По умолчанию, все операционные системы семейства Windows автоматически получают и обновляют корневые сертификаты с сайта Microsoft. Компания MSFT в рамках программы корневых сертификатов Microsoft Trusted Root Certificate Program, ведет и публикует в своем онлайн хранилище сертификаты для клиентов и устройств Windows. Если проверяемый сертификат в своей цепочке сертификации относится к корневому CA, который участвует в этой программе, Windows автоматически скачает с узла Microsoft Update и добавит такой корневой сертификат в доверенные на вашем компьютере.
Windows запрашивает обновление списка корневых сертификатов (certificate trust lists — CTL) один раз в неделю. Если в Windows отсутствует прямой доступ к каталогу Windows Update, то система не сможет обновить корневые сертификаты, соответственно у пользователя могут быть проблемы с открытием сайтов (SSL сертификаты которых подписаны недоверенными CA, см. статью об ошибке в Chrome Этот сайт не может обеспечить безопасное соединение), либо с установкой запуском подписанных приложений или скриптов.
В этой статье попробуем разобраться, как в Windows вручную обновить список корневых сертификатов в TrustedRootCA в изолированных сетях, или компьютерах/серверах без прямого подключения к Интернету.
Содержание:
- Управление корневыми сертификатами в Windows 10 и 11
- Включить/отключить автоматическое обновление корневых сертификатов в Windows
- Ручное обновление корневых сертификатов в Windows 10 и 11
- Список корневых сертификатов в формате STL
- Обновление корневых сертификатов в Windows с помощью GPO в изолированных средах
- Обновление корневых сертификатов в Windows 7
- Утилита rootsupd.exe для обновления сертификатов в Windows XP
Примечание. Если ваши компьютеры выходят в Интернет через прокси-сервер, для автоматического обновления корневых сертификатов Microsoft рекомендует открыть прямой доступ (bypass) к веб-узлам Microsoft. Но это не всегда возможно/применимо.
Управление корневыми сертификатами в Windows 10 и 11
Как посмотреть список корневых сертификатов на устройстве Windows?
- Чтобы открыть хранилище корневых сертификатов компьютера в Windows /Windows Server, запустите консоль
mmc.exe
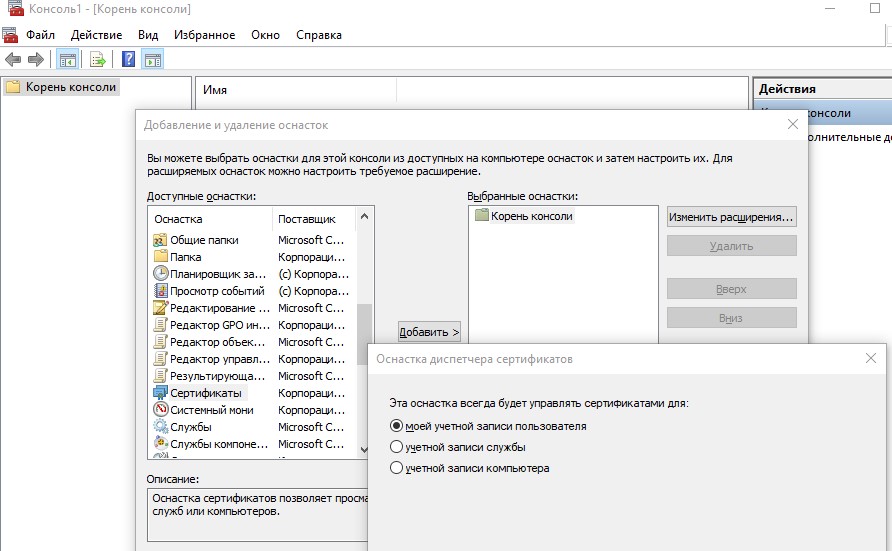
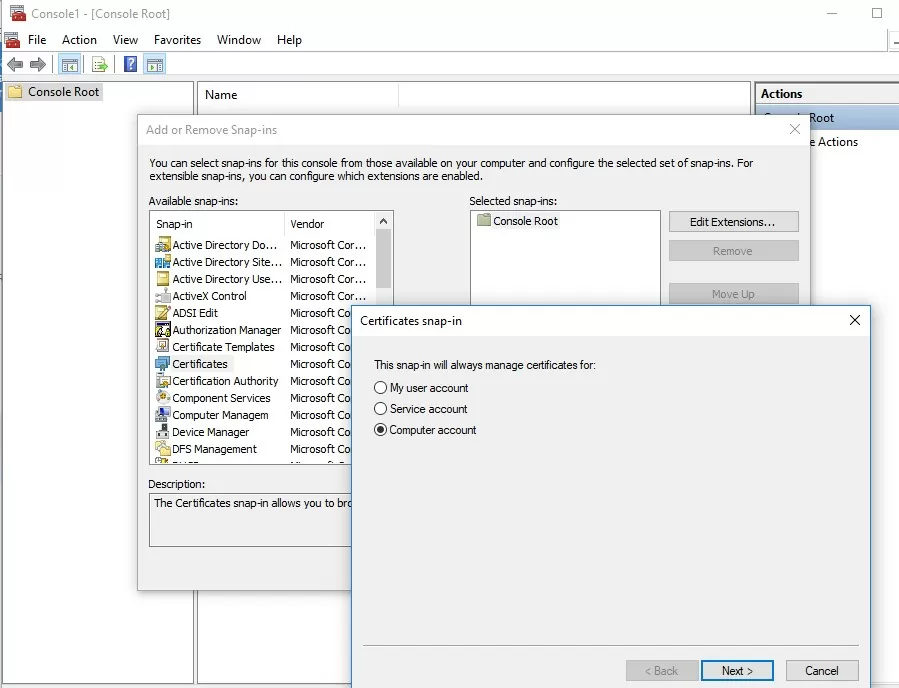
; - Нажмите Файл (File) -> Добавить или удалить оснастку (Add/Remove Snap-in), в списке оснасток выберите Сертификаты (Certificates) -> Добавить (Add);
- В диалоговом окне выберите что вы хотите управлять сертификатами учетной записи компьютера (Computer account);
- Далее -> Ok -> Ok;
- Разверните Certificates (Сертификаты) -> Trusted Root Certification Authorities Store (Доверенные корневые сертификаты). В этом списке содержится список доверенных корневых сертификатов вашего компьютера.
Вы можете вывести список доверенных корневых сертификатов на вашем компьютере со сроками их действия с помощью PowerShell:
Get-Childitem cert:\LocalMachine\root |format-list
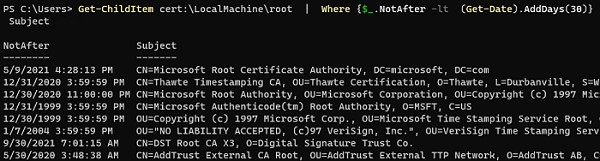
Можно вывести список истекших сертификатов, или которые истекут в ближайшие 30 дней:
Get-ChildItem cert:\LocalMachine\root| Where {$_.NotAfter -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(30)} |select NotAfter, Subject
В целях безопасности рекомендует периодически проверять хранилище доверенных сертификатов на наличие поддельных сертификатов с помощью утилиты Sigcheck. Утилита позволяет сравнить список сертификатов, установленных на компьютере со списком корневых сертификатов на сайте Microsoft (можно скачать офлайн файл с актуальными сертификатами authrootstl.cab).
