In this article, we are going to learn ‘Step by Step Configure WDS Server (Windows Deployment Services) On Windows Server 2016’. Due to the increase in information technology (IT) solutions in organizations, the number of actual and virtual server images has also increased. Due to this situation, the deployment of operating systems takes longer to complete and requires valuable institutional resources. As a result, companies are looking for new ways to automate the service delivery process. Virtual machine environments have become ubiquitous in a datacenter and having the ability to deploy virtual server roles and workloads while deploying an operating system is an important part of the application process.
Windows Deployment Services (WDS) is a service role that allows you to deploy the Windows operating system to a PXE-enabled client. You can install a Windows operating system on a PXE-capable client without the need for physical media. Besides, it allows you to deploy a Windows operating system to multiple clients at the same time. In this way, reducing the entire installation time. WDS makes your life easier. You do not have to go to another room in the same room to deploy the operating system with the necessary software and drivers. Administrators can schedule schedules for deployment. The next day when you come in and log in to your computer, you will be installing a new operating system. In addition, drivers and software have been installed.
WDS Functions:
• Allows you to install a network-based operating system.
• Facilitate the process of deployment.
• Supports deployment of computers without any installed operating system.
• Provide end-to-end deployment solutions for clients and server computers.
• Use existing technologies like Windows PE, Windows Image File (.wim) and virtual hard disk (.vhd and .vhdx) image files, and image-based deployment.
Hardware Requirements:
- RAM: minimum of 4GB
- Processor: 64-bit processor
- Hard Drive Space: At least 10GB Or Depend On OS ISO and Software’s Size.
Prerequisites to Configure WDS Server:
Before configuring the WDS server, your server must be sure that the following requirements are met.
1)Changed Windows Server Hostname.
2)Turn off Windows Server Firewall.
3)Set Static IP on Windows Server.
4)Install and Configure DHCP Role.
You have learned in the previous article that ‘How To Configure DHCP Server Role on Windows Server 2016‘ Now let’s configure the DHCP Scope for this. Now go to Server Manager and right-click on the DHCP server and click on DHCP Manager.
Also Read – How To Configure DHCP Server Role on Windows Server 2016.
Now firstly expand the domain, then right-click on IPV4 and create a new scope.
The new scope window will open, then click on Next for further process.
Enter a scope name to identify which is the scope, and then click on Next.
Set the IP address range as the snapshot below. As you set up the IP address range, the IP address will be assigned to the client in the same range. Also, give the Length and Subnet mask and click on Next.
If you want to exclude the IP address set in the DHCP server, you can add it to the IP address ‘Exclusions and Delay‘. I’m not adding the IP address, if you want to, you can add the IP address.
The default 8 days in lease duration is set, which means that the client can use an IP address for 8 days. If you want to change the lease duration, you can change it.
If you want to have options like DNS servers and WiNS, click the yes button. Then click Next.
Set the IP address of these routers or default gateways, then click on the add button.
Enter the DNS server IP addresses that you would like your client to use
If you do not have a DNS server in the network, use the WINS server.
You can see that all the steps are done, now just click yes to activate the created scope.
The created new scope has been completed. Now click Finish.
Now you can see in the following snap New Scope has been activated.
Also Read – Configuration Of DHCP Reservation On Windows Server 2016.
Follow the below Steps To Install and Configure WDS Server (Windows Deployment Services) On Windows Server 2016:
Installation of WDS:
Step 1. Open Server Manager.
Step 2. Click Add Role and Features.
Step 3. Read the important requirements and try to meet them (this includes a strong password for the administrator account, stable IP configuration, and installation of the latest security updates). Click next to continue.
Step 4. Choose Roll-based or Feature-based installation and click Next.
Step 5. Select the destination server for WDS from the server pool and click Next.
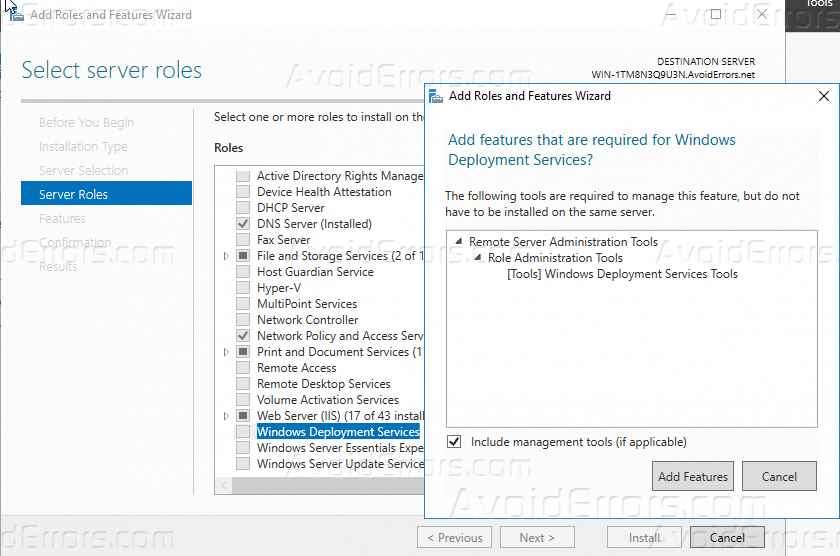
Step 6. Select Windows Deployment Services from the server role. When you check that option, a new window will pop up. Click Add Features.
Step 7. Click Next two times.
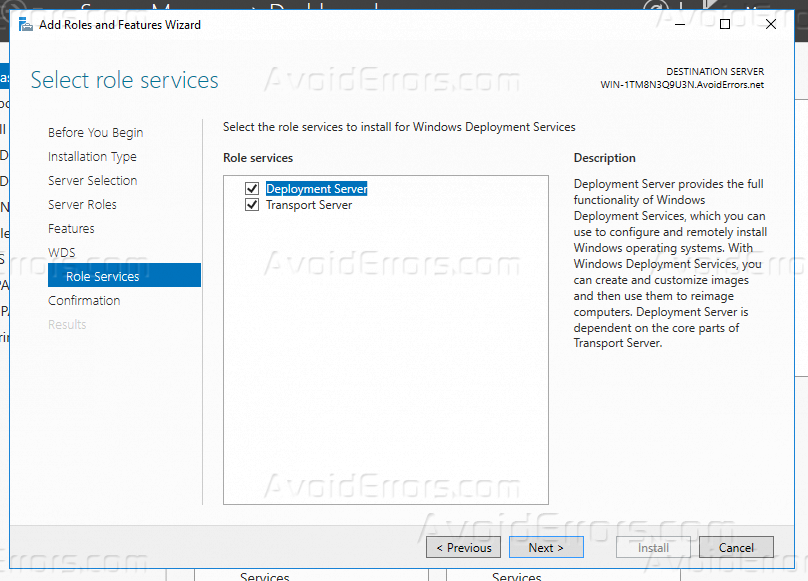
Step 8. Click Next (Leave default selection of both deployment and transport server)
Step 9. Click Install
Step 10. Wait for the installation to complete. It may take several minutes to close.
Configuration of WDS:
Step 1. Open Server Manager Dashboard. Tools -> click Windows Deployment Services.
Step 2. Right-click on your WDS server and then click Configure Server.
Step 3. Read the pre-requisites and click next.
Step 4. Choose “Integrate with Active Directory“, If you have configured AD on my network. If you do not have AD configured and you are configuring WDS in standalone mode, select the standalone server. Click Next
Step 5. Provide a route to your NTFS drive where you want to store a boot image, install images, PXE boot files and WDS management tools. Click Next.
Step 6. I have configured DHCP on the same WDS server. So check both boxes and click next.
Step 7. Choose ‘Respond to all client computers‘ (known and unknown).
Step 8. Wait for the wizard to finish (this may take a few minutes to complete).
Step 9. Click Finish.
Add Install Images to WDS:
When you configure Windows Deployment Services on your server, the next step is to add an image to your WDS to the client machine. There are two types of images that you need to add. There is an install.wim (actual Windows installation files) and the other is boot.wim (used to boot client machines).
Step 1. Open windows deployment services console.
Step 2. Expand your server.
Step 3. Right-click on Install Images and then click Add Install Image.
Step 4. Provide the image group name and then click Next.
Step 5. Browse to the source folder (located on your Windows installation CD/DVD or local hard drive).
Step 6. Choose the install.wim file and click Next.
Step 7. Click Next.
Step 8. Select Image and Click Next.
Step 9. Check Summary and Click Next.
Step 10. Wait for the file to be copied. (This can take several minutes to complete).
