDIA TU116 — High Definition Audio Controller
Звуковой адаптер Realtek ALC897 @ Intel HD Audio Controller
Хранение данных
IDE-контроллер Стандартный контроллер SATA AHCI
Контроллер хранения данных Контроллер дискового пространства (Майкрософт)
Дисковый накопитель Generic USB CF Reader USB Device
Дисковый накопитель Generic USB MS Reader USB Device
Дисковый накопитель Generic USB SD Reader USB Device
Дисковый накопитель Generic USB SM Reader USB Device
Дисковый накопитель SAMSUNG SP2504C (250 ГБ, 7200 RPM, SATA-II)
Дисковый накопитель ST3160827AS (160 ГБ, 7200 RPM, SATA)
Дисковый накопитель WDC WD10EZRX-00A8LB0 (1 ТБ, SATA-III)
Дисковый накопитель WDC WD1502FAEX-007BA0 (1500 ГБ, 7200 RPM, SATA-III)
Дисковый накопитель WDC WDS120G2G0A-00JH30 (120 ГБ, SATA-III)
SMART-статус жёстких дисков OK
Разделы
C: (NTFS) 111.1 ГБ (16.9 ГБ свободно)
D: (NTFS) 149.0 ГБ (89.6 ГБ свободно)
E: (NTFS) 1397.3 ГБ (1282.9 ГБ свободно)
F: (NTFS) 393.0 ГБ (203.2 ГБ свободно)
G: (NTFS) 538.5 ГБ (142.1 ГБ свободно)
H: (NTFS) 232.9 ГБ (132.0 ГБ свободно)
Общий размер 2821.8 ГБ (1866.8 ГБ свободно)
Ввод
Клавиатура Клавиатура HID
Клавиатура Клавиатура HID
Клавиатура Стандартная клавиатура PS/2
Мышь HID-совместимая мышь
Мышь HID-совместимая мышь
Сеть
Первичный адрес IP 192.168.10.39
Сетевой адаптер Bluetooth Device (Personal Area Network)
Сетевой адаптер Microsoft Wi-Fi Direct Virtual Adapter #5
Сетевой адаптер Microsoft Wi-Fi Direct Virtual Adapter #6
Сетевой адаптер Realtek Gaming 2.5GbE Family Controller (192.168.10.39)
Сетевой адаптер TAP-Windows Adapter V9
Сетевой адаптер TP-Link Wireless N PCI Express Adapter
Контроллер USB1 nVIDIA TU116 — USB Type-C Port Policy Controller
Контроллер USB3 Intel Tiger Point PCH — USB 3.2 Gen 2×1 (10 Gb/s) xHCI Host Controller
Контроллер USB3 nVIDIA TU116 — USB Type-C xHCI Controller
USB-устройство Generic Bluetooth Adapter
USB-устройство Logitech USB Camera (B910 HD Webcam)
USB-устройство USB-видеоустройство
USB-устройство USB-устройство ввода
USB-устройство USB-устройство ввода
USB-устройство USB-устройство ввода
USB-устройство Аудио устройства USB
USB-устройство Запоминающее устройство для USB
USB-устройство Неизвестное USB-устройство (сбой запроса дескриптора устройства)
USB-устройство Составное USB устройство
USB-устройство Универсальный USB-концентратор
USB-устройство Универсальный USB-концентратор
DMI
DMI поставщик BIOS American Megatrends International, LLC.
DMI версия BIOS F7c
DMI производитель системы Gigabyte Technology Co., Ltd.
DMI система Z590 GAMING X
DMI системный UUID D8025E03-D3045605-1E06ED07-00080009
DMI производитель системной платы Gigabyte Technology Co., Ltd.
DMI системная плата Z590 GAMING X
DMI тип шасси Настольный