In the Windows operating system, there is a feature called file sharing. On one computer, you can set up windows-shared folder that will be accessible to all computers on the local network. This is done using the SMB protocol, which has several versions. In Linux, you can open and create shared folders using Samba.
The Samba server supports all versions of the SMB protocol. However, there are some compatibility issues. In this article, I will explain how to access a Windows Shared folder in Linux using popular desktop environments and the command line.
Table of Contents
- Why It May Not Work?
- Ensure that Everything is Set Up Correctly in Windows
- Finding Shares in Linux Terminal
- Open Shared Folder in KDE Dolphin
- Open Share in GNOME Nautilus
- Mounting a Shared Folder in the Terminal
- Wrapping Up
Why It May Not Work?
In older versions of Linux distros and Windows 7 everything worked fine because they used the SMB1 protocol. However, there have been several changes recently. In 2017, the Wannacry virus emerged, which exploited vulnerabilities in the SMB1 protocol. As a result, modern versions of Windows have disabled support for SMB1 and now use SMB3 by default. Samba has also disabled SMB1 since version 4.11. However, SMB2 and SMB3 lack support for device discovery in the local network.
In general, this is no longer necessary because there is a network discovery protocol called Zeroconf. In Linux, its open-source implementation, Avahi, is used. Linux servers and NAS storage can publish themselves on the local network using this protocol. So that, there is no need to support it in SMB. However, Microsoft decided to use its own protocol called WS-Discovery, and that’s where the problems began.