Steps 11. Click On Finish.
Steps 12. As you can see on the output above we have successfully added the install.wim Image File.
Add Boot Image to WDS:
Step 1. In the Windows deployment services console, right-click boot image.
Step 2. Click on the Add boot image.
Step 3. Browse to the source folder of your CD/DVD and locate boot.wim.
Step 4. Click Next.
Step 5. Rename Image File and Click Next.
Step 6. Check Summary and Click Next.
Step 7. Wait for the file to be copied. (This can take several minutes to complete).
Steps 8. Click On Finish.
Steps 9. As you can see on the output above we have successfully added the boot.wim Image File.
Configure DHCP Scope Options:
Enabling bare-metal client systems on Windows Deployment Services (WDS) PXE-boot to kickstart the process of deploying Windows PE on a client system and running the Windows system. In some WDS environments, you might want to configure the following DHCP options to direct your PXE clients to the correct network boot file.
Steps 1. Now go to Server Manager and right-click on the DHCP server and click on DHCP Manager.
Steps 2. Right, click on Scope Options and click Configure Options.
Steps 3. Add Boot Server Hostname or IP in cope Options.
66 = DNS name of the WDS server
Steps 4. Option 67 Where can you get the boot file name to configure? This name will be something similar to boot\x64\wdsnbp.com where this route corresponds to the Remount folder on the WDS server.
67 = boot file name
Steps 5. Finally, we can start the WDS server. The WWS server has not been configured only. Right-click on the WDS server. hover your mouse over all the tasks, then click Start. Soon after the WDS server starts.
Note – Connect LAN with WDS server to switch or the client computer and start WDS server.
As you can see on the output above we have successfully started the WDS server.
Also Read – Step by Step Configure MDT Server (Microsoft Deployment Toolkit) on windows server 2016
Deploy Windows with WDS:
Steps 1. The client will want to install the Windows os of the system. First of all, connect the first WDS server to the client computer with a LAN cable. To confirm the same you can use the DHCP Address Lease.
Steps 2. Boot Client System With Network.
Steps 3. Check WDS IP and Hostname and press F12 to Deploy Windows.
The machine is booting via network and windows os files loading starts.
Steps 4. Select your location and Keyboard Language.
Steps 5. Enter WDS Credentials and connect WDS.
Now you can install windows on a client computer with a normal windows installation process.
Also Read – System Requirement and Installation Windows Server 2016.
That’s all, In this article, we have explained step by Step Configure WDS Server (Windows Deployment Services) On Windows Server 2016. I hope you enjoy this article. If you like this article, then just share it. If you have any questions about this article, please comment.
Windows Deployment Services(WDS) is the key of deploying automated-based installations of standard or custom images to servers in a network. WDS server store the installation files and help you to manage the boot and operating system files used in the network installations. Like capturing image firstly, then deploying them on client computers with all drivers and applications you need for your network. Update operating system, drivers and applications then take an image of the template computer. The computer you take capture image from is called template computer. Sysprep is the tool that you can image through from a template computer and store the image on WDS server to deploy on WDS clients.
WDS makes your life easy. You don’t need to move from one room to another room deploying operating system with needed softwares and drivers. Administrators can make schedule for deployment. Next day when you come and login to your computer, you see the new operating system installed. In addition, drivers and softwares have been installed.
These are some other methods of deploying operating system on client computers:
- DVD: You can go to computers one by one with a shiny disk in hand and install operating system on. For an enterprise network you need lots of disks and it takes a long time. This method can be implemented on
- Bootable Flash memory: You can install operating system using bootable flash memory. When the flash memory is bootable, you copy all operating system files in, and plug the flash to computers. For the process you need lots of flash memories.
Topics covered in this post:
- WDS Advantages
- WDS Images
- Hardware Requirements
- Prerequisites
- Install WDS role Graphically
- Installation WDS role through PowerShell
- WDS Basic Configuration
- Add Install Image
- Add Boot Image
- Conclusion
WDS Advantages:
- Install Windows 7, 8, 8.1 or 10 remotely.
- You can install Windows with needed softwares and drivers simultaneously.
- Install Windows on large number of computers at one time.
WDS Images
WDS uses four image: Install image, Boot image, Discover image and Capture image. The minimum of requirement is boot and install images.
- Install Image: It is the actual operating system. It is found in the operating system media\sources\install.wim.
- Boot Image: It is Windows PE image. You can find it the operating system media\sources\boot.wim.
- Discover Image: This image is used by WDS clients which don’t support PXE boot. You create the image using boot.wim image from media file and Windows Assessment Tool Kit (ADK) to create a discover image.
- Capture Image: This image is custom install image. You capture the image from a template computer using Sysprep, and deploy the image on client computes.
Hardware Requirements
- RAM: minimum of 2GB
- Processor: 64-bit processor
- Hard Drive Space: At least 6GB
Prerequisites
- AD DS: The deployment server must be either member server (joined to a domain) or a domain controller. If you want to install (AD DS), read this article: Install Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) on Windows Server 2016
- DNS: An active DNS (Domain Name Services) is required for Preboot eXecution Environment (PXE). Refer to this link for completely step by step guide. Install DNS Server on Windows Server 2016 fully step by step
- DHCP: It is needed for supporting PXE boot. Refer to this link for completely step by step guide. Install DHCP Server on Windows Server 2016 step by step
- NTFS volume: The volume which contains images must be NTFS format.
- Credentials: Make sure that you have logged on with an account that have permissions to do this tasks.
Install Graphically
Undoubtedly the easiest way of installing a role is graphical interface.
1. First of all press the Start Menu button. Then select the Server Manager.

