This is part 1 of a 4 part series where we will configure System Center Configuration manager (SCCM) in a Windows Server 2019 environment.
SCCM enables the management, deployment and security of devices and applications across an enterprise. Most system administrators use SCCM for endpoint protection, patch management and software distribution.
Prerequisites
- Download trial version of Windows Server 2019 from Microsoft
- Download and install Oracle VM.
For a quick overview on virtualbox, visit https://www.nakivo.com/blog/use-virtualbox-quick-overview
VM setup overview
-
STDC01
Role: Domain Controller
Memory: 4GB
Storage HDD: 50GB
Static IP: 192.168.1.10 -
SQL01
Role: Domain Controller
Memory: 8GB
Storage HDD: 60GB
Static IP: 192.168.1.11 -
SCCM01
Role: Domain Controller
Memory: 8GB
Storage HDD: 2 X 80GB each
Static IP: 192.168.1.12
Create virtual machine
-
Select New from VirtualBox Manager.
-
Input Name, Version and Memory and click on Create.
-
Accept default settings and Click on Create
Install Windows Server 2019
-
Click on STD01 VM and Start
-
Select start-up disk. Find downloaded ISO file and select it (e.g. 17763.737.190906-2324.rs5_release_svc_refresh_SERVER_EVAL_x64FRE_en-us_1.iso). Then click Start for installing windows server 2019
-
Click on Install Now.
-
In Windows Setup Box Click Next.
-
Select Windows Server 2019 Datacenter Evaluation (Desktop Experience). Click Next.
-
Tick I accept the license terms and Click on Next
-
Select Custom: Install Windows only (Advance)
-
Accept Default settings. Click Next unless you want to create new partition and install drivers
-
After Windows installation has finished, you will be required to enter Administrator Password:
-
Press CTRL + ALT + DELETE TO UNLOCK (If this combination doesn’t work then just click Right CTRL + DELETE KEY TO UNLOCK)
-
Provide Administrator Password for login and hit Enter key
Initial Setup (Static IP, Remote Desktop, IE Enhance Security Configuration and Computer Name)
-
Navigate to Server Manager and,
- Click on Local Server
- Click on IE Enhanced Security Configuration
- In IE Enhanced Security Configuration turn off both Administrators and Users
- Click on OK
-
Now we are going to assign Static IP to this machine.
-
Right Click on Ethernet and Select Properties.
-
Click on Internet Protocol Version 4(TCP/IPv4). Select Properties.
-
Type IP address, Subnet mask, Default gateway and DNS IPs as it is shown in window:
-
Configure Remote Desktop and Computer name as mentioned above e.g. STDC01
-
Click Remote Desktop then select Remote Tab
-
Select Allow remote connections to this computer and Click OK
-
Click on Computer Name Tab and click on Change.
-
Type Computer name: STDC01 and click OK.
-
-
Restart computer to apply changes.
At this point, we have finalized initial setup for the first VM, repeat the same steps for the other two VMs SQL01 and SCCM01.
Conclusion
This concludes part 1 of this series, thank you for reading through till the end. I hope I was able to articulate Initial windows setup server in the simplest way with examples.
In the next part of this series, we will explore installation and configuration of AD DS, DNS and DHCP in Windows Server 2019.
This post will show the step-by-step process on how to install System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) version 1902 as a Standalone Primary Server in a Windows Server 2019 lab environment from scratch and later on we will upgrade it to SCCM Current Branch version 1906.
I have broken down this post in a series of steps:
- Step 1. Primary Site Server Installation Prerequisites
- Virtual Environment
- Installation Media
- AD Accounts
- Server Configuration
- Create System Management Container and Delegate of Permission
- Extend Active Directory Schema for SCCM 1902
- Configure Windows Firewall
- Step 2. Install Web Server (IIS) Role and other Features
- Step 3. Installing and Configuring SQL Server 2017
- SQL Server 2017 Installation
- MS SQL Server Management Studio Installation
- Configure SQL Server Memory Allocation
- Step 4. Windows ADK Installation
- Installing Windows ADK for Windows 10
- Installing Windows PE add-on
- Step 5. Install Windows Server Update Services
- Step 6. Configuration Manager 1902 Installation
- Step 7. Configuration Manager 1906 Upgrade Installation
- Step 8. Optional: MDT 8456 Installation and ConfigMgr Integration
Step 1. Primary Site Server Installation Prerequisites
Virtual Environment
For the virtual environment I usually use Hyper-V in Windows 10/Windows Server 2016/2019 or VMWare Workstation.

- A host computer with enough disk space (1TB to 2TB SSD recommended) and RAM (32GB or higher)
- Virtual Machines:
- DC01 = Domain Controller (I have a server core setup)
- C:\ | Windows | 80 GB
- 2GB RAM
- CM01 = Primary Site Server (Domain joined)
- Recommend Partition setup:
- C:\ | Windows | 100 GB
- D:\ | SCCM / SQL /Logs | 200 GB
- 16 GB RAM or higher is recommended (70% to be allocated for the database)
- Recommend Partition setup:
- DC01 = Domain Controller (I have a server core setup)
Installation Media
What you need:
- Windows Server 2019
- SCCM 1902
- SQL Server 2017
- MS SQL Management Studio
- Windows ADK 1903 and Windows PE add-on
Download the iso files from your Visual Studio Subscription or Microsoft Evaluation Center
AD Accounts
For this installation I have created accounts
- SCCMAdmin – account to be used for administering ConfigMgr
- SQLSvrAgent – account to be used as the SQL Server Account
You can go ahead and create the rest of the required SCCM Accounts
- SCCM Network Access Account
- SCCM Client Push Install Account
- SCCM Domain Join Account (for OSD)
- SCCM Admins Group
- SCCM SQL Reporting Account (If you’re uninstalling Reporting Services)
Server Configuration
Add LAB\SCCMAdmin and LAB\CM01 to the local Administrators group for CM01.

Create System Management Container and Delegate of Permission
Open ADSI Edit to create the System Management container

In the left pane, browse the Default naming context > expand DC and look for CN=System > make a right-click > in the context menu select New > Object…

In the Create Object window, scroll and select container and click Next.

In the Value: type System Management (it’s important to take note of the spelling, capitalization and the space between the two words).

click Finish to close the window.
Launch Active Directory Users and Computers and on the View tab, click on Advance Features

Browse for System > System Management > Right-click and select Delegate Control.

In the Delegation of Control Wizard click Next.

Add the Primary Site Server, CM01 once the server is added, click Next.
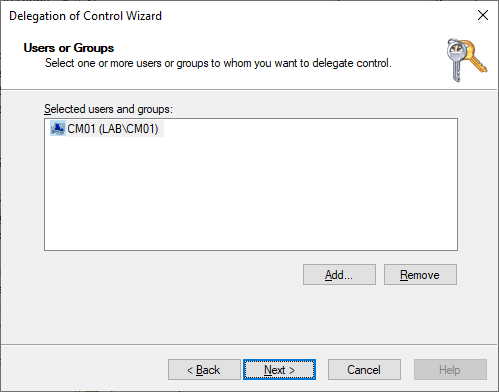
In the Task to Delegate, select Create a custom task to delegate click Next.

In the Active Directory Object Type select This folder, existing objects in this folders, and creation of new objects in this folder and click Next.

Tick on the 3 permissions General, Property-specific and Creation/deletion of specific child objects. Under Permissions tick on Full Control and click Next.

Click Finish to close the wizard.

Back in the System Management Properties, confirm that the Primary Site Server has Full Control Permission.

Note: As my Domain Controller was installed as a Server Core, I installed the Remote Server Administrator Tool (RSAT) for ADDS in the Primary Site Server to have access to the Active Directory Services Interface (ADSI Edit) tooland Active Directory Users and Computers.
Extend Active Directory Schema for SCCM 1902
In the Primary Site Server, mount the installation file of System Center Configuration Manager 1902 and browse to its directory <Drive>:\SMSSETUP\BIN\X64\ you’ll find the extadsch.exe file.

You can either double click on it or run it from your command prompt

When you run the Extadsh.exe its actually running ConfirMgr_ad_schema.ldf, this LDF file contains the instructions for what needs to be changed in Active Directory to support the schema extensions.
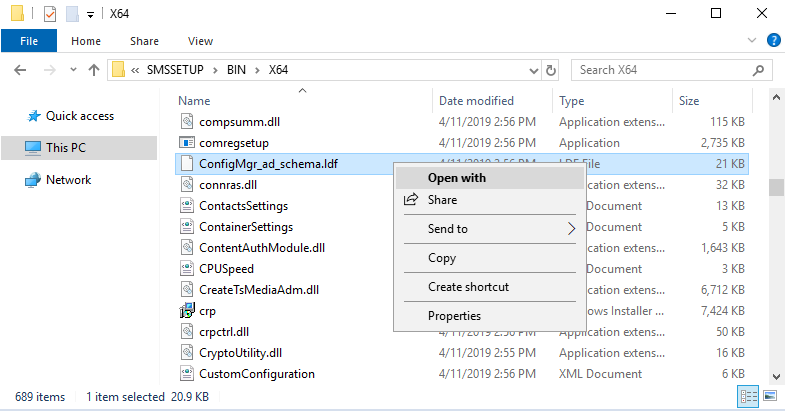
You can examine its content by opening ConfirMgr_ad_schema.ldf in Notepad.

If you’re curious go and browse through the SMS Schema Attributes. This will give you better understanding on how Active Directory schema extensions work for Configuration Manager.

From the LDF file:
# ———————————————————————-
# This section adds a new attribute for SMS Capabilities information. This is a
# new attribute for SMS V4.
#
# This attribute updates the MS-SMS-Management-Point class.
# ———————————————————————-
dn: CN=mS-SMS-Capabilities,CN=Schema,CN=Configuration,DC=x ← this is the path of where the change is going to happen
changetype: add ← it’s going to add something
objectClass: top
objectClass: attributeSchema ← theres an obect class that attributes schema
cn: mS-SMS-Capabilities ←in this folder location
attributeID: 1.2.840.113556.1.6.29.2.1.14 ← here is the ID
attributeSyntax: 2.5.5.4 ←Syntax value
#schemaIDGUID:: y1C8EEwlBkWgB+T2V+XESA== ← here its showing the GUID
isSingleValued: TRUE
oMSyntax: 20
searchFlags: 0
isMemberOfPartialAttributeSet: TRUE
dn:
changetype: modify
replace: schemaupdatenow ← this portion will update the schema
schemaupdatenow: 1
For more information about Extending the Schema in Configuration Manager go to this link
In the root directory for your Primary Site Server, you’ll see a small text file ExtADSch.txt and when you open it, you’ll find the line: Successfully extended the Active Directory schema.

