Рассмотрим установку сервера ejabberd на компьютеры под управлением ОС Windows в стандартной конфигурации для использования в локальной сети с открытым доступом из Интернет и с использованием службы DynDNS.
Предполагается, что у Вас уже установлена операционная система, настроен доступ в Интернет, а доменное имя на DynDNS (допустим, это будет myjabber.ath.cx) указывает на внешний адрес Вашего компьютера (либо тот, который доступен из Вашей локальной сети, если Вы настраиваете сервер без возможности подключения к нему из Интернета).
Первым делом скачайте программу-установщик на свой компьютер, сделать это можно на официальном сайте Process One на странице загрузки. После скачивания запустите файл и приступайте к установке.
Установка сервера[править]
После запуска установщика первым делом появится диалог выбора языка. Выберите русский и нажмите «OK«. Запустится мастер установки, который поможет выполнить Вам все необходимые шаги. Во время работы мастера Вам придется ответить на следующие вопросы:
- Принятие лицензионного соглашения. Ejabberd распространяется на условиях лицензии GPL.
- Каталог для установки программы. Здесь будут находиться основные исполняемые файлы сервера и файлы конфигурации, а также база данных пользовательских аккаунтов под названием Mnesia.
- Доменное имя сервера. Как уже говорили выше, пусть это будет myjabber.ath.cx.
- Логин администратора. Вместе с доменным именем он составит Jabber ID администратора сервера.
- Пароль администратора.
- Вариант конфигурации сервера. Кластеры используются только на высоконагруженных серверах, поэтому отвечаем «Нет«.
После ответа на эти вопросы начнется процесс установки, во время которого будут выполнены основные настройки сервера. После установки сервер займет на диске около 15 Мб. Для окончания установки осталось выполнить лишь несколько шагов.
-
Выбираем язык
-
Запуск мастера установки и настройки
-
Знакомимся с лицензионным соглашением
-
Выбираем каталог для установки
-
Вводим домен сервера
-
Вводим логин администратора
-
Вводим пароль администратора
-
Выбираем тип конфигурации сервера
-
Установка сервера
-
Установка завершена
Запуск сервера[править]
Сервер добавляет себя в список сервисов системы, но не запускается автоматически. Для запуска в ручном режиме сделайте двойной щелчок по ярлыку «Запустить ejabberd» на рабочем столе, а для запуска сервера при старте системы измените в «Панель управления -> Администрирование -> Сервисы» тип запуска сервиса ejabberd с «Ручной» на «Автоматический«.
Если при попытке запуска сервера возникает следующее сообщение об ошибке:
Starting ejabberd... ./ejabberdctl: erl.exe: can't execute: (14001) Error 14001 There is a problem starting Erlang. If the error you see is 14001, you need to install: Microsoft Visual C++ 2005 SP1 Redistributable Package You can download that installer from www.microsoft.com You can also check the ejabberd Administrator Guide
то потребуется дополнительно установить Microsoft Visual C++ 2005 SP1, скачать его можно с официального сайта Microsoft.
После успешного запуска сервера откроется информационная веб-страница в браузере.
Панель администратора и клиент, подключенный к серверу
С этого момента к Вашему серверу можно подключаться с других компьютеров, пользователи могут заводить учетные записи, общаться между собой и устраивать конференции.
Используя свой администраторский аккаунт, Вы можете выполнять некоторые административные функции прямо из своего Jabber-клиента, например, можно создавать новые учетные записи и просматривать список подключенных пользователей. Эти функции доступны через браузер сервисов. Также становятся доступны стандартные функции администратора — рассылка массовых сообщений для всех пользователей и установка так называемого «Сообщения дня».
Кроме того, Вы можете получить доступ к веб-интерфейсу, через который можно управлять настройками сервера и смотреть статистику.
Авторизация в панели администратора
Этот интерфейс доступен на Вашем компьютере по адресу http://localhost:5280/admin. Для авторизации введите в поле «Пользователь» полный Jabber ID администратора, а в поле «Пароль» — пароль, введенный Вами при установке сервера.
Ссылки[править]
- Настройка ведения логов в конференции
Время на прочтение4 мин
Количество просмотров9.9K
Prosody — это легковесный кроссплатформенный XMPP-сервер, написанный на языке программирования Lua. На хабре есть несколько статей по настройке prosody в стандартном варианте — в linux. Настройка в windows содержит несколько подводных камней, о которых я постараюсь рассказать.

Сперва расскажу о плюсах и минусах данного решения. Плюсы: экстремальная легковесность.
На скриншоте — типичное потребление ресурсов prosody+служебной утилиты srvany, которую я использовал для создания службы. Ещё к плюсам можно отнести модульность и поддержку многих XEP.
И минусы: отсутствие GUI (для кого-то это не минус), для настройки под windows нужно поработать напильником. Настройка под windows сложнее аналогичной настройки под linux.
Первый подводный камень ожидает нас уже на этапе скачивания дистрибутива. Для windows можно скачать, как инсталлятор, так и просто архив с prosody. Дело в том, что все до единого bat-файлы содержат строчку
if exist Uninstall.exe set datastore=%APPDATA%\Prosody
Это значит, что если найден деинсталлятор, то все данные сервера будут храниться в %APPDATA% запустившего сервер пользователя. Это не то, что нам нужно, поэтому, для того, чтобы хранить данные там же, где хранится всё остальное, нужно либо использовать дистрибутив с архивом вместо инсталлятора, либо переименовать после инсталляции файл uninstall.exe, например, в uninstall.bkp.exe. Скачиваем и устанавливаем необходимый дистрибутив.
Второй подводный камень — prosody под windows не имеет службы. Будем считать, что вас не устраивает каждый раз для запуска prosody логиниться под пользователя и запускать bat-файл prosody.bat. Для создания службы prosody я предлагаю использовать утилиту srvany, входящую в Windows Server 2003 Resource Kit Tools. Даже если ОС на вашем сервере будет отличаться от server 2003, srvany должна нам помочь.
