Все способы:
- Почему Microsoft Store может не устанавливаться
- Способ 1: Использование команды WSReset
- Способ 2: Восстановление Microsoft Store через PowerShell
- Способ 3: Предварительная загрузка пакетов для Microsoft Store
- Способ 4: Перенос файлов Microsoft Store с другой копии Windows
- Способ 5: Установка Microsoft Store через файл APPX
- Способ 6: Сброс Windows 10 с сохранением личных файлов
- Дополнительные рекомендации
- Вопросы и ответы: 120
Почему Microsoft Store может не устанавливаться
Microsoft Store является стандартным компонентом Windows 10, но существуют ситуации, когда его установка может быть невозможна или значительно затруднена:
- Специальные версии Windows 10. Корпоративные версии Windows 10 LTSC/LTSB (Long-Term Servicing Channel/Branch) изначально не содержат Microsoft Store и не предусматривают его прямую установку, так как эти версии разработаны для критически важных систем с минимумом компонентов.
- Модифицированные сборки. Пользовательские сборки Windows 10, в которых удалены компоненты фреймворка Windows Runtime (WinRT), делают невозможной установку Microsoft Store, так как отсутствуют необходимые зависимости.
- Проблемы с учетной записью Microsoft. Windows 10 требует связанную учетную запись Microsoft для полноценной работы Microsoft Store. Если на компьютере настроена только локальная учетная запись без подключения к серверам Microsoft, установка Store может завершиться ошибкой.
- Поврежденный системный компонент AppX. Если компонент системы, отвечающий за установку приложений AppX (в формате которых распространяется Microsoft Store), поврежден, никакие методы установки через PowerShell или wsreset не помогут.
- «Убитые» системные компоненты. В случае использования программ типа «Windows Debloater», которые агрессивно удаляют встроенные компоненты Windows, могут быть безвозвратно удалены файлы, необходимые для работы Microsoft Store.
Ниже представлены различные способы установки Microsoft Store в Windows 10, от самых простых до более сложных, требующих определенных навыков.
Способ 1: Использование команды WSReset
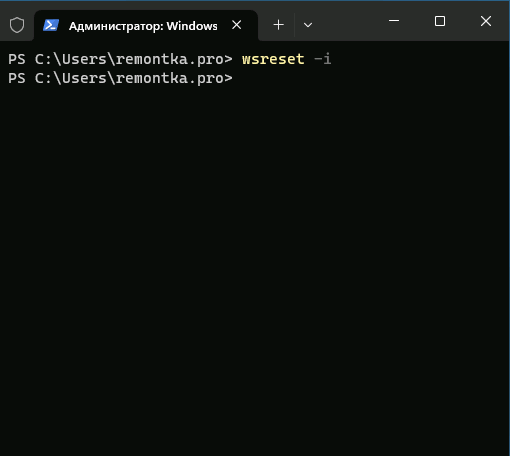
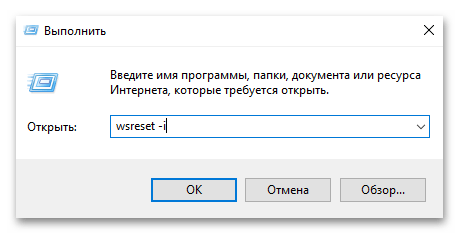
Самый простой способ установки Microsoft Store — использовать встроенную команду WSReset с параметром -i, которая инициирует загрузку и установку приложения из источников Microsoft.
- Нажмите комбинацию клавиш Win + R для вызова диалогового окна «Выполнить». В появившемся окне введите команду
wsreset -iи нажмите Enter. - После выполнения команды система попытается автоматически загрузить и установить Microsoft Store из онлайн-репозитория Microsoft. Дождитесь завершения процесса установки, который может занять некоторое время в зависимости от скорости вашего интернет-соединения.
- После установки Microsoft Store должен появиться в меню «Пуск», и вы сможете запустить его для проверки работоспособности.
- Если этот метод не работает, то, скорее всего, проблема связана с отсутствием необходимых компонентов системы, и стоит перейти к следующим способам установки.

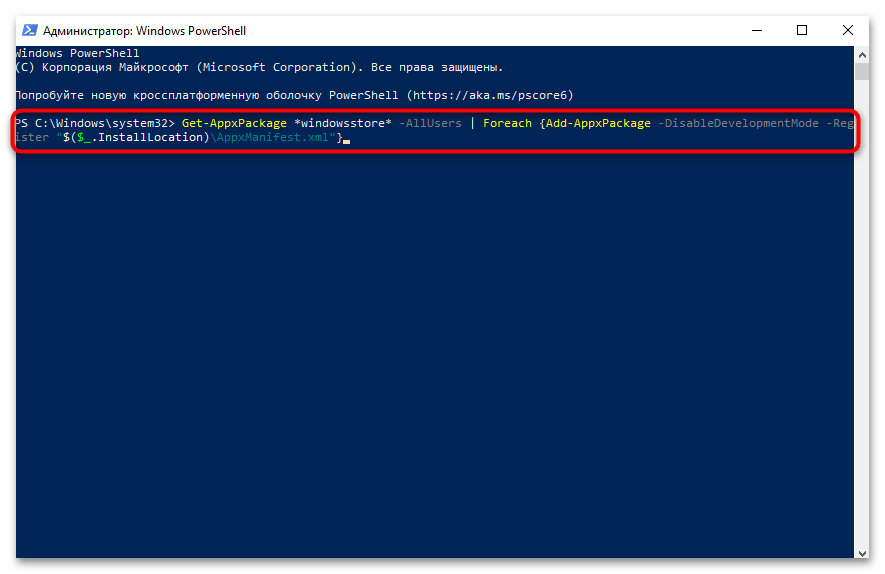
Способ 2: Восстановление Microsoft Store через PowerShell
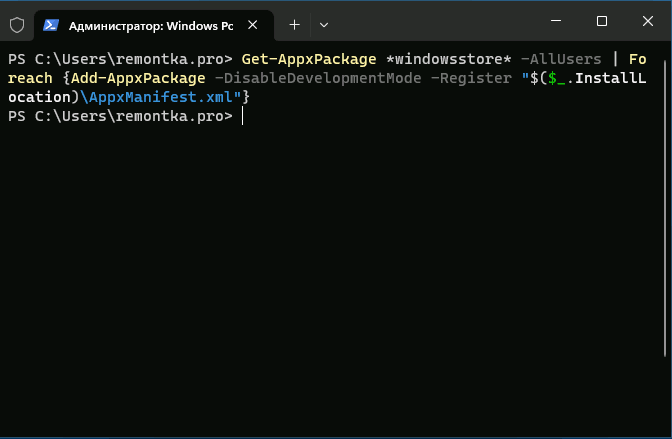
Этот метод позволяет восстановить Microsoft Store с помощью PowerShell, что особенно полезно, когда команда WSReset не работает или когда Microsoft Store был удален из системы.
- Нажмите комбинацию клавиш Win + X и выберите пункт Windows PowerShell (администратор) в появившемся меню.
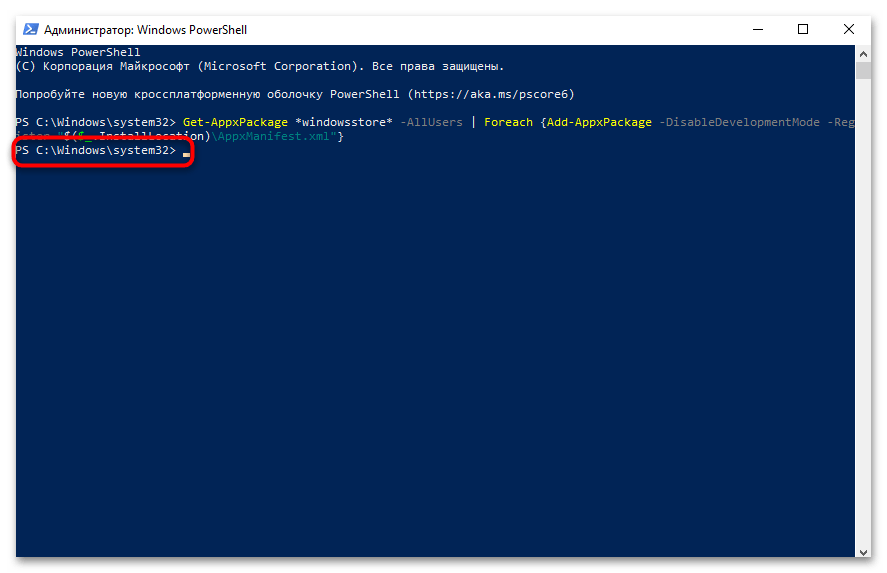
- В открывшемся окне PowerShell вставьте команду
Get-AppxPackage *windowsstore* -AllUsers | Foreach {Add-AppxPackage -DisableDevelopmentMode -Register "$($_.InstallLocation)\AppxManifest.xml"}и нажмите Enter. - Дождитесь завершения выполнения команды. Это может занять несколько минут, в зависимости от производительности вашего компьютера.
- Если у вас возникает ошибка или команда не находит пакет Microsoft Store, возможно, он был полностью удален из системы. В этом случае вам потребуется загрузить пакеты зависимостей и сам пакет Microsoft Store. Об этом будет рассказано в следующем методе.
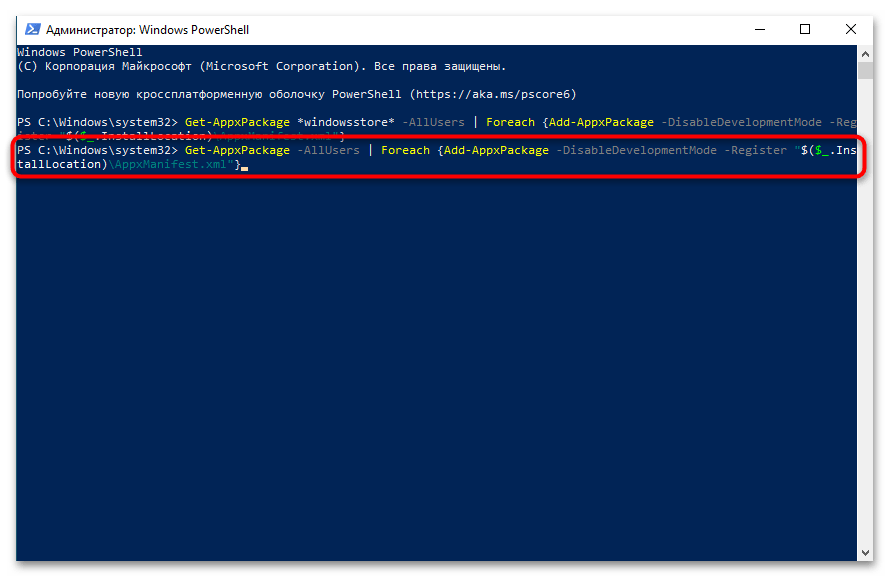
- Если вы столкнулись с ошибкой, связанной с отсутствием файлов, попробуйте выполнить следующую команду для восстановления всех системных приложений:
Get-AppxPackage -AllUsers | Foreach {Add-AppxPackage -DisableDevelopmentMode -Register "$($_.InstallLocation)\AppxManifest.xml"} - После успешного выполнения команды перезагрузите компьютер и проверьте, появился ли Microsoft Store в меню «Пуск».
Способ 3: Предварительная загрузка пакетов для Microsoft Store
Для полноценной работы Microsoft Store требуется установка нескольких компонентов и пакетов зависимостей. Данный вариант будет особенно полезен, если в вашей системе полностью отсутствуют необходимые файлы и при выполнении предыдущих команд появляются разнообразные ошибки.
Перед установкой Microsoft Store необходимо убедиться, что в системе присутствуют следующие обязательные пакеты:
- Microsoft.VCLibs.140.00;
- Microsoft.NET.Native.Framework;
- Microsoft.NET.Native.Runtime;
- Microsoft.UI.Xaml.
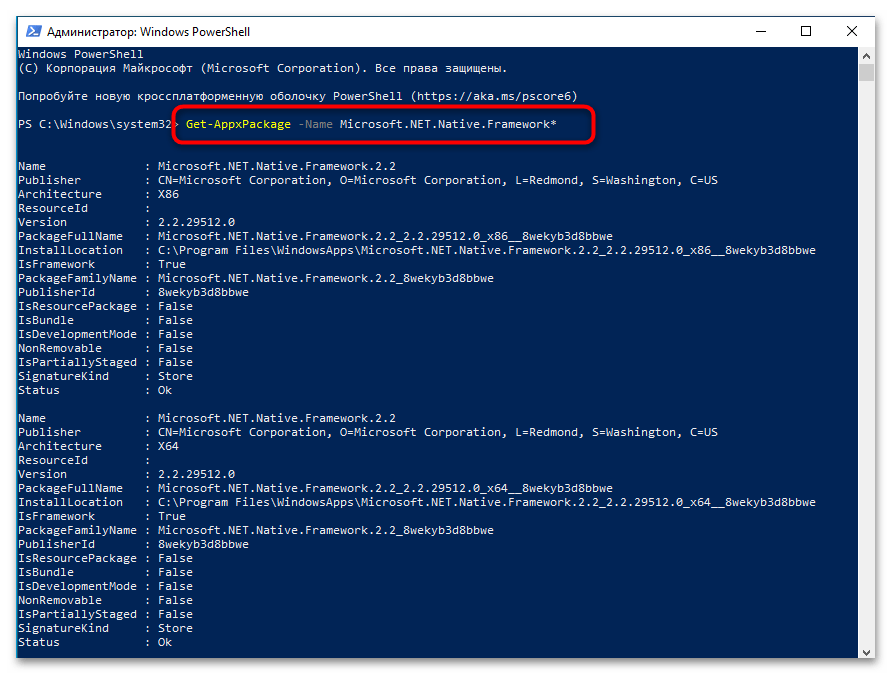
Для этого используйте уже знакомый PowerShell, введя команду Get-AppxPackage -Name + имя пакета (можете скопировать его из списка выше). Так проверните со всеми пакетами, посмотрите, какие будут обнаружены, а какие отсутствуют. Отталкивайтесь от этого при выполнении дальнейших действий.
Для загрузки этих пакетов в случае отсутствия любого из них можно использовать официальный сайт Microsoft или специализированные ресурсы. Удобнее всего скачать их с сайта для генерировании ссылок.
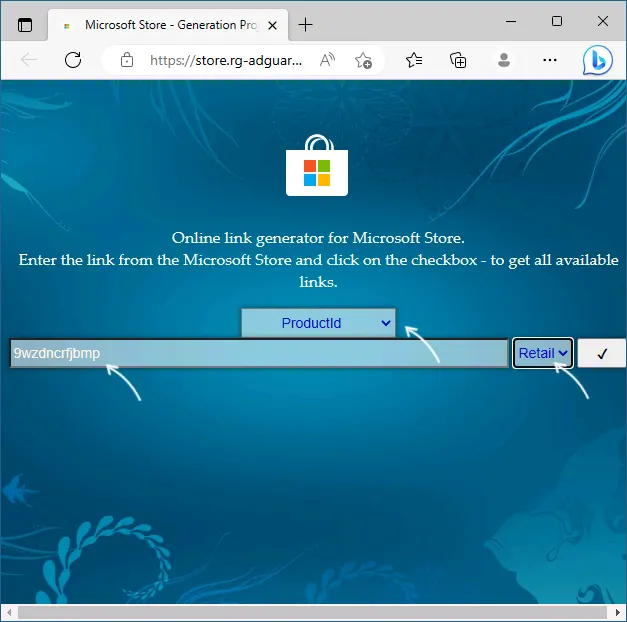
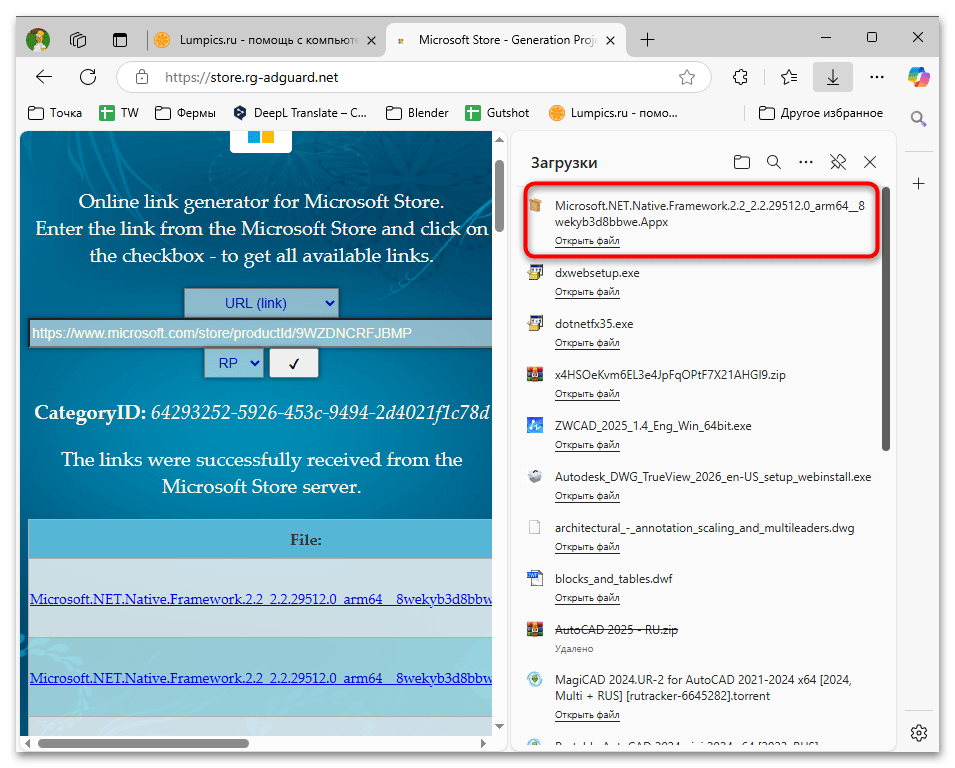
- Посетите сайт Online link generator for Microsoft Store по ссылке выше (неофициальный, но безопасный ресурс для загрузки пакетов из Microsoft Store).