At the time of writing this article, Linux system has issues with discovering shared folders in the local network. The Nautilus file manager in GNOME does not support WS-Discovery at all, and there are no production-ready terminal utilities for it either. You can track the current status of implementing WS-Discovery support in this GVFS issue. However, in 2020, the KDE team added support for this protocol in the Dolphin file manager using kdsoap-ws-discovery-client.
Later, a program for KDE called Smb4k appeared, which can discover network resources using Avahi and the WS-Discovery protocol, but it needs to be compiled with a special option. So that, in GNOME, you can only open a Windows shared folder by knowing the IP address of the computer where it is located. Whereas in KDE, it is a bit more convenient to do so.
Ensure that Everything is Set Up Correctly in Windows
Previously, it was enough to go to File Explorer and enable file sharing there. But it no longer works that way. First, you need to make your current network private in Windows. By default, only private networks are considered secure, and Windows machines can be discovered in them. To do this, open Settings -> Network & Internet -> Ethernet and select Network Profile Type -> Private Network:
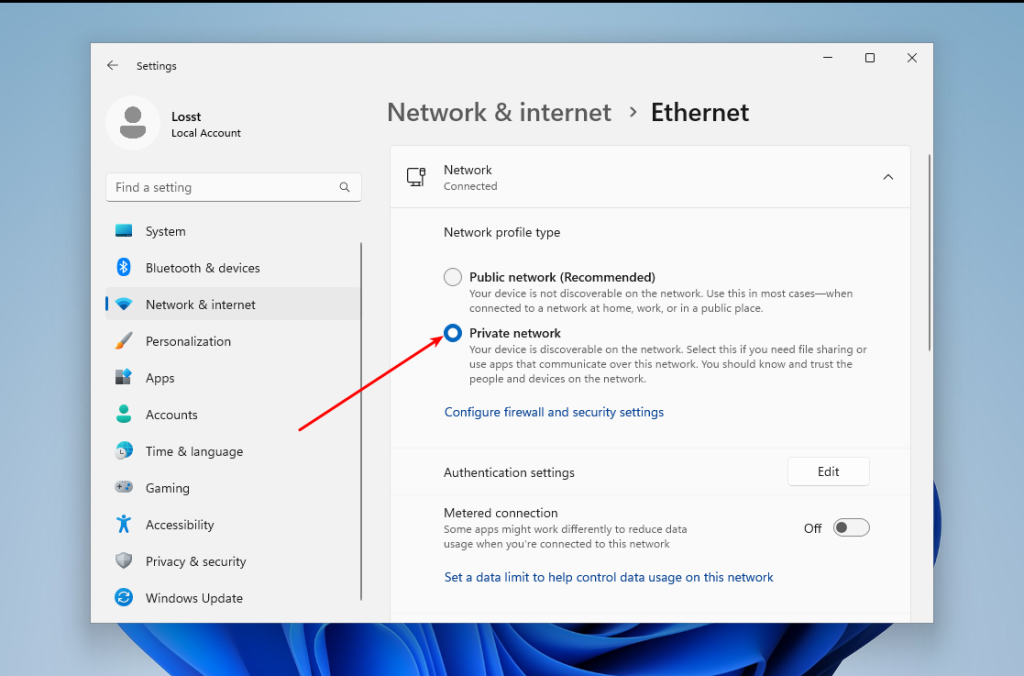
If your current network is wireless, you should do the pretty same thing. Next, go back and select Advanced Sharing Settings. In this window, enable Network discovery and File and printer sharing:
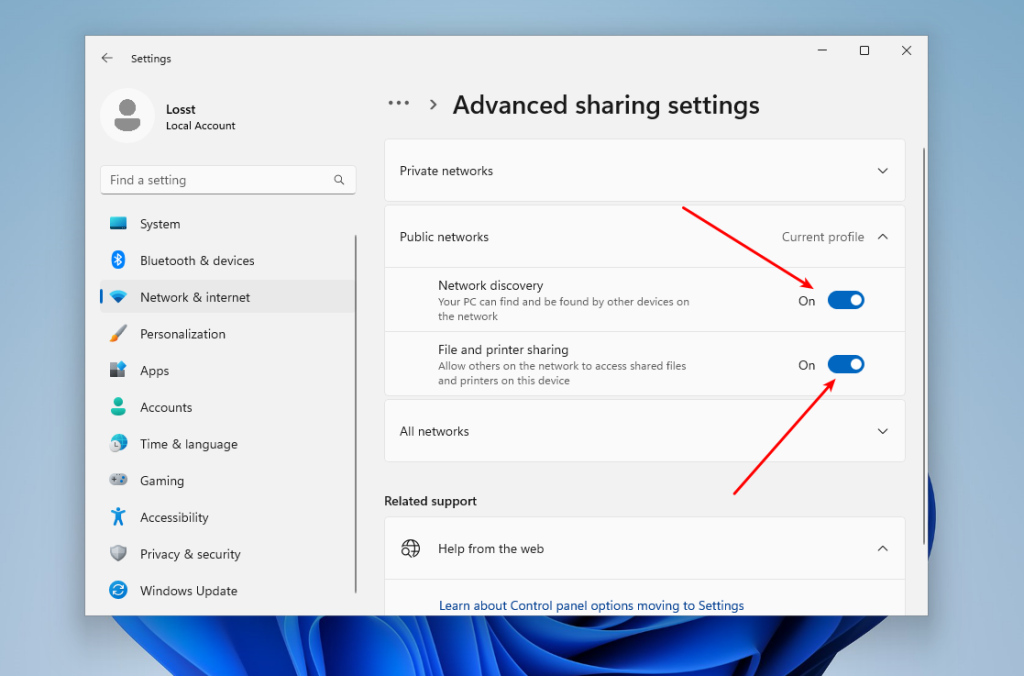
Finally, you need to ensure that the firewall is configured correctly and allows SMB connections. To do this, go back to the main Settings menu, then open Privacy & Security -> Firewall & network protection. Click on Allow an app through the firewall:
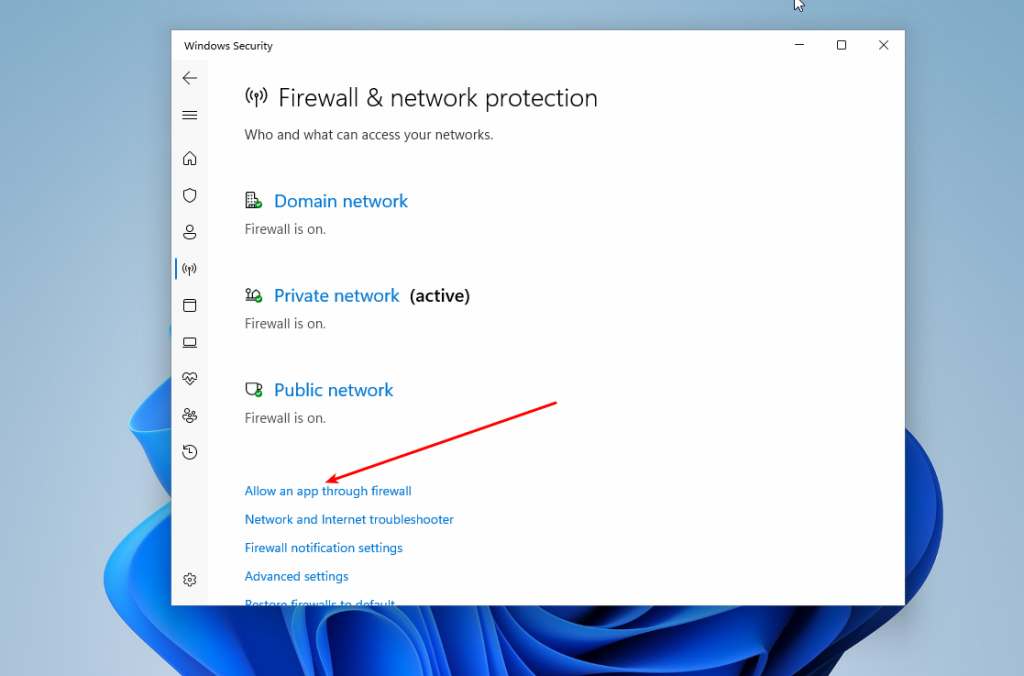