- Устанавливаем resource kit, соглашаемся с предупреждениями о несовместимости с ОС, если они будут.
- Открываем командную строку cmd от имени администратора, выполняем следующее (вставьте свой путь к srvany):
instsrv.exe Prosody "C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Resource Kits\Tools\srvany.exe" - Открывaем regedit, идём в «HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Prosody«
- Создаём раздел «Parameters«.
- В разделе «Parameters» создаём строковый параметр «Application» со значением «C:\Program Files (x86)\Prosody\prosody.bat» (подставьте свой путь).
Служба создана, можно выставить ей тип запуска «автоматически«. Внимание! Остановить созданную таким образом службу нельзя, для остановки завершите процессы srvany и lua. До тех пор, пока не сделаны все настройки, службу запускать не надо.
Настроим prosody. Для этого запустим bat-файл editconfig.bat. Все опции документированы, я не буду описывать всю настройку досконально. Документация по модулям может быть найдена на официальном сайте.
Рекомендуется использовать tls для шифрования сессий. Есть несколько вариантов настройки tls:
- Можно получить бесплатный сертификат на год у StartCom. Если вы планируете открыть доступ к jabber-серверу из интернета.
- Можно использовать самоподписанный сертификат. При первоначальном подключении к такому серверу клиенты, обычно, выдают множественные предупреждения.
Генерация самоподписанного сертификата
Использовать prosodyctl для генерации сертификата в windows мы не можем, т.к. эта утилита не портирована. Необходимо
- скачать openssl для windows
- Указать конфигурационный файл openssl.cnf из поставки prosody (лежит в папке cert). Для этого необходимо открыть командную строку и выполнить следующее (указав свой путь):
set OPENSSL_CONF=C:\Program Files (x86)\Prosody\certs\openssl.cnf - Перейти в директорию с распаковынным openssl и сгенерировать сертификаты:
openssl req -new -x509 -days 1825 -nodes -out "prosody.crt" -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout "prosody.key"
- Можно просто отключить модуль tls (хоть он и помечен, как generally required) или не указывать путь к сертификатам в конфигурационном файле. Это подойдёт для небольшого корпоративного офиса.
Если вы настраиваете корпоративный сервер, то вам понадобится включить модуль groups для общего ростера.
Необходимо раскомментировать соответствующую строчку в конфиге для того, чтобы загружать модуль groups при старте сервера, подготовить текстовый файл с описанием групп и указать путь к файлу:
modules_enabled = {
-- Other modules
"groups"; -- Enable mod_groups
}
groups_file = "groups.txt"
Создадим groups.txt в поддиректории data. Если вы планируете использовать кириллицу, то правьте файл с помощью notepad++ или любого другого продвинутого текстового редактора в режиме UTF-8. Следующий пример файла взят из официальной документации:
[Support Team]
support@example.com
john.doe@example.com
[Development Team]
hardworkingdeveloper@example.net=Joe Coder
other.dev@example.com=Mel
Здесь есть один нюанс. Пользователи каждой группы видят только тех, кто входит в эту же группу. О других случаях официальная документация молчит. Взглянув на исходный код модуля видно, что если поставить + перед названием группы, то она становится общей — эту группу видят все.
[+Support Team]
support@example.com
john.doe@example.com
[+Development Team]
hardworkingdeveloper@example.net=Joe Coder
other.dev@example.com=Mel
Добавлять в группу можно даже несуществующих на данный момент пользователей.
Во время конфигурации можно запускать prosody из стартового скрипта prosody.bat для проверки результата. Запускайте скрипт от администратора во избежание проблем. После окончательной настройки запустите созданную ранее службу prosody. Управлять prosody на ходу можно, используя модули admin_adhoc и admin_telnet.
Под катом чисто техническая статья про настройку Jabber-сервера под Linux и клиентов к нему под Windows с одновременным прикручиванием формирования контакт-листа из AD LDAP с SSO-авторизацией посредством Kerberos.
Сперва небольшой обзор имеющихся доступных решений.
Как ни странно, из актуальных Jabber-серверов SSO / GSSAPI поддерживают все три: eJabberd, Openfire, Prosody. Первый я не осилил ввиду зубодробительности erLang-а. Точнее, в дефолтной конфигурации его запустить как раз плюнуть (спасибо дистростроителям). Но вот если надо прикрутить что-то эх-такое, чего изначально не было предусмотрено в конструкции, возникает дикая попа-боль. Второй весьма user-friendly, большинство фич работают из коробки. Но это Java со всеми вытекающими. В частности, даже банальное подсовывание SSL-сертификата сразу превращается в увлекательнейший траходром. Третья лишена большинства недостатков первых двух, но она отвратительно (точнее, почти вообще никак) не документирована и не масштабируется. В том плане, что до 100…150 пользователей работает ОК, потом начинает тупить, тормозить и валиться. Конкретно мне больше и не надо, поэтому я взял в качестве сервера Prosody. О ней и пойдет дальнейший разговор.
Касаемо клиентов. Всего хоть как-то GSSAPI под виндой сейчас поддежривают: Miranda, Psi, Spark, Pidgin.
Miranda хороша-красива, когда «обвешана». На «голую» (без плагинов) без слёз не взглянешь. Если же надо обновить версию, то «обвес» придётся формировать заново. Она не enterprise-friendly. Она глючновата в плане интерфейса. Может, например, почему-то не показать поступившее входящее сообщение. Может обвалиться после очередного обновления винды. Не проверяет SSL-сертификат сервера на валидность. Одним словом, мы попробовали, попользовались, нам не понравилось.
Что касается Psi, то для реализации GSSAPI там надо самостоятельно собирать Qt-шную библиотеку под названием qca-wingss. Готового бинарника я ожидаемо не нашёл, а скопилировать самостоятельно ниасилил.
Spark — это опять же Java, со всеми вытекающими. Кто желает, может пользовать. Меня от неё тошнит.