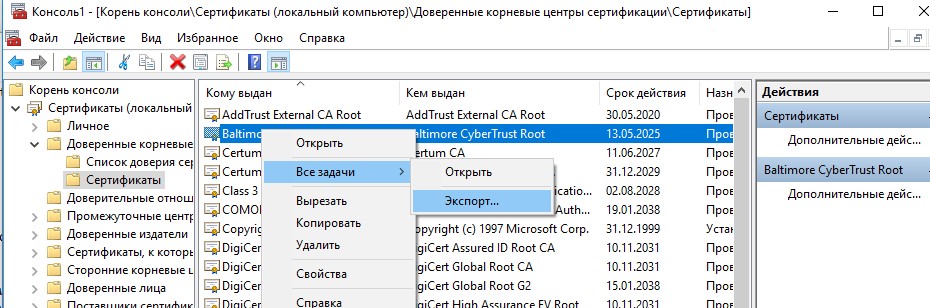
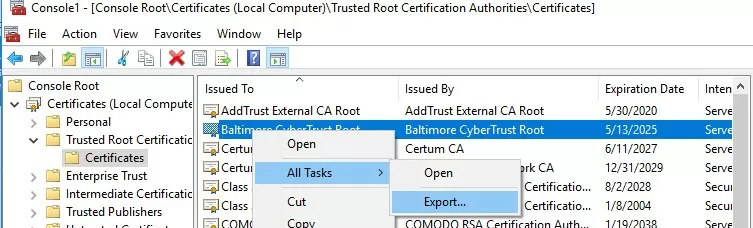
Вы можете вручную перенести файл корневого сертификата с одного компьютера на другой с помощью функцию Экспорта/Импорта.
- Вы можете экспортировать любой сертификат .CER в файл, щелкнув по нему и выбрав “Все задачи” -> “Экспорт”;
- Затем с помощью команды Импорт можно импортировать этот сертификат на другом компьютере.
Включить/отключить автоматическое обновление корневых сертификатов в Windows
Как мы уже упомянули, Windows по умолчанию сама обновляет корневые сертификаты. Вы можете включить или отключить обновление сертификатов в Windows через GPO или реестр.
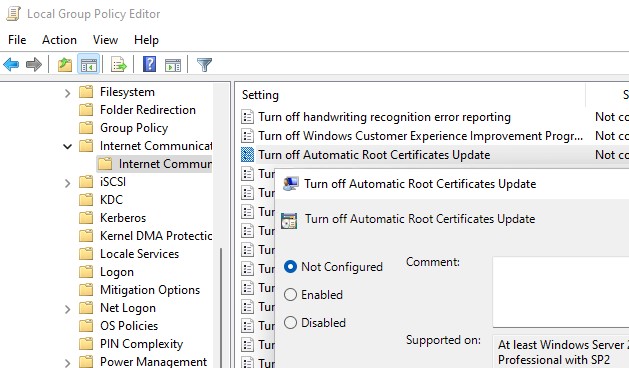
Откройте локальный редактор групповой политики (gpedit.msc) и перейдите в раздел Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Internet Communication Management -> Internet Communication.
Параметр Turn off Automatic Root Certificates Update в этом разделе позволяет отключить автоматическое обновление корневых сертификатов через сайт Windows Update. По умолчанию это политика не настроена и Windows всегда пытается автоматически обновлять корневые сертификаты.
Если эта политика не настроена, а сертификаты не обновляются автоматически, проверьте не включен ли вручную параметр реестра, отвечающий за эту настройку. Проверьте значение параметра реестра с помощью PowerShell:
Get-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\SystemCertificates\AuthRoot' -Name DisableRootAutoUpdate
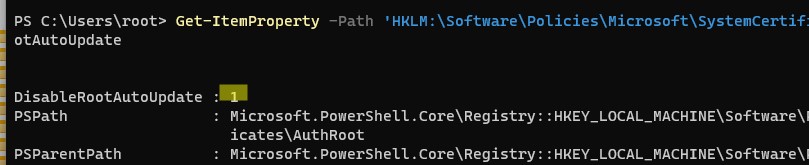
Если команда вернет, что значение ключа
DisableRootAutoUpdate=1
, значит на вашем компьютере отключено обновление корневых сертификатов. Чтобы включить его, измените значение параметра на 0.
Ручное обновление корневых сертификатов в Windows 10 и 11
Утилита управления и работы с сертификатами Certutil (появилась в Windows 10, для Windows 7 доступна в виде отдельного обновления), позволяет скачать с узлов Windows Update и сохранить в SST файл актуальный список корневых сертификатов.
Для генерации SST файла, на компьютере Windows 10/11 с доступом в Интернет, выполните с правами администратора команду:
certutil.exe -generateSSTFromWU c:\PS\roots.sst
Updated SST file. CertUtil: -generateSSTFromWU command completed successfully.

В результате в целевом каталоге появится файл SST, содержащий актуальный список сертификатов. Дважды щелкните по нему для открытия. Данный файл представляет собой контейнер, содержащий доверенные корневые сертификаты.
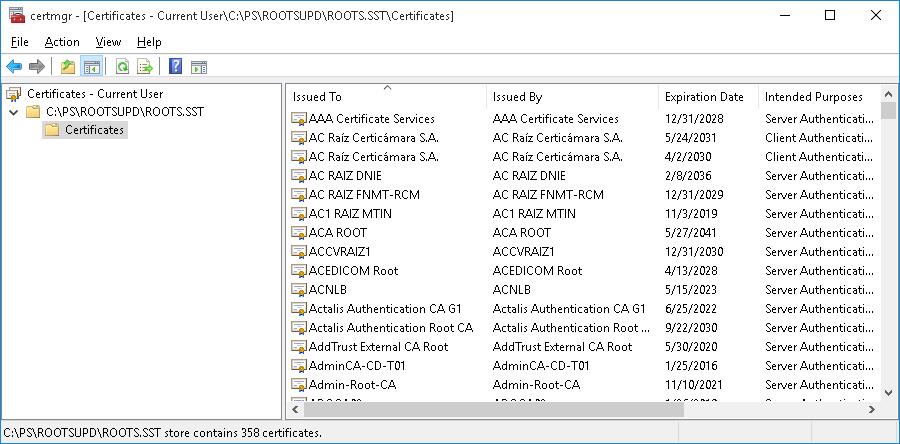
В указанном каталоге появится файл SST, содержащий актуальный список сертификатов. Данный файл представляет собой контейнер, содержащий доверенные корневые сертификаты. Дважды щелкните по нему.
В открывшейся
mmc
консоли вы можете экспортировать любой из полученных сертификатов. В моем случае, список сертификатов содержал 436 элементов. Естественно, экспортировать сертификаты и устанавливать по одному не рационально.
Для установки всех сертификатов из SST файла и добавления их в список корневых сертификатов компьютера можно воспользоваться командами PowerShell:
$sstStore = ( Get-ChildItem -Path C:\ps\rootsupd\roots.sst )
$sstStore | Import-Certificate -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\Root
Запустите оснастку certmgr.msc и убедитесь, что все сертификаты были добавлены в хранилище Trusted Root Certification Authority. В нашем примере на Windows 11 количество корневых сертификатов увеличилось с 34 до 438.
