За что отвечает параметр «LargeSystemCache»
«LargeSystemCache» является параметром системного реестра в Windows 10. Он определяет, будет ли выделено дополнительное пространство в оперативной памяти устройства для его использования в качестве системного кэша. Параметр принимает всего два значения: «0» (отключено) и «1» (включено).
Выбирать режим работы следует исходя из характеристик компьютера. Если у вас установлена оперативная память относительно большого объема (свыше 4 ГБ), активация параметра значительно ускорит обработку информации в операционной системе. Особенно это будет заметно при работе с большими файлами и базами данных. Но если устройство не сильно мощное, это, наоборот, спровоцирует дополнительные подтормаживания Windows 10 во время запуска и использования программного обеспечения.
Подробнее: Как посмотреть характеристики комплектующих компьютера с Windows 10
Редактирование параметра
Изменить значение параметра «LargeSystemCache» можно только в системном реестре, самостоятельно его открыв и внеся правки. Приведенное ниже руководство поможет вам в этом.
Важно! Редактирование системного реестра — это процедура, которая может серьезно навредить Windows 10, особенно, если вы не делали этого ранее. Важно четко следовать представленной в этой статье инструкции, чтобы добиться желаемого результата без последствий в виде появления ошибок. Если указанного раздела или параметра у вас не будет, рекомендуется прервать выполнение описанных действий и отказаться от изменения параметра «LargeSystemCache».
Читайте также: Восстановление системного реестра в Windows 10
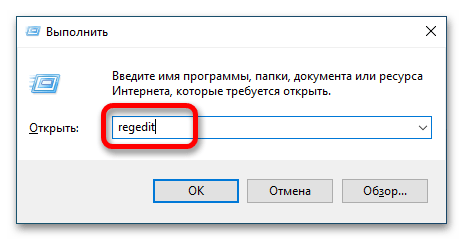
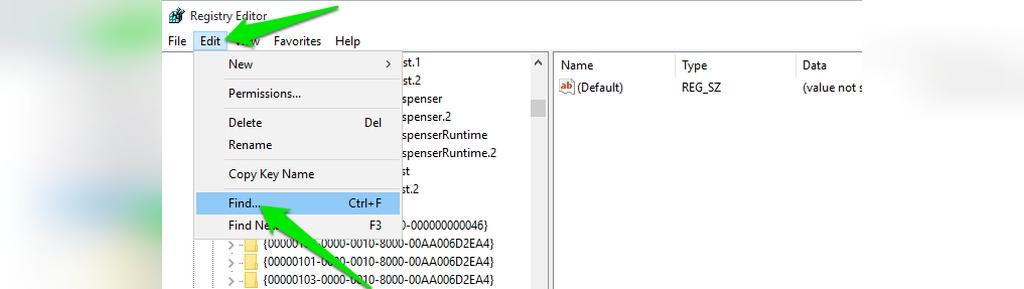
- Откройте «Редактор реестра» любым доступным способом. Проще всего это сделать посредством утилиты «Выполнить». Вызовите ее сочетанием клавиш Win + R, после чего введите в поле «Открыть» команду
regeditи нажмите по клавише Enter.Читайте также: Как открыть «Редактор реестра» в Windows 10
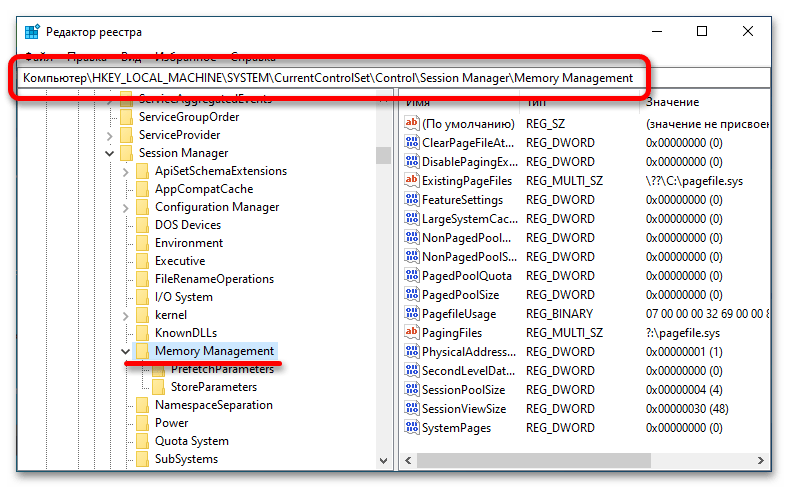
- В появившемся окне проследуйте по указанному ниже пути. Для этого вы можете воспользоваться древовидной структурой каталогов в левой части интерфейса или адресной строкой вверху. Во втором случае достаточно будет вставить приведенный ниже адрес и нажать по клавише Enter.