Configure Windows Firewall
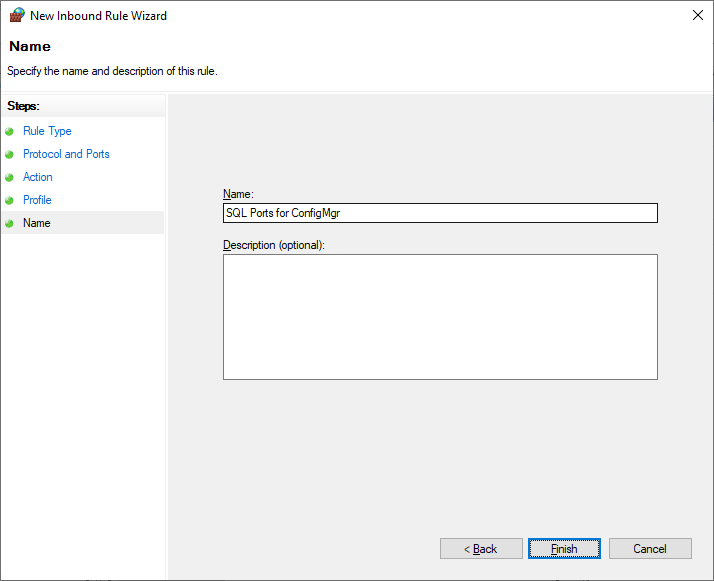
To open TCP port 1433 and 4022 for SQL replication you need to launch the Windows Defender Firewall and Advance Security to do that, press Windows logo key, type wf.msc and click on it

In the Windows Defender Firewall and Advance Security right-click Inbound Rules, and then click New Rule.
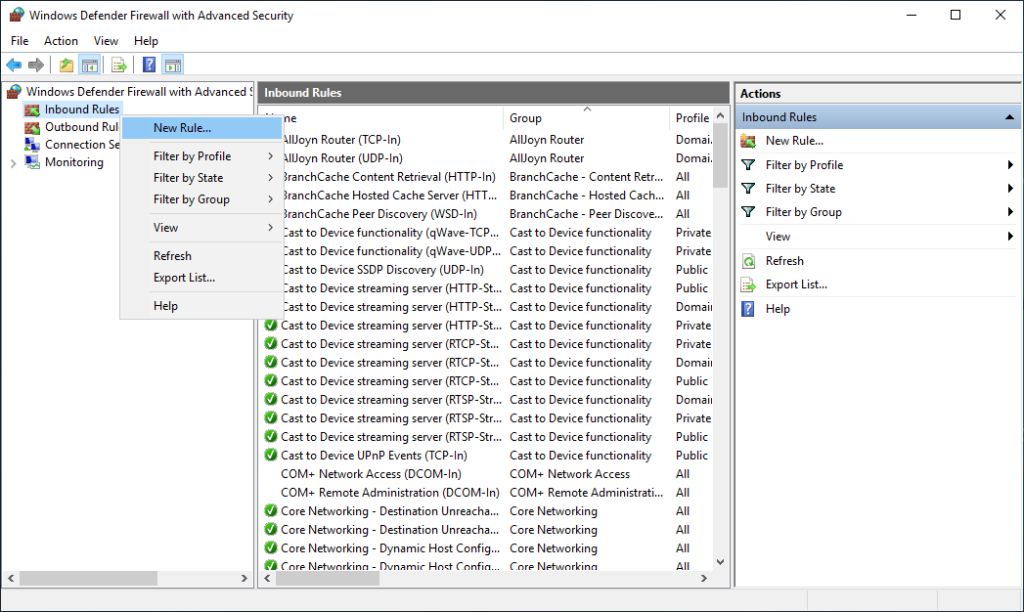
In the Rule Type dialog box, select Port and then click Next.

In the Protocol and Ports dialog box, select TCP. Select Specific local ports, and then type port numbers 1433 for SQL Server default instance and 4022 for Inter-site communications use the SQL Server Service Broker. Click Next.

In the Action dialog box, select Allow the connection, and then click Next.

In the Profile dialog box, select Domain and then click Next.

In the Name dialog box, type a profile name,like SQL ports for ConfigMgr and then click Finish.
Step 2. Install Web Server (IIS) Role and other Features
In the Primary Site Server we will need to install the follow Roles and Features from the Server Manager:
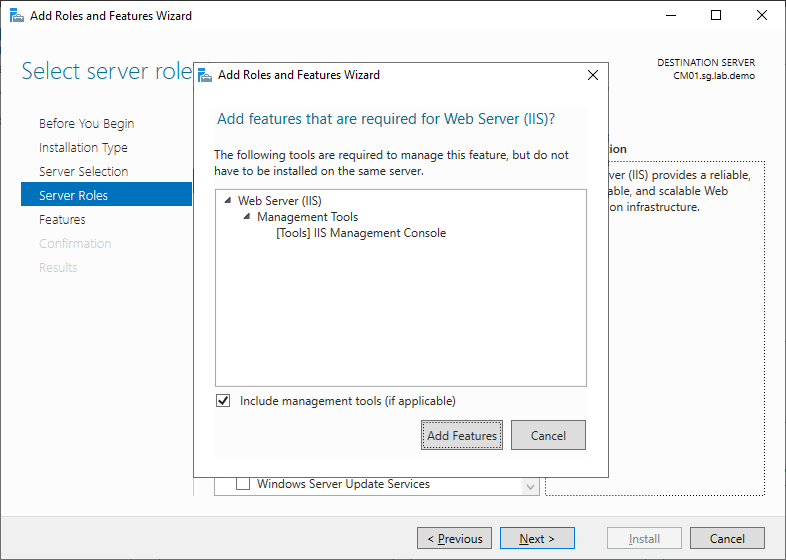
In the Server Roles, select Web Server (IIS)
When prompted to “Add features that are required for Web Server (IIS)?” click the Add Features button.and click Next.
In Features, select .NET Framework 3.5 Feature and Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS)

Note: BITS – is the technology that allows us to throttle all the network communication that occurs between servers to client where it utilizes idle bandwidth to transfer data.

Still in the Features page, scroll down and select Remote Differential Compression (RDC) and click Next.
Note: RDC – is a client–server synchronization algorithm which BITS leans on to ensure that the files goes in the most efficient way possible.
In the Web Server Role (IIS) > Role Services select the following:
Web Server (IIS)
- Web Server
- Common HTTP Features: Default Document, Directory Browsing, HTTP Errors Static Content, HTTP Redirection
- Health and Diagnostics: HTTP logging, Logging tools, Request Monitor Tracing, Tracing
- Performance: Static Content Compression
- Security: Windows Authentication
- Application Development: .NET Extensibility 3.5, .NET Extensibility 4.7, ASP.NET 3.5, ASP.NET 4.7, ISAPI Extensions, ISAPI Filters
- Management Tools
- IIS Management Console
- IIS 6 Management Compatibility: IIS 6 Metabase Compatibility, IIS 6 WMI Compatibility
- IIS Management Scripts and Tools

In the Add Roles and Feature Wizard > Confirm installation selection page, review the Roles and Features selected:
- NET Framework 3.5 Features
- .NET Framework 4.7 Features
- Background Intelligent Transfer (BITS)
- Remote Differential Compression
- Web Server (IIS)
- Web Server
- Common HTTP Features: Default Document, Directory Browsing, HTTP Errors Static Content, HTTP Redirection
- Health and Diagnostics: HTTP logging, Logging tools, Request Monitor Tracing, Tracing
- Performance: Static Content Compression
- Security: Windows Authentication
- Application Development: .NET Extensibility 3.5, .NET Extensibility 4.7, ASP.NET 3.5, ASP.NET 4.7, ISAPI Extensions, ISAPI Filters
- Management Tools
- IIS Management Console
- IIS 6 Management Compatibility: IIS 6 Metabase Compatibility, IIS 6 WMI Compatibility
- IIS Management Scripts and Tools
- Web Server
Click the Install button to complete the installation of the Web Server Roles and Features.

Verify that the installation is successful from this point you can now click the Close button to proceed to the next step.

Step 3. Installing and Configuring SQL Server 2017
SQL Server 2017 Installation
In this section we will install and configure the Primary Site’s database server and it’s components. Go a head an mount the SQL Server 2017 installer and run the setup.exe.
In the SQL Server Installation Center > Installation, click on the New Server stand-alone installation or add features to an existing installation.

In the Product Key page, choose for the Evaluation or enter a product key then click Next to continue.

Agree to the License Terms then click Next.

In the Microsoft Update we’ll skip the check updates for now, click Next.

In the Install Rules, make sure that everything pass else rectify by clicking the Status links, as for Windows Firewall we’ll ignore the Warning as the required ports for SQL replication was previously configured. We will now and proceed to the Feature Selection page.

In the Feature Selection, tick the Database Engine Services then click Next.

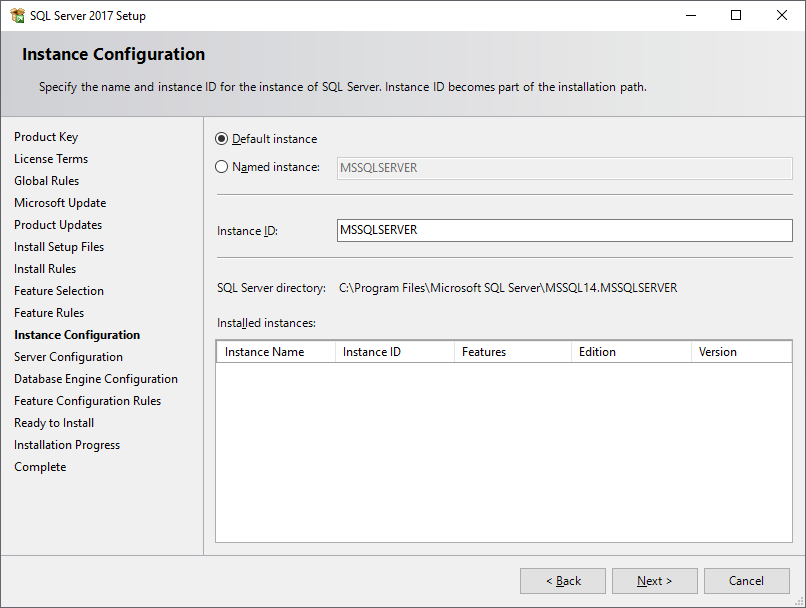
In the Instance Configuration, leave the default instance ID, MSSQLSERVER click Next to continue.
In the Server Configuration, Service Accounts tab, make sure to configure ALL SQL services to run under a domain user account (e.g., LAB\SQLSvrAgent) instead of the local system or network services.
Note: Best practice in Production, the SQL Server Agent and SQL Server Database Engineer should each have a domain accounts. For their account’s passwords should be configured not to expire and cannot be changed (so make sure these service accounts are restricted not have an interactive logon rights as well).

…Moving on, in the same window click the Collation tab.

In the Database Engine Configuration, click Add Current User or add another user/SCCM Admin groups and click Next.

SQL Server 2017 is ready to install, click the Install button.

Note: Notice the Configure file path, you can go to the directory and explore the ConfigurationFile.ini if you’re interested to install SQL Server using the configuration file.

Confirm that SQL Server 2017 is successfully installed, click the Close button to complete the installation.

MS SQL Server Management Studio Installation
Beginning SQL Server 2016 the release of SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) was a stand-alone install outside of the SQL Server release. That is why we need to do a separate install of the SSMS.
Download and install SSMS

After the installation is complete you are required to restart the Primary Server.

Configure SQL Server Memory Allocation
Launch the SQL Server Management Studio, Right-click on the CM01 (SQL Server) and select Properties.

In the Server memory options I have set the Minimum and Maximum memory size to 12288 if it’s not set to at least 8192 you’ll have a little warning during the installation of Config Manager. Setting the Memory b/w 2048 to 4096 will still work.
By default the Minimum server memory (in MB) is set to 0 and the Maximum server memory (in MB) is set to 2147483647.