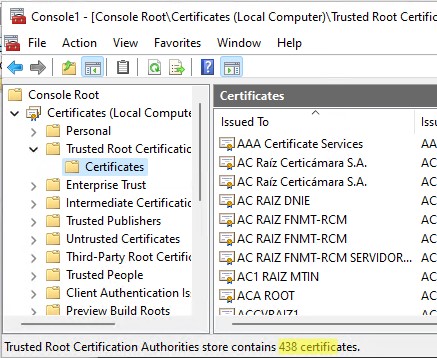
Чистая копия Windows после установки содержит в корневом хранилище лишь небольшое количество сертификатов. Если компьютер подключен к интернету, остальные корневые сертификаты будут устанавливаться автоматически (по требованию), если ваше устройство попытается получить доступ к HTTPS сайту/SSL сертификату, в чей цепочке доверия есть отпечаток из CTL Microsoft. Поэтому как правило, нет необходимости добавлять в свое локальное хранилище сразу все сертификаты, доверенные Microsoft.
Список корневых сертификатов в формате STL
Есть еще один способ получения списка сертификатов с сайта Microsoft. Для этого нужно скачать файл http://ctldl.windowsupdate.com/msdownload/update/v3/static/trustedr/en/authrootstl.cab (обновляется дважды в месяц).С помощью любого архиватора (или проводника Windows) распакуйте содержимое архива authrootstl.cab. Он содержит один файл authroot.stl.

Файл authroot.stl представляет собой контейнер со списком отпечатков (thumbprint) доверенных сертификатов Microsoft в формате Certification Trust List.
Данный файл можно установить в системе с помощью утилиты certutil:
certutil -enterprise -f -v -AddStore "Root" "C:\PS\authroot.stl"
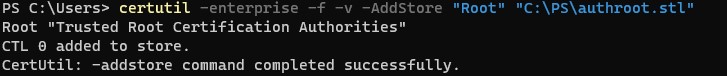
Root "Trusted Root Certification Authorities" CTL 0 added to store. CertUtil: -addstore command completed successfully.
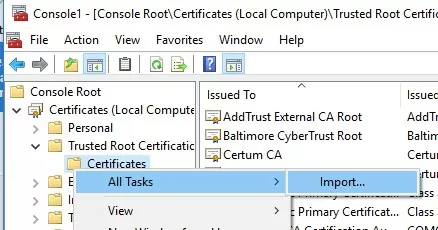
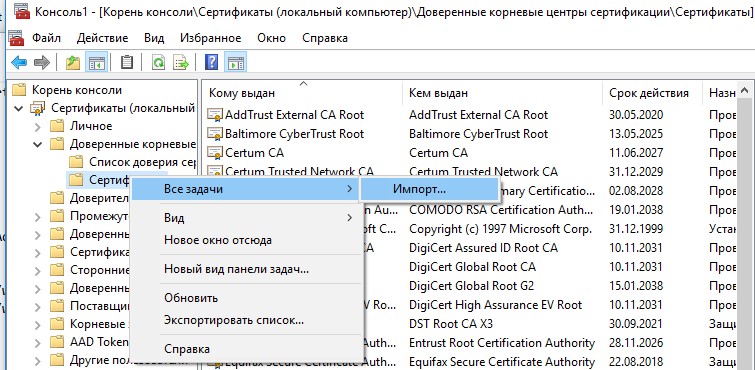
Также вы можете импортировать сертификаты из консоли управления сертификатами (Trust Root CertificationAuthorities –>Certificates -> All Tasks > Import). Укажите путь к вашему STL файлу сертификатами.
После выполнения команды, в консоли управления сертификатами (
certmgr.msc
) в контейнере Trusted Root Certification Authorities (Доверенные корневые сертификаты) появится новый раздел с именем Certificate Trust List (Список доверия сертификатов).
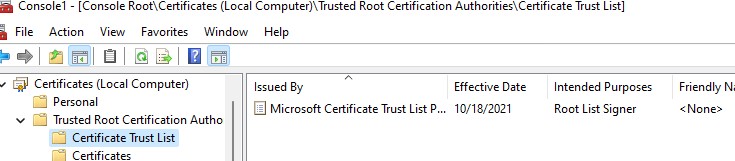
Аналогичным образом можно скачать и установить список с отозванными сертификатами, которые были исключены из программы Root Certificate Program. для этого, скачайте файл disallowedcertstl.cab (http://ctldl.windowsupdate.com/msdownload/update/v3/static/trustedr/en/disallowedcertstl.cab), распакуйте его и добавьте в раздел Untrusted Certificates командой:
certutil -enterprise -f -v -AddStore disallowed "C:\PS\disallowedcert.stl "
Обновление корневых сертификатов в Windows с помощью GPO в изолированных средах
Если у вас возникла задача регулярного обновления корневых сертификатов в изолированном от Интернета домене Active Directory, есть несколько более сложная схема обновления локальных хранилищ сертификатов на компьютерах домена с помощью групповых политик. В изолированных сетях Windows вы можете настроить обновление корневых сертификатов на компьютерах пользователей несколькими способами.
Первый способ предполагает, что вы регулярно вручную скачиваете и копируете в вашу изолированную сеть файл с корневыми сертификатами, полученный так:
certutil.exe –generateSSTFromWU roots.sst
Затем сертификаты из данного файла можно установить через SCCM или PowerShell логон скрипт в GPO:
$sstStore = ( Get-ChildItem -Path \\dc01\SYSVOL\winitpro.ru\rootcert\roots.sst )
$sstStore | Import-Certificate -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\Root
Второй способ предполагает получение актуальных корневых сертификатов с помощью команды:
Certutil -syncWithWU -f \\dc01\SYSVOL\winitpro.ru\rootcert\
В указанном сетевом каталоге появится ряд файлов корневых сертификатов (CRT) и в том числе файлы (authrootstl.cab, disallowedcertstl.cab, disallowedcert.sst, thumbprint.crt).
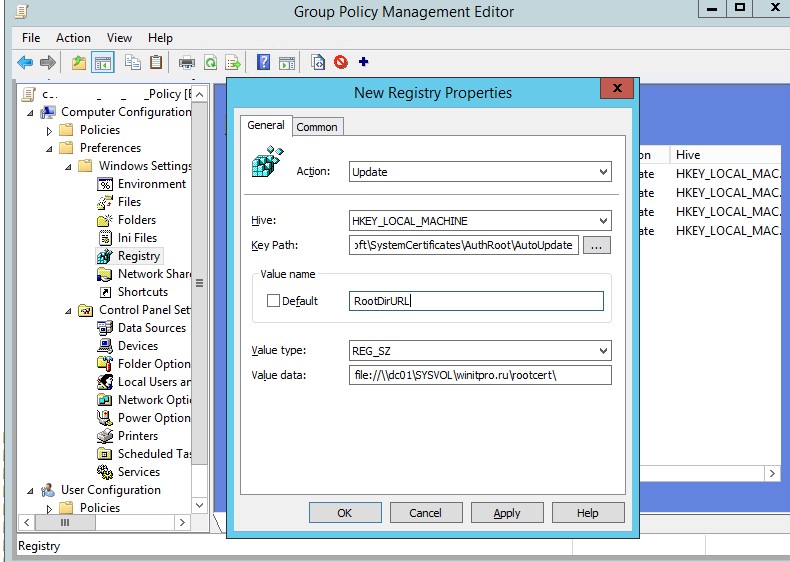
Затем с помощью GPP нужно изменить значение параметра реестра RootDirURL в ветке HKLM\Software\Microsoft\SystemCertificates\AuthRoot\AutoUpdate. Этот параметр должен указывать на сетевую папку, из которой клиентам нужно получать новые корневые сертификаты. Перейдите в секцию редактора GPO Computer Configuration -> Preferences -> Windows Settings -> Registry. И создайте новый параметр реестра со значениями:
Action: Update
Hive: HKLM
Key path: Software\Microsoft\SystemCertificates\AuthRoot\AutoUpdate
Value name: RootDirURL
Type: REG_SZ
Value data: file://\\dc01\SYSVOL\winitpro.ru\rootcert\
Осталось назначить эту политику на компьютеры и после обновления настроек GPO на клиенте проверить появление новых корневых сертификатов в хранилище.