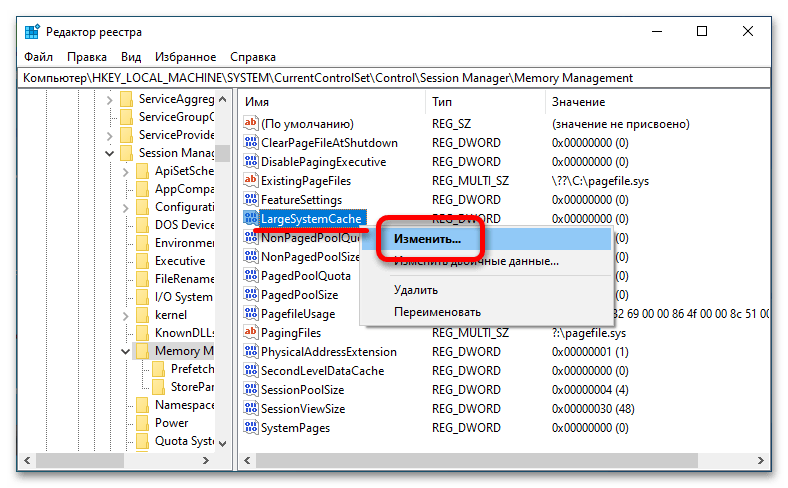
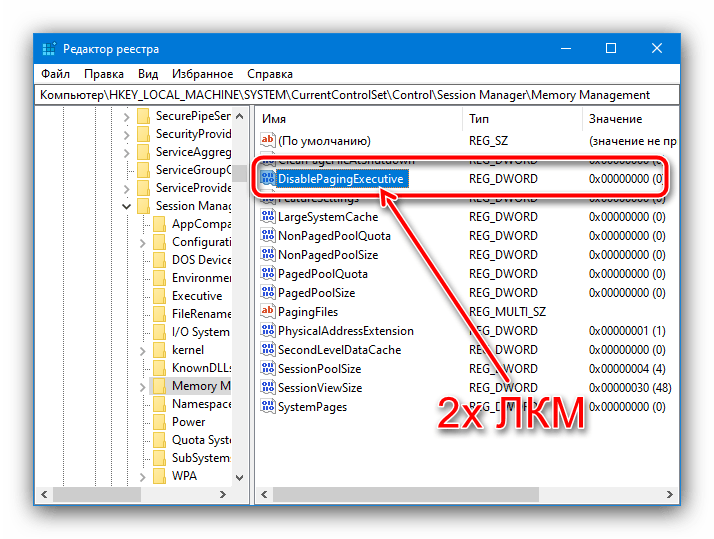
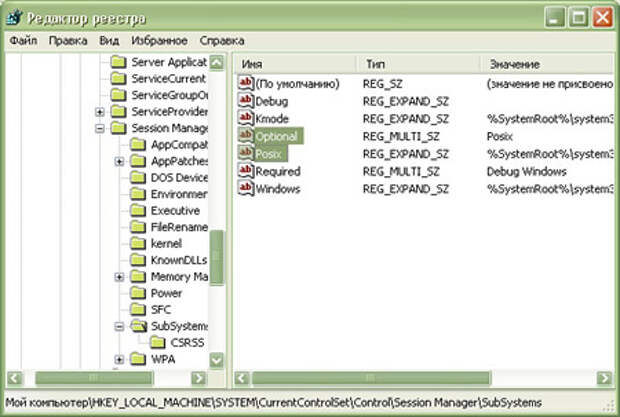
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management - Находясь в директории «Memory Management», отыщите параметр под именем «LargeSystemCache» и откройте окно его свойств. Для этого кликните по названию правой кнопкой мыши и в появившемся контекстном меню выберите пункт «Изменить».