Make sure that File and printer sharing and Network discovery are enabled for Private networks:
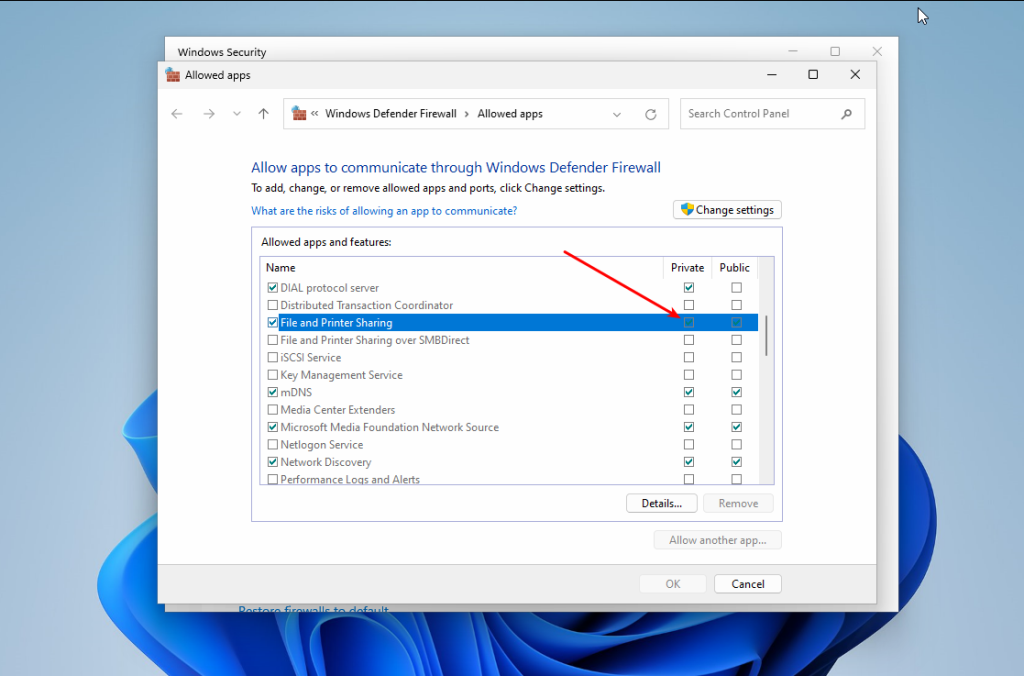
That’s it. Now you can go to your Linux machine.
Although there are no command-line tools for working with WS-Discovery, you can try to find devices with shared resources using Nmap. This program cannot search for resources like Avahi does, but it can help you find IP addresses with an open port 445. This port is used by SMB. To do this, you need to install the following packages (Ubuntu):
sudo apt install nmap smbclient
Or Fedora:
sudo dnf install nmap samba-client
Also, you need to find out the IP address range of your local network. You can take your IP address and mask and just replace the fourth digit with zero. For example:
ip -br a
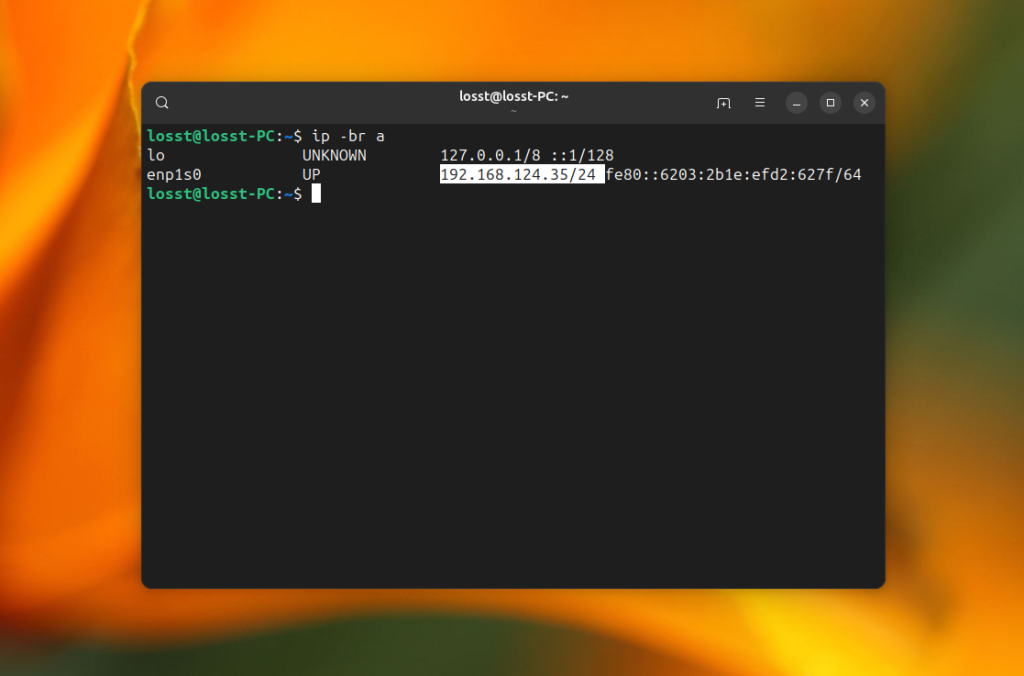
The command for the search will look like this. Replace 192.168.124.0/24 with your local network address range and run it in the the terminal window with sudo privileges:
nmap -p 445 --open -n -Pn 192.168.124.0/24
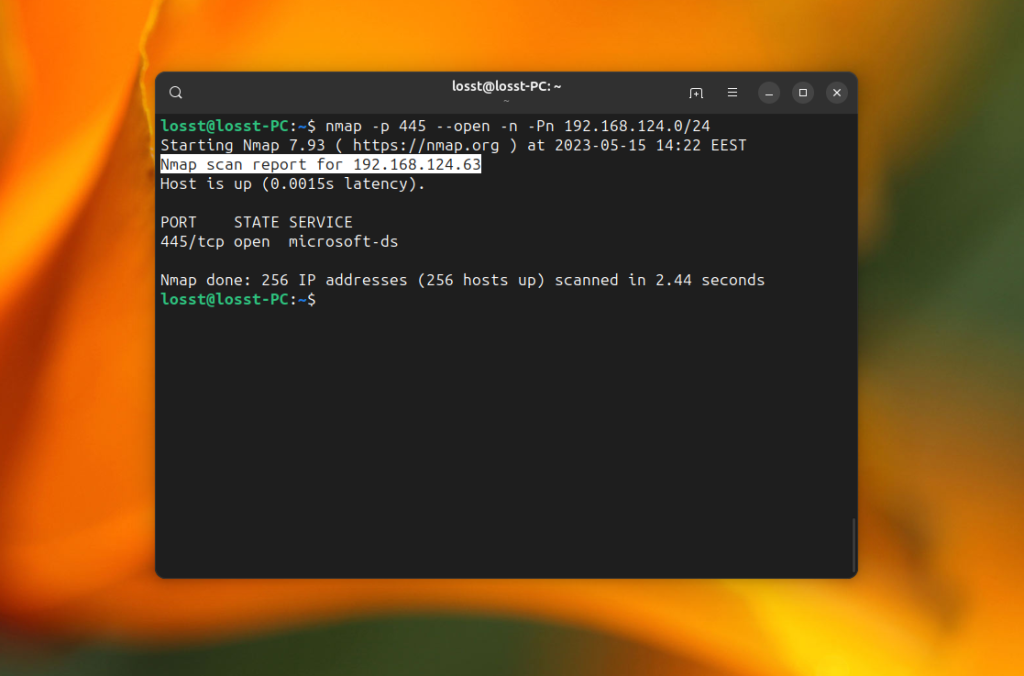
The -p option specifies the port 445, -Pn option disables ICMP discovery and treats all IP addresses as alive, -n disables DNS hostname resolution. The command may take quite a while, but as a result, it will find hosts with open port 445 if such hosts exist in your local network:
This can’t be considered as normal network discovery, but it works. Now you can use smbclient to see which shared folders are on the server that you found. For example:
smbclient -L 192.168.124.63
The command will ask you to enter the share password. Usually, it is password for your Windows user, and then it will show all available shared folders:
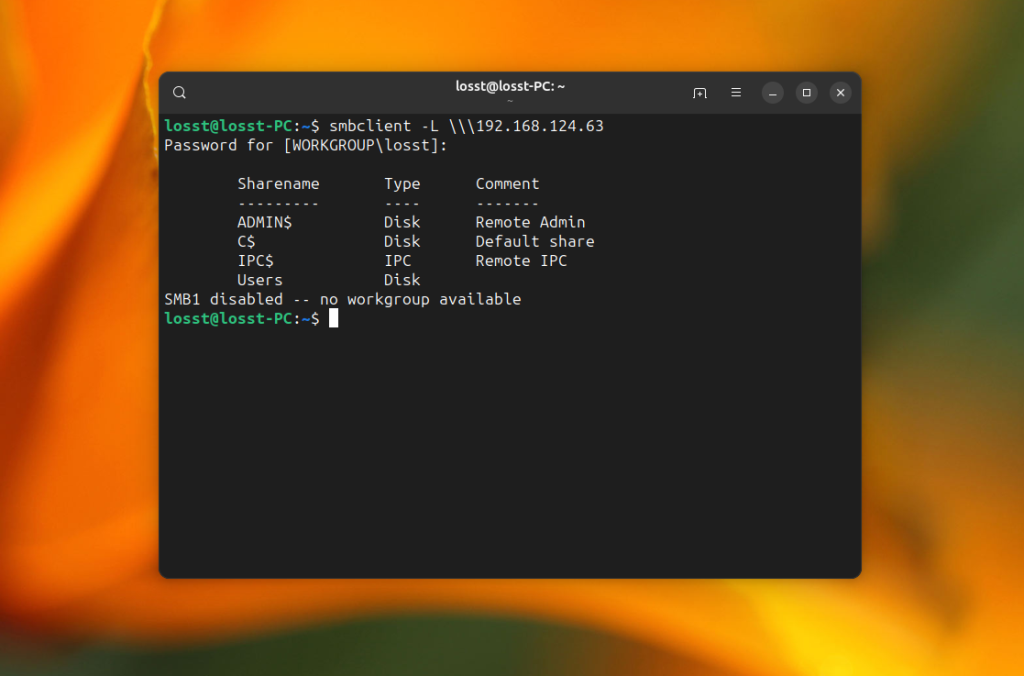
Now let’s have a look at how to mount them.