Остался Pidgin. Но и тут всё не слава богу. Во-первых, последняя виндовая версия, которая ещё умеет GSSAPI — это 2.10.11. В более свежих поддержку GSSAPI/SSPI выпилили (это касается только виндовых сборок; под линуксом всё нормально). Во-вторых, на клиентские машины нужно дополнительно ставить MIT Kerberos for Windows. Берут здесь. В более-менее «стандартной» конфигурации каких-то дополнительных настроек не требуется, в не совсем типичных случаях его тоже потребуется «подкрутить».
Окей, с выбором софта более-менее разобрались. Теперь некоторые неочевидные нюансы. Полностью процесс «от А до Я» расписывать не буду. Потому что в энторнетах есть некоторое количество хаутушек, да и админ, взявшийся за подобную задачу, наверняка уже обладает некоторыми навыками и компетенцией. Расскажу о том, во что «влетел» конкретно я.
Что касается сервера. Документация к нему не отличается точностью и полнотой. Там есть определённая путаница. Следует учитывать, что до версии 0.8 данный механизм был реализован в модуле «mod_saslauth» через прокладку в виде saslauthd. После версии 0.8 функционал был перенесён в отдельный модуль «mod_auth_cyrus», а saslauthd больше не нужен. То есть пакет «sasl2-bin» можно и не ставить, а руководствоваться нужно вот этой статьёй.
Далее. Как всегда, требуется сформировать в системе правильный конфиг «/etc/krb5.conf» и сгенерировать keytab. И самое главное, prosody должна иметь доступ на чтение и к тому, и к другому. Если вовремя не вспомнить, что в Debian-е по умолчанию она запускается из-под отдельного непривилегированного пользователя, то могут возникнуть весьма трудно диагностируемые проблемы и странные совершенно неинформативные фатальные ошибки в логах.
Кроме того, если в том же OpenFire функционал импорта пользователей из AD реализован «из коробки», то в случае c Prosody его придётся колхозить самостоятельно, ручками. Это не так уж и сложно, но это нужно сделать. Об этом я напишу во второй части.
Теперь что касается клиента.
Pidgin-а ставим как обычно, но не свежее версии 2.10.11. С MIT Kerberos никаких премудростей нет, обычный wizard типа «xyяк, xyяк и в продакшн» «next, next и готово». На последнем шаге он спросит, надо ли автоматически стартовать при логине пользователя и надо ли сразу получать Kerberos-тикеты. Ответ: нет, не надо. Впрочем, на самом деле пофиг. Будет работать и так, и так.
В самом Pidgin-е в настройках аккаунта указываем только логин, имя домена и ресурс. Поле «пароль» оставляем пустым. Примерно так.
Если по условию задачи Kerber-осовский Realm совпадает с Jabber-овым доменом, то больше никаких действий предпринимать не нужно. Всё заведётся, пользователь успешно залогинится. В противном случае придётся совершить ещё ряд небольших шаманств.
Во-первых, сделать текстовый файл с названием «krb5.ini» по аналогии с линуксовым «krb5.conf» с указанием KDC и сопоставлением сущностей «domain» и «realm». Чтобы оно понимало, из какого Realm-а запрашивать ключи для того или иного домена и где вообще искать KDC (Key Distribution Center). Упомянутый «krb5.ini» следует положить либо в «c:\windows», либо в профиль пользователя (по желанию админа). Во вторых, после неудачной попытки залогиниться нужно назначить «Default Ticket» прямо в интерфейсе MIT Kerberos (на скриншоте обвёл синим прямоугольником). Это требуется сделать ровно один раз. Возможно, данную настройку можно выполнить и через реестр. Не знаю, настолько глубоко не ковырял.
Как-то так и настраивается SSO-аутентификация. Про формирование ростера (списка контактов и групп) читайте в следующем псто.
|
Установка и настройка JABBER сервера OpenFire
Добавлять комментарии могут только зарегистрированные пользователи. |
|
Introduction
This document describes the necessary steps required for deployment of Cisco Jabber for Windows basic features.
Prerequisites
Cisco recommends you have a basic understanding of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM) administration web page as well as experience with basic phone configurations.
Software Requirements
This guide assumes these software versions are in use:
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM) version 10.x or higher
- Cisco Unified IM and Presence (IM&P) version 10.x or higher
- Cisco Unity Connection (CUXN) version 10.x or higher
- Jabber for Windows 11.8 or higher
- Microsoft Windows 10 (32 bit and 64 bit)
- Microsoft Windows 8 (32 bit and 64 bit)
- Microsoft Windows 7 Service Pack 1 or later (32 bit and 64 bit)
Hardware Requirements
The hardware specifications are the suggested minimum requirements for Cisco Jabber for Windows on a Microsoft operating system:
- CPU
- Mobile AMD Sempron Processor 3600+ 2 GHz
- Intel Core2 CPU T7400 at 2. 16 GHz
- Intel Atom
- RAM
- 2 GB (128 MB Free)
- Free Disk Space
- 256 MB
Background Information
This is a quick start guide and does not cover any of the advanced features supported by Cisco Jabber for Windows.
Phone Services
Jabber Softphone
Jabber for Windows provides an option to supply phone services through a Cisco Unifed Client Services Framework devices which is often referred to as a CSF or Softphone.
To configure a CSF device, log into the CUCM Administration web page and navigate to Device > Phone.
From Find and List Phones menu select Add New.
Once on the Add a New Phone menu, search the phone type drop down for the Cisco Unifed Client Services Framework device type. Once selected, click Next.
The table (Table 1.0) contains all the fields that must be configured to set up a Cisco Unified Client Services Framework (CSF) device in CUCM. The majority of required fields have default configurations which you do not need to manual configured unless otherwise required for your deployment. You must manually configure all the fields where the Configured by Default column in the table is set to NO.
Tip: Cisco recommends that all Client Services Framework devices be configured with a device name prefix of CSF. For example, you provision a user named Holly Day with a CSF device. Her CUCM end user user ID is hday so her CSF device name would be CSFHDAY.