Политика Turn off Automatic Root Certificates Update в разделе Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Internet Communication Management -> Internet Communication settings должна быть выключена или не настроена.
Обновление корневых сертификатов в Windows 7
Несмотря на то, что Windows 7 уже снята с поддержки, есть много пользователей и компаний, в которых она еще используется.
После установки чистой Windows 7 из образа вы может столкнуться, что многие современные программы и инструменты на ней не работают из-за того, что они подписаны с помощью новых сертификатов. В частности, были жалобы, что в Windows 7 64 без обновления сертификатов не удается установить .Net Framework 4.8. или
vs_Community.exe с ошибкой:
installer manifest failed signature validation
Чтобы обновить корневые сертификаты в Windows 7, нужно скачать и установить MSU обновление: KB2813430.
После этого вы можете использовать утилиту certutil для генерации SST файла с сертификатами (на этом или на другом компьютере):
certutil.exe -generateSSTFromWU c:\ps\roots.sst
Теперь можно импортировать сертификаты в доверенные:
MMC -> add snap-in -> certificates -> computer account > local computer. Перейдите в раздел Trusted root certification authority, выберите All Tasks -> Import, найдите ваш SST файл (в типе файлов выберите Microsoft Serialized Certificate Store — *.sst) -> Open -> Place all certificates in the following store -> Trusted Root Certification Authorities
Утилита rootsupd.exe для обновления сертификатов в Windows XP
В Windows XP для обновления корневых сертификатов использовалась утилита rootsupd.exe. В этой утилита содержится список корневых и отозванных сертификатов, зашитых в которой регулярно обновлялся. Сама утилита распространялась в виде отдельного обновления KB931125 (Update for Root Certificates).
- Скачайте утилиту rootsupd.exe, перейдя по ссылке (по состоянию на 15.07.2019 ссылка не работает, возможно в Microsoft решили убрать ее из общего доступа. На данный момент вы можете скачать утилиту с сайта kaspersky.com — http://media.kaspersky.com/utilities/CorporateUtilities/rootsupd.zip);
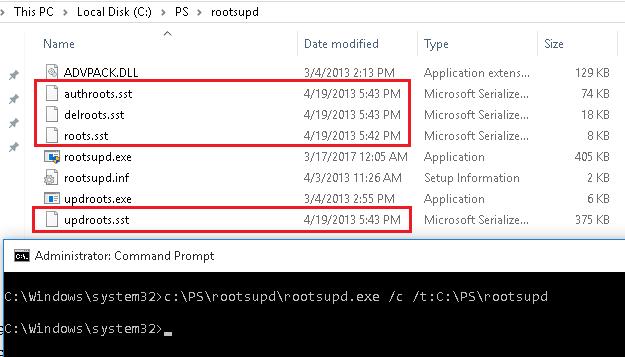
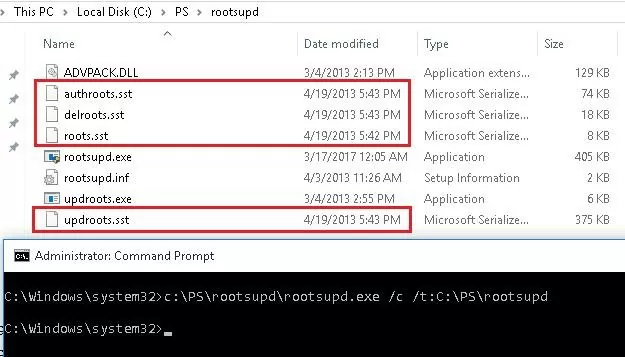
- Для установки корневых сертификатов Windows, достаточно запустить файл rootsupd.exe. Но мы попробуем более внимательно рассмотреть его содержимое, распаковав его с помощью команды:
rootsupd.exe /c /t:C:\PS\rootsupd - Сертификаты содержатся в SST файлах: authroots.sst, delroot.sst и т.п. Для удаления/установки сертификатов можно воспользоваться командами:
updroots.exe authroots.sst
updroots.exe -d delroots.sst
Но, как вы видите, дата создания этих файлов 4 апреля 2013 (почти за год до окончания официальной поддержки Windows XP). Таким образом, с этого времени утилита не обновлялась и не может быть использована для установки актуальных сертификатов. Однако нам чуть позже понадобится файл updroots.exe.
Была информация, что утилиту updroots.exe нежелательно использовать в современных билдах Windows 10 1803+, т.к. она может сломать корневой сертификат Microsoft Root Certificate Authority.
В этой статье мы рассмотрели несколько способов обновления корневых сертификатов на компьютерах Windows, изолированных от Интернета.
Readers help support Windows Report. We may get a commission if you buy through our links.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Root certificates are public key certificates that help your browser determine whether communication with a website is genuine and is based upon whether the issuing authority is trusted and if the digital certificate remains valid.
Suppose a digital certificate is not from a trusted authority. In that case, you’ll get an error message like There is a problem with this website’s security certificate, and the browser might block communication with the website.
Windows 10 has built-in certificates and automatically updates them. However, you can manually add more root certificates to Windows 10 from certificate authorities (CAs).
Where is the Trusted Root Certificate Store in Windows 10?
The Trusted Root Certificate store in Windows 10 is a collection of root certificates for Certificate Authorities (CAs) considered trustworthy by the operating system.
This store is used to validate digital certificates and establish secure connections over the internet.
You must access the Microsoft Management Console to access the Trusted Root Certificate store in Windows 10.
The trusted Root Certificate store is, however, located in the root of the Registry path below:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
How do I add a certificate to the trusted root on Windows 10?
- Install certificates from trusted CAs
- Install Trusted Root Certificates with the Microsoft Management Console
1. Install certificates from trusted CAs
- First, you’ll need to download a root certificate from a CA. For example, you could download one from the GeoTrust site.
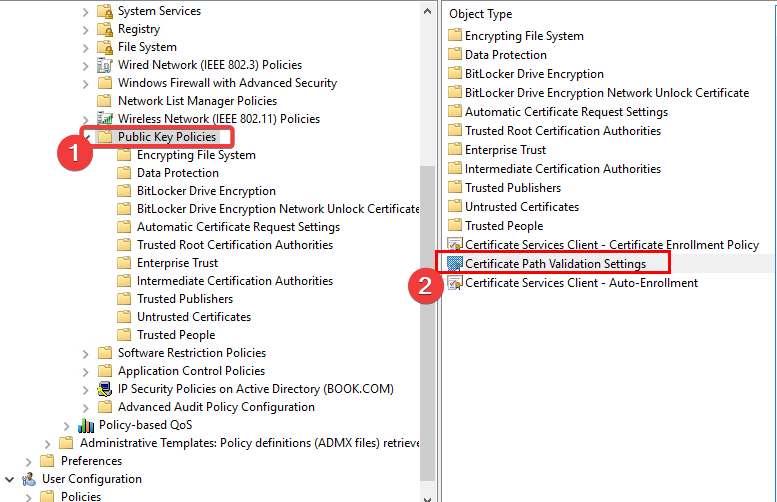
- Next, press Win key + R, enter secpol.msc in Run’s text box, and hit Enter (Windows 10 Home edition doesn’t include the Local Security Policy editor. If your Windows key doesn’t work, check our quick guide to fix it).