To open a shared folder in KDE, you can use the Dolphin file manager. As I mentioned earlier, here you can see all available computers that have network drive on the local network. To do this, run Dolphin, then open Network, and then Shared Folders (SMB):
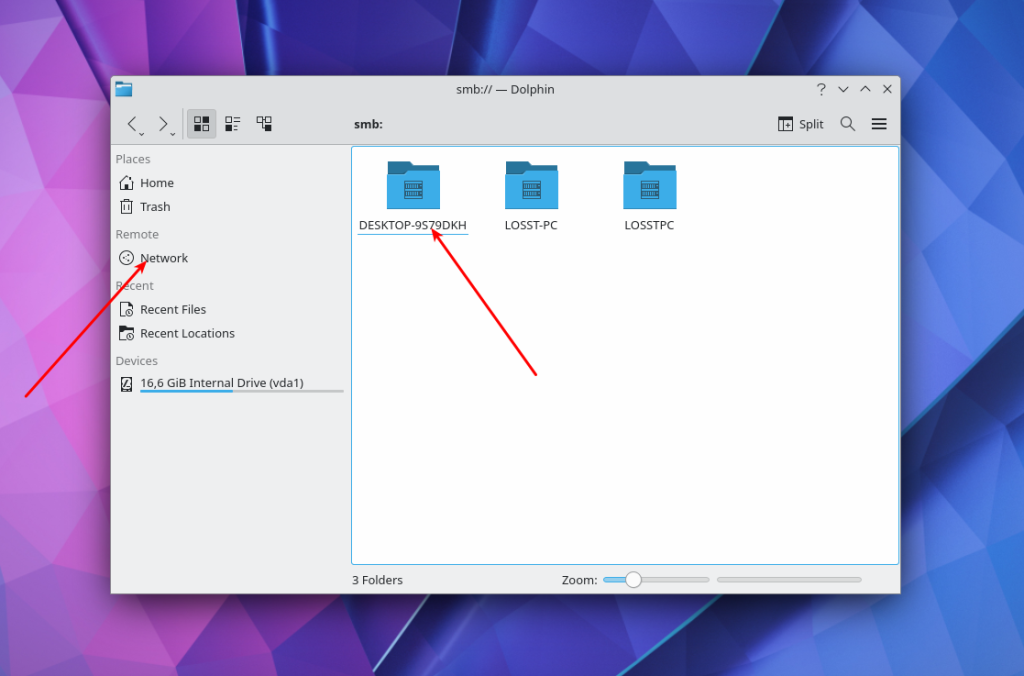
Click on one of the resources and enter the username and password to view the available folders:
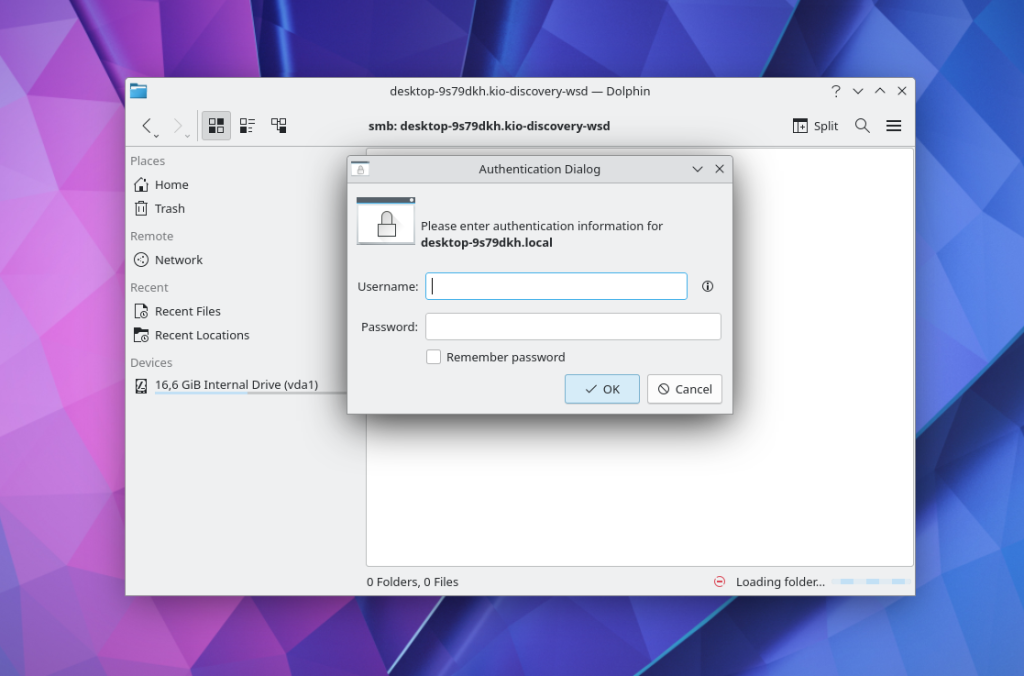
This is what shared folders from Windows 11 look like. Here you can find windows files:
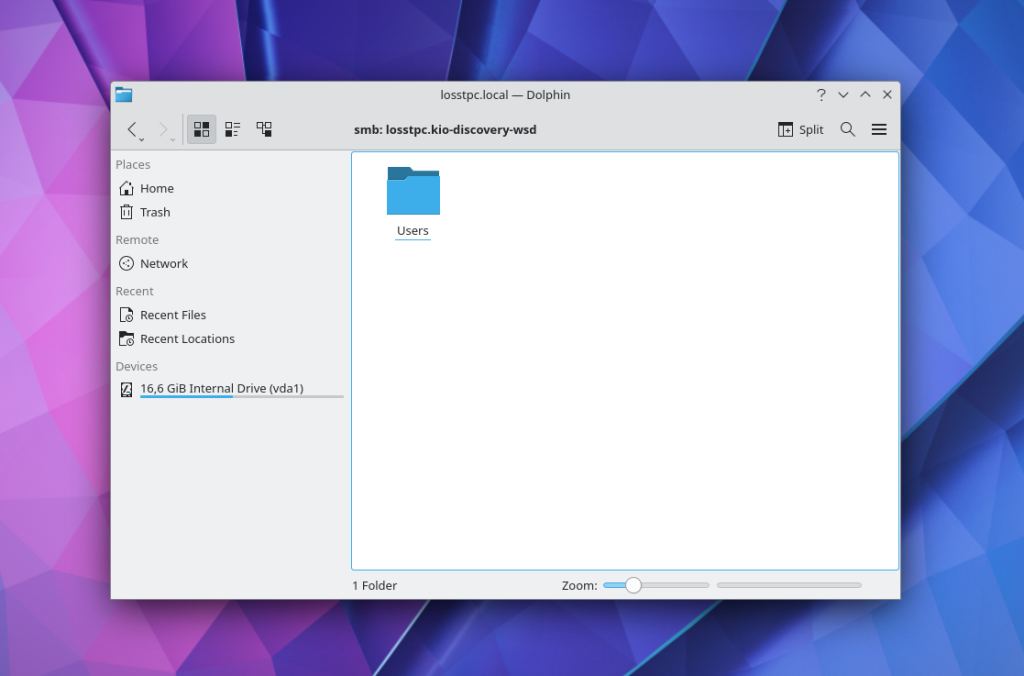
If network discovery does not work in your case, you can still enter the IP address of the resource in the text field at the top of the window and connect to it. For example, smb://192.168.124.63/
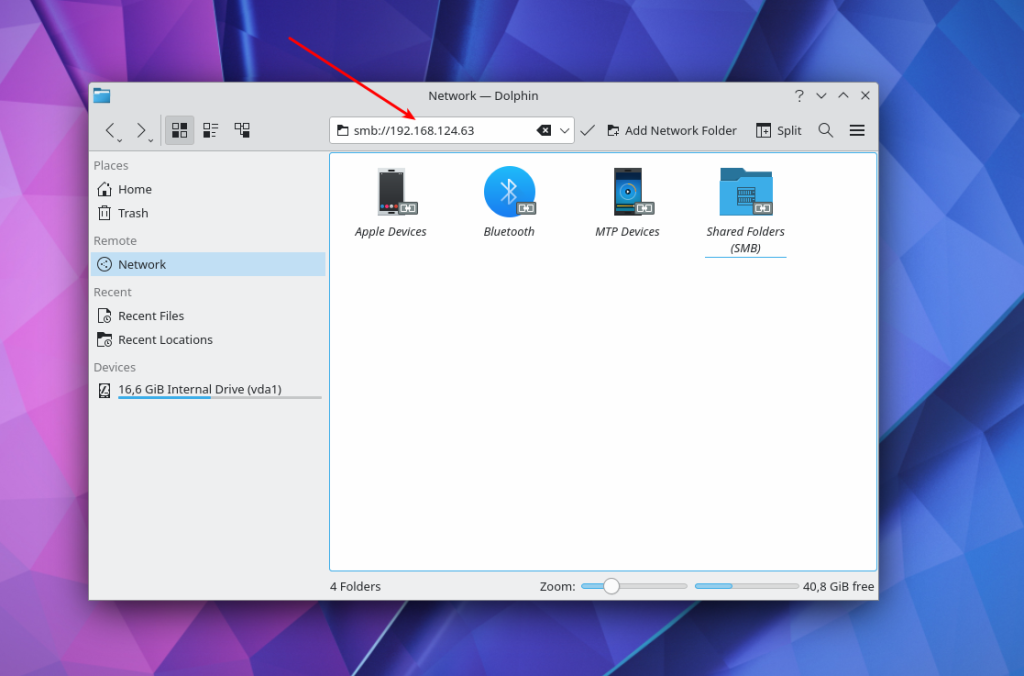
If you want to connect to a Windows shared folder in the GNOME graphical interface, you can use the Nautilus file manager. Open Other Locations and find at the bottom of the window the inscription Connect to Server and a field for entering an address.