Table 1.0
| Required Fields | Default Parameter | Configured by Default | Description |
| Device Name | Must be manually added, and device name must begin with CSF. | NO | Enter a name to identify software-based telephones. |
| Device Pool | Must select one of the available device pools. | NO | Choose the device pool to which you want this phone assigned. The device pool defines sets of common characteristics for devices, such as region, date/time group, and softkey template. |
| Phone Button Template | Standard Client Service Framework | NO | Choose the appropriate phone button template. The phone button template determines the configuration of buttons on a phone and identifies which feature (line, speed dial, and so on) is used for each button. |
| Common Phone Profile | Standard Common Phone Profile | YES | Choose a common phone profile from the list of available common phone profiles. |
| Location | Hub_None | YES | Use locations to implement call admission control (CAC) in a centralized call-processing system. The location specifies the total bandwidth that is available for calls to and from this location. A location of Hub_None means that the locations feature does not keep track of the bandwidth that this Cisco Unified IP Phone consumes. A location of Phantom specifies a location that enables successful CAC across intercluster trunks that use H.323 protocol or SIP. |
| Built In Bridge | Default | YES | Enable or disable the built-in conference bridge for the barge feature with the Built In Bridge drop-down list box (choose On, Off, or Default). |
| Device Mobility Mode | Default | YES | Turn the device mobility feature on or off for this device or choose Default to use the default device mobility mode. Default uses the value for the Device Mobility Mode service parameter for the device. |
| Owner User ID | Set the user ID | NO | From the drop-down list box, choose the user ID of the assigned phone user. The user ID gets recorded in the call detail record (CDR) for all calls made from this device. Assigning a user ID to the device also moves the device from Unassigned Devices to Users in the License Usage Report. |
| Use Trusted Relay Point | Default | YES | From the drop-down list box, enable or disable whether Cisco Unified CM inserts a trusted relay point (TRP) device with this media endpoint. A Trusted Relay Point (TRP) device designates an MTP or transcoder device that is labeled as Trusted Relay Point. |
| Always Use Primary Line | Default | YES | From the drop-down list box select (Off, On or Default). Default — Cisco Unified Communications Manager uses the configuration from the Always Use Prime Line service parameter, which supports the Cisco CallManager service. |
| Always Use Prime Line for Voice Message | Default | YES | From the drop-down list box, select (Off, On or Default). Default — Cisco Unified CM uses the configuration from the Always Use Prime Line for Voice Message service parameter, which supports the Cisco CallManager service. |
| Packet Capture Mode | None | YES | This exists to troubleshoot encryption only; packet capturing can cause high CPU usage or call-processing interruptions. |
| BLF Presence Group | Standard Presence Group | YES |
Choose a Presence group for the end user. The selected group specifies the devices, end users, and application users that can monitor this directory number. The default value for Presence Group specifies Standard Presence group, configured with installation. |
| Device Security Profle | Must be manually selected | NO | You must apply a security profile to all phones that are configured in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration. Installing Cisco Unified Communications Manager provides a set of predefined, nonsecure, security profiles for auto-registration. To enable security features for a phone, you must configure a new security profile for the device type and protocol and apply it to the phone. If the phone does not support security, choose a nonsecure profile. |
| SIP Profile | Must be manually selected | NO | Choose the default SIP profile or a specific profile that was previously created. SIP profiles provide specific SIP information for the phone such as registration and keepalive timers, media ports, and do not disturb control. |
| Certificate Operation | No Pending Operation | YES | This field is related to CAPF enrollment. |
| DND Option | Ringer Off | YES | When you enable DND on the phone, this parameter allows you to specify how the DND features handle incoming calls. |
| Video Calling | Enabled | YES | Turns video capabilities on and off. |
| Automatically Start in Phone Control | Disabled | YES | If enabled, start the client in desktop phone control mode. |
| Automatically Control Tethered Desk Phone | Disabled | YES | If enabled, the client automatically controls the tethered desktop phone. |
| Extend and Connect Capability | Enabled | YES | Indicates if Extend and Connect capabilities are enabled for the client. This allows the client to monitor and control calls on 3rd party PBX, PSTN, and other remote phones. |
| Display Contact Photos | Enabled | YES | Indicates if contact photo retrieval and display is enabled or disabled for the client. |
| Number Lookups on Directory | Enabled | YES | Indicates if phone number lookups with the Corporate Directory are enabled or disabled for the client. |
| Analytics Collection | Disabled | YES | Indicates if analytics collection is enabled or disabled for the client. |
Once you have configured all the required fields for the CSF configuration, save the configuration with the Save button.
Now that you have created a CSF, you need to add a directory number to the device. This can be done by selecting the Add a new DN option located at the top left of the CSF configuration.
Note: This document does not cover the complete line configuration for the CSF device. Line configuration is a standard configuration that must be performed for all phones and is not a configuration that is specific to CSF devices.
Tip: Once you have a directory, number your CSF device make sure to associate the CUCM end user to the directory number. Scroll to the bottom of the directory number configuration to Associate End Users. This configuration is required if you plan to use Jabber for phone presence.
Jabber Deskphone
Jabber for Windows also has the capability to perform Cisco Computer Telephony Integration (CTI) with Cisco deskphones. This allows Jabber for Windows users to use their Cisco deskphone as their Jabber telephony device when perform call actions from the Jabber user interface.
Deskphone Configuration
To setup Jabber for Windows CTI integration, complete these steps:
Access the CUCM Administration web page and navigate to Device > Phone.
From the Find and List Phones menu, search for and select the Jabber users deskphone.
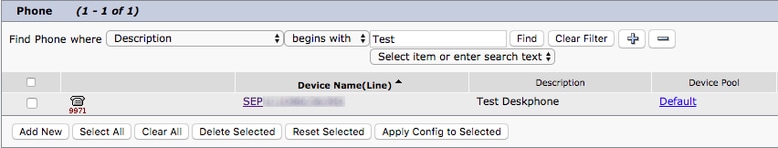
When presented with the Phone Configuration menu, verify the two listed:
- Verify that the Allow Control of Device from CTI check box is checked.