- В отобразившемся на экране окне введите в поле «Значение» цифру «0» (без кавычек) для отключения или «1» (без кавычек) для включения параметра. После нажмите по кнопке «ОК», чтобы сохранить внесенные изменения.
Выполнив все описанные действия, компьютер необходимо перезапустить, в противном случае изменения не отразятся на работе операционной системы.
Примечание! Если вашей целью изначально было расширение системного кэша, рекомендуется обратиться за помощью к другой нашей статье, в которой автор подробно описывает все действия для выполнения поставленной задачи.
Подробнее: Увеличение системного кэша в Windows 10
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
а именно значение вот этого ключа:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management\LargeSystemCache
в win2k и winxp по-умолчанию он включен (LargeSystemCache == 0x00000001). что было замечено лично мной:
если большой кэш выключен, то любые дисковые операции происходят более «плавно», но на больших обьемах заметно постепенное подтормаживание (например копируем DVD на винт — вначале скорость 10-15 мег в секунду, а под конец может упать и до 2 мег).
если большой кэш включен, то он имеет свойство моментально заполняться если приемник не справляется с записью и доходит до сваливания в своп всего что запущено на данный момент (например копируем пару гиг с быстрого винта на более медленный — в результате размер System Cache стремится к обьему оперативки и потом система практически «достается» из свопа)
можно ли регулировать эти параметры более плавно? например хотелось бы чтобы сброс на диск происходил большими кусками (как с включенным LSC), но не сьедал при этом всю память подчистую (50-60% в критических случаях и не больше).
Shortcuts
Tweaks to optimize Windows for low latency online gaming
2014-04-01 (updated: 2021-01-08) by
Tags: gaming, mmo, tweaks
Online Gaming can often benefit from some fine-tuning of Windows TCP/IP settings and the Network Adapter properties. This article is intended to supplement our general broadband tweaks and list only TCP/IP settings that are specific to online gaming and reducing network latency. Some of these settings are also mentioned in our general tweaking articles, however, the emphasis here is on latency rather than throughput, and we have complemented the tweaks with more gaming-specific recommendations and settings that give priority to multimedia/gaming traffic, and may be outside of the scope of other broadband tweaks that focus on pure throughput.
Some proficiency in using Command Prompt/PowerShell and editing the Windows Registry is expected. The Windows Registry can be accessed from the Start/Windows button -> type: regedit. Backing up your Registry before any edits is highly recommended, as mistakes can cause serious issues for the operating system.
Disable Nagle’s Algorithm
(TCP Optimizer «Advanced Settings» tab)
This tweak works with all versions of Windows from Windows XP to Windows 8.1/10/2012 server. This is the same as listed in our general tweaking articles per OS.
Nagle’s algorithm is designed to allow several small packets to be combined together into a single, larger packet for more efficient transmissions. While this improves throughput efficiency and reduces TCP/IP header overhead, it also briefly delays transmission of small packets. Disabling «nagling» can help reduce latency/ping in some games. Keep in mind that disabling Nagle’s algorithm may also have some negative effect on file transfers. Nagle’s algorithm is enabled in Windows by default. To implement this tweak and disable Nagle’s algorithm, modify the following registry keys.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\Interfaces\{NIC-id}
There will be multiple NIC interfaces listed there, for example: {1660430C-B14A-4AC2-8F83-B653E83E8297}. Find the correct one with your IP address listed. Under this {NIC-id} key, create a new DWORD value:
«TcpAckFrequency»=1 (DWORD value, not present by default interpreted as 2, 1=disable nagling, specifies number of outstanding ACKs before ignoring delayed ACK timer). For gaming performance, recommended is 1 (disable). For pure throughput and data streaming, you can experiment with small values over 2. Wifi performance may see a slight improvement with disabled TcpAckFrequency as well.
In the same location, add a new DWORD value:
TCPNoDelay=1 (DWORD, not present by default, 0 to enable Nagle’s algorithm, 1 to disable)
To configure the ACK interval timeout (only has effect if nagling is enabled), find the following key:
TcpDelAckTicks=0 (DWORD value, not present by default interpreted as 2, 0=disable nagling, 1-6=100-600 ms). Note you can also set this to 1 to reduce the nagle effect from the default of 200ms without disabling it.