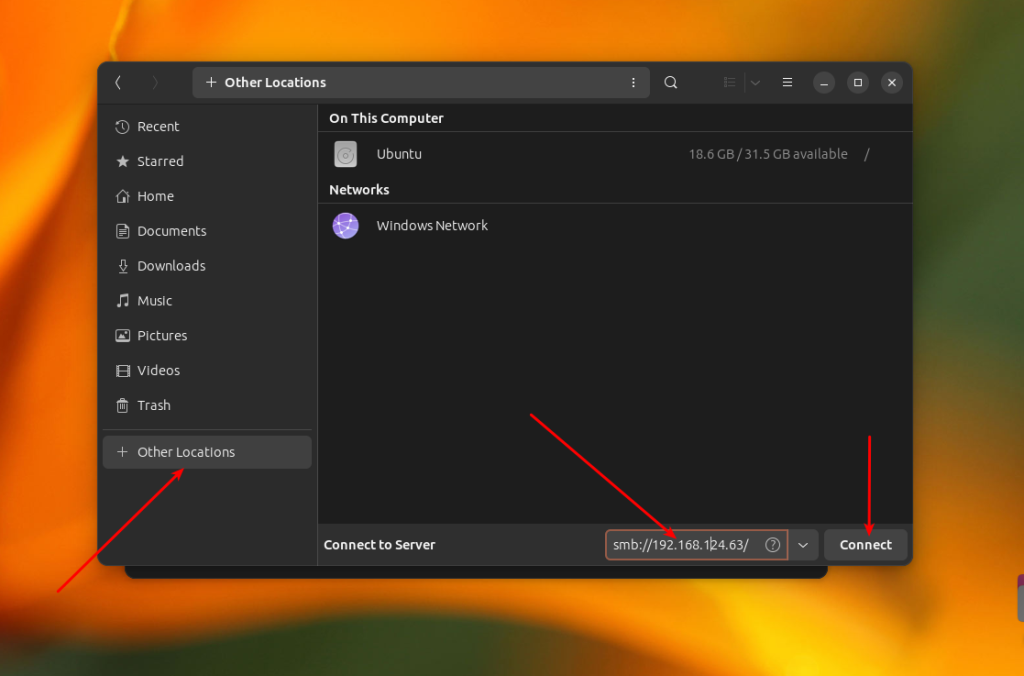
There’s no point in opening the Windows Network item, because GVFS, which is used in GNOME for disk mounting, does not support the WS-Discovery protocol. To connect to a remote windows share located on a server with IP 192.168.124.63, enter this address and press the Connect button:
smb://192.168.124.63
In the next window, you need to enter a password and after that, you can view the files of the shared folder:
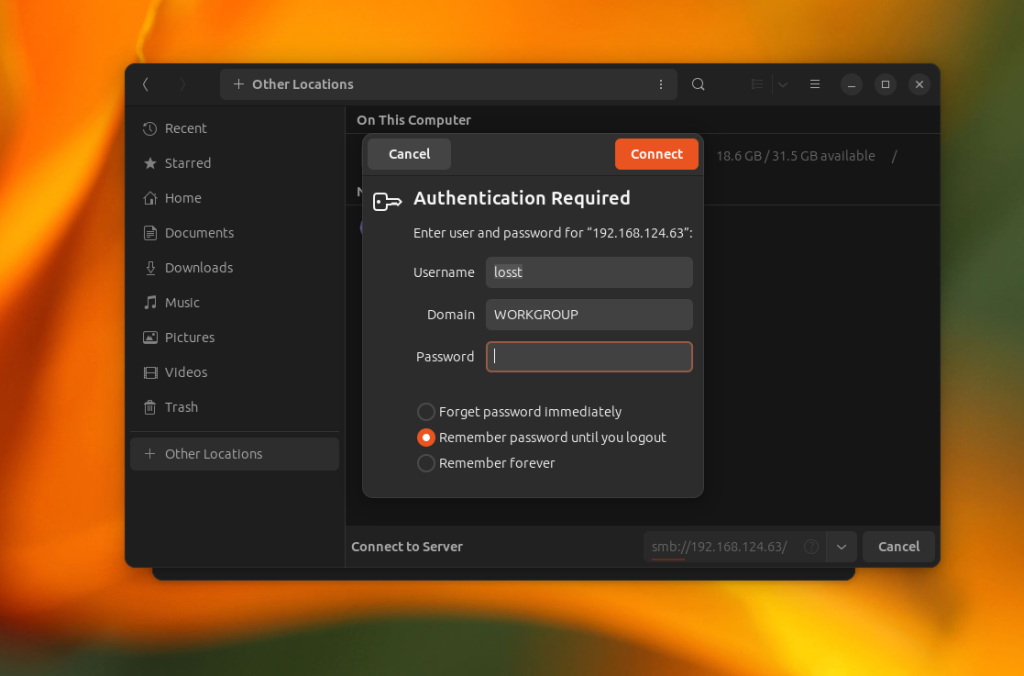
After this, you can browse your windows folders.
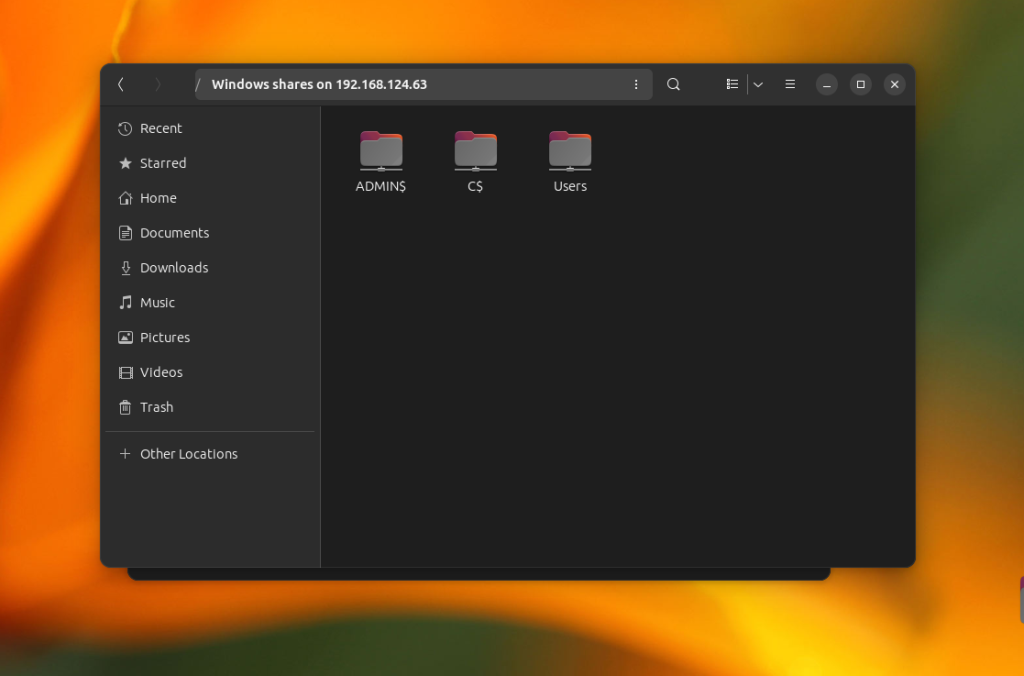
Additionally, you can use a shortcut on the left panel to access a remote share which is already mounted.