- Confirm the device Owner User ID is set to the Jabber for Windows user CUCM user ID.
CTI UC Services Setup
Next, you setup the CTI UC services that is to be used by the Jabber client to connect to the CUCM CTI Manager service. Navigate to User Management > User Settings > UC Service.
Once on the Find and List UC Services page, select Add New.
When presented with the UC Service Configuration page, select CTI from the UC Service Type drop down, then select Next.
Then, you are presented with the UC Service Configuration page. Here, configure a Name for the CTI UC Service as well as provide the IP, Hostname, or Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the CUCM server that has the CTI service active.
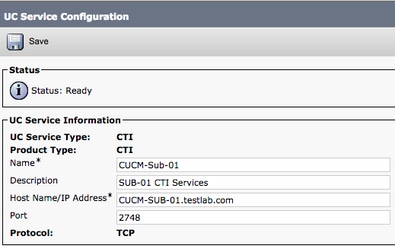
Note: Up to three CTI UC Services can be assigned to a UC Service Profile.
Now that we have defined the CTI UC Service(s), we assign them to the Service Profile. Navigate to User Management > User Settings > Service Profile.
From the Find and LIst Service Profiles menu, search for and select the service profile used by your Jabber for Windows users or create a new service profile with Add New.
Once on the Service Profile Configuration page, scroll down to the CTI Profile section and assign the CTI UC Services to the service profile, then select Save.
Note: This document does not cover the configuration of a new new Cisco deskphone as this is a basic CUCM administration task.
To view the list of (CTI) supported devices, navigate to CUCM Cisco Unified Reporting and select the Unified CM Phone Feature List Report. Next select CTI controlled from the Feature drop-down list.
Configuration of the Voicemail
Jabber for Windows is able to retrieve and playback voicemail messages that have been stored on Cisco Unity Connection. To setup voicemail for Jabber for Windows, complete these steps:
Unity Connection Configuration
Access the Cisco Unity Connection web administration web page and navigate to Users > Users.
When presented with Search Users page, search for and select your Jabber for Windows users mailbox.
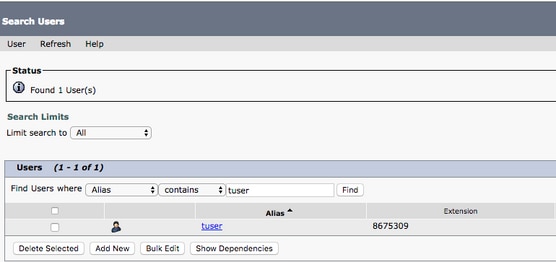
Once presented with the Edit User Basics page of the user Mailbox, notate the Calls of Service that is configured.
Via the left hand navigation pane, navigate to Class of Service > Class of Service.
When presented with the Search Class of Service page, search for and select the class of service you previously notated.
Once on the Edit Class of Service page, verify:
- The check box is checked for the Allow Users to Use the Web Inbox and RSS Feeds feature.
- The Allow Users to Use Unified Client to Access Voicemail feature is enabled by the box near the feature name.
Once the Class of Service configuration has been verified, navigate to System Settings > Advanced > API Settings in the left navigation pane. Enable all three presented on the API Configuration page.
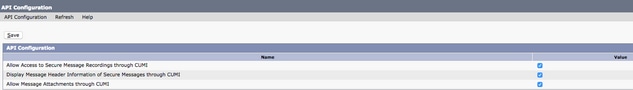
CUCM Configuration
Now that Unity Connection is setup, you move to the CUCM configuration for Jabber for Windows voicemail. Navigate to User Management > User Settings > UC Service.
Once on the Find and List UC Services page, select Add New.
When presented with the UC Service Configuration page, select Voicemail from the UC Service Type drop down, then select Next.
Once presented with the UC Service Configuration page, select Unity Connection from the Product Type dropdown. You need to configure a Name for the VoicemailUCService as well as provide theIP, Hostname or Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the Unity Connectionserver that acts as the REST and Jettyservices.
Note: Up to three VoicemailUCServices can be assigned to aUCService Profile.
Now that the Voicemail UC Service(s) are defined, you assign them to the Service Profile. Navigate to User Management > User Settings > Service Profile.
From the Find and LIst Service Profiles menu, search for and select the service profile used by your Jabber for Windows users or create a new service profile with Add New.
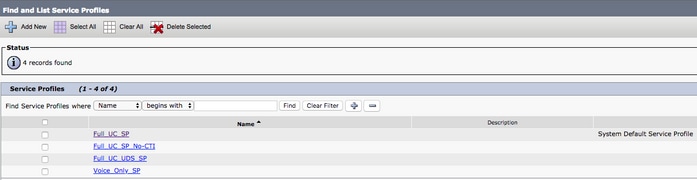
Once on the Service Profile Configuration page, scroll down to theVoicemail Profile section and assign the Voicemail UC Service(s) to the service profile, then select Save.
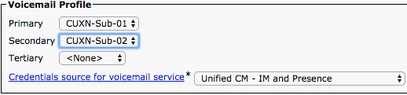
Note: The Jabber for Windows setup assumes that Unity Connection is LDAP authentication. In cases where mailboxes are not LDAP integrated, please refer to the Cisco On-Premises Deployment Guide.
Configuration of the Directory
Jabber for Windows is dependent on directory services for resolution of corporate contacts. Jabber is able to perform directory resolution through Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) or CUCM User Data Services (UDS). Please refer to the next sections for information on configuration of LDAP or UDS directory services for Jabber for Windows.
LDAP Directory Services
Jabber for Windows supports three well known LDAP directory services:
- Active Directory Domain Services
- OpenLDAP
- Active Directory Lightweight Directory Service (AD LDS)
This guide provide the steps to configure Jabber for Windows 11.8 or higher to integrate with Active Directory Domain Services, as this is the most common integration.