Click OK to close the Server Properties window and complete the SQL configuration.
Step 4. Windows ADK Installation
In any Configuration Manager deployment I strongly recommend to install the lasted Windows 10 ADK in preparation for Windows 10 Operating Systems Deployment with Configuration Manager, the Windows ADK is a required external dependency.
Note: As of this blog post, the latest version of ADK is 1903.
From docs.microsoft.com: The following table lists the versions of the Windows 10 ADK that you can use with different versions of Configuration Manager.

In this section we will install Windows ADK 1903 and Windows PE add-on for ADK
Installing Windows ADK for Windows 10
Download and run the adksetup.exe

The installation is very straight forward, in the Specify Location leave the default and click Next.

In the Select the features you want to install, as for this installation we will only select the following:
- Deployment Tools
- Imaging and Configuration Designer – this can be used later on for provisioning packages.
- Configuration Designer
- User State Migration Tool
After selecting the features to to install, click Install button.

You’ll get the Welcome screen to Windows 10 ADK once the installation is completed. Click Close to finish the installation.

Installing Windows PE add-on
Starting Windows 10 1809, Windows Preinstallation Environment (PE) has been released separately from the Windows ADK.
To add Windows PE to the ADK installation, we need to download the Windows PE add-on and run the included installer after installing the ADK.
Similarly to Windows ADK the WinPE Add-on is a straight forward install. Download and run the adkwinpesetup.exe
In the Specify Location, click Next.
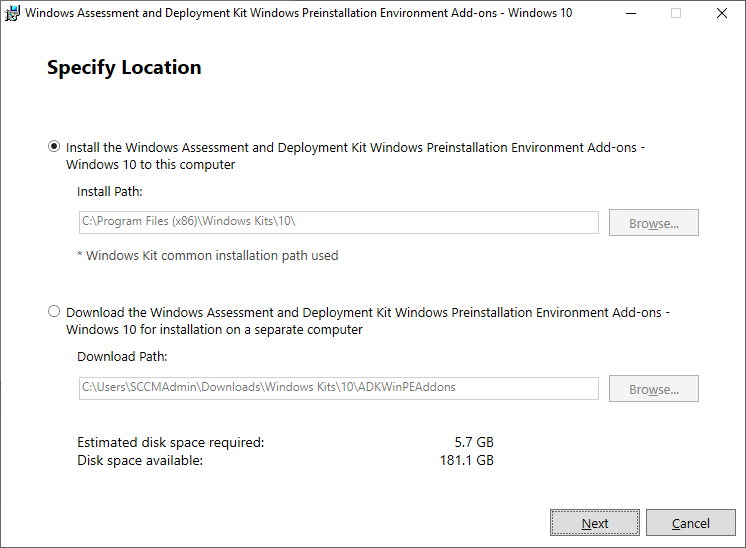
There’s nothing else to select in the Select the features you want to install other than Windows PE. Click the Install button to complete the installation.

Step 5. Install Windows Server Update Services
For us to deploy software updates using Configuration Manager we need to install the WSUS Server Role. WSUS will be later on be integrated with the Software Update Point (SUP) Site System Role.
In the Server Manager select Windows Server Update Services and click Next.

In the Role Services, tick WSUS Services and SQL Server Connectivity, in this example we will make use of the SQL Server database that we just installed in Step 3 instead of Windows Internal Database (WID).

In the Content location selection define a local or network share to store the updates. In this example I have pointed it to C:\WSUS.
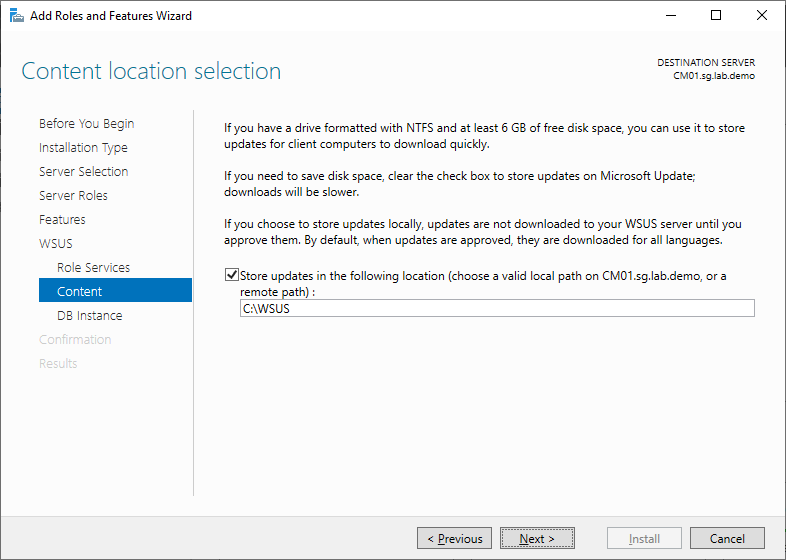
For the Database Instance Selection we’ll use the Primary Site’s database CM01.sg,lab.demo.

Click Install to proceed installing the WSUS role.

In the Installation progress once you see the installation succeeded go and click on the Launch Post-Install task then click on the Close button.

You can see the status of the Post-deployment Configuration from the Server Manager. Verify that the Configuration is completed.

We can also verify from SSMS that SUSDB has been created under the Databases.

Step 6. Configuration Manager 1902 Installation
Finally after all the preparation we are now ready to the install SCCM 1902. Go and mount the SCCM 1902 ISO and run the Setup.exe.
Download Required Prerequisite Files
Optional: We can download the required prerequisite files prior to the installation of Configuration Manager. This is usually done if your server is in an isolated network.

After click the Download required prerequisite files the Configuration Manager Setup Downloader will pop-up, select a directory where to download the file and click Download.
The downloader tool will close automatically after the download is complete, for this download I got 56 files in my Prereqs folder.

Install SCCM v1902
In the SCCM installation screen click Install

Click Next.

Select Install a Configuration Manager primary and tick the Use typical installation options for stand-alone primary site box.
A pop-up box will appear, read through and click on the Yes button.

In the Product Key. select an option and click on Next.
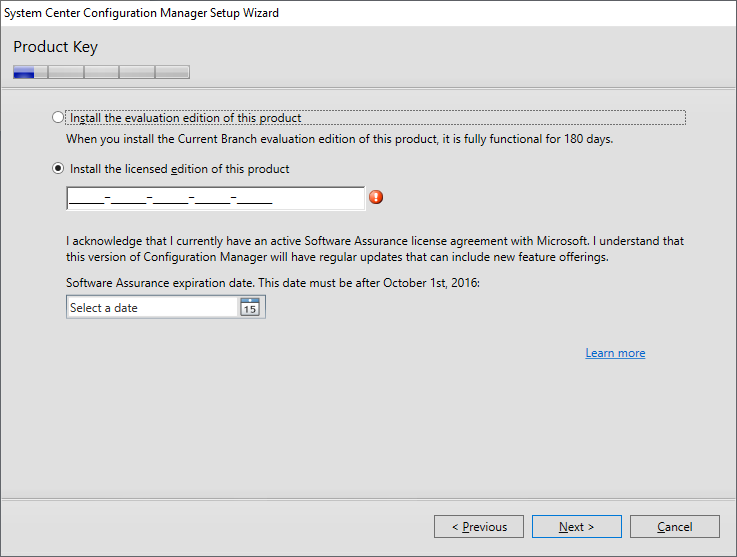
In the Product License Terms, tick all the 3 boxes and click Next.

For the Prerequisite Downloads we’ll be using the Use previously downloaded file option and point it the folder where we downloaded the files.

Let wizard finish verifying the files

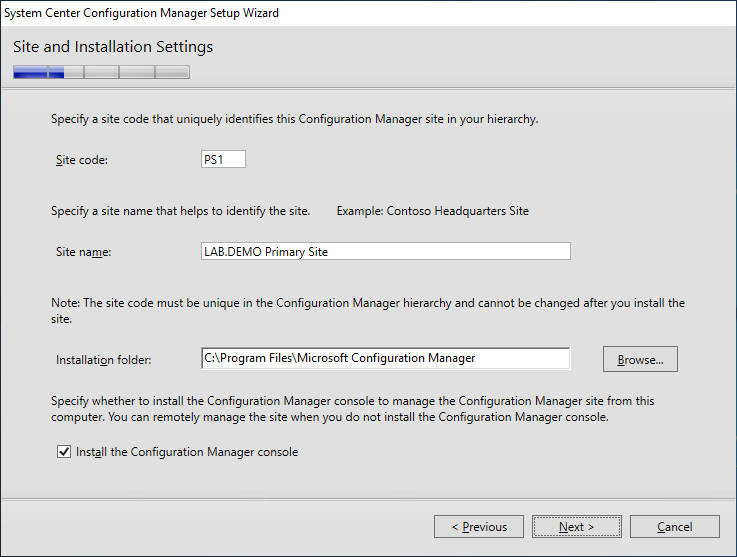
In the Site and Installation Settings , enter a 3 character site code and site name that normally pertains to the site location and click Next.
In the Diagnostic and Usage Data click Next.

In the Service Connection Point Setup in this example, we will select the Yes, let’s go connected (recommended) as my server has internet connectivity, if you’re server is in an isolated network select the Skip this for now option.

Click the Next button for the final Prerequisite Check.

In the Prerequisite Check page, make sure there’s no problem found and if there is fix it first before clicking the Begin Install button.

After clicking the Begin Install you’ll be brought to the Install page to see the over all progress. You may want to grab a coffee or a beer at this point (you deserve it) and come back after an hour.

To see the detailed progress you can click the View log button, make sure to set and use CM Trace.exe as the default log viewer.
Note: CMTrance can be found in the SCCM installer’s directory e.g., D:\SMSSETUP\TOOLS

After an hour later, your Configuration Manager 1902 installation core setup is completed – Congratulations!
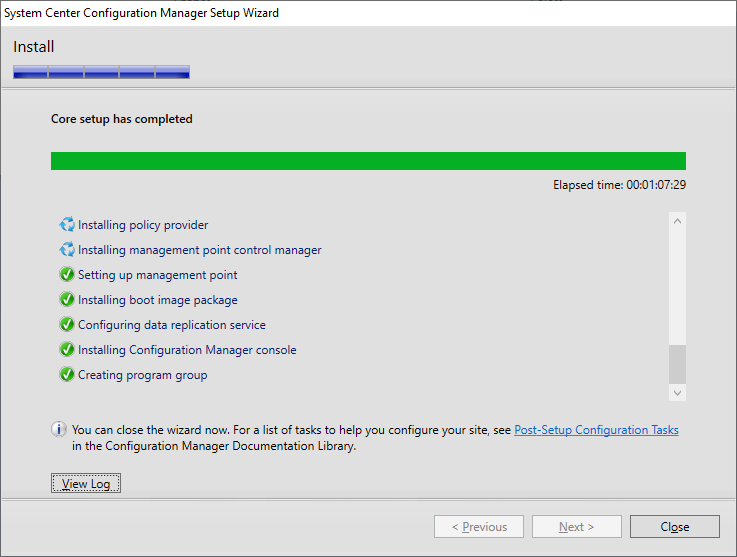
There’s a Post-Setup-Configuration Tasks link in the wizard which will lead you this Post-update checklist link: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/p/?LinkId=626562 go ahead an open the link

for version 1902 here’s the post-update check list: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sccm/core/servers/manage/checklist-for-installing-update-1902#post-update-checklist
Now go ahead launch the SCCM Console and open the About window

and verify that the SCCM version is on 1902.