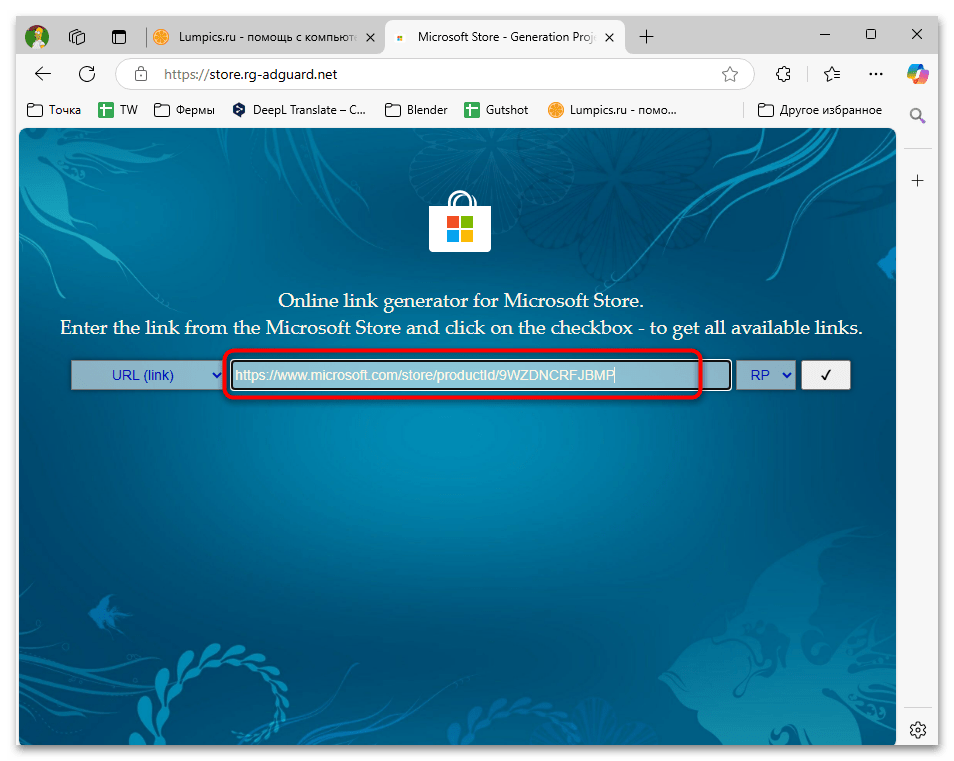
- В поле ввода URL вставьте ссылку на поиск необходимых пакетов:
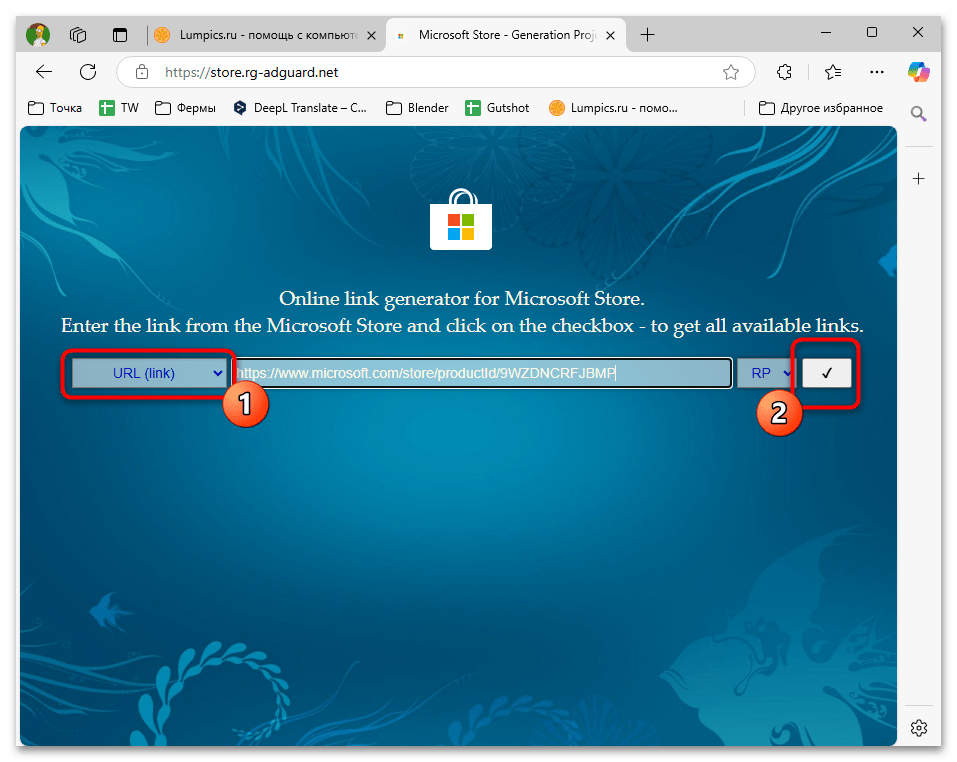
https://www.microsoft.com/store/productId/9WZDNCRFJBMP. - Выберите в выпадающем списке тип «URL (Link)» и нажмите кнопку для проверки данных.
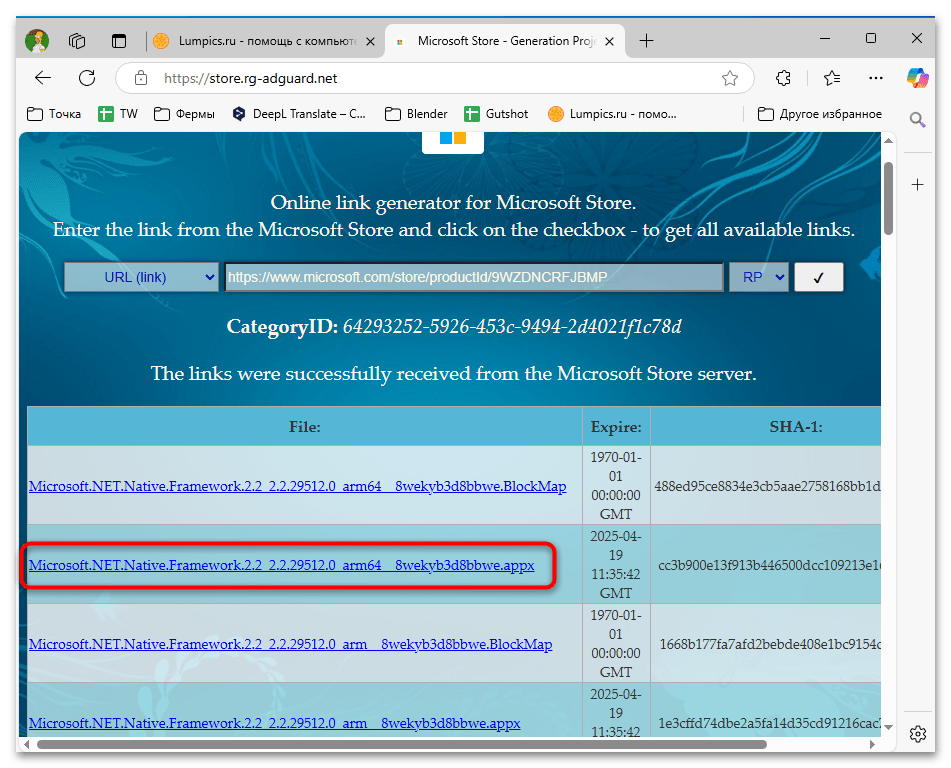
- Среди отображаемых файлов найдите и скачайте необходимые пакеты зависимостей (.appx или .appxbundle файлы):
- Microsoft.VCLibs.140.00__x64.appx;
- Microsoft.NET.Native.Framework..appx;
- Microsoft.NET.Native.Runtime..appx;
- Microsoft.UI.Xaml..appx;
- WindowsStore_.appxbundle (сам Microsoft Store).
- После загрузки всех необходимых пакетов, установите их в следующем порядке. Для установки каждого пакета дважды щелкните по нему и следуйте инструкциям на экране:
- Сначала установите Microsoft.VCLibs;
- Затем Microsoft.NET.Native.Framework;
- Потом Microsoft.NET.Native.Runtime;
- Далее Microsoft.UI.Xaml;
- И наконец, сам пакет WindowsStore.
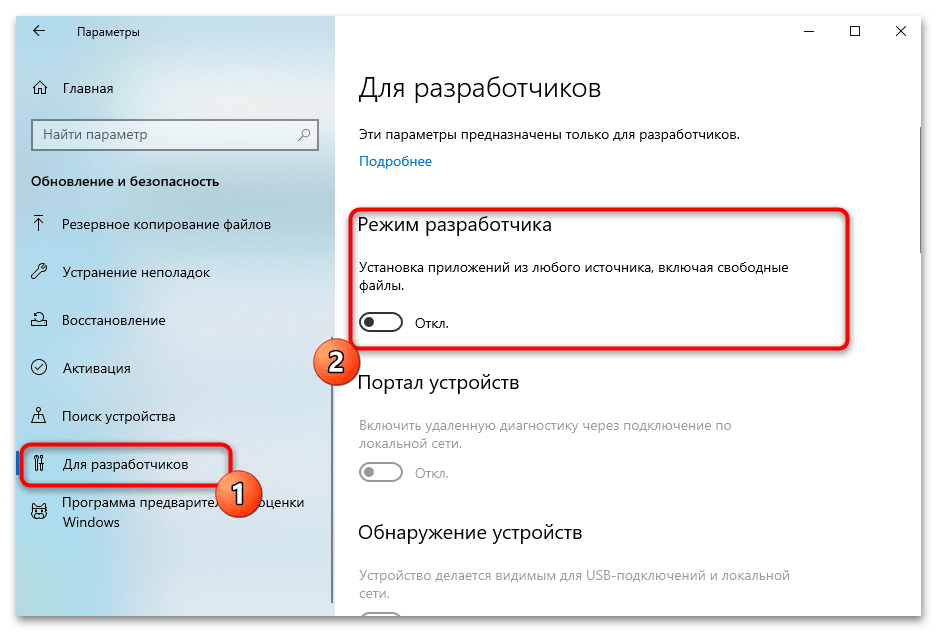
- Если при установке пакетов возникает ошибка о том, что разработчик приложения не надежный, вам нужно включить режим разработчика в настройках Windows. Для этого откройте «Параметры» — «Обновление и безопасность» — «Для разработчиков» и выберите «Режим разработчика».
- После установки всех пакетов перезагрузите компьютер и проверьте наличие Microsoft Store в меню «Пуск».
Перейти к онлайн-сервису Online link generator for Microsoft Store
Вам нужно скачивать файлы следующей архитектуры:
- Для 64-битной версии Windows 10 (большинство современных компьютеров). выбирайте файлы с пометкой x64.
- Для 32-битной версии Windows 10 (устаревшие компьютеры). выбирайте файлы с пометкой x86.
- Для устройств на базе ARM (некоторые планшеты Surface и другие). выбирайте файлы с пометкой ARM или ARM64.
При загрузке пакетов, таких как Microsoft.NET.Native.Framework, Microsoft.VCLibs и других зависимостей, обязательно выбирайте версию, соответствующую архитектуре вашей системы. Несоответствие архитектуры приведет к ошибке при установке.
Кроме того, если вы используете сайт store.rg-adguard.net или другие ресурсы для загрузки пакетов, обратите внимание, что некоторые пакеты имеют универсальные версии (помеченные как «neutral»), которые работают на любой архитектуре.
Способ 4: Перенос файлов Microsoft Store с другой копии Windows
Этот метод предполагает использование работающей копии Windows 10 в качестве источника файлов Microsoft Store. Это может быть другой физический компьютер, ноутбук, виртуальная машина или даже «чистая» система, установленная на другой раздел вашего жесткого диска. Преимущество этого метода в том, что вы получаете гарантированно совместимые файлы, которые уже работают в системе той же версии, что и ваша. Особенно полезен этот способ, когда другие не помогают из-за отсутствия доступа к интернету или проблем с загрузкой официальных пакетов.
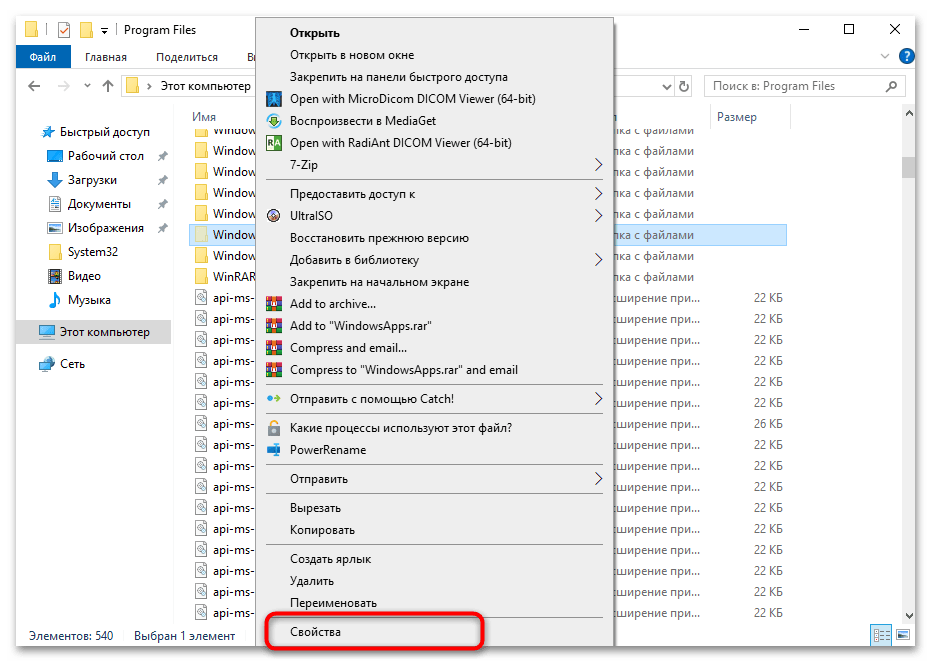
- На компьютере с рабочим Microsoft Store откройте проводник и перейдите по следующему пути:
C:\Program Files\WindowsApps. - Обратите внимание, что для доступа к этой папке вам потребуются права администратора. Если у вас нет доступа к папке, выполните следующие шаги. Сначала щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по папке WindowsApps и выберите «Свойства».
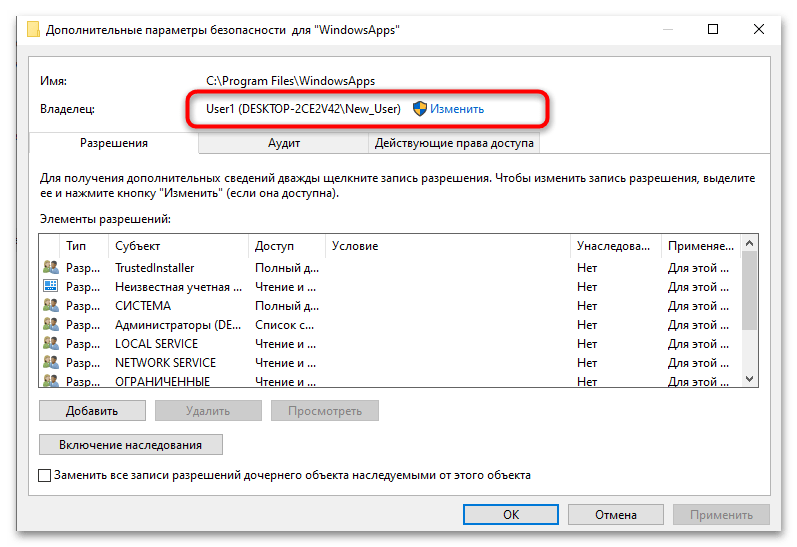
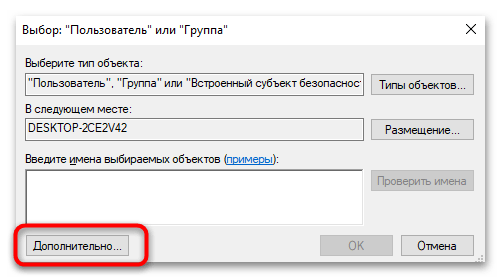
- Перейдите на вкладку «Безопасность» и нажмите «Дополнительно».