If you want to mount windows share in the terminal, you can use cifs-utils and the mount command. Firstly, install the cifs-utils package. The command for Ubuntu:
sudo apt install cifs-utils
In Fedora:
sudo dnf install cifs-utils
Now, you can execute the mount command specifying the cifs file system type and the username option. Note that you can’t mount the root of the cifs share, you need to add any folder in the path. For example, Users on 192.168.124.63:
sudo mount -t cifs -o username=losst //192.168.124.63/Users /mnt/
If you want to have write access to the windows share folder, you need to add the uid option with the identifier of your user. For the first user, it’s usually 1000:
sudo mount -t cifs -o username=losst,uid=1000 //192.168.124.63/Users /mnt/
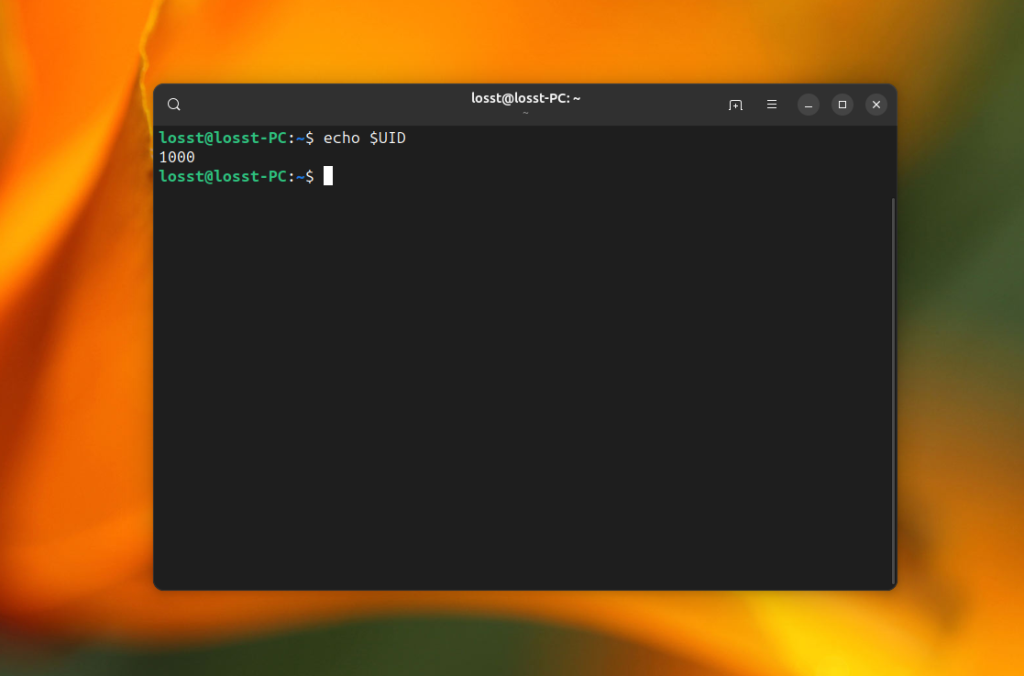
You can find the identifier of the current user in the UID environment variable:
echo $UID
If you want to mount share automatically at system startup, you need to save the share username and password in a credentials file, for example, /etc/share/windows-credentials. For instance:
sudo mkdir -p /etc/share/
username=losst
password=password
domain=workgroup
And then add the following line to the /etc/fstab file:
//192.168.124.63/Users /mnt/share cifs credentials=/etc/share/windows-credentials,uid=1000,nofail 0 0
The nofail option is needed to allow your computer to boot even if the remote folder could not be mounted. After this, reload systemd settings:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Create the mount point directory:
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/share
You can check that everything is working using the following command:
sudo mount /mnt/share
If everything is ok, you could see contents of mounted share in the /mnt/share folder:
Wrapping Up
In this article, we looked at how to mount Windows network share in Linux using a graphical interface or in the terminal. Despite some difficulties, this can be used quite effectively. Do you know any other applications or scripts which can help with that? Share their names in the comments section below.
The article is distributed under Creative Commons ShareAlike 4.0 license. Link to the source is required.
In this article, we’ll look at how to mount a shared network folder hosted on a Windows computer in Linux. Windows uses the SMB (Server Message Block) protocol, formerly known as CIFS (Common Internet File System) to share and access shared folders over the network. On Linux, you can use the cifs-utils or Samba client to access Windows network shares via SMB protocol.
Hint. Port TCP/445 is used to access the shared network folder via SMB/CIFS. UDP ports 137, 138, and TCP ports 139 are used for name resolution. If these ports are closed, you will only be able to connect to a shared folder on Windows by using a host IP address.
You can mount a shared folder hosted on a Windows computer using the tools in the cifs-util package. Run this command to install the package:
- Ubuntu/Debian:
$ sudo apt-get install cifs-utils - CentOS/Oracle/RHEL:
$ sudo dnf install cifs-utils
Create a mount point:
$ sudo mkdir /mnt/shareYou can now mount the SMB share from a Windows computer using the User03 account:
$ sudo mount.cifs //192.168.31.33/backup /mnt/share -o user=User03You must have a Windows user password to connect to a shared folder.
You can set additional parameters when mounting a network SMB folder:
$ sudo mount -t cifs -o username=User03,password=PasswOrd1,uid=1000,iocharset=utf8 //192.168.31.33/backup /mnt/share- //192.168.31.33/backup – shared network folder in Windows;
- /mnt/share – mount point;
- -t cifs – specify the type of file system to mount;
- -o mount options (this option can only be used as root, so sudo is used in the command above);
- username=User03,password=PasswOrd1 – Name and password of the Windows user who has permission to access the share. If anonymous access to the network folder is allowed on Windows, you can specify the guest username here;
- iocharset=utf8 – enable support for UTF8 encoding to display the name of files on SMB shares;
- uid=1000 – use this Linux user as the owner of the files in the mounted folder.

By default, Windows shares will be mounted on Linux with full permissions (0755). Add the following options to the command if you want to change the default mount permissions:
dir_mode=0755,file_mode=0755
Add the following line to the /etc/hosts file if you want to use the computer name instead of the IP address when mounting a Windows share:
IP_ADDRESS HOSTNAME
If you do not want to enter Windows user credentials in the mount command, you can save them to a file.
For example:
$ mcedit ~/.windowscredentialsInsert into the file:
username=User03
password=PasswOrd1
If you need to use a user account from an Active Directory domain, you will need to add a third line to the file:
domain = poweradm.com
To anonymously mount a Windows folder:
username=guest
password=
Change file permissions:
$ chmod 600 ~/.windowscredentialsWhen mounting a shared folder, you can now specify the file path instead of the plaintext credentials:
$ sudo mount -t cifs -o credentials=/home/sysops/.windowscredentials,uid=1000,iocharset=utf8 //192.168.31.33/backup /mnt/shareUnmount a shared SMB folder:
$ sudo umount /mnt/shareAutomatically Mount Network SBM Shares on Linux
The /etc/fstab file can be used to enable the automatic mounting of a Windows-shared folder on Linux.