Don’t configure the Configuration Manager server yet as we will update it first to version 1906 in the next step.
Step 7. Configuration Manager 1906 Upgrade Installation
Before we begin to upgrade our SCCM 1902 to 1906 you may want go through on the what’s new in version 1906 of SCCM Current branch https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sccm/core/plan-design/changes/whats-new-in-version-1906
Support for Configuration Manager current branch versions
Also its good to get to know about the Servicing Support/end of support dates for Configuration Manager versions from this link: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-ca/sccm/core/servers/manage/current-branch-versions-supported

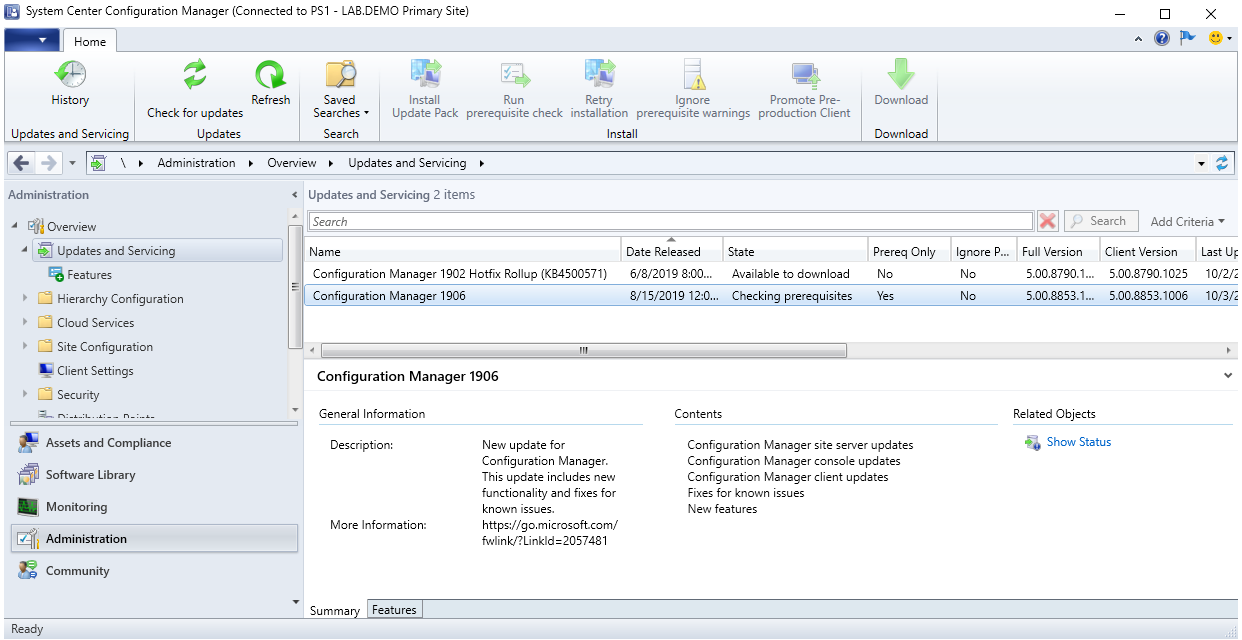
SCCM 1906 Prerequisite Check
Launch the SCCM console and go to Administration > Updates and Servicing and verify that the Configuration Manager 1906 is in Ready to install State. (This will appear if your SCCM is connected to the internet for sometime)

Highlight Configuration Manager 1906 and Run prerequisite check

You will see that the Status is now Checking prerequisites.
We can see the progress by opening the C:\ConfigMgrPrereq.log with CMTrace.

Alternatively we can also view the progress from the Monitoring workspace > Updates and Servicing Status right-click on the Configuration Manager 1906 and select Show Status.

The Update Pack Installation Status window will pop-up. At anytime you can click the OK button to close the window.

Back in the SCCM Console wait until the Prerequisite check passed

Select and right-click the Configuration Manager 1906 update and select Install Update Pack

SCCM 1906 Update
The Configuration Manager Updates Wizard will launch and in the General click on Next.

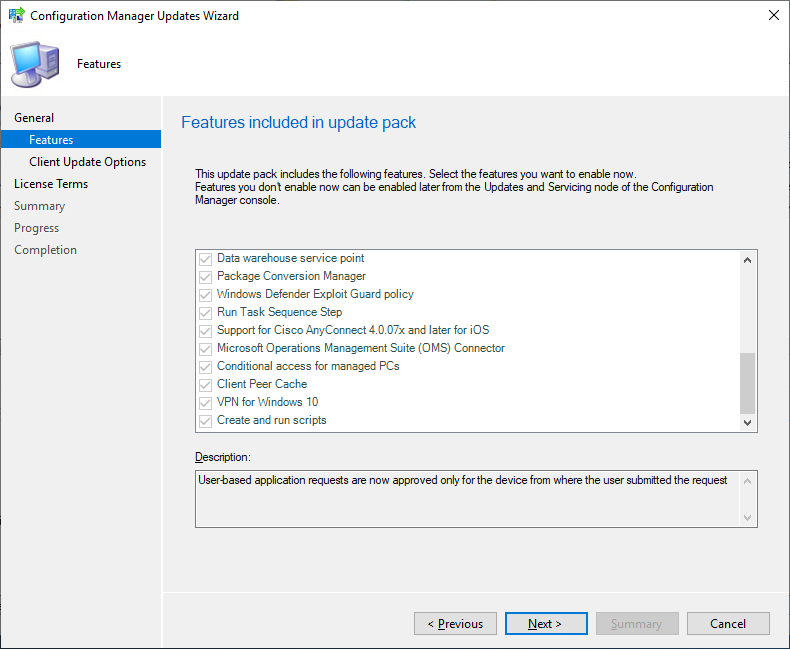
In the Features, select the feature you need to install, in my case the check boxes are pre-selected already I just needed to click Next.
Note: if you don’t want to select any of the features you can always enable it later, from the SCCM console Administration workspace > Updates and Servicing > Features.
In the Client Update Options, I will select Upgrade without validating as I don’t have any active client yet.

In the License Terms tick and accept the license terms box and click Next and in the Summary click on Next.

Click Close and go back to the SCCM Console to monitor the progress of the update.
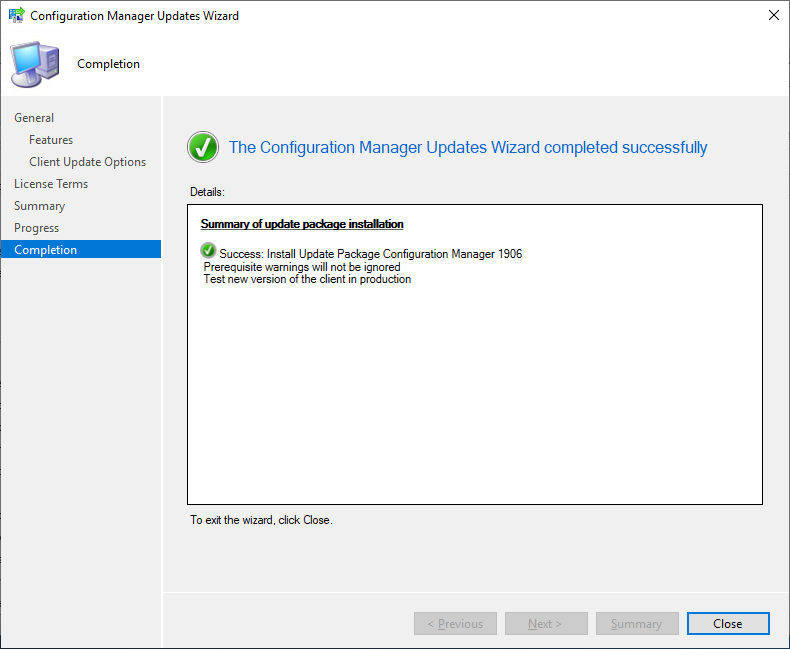
In the Monitoring workspace > Updates and Servicing Status you can see that the status is Installing, go and right-click on the Configuration Manager 1906 and select Show Status to further view the detailed status.

It will take something for the installation to complete. Once completed, click the OK button to close the Status window.

In the SCCM Console, you will get a notification that “A new version of the console is available…. ” go and click on the Install the new console version link.

The SCCM console will close and go through the installation process.

You can view the progress from the log files C:\ConfigMgrAdminUISetup.log and C:\ConfigMgrAdminUISetupVerbose.log and after the installation is completed the new SCCM Console will automatically launch.
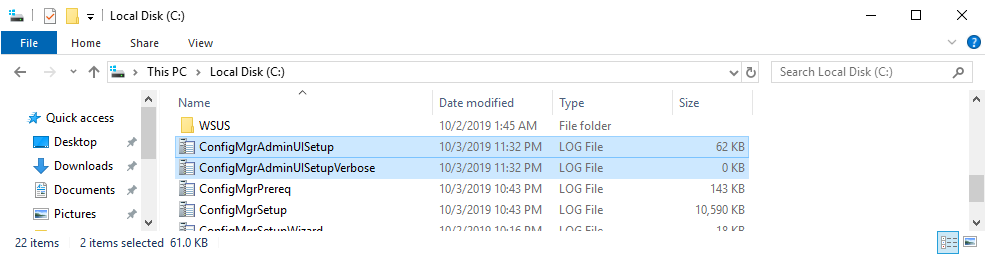
In the console, go and verify that the SCCM version is now in 1906.

We can refer the Configuration Manager versions from this link: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sccm/core/servers/manage/updates#supported-versions

We can further confirm the Primary Site version from its Properties you can see that the Version and Build number refers back from the table above.

Later on you may see a Configuration Manager 1906 Hotfix Rollup, you can go a head and install it as at this point our SCCM Lab is still empty, the procedure of install the hotfix is the same as the SCCM 1906 Update do Run prerequisite check and Install Update Pack.

That concludes our SCCM 1906 installation process. Congratulation you made it this far!
Step 8. Optional: MDT 8456 Installation and ConfigMgr Integration
This section will show how to integrate the Microsoft Deployment Toolkit with Configuration Manager 1906 and understand the benefits of integrating MDT with SCCM.
I strongly recommend that you always include MDT to your SCCM infrastructure as this will add many enhancements (280 to be exact) in the Windows Operating System Deployment with Configuration Manager. enhancements that MDT adds to Configuration Manager.
Note: as of writing the latest version used is MDT 8456
Install MDT
After you download MDT copy it over to your Primary Site Server and run the MicrosoftDeploymentToolkit_x64.msi file.
In the MDT Setup Wizard click Next
Accept the License Agreement and click on Next
In the Custom Setup leave the defaults (as we will not be using MDT as the deployment tool) and click Next.

In the CEIP click Next
In the next page, click Install.

Once the MDT setup is complete click the Finish button to close the window.

Integrate MDT 8456 with SCCM 1906
To integrate MDT with SCCM we need to run the Configure ConfigMgr Integration as administrator from the Start Menu > Microsoft Deployment Toolkit

In the Options, the Install the MDT extensions for Configuration Manager is selected by default. The check boxes have been ticked, the Site server name and Site code boxes have been automatically populated with the SCCM server details. Click Next to proceed.