- Нажмите «Изменить», чтобы перейти к меню изменения владельца для данной директории.
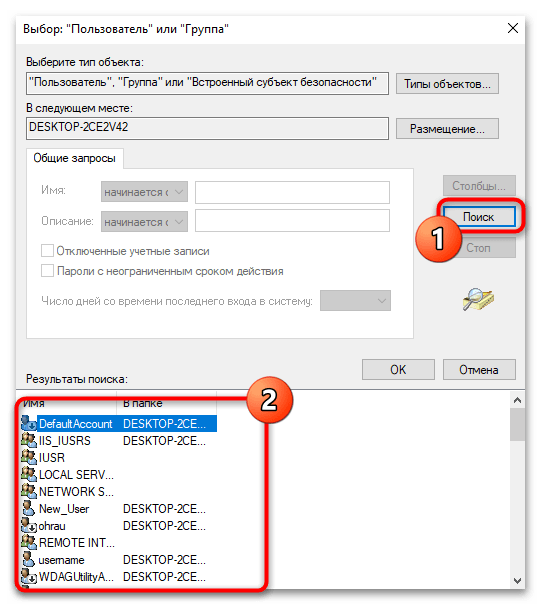
- Можете ввести имя пользователя вручную, но удобнее будет обнаружить его через «Дополнительно».
- Выполните поиск и отыщите свою учетную запись. Назначьте ее в качестве владельца данной директории.
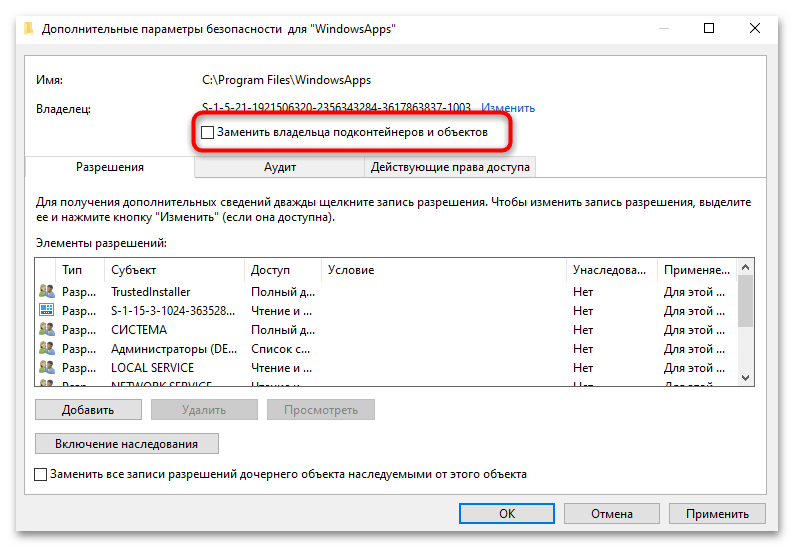
- Установите флажок «Заменить владельца подконтейнеров и объектов» и нажмите «ОК».
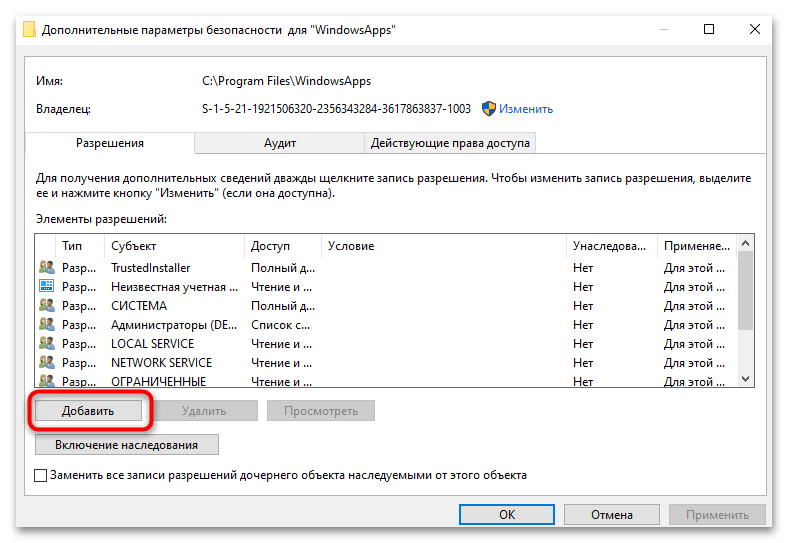
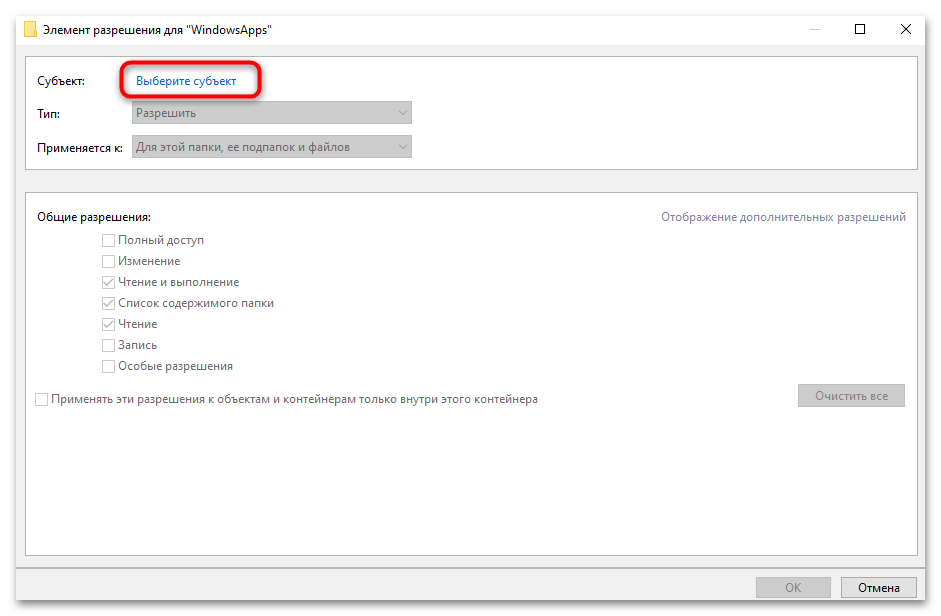
- Вернувшись в окно дополнительных параметров безопасности, нажмите «Добавить».
- Нажмите «Выбрать субъект» и введите имя вашей учетной записи.
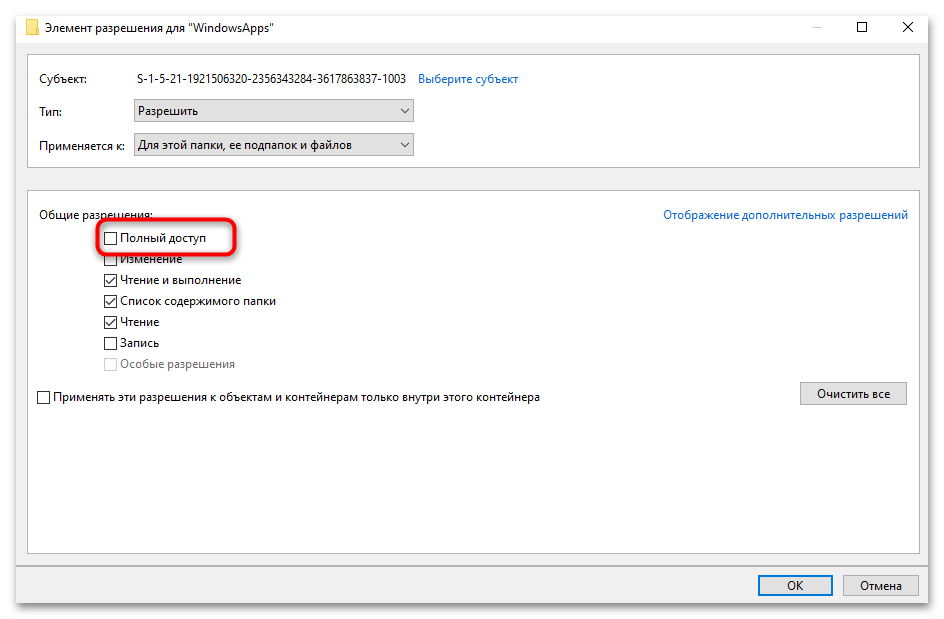
- Установите «Полный доступ» в разделе основных разрешений и нажмите «ОК».
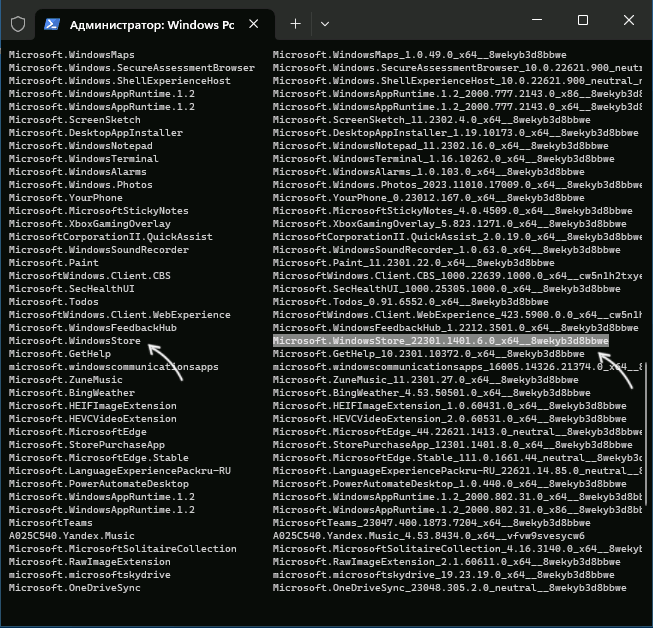
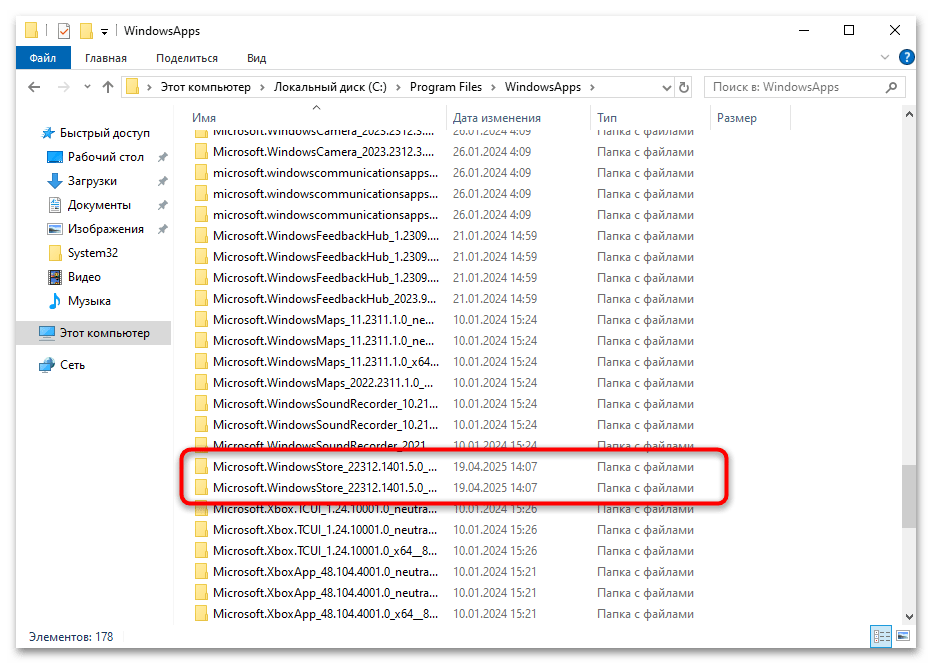
- После получения доступа найдите в папке WindowsApps все папки, начинающиеся с Microsoft.WindowsStore и Microsoft.StorePurchaseApp. Скопируйте эти папки на внешний носитель.
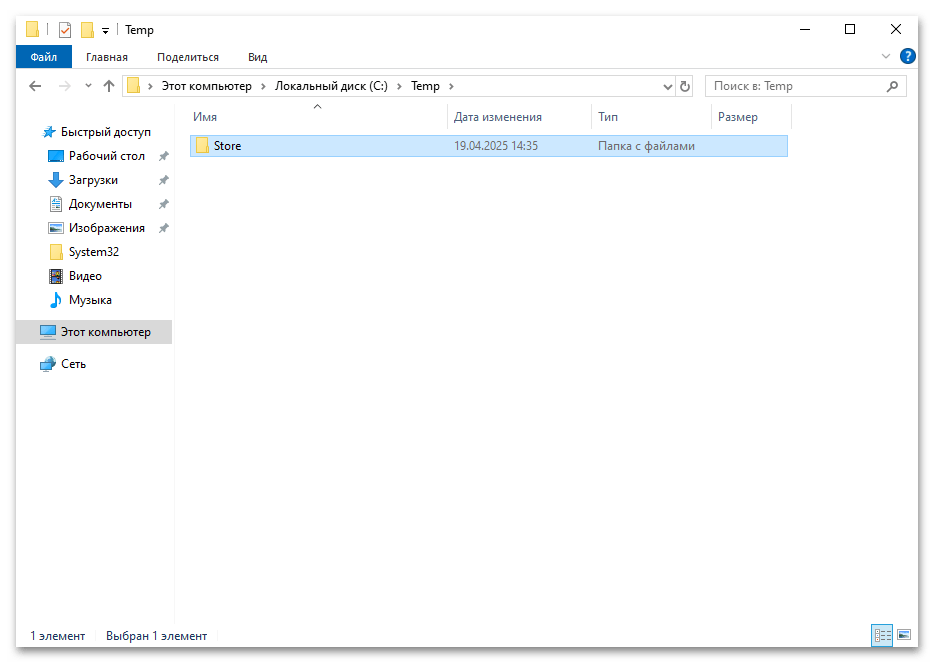
- На целевом компьютере, где отсутствует Microsoft Store, создайте временную папку, например, C:\Temp\Store. Скопируйте в эту папку все файлы, перенесенные с другого компьютера.
- Откройте PowerShell от имени администратора и выполните следующую команду для каждого пакета (заменяя путь на актуальный):
Add-AppxPackage -Register "C:\Temp\Store\Microsoft.WindowsStore_xxxxxxxxx\AppxManifest.xml" -DisableDevelopmentMode - Повторите команду для всех скопированных пакетов, изменяя путь соответствующим образом.
- После установки всех пакетов перезагрузите компьютер и проверьте, появился ли Microsoft Store в меню «Пуск».

Способ 5: Установка Microsoft Store через файл APPX
Этот метод подразумевает загрузку и установку пакета APPX, содержащего Microsoft Store, вручную. Он особенно полезен, если стандартные методы восстановления не помогли.
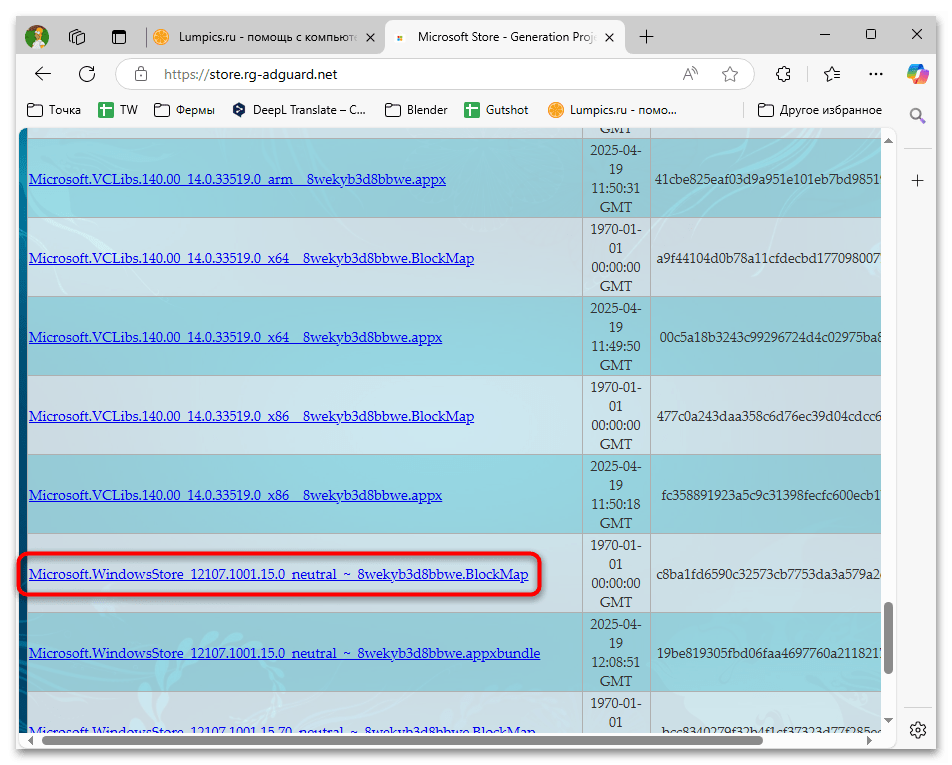
- Сначала понадобится загрузить пакет Microsoft Store. Его можно найти на официальных ресурсах Microsoft или с помощью сайта https://store.rg-adguard.net/, как описано в Способе 3. Обычно пакет будет называться примерно как
Microsoft.WindowsStore_12107.1001.15.0_neutral_~_8wekyb3d8bbwe.BlockMap. - После загрузки файла .appx или .appxbundle с приведенного выше сайта, щелкните по нему правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Свойства».