For Server Operating Systems that have Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ) installed, or if you have the MSMQ registry hive present, also add TCPNoDelay to:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\MSMQ\Parameters
TCPNoDelay=1 (DWORD, not present by default, 0 to enable Nagle’s algorithm, 1 to disable)
Note: Reportedly, disabling Nagle’s algorithm can reduce the latency in many MMOs like Diablo III and WoW (World of Warcraft) by almost half! Yes, it works with Windows 7 and Windows 8.
Network Throttling Index Gaming Tweak
(TCP Optimizer «Advanced Settings» tab)
Works with all current versions of Windows from Vista to 8.1/10/2012 Server.
Windows implements a network throttling mechanism to restrict the processing of non-multimedia network traffic to 10 packets per millisecond (a bit over 100 Mbits/second). The idea behind such throttling is that processing of network packets can be a resource-intensive task, and it may need to be throttled to give prioritized CPU access to multimedia programs. In some cases, such as Gigabit networks and some online games, for example, it is beneficial to turn off such throttling all together for achieving maximum throughput.
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Multimedia\SystemProfile]
«NetworkThrottlingIndex»=dword:ffffffff (DWORD, default: 10, recommended: 10 for media sharing, ffffffff for gaming and max throughput, valid range: 1 through 70 decimal or ffffffff to completely disable throttling)
It is only recommended to change this setting in saturated Gigabit LAN environments, where you do not want to give priority to multimedia playback. Reportedly, disabling throttling by using ffffffff can also help reduce ping spikes in some online games. Games that may be affected by this throttling: Source Engine games (TF2, Left 4 Dead, CS:S), HoN, CoD, Overlord series.
System Responsiveness Gaming Tweak
(TCP Optimizer «Advanced Settings» tab)
Exists in all versions of Windows from Vista to 8.1/10/2012 Server.
Multimedia applications use the «Multimedia Class Scheduler» service (MMCSS) to ensure prioritized access to CPU resources, without denying CPU resources to lower-priority background applications. This reserves 20% of CPU by default for background processes, your multimedia streaming and some games can only utilize up to 80% of the CPU. This setting, in combination with the «NetworkThrottlingIndex» can help some games and video streaming. We recommend reducing the reserved CPU for background processes from the default of 20%.
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Multimedia\SystemProfile]
«SystemResponsiveness»=dword:00000000 (default: 20, recommended: decimal 10 for general applications, 0 for pure gaming/streaming)
Note: In Server operating systems (Windows 2008/2012 Server), SystemResponsiveness is set to 100 by default, denoting that background services should take priority over any multimedia applications.
Turn off LargeSystemCache
(TCP Optimizer «Advanced Settings» tab)
For local network large file transfers, this registry settings allows for better throughput and eliminates some file sharing event log errors (Event ID 2017 error). However, reportedly it has issues with some ATI Video card drivers and certain applications performance. Therefore we recommend turning it off (set to zero) for gaming.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management
LargeSystemCache=0 (DWORD, default value: 0, recommended value: 1 for LAN throughput, 0 for gaming)
A value of zero establishes a cache of ~8 MB, a value of 1 allows the cache to expand up to the amount of physical memory minus 4 MB, as necessary.
Disable Game Bar and Game Mode under Windows 10 Creators update
Windows 10 Creators’ update introduced a «Game Bar» to to help Xbox integration and gaming in general, however, they can reportedly cause stuttering during gaming, especially with Windows 10 builds prior to v1709.
More Gaming Tweaks
This section includes gaming-specific tweaks not listed in our general tweaking articles (and not implemented by the TCP Optimizer).
In the same Registry hive as the above two tweaks, you can also change the priority of Games, compared to other types of traffic. These tweaks only affect games that communicate with e Multimedia Class Scheduler Service (MMCSS). Below is a list of the settings and default/recommended values:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Multimedia\SystemProfile\Tasks\Games]
«Affinity»=dword:00000000 (DWORD, default: 0, recommended: 0. Both 0x00 and 0xFFFFFFFF indicate that processor affinity is not used)
«Background Only»=»False» (REG_SZ, default: «False», recommended: «False», possible values are True or False). Indicates whether this is a background task.
«Clock Rate»=dword:00002710 (DWORD, default: 2710, recommended: 2710). The maximum guaranteed clock rate the system uses if a thread joins disk task, in 100-nanosecond intervals.