2. Click on Add roles and features for installing WDS role.

2. Skip the Before you begin page. Leave the Select a server from the server pool checked. From Server Pool select the server which you want to install the role on. Click on Next button.

3. In the Select server roles page, select Windows Deployment Services. A windows pops up and asks you to add some features for management. Click on Add Features button then click on Next button.

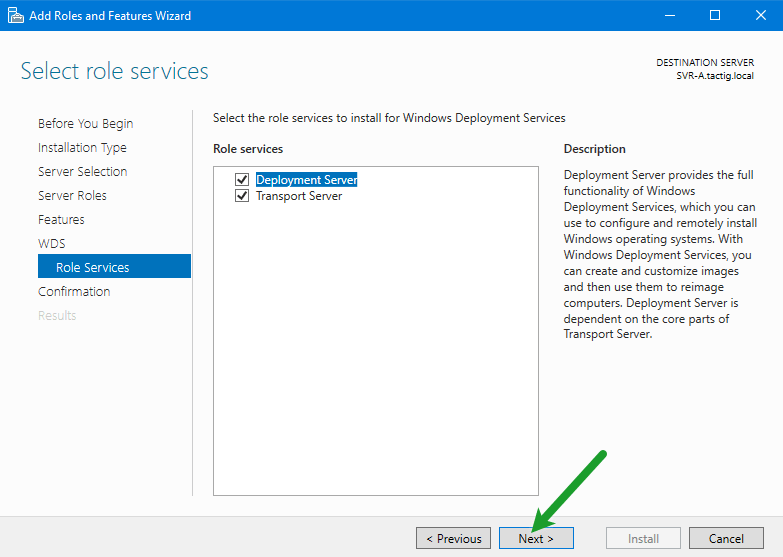
4. You have got nothing to do in Features page. In the WDS page, some essential information is written. In Role Services page you got two options:
- Deployment Server: It is the deployment server with management tools.
- Transport Server: It is WDS core service, but doesn’t include management tools. You need to use scripts for every task that you want to do. Therefor you need to select both of them.
Click on Next button.
5. In the Confirm installation selections page, click on Install button. No reboot is needed after the installation.