Verify that the integration is successful. Click Finish to close the window.

In the SCCM 1906 Console, go to the Software Library workplace > Overview > Operating Systems > Task Sequences
You will that there will a Create MDT Task Sequence available in ribbon.

Summary
In this post we have completed the following
- Build a SCCM 1902 lab environment
- Upgrade SCCM 1902 to 1906
- Integrate MDT with SCCM
Now you are ready to perform Software Deployment Services and Operating System Deployment with the lab that we’ve built. Thanks for taking time to read this post.
This post covers the steps to deploy Windows Server 2019 using SCCM. Windows Server 2019 is the latest server operating system by Microsoft. I must say that after Windows Server 2012 R2, this is my favorite server operating system. My current SCCM 1810 lab is set up on Windows Server 2019 and so far it is the best server operating system by Microsoft.
You can download evaluation version of Windows Server 2019 from here. Windows Server 2019 includes the following new features :-
- Hybrid capabilities with Azure
- Enhanced security
- Faster app innovation
- Unprecedented hyper-converged scale
Table of Contents
Steps to Deploy Windows Server 2019 Using SCCM
To make it easier to deploy Windows Server 2019, I will be breaking the complete deployment into steps. Windows Server 2019 is available in Standard and DataCenter editions. I will be deploying server 2019 DataCenter edition using SCCM 1810 in my lab setup.

You get two options while you install Windows Server 2019.
- Server Core – It’s a smaller installation that includes the core components of Windows Server and supports all server roles, but does not include a local graphical user interface (GUI).
- Server with Desktop Experience – This is the complete installation and includes a full GUI for customers.
In my lab setup, I have installed SCCM 1810. Ensure that you are using latest version of Windows ADK. My current lab setup includes ADK version 1809.
STEP 1 – Import Windows Server 2019 OS
Let’s start by importing the Windows Server 2019 operating system in Configuration Manager. First of all, mount the Windows Server 2019 ISO. Copy all the files and paste the files in sources folder. This will make it easy for us to import it into the SCCM.
In the SCCM console, click Software Library > Operating Systems. Right click Operating System Images and click Add Operating System Image.
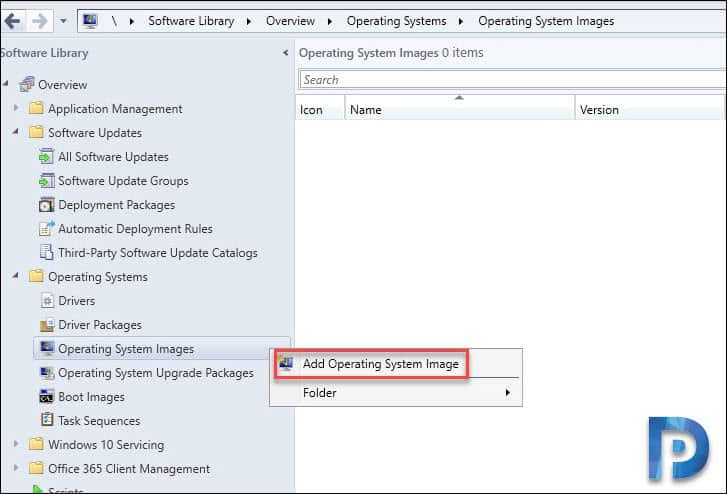
Specify the data source by providing the path to install.wim file. We need only the .wim file out of all the files inside that folder. The install.wim file is located under Sources folder of operating system media. Click Next.
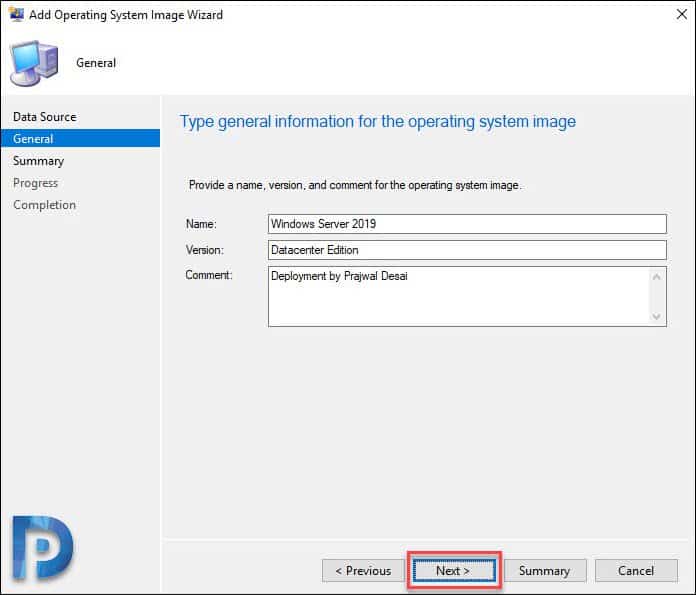
Specify Name, Version and Comment. Click Next.
Click Next on Summary Page.

Finally on Completion window, click Close.
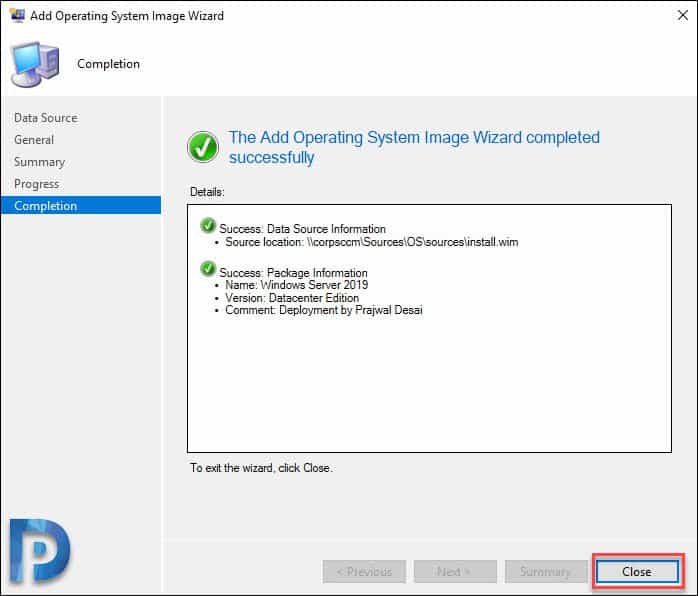
In the above steps, we successfully imported Windows Server 2019 operating system. Now you must distribute the content to distribution point(s). Right click Windows Server 2019 OS and click Distribute Content. In the next step, select the distribution points and complete the wizard. If you see Content Status as green, that confirms the content is available with distribution point.
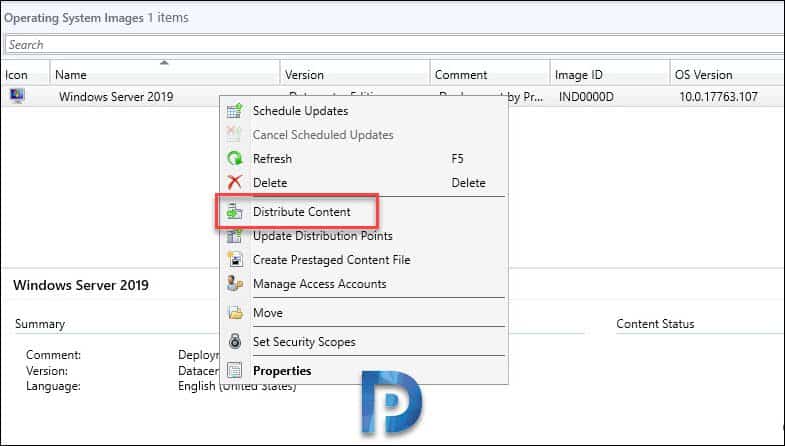
STEP 2 – Create Windows Server 2019 SCCM Task Sequence
In this step we will create SCCM task sequence to deploy Windows Server 2019. Go to Software Library > Operating Systems > Task Sequences. Right click anywhere on the right pane and click Create Task sequence.
In the Create Task Sequence wizard, click Install an existing image package. Click Next.
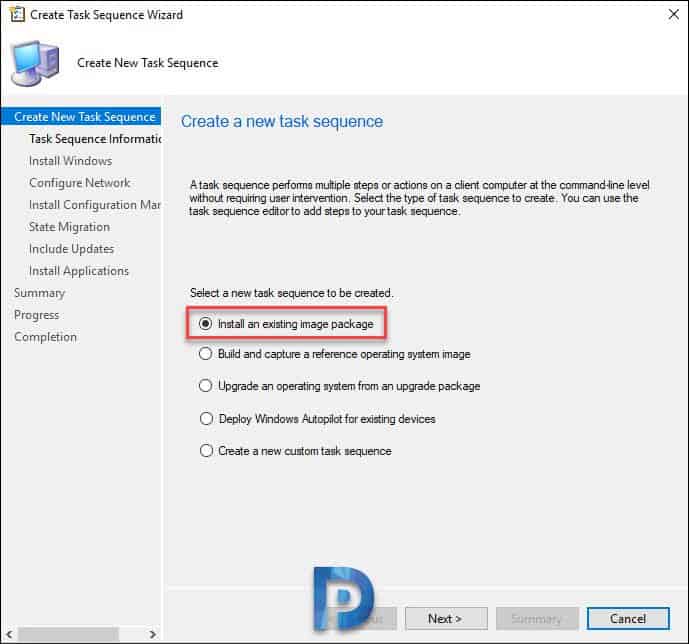
Specify Task sequence name and description. Click Browse and select 64-bit boot image. Click Next.
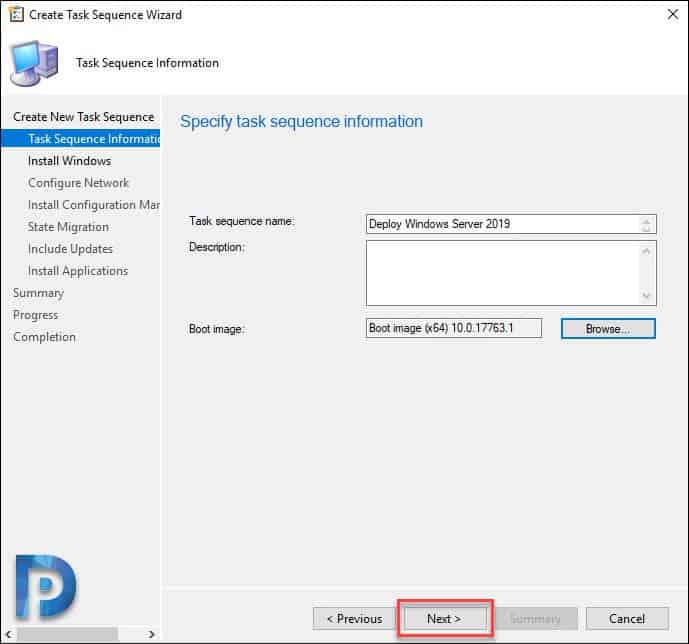
Specify the image package which is Windows Server 2019. Again you might see two options, Datacenter and Standard. Based on your requirement select the OS edition.
Select partition and format target computer before installing the operating system. Uncheck Configure task sequence for use with BitLocker.
Licensing – You may specify the product key or if you have KMS server that activates the OS, leave it blank.
For local admin password, there are two options.
- Randomly generate the local admin password and disable account on all supported platforms.
- Enable the account and specify the local admin password.
Both the options are self-explanatory. Since I am deploying the OS in lab setup, I will be going with second option. Click Next.