Access the CUCM Administration web page and navigate to User Management > User Settings > UC Service.
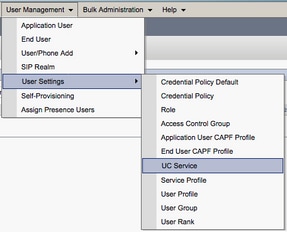
Once on the Find and List UC Services page, select Add New.
When presented with the UC Service Configuration page, select the Directory from the UC Service Type drop down and select Next.
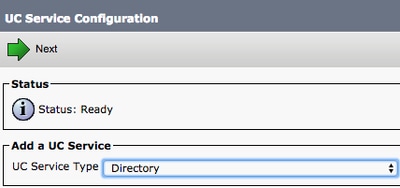
On the UC Service Configuration page, select Enhanced Directory from the Product Type drop down. You also need to configure a Name for the Directory UCService as well as provide theIP, Hostname or Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the directory server.
By default, the Connection Type is set to Global Catalog which assumes that a Microsoft Domain Controller is used as the the directory source. If a Global Catalog server is in use, the Port number in the configuration must be set to 3268. Cisco does recommend the use of a Global Catalog server as a directory resource as it provides more efficient resolutions of queries.
Tip: In cases where you do not have a domain controller for Microsoft Active Directory Domain Services, the Directory UC Service must have the Port set to 389 to Connection Type must be set to Ldap.
Note: Up to three DirectoryUCServices can be assigned to aUCService Profile.
Now that the Directory UC Service(s) are defined, you assign them to the Service Profile. Navigate to User Management > User Settings > Service Profile.
From the Find and LIst Service Profiles menu, search for and select the service profile used by your Jabber for Windows users or create a new service profile with Add New.
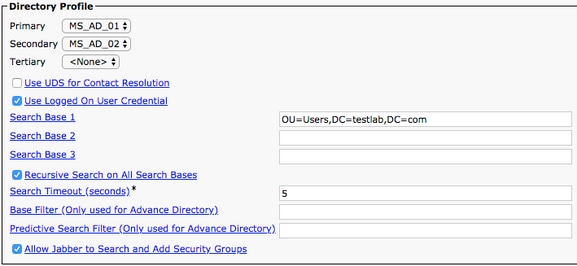
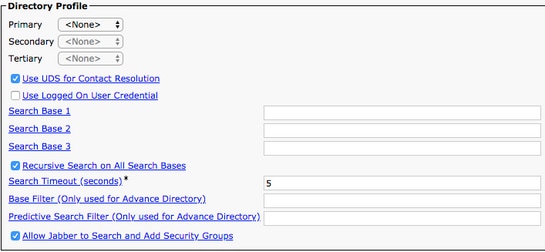
Once on the Service Profile Configuration page, scroll down to theDirectory Profile section and assign theDirectory UC Service(s) to the service profile. You also need to define the Active Directory search base, this can be the organization unit or directory where your corporate users exist.
While in the Directory Profile section, you also have to configure a directory authentication method. Check the check box near the Use Logged On User Credential to prevent anonymous queries and force Jabber to authenticate with the credentials that were entered during Jabber log in. If the Use Logged On User Credential is left unchecked, Jabber can attempt to perform anonymous access to the directory server. Anonymous directory access is not recommended by Cisco.
Once you are done with the Directory Profile, select Save.
Note: If you are in CUCM 10.X — 11.5.X, the Directory Profile section of the Service Profile also include username and password fields that allow for a distinguished name to be used as the user ID that is authorized to run queries on the LDAP server. In CUCM 12.X, if you want to use a single user ID for authentication for directory services, you need to use the ConnectionUsername and ConnectionPassword parameters in the jabber-config.xml.
Caution: Cisco Jabber queries contact source with various attributes. Not all of these attributes are indexed by default. To ensure efficient searches, the attributes used by Cisco Jabber must be indexed on the directory server. For more information, please refer to the LDAP Prerequisites section of the Jabber Planning Guide.
UDS Directory Services
CUCM User Data Services (UDS) provides a contact source API that can be used by Jabber over Cisco Expressway mobile and remote access for the contact resolution, and it is an optional contact service for clients on the corporate network. The UDS contact source uses the Unified CM end user table information to provide a directory resolution.
Access the CUCM Administration web page and navigate to User Management > User Settings > Service Profile.
From the Find and LIst Service Profiles menu, search for and select the service profile used by your Jabber for Windows users or create a new service profile with Add New.
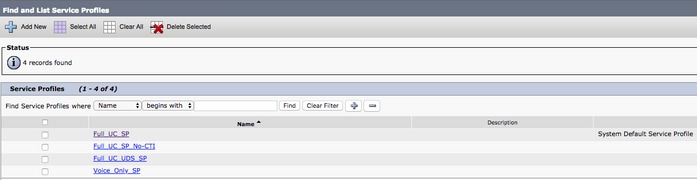
Once on the Service Profile Configuration page, scroll down to theDirectoryProfile section and check the check box labeled Use UDS for Contact Resolution, then select Save.
Once UDS Is enabled on the service profile, Jabber for Windows automatically discovers the CUCM UDS servers during the Jabber log in process.