Installation through PowerShell
PowerShell is a powerful tool in Windows Server 2016. You need to know how to use it.
1. Press Windows button and select Windows PowerShell. Make sure you run PowerShell as an administrator. Right-click on and click Run as administrator. Also you can run PowerShell as an administrator with command. Open PowerShell as standard user and type this command to run it as an administrator: Start-Processs PowerShell.exe -Verb RunAS. Then press the Enter button.

2. Install-WindowsFeature is a command for installing roles on server. You need to run this command: Install-WindowsFeature -Name WDS -ComputerName <Server_Name> -IncludeManagementTools
After -ComputerName parameter, type your server’s name. In my case it is SVR-A. Then press the Enter button. While WDS installed successfully on your server, the summary would be shown to you. Saying that role installed successfully and no reboot is needed.
The -IncludeMnagementTools parameter installs the management tools. If you don’t type the parameter you won’t have the management tools. It means you just have installed the core services.

WDS Basic Configuration
Finally role was installed. We need to configure WDS server and use it across the network.
1. In Server Manger console, in the menu bar, click on the Tools. Then click on Windows Deployment Service. In addition, you can open it through Run. In the Run just type wdsmgmt.msc and press Enter button.
2. Windows Deployment Services console is opened. But the WDS server is not configured yet. For the purpose, right-click WDS server below the Servers. Select Configure Server.

3. In Install Options page two options are visible. Select the Integrated with Active Directory option if your WDS server is a member of a domain. If it is standalone server, select the Standalone server option. Click on Next button.

4. Select the folder in which you want to store WDS server files, like images and drivers. Click on Browse button and specify the path. Click on Next button.

5. In the Proxy DHCP Server page, leave both Do not listen on DHCP and IPv6 ports and Configure DHCP options for Proxy DHCP options selected. Click on Next button.

6. In PXE Server Initial Settings page, select Respond to known-client computers. This option is secure. Click on Next button.

7. Finally we are done. Below the green line we got a message which says that this serve still can’t respond WDS clients. Finish the wizard.

8. At the very end we can start the WDS server. WDS server is just configured not started. Right-click on WDS server which in my case is SVR-A, hover your mouse point on All Tasks, then click on Start. Soon after the WDS server would be started.

Add Install Image
1. Before you add install image, create some groups for different operating system install images. Before you add an install image, you need to an image group. You can easily manage your image in groups. Right-click on Install image. Click on Add Image group. A small windows opens, type name of the group inside and click on Ok button.

2. Now which groups are created, right-click on the group which you want to add install image in. Select Add Install Image option.

3. Specify the path. The path is simple: Whatever is your file media letter:\sources\install.wim. In my case path is E:\sources\install.wim. Click on Next button.

4. In the Available page of the wizard, select the install images that you need for your network. I need Windows 10 Pro for my network. While done, click on Next button.

5. It takes a while, when WDS server copies install.wim image from media file. At the end click on Finish button to close the wizard.

Windows 10 Pro Install image was added to WDS server.

Add Boot Image
1. Right-click on Boot Images and click on Add Boot Image.

2. Specify path of the file which contains the image. Install and boot images located in the same folder with Install image. Boot image path: media file:\sources\boot.wim. In my case path is E:\sources\install.wim.

3. Name the image. Select a friendly name for the image you can recognize. Click on Next button.

4. Image was added to the server. Finish the wizard by clicking on Finish button.

Microsoft Windows Setup (x64) Boot Image was added to WDS server.