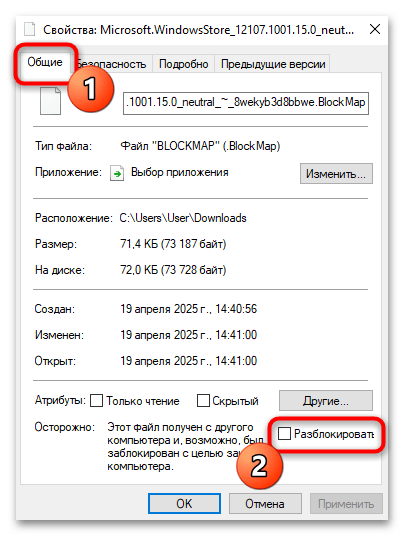
- Перейдите на вкладку «Общие» и в нижней части окна поставьте галочку напротив «Разблокировать» (если такая опция присутствует), затем нажмите «ОК».
- Теперь дважды щелкните по файлу, чтобы начать процесс установки. Если система не распознает формат .appx, вам потребуется сначала включить режим разработчика, как это уже было показано ранее.
- После включения режима разработчика попробуйте снова установить пакет Microsoft Store.
- Если во время установки появляется ошибка о зависимостях, вам может потребоваться установить сначала дополнительные пакеты, как описано в Способе 3.
Если все предыдущие методы не помогли, можно прибегнуть к сбросу Windows 10 с сохранением личных файлов. Это более радикальный метод, но он гарантированно вернет стандартные компоненты системы, включая Microsoft Store.
- Сделайте резервную копию важных данных перед началом процесса, хотя Windows предлагает опцию сохранения личных файлов.
- Откройте «Параметры» Windows, нажав комбинацию клавиш Win + I или отыскав его через меню «Пуск».
- Перейдите в раздел «Обновление и безопасность».
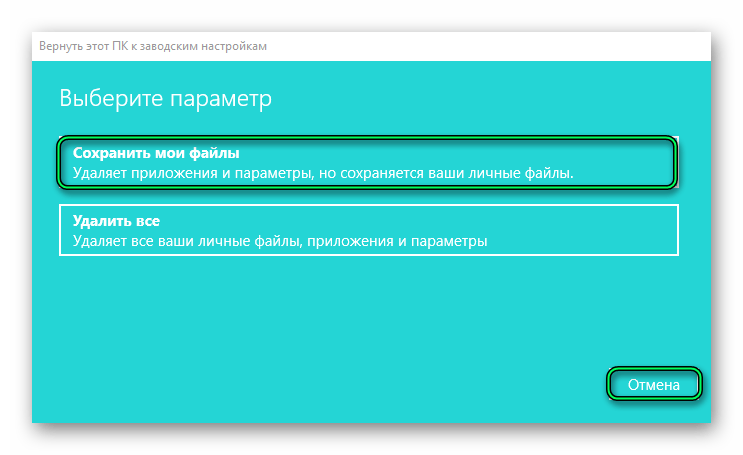
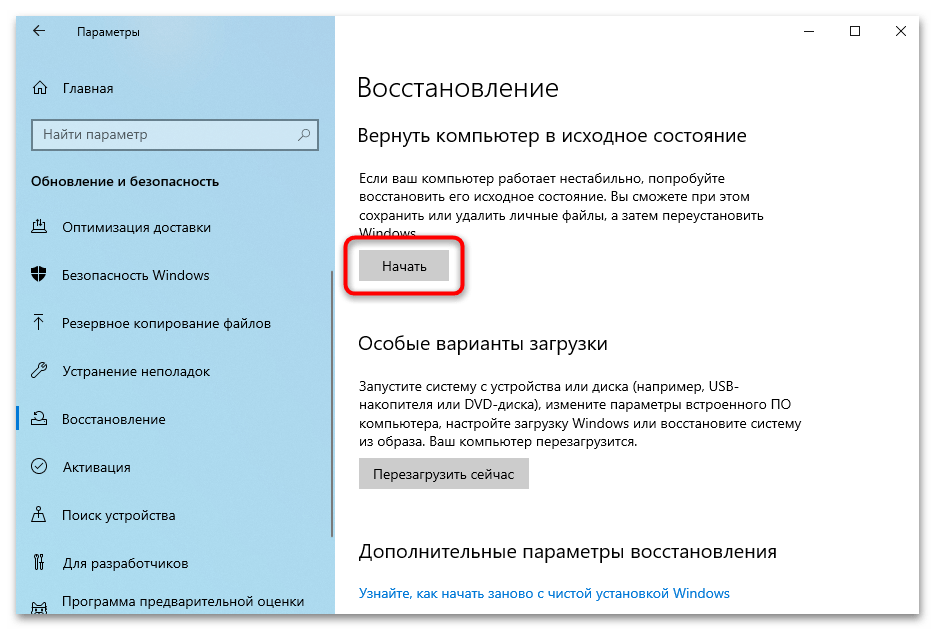
- Выберите «Восстановление» в левой панели. В разделе «Вернуть компьютер в исходное состояние» нажмите кнопку «Начать».
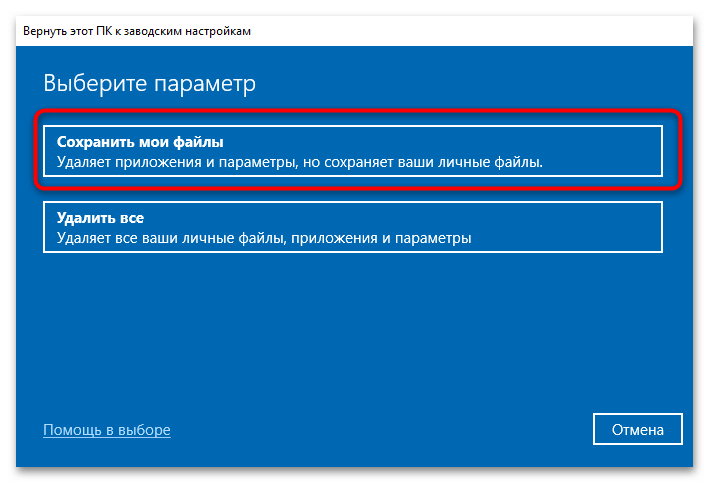
- Выберите опцию «Сохранить мои файлы», чтобы сохранить все личные данные при сбросе Windows.
- Следуйте инструкциям на экране для завершения процесса сброса.
- После сброса Windows 10 Microsoft Store должен быть доступен по умолчанию, так как будут восстановлены все стандартные компоненты системы.
- Обратите внимание, что вам потребуется переустановить все программы, которые были установлены ранее, так как сброс затрагивает только системные файлы, сохраняя личные данные.
Дополнительные рекомендации
Перед тем как приступить к установке Microsoft Store, рекомендуем ознакомиться с несколькими важными советами, которые могут значительно упростить процесс. Эти рекомендации основаны на опыте множества пользователей и специалистов, сталкивавшихся с различными проблемами при установке Microsoft Store. Следование этим советам поможет избежать распространенных ошибок и сделает процесс восстановления приложения более эффективным.
- Перед началом любой операции по восстановлению Microsoft Store убедитесь, что ваша система обновлена до последней версии Windows 10.
- Если вы используете модифицированную версию Windows 10, рассмотрите возможность перехода на официальную версию для обеспечения полной совместимости со всеми компонентами Microsoft.
- В случае с корпоративными компьютерами, обратитесь к системному администратору, так как Microsoft Store мог быть отключен намеренно в соответствии с политикой организации.
- Если вы не можете установить Microsoft Store ни одним из указанных способов, возможно, стоит рассмотреть чистую установку Windows 10 с официального образа Microsoft.
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
Если вы удалили Microsoft Store с компьютера, или его изначально не было, например, в версиях LTSC/LTSB, магазин приложений сравнительно просто можно установить.
В этой пошаговой инструкции о том, как установить Microsoft Store в Windows 11 и Windows 10 несколькими способами: один из них, вероятнее всего, сработает в вашей ситуации.
Установка Microsoft Store с помощью WSReset.exe
В Windows 11/10, причем даже в версиях, поставляющихся без магазина Microsoft Store (ранее — Windows Store), присутствует встроенная утилита wsreset.exe, позволяющая, в том числе, выполнить переустановку магазина приложений.
Шаги будут следующими:
- Запустите Windows PowerShell или Терминал от имени Администратора: нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по кнопке «Пуск» и выберите соответствующий пункт в контекстном меню.
- Введите команду
wsreset -i
и нажмите Enter.
- Выполнение команды займет время, при этом процесс отображаться не будет: дождитесь, когда снова появится приглашение для ввода команды — окно консоли можно закрыть.
- Через некоторое время (не моментально) вы увидите уведомление о том, что Microsoft Store был установлен в системе.
- Значок Microsoft Store появится в меню Пуск, при необходимости вы можете закрепить его в панели задач — нажмите по нему правой кнопкой мыши и выберите нужный пункт меню.
Этот способ работает как обычных домашней и профессиональной, так и в корпоративных редакциях Windows.
Windows PowerShell
Ещё одна возможность установки магазина Microsoft Store — использование команды развертывания пакета приложения, может не работать в некоторых редакциях Windows 11/10:
- Запустите PowerShell или Терминал от имени Администратора, используя контекстное меню кнопки «Пуск».
- Введите команду
Get-AppxPackage *windowsstore* -AllUsers | Foreach {Add-AppxPackage -DisableDevelopmentMode -Register "$($_.InstallLocation)\AppxManifest.xml"}и нажмите Enter.
- Дождитесь завершения установки пакета.
В результате Microsoft Store будет установлен и доступен в меню «Пуск».
Если команда сообщила об ошибках, можно попробовать следующий вариант:
- Введите команду
Get-AppxPackage -AllUsers | Select Name, PackageFullName
в Windows PowerShell.
- Отобразится список приложений, доступных в системе среди них может оказаться Microsoft.WindowsStore. При его наличии, выделите полное имя приложения в правом столбце и скопируйте его в буфер обмена (Ctrl+C).
- Введите команду (вставив вместо полное_имя скопированный текст):
Add-AppxPackage -DisableDevelopmentMode -Register "C:\Program Files\WindowsApps\полное_имя\AppxManifest.xml"
и нажмите Enter.
- Дождитесь завершения установки.
Скачивание Microsoft Store и его установка вручную
Вы можете скачать файл приложения «Microsoft Store» последней версии и установить его вручную, так же с помощью PowerShell:
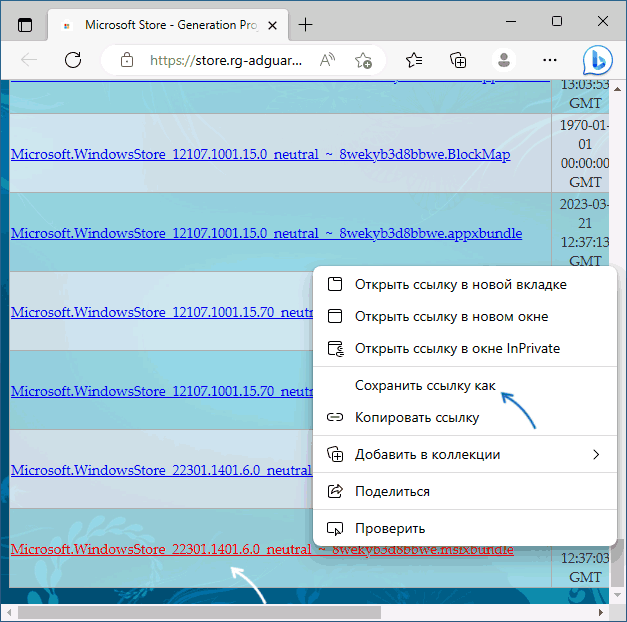
- Зайдите на сайт https://store.rg-adguard.net/ выберите «ProductId», укажите значение 9wzdncrfjbmp а в последнем поле выберите «Retail» и нажмите по кнопке с «галочкой».
- Отобразится список пакетов с указанным ID, нас интересует файл (версия может отличаться)
Microsoft.WindowsStore_22301.1401.6.0_neutral_~_8wekyb3d8bbwe.msixbundle
нажмите по нему правой кнопкой мыши, выберите пункт «Сохранить ссылку как» и укажите место сохранение (простое нажатие по файлу для скачивания может работать неправильно). Не закрывайте страницу, она может пригодиться далее.
- Скопируйте путь к скачанному файлу (правый клик по файлу в проводнике — копировать как путь).
- Откройте PowerShell или Терминал от имени Администратора.
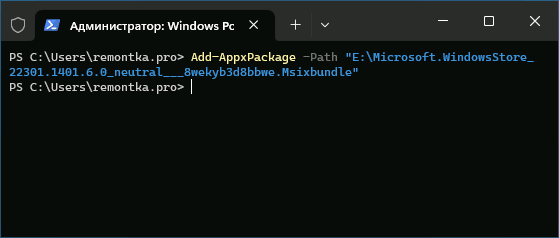
- Введите команду (путь можно вставить из буфера обмена):
Add-AppxPackage -Path путь_к_файлу.msixbundle
и дождитесь завершения установки Microsoft Store.
- Если на 5-м шаге вы получили сообщение об ошибке, дополнительно скачайте
Microsoft.UI.Xaml.2.7_7.2109.13004.0_x64__8wekyb3d8bbwe.appx
с той же страницы, выполните установку приложения с помощью той же команды, а уже после этого — установите первый скачанный файл.
Теоретически, могут потребоваться также пакеты NET.Native.Runtime и VCLibs (x86 и x64) с той же страницы загрузок, но обычно они уже установлены на компьютере.
Вероятнее всего, один из предложенных способов, при наличии необходимых для работы Microsoft Store компонентов (.NET, распространяемые компоненты Visual C++) сработает. Если же этого не произошло, несколько дополнительных вариантов:
- Использовать установщик LTSC-Add-MicrosoftStore — он устанавливает старую версию Microsoft Store, но в дальнейшем она обновляется автоматически. Использование: скачать архив ZIP, распаковать, запустить Add-Store.cmd от имени администратора.
- С другого компьютера или из виртуальной машины скопировать папки, относящиеся к WindowsStore из папки C:\Program Files\WindowsApps (потребуется получать права на доступ к папке, может привести к проблемам с работой встроенных приложений) в аналогичную папку на текущем компьютере, затем использовать команду PowerShell
ForEach ($folder in get-childitem) {Add-AppxPackage -DisableDevelopmentMode -Register "C:\Program Files\WindowsApps\$folder\AppxManifest.xml"} - Запустить сброс системы (если изначально она поставлялась с магазином приложений), это можно сделать и с сохранением данных: Как сбросить Windows 11, Как сбросить Windows 10.
Надеюсь, один из предложенных вариантов помог выполнить установку Microsoft Store на вашем компьютере или ноутбуке.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The following is a list of Microsoft Windows components.