$ sudo mcedit /etc/fstabAdd the following string to the file to connect the SMB shared folder:
//192.168.31.33/backup /mnt/share cifs user,rw,credentials=/home/sysops/.windowscredentials,iocharset=utf8,nofail,_netdev 0 0
- rw – mount SBM folder in read/write mode
- nofail – resume Linux boot if file system mount fails
- _netdev – indicates that the filesystem is network connected. Linux will not mount such filesystems until networking has been successfully initialized on the host.
You can specify the version of the SMB protocol to be used for the connection (SMB version 1.0 is insecure and disabled by default in modern Windows versions). Add the parameter vers=3.0 to the end of the cifs connection string.
//192.168.31.33/backup /mnt/share cifs user,rw,credentials=/home/sysops/.windowscredentials,iocharset=utf8,nofail,_netdev,vers=3.0 0 0
If an incompatible (old version) of SMB is used on the remote Windows host, a connection error will occur:
mount error(112): Host is down
or
mount error(95): Operation not supported
To immediately mount a shared folder from the fstab configuration file
$ mount -aHow to Access Windows Share on Linux with a Samba Client
Install the samba-client on Linux:
- Ubuntu/Debian:
$ sudo apt-get install smbclient - CentOS/Oracle/RHEL:
$ sudo dnf install smbclient
To view the SMB hosts on the local network:
$ smbtree -NList the SMB folders that are available on a remote Windows host:
$ smbclient -L //192.168.31.33 -NIf you have disabled anonymous access in Windows, you will get an error:
session setup failed: NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED
In this case, you must specify the Windows user account that you want to use to access the shared folder:
$ smbclient -L //192.168.31.33 -U User03Add the -W option if you want to use a domain user account:
$ smbclient -L //192.168.31.33 -U User03 –W Domain
To establish an interactive connection to a Windows network share, use the following command
$ smbclient //192.168.31.33/backup -U User03 -W Domainor
$ smbclient //192.168.31.33/backup -U User03To access the SMB folder anonymously:
$ smbclient //192.168.31.33/backup -U EveryoneAfter logging in, the following prompt will appear:
smb: \>List the files in a shared SMB folder:
dir
Download the file from the Windows shared folder:
get remotefile.txt /home/sysops/localfile.txtSave a local file from Linux to an SMB directory:
put /home/sysops/localfile.txt remotefile.txtYou can run multiple smbclient commands one after the other:
$ smbclient //192.168.31.33/backup -U User03 -c "cd MyFolder; get arcive.zip /mnt/backup/archive.zip"You can use the help command to display a full list of commands in smbclient. The syntax of the smbclient commands is similar to the ftp client commands.
An error may occur when using the smbclient command:
Unable to initialize messaging context
smbclient: Can't load /etc/samba/smb.conf - run testparm to debug it.
Create the file /etc/samba/smb.conf to fix the error.
If the SMB 1.0 protocol is disabled on the Windows host, the smbclient connection will fail:
Reconnecting with SMB1 for workgroup listing.
protocol negotiation failed: NT_STATUS_CONNECTION_RESET
Unable to connect with SMB1 -- no workgroup available.
Accessing Windows shared folders from Linux involves using the Samba (SMB) protocol, which allows interoperability between Linux/Unix servers and Windows-based clients. Here’s a step-by-step guide to access Windows shared folders from a Linux machine:
Method 1: Using File Manager
Most modern Linux distributions come with file managers that support browsing SMB shares directly.
- Open your File Manager:
- For example, if you are using GNOME, open the Nautilus file manager.
- In KDE, use Dolphin.
- Connect to the Server:
- In Nautilus, go to
Other Locationsand entersmb://<windows_ip_address>/<shared_folder_name>. - In Dolphin, use the address bar and enter
smb://<windows_ip_address>/<shared_folder_name>.
- In Nautilus, go to
- Authentication:
- If the shared folder requires authentication, you will be prompted to enter your username and password.
Method 2: Using the Command Line
You can use the smbclient tool or mount the share using cifs filesystem.
Using smbclient (for browsing and accessing files)
- Install smbclient:
sudo apt-get install smbclient # Debian/Ubuntu sudo yum install samba-client # CentOS/RHEL sudo dnf install samba-client # Fedora - Access the Shared Folder:
smbclient //windows_ip_address/shared_folder -U username- Replace
windows_ip_addresswith the IP address of the Windows machine. - Replace
shared_folderwith the name of the shared folder. - Replace
usernamewith your Windows username.
- Replace
- Browse the Share:
- After entering your password, you will be in the smbclient interactive shell, where you can use commands like
ls,cd,get, andputto interact with files.
- After entering your password, you will be in the smbclient interactive shell, where you can use commands like
- Install cifs-utils:
sudo apt-get install cifs-utils # Debian/Ubuntu sudo yum install cifs-utils # CentOS/RHEL sudo dnf install cifs-utils # Fedora - Create a Mount Point:
sudo mkdir /mnt/windows_share - Mount the Share:
sudo mount -t cifs //windows_ip_address/shared_folder /mnt/windows_share -o username=windows_username,password=windows_password,workgroup=WORKGROUP- Replace
windows_ip_addresswith the IP address of the Windows machine. - Replace
shared_folderwith the name of the shared folder. - Replace
windows_usernameandwindows_passwordwith your Windows credentials. - Replace
WORKGROUPwith your network workgroup name if different.
- Replace
- Access the Mounted Share:
- Now you can access the shared folder at
/mnt/windows_share.
- Now you can access the shared folder at
- Unmount the Share:
sudo umount /mnt/windows_share
Method 3: Permanent Mount via fstab
- Edit fstab File:
- Add an Entry:
//windows_ip_address/shared_folder /mnt/windows_share cifs username=windows_username,password=windows_password,workgroup=WORKGROUP,iocharset=utf8,sec=ntlm 0 0 - Mount All Filesystems:
- This ensures the shared folder is mounted automatically at boot.
By following these steps, you should be able to access Windows shared folders from your Linux machine easily.
Обновлено:
Опубликовано:
Используемые термины: CIFS, Linux.
Протокол CIFS (SMB) позволяет работать с общими папками. В инструкции будет рассказано, как в системах на базе Linux можно настроить клиент для подключения к файловому серверу, который работает по данному протоколу.
Подготовительная работа
Синтаксис mount
Ручное монтирование
Автоматическое монтирование
Примеры
Дополнительная информация
Подготовка
Установка пакетов
Для монтирования общей папки необходимо установить набор утилит для работы с CIFS (в противном случае, мы получим ошибку mount.cifs команда не найдена).
а) Для систем RPM (РЕД ОС, Rocky Linux, CentOS):
yum install cifs-utils
б) Для DEB-систем (Astra Linux, Debian, Ubuntu):
apt update
apt install cifs-utils
Сетевые порты
Если мы будем монтировать сетевую папку, сервер которой находится за брандмауэром, необходимо открыть следующие порты:
- 137/UDP
- 138/UDP
- 139/TCP
- 445/TCP
Данные команды нет необходимости выполнять на клиентах. Только на стороне сервера.
В зависимости от используемого типа фаервола, команды будут отличаться.