Conclusion
Finally we are done with WDS basic configurations. For any kind of question feel free end leave a comment below the post. Thank you for reading the post.
Windows Deployment Services is a technology for deploying Windows on multiple computers without using CD/DVD on each computer. If you have already configured WDS on server 2012 R2, configuring it on WDS on server 2016 can be a piece of cake for you.
Following are step-by-step instructions.
Installation of WDS
Step 1. Open server manager.
Step 2. Click on Add roles and features.
Step 3. Read important prerequisites and try to meet them (This includes a strong password for the administrator account, static IP configuration, and installation of the latest security updates). Click Next to continue.
Step 4. Choose Role-based or feature-based installation and click Next.
Step 5. Choose a destination server for WDS from server pool and click Next.
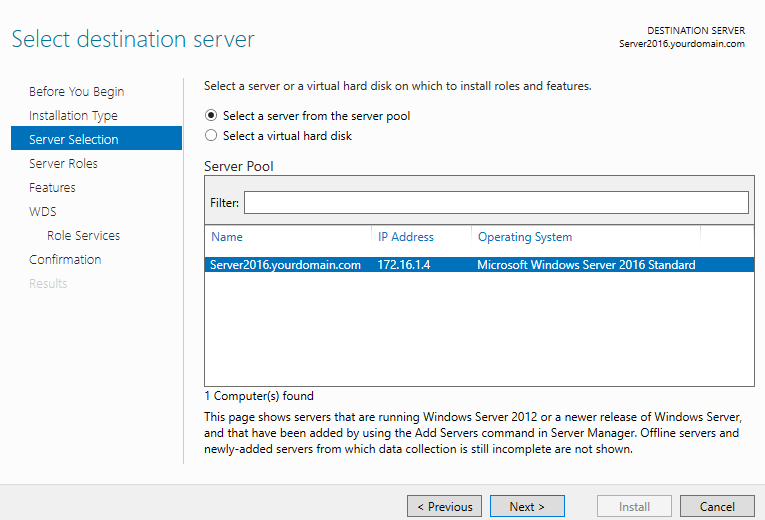
Step 6. Choose Windows Deployment Services from server roles. As soon as you check that option, a new window will pop up. Click on Add features.
Step 7. Click Next
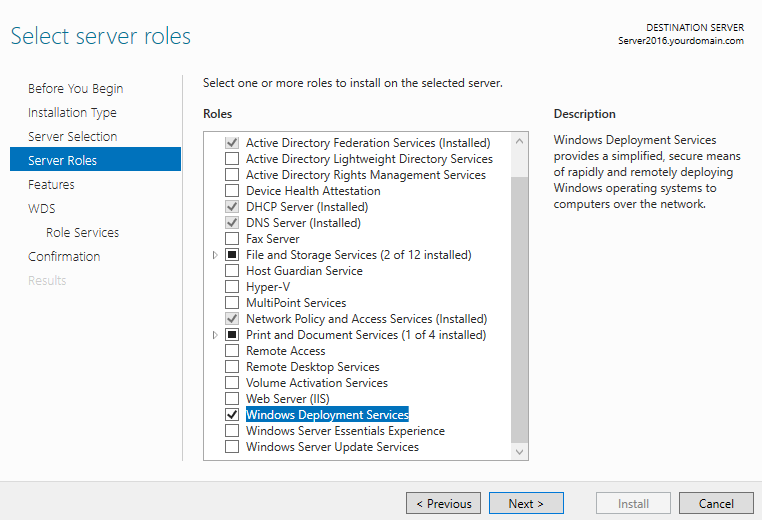
Step 8. Click Next two times.
Step 9. Click Next (Leave default selection of both deployment and transport server)
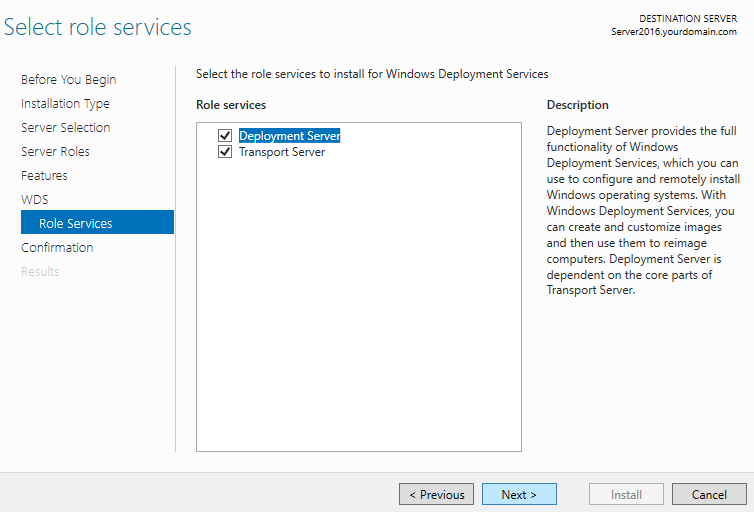
Step 10. Click Install (Wait for the installation to finish. This can take several minutes to complete).
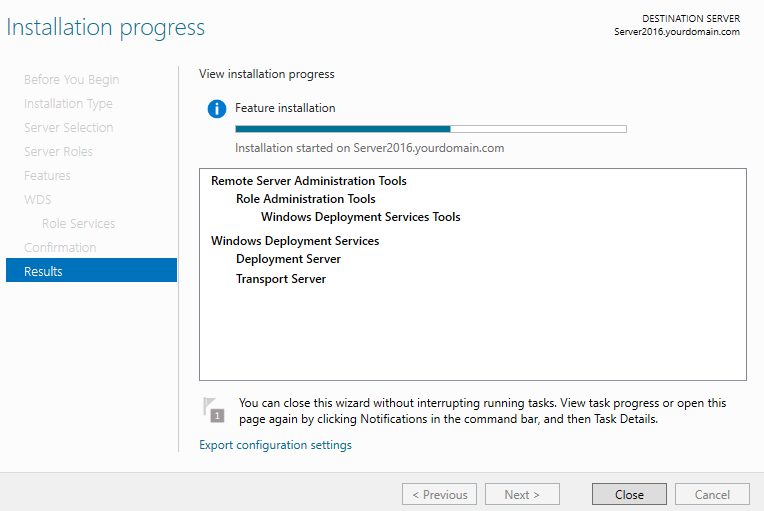
Configuration of WDS
Step 1. Open server manager dashboard. Click Tools -> Windows Deployment Services.
Step 2. Right-click your WDS server and then click on Configure Server.
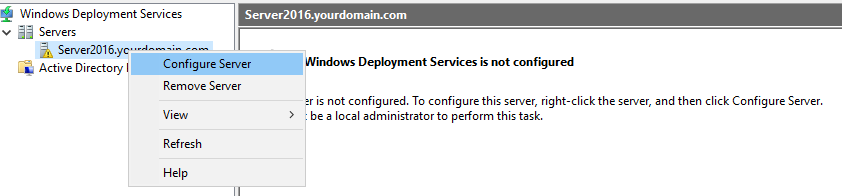
Step 3. Read important pre-requisites and click Next.
Step 4. Choose “Integrated with Active Directory“. I have an AD configured on my network. If you don’t have an AD configured and you are configuring WDS in standalone mode, choose standalone server. Click Next.
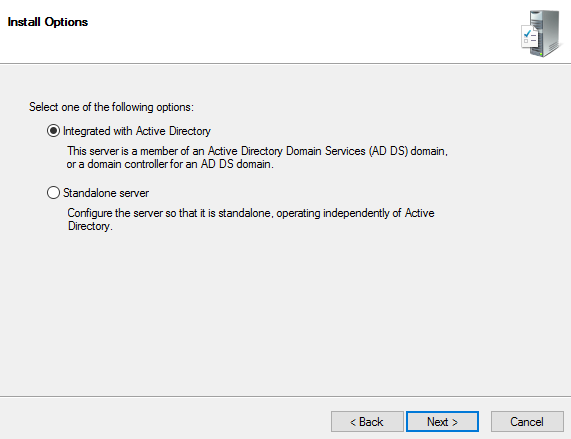
Step 5. Provide the path on your NTFS drive where you would like to store boot images, install images, PXE boot files and WDS management tools. Click Next.
Step 6. I have configured DHCP on the same WDS server. So check both boxes and click Next.
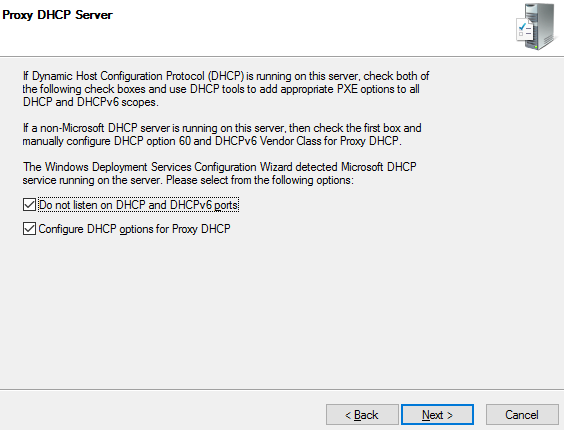
Step 7. Choose ‘Respond to all client computers‘ (known and unknown).
Step 8. Wait for the wizard to finish (This can take several minutes to complete).
Step 9. Click Finish.
Now your WDS is configured. Read my next article on how to add windows images to WDS for deployment on client computers.
Before we deploy images to our machines, let’s talk about images and the difference between them. If you click on Boot Images and if you right-click on your boot image you will see Capture Image and Discover Image options.