- Then, click Public Key Policies and Certificate Path Validation Settings to open a Certificate Path Validation Settings Properties window.
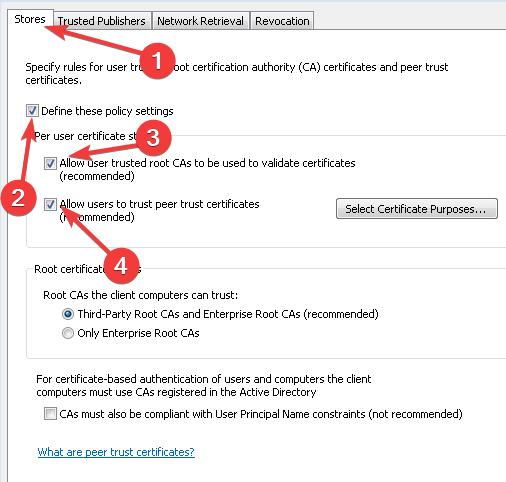
- Click the Stores tab and select the Define these policy settings check box, then tick its two checkboxes.
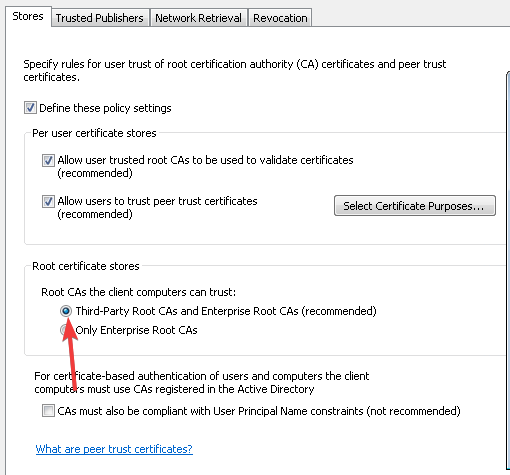
- Select the Third-Party Root CAs and Enterprise Root CAs checkboxes and press the Apply then OK buttons to confirm.
- Press the Win key + R hotkey, type certmgr.msc in Run’s text box, and hit Enter.
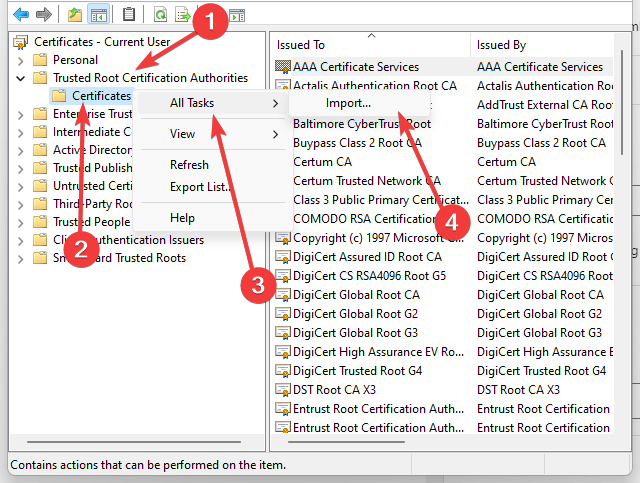
- Click Trusted Root Certification Authorities, right-click Certificates, select All Tasks, and Import.
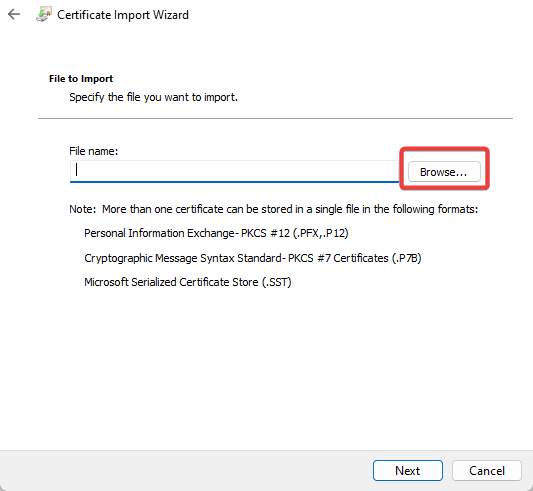
- Press the Next button, click Browse, and select the digital certificate root file saved to your HDD.
- Press Next again to select Automatically select the certificate store based on the type of certificate option.
- Then you can press Next and Finish to wrap up the import wizard. A window will open, confirming that the import was successful.
Most Windows 10 users have no idea how to edit the Group Policy. Learn how you can do it by reading our simple article.
If you don’t have the Group Policy Editor on your Windows PC, get it right now in just a couple of easy steps with our guide on installing the Group Policy Editor on Windows 10.
2. Install Trusted Root Certificates with the Microsoft Management Console
-
1. Press the Win key + R hotkey to open the Run dialog.
-
2. Input mmc in Run and press Enter to open the window below.
-
3. Click File and then select Add/Remove Snap-ins to open the window in the snapshot below.
-
4. Next, you should select Certificates and press the Add button.
-
5. A Certificates Snap-in window opens from which you can select Computer account >Local Account, and press the Finish button to close the window.
-
6. Then press the OK button in the Add or Remove Snap-in window.
-
7. Now you can select Certificates and right-click Trusted Root Certification Authorities on the MMC console window as below.
-
8. Then you can click All Tasks > Import to open the Certificate Import Wizard window.
-
9. From the Certificate Import Wizard window, you can add the digital certificate to Windows.
You can also install root certificates on Windows 10/11 with the Microsoft Management Console. The process is easy and simple, and the console can be accessed via the Run dialog.
If Microsoft Management Console can’t create a new document, follow our guide’s easy steps to solve the issue.
Can’t load the Microsoft Management Console? Our step-by-step guide will help you sort things out.
How to add the certificate to Trusted Root Certification Authorities store using the command line?
- Press Windows + R, type cmd, and hit Ctrl + Shift + Enter.
- Type the script below and hit Enter (Substitute your certificate’s path for C:\Users\Downloads and your certificate’s name for mycertificate):
certutil -addstore root C:\Users\\Downloads\mycertificate.cer
Now you’ve installed a new trusted root certificate in Windows 10. Similarly, you can add many more digital certificates to that OS and other Windows platforms.
Ensure that the third-party digital certificates come from trusted CAs, such as GoDaddy, DigiCert, Comodo, GlobalSign, Entrust, and Symantec.
If you have any more suggestions or questions, leave them in the comments section below, and we’ll certainly check them out.
Matthew Adams
Windows Hardware Expert
Matthew is a freelancer who has produced a variety of articles on various topics related to technology. His main focus is the Windows OS and all the things surrounding it.
He is passionate about the tech world, always staying up-to-date with the latest and greatest. With an analytical view, he likes problem-solving, focusing on errors and their causes.
In his free time, he likes to read and write about history and tries to always develop new skills.
Download Windows Speedup Tool to fix errors and make PC run faster
In one of our earlier posts, we have seen what Root Certificates are. There may be times, when some companies or users may feel the need to manage and configure Trusted Root Certificates, to prevent other users in the domain from configuring their own set. In this post, we will see how to manage Trusted Root Certificates & add certificates to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store in Windows 11/10.
To add certificates to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store for a local computer, from the WinX Menu in Windows 11/10, open Run box, type mmc, and hit Enter to open the Microsoft Management Control.