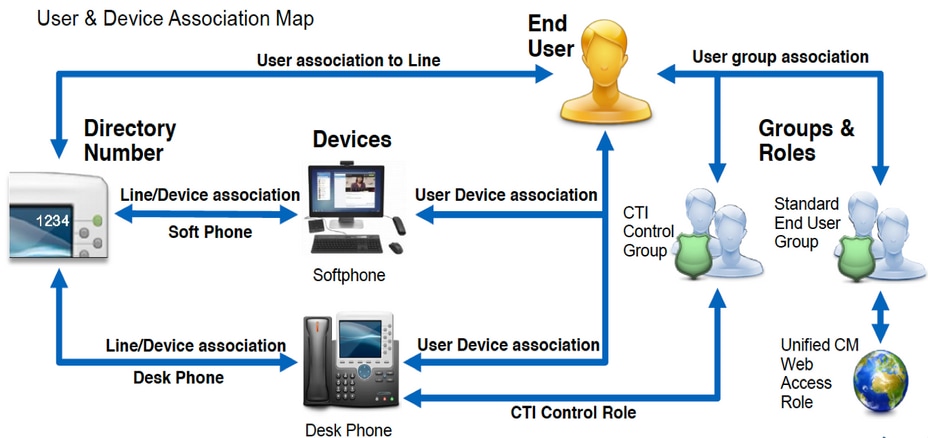
Configuration of the CUCM End Users
The CUCM end user configuration is a crucial step for Jabber for Windows as many of Jabbers features are dependent on this configuration. The image depicts all the Jabber configurations that are dependent on the CUCM end user configuration.
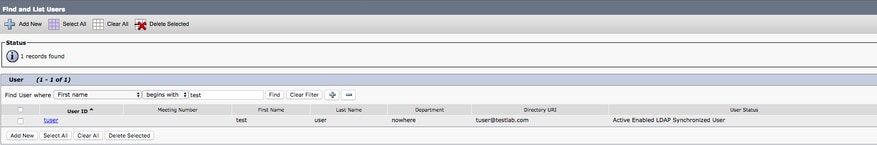
To configure the Jabber for Windows CUCM end user, access the CUCM Administration web page and navigate to User Management > End User.
From the Find and LIst Users menu, search for and select the CUCM end user you wish to configure for Jabber for Windows.
Once on the End User Configuration web page, scroll down to the Service Settings section. Here you can assign the end user the services you want them to use. To enable a user to be able to log in to Jabber for Windows, you must enable the Home Cluster service by the check box next to the service name.
If your end target is to use Jabber for Windows for instant messaging, you need to enable their end user for the service by the check box next to the field labeled Enable User for Unified IM and Presence.
Next, you want to assign a service profile with a service profile from the UC Service Profile drop down. The service profile is used to provide the Jabber client with CUCM UC service configuration. .
Note: If you do not assign a service profile to the CUCM end user, then the system automatically uses the service profile that is set as the system default service profile.

Next, scroll down to the Device Information section. Here you can manage the CUCM end users controlled devices. Assign the user their softphone and/or deskphone devices. CUCM provides this list of device to Jabber for Windows during Jabber log in.
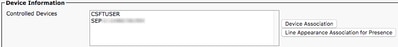
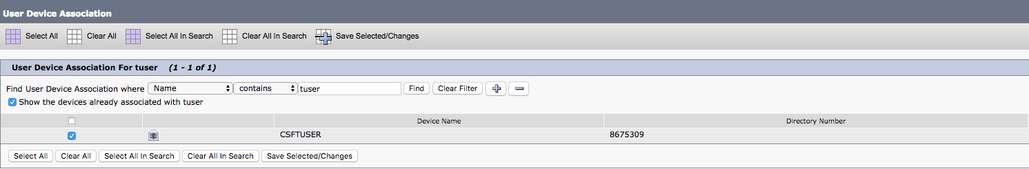
You can assign a device to a user with the Device Association button. You are presented with the User Device Association menu. From here you can search for the CUCM end users devices. When you find a device, place a check mark in the check box next to the device and select Save Selected Changes.
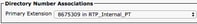
Now scroll down to the Directory Number Association section and select the CUCM end users primary extension from the Primary Extension drop down.
Scroll down to the Permissions Information section. Here you assign the permissions that are needed by Jabber for Windows.
The table (Table 1.1) lists all the required roles, their privileges and the reason why Jabber needs the role assigned.
Table 1.1
| Roles | Privileges/Resources | Jabber Role Usage |
| Standard CCM End Users | Grant an end user log-in rights to the Cisco Unified CM User Options. | Jabber SOAP Authentication |
| Standard CCMUSER Administration | Allows access to the Cisco Unified CM User Options. | Jabber SOAP Authentication |
| Standard CTI Allow Control of Phones Supporting Rollover Mode | Allows control of all CTI devices that support rollover mode. | Used for CTI Control of Cisco Unified IP Phone 6900 series. |
| Standard CTI Allow Control of Phones Supporting Connected Xfer and conf | Allows control of all CTI devices that support connected transfer and conferencing. | Used for CTI Control of Cisco Unified IP Phone 9900, 8900, or 8800 series or DX series. |
| Standard CTI Enabled | Enables CTI application control. | Used for CTI control of all other Jabber compatible CTI devices. |
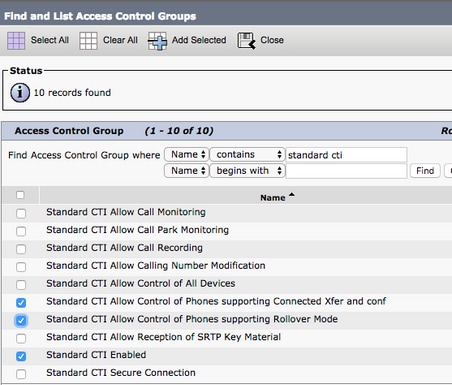
To assign a permission group to the CUCM end user, select the Add to Access Control Group button.

Then search for the access control group you would like to add, and select the checkbox located near the access control groups name. When finished, select the Add Selected button.
Service Discovery
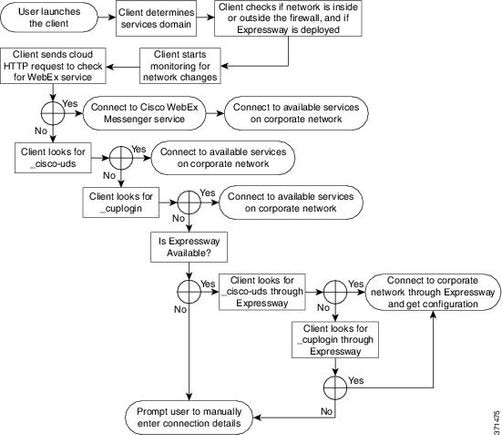
For the Cisco Jabber client to be able to log in, it must first be aware of the services (CUCM, IM&P or Expressway) it uses for authentication and configuration retrieval. Cisco recommends to set up automatic service discovery through the use of Domain Name System (DNS) Service Location Records (SRV) as this provides a seamless user experience and ease of administration.