We will start with Discover Image
DISCOVER IMAGE
In certain circumstances, I may have a situation where I may have some clients that are unable to communicate over PXE, maybe client does not support PXE or you are sending those images over a very slow link or where you’ve got a high security environment. It can happen when your network team doesn’t like that traffic passing over the network. When that’s the case, you can actually burn a copy of this boot image to a DVD or burn it to a USB stick by creating what is called a Discover Image. This Discover Image, the whole job of this is just simply to get that bootstrapping information, that WinPE content, onto that machine so that it can boot up and then use your usual Windows protocols to communicate back to our WDS server and download the install image to be deployed.
To create a Discover Image click on Boot Images –> Right-click on your boot image and select Create Descover Image
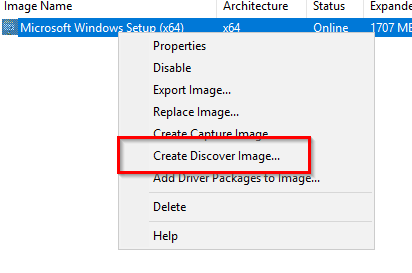
Give it a name and description, then specify the location where you want to save it to. If needed you can specify the WDS server. Click Next


The last step is to save this to example USB drive and boot the computer to the media.
CAPTURE IMAGE
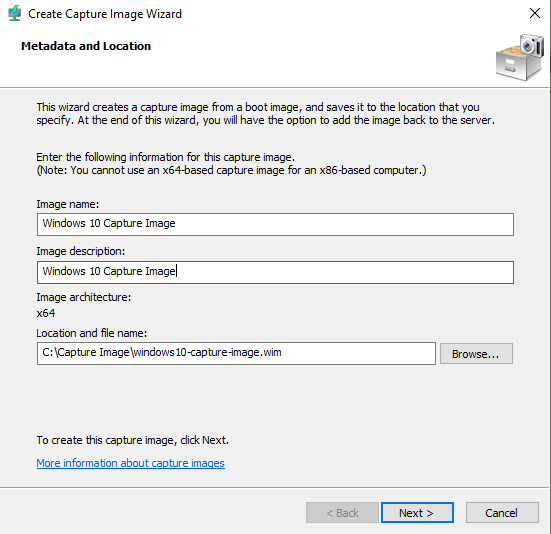
In other circumstances, you may not necessarily be interested in the actual install image right off the USB. You may want to configure a custom image that includes applications, different configurations that are specific to the needs of that user or group. Well, in that case, you can actually go about creating that machine as a golden image or a reference image, and then capture the contents of that image through what is called a Capture Image. Before creating capture image make sure that you have OS deployed with all apps and customizations you need. Then run sysprep on the machine you would like to use for golden image with OOBE, Generalize and Shutdown options. I imported Windows 10 boot image this time. To create a Capture Image, click on Boot Images –> Right-click on your boot image and select Create Capture Image

Give it a name, description and the location where you want to save it. Click Next
After a few minutes we will be able to see it under the Boot Images. Click the Add image to the WDS now

Follow the steps and here it is

Now change the boot order to boot from the network and start the sysprepped VM. Select the Capture Image we created.