Configuration and maintenance
[edit]
| Component | Description | Command | Introduced |
|---|---|---|---|
| Settings | Allows users to change system settings, similar to the Control Panel, but has less options[1] | start ms-settings:
|
Windows 8 |
| Control Panel | |||
| Control Panel | Allows users to view and change basic system settings and controls, such as adding hardware, adding and removing software, controlling user accounts, and changing accessibility options | control.exe
|
Windows 1.0 |
| Device Manager | Allows the user to display and control the hardware attached to the computer, and control what device drivers are used | devmgmt.msc
|
Windows 95 |
| Windows Mobility Center | Centralizes the most relevant information related to mobile computing | mblctr.exe
|
Windows Vista |
| Security and Maintenance | Centralizes and reports on the status of anti-virus, Automatic Updates, Windows Firewall, and other security-related components of the operating system | Windows XP SP2 | |
| Administrative Tools | |||
| Microsoft Management Console | Provides system administrators and advanced users with a flexible interface through which they may configure and monitor the system | mmc.exe
|
Windows NT 4.0 Option Pack |
| Windows System Assessment Tool | Built-in benchmarking tool that analyzes the different subsystems (graphics, memory, etc.), and uses the results to allow for comparison to other Windows Vista systems, and for software optimizations. It rates the computer’s performance using the Windows Experience Index. | winsat.exe
|
Windows Vista |
| System Restore | Allows for the rolling back of system files, registry keys, installed apps, etc., to a previous state in the event of a system failure | rstrui.exe
|
Windows Me |
| Windows Recovery Environment | Helps diagnose and recover from serious errors which may prevent Windows from booting successfully, or restore the computer to a previous state using System Restore or a backup image | shutdown /r /o
|
Windows Vista |
| Microsoft Drive Optimizer | Rearranges files stored on a hard disk to occupy contiguous storage locations in order to optimize computer performance | dfrgui.exe
|
Windows 95, Windows 2000 |
| Event Viewer | Lets administrators and users view the event logs on a local or remote machine | eventvwr.msc
|
Windows NT 3.1 |
| Resource Monitor (previously Reliability and Performance Monitor) |
Lets administrators view current system reliability and performance trends over time | resmon.exe
|
Windows Vista |
| Logical Disk Manager | Logical volume manager developed by Microsoft in conjunction with Veritas Software | diskmgmt.msc
|
Windows NT 4.0 (Separate Tool), Windows 2000 |
| Registry Editor | Allows users to browse and edit the Windows registry | regedit.exe
|
Windows 3.1 |
| Windows Task Scheduler | Allows users to script tasks for running during scheduled intervals | taskschd.msc
|
Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 |
| Software installation and deployment | |||
| Windows Update | An online service providing updates such as service packs, critical updates and device drivers. A variation called Microsoft Update also provides software updates for other Microsoft products. | control.exe update
|
Windows 98 |
| Windows Installer | An engine for the management of software installation. Includes a GUI framework, automatic generation of the uninstallation sequence and deployment capabilities for corporate networks. | msiexec.exe
|
Office 2000 |
| ClickOnce | Technology for deploying .NET Framework-based software via web pages, with automatic update capabilities. Intended for per-user only applications. | mage.exe and mageUI.exe
|
.NET Framework 2.0 |
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Action Center | View notifications sent from apps and change common settings | Windows 7 |
| Windows Command Prompt | Text-based shell (command line interpreter) that provides a command line interface to the operating system | Windows NT 3.1 |
| PowerShell | Command-line shell and scripting framework. | Windows XP |
| Windows Shell | The most visible and recognizable aspect of Microsoft Windows. The shell provides the container inside of which the entire graphical user interface is presented, including the taskbar, the desktop, Windows Explorer, as well as many of the dialog boxes and interface controls. In Windows Vista, a new compositing glass-like user interface called Windows Aero has been shown. | Windows 95 |
| File Explorer (previously Windows Explorer) |
Provides an interface for accessing the file systems, launching applications, and performing common tasks such as viewing and printing pictures | Windows 95 |
| Windows Search | Starting with Windows Vista, search is a tightly shell-integrated component of Windows. A downloadable Windows Desktop Search software is available for Windows XP and older versions. | Windows Vista, downloadable for older versions |
| Search Folders | Virtual folders that retrieve items based on queries rather than hierarchical folder trees on disk. | Windows Vista |
| Special folders | Folders which are presented to the user through an interface as an abstract concept, instead of an absolute path. This makes it possible for an application to locate where certain kinds of files can be found, regardless of what version or language of operating system is being used. See also Windows Shell namespace. | Windows 95 |
| Start menu | Serves as the central launching point for applications. It provides a customizable, nested list of apps for the user to launch, as well as a list of most recently opened documents, a way to find files and get help, and access to the system settings. By default, the Start Button is visible at all times in the lower left-hand corner of the screen. | Windows 95 |
| Taskbar | The application desktop bar which is used to launch and monitor applications | Windows 95 |
| Task View | Displays all open windows and activities (via timeline) at a glance and switch between virtual desktops, starting in version 2004, users can now rename desktops | Windows 10 |
| File associations | Used to open a file with the appropriate app. Users can assign file associations uniquely to specific actions, known as verbs. | Windows 1.0 |
Applications and utilities
[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Easy Transfer | Used to transfer many files at once from one computer to another | Windows Vista |
| Contacts | Keeps a single list of contacts that can be shared by multiple apps | Windows Vista |
| Camera | Allows the user to take pictures or record video[2] | Windows 8 |
| Calculator | Calculation application | Windows 1.0 |
| Calendar | Calendaring application | Windows Vista |
| Character Map | Utility to view and search characters in a font, copy them to the clipboard and view their Windows Alt keycodes and Unicode names | Windows 3.1 |
| Cortana | Digital personal assistant | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Edge | Web browser | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Feedback Hub | Platform for exchanging communication with Windows Insiders and developers | Windows 10 Version 1607 |
| Groove Music (previously Xbox Music) |
Digital media player and media library application that is used for playing audio. In addition to being a media player, Groove includes the ability to copy music to compact discs, synchronize content with a digital audio player (MP3 player) or other mobile devices, and let users purchase or rent music from the Windows Store. | Windows 8 |
| Movies & TV (previously Xbox Video) |
Digital media player and media library application that is used for playing video. In addition to being a media player, Movies & TV lets users purchase or rent movies and TV episodes from the Windows Store. | Windows 8 |
| OneDrive (previously SkyDrive) |
Freemium cloud storage folder and sync service | Windows 8 |
| Microsoft OneNote | Integrated note-taking app, based on the Microsoft Office product of the same name | Windows 8 |
| On-Screen Keyboard (osk.exe) | Virtual keyboard | |
| Paint 3D | Simple graphics painting app | Windows 10 Version 1703 |
| Photos | Simple image viewer | Windows 8 |
| Steps Recorder (called Problem Steps Recorder in Windows 7) |
Utility that allows the user to capture steps they took to reproduce a problem | Windows 7 |
| Windows To Go | Utility to create bootable versions of Windows 8 and above | Windows 8 |
| Notepad | Simple text editor | Windows 1.0 |
| Narrator | Screen reader utility that reads dialog boxes and window controls in a number of the more basic applications for Windows | Windows 2000 |
| Sound Recorder | Simple audio recording app that can record from a microphone or headset, and save the results in WAVE format and Windows Media Audio format in some Windows versions | Windows 3.0 Multimedia Extensions |
| Skype | Messaging and calling service | Windows 8.1, downloadable for previous versions |
| Sticky Notes | Tool for jotting notes on the desktop | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition |
| Private Character Editor | Utility to create private use characters as defined under Unicode and various East Asian encoding schemes | Windows 3.1 East Asian editions |
| Remote Desktop Connection | Client implementation of the Remote Desktop Protocol; allows a user to securely connect to a computer running Terminal Services (Remote Desktop on Windows XP and Server 2003) and interact with a full desktop environment on that machine, including support for remoting of printers, audio, and drives. | Windows XP, downloadable for previous Windows versions |
| Remote Assistance | Allows a user to temporarily take over a remote computer over a network or the internet to offer help with and resolve issues | Windows XP |
| Mobility Center | Allows a user to adjust settings related to mobile computing | Windows Vista |
| Speech Recognition | Allows a user to input voice commands | Windows Vista |
| IExpress | Allows users to create self-extracting, self-installing INF installation-based packages | Internet Explorer 6 |
| Xbox Console Companion (previously Xbox and Xbox Games) |
Account manager for Xbox Live user accounts and a screen recording tool | Windows 8 |
| Xbox Game Bar | Provides a overlay for compatible games allowing for screen capture, chatting over the Xbox network, showing the frame rate of games, and playing music via Spotify[3][4] | Windows 10 May 2019 Update (Version 1903)[5] |
| Magnifier | Screen enlargement app | Windows 98 |
| Fax and Scan | Integrated faxing and image scanning application | Windows Vista, older faxing and scanning applications were present in previous Windows versions |
| Photo Viewer | Simple image viewer that can play a simple slideshow | Windows XP |
| Email aggregator | Windows Vista | |
| Maps | Map viewer that allows users to look for locations, and plan routes | Windows 8 |
| Media Center | Designed to serve as a home-entertainment hub, to be viewed from a distance up to 3 meters (~10 feet) and controlled by specially designed remote controls. Lets users browse and view pictures, videos, and music from local hard drives, optical drives, and network locations, along with viewing, recording and deferred-playing live TV. Features an interactive TV guide with scheduled recording capabilities. Can also be used for visualization of other information (like sports scores) within the interface | Windows XP Media Center Edition |
| Task Manager | Provides information about computer performance and displays details about running applications, processes, network activity, logged-in users, and system services | Windows 3.0 |
| Disk Cleanup | Utility for compacting rarely used files and removing files that are no longer required | Windows 98 |
| Snipping Tool | Screen-capture tool that allows for taking screenshots (called snips) | Experience Pack for Windows XP Tablet PC Edition 2005 |
| Microsoft Store (previously Windows Store) |
Initially known as Windows Store, it started as an app store for Windows 8. In Windows 10, it expanded into a broad digital distribution platform for apps, games, music, digital video and e-books. In 2017, it was renamed Microsoft Store and started offering hardware in United States, Canada and United Kingdom. | Windows 8 |
| MSN apps | Provide information from MSN web services | Windows 8 |
| Alarms & Clock(pre Alarms) | App that allows Windows users to set alarms, stopwatches, timers, and view a world clock | Windows 8 |
| Windows Security (previously Windows Defender Security Center) |
Antivirus | Windows 10 Version 1703 |
| Solitaire Collection | Set of solitaire card games | Windows 10 Version 1507, downloadable for Windows 8.x |
Windows Server components
[edit]
| Component | Description | Supported by |
|---|---|---|
| Active Directory | A set of technologies introduced with Windows 2000 that allows administrators to assign enterprise-wide policies, deploy apps to many computers, and apply critical updates to an entire organization. Active Directory stores information and settings relating to an organization in a central, organized, accessible database. Networks can vary from a small installation with a few objects, to global-scale directories with millions of objects. Related topics: Domain controller, Flexible single master operation |
Windows 2000 and later server versions |
| Group Policy | Provides centralized management of user and computer settings in an Active Directory environment. Group policy can control a target object’s registry, NTFS security, audit and security policy, software installation, logon/logoff scripts, folder redirection, and Internet Explorer settings. Policy settings are stored in Group Policy Objects (GPOs), and may be linked to one or more sites, domains or organizational units. Related topics: Administrative Templates |
Windows 2000 and later |
| Internet Information Services | Web server | Windows NT family |
| Component | Description | Supported by |
|---|---|---|
| FAT12, FAT16 | The original file systems used with MS-DOS. The standard file systems used with Windows 1.0 through Windows 95. | All versions |
| FAT32 | Extensions to FAT supporting larger disk sizes. The standard file system for Windows 98 and Me. | Windows 95 OSR2 and later versions |
| NTFS | Standard file system of Windows NT; supports security via access-control lists, as well as file system journaling and file-system metadata. Windows 2000 added support for reparse points (making NTFS junction points and Single instance storage possible), Hard links, file compression, and Sparse files. Encryption of data is provided by Encrypting File System. Symbolic links and transactioning of file operations via Transactional NTFS are features new to Windows Vista. Although Windows 9x operating systems cannot read or write NTFS formatted disks, they can access the data over a network if it is shared by a computer running Windows NT. | Windows NT (all versions) |
| ISO 9660 (CDFS) | The predominant file system for CD-ROM and DVD-ROM media. Windows includes support for Joliet extensions and the ISO 9660:1999 standard. ISO 9660:1999 is supported since Windows XP. | MS-DOS and Windows 9x via extensions, such as MSCDEX.EXE (Microsoft CDROM Extension), natively in Windows NT 3.5 |
| Universal Disk Format (UDF) | A file system for storing files on optical media. It is an implementation of the ISO/IEC 13346 standard (also known as ECMA-167). It is considered to be a replacement of ISO 9660. Successive versions of Windows have supported newer versions of UDF. | Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista |
| HPFS | High-Performance File system, used on OS/2 computers. Read and write capability in Windows 95 (where it also listed network computer NTFS-formatted drives as «HPFS», even though it had no direct NTFS capabilities). HPFS write support was dropped in Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 98, and dropped altogether shortly before the release of Windows 2000. | Windows 95 (Read/write), Windows 98, Windows NT (read), 3.1/3.51 (read/write/boot) |
| ReFS | A newer file system, based on NTFS. This system adds built-in integrity checking and removes the need for chkdsk, among other features. The maximum partition size is 1 YB. | Windows Server 2012, Windows 8.1 |
| Component | Acronym | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Windows kernel (Windows NT)
Main article: Architecture of Windows NT |
||
| Ntoskrnl.exe | The Windows kernel image. Provides the kernel and executive layers of the kernel architecture, and is responsible for services such as hardware virtualization, process and memory management, etc. | |
| hal.dll | HAL | Provides and handles the interaction between software and hardware via the Hardware Abstraction Layer. |
| kernel32.dll | This application provides kernel operations to apps in the Win32 mode, like memory management, I/Os, process creation, etc. | |
| Core processes (Windows NT) | ||
| System Idle Process | SIP | A counter which measures how much idle capacity the CPU has at any given time. The process runs in the background and monitors processing bandwidth, occupied memory and the Windows virtual paging file. |
| Session Manager Subsystem | SMSS | Performs several critical boot-time operations, such as the creation of environment variables, starting CSRSS, and performing file-copy operations that were queued up from before the system was booted (pending file rename operations). During system operation, it handles Windows File Protection and the creation of logon sessions via Winlogon. |
| Client/Server Runtime Subsystem | CSRSS | User-mode side of the Win32 subsystem. Provides the capability for applications to use the Windows API. |
| Local Security Authority Subsystem Service | LSASS | Responsible for enforcing the security policy on the system. Verifies users logging on to the computer and creates security tokens. |
| Winlogon | Responsible for handling the secure attention key, loading the user profile on logon, and optionally locking the computer when a screensaver is running. On Windows NT systems prior to Windows Vista, Winlogon is also responsible for loading GINA libraries which are responsible collecting logon credentials from the user. | |
| Svchost.exe | A generic host process name for services that run from dynamic-link libraries (DLLs). Several Svchost processes are typically present on a Windows machine, each running in a different security context, depending on what privileges the contained services require. | |
| Windows on Windows and WoW64 | WoW | An abstraction layer that allows legacy code to operate on more modern versions of Windows; typically this means running 16-bit Windows applications on 32-bit Windows, and 32-bit applications on 64-bit Windows. |
| Virtual DOS machine | NTVDM | Allows MS-DOS apps to run on Intel 80386 or higher computers when there is already another operating system running and controlling the hardware. Introduced in Windows 2.1; not available in any 64-bit edition of Windows. |
| System startup (Windows NT)
Main article: Booting process of Windows |
||
| NTLDR, IA64ldr, Winload | The bootloader; performs basic system initialization options such as loading the hardware abstraction layer and boot-time device drivers, prior to passing control to the Windows kernel. In versions prior to Vista, NTLDR and IA64ldr also display menus to the user if multiple operating systems are defined in boot.ini, or if F8 is pressed. | |
| Recovery Console | Provides the means for administrators to perform a limited range of tasks using a command line interface, primarily to aid in recovering from situations where Windows does not boot successfully. | |
| ntdetect.com | Used during the boot process to detect basic hardware components that may be required during the boot process | |
| Windows Boot Manager | In Windows Vista and later operating systems, displays boot menus to the user if multiple operating systems are configured in the system’s Boot Configuration Data. | |
| Graphical subsystem | ||
| Desktop Window Manager | DWM | The compositing manager introduced in Windows Vista that handles compositing and manages special effects on screen objects in a graphical user interface |
| Graphics Device Interface | GDI/GDI+ | The kernel graphics component for representing graphical objects and transmitting them to output devices such as monitors and printers |
| Windows USER | The Windows USER component provides core user interface, messaging and visual elements |
This list is not all-inclusive.