а) iptables (как правило, на системах DEB):
iptables -I INPUT -p tcp —dport 445 -j ACCEPT
iptables -I INPUT -p udp —dport 137:138 -j ACCEPT
iptables -I INPUT -p tcp —dport 139 -j ACCEPT
Применяем настройки:
apt install iptables-persistent
netfilter-persistent save
б) firewalld (как правило, на системах RPM):
firewall-cmd —permanent —add-service=samba
firewall-cmd —reload
Синтаксис
mount.cifs <папка на сервере> <во что монтируем> <-o опции>
* вместо mount.cifs можно написать mount -t cifs.
Пример:
mount.cifs //192.168.1.1/public /mnt
* простой пример монтирования папки public на сервере 192.168.1.1 в локальный каталог /mnt.
Если нам не известны расшаренные папки на сервере, мы можем воспользоваться утилитой smbclient. Для начала установим ее.
а) на RPM (Rocky Linux / РЕД ОС / Red Hat / CentOS / Fedora):
yum install samba-client
б) на Deb (Debian / Ubuntu / Astra Linux / Mint):
apt install samba-client
Теперь вводим:
smbclient -L 192.168.1.1
или, при необходимости авторизоваться на файловом сервере:
smbclient -L 192.168.1.1 -U username
Ручное монтирование
Теперь монтирование можно выполнить следующей командой:
mount.cifs //192.168.1.10/share /mnt -o user=dmosk
* в данном примере будет примонтирован каталог share на сервере 192.168.1.10 в локальную папку /mnt под учетной записью dmosk.
То же самое, с использованием домена:
mount.cifs //192.168.1.10/share /mnt -o user=dmosk,domain=dmosk.local
Автоматическое монтирование CIFS через fstab
Для начала создаем файл, в котором будем хранить данные авторизации при подключении к общей папке:
vi /root/.smbclient
И добавляем в него данные следующего вида:
username=dmosk
password=dPassw0rd
domain=dmosk.local
* в этом примере создана пара логин/пароль — dmosk/dPassw0rd; domain указывать не обязательно, если аутентификация выполняется без него.
Задаем права на созданный файл, чтобы доступ был только у пользователя, скажем, root:
chmod 600 /root/.smbclient
chown root:root /root/.smbclient
Теперь открываем конфигурационный файл fstab:
vi /etc/fstab
и добавляем в него следующее:
//192.168.1.10/share /mnt cifs user,rw,credentials=/root/.smbclient 0 0
* в данном примере выполняется монтирование общей папки share на сервере с IP-адресом 192.168.1.10 в каталог /mnt. Параметры для подключения — user: позволяет выполнить монтирование любому пользователю, rw: с правом на чтение и запись, credentials: файл, который мы создали на предыдущем шаге.
Чтобы проверить правильность настроек, вводим следующую команду:
mount -a
Примеры использования опций
Версии SMB
Если на стороне Windows используется старая или слишком новая версия протокола SMB, при попытке монтирования мы можем получить ошибку mount error(112): Host is down. Чтобы это исправить, указываем версию:
mount.cifs //192.168.1.10/share /mnt/ -o vers=1.0
* монтирование по протоколу SMB1.0
Монтирование от гостевой учетной записи
Если сервер принимает запросы без логина и пароля, то клиент подключается, как гость:
mount.cifs //192.168.1.10/share /mnt -o guest
или в fstab:
//192.168.1.10/share /mnt cifs guest 0 0
Для монтирования шары Windows, иногда, недостаточно указать опцию guest. Нужно делать так:
mount.cifs //192.168.1.10/share /mnt -o user=guest,pass=»
Или в fstab:
//192.168.1.10/share /mnt cifs guest,pass 0 0
Права на примонтированные каталоги
При монтировании папки мы можем указать определенные права:
mount.cifs //192.168.1.10/share /mnt -o file_mode=0777,dir_mode=0777
Для указания владельца, который будет назначен для примонтированного каталога, используем:
mount.cifs //192.168.1.10/share /mnt -o uid=33,gid=33
* чтобы посмотреть идентификаторы пользователя, вводим id -u <имя пользователя> и id -g <имя группы>.
Читайте также
Дополнительная информация по теме:
1. Как во FreeBSD примонтировать CIFS.
2. Как настроить автоматическое монтирование дисков в системах Linux.
3. Установка и настройка файлового сервера Samba на Ubuntu или Debian.
4. Установка и настройка файлового сервера Samba на CentOS.
5. Пример скрипта для создания резервной копии файлового сервера.
If you need to access Windows shared folders from Ubuntu, it can be done easily by installing and configuring Samba. Samba is a software suite that provides file and print services for Windows clients, and it allows Linux and Windows machines to share files and printers. By using Samba, you can create Linux shares that can be accessed by Windows clients, as well as access Windows shares from Linux machines.
In this guide, we will walk you through the process of accessing Windows shared folders from Ubuntu using Samba. We will cover the following steps:
- Install Samba on Ubuntu
- Configure Samba on Ubuntu
- Access Windows shared folder from Ubuntu
By following these steps, you will be able to access Windows shared folders from Ubuntu and easily transfer files between the two operating systems.
Step 1: Update Ubuntu
Before installing Samba, it’s always a good idea to update Ubuntu to ensure that you have the latest software and security patches. You can do this by opening a terminal and running the following commands:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgradeStep 2: Install Samba
Before you can mount a Windows shared folder on Ubuntu, you need to make sure that Samba is installed on Ubuntu. If you have not already installed Samba, you can do so by running the following command in the terminal:
sudo apt-get install samba
Step 3: Find the IP address of the Windows machine
Before you can mount the Windows shared folder on Ubuntu, you need to know the IP address of the Windows machine. You can find this by opening a Command Prompt on the Windows machine and running the command:
ipconfig
Look for the IPv4 address, which should look something like “192.168.1.10”. Note down this IP address.
Step 4: Create a mount point
Before you can mount the Windows shared folder on Ubuntu, you need to create a mount point on Ubuntu. This is the folder where the Windows shared folder will be mounted. You can create a mount point by running the following command in the terminal:
sudo mkdir /mnt/windows
This will create a folder called “windows” in the “/mnt” directory.
Step 5: Mount the Windows shared folder
To mount the Windows shared folder on Ubuntu, you need to run the following command in the terminal:
sudo mount -t cifs //windows_ip/shared_folder /mnt/windows -o username=windows_username,password=windows_passwordReplace “windows_ip” with the IP address of the Windows machine that you noted down earlier, “shared_folder” with the name of the shared folder on the Windows machine, “windows_username” with your Windows username, and “windows_password” with your Windows password.
Step 6: Verify the mount
Once you have mounted the Windows shared folder on Ubuntu, you can verify the mount by running the following command in the terminal:
ls /mnt/windows
This should display the contents of the Windows shared folder.
Step 7: Automate the mount
If you want the Windows shared folder to be automatically mounted every time you start Ubuntu, you can add the mount command to the “/etc/fstab” file. To do this, open the “/etc/fstab” file in a text editor using the following command:
sudo nano /etc/fstabAdd the following line to the end of the file:
//windows_ip/shared_folder /mnt/windows cifs username=windows_username,password=windows_password 0 0Save the file and exit the text editor.
Now, every time you start Ubuntu, the Windows shared folder will be automatically mounted to the “/mnt/windows” directory.
By following these steps, you can easily mount a Windows shared folder on Ubuntu using Samba, and access files on the Windows machine from Ubuntu.
You may visit websites homepage for coding related article.