You can either join the machine to workgroup or join it to domain. If you are joining it to the domain, select the domain and domain OU. Specify an account that has enough permissions to join this client to domain. Click Next.
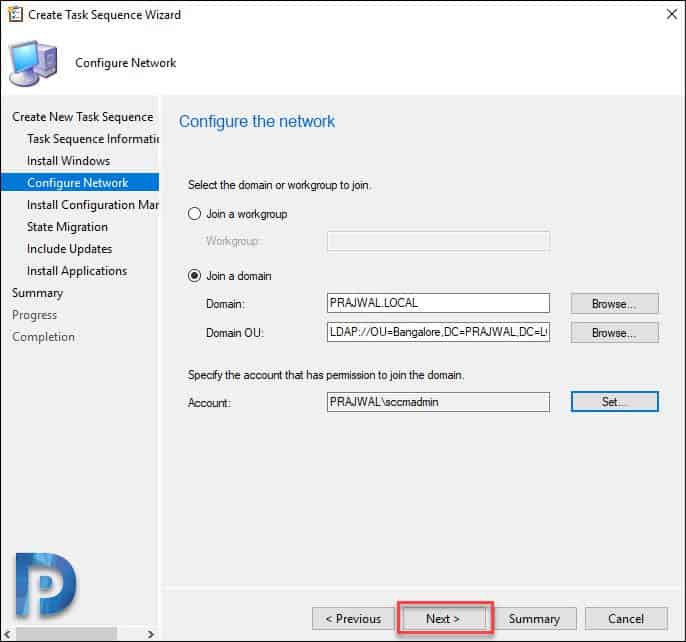
Click Next.
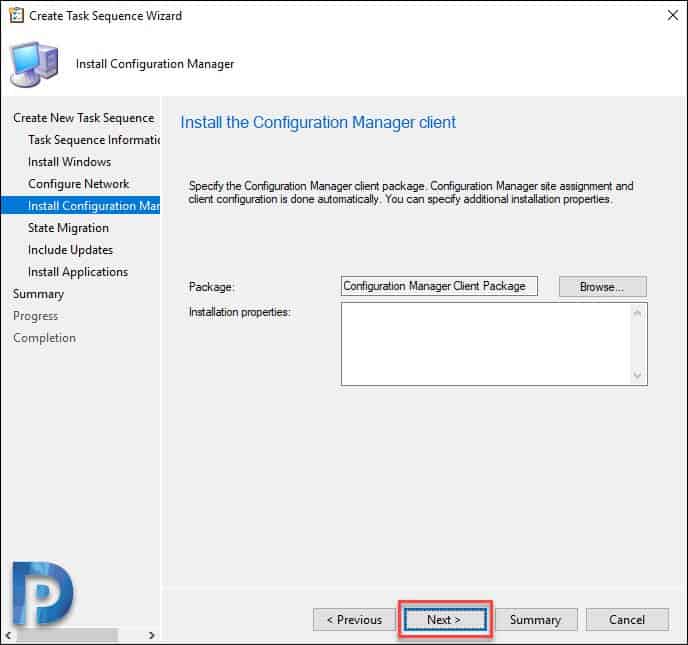
We will not capture any user settings, so click Next.

At this point, I am selecting do not install any software updates. Click Next.
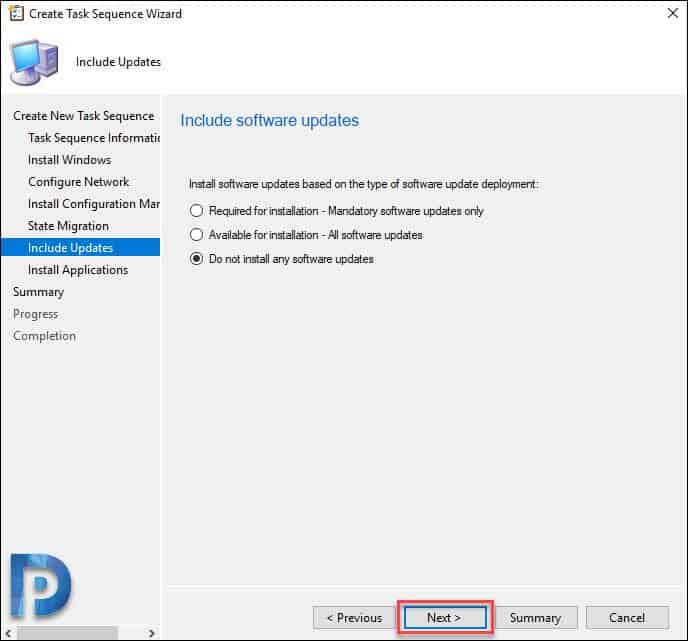
Select if you wish to deploy any applications along with operating system. Click Next.
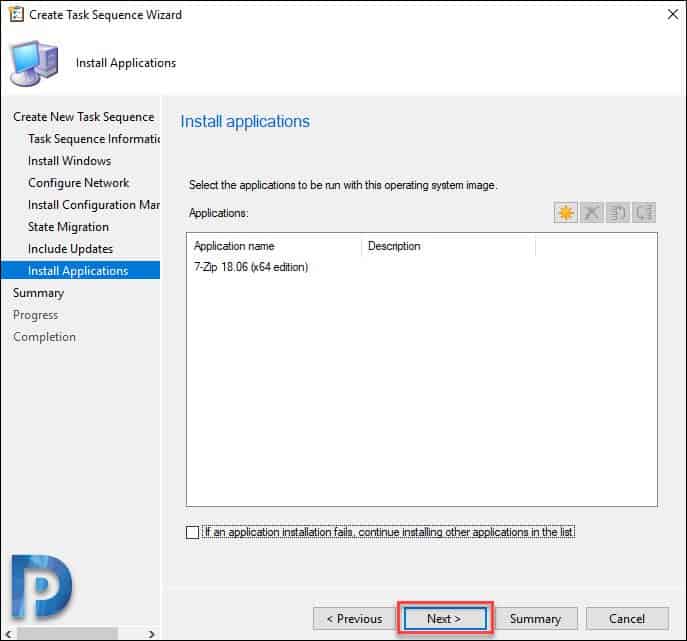
On Summary page, verify all the details. Click Next. Click Close.
STEP 3 – Deploy Windows Server 2019 Task Sequence
In the above step, we created Windows Server 2019 SCCM task sequence. We will now deploy the task sequence. Right click Windows Server 2019 SCCM task sequence and click Deploy.
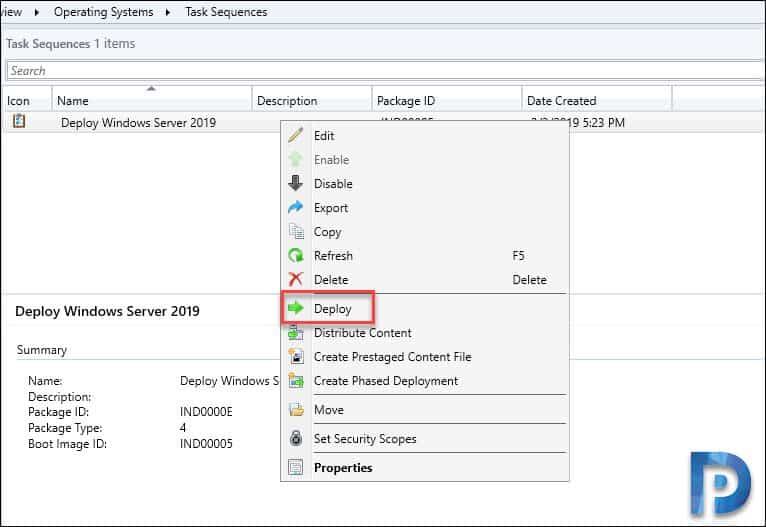
Click Browse and select the collection. Click Next.
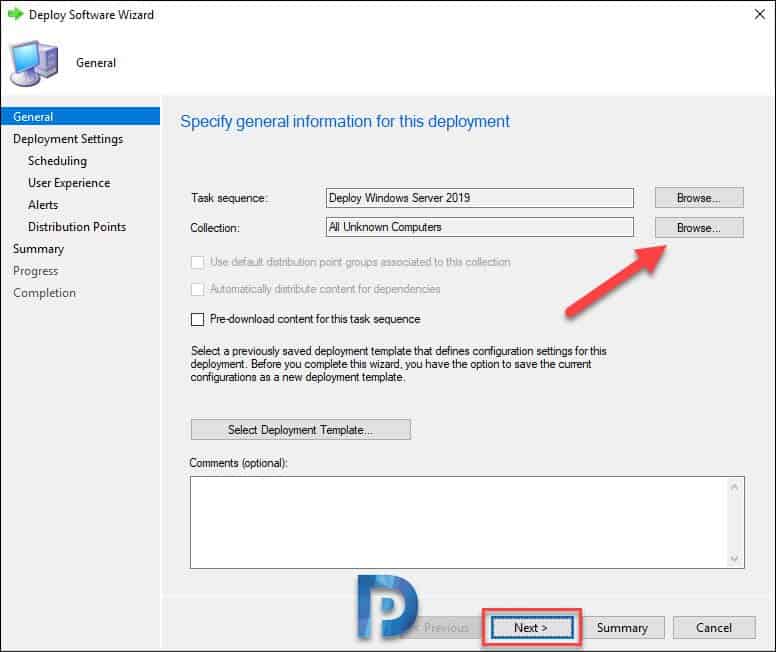
Under Deployment Settings, ensure the action is Install and purpose is Available. Click the drop-down and select Only Media and PXE. Click Next.
You can schedule the deployment by selecting the date and time. In addition to that you can also schedule when the deployment will expire. Click Next.
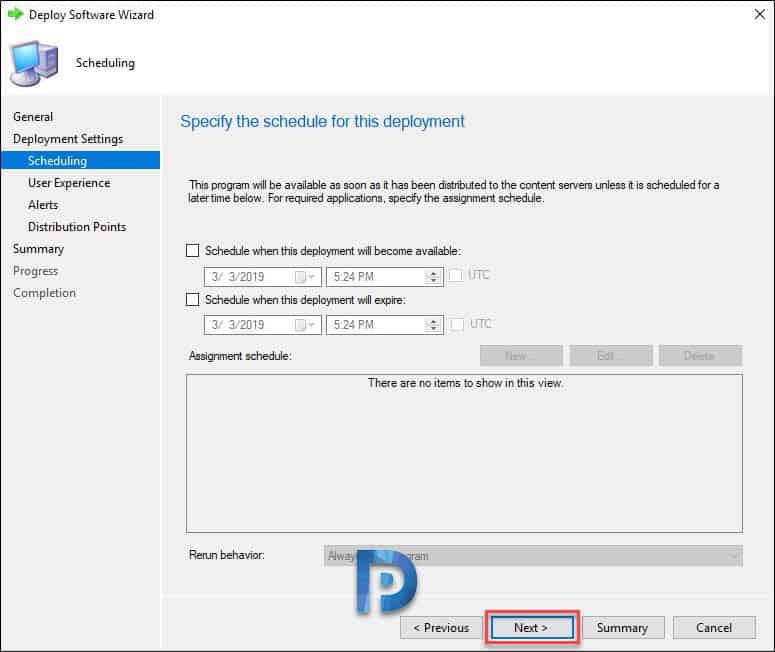
Making no changes to any settings, click Next.
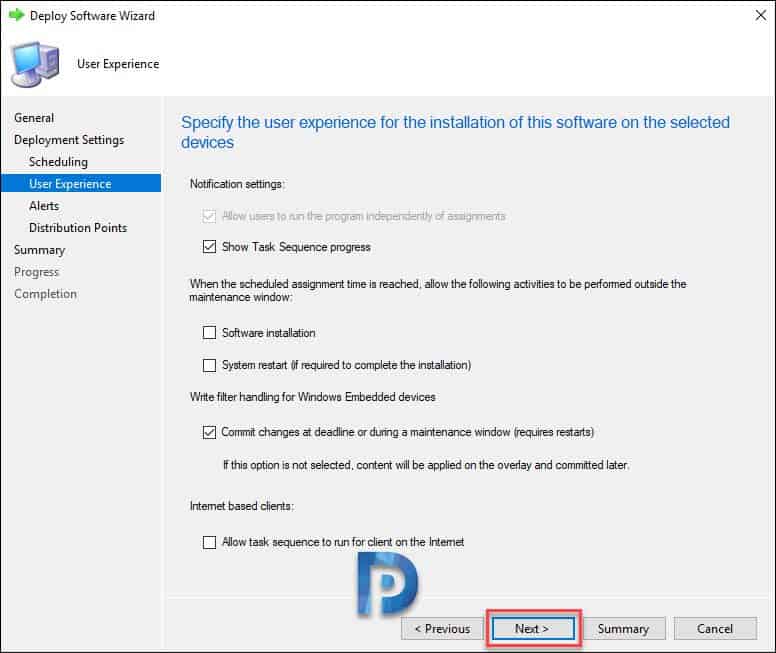
Click Next.
Nothing to select anything here, click Next.
On the summary page, verify the details and click Next.