| Display name | Service key name | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active Directory Service | NTDS | Network Authentication Management | Windows 2000 Server |
| Alerter service | Alerter | Sends administrative alerts over the network to client computers, administrators and users | Windows NT |
| Application Layer Gateway service |
ALG | Provides support for plugins that allow network protocols to pass through Windows Firewall and work behind Internet Connection Sharing | Windows 2000 |
| Application Experience service | Processes application compatibility cache requests for applications as they launch[6] | ||
| Application Management | AppMgmt | Processes requests to enumerate, install, and remove applications that are installed on the computer or deployed through an organization’s network | Windows 2000 |
| Background Intelligent Transfer Service |
BITS | Transfers files between machines using idle network bandwidth. Used by Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, and Systems Management Server to deliver software updates to clients, as well as by Windows Messenger. | Windows XP |
| Computer Browser | Browser | Crawls neighboring computers on the network and locates shared resources. One of the computers acts as the Master Browser and supplies this information to other computers designated as browsers.[7] | Windows for Workgroups |
| Delivery Optimization | DoSvc | A peer-to-peer distribution service that downloads Windows updates and Microsoft Store apps from the local network or Internet peers, and redistributes them to others. Can be configured using either the Settings app or Group Policy. The Settings app can turn it on or off, and specify whether the service operates on the local network only, downloads from and uploads to the Internet peers as well. Group Policy allows finer control.[8][9] Delivery Optimization relies on a centralized web service that does not index contents under 10 MB. Computers without Internet access cannot use Delivery Optimization.[10] | Windows 10 Anniversary Update[8] |
| Distributed Link Tracking | TrkWks, TrkSrv | Used to track links to files on NTFS volumes. Windows uses these services to find linked files if they are renamed or moved (locally or to another machine).[11] | Windows 2000 |
| Distributed Transaction Coordinator |
MSDTC | Allows transactional components to be configured through COM+ by coordinating transactions that are distributed across multiple computers and/or resource managers, such as databases, message queues, file systems, and other transaction–based resource managers.[12] | Windows 2000 and later NT-based |
| DNS Client | DNSCache | Resolves and caches domain names (e.g. “en.wikipedia.org”) to IP addresses | Windows 2000 |
| Event Log | EventLog | Stores and retrieves events that can be viewed in the event viewer. Part of services.exe.[13] | Windows NT |
| Extensible Authentication Protocol | EAPHost | Provides EAP authentication to connecting clients | Windows 2000 |
| Indexing Service | CISVC | Indexes contents and properties of files on local and remote computers; provides rapid access to files through flexible querying language.[14] | Windows 2000 and later NT-based |
| Interactive Services Detection | UI0Detect | For compatibility; when a service-displayed user interface is detected, it gives the user an option to switch to Session0 to see it | Windows Vista |
| Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) | SharedAccess | When enabled, it allows other computers on the local network to access an internet connection that is available to the host computer | Windows 2000;[15] Windows Vista onward[16] |
| Network Location Awareness | NLA | Manages network configurations and information, and notifies applications of changes | Windows XP |
| Network Store Interface Service | NSIS | Collects routing information of active network interfaces, shares this with other services and notifies applications of changes | Windows XP |
| NTLM Security Support Provider | NTLMSSP | Uses the NTLM MS-CHAP protocol to encapsulate and negotiate options in order to provide signed and sealed communication. Deprecated now in favor of Kerberos authentication. | Windows NT |
| Peer Name Resolution Protocol | PNRPSvc | Resolves domain names using Peer Name Resolution Protocol | Windows XP |
| Plug and Play | PlugPlay | Enables autodetection and configuration of hardware | Windows 2000 |
| Windows Print spooler [fr] | Spooler | Manages printer devices and moves files into memory for printing | Windows 95, Windows NT |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) | RpcSs | Provides Remote Procedure Call features via remotely accessible Named Pipes | Windows NT family |
| Routing and Remote Access Service | RRAS | API and server software that enables applications to administer the routing and remote-access service capabilities of the operating system, to function as a network router. | Windows 2000 |
| Secondary Logon | SecLogon | Allows users to run apps with a different account than the one they logged in with. Allows non-administrative accounts to perform administrative tasks.[17] | |
| Security Account Manager | SamSs | Manages user account security information | Windows NT family |
| System Event Notification Service | SENS | Monitors system events, such as network, power, logon, logoff, terminal services session connection and disconnection, and delivers these to applications and other system components.[18] | Windows 2000 |
| Superfetch | SysMain | Monitors file usage patterns and boosts system speed by caching frequently accessed files to RAM[19] | Windows Vista |
| Task Scheduler | Schedule | Lets users setup and schedule automated tasks | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 |
| TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper | LmHosts | Enables support for NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) service and NetBIOS name resolution | Windows NT family |
| Volume Shadow Copy | VSS | Creates multiple versions of files that change. The ability to store persistent snapshots was added in Windows Server 2003.[20] | Windows XP |
| Windows Audio | AudioSrv | Manages audio devices for Windows-based apps. Controls all audio functions. | Windows XP |
| Windows Error Reporting | WERSvc | Generates error logs and reports errors. On Windows Vista and later, it notifies of solutions. | Windows XP |
| Windows Firewall | MpsSvc | Blocks unauthorized network connections to and from the computer | Windows Vista |
| Windows Firewall(née Internet Connection Sharing) | SharedAccess | Provides a simple firewall feature which was introduced in Windows XP. It also shares the internet on the local network, if the internet connection sharing feature is turned on.[21] | Windows XP only[22][23] |
| Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) | STISvc | Handles scanner and camera inputs | Windows Me |
| Windows Time | W32Time | Synchronizes the system time with external time servers. From Windows Server 2003 forward, full and compliant NTP support is provided.[24] | Windows 2000 |
| Windows Update | WUAUServ | Provides updates for the operating system and its installed components | Windows XP |
| Wireless Zero Configuration | WZCSvc (XP), WLANSvc | Configures and manages 802.11 wireless adapters | Windows XP, Server 2003 only |
| Windows Messenger service | Messenger | Allows users to send pop-up messages to other computers over the network | Windows NT family |
| WebClient[25] | Enables Windows-based apps to create and interact with Internet-based files | Windows XP |
- Direct3D
- DirectDraw
- DirectInput
- DirectMusic
- DirectPlay
- DirectShow
- DirectSound
- DirectX Media Objects
- DirectX plugin
- DirectX Video Acceleration
- Administrative share
- Distributed File System
- My Network Places (formerly Network Neighborhood)
- Network Access Protection
- Remote Installation Services
- Server Message Block
- Windows Rights Management Services
Scripting and command-line
[edit]
- Batch file
- CHKDSK
- Cmd.exe
- ComSpec
- Ipconfig
- Net / Net Send
- Netdom.exe: Windows Domain Manager
- Netsh
- Netstat
- QBasic
- Regsvr32
- Robocopy
- Win32 console
- Windows Script Host
- Windows PowerShell
- XCOPY
- Commit charge
- Kernel Transaction Manager
- Win32 Thread Information Block
- Assembly
- CLI Languages
- Metadata
- .NET Remoting
- ADO.NET
- ASP.NET
- Base Class Library
- Common Intermediate Language
- Common Language Infrastructure
- Common Language Runtime
- Common Type System
- Virtual Execution System
- Windows CardSpace
- Windows Communication Foundation
- Windows Forms
- Windows Presentation Foundation
- Windows Workflow Foundation
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| AppLocker | Policy-based component that enables or disables execution of software based on rules such as location, properties and digital signature | Windows 7 Professional, Enterprise and Ultimate editions Windows Server 2008 R2 |
| BitLocker Drive Encryption | Disk encryption software, designed to protect data by providing encryption for entire volumes | Windows Vista Enterprise and Ultimate editions, Windows Server 2008 |
| Credential Guard | Virtualization-based isolation of stored credentials to prevent theft and pass-the-hash attacks. | Windows 10 Enterprise, Education, IoT Enterprise, or , Windows Server 2016 |
| Data Execution Prevention | Security feature that is intended to prevent an application or service from executing code from a non-executable memory region | Windows XP Service Pack 2 |
| Encrypting File System | File system driver that provides file system-level encryption | Windows 2000 |
| Security Account Manager | Database stored as a registry file | Windows NT 3.1 |
| SYSKEY | Utility that encrypts the hashed password information in a SAM database using a 128-bit encryption key | Windows NT 4.0 Service Pack 3 |
| User Account Control | Technology and security infrastructure utility that aims to improve the security of Microsoft Windows by limiting application software to standard user privileges until an administrator authorizes an increase | Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 |
| Windows Firewall | Utility designed to block unauthorized access while permitting authorized communications. An earlier edition known as Internet Connection Firewall that was disabled by default was included with the original Windows XP release. | Windows XP Service Pack 2 |
| Windows Defender | Security utility to prevent, remove and quarantine malware (viruses, Trojan horses, etc.) | Downloadable for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 |
| Windows Resource Protection | Protects Registry keys and folders in addition to critical system files | Windows Vista |
Deprecated components and apps
[edit]
| Component | Description | Category | Introduced | Last OS included | Superseded by |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Pinball | Pinball game | Game | Plus! 95 for Windows 95 | Windows XP | — |
| ActiveMovie | Streaming media technology | API | Windows 95 | Windows Me | DirectShow |
| Cardfile | Personal information manager | Personal organizer | Windows 1.0 | Windows Me | Outlook Express, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail |
| Chess Titans | Chess game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Microsoft Chess |
| DriveSpace | Disk compression utility | Data compression | MS-DOS | Windows Me | — |
| Windows DVD Maker | DVD authoring software | Video | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | — |
| File Manager | File manager app | File manager | Windows 3.0 | Windows Me | Windows Explorer |
| FreeCell | FreeCell game | Game | Win32s | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| Hearts | Version of the Hearts game using Black Lady scoring | Game | Windows for Workgroups 3.11 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Hearts |
| Windows Insider | Windows 10 Version 1507 | Windows 10 Version 1511 | Feedback Hub | ||
| Windows Help and Support | Online and offline reference manual for troubleshooting. | Utility | Windows Me | Windows 8.1 | Microsoft Tips or Get Started |
| HyperTerminal | Communication utility based on a low end version of HyperACCESS | Communication | Windows 95 | Windows XP | — |
| Hold ‘Em | Version of the Texas hold ’em game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | — |
| Hover! | Video game in a combination of bumper cars and capture the flag | Game | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | — |
| InkBall | Game where the user tries to get colored balls into the correct holes | Game | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | Windows Vista | — |
| Internet Explorer | Web browser | Web browser and FTP client. See also: Internet Explorer versions, Features, History, Removal, Browser Helper Objects | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 | Windows 10 | Microsoft Edge |
| Microsoft Mahjong | Version of the Mahjong solitaire game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Microsoft Mahjong |
| Windows Mail | E-mail client | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | Mail (Windows) | |
| Internet Mail and News | E-mail and news client | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | Outlook Express, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail | |
| Minesweeper | Version of the minesweeper game | Game | Microsoft Entertainment Pack, Windows 3.1 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Minesweeper |
| Media Control Interface | An app that can play media files and record sound by passing commands as strings. | API | Windows 3.0 | Windows Me | — |
| Windows Media Player | Digital media player app | Media player | Windows 3.0 Multimedia Extensions | Windows 10 | Windows Media Player, Movies & TV, or Groove Music |
| Microsoft Calendar | Calendaring app | Personal organizer | Windows 1.0 | Windows 3.1 | Windows Calendar, Windows Live Mail, or the Calendar app for Windows |
| Microsoft Diagnostics | Tool that provides detailed technical information about user’s software and hardware | Diagnostics | MS-DOS | Plus! 95 for Windows 95 | Microsoft System Information |
| Microsoft Fax | Faxing app | Fax | Windows 95 | Windows XP | Windows Fax and Scan |
| Microsoft Private Folder | Tool to protect private data | Personal organizer | Windows XP | Windows XP | |
| Windows Help | Documentation browser that used a proprietary format | Online help | Windows 3.0 | Windows XP | Microsoft Help |
| Windows Feedback | Windows 10 Version 1507 | Windows 10 Version 1511 | Feedback Hub | ||
| NTBackup | Built-in backup app | Backup | Downloadable for Windows NT 4.0 | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 | Backup and Restore, Windows Server Backup |
| Outlook Express | E-mail client | Internet Explorer 4 | Windows XP | Windows Mail or Windows Live Mail | |
| Paint | Simple graphics painting app | Application | Windows 1.0 | — | — |
| Program Manager | Shell composed of a task-oriented graphical user interface, consisting of icons (shortcuts for apps) arranged into app groups. | GUI | Windows 3.0 | Windows XP | Windows Explorer |
| Purble Place | Educational game for children, teaching pattern recognition, shapes, and colors | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | — |
| Reader | e-book reader | e-book reader | Windows 8 | Windows 10 Creators Update | Microsoft Edge (PDF), XPS Viewer (XPS), Photos (TIFF)[26] |
| Reversi | Version of Reversi. | Game | Windows 1.0 | Windows 3.0 | Internet Reversi only on Windows Me and Windows XP |
| Solitaire | Klondike Solitaire game | Game | Windows 3.0 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| Spider Solitaire | Spider Solitaire game | Game | Microsoft Plus! 98 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| System File Checker | Utility that allows users to scan for and restore corruptions in Windows system files | Security | Windows 98 | Windows Server 2003 | Windows Resource Protection |
| Tinker | Puzzle game in which the player controls a robot through various mazes and obstacle courses | Game | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | — |
| Video for Windows | Multimedia framework | API | Windows 3.1 | Windows 95 | DirectShow |
| Windows Address Book | List of contacts that can be shared by multiple apps | Contact manager | Internet Explorer 3 | Windows XP | Windows Contacts, People, or Windows Live Mail |
| Windows Desktop Gadgets | Widget engine for Microsoft Gadgets | User interface | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Live tiles |
| Windows File Protection | Sub-system in the operating system, aims to prevent apps from replacing critical Windows system files. | Security | Windows Me as System File Protection | Windows XP | Windows Resource Protection |
| Windows Journal | Notetaking application that allows for the creation of handwritten notes | Accessories | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | Windows 10 Threshold 2 | General improvements in Ink API |
| Windows Messaging | E-mail client | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | Internet Mail and News, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail | |
| Windows Messenger | Instant messaging client | Internet messaging | Windows XP | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 | Windows Live Messenger or Skype |
| Windows Movie Maker | Non-linear video editing software | Video | Windows Me | Windows Vista | Windows Live Movie Maker or Microsoft Photos |
| Microsoft NetMeeting | Video conferencing client | Web conference | Windows 95 OSR2 | Windows XP | Windows Meeting Space |
| Windows Photo Gallery | Image organizer | Photo | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | Windows Live Photo Gallery or Microsoft Photos |
| Windows Picture and Fax Viewer | Image viewer | Photo | Windows XP | Windows XP | Windows Photo Gallery, Windows Fax and Scan, Windows Live Photo Gallery, Windows Photo Viewer, or Microsoft Photos |
| WordPad | Simple word processor with basic formatting, successor to Microsoft Write. It has facilities to format and print text, but lacks intermediate features such as a spell checker and thesaurus. | Word processor | Windows 95 | Windows 11, version 23H2 | None |
| Microsoft Write | Simple word processor | Word processor | Windows 1.0 | Windows NT 3.51 | WordPad |
- ClearType
- Media Foundation
- Windows Driver Foundation
- Windows Imaging Component
- Windows Management Instrumentation
Miscellaneous (to be categorized)
[edit]
- ActiveSync
- Compatibility Appraiser collects telemetry information.[27]
- DMRC (Device Metadata Retrieval Client) interfaces to metadata about devices from Windows 7 onwards.[28]
- I/O technologies
- Macro Recorder
- Microsoft Agent
- Prefetcher
- ReadyBoost
- Sync Center
- Text Services Framework
- Universal Audio Architecture
- Windows Color System
- Windows Diagnostic Infrastructure (WDI)[29]
- Windows Mobile Device Center
- Windows Rally
- Windows Registry
- Windows Speech Recognition
- XML Paper Specification
- Outline of Microsoft
- List of Unix daemons
- List of games included with Windows
- ^ Shultz, Greg (February 28, 2015). «Control Panel and Settings: Why are both still UI options in Windows 10?». TechRepublic. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ «Get $Windows Camera from the Microsoft Store». apps.microsoft.com. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ «Xbox Support». support.xbox.com. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ Hoffman, Chris (January 4, 2021). «How to See FPS in Any Windows 10 Game (Without Extra Software)». How-To Geek. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ The Xbox Game Bar Team (May 22, 2019). «Introducing the New Xbox Game Bar». Xbox Wire. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved August 21, 2019.
- ^ «System Services». technet.microsoft.com. Microsoft. 2014. Archived from the original on November 5, 2017. Retrieved September 2, 2014.
The Application Experience service (AELookupSvc) is a part of the Application Compatibility Administrator. It processes application compatibility lookup requests for applications as they are started, provides support for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista–based computers running apps in compatibility mode, reports on compatibility issues, and automatically applies software updates to apps.
- ^ «Description of the Microsoft Computer Browser Service». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2015. Retrieved November 3, 2017.
- ^ a b Mackie, Kurt (August 16, 2016). «Microsoft Clarifies Windows 10 ‘Delivery Optimization’«. Redmond Magazine. 1105 Enterprise Computing Group. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
- ^ Hachman, Mark (March 29, 2017). «How Delivery Optimization in Windows 10 Creators Update helps avoid data overage fees». PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on August 25, 2017. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
- ^ Halfin, Dani; Poggemeyer, Liza; Lich, Brian; Kieselbach, Oliver; Childs, Andrew (April 30, 2018). «Configure Delivery Optimization for Windows 10 updates». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 23, 2018. Retrieved July 23, 2018.