On the WDS Image Capture Wizard click next. On the Directory to capture select the volume and give your image a name and the description

New Image Location –> Enter the name and location, check Upload image to a WDS server and connect to your WDS. (Just to point that I went to WDS server and created Windows 10 Image Group)

After the completion of capturing install image click on Finish to close the wizard.
Once done, go back to your WDS and refresh the View.

Now if we boot client again we will have option to use the new golden image. Select the first option
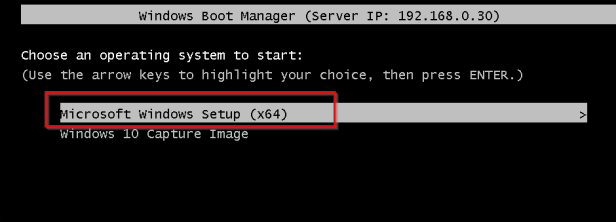
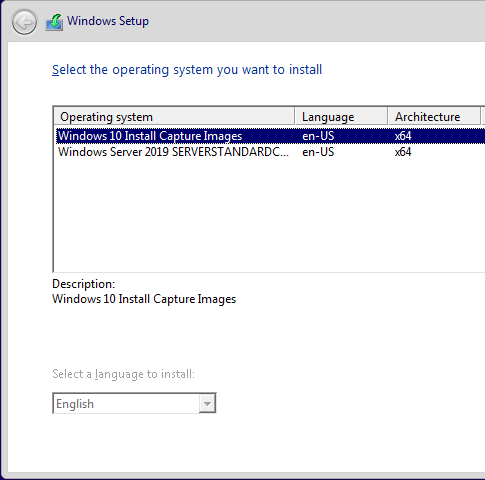
Choose the local and keyboard input and specify the domain credentials

Select the image and follow the wizard and that’s it.
PENDING DEVICES
Before we proceed I would like to point that I created new Hyper-V Gen2 VM that I will use from now on. Make sure that you change boot option to boot from network.
INFO: To be able to boot gen2 VM from network you will need to configure these 2 options on your DHCP server.
66 –> wds.domain.com
67 –> Boot\x64\wdsmgfw.efi

Let’s power it on so that we can take a look at the steps we’re going to go through in order to connect up to WDS. When you boot your machine you will notice like WDS is saying: All right, well, here is your connection. You are now waiting approval from the administrator. If you remember from the first post, I checked the box that said we need to approve any unknown computers before we deploy an operating system to them.

Go back to your WDS server and click on Pending Devices

If you right-click on it you will have options: Approve, Name and Approve and Reject. If you remember from the first post, we were talking about how WDS kind of wants to give this machine a randomized name (AD DS Tab on server properties), which, for a lot of environments, this isn’t going to fly because we want to give those machines a specific name. Well, it’s this name and approve right here where I can define more information about the machine, specifically the name that I want to give it as I go through deploying this operating system. Click on Name and Approve

Approve Pending Device Wizard pops up, Give your device a name and specify where you will store the machine, in which OU. Click Next

I can identify what the referral server would be, or essentially where it should get its boot. wim file, also which boot program and which boot image it should download as well. These can all be left blank if you just want to choose the defaults. Click Next

Here I can identify what the unattend file should be for getting that machine bootstrapped. I don’t have any file so I will skip this step. We will discuss more about Automation and WDS in the third post. Click Next

Choosing Next again allows me to identify what the user settings and device settings should be. Once done, click finish

This will now complete the name and approve process, and if I flip back over to my VM machine, we should see that WDS has given the instruction here to this machine to begin deploying the boot. wim file and bootstrapping itself into Windows PE. Notice here that we’re now booting into Windows PE. This is, as I said, the boot. wim right here that we’re downloading from our Windows Deployment Server.

Now, just follow the wizard, choose the desired image to install and next, next finish.

REMOVE PENDING, REJECTED AND APPROVED DEVICES
Once device is approved it will stay under the pending devices. We can remove those entries from the list by starting powershell and typing
Approved Devices
wdsutil /delete-autoadddevices /devicetype:approveddevices
Rejected Devices
wdsutil /delete-autoadddevices /devicetype:rejecteddevices
Pending Devices
wdsutil /delete-autoadddevices /devicetype:pendingdevices
MULTICAST TRANSMISSION
Multicast transmission is used when you need to deploy image to a large number of clients without overloading your network. Let’s say that we need to deploy windows 10 image to 50 clients. With multicast you will send this image only once and not 50 times. You can accomplish this only if you are using scheduled cast. If you do an automatic cast the number would be greater as each new machine that boots up after the first would have missed parts of the stream and the WDS server would have to re-stream the parts that were missed. Let’s see how we can configure this.
In your WDS console, Right-click on multicast transmissions and then click create multicast transmission.
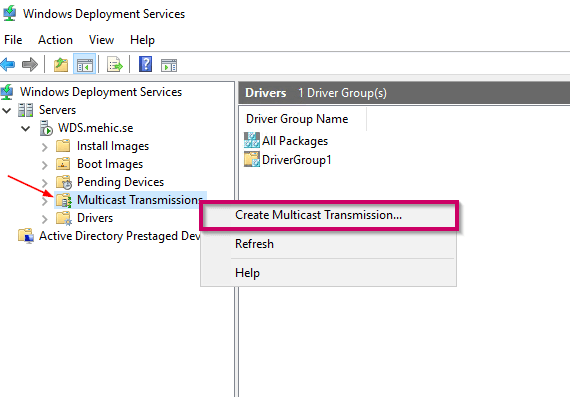
Enter the name and click next