On Completion page, click Close.
STEP 4 – Deploy Windows Server 2019 Using SCCM
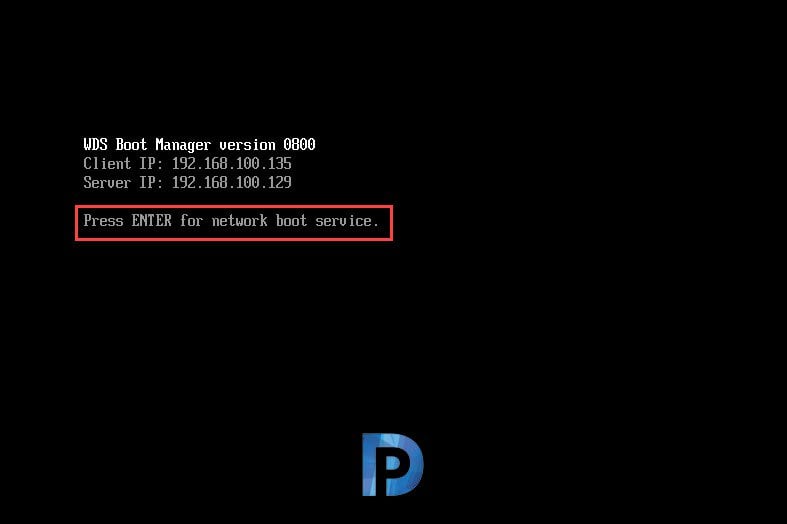
Now we are ready to deploy Windows Server 2019 using SCCM. In my lab setup, I have created a VM with no operating system. The VM is set to boot from network. Press Enter to network boot.
The boot image is downloaded first. On the task sequence welcome page, click Next.
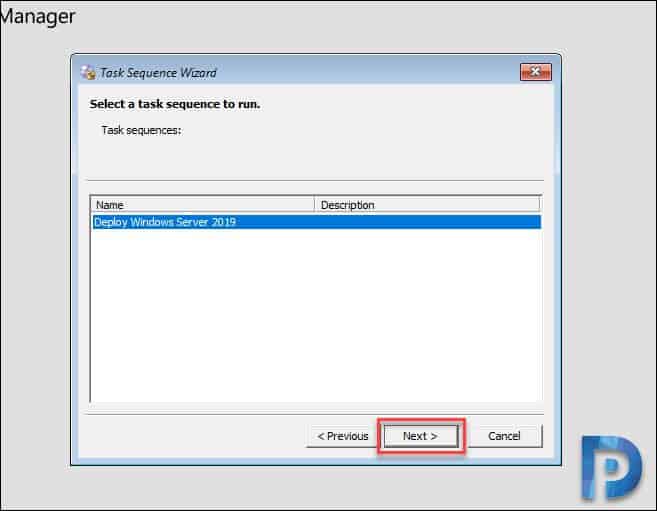
Select the Windows Server 2019 task sequence and click Next.
The task sequence execution begins. The wizard is now downloading install.wim file.

We are now at Applying Operating System image step.
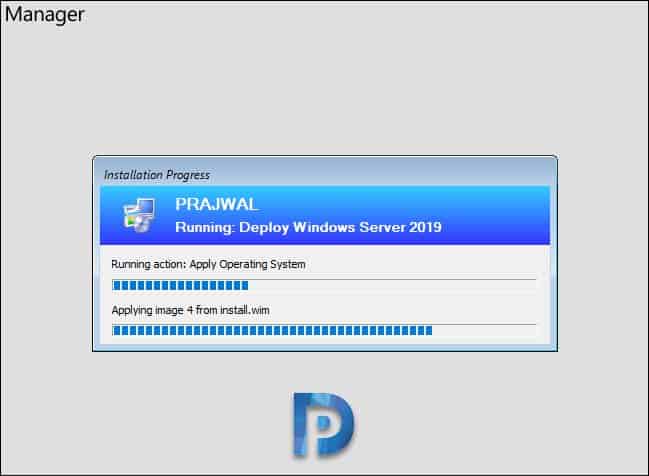
The operating system is installed, the wizard is now installing the selected applications.

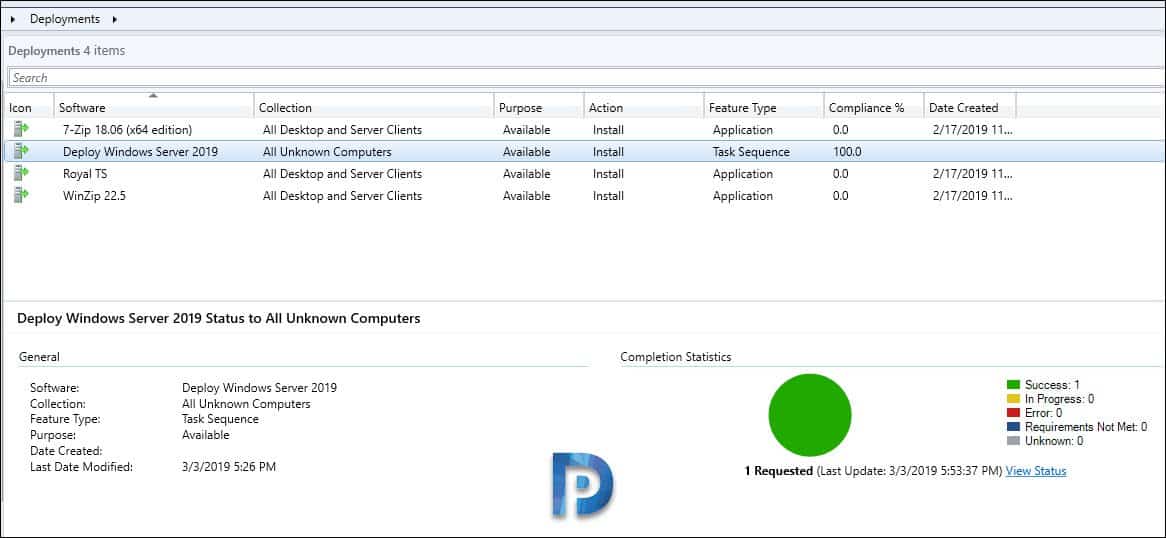
You can also go the deployments under Monitoring and verify the installation status. We see that we had a successful deployment of Windows Server 2019 using SCCM 1810.
Still Need Help?
If you need further assistance on the above article or want to discuss other technical issues, check out some of these options.
Следующий цикл статей будет посвящен установке и настройке System Center Service Manager 2019. В данной публикации мы остановимся на программно-аппаратных требованиях к компонентам системы Service Manager. Далее мы обзорно рассмотрим основные шаги установки и настройки системы. Перед тем, как мы перейдем к обсуждению непосредственно требований предлагаю рассмотреть основные шаги по установке и настройке системы, которые, собственно, и лягут в основу нескольких следующих публикаций.
Основные шаги установки данного программного продукта приведены ниже:
- Подготовка серверов и установка необходимых предварительных компонентов.
- Установка Microsoft SQL Server.
- Установка сервера управления.
- Установка сервера хранения данных.
- Установка портала самообслуживания.
Основные шаги настройки Service Manager следующие:
- Выполнение первоначальных настроек в системе.
- Конфигурирование коннекторов к смежным системам.
- Настройка ролей безопасности.
- Настройка предложений запросов и услуг.
- Настройка уведомлений.
- Настройка рабочих процессов.
Подготовка серверов и установка предварительных требований
В данной публикации мы рассмотрим исключительно программно-аппаратные требования к системе. Сразу отмечу, что для нашей демо-среды требования будут значительно отличаться от рекомендуемых требований, т.к. наше тестовое развертывание будет предназначено исключительно для демонстрации “живой” системы.
С детальным перечнем предварительных требований можно ознакомится на странице с соответствующей документацией продукта. Мы же далее остановимся только на основных моментах.
Предварительные требования к операционным системам серверов с компонентами системы
Установка компонентов системы Service Manager (сервер управления, сервер хранения данных, сервер баз данных и портал самообслуживания) может быть выполнена на следующие серверные операционные системы:
- Windows Server 2016 (Standard или Datacenter), в т.ч. в варианте Server Core.
- Windows Server 2019 (Standard или Datacenter), в т.ч. в варианте Server Core.
Исключение – портал самообслуживания. Для него необходима ОС Windows 2012 R2, либо выше.
Предварительные требования к операционным системам для работы с консолью Service Manager
Для работы с Service Manager используется специальная консоль. Консоль Service Manager может быть установлена на следующие операционные системы:
- Windows Server 2016 (Standard или Datacenter).
- Windows Server 2019 (Standard или Datacenter).
- Windows 10.
Основные требования к серверу баз данных
Помимо требований к операционной системе для сервера баз данных накладываются также требования и к версии Microsoft SQL Server. Service Manager 2019 поддерживает работу со следующими версиями SQL Server:
- SQL Server 2016.
- SQL Server 2017.
- SQL Server 2019 (CU8 и выше).
Программные требования для серверов с компонентами системы Service Manager
Для серверов с компонентами системы Service Manager помимо требований к версии операционной системы также присутствуют требования к дополнительному программному обеспечению. В таблице ниже приведена краткая сводка по необходимому дополнительному ПО для компонентов системы.
| Компонент системы | Необходимое дополнительно ПО |
| Сервер управления | .NET Framework 3.5 SQL Server Native client; Microsoft Report Viewer Redistributable. |
| Сервер хранения данных | SQL Server Native client. |
| Сервер баз данных | SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS); SQL Server Analysis Management Objects. |
| Сервер с порталом самообслуживания | Роль IIS и включенный ASP.NET 4.5; SQL Server Analysis Management Objects. |
| Консоль Service Manager | Microsoft Report Viewer Redistributable; Microsoft Excel (если нужно смотреть аналитику через кубы с рабочего места); .NET Framework 3.5 SQL Server Analysis Management Objects. |
Аппаратные требования
Для серверов и рабочих станций, на которые будут устанавливаться компоненты системы Service Manager рекомендуются аппаратные конфигурации, которые приведены в таблице ниже:
| Компонент системы | Кол-во ядер ЦПУ (2,66 ГГц)(min/max) | Объем ОЗУ, ГБ (min/max) | Доступное место на диске, ГБ (min/max) |
| Сервер управления | 4/4 | 8/8 | 10/10 |
| Сервер хранения данных | 4/4 | 8/16 | 10/10 |
| База данных сервера управления | 8/8 | 8/32 | 80/80 |
| База данных сервера хранения данных | 8/8 | 8/32 | 400/400 |
| Консоль Service Manager | 2/2 | 4/4 | 10/10 |
| Портал самообслуживания | 4/4 | 8/16 | 80/80 |
| Портал самообслуживания (совмещенный с ролью дополнительного сервера управления) | 8/8 | 16/32 | 80/80 |
Если какие-то компоненты устанавливаются совместно, например, база данных сервера управления и база данных сервера хранения данных, то требования суммируются.
Необходимые учетные записи
В процессе развертывания системы Service Manager необходимо будет указать учетные записи, от имени которых будут стартовать службы SCSM. Крайне рекомендуется использовать учетные записи отдельных пользователей Active Directory а не учетную запись локальной системы, т.к. если служба будет работать от УЗ локальной системы, то у неё будет гораздо больше разрешений, чем это необходимо. Для доменной же учеткной записи автоматически будут выданы только необходимые разрешения в процессе установки. В таблице ниже приведен перечень необходимых учетных записей и для чего они нужны.
| Название учетной записи (пример) | Назначение учетной записи | Примечание |
| SCSMService | Учетная запись службы сервера управления | Необходимы права локального администратора на сервере управления и сервере хранения данных |
| SCSMWorkflow | Учетная запись для запуска рабочих процессов, в т.ч. и для уведомлений по электронной почте | Необходимо разрешение “Logon as a Service” на сервере управления |
| SCSMReplication | Учетная запись для служб отчетов и аналитики | |
| SCSMSQLService | Сервисная учетная запись для SQL |
Схема тестового развертывания
Для последующего развертывания нашей тестовой среды мы будем использовать схему решения, которая приведена ниже.