- ^ «Distributed Link Tracking on Windows-based domain controllers». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 25, 2015. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC)». Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Event Log». Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «What is Indexing Service?». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2011. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Windows 2000 Professional and Server Service Pack 4 Services Configuration by Black Viper» Archived December 17, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, notice that the service is listed on this page. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows Firewall» Archived February 13, 2020, at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Secondary Logon (Run As): Starting Programs and Tools in Local Administrative Context». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on March 6, 2015. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «System Event Notification Service». The Elder Geek. Archived from the original on October 26, 2008. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Myth Busted: Why Disabling SuperFetch on Vista and Windows 7 Is a Bad Idea», retrieved April 2013
- ^ «What Is Volume Shadow Copy Service?: Data Recovery». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on August 26, 2017. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)» Archived September 10, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows 2000 Professional and Server Service Pack 4 Services Configuration by Black Viper» Archived December 17, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, Notice the absence of the service on this page. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)» Archived February 13, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Notice that XP is the operating system listed. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «How Windows Time Service Works: Windows Time Service». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on April 22, 2016. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ Minasi, Mark; Layfield, Rhonda; Justice, Lisa (2006). Mastering Windows Server 2003: upgrade edition for SP1 and R2 (12 ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 56. ISBN 978-0-470-05645-5. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved July 21, 2010.
There is also a client piece for WebDAV built into XP, 2003, R2, and Vista, called the WebClient Service.
- ^ «Microsoft replaces standalone PDF reader app with Edge». MSPoweruser. November 26, 2017. Archived from the original on August 19, 2019. Retrieved August 19, 2019.
- ^ Leonhard, Woody (April 20, 2015). «KB 2952664 triggers daily telemetry run in Windows 7 — and may be snooping on users: Microsoft bills the ‘compatibility update’ as way to ease the upgrade process to Windows 10 — but it’s collecting data daily». Operating Systems. InfoWorld. InfoWorld, Inc. Archived from the original on June 2, 2017. Retrieved August 23, 2016.
The Microsoft Compatibility Appraiser task runs %windir%\system32\rundll32.exe appraiser.dll,DoScheduledTelemetryRun with the description ‘Collects program telemetry information if opted-in to the Microsoft Customer Experience Improvement Program.’
- ^ Compare: Tulloch, Mitch; Northrup, Tony; Honeycutt, Jerry; Wilson, Ed (2010). Windows 7 Resource Kit. Windows 7 Resource Kit, Microsoft Corporation. Vol. 1. Microsoft Press. p. 708. ISBN 9780735627000. Archived from the original on January 11, 2022. Retrieved August 18, 2016.
The DMRC [(Device Metadata Retrieval Client)] checks the computer’s local metadata cache and metadata store for metadata that applies to the device.
- ^ Solomon, David A.; Russinovich, Mark E.; Ionescu, Alex (June 17, 2009). Windows Internals. Developer Reference (5 ed.). Microsoft Press (published 2009). ISBN 9780735637962. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved October 24, 2016.
The Windows Diagnostic Infrastructure (WDI) helps to detect, diagnose, and resolve common problem scenarios with minimal user intervention.
Если у Вас по каким-либо причинам отсутствует магазин приложений Windows — Microsoft Store, к примеру если у Вас установлена Windows 10 Корпоративная, т.к в корпоративных версиях Windows — Microsoft Store вырезан производителем. Так же, инструкция подойдет, если у Вас данное приложение отсутствует по любой другой причине.
— Для установки приложения Microsoft Store необходимо открыть PowerShell с правами администратора. Найти его Вы можете через меню «Поиск» на панели задач => Правой кнопкой мыши по результату поиска => Открыть от имени администратора.
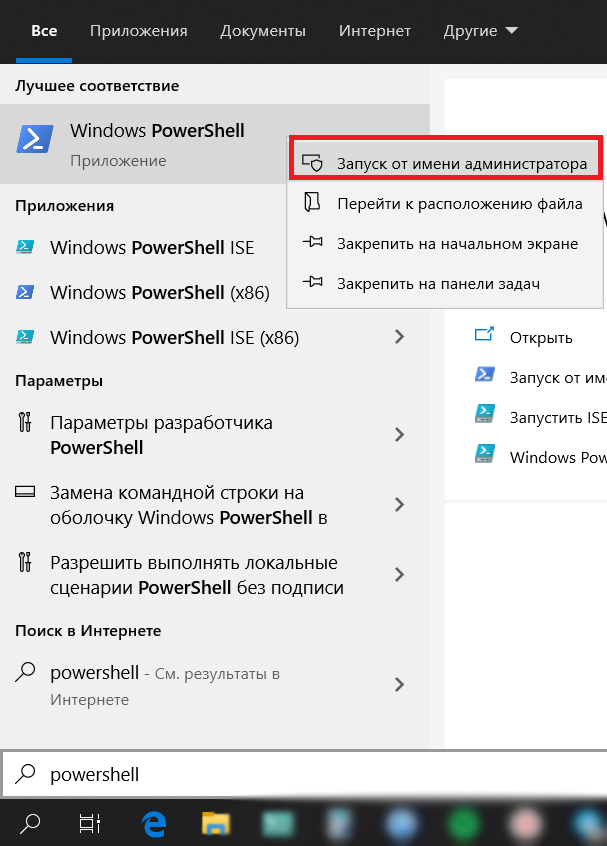
— В окно PewerShall введите следующую команду и нажмите Enter: Get-AppxPackage *windowsstore* -AllUsers | Foreach {Add-AppxPackage -DisableDevelopmentMode -Register «$($_.InstallLocation)\AppxManifest.xml»}
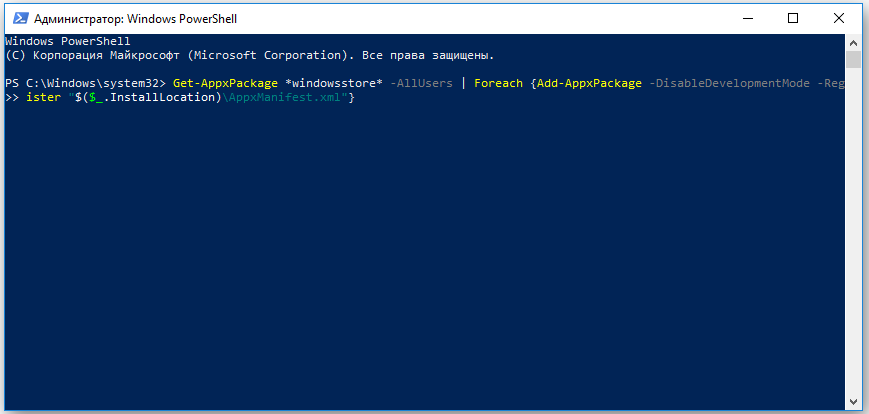
— После завершения процедуры загрузки приложения Вы можете найти Microsoft Store у Вас в меню «Пуск».
Так же Вы можете найти данное приложение через поиск в системе.
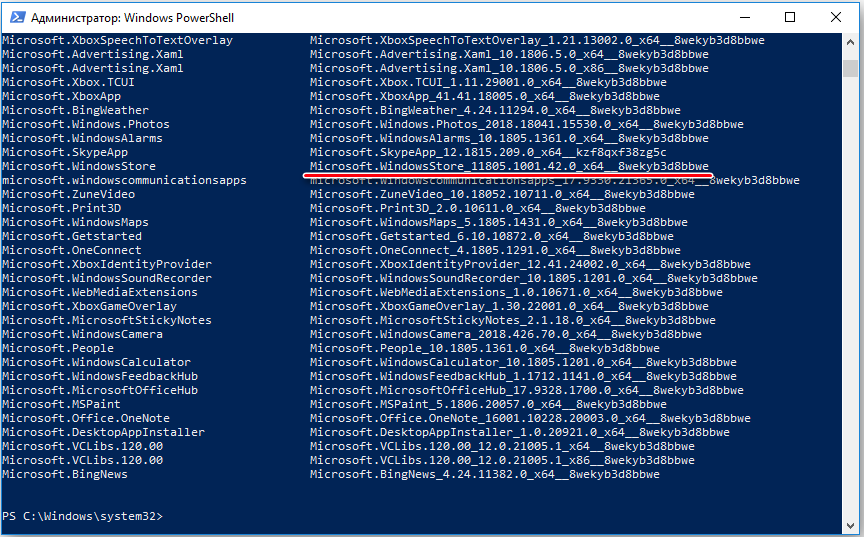
— Если же у Вас выходит ошибка при запуске Microsoft Store, либо при загрузке или установки магазина приложений произошла ошибка, возвращаемся обратно в PowerShell, открываем его от имени администратора и вводим следующую команду: Get-AppxPackage -AllUsers | Select Name, PackageFullName
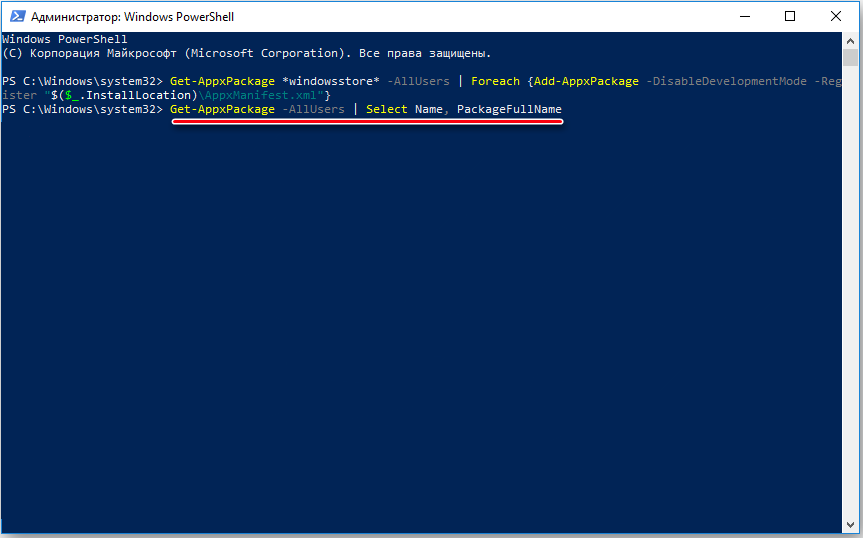
— Далее в списке компонентов найдите компонент Microsoft.WindowsStore. Скопируйте текст из правого столбца и вставьте его следующим образом в поле ввода PowerShell: Add-AppxPackage -DisableDevelopmentMode -Register «C:\Program Files\WindowsAPPS\СКОПИРОВАННЫЙ_ТЕКСТ\AppxManifest.xml»
Вместо надписи «СКОПИРОВАННЫЙ_ТЕКСТ» соответственно вставляете то поле из правого столбца.
Помимо всего, мы рекомендуем использовать только оригинальные дистрибутивы Windows 10, скачать их можете в нашем каталоге. А так же, рекомендуем использовать лицензионные ключи активации для активации Windows 10. Приобрести их можете по самым низким ценам в нашем интернет-магазине на следующей странице. От 1490 ₽, моментальная доставка в автоматическом режиме на Вашу электронную почту.
Лицензионный ключ активации Windows 10 от
При переходе на Windows 10 мы знакомимся с новым сервисом Microsoft Store. Это встроенное приложение, которое обладает массой функций и возможностей. Но так случается, что после чистой установки пользователи не находят его или оно работает некорректно. Часто неопытные пользователи сами удаляют Магазин, а потом задаются вопросом, как его вернуть.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим неполадки, которые могут возникнуть вследствие отсутствия Microsoft Store. Или при его случайном удалении. А также подробно распишем способы решения проблем:
- как его установить;
- как восстановить после удаления;
- что делать если Microsoft Store самопроизвольно закрывается;
- как его отключить, если он съедает часть системных ресурсов.
Возможности Microsoft Store
Microsoft Store — это встроенный в операционную систему сервис-магазин от Майкрософт. Он позволяет загружать на ПК программы и приложения, скачивать темы оформления и игры. В магазине очень много контента, как платного, так и бесплатного. Он постоянно дорабатывается и улучшается, становится производительнее и полезнее для всех пользователей ОС Windows 10.
В скором времени он сможет полностью заменить большую часть стороннего софта, который в процессе работы скачивается и устанавливается на ПК с внешних источников. Скачивание приложений из магазина полностью безопасно. Каждое новое приложение или игра перед добавлением в Microsoft Store проверяется центром сертификации.
Не работает Microsoft Store: как исправить
При возникновении проблем с Microsoft Store и его некорректной работы можно попробовать исправить ситуацию штатными средствами.
Выход и последующий вход в учётную запись
- Запускаем приложение и выходим из своего аккаунта.
- Закрываем Microsoft Store.
- Снова запускаем его и выполняем вход.
- Проверяем, правильно ли работает приложение.
Сброс кэша Microsoft Store, если он закрывается при запуске
В процессе работы с Microsoft Store данные скапливаются в кэше. Кэш можно очистить, чтобы восстановить функционирование системы и работоспособность магазина. См. также: как очистить кэш на компьютере с Windows 10.
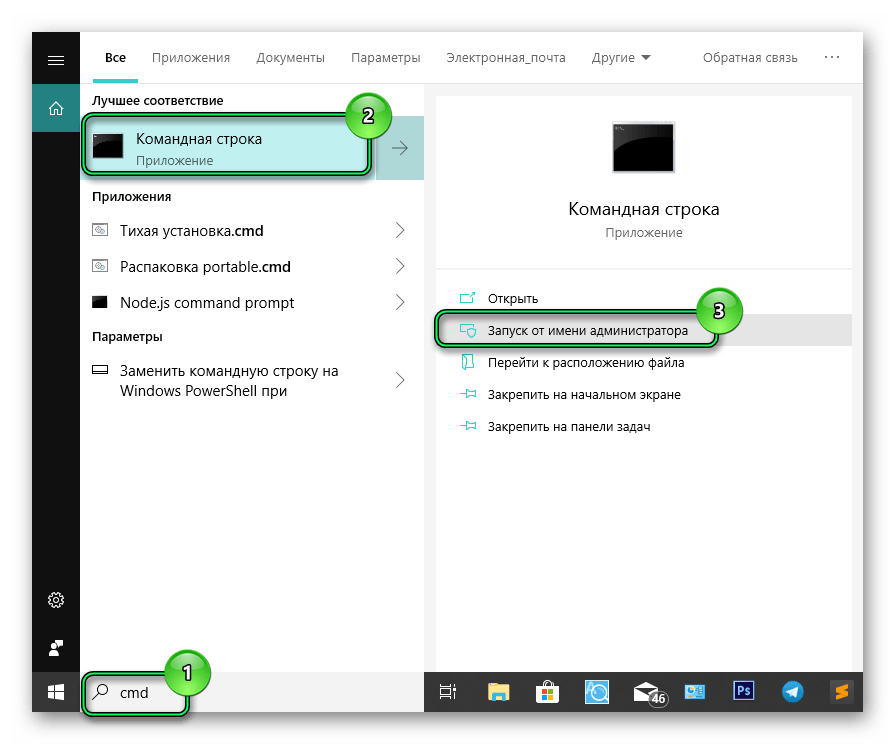
- Для этого закрываем Магазин, если он был запущен.
- Запускаем консоль командной строки с правами администратора. В поиске Windows пишем cmd и в результатах выдачи выбираем соответствующий пункт.
- Вводим в консоли команду WSReset и нажимаем клавишу Ввод.
- Ждем окончания процедуры. Microsoft Store должен автоматически запустится.
Восстановление системы
Если Microsoft Store ни с того ни с чего начал работать неадекватно, это может быть следствием работы вирусов. Встроенные средства Виндоус могут восстановить систему до того момента, когда Магазин работал нормально. Раздел восстановления находится в «Параметрах»/«Обновление и безопасность».
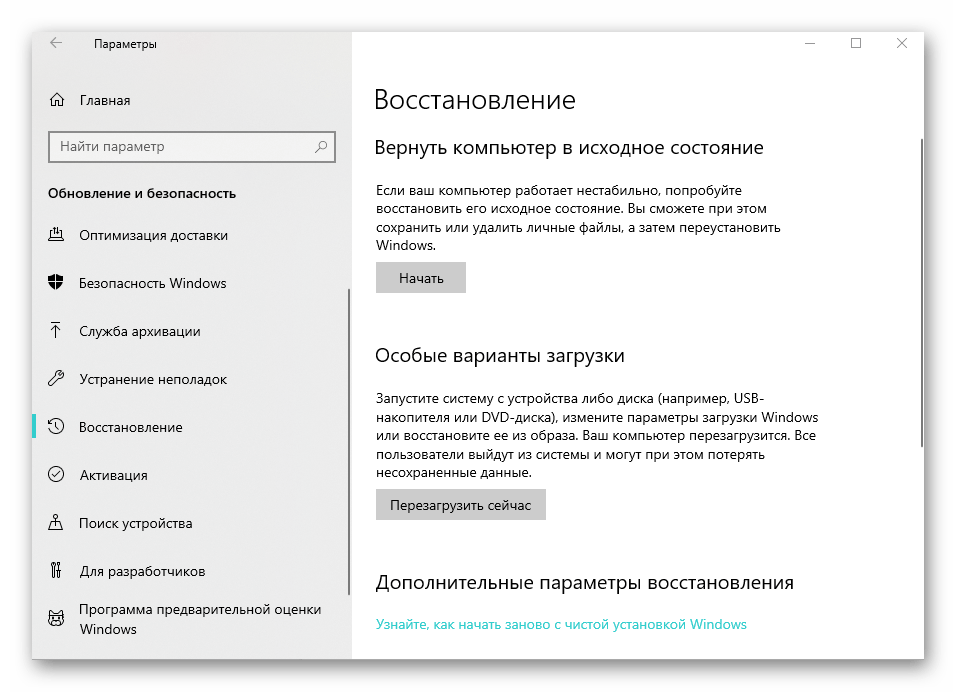
- Здесь выбираем «Начать» и следуем дальнейшей инструкции. Вариант восстановления с сохранением пользовательских файлов не затронет личные данные. Будет произведено удаление всех сторонних программ и приложений, которые были установлены за весь период работы.