Press the File menu link and select Add/Remove Snap-in. Now under Available snap-ins, click Certificates, and then click Add.
Click OK. In the next dialog box, select Computer account and then on Next.
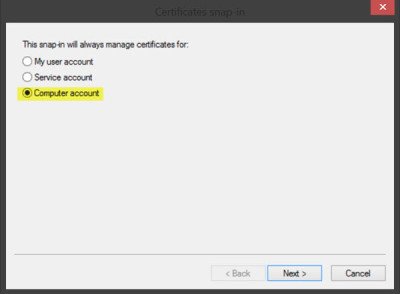
Now select Local computer and click on Finish.
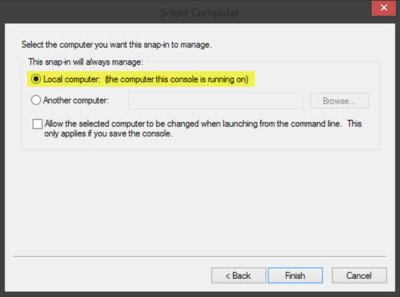
Now, back in MMC, in the console tree, double-click on Certificates and then right-click on Trusted Root Certification Authorities Store. Under All tasks, select Import.
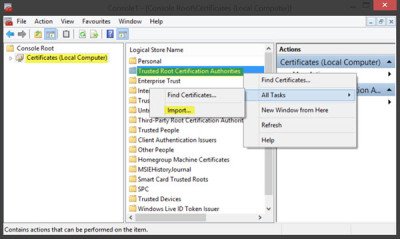
The Certificate Import Wizard will open.
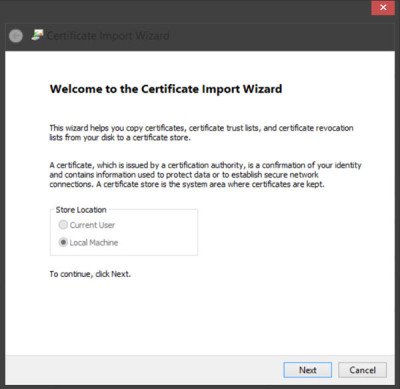
Follow the instructions in the wizard to complete the process.
Now let us see how to configure and manage trusted root certificates for a local computer. Open MMC and press the File menu link and select Add/Remove Snap-in. Now under Available snap-ins, click Group Policy Object Editor, and then click Add. Select the computer whose local GPO you want to edit, and click Finish / OK.
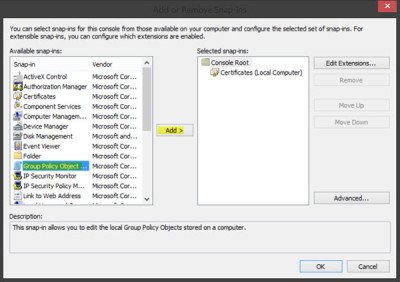
Now, back in the MMC console tree, navigate to Local Computer Policy > Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings. Next Public Key Policies. Double-click Certificate Path Validation Settings, and then select the Stores tab.
Read: Manage certificates using Certificate Manager or Certmgr.msc.
Here, select the Define these policy settings, Allow user trusted root CAs to be used to validate certificates and Allow users to trust peer trust certificates checkboxes.
Finally, under Stores tab > Root certificate stores, select one option under Root CAs that the client computers can trust and click OK. If in doubt, go with the recommended option.
To see how you can manage trusted root certificates for a domain and how to add certificates to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store for a domain, visit Microsoft.
RCC is a free Root Certificates Scanner that can help you scan Windows Root Certificates for untrusted ones.
Anand Khanse is the Admin of TheWindowsClub.com, a 10-year Microsoft MVP (2006-16) & a Windows Insider MVP (2016-2022). Please read the entire post & the comments first, create a System Restore Point before making any changes to your system & be careful about any 3rd-party offers while installing freeware.
All Windows versions have a built-in feature for automatically updating root certificates from the Microsoft websites. MSFT, as part of the Microsoft Trusted Root Certificate Program, maintains and publishes a list of trusted certificates for clients and Windows devices in its online repository. If the verified certificate in its certification chain refers to the root CA that participates in this program, the system will automatically download this root certificate from the Windows Update servers and add it to the trusted ones.
Windows updates a trusted root certificate list (CTL) once a week. If Windows doesn’t have direct access to the Windows Update, the system won’t be able to update the root certificates. So a user may have some troubles when browsing websites (which SSL certificates are signed by an untrusted CA – see the article about the “Chrome SSL error: This site can’t provide a secure connection”), or with installing/running signed scripts and apps.
In this article, we’ll try to find out how to manually update the list of root certificates in TrustedRootCA in disconnected (isolated) networks or computers/servers without direct Internet access.
Contents:
- Managing Trusted Root Certificates in Windows 10 and 11
- How to Disable/Enable Automatic Root Certificates Update in Windows?
- Certutil: Download Trusted Root Certificates from Windows Update
- Certificate Trust List (STL) in Windows
- Updating Trusted Root Certificates via GPO in an Isolated Environment
- How to Update Trusted Root Certificates in Windows 7?
- Updating Root Certificates on Windows XP Using the Rootsupd.exe Tool
Note. If your computers access the Internet through a proxy server, Microsoft recommends that you open direct access (bypass) to Microsoft Web sites to automatically renew root certificates. However, it isn’t always possible or applicable due to corporate restrictions.
Managing Trusted Root Certificates in Windows 10 and 11
How to see the list of trusted root certificates on a Windows computer?
- To open the root certificate store of a computer running Windows 11/10/8.1/7 or Windows Server 2022/2019/2016, run the mmc.exe console;
- Select File -> Add/Remove Snap-in, select Certificates (certmgr) in the list of snap-ins -> Add;
- Select that you want to manage certificates of local Computer account;
- Next -> OK -> OK;
- Expand the Certificates node -> Trusted Root Certification Authorities Store. This section contains the list of trusted root certificates on your computer.
In the mmc console, you can view information about any certificate or remove it from trusted ones.
You can also get a list of trusted root certificates with their expiration dates using PowerShell:
Get-Childitem cert:\LocalMachine\root |format-list
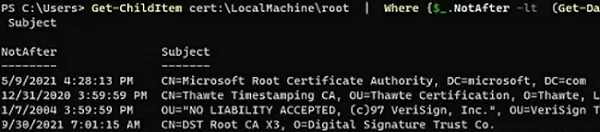
You can list the expired certificates, or which expire in the next 60 days:
Get-ChildItem cert:\LocalMachine\root|Where {$_.NotAfter -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(60)}|select NotAfter, Subject
For security reasons, it’s recommended that you periodically check the certificate trust store on your computer for suspicious and revoked certificates using the Sigcheck tool. This tool allows you to compare the list of certificates installed on the computer with the list of root certificates on the Microsoft website (you can download an offline file with up-to-date certificates authrootstl.cab).
You can manually transfer the root certificate file between Windows computers using the Export/Import options.
- You can export any certificate to a .CER file by clicking on it and selecting All Tasks -> Export;
- You can import this certificate on another computer using the option All Tasks -> Import.
How to Disable/Enable Automatic Root Certificates Update in Windows?
As we mentioned, Windows automatically updates root certificates. You can enable or disable certificate renewal in Windows through a GPO or the registry.
Open the Local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc) and go to Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Internet Communication Management -> Internet Communication.
The Turn off Automatic Root Certificates Update option in this section allows you to disable automatic updating of root certificates through the Windows Update sites. By default, this policy is not configured and Windows always tries to automatically renew root certificates.