Сводная таблица по планируемым серверам приведена ниже:
| Имя сервера | Назначение | vCPU | ОЗУ, ГБ | Дисковая подсистема | IP-адрес |
| dc01.itproblog.ru | Контроллер домена | 2 | 4 | Диск 1 – 120 ГБ. | 10.10.10.10/24 |
| scsm01.itproblog.ru | Сервер управления | 4 | 8 | Диск 1 – 120 ГБ. | 10.10.10.11/24 |
| scsmdw01.itproblog.ru | Сервер хранения данных | 4 | 8 | Диск 1 – 120 ГБ. | 10.10.10.12/24 |
| scsmssp01.itproblog.ru | Портал самообслуживания | 4 | 4 | Диск 1 – 120 ГБ. | 10.10.10.13/24 |
| sql01.itproblog.ru | Сервер баз данных (Microsoft SQL 2019) | 4 | 10 | Диск 1 – 120 ГБ. Диск 2 – 200 ГБ. |
10.10.10.14/24 |
| wrk.itproblog.ru | Рабочая станция с консолью Service Manager | 4 | 8 | Диск 1 – 120 ГБ. | 10.10.10.15/24 |
Дальнейшие шаги
Перед тем, как мы перейдем к рассмотрению непосредственно установки компонентов системы Service Manager необходимо выполнить ряд подготовительных действий, на основе тех данных, что приведены выше. А именно:
- Установить на все сервера и рабочие станции поддерживаемые операционные системы. В нашей тестовой среде будет использоваться Windows Server 2019 Datacenter и Windows 10 Pro.
- Установить все последние обновления.
- Установить роль Active Directory Domain Services на сервер для контроллера домена и создать новый тестовый лес. Имя нашего тестового леса – itproblog.ru.Я не буду останавливаться на том, как выполнить шаги выше, т.к. в любом поисковике можно найти десяток уже готовых статей и руководств.
В следующей публикация мы уже перейдем непосредственно к развертыванию Service Manager. Самым первым нашим развертыванием будет установка сервера баз данных для Service Manager.
SCSM 2019 Предварительные требования.
SCSM 2019 Установка сервера баз данных.
SCSM 2019 Установка сервера управления.
SCSM 2019 Установка сервера хранения данных.
SCSM 2019 Установка портала самообслуживания.
SCSM 2019 Установка консоли.
Introduction
This multi-part guide will show you how to install the latest baseline version of Configuration Manager from Microsoft. The latest available baseline version is System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) version 1902 as of April the 10th 2019. I blogged how to upgrade to 1902 here. This guide is aimed a new installations of SCCM. Baseline media is used to install new ConfigMgr sites or to upgrade from supported versions, for more information about baseline media please see my blog post here.
Note: The SCCM 1902 Current Branch media is not yet available on MSDN or VLSC. When the new baseline media is released I’ll update this note.
This series is broken down into the following parts:-
- Part 1 – Get the lab ready, configure ADDS
- Part 2 – Join CM01 to Domain, add users, create the Systems Management container, delegate permission (This part)
- Part 3 – Role and Feature installation, installation of WDS and ADK
- Part 4 – Configure and install SQL Server 2017
- Part 5 – Configure and install SCCM 1902 Current Branch
- Part 6 – Post configuration
You can use this multi-part guide to get a hierarchy up and running on Windows Server 2019 using SQL Server 2017. The concept behind this is to guide you through all the steps necessary to get a working Configuration Manager Primary site installed (for lab use) using manual methods or automated using PowerShell. This gives you the power to automate the bits that you want to automate, while allowing you to manually do other tasks when needed. You decide which path to take. PowerShell knowledge is desired and dare I say required if you are in any way serious about Configuration Manager.
I will show you how to do most steps via two methods shown below, it’s up to you to choose which method suits you best but I highly recommend automating everything that you can, using PowerShell.
- Method #1 – Do it manually
- Method #2 – Automate it with PowerShell
Downloads
The scripts used in this part of the guide are available for download here. Unzip to C:\Scripts. The scripts are placed in the corresponding folder (Part 1, Part 2 etc) and sorted into which server you should run the script on (DC01 or CM01).
Scripts.zip 7.83 kB · 0 downloads
Step 1. Join CM01 to the domain
Note: Perform the following on the ConfigMgr server (CM01) as Local Administrator
- Method #1 – Do it manually
To join the domain manually, login to CM01. Start Windows File Explorer. Right-click on This-PC and choose Properties. The System screen will appear. Click on Change settings to the right of Computer name. For the option To rename this computer or change its domain or workgroup, click Change, click Change and for Member of select Domain, enter the Domain details used in Part 1 of this series and then click OK.
and enter domain join credentials as appropriate when prompted. Once done you’ll get notification that you’ve joined the domain.
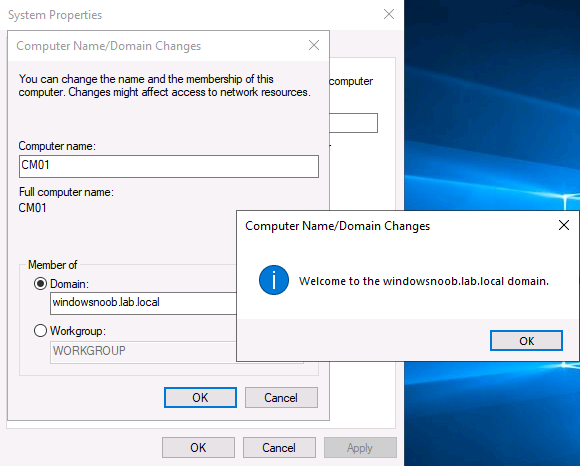
Click OK and click Restart Now when prompted.
- Method #2 – Automate it with PowerShell
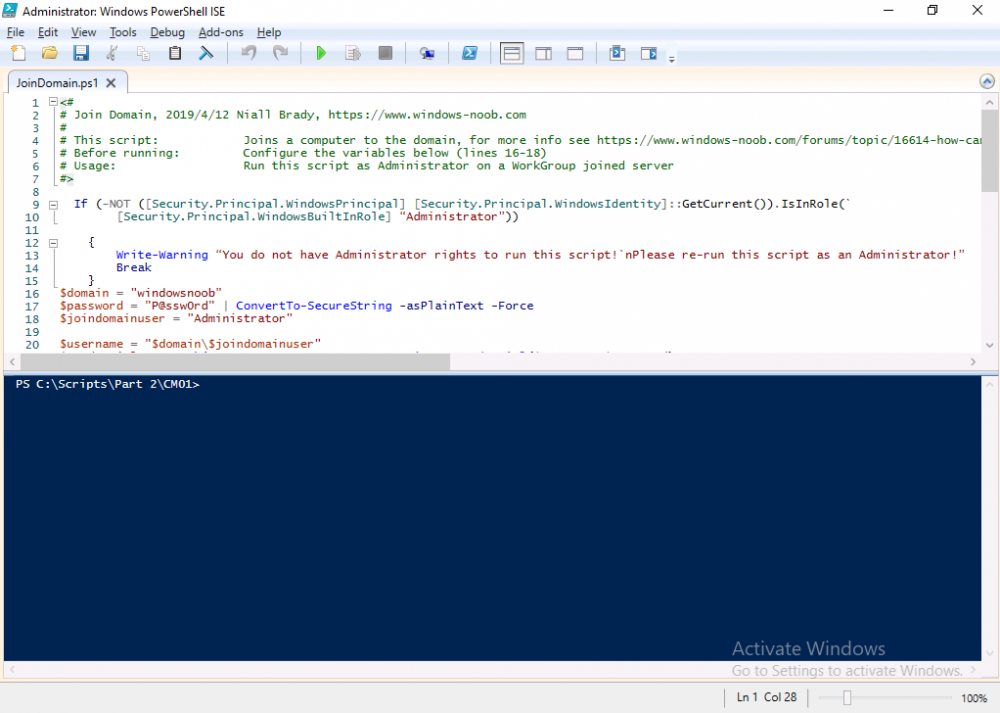
To join the domain automatically, use the joindomain.ps1 PowerShell script.
1. Copy the script to C:\Scripts on CM01
2. Edit the variables (lines 16-18) as desired before running.
3. Start Windows PowerShell ISE as Administrator and run the script by clicking on the green triangle.
Step 2. Add Users to Active Directory
- Method #1 – Do it manually
To create users manually, click on Start and choose Windows Administrative Tools and then select Active Directory Users and Computers. In Active Directory Users and Computers, add new users by expanding <domain name>, select Users and right click, choose New then select User.
You can continue reading the rest of this guide over @ windows-noob.com here.
This entry was posted in 1902, baseline version. Bookmark the permalink.