Параметр «Удалить все» вернет Windows 10 к первоначальному состоянию. Он чем-то похож на полную переустановку системы. Только для этого не нужен загрузочный диск с образом Windows. Личные данные и программы будут удалены.
Установка магазина Windows Store
Как мы уже писали в начале статьи, устанавливать Microsoft Store отдельно не нужно. Он уже встроен в систему по умолчанию. Но если вам посчастливилось установить не совсем лицензионную сборку, в которой он был изъят или случайно удален, то здесь вы получите рекомендации по возвращению его назад.
Особые разрешения для WindowsApps
Для дальнейших действий нам нужны права владельца ПК, чтобы иметь возможность вносить изменения в каталог WindowsApps.
Примечание: этот способ сработает, если вы не удаляли каталог WindowsApps.
Теперь по порядку:
Способ 1: восстановление после удаления
Теперь можно приступать к восстановлению Microsoft Store. Делается это двумя способами. В обоих случаях мы будем работать с оболочкой Windows PowerShell, запущенной от имени администратора.
- В консоли пишем команду:
Get-AppxPackage *windowsstore* -AllUsers | Foreach {Add-AppxPackage -DisableDevelopmentMode -Register «$($_.InstallLocation)\AppxManifest.xml»}
Не пугайтесь длинной команды. Просто копируем её через контекстное меню или с помощью комбинаций клавиш Ctrl+C. И вставляем в PowerShell с помощью Ctrl+V. Вставка команды из буфера обмена с помощью контекстного меню (копировать/вставить) здесь не работает.
- Дожидаемся завершения операции и пробуем найти Microsoft Store через поиск Windows.
Способ 2: восстановление после удаления
Если первый способ не сработал, то попробуем пойти другим путем. Для этого метода нам также понадобится консоль PowerShell. Не забываем, что работать в приложении нужно от имени администратора, иначе ничего не получится.
- Для этого метода нужно в консоль ввести команду:
Get-AppxPackage -AllUsers | Select Name, PackageFullName
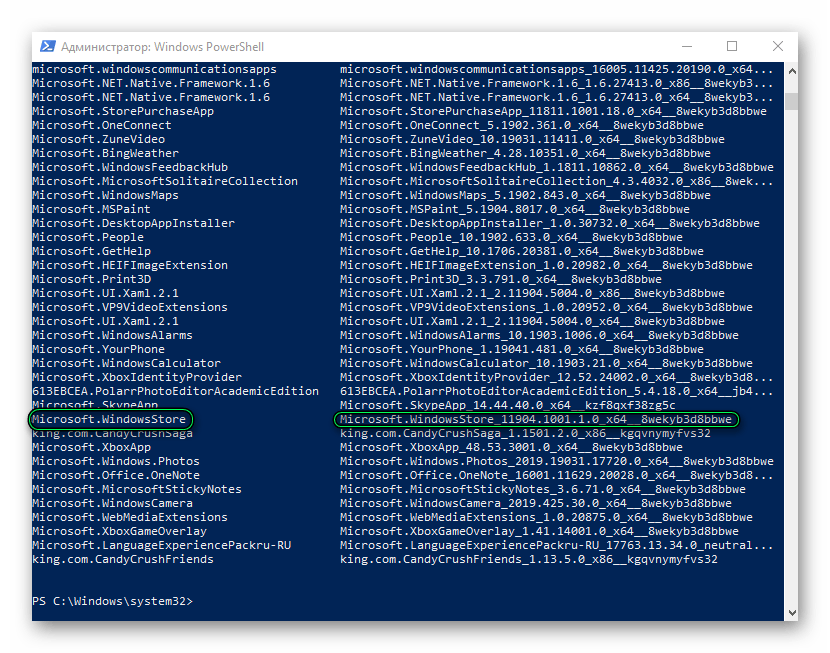
- Откроется список приложений Windows. Находим здесь Microsoft.WindowsStore. Из правой колонки нам нужно скопировать значение. В моем случае команда ниже. У вас, в зависимости от версии Windows, цифры после названия могут отличаться.
Microsoft.WindowsStore_11904.1001.1.0_x64__8wekyb3d8bbwe
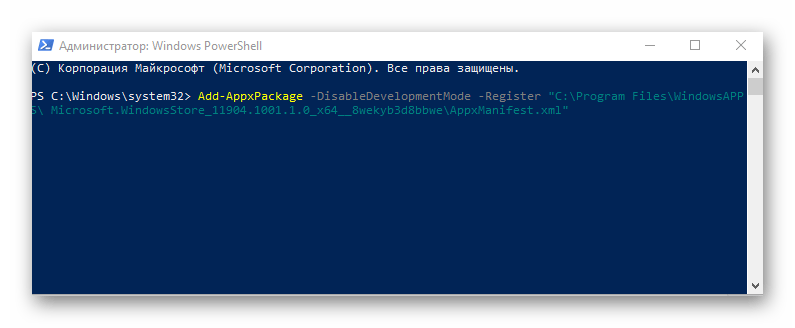
- В код вставляем значение со своего компьютера. (В коде ниже вставлено значение из моего).
Add-AppxPackage -DisableDevelopmentMode -Register «C:\Program Files\WindowsAPPS\ Microsoft.WindowsStore_11904.1001.1.0_x64__8wekyb3d8bbwe\AppxManifest.xml»
Способ 3: копирование файлов с другого компьютера
Если вышеперечисленные способы не принесли успеха, можно скопировать файлы Microsoft Store с другого ПК, на котором установлена Windows 10 точно такой же редакции и разрядности. Также файлы можно взять и с виртуальной машины, установленной в среде VirtualBox. Информацию о том, как установить виртуальную машину и развернуть в ней Windows 10, можно на сайте разработчика виртуальной машины.
- Запускаем Windows 10, открываем видимость скрытых папок.
- Становимся владельцем, как описано выше в инструкции.
- Копируем файлы из папки WindowsApps на другом ПК и переносим их в нашу папку с помощью клавиш Ctrl+V.
Совет: лучше скопировать всю папку WindowsApps и вставить её в папку Program Files с замещением.
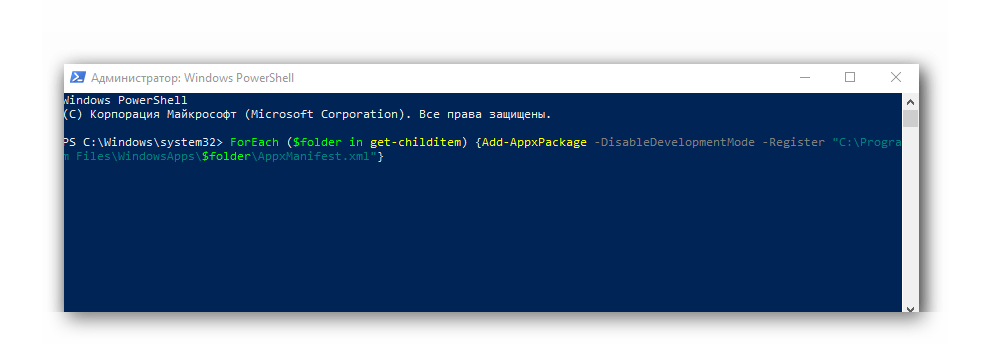
- Снова запускаем утилиту PowerShell и выполняем команду:
ForEach ($folder in get-childitem) {Add-AppxPackage -DisableDevelopmentMode -Register «C:\Program Files\WindowsApps\$folder\AppxManifest.xml»}
- Проверяем приложение через поиск.
Примечание: в случае успешной установки одним из вышеперечисленных способов кнопка Microsoft Store не появится на панели задач. Ее нужно будет закрепить там вручную.

Обновление системы
Данный способ заключается в полном обновлении системы с сохранением пользовательских файлов. Для обновления нам понадобится образ Windows 10.
Скачать его можно на официальном сайте. Монтируем образ в виртуальный привод с помощью программы UltraISO и запускаем установку прямо из среды Windows.
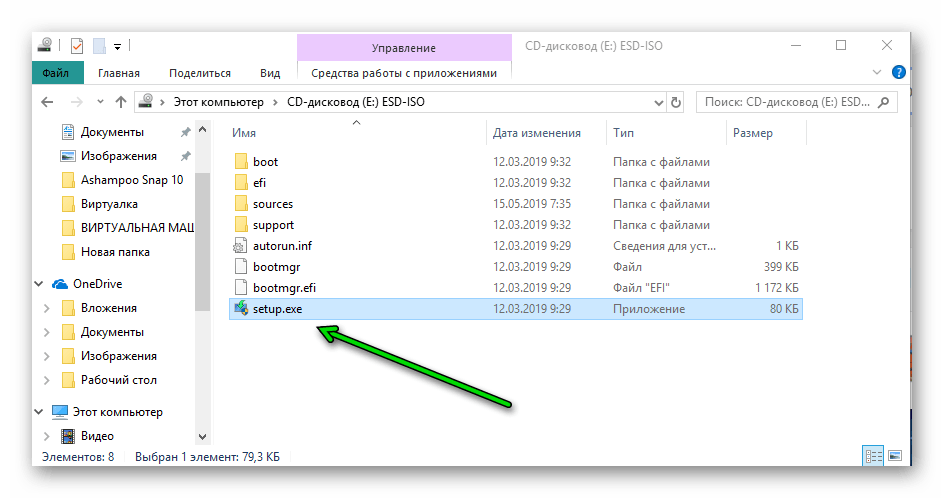
- Для запуска восстановления запускаем файл setup.exe.
- Далее выбираем язык и кликаем «Установить».
- В окне выбора типа установки выбираем «Обновление».
В этом случае будет произведена установка Windows с сохранением всех установленных приложений и пользовательских файлов. По окончании установки/обновления Microsoft Store будет на месте.
Отключение Microsoft Store
Отключить Microsoft Store, чтобы он не забирал системные ресурсы, можно через редактор групповых политик.
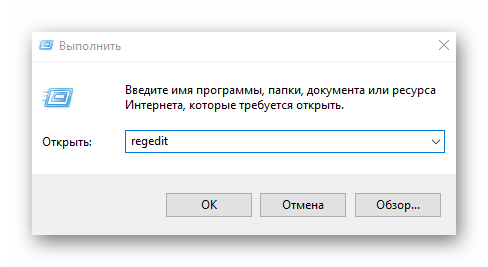
- Для этого запускаем утилиту «Выполнить» с помощью комбинации Win+R.
- Пишем в ней команду gpedit.msc и кликаем OK.
Проходим по пути:
Отключения Microsoft Store через редактор реестра
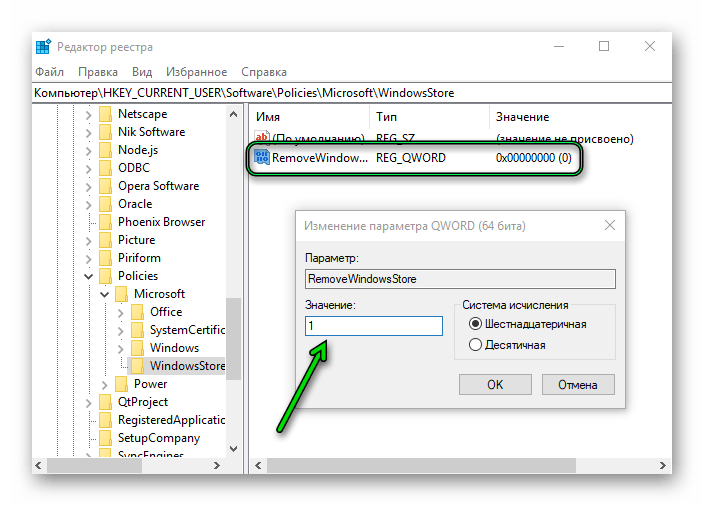
Для этого способа нам понадобится редактор реестра:
- Запускаем утилиту «Выполнить» и пишем в диалоговом окне команду regedit.
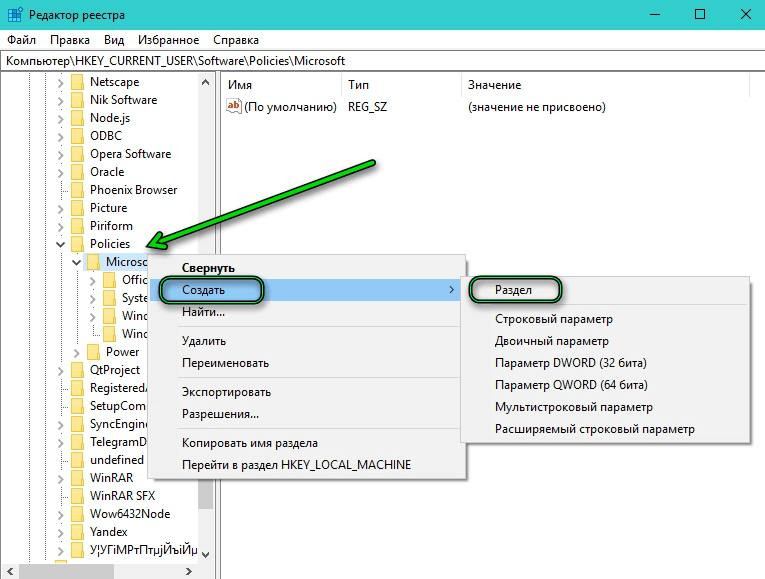
- Дальше раскрываем ветку HKEY_CURRENT_USER/Software/Policies/Microsoft
- Выполняем правый клик на папке Microsoft и выбираем «Создать»/«Раздел» — даём ему имя Windows Store.
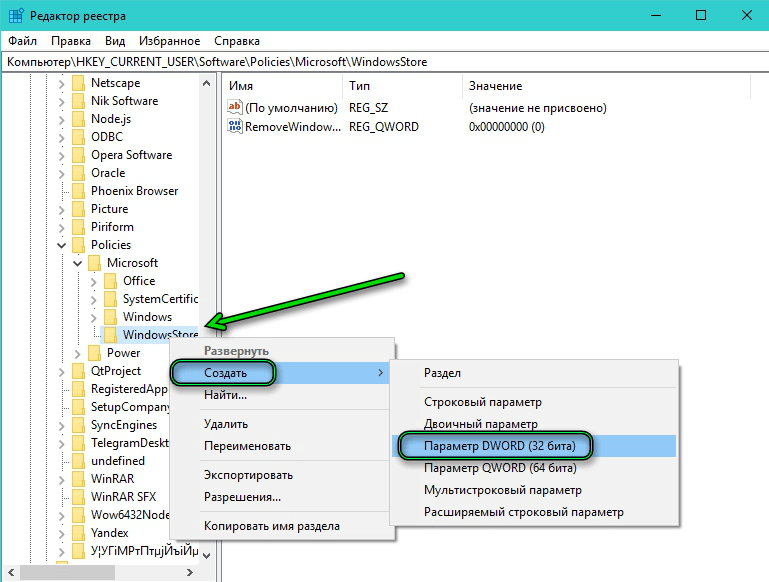
- Выполняем правый клик мышкой на вновь созданном разделе и выбираем «Создать» / «Параметр DWORD (64 бита)» (если у вас 32-разрядная система, то выбираем соответствующий параметр).
- Называем его Remove Windows Store — меняем значение параметра с 0 на 1.
- Чтобы включить Магазин, то снова меняем параметр на 0 или удаляем раздел Windows Store из редактора реестра.
Как мы видим, ничего сложного нет. Большую часть проблем с Windows и ее приложениями можно решить штатными средствами. Магазин на самом деле занимает совсем немного места на диске и практически не влияет на быстродействие системы. Не стоит беспорядочно удалять из системы то, что вам кажется лишним или ненужным. В какой-то момент эта программа может понадобиться. А можно случайно удалить какой-то системный файл и Windows просто не запустится, после чего останется только переустанавливать систему.
Post Views: 25 317