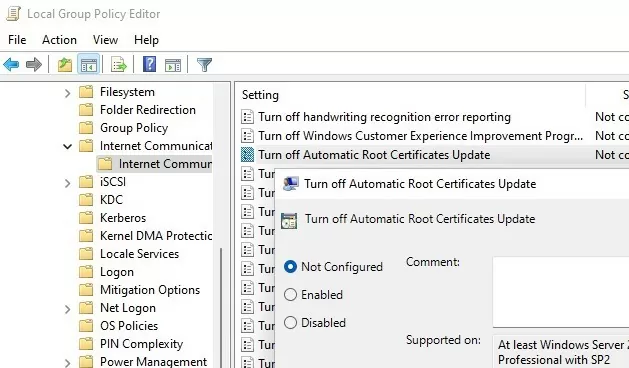
If this GPO option is not configured and the root certificates are not automatically renewed, check if this setting is manually enabled in the registry. Check the value of the registry parameter using PowerShell:
Get-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\SystemCertificates\AuthRoot' -Name DisableRootAutoUpdate
If the command returns that the value of the DisableRootAutoUpdate registry parameter is 1, then the updating of root certificates is disabled on your computer. To enable it, change the parameter value to 0.
Certutil: Download Trusted Root Certificates from Windows Update
Certutil.exe CLI tool can be used to manage certificates (introduced in Windows 10, for Windows 7 is available as a separate update). It can be used to download an up-to-date list of root certificates from Windows Update and save it to an SST file.
To generate an SST file on a computer running Windows 10 or 11 and having direct access to the Internet, open the elevated command prompt and run the command:
certutil.exe -generateSSTFromWU C:\PS\roots.sst
Updated SST file. CertUtil: -generateSSTFromWU command completed successfully.
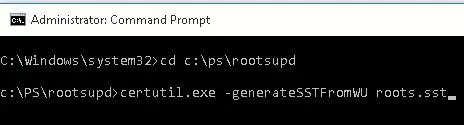
As a result, an SST file containing an up-to-date list of root certificates will appear in the target directory. Double-click to open it. This file is a container containing trusted root certificates.
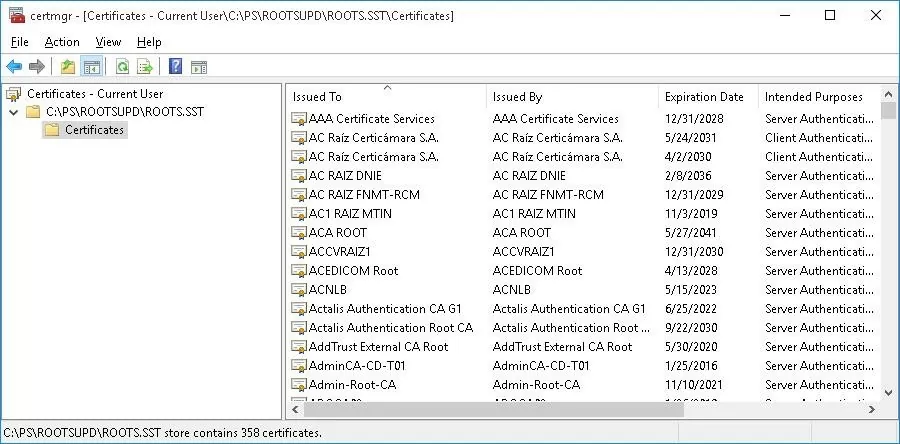
As you can see, a familiar Certificate Management snap-in opens, from which you can export any of the certificates you have got. In my case, there have been 358 items in the list of certificates. Obviously, it is not rational to export the certificates and install them one by one.
Tip. The certutil -syncWithWU command can be used to generate individual certificate files. The certificates obtained in this way can be deployed to Windows devices using GPO.
You can use PowerShell script to install all certificates from the SST file and add them to the list of trusted root certificates on a computer:
$sstStore = ( Get-ChildItem -Path C:\ps\rootsupd\roots.sst )
$sstStore | Import-Certificate -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\Root
Run the certmgr.msc snap-in and make sure that all certificates have been added to the Trusted Root Certification Authority. In my example on Windows 11, the number of root certificates increased from 34 to 438.
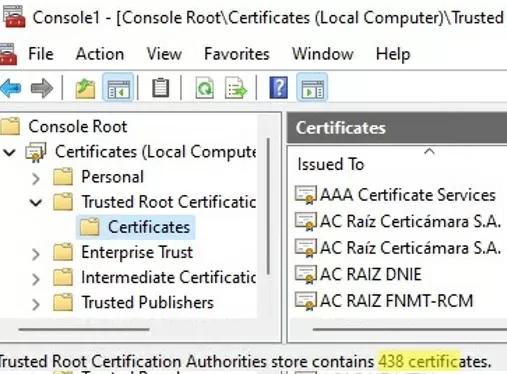
A clean copy of Windows after installation contains only a small number of certificates in the root store. If the computer is connected to the Internet, the rest of the root certificates will be installed automatically (on demand) if your device access an HTTPS site or SSL certificate that has a fingerprint from Microsoft CTL in its trust chain. Therefore, as a rule, there is no need to immediately add all certificates that Microsoft trusts to the local certification store.
Certificate Trust List (STL) in Windows
A Certificate Trust List (CTL) is simply a list of data (such as certificate hashes) that is signed by a trusted party (by Microsoft in this case). The Windows client periodically downloads from Windows Update this CTL, which stores the hashes of all trusted root CAs. It should be understood that this CTL doesn’t contain the certificates themselves, only their hashes and attributes (for example, Friendly Name). Windows devices can download a trusted certificate from Certificate Trust List on demand.
You can manually download and install the CTL file. To do it, download the file http://ctldl.windowsupdate.com/msdownload/update/v3/static/trustedr/en/authrootstl.cab (updated twice a month). Using any archiver (or even Windows Explorer), unpack the contents of the authrootstl.cab archive. It contains a single authroot.stl file.

The Authroot.stl file is a container with a list of trusted certificate thumbprints in Certificate Trust List format.
You can install this CTL file to a Trusted Root Certificate Authority using the certutil command:
certutil -enterprise -f -v -AddStore "Root" "C:\PS\authroot.stl"

root "Trusted Root Certification Authorities" CTL 0 added to store. CertUtil: -addstore command completed successfully.
You can also import certificates using the certificate management console (Trust Root Certification Authorities -> Certificates -> All Tasks -> Import). Specify the path to your STL file with certificate thumbprints.
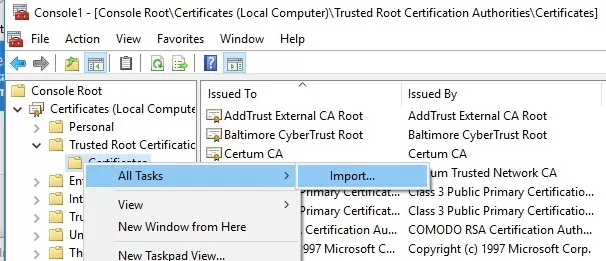
After you have run the command, a new section Certificate Trust List appears in Trusted Root Certification Authorities container of the Certificate Manager console (certmgr.msc).