The image is a graphical depiction of the Jabber automatic service discovery process.
To add DNS SRV record to Microsoft DNS Manager, navigate to your domain and expand the tree. Right click the _tcp folder and select Other New Records…
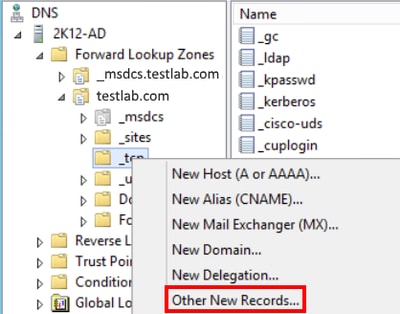
When presented with the Resource Record Type window, highlight the Service Location (SRV) then select Create Record…
Next you see the New Resource Record pane. Here, you can configure a SRV record for each of the CUCM servers that are to be used for Jabbers initial UDS home cluster lookup.
This is a configuration example for the_cisco-udsSRV record. In this example the _cisco-uds record resolves to three CUCM nodes within a CUCM cluster.
_cisco-uds._tcp.<domain_name>.com SRV service location:
priority = 6
weight = 30
port = 8443
svr hostname = cucm3.<domain_name>.com
_cisco-uds._tcp.<domain_name>.com SRV service location:
priority = 2
weight = 20
port = 8443
svr hostname = cucm2.<domain_name>.com
_cisco-uds._tcp.<domain_name>.com SRV service location:
priority = 1
weight = 5
port = 8443
svr hostname = cucm1.<domain_name>.com
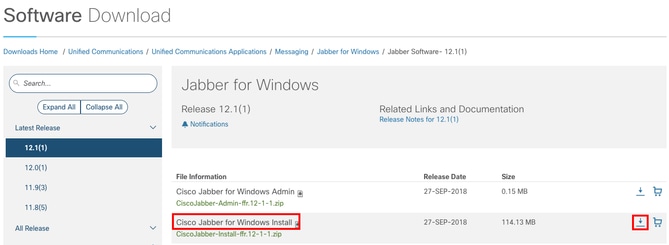
Download Jabber
Open your web browser of choice and navigate to Cisco Software Download. Once on the download home page, search for Jabber for Windows. Once you are presented with download options, select the Cisco Jabber for Windows Install download as seen in the screenshot:
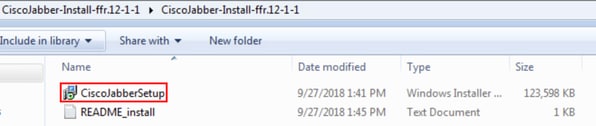
Installation of Jabber
Choose the Cisco Jabber for Windows installer that you previously downloaded. Unzip the Jabber installation folder and select the CiscoJabberSetup.msi.
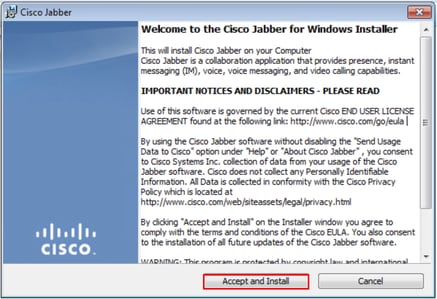
Once the Jabber for Windows installation launches, please read through the notices and disclaimers. If you wish to continue with the installation, select Accept and Install.
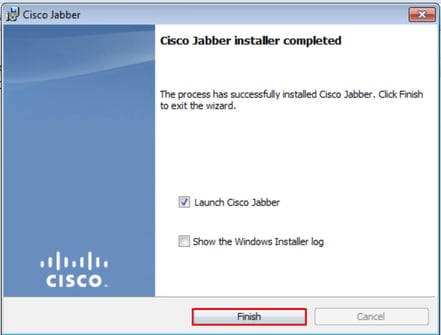
When the Jabber installation has finished, you are presented with the Cisco Jabber installer completed window. To complete the install, select Finish.
Log into Jabber
To perform a log in on Jabber for Windows, choose the Jabber application on the Microsoft Windows machine and launch it.
- Windows 7
- Navigate to the Windows Start Menu > All Programs > Cisco Jabber > Cisco Jabber or select the Jabber desktop icon, if applicable.
- Windows 10
- Navigate to the Windows Start Menu > Cisco Jabber > Cisco Jabber or select the Jabber desktop icon, if applicable.
Once the Jabber application has been launched, provide the Jabber username and the domain that is used for service discovery (example. tuser@testlab.com).
Note: By default, Jabber uses the User Principal Name (UPN) of the logged in Windows session to retrieve the domain used for service discovery. The screenshot assumes that UPN discovery is not in use.
Once service discovery has finished, you are prompted to provide the credentials for Jabber log. Provide a valid Jabber username and password and select Sign In.
Related Information
- Jabber — How to Clear Cache
- Jabber — Create a Problem Report
- Jabber — Upload a jabber-config.xml File to CUCM
- Jabber — Troubleshoot Cannot Communicate with Server (On Prem)
- Jabber — Collect Logs for Phone Issues
- Jabber — Troubleshoot Audio Issues
- Jabber — Troubleshoot Contact Resolution Issues
- Jabber — Create a Softphone Device on CUCM
- Jabber — Configure UC Services and Service Profile
- Jabber — Set IM-Only and Phone-Only Mode Options
- Jabber — Create a Jabber Client Configuration UC Service in CUCM 12.5+
- Troubleshoot Jabber Login