Choose the Image group and the image and click next
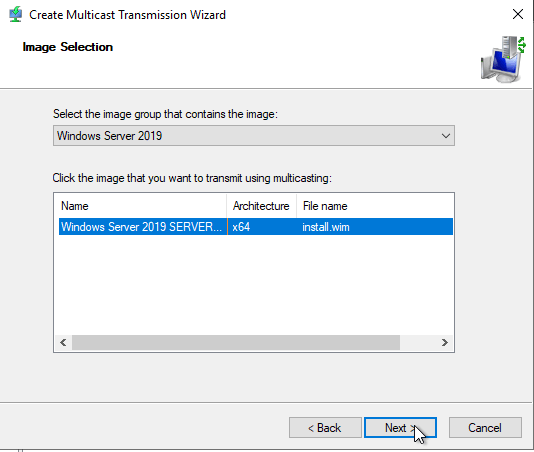
Here you have the choice to choose between Auto-Cast and the Scheduled cast. I will select Scheduled-cast and I will mark the first box. It will allow me to provide a threshold which means, wait until 5 clients request the image. Once done, start the transmission. Second box will give us option to schedule and start the cast at the specific time. Click next and finish
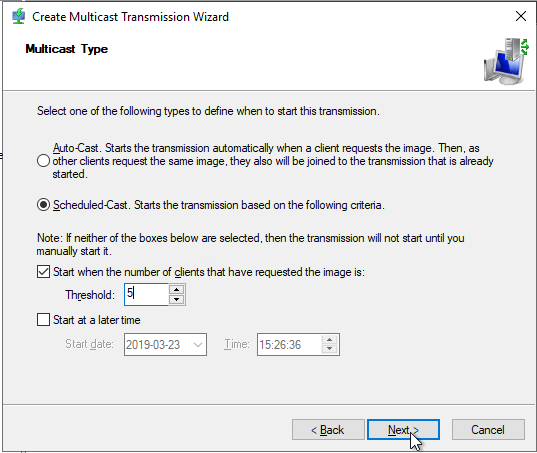

If we right-click on the transmission we will have the option to view the properties, to force the start if needed and to deactivate/delete the transmission.
ACTIVE DIRECTORY PRESTAGED DEVICES
Everything that we’re doing so far has to do with WDS working hand-in-hand with active directory to get these machines built and also to get them inserted into our active directory domain. But in certain circumstances, we may not necessarily, based off of the configuration that you’ve set, have that ability natively built into WDS. For that reason, we have this ability here, with our active directory prestaged devices, to identify devices that we want to automatically add in once those devices boot up. When those devices boot up, if we have some unique identifier for that device, like the MAC address or like that GUID, we can use either of those unique identifiers as a way of mapping that machine to an active directory account. These clients are also called known clients.

Here I need to identify a name and a device ID for a specific machine. This device ID can be one of a couple of different items like MAC address or GUID. If I click Next, this will tell me again the same things like I saw before: Who is my referral server? What’s my policy for when that machine attempts to boot etc so I will not go through the wizard again.

That’s it. I hope you enjoyed. I am planing to create a third post and it that one we will go through zero-touch installation. If there is interest I will make a third one with automation.
Stay Tuned!
Cheers,
Nedim
Windows Deployment Services (WDS) is a server technology from Microsoft for network-based installation of Windows operating systems. It is the successor to Remote Installation Services. WDS is intended to be used for remotely deploying Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2016, but also supports other operating systems because unlike its predecessor RIS, which was a method of automating the installation process, WDS uses disk imaging, in particular, the Windows Imaging Format (WIM).
WDS is included as a Server Role in all 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Windows Server and is included as an optionally installable component with Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2.
With this tutorial, we are going to explain how you can install and configure WDS role in Windows Server 2016 step by step.
Install WDS Role:
1. Open “Server Manager” and click “Add roles and features” and then click Next twice to skip the introduction pages of the installation wizard.
2. Select your server from the server pool.
3. From the roles list check on “Windows Deployment Services” once you click on it the installation wizard will pop up to add its features click on “Add Features” then click Next.
4. On the Features page of the installation wizard leave it as default and click Next.
5. This is a page about WDS information, you can read it to gain some info and then click Next.
6. Leave the role services that selected as default and click Next.
7. On the confirmation page of the wizard, click Install.

8. WDS role is installing now once the installation is complete we will move the second part of the tutorial and it’s about how to configure WDS.

Configure WDS Role:
After the installation of the role is done successfully please follow the below steps to configure it.
1. From dashboard click on Tools and select “Windows Deployment Services”.
2. On the console page of WDS, expand “Servers” and then right click on your server and click “Configure Server”.

3. On the configuration wizard, you can read the first page and then click Next.

4. On the installation options page, select “Integrated With Active Directory” and then click Next.
5. On this page, select the location that you want to save on it the windows images and the configuration files and then click Next.
6. On the “PXE Server Initial Settings” page choose “Respond to all client computers (Know and unknown)” and click Next.

7. On the Operation Complete page, uncheck “Add images to the server now” and click Finish.
8. Now “Windows Deployment Services” is installed on Windows Server 2016 successfully.

Summary
After this tutorial, you should be able to know how you can install and configure WDS role in Windows Server 2016, if you have any inquiry regarding this tutorial please comment below.