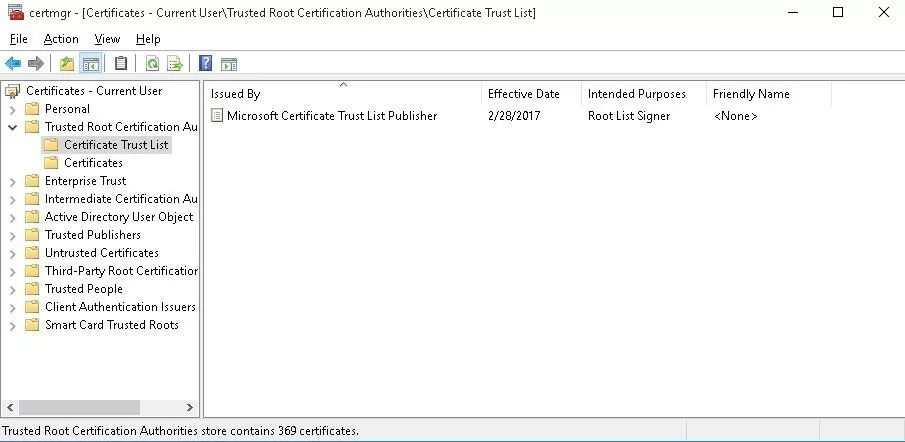
In the same way, you can download and install the list of the revoked (disallowed) certificates that have been removed from the Root Certificate Program. To do it, download the disallowedcertstl.cab file (http://ctldl.windowsupdate.com/msdownload/update/v3/static/trustedr/en/disallowedcertstl.cab), extract it, and add it to the Untrusted Certificates store with the command:
certutil -enterprise -f -v -AddStore disallowed "C:\PS\disallowedcert.stl"
Updating Trusted Root Certificates via GPO in an Isolated Environment
If you have the task of regularly updating root certificates in an Internet-isolated Active Directory domain, there is a slightly more complicated scheme for updating local certificate stores on domain-joined computers using Group Policies. You can configure root certificate updates on user computers in the disconnected Windows networks in several ways.
The first way assumes that you regularly manually download and copy a file with root certificates to your isolated network. You can download the file with current Microsoft root certificates as follows:
certutil.exe –generateSSTFromWU roots.sst
Then the root certificates from this file can be deployed via SCCM or PowerShell Startup script in GPO:
$sstStore = (Get-ChildItem -Path \\fr-dc01\SYSVOL\woshub.com\rootcert\roots.sst )
$sstStore | Import-Certificate -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\Root
The second way is to download the actual Microsoft root certificates using the command:
Certutil -syncWithWU -f \\fr-dc01\SYSVOL\woshub.com\rootcert\
A number of root certificate files (CRT file format) will appear in the specified shared network folder (including files authrootstl.cab, disallowedcertstl.cab, disallowedcert.sst, thumbprint.crt).
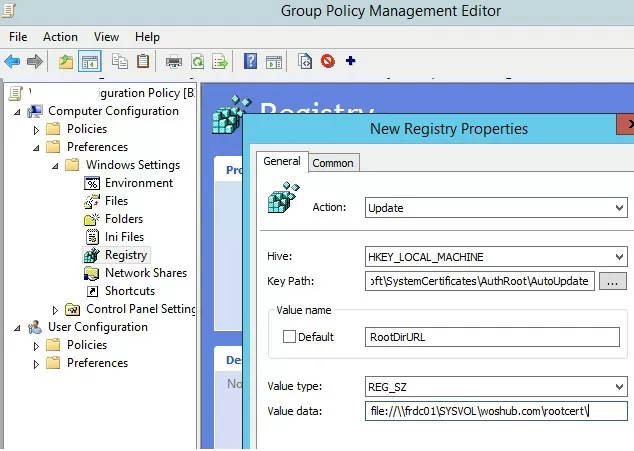
Then use the Group Policy Preferences to change the value of the registry parameter RootDirURL under HKLM\Software\Microsoft\SystemCertificates\AuthRoot\AutoUpdate. This parameter should point to the shared network folder from which your Windows computers will receive new root certificates. Run the domain GPMC.msc console, create a new GPO, switch to the edit policy mode, and expand the section Computer Configuration -> Preferences -> Windows Settings -> Registry. Create a new registry property with the following settings:
- Action: Update
- Hive: HKLM
- Key path: Software\Microsoft\SystemCertificates\AuthRoot\AutoUpdate
- Value name: RootDirURL
- Type: REG_SZ
- Value data: file://\\fr-dc01\SYSVOL\woshub.com\rootcert\
It remains to link this policy on a computer`s OU and after updating GPO settings on the client, check for new root certificates in the certstore.
The GPO parameter Turn off Automatic Root Certificates Update under Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Internet Communication Management -> Internet Communication settings should be disabled or not configured.
How to Update Trusted Root Certificates in Windows 7?
Despite the fact that Windows 7 is now is at the End of Support phase, many users and companies still use it.
After installing a clean Windows 7 image, you may find that many modern programs and tools do not work on it as they are signed with new certificates. In particular, there have been complaints that .Net Framework 4.8 or Microsoft Visual Studio (vs_Community.exe) cannot be installed on Windows 7 SP1 x64 without updating root certificates.
The installer manifest failed signature validation.
Or
NET Framework has not been installed because a certificate chain could not be built to a trusted root authority.
To update root certificates in Windows 7, you must first download and install MSU update KB2813430 (https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/topic/an-update-is-available-that-enables-administrators-to-update-trusted-and-disallowed-ctls-in-disconnected-environments-in-windows-0c51c702-fdcc-f6be-7089-4585fad729d6)
After that, you can use the certutil to generate an SST file with root certificates (on current or another computer):
certutil.exe -generateSSTFromWU c:\ps\roots.sst
Now you can import certificates into trusted ones:
Run MMC -> add snap-in -> certificates -> computer account > local computer. Right click Trusted root certification authority, All Tasks -> Import, find your SST file (in the file type select Microsoft Serialized Certificate Store — *.sst) -> Open -> Place all certificates in the following store -> Trusted Root Certification Authorities.
Updating Root Certificates on Windows XP Using the Rootsupd.exe Tool
In Windows XP, the rootsupd.exe utility was used to update the computer`s root certificates. The list of root and revoked certificates in it was regularly updated. The tool was distributed as a separate update KB931125 (Update for Root Certificates). Let’s see if we can use it now.
- Download the rootsupd.exe utility using the following link http://download.windowsupdate.com/msdownload/update/v3/static/trustedr/en/rootsupd.exe. At the moment (January 2021) the link doesn’t work, Microsoft decided to remove it from the public. Today you can download the rootsupd.exe from the Kaspersky website — http://media.kaspersky.com/utilities/CorporateUtilities/rootsupd.zip;
- To install the Windows root certificates, just run the rootsupd.exe file. But we will try to examine its contents more carefully. Extract the certificates from the executable file with the command:
rootsupd.exe /c /t: C:\PS\rootsupd - Certificates are stored in SST files, like authroots.sst, delroot.sst, etc. To remove or install certificates, you can use the following commands:
updroots.exe authroots.sst
updroots.exe -d delroots.sst
However, as you can see, these certificate files were created on April 4, 2013 (almost a year before the end of official support for Windows XP). Thus, since then the tool has not been updated and cannot be used to install up-to-date certificates.
But you can use cerutil tool in Windows 10/11 to download root.sst, copy that file in Windows XP and install the certificate using updroots.exe:
updroots.exe c:\temp\roots.sst
There is information that the updroots.exe tool is not recommended for use in modern builds of Windows 10 1803+ and Windows 11, as it can break the Microsoft root CA on a device.
In this article, we looked at several ways to update trusted root certificates on Windows network computers that are isolated from the Internet (disconnected environment).
Provide feedback
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
Sign up