«GPU Priority»=dword:00000008 (DWORD, default: 2, recommended: 8. range: 0-31). The GPU priority. Not used in Windows XP and 2003.
«Priority»=dword:00000002 (DWORD, default: 2, recommended: leave alone if using «Scheduling Category» below, set to 6 otherwise for gaming, possible values are 1-8). The task priority, ranging from 1(low) to 8(high). Note for tasks with Scheduling Category of «High», this value is always treated as 2.
«Scheduling Category»=»High» (REG_SZ, default: «Medium», recommended: «High». possible values: Low, Medium, High)
«SFIO Priority»=»High» (REG_SZ, default: «Normal», recommended: «High») The scheduled I/O priority, possible values are Idle, Low, Normal, or High.
Reference: Multimedia Class Scheduler Service
Congestion Control Provider
The TCP Congestion Control Algorithm controls how well, and how fast your connection recovers from network congestion, packet loss, and increase in latency. Microsoft changed the default «congestion provider» from CTCP to CUBIC with the Windows Creators update.
Possible settings are: none, CTCP, CUBIC, DCTCP, New-Reno
Recommended: CTCP for gaming and latency sensitive apps, CUBIC for pure throughput
To see the current setting, in PowerShell use: Get-NetTCPSetting | Select SettingName, CongestionProvider (in later Windows 10 builds, the default used template «SettingName» is «Internet». For more info se our Windows 10 Tweaks article)
Note: If using CTCP and with lossy connections (good possibility of congestion/packet loss), you may also want to enable ECN.
ECN Capability
(Editable with the TCP Optimizer)
ECN (Explicit Congestion Notification, RFC 3168) is a mechanism that provides routers with an alternate method of communicating network congestion. It is aimed to decrease retransmissions. In essence, ECN assumes that the cause of any packet loss is router congestion. It allows routers experiencing congestion to mark packets and allow clients to automatically lower their transfer rate to prevent further packet loss. Traditionally, TCP/IP networks signal congestion by dropping packets. When ECN is successfully negotiated, an ECN-aware router may set a bit in the IP header (in the DiffServ field) instead of dropping a packet in order to signal congestion. The receiver echoes the congestion indication to the sender, which must react as though a packet drop were detected. ECN is disabled by default in modern Windows TCP/IP implementations, as it is possible that it may cause problems with some outdated routers that drop packets with the ECN bit set, rather than ignoring the bit.
Possible settings are: enabled, disabled, default (restores the state to the system default).
Default state: disabled
Recommendation: «enabled» for gaming only with routers that support it, after testing. It’s effects are more noticeable in the presence of congestion/packet loss. Disable for pure throughput with no packet loss.
ECN works well for short-lived, interactive connections like gaming and HTTP requests with routers that support it, in the presence of congestion/packet loss. It can be disabled if tuning for pure bulk throughput with large TCP Window, no regular congestion/packet loss, or with outdated routers that do not support ECN.
To change using netsh:
netsh int tcp set global ecncapability=enabled
(alternative syntax: netsh int tcp set global ecn=enabled)
To change using PowerShell cmdlets in Windows 8.1/2012 Server R2 :
Set-NetTCPSetting -SettingName InternetCustom -EcnCapability Disabled
(for Windows 8/2012, the name of the template in the above command is «Custom» instead of «InternetCustom»)
Notes:
ECN is only effective in combination with AQM (Active Queue Management) router policy. It has more noticeable effect on performance with interactive connections, online games, and HTTP requests, in the presence of router congestion/packet loss. Its effect on bulk throughput with large TCP Window are less clear. Currently, we only recommend enabling this setting in the presence of packet loss, with ECN-capable routers. Its effects should be tested. We also recommend using ECN if you are enabling the CoDel scheduling algorithm to combat bufferbloat and reduce latency.
Use caution when enabling ECN, as it may also have negative impact on throughput with some residential US ISPs. Some EA multiplayer games that require a profile logon do not support ECN yet (you will not be able to logon). Note that if supported, ECN can reduce latency in some games with ECN-capable routers in the presence of packet loss (dropped packets).
See also: Wikipedia — ECN, RFC 3168
Disable Receive Segment Coalescing State (RSC)
(Editable with the TCP Optimizer) This is applicable to Windows 8/10/2012 Server, not available for earlier Windows versions.
Receive Segment Coalescing (RSC) allows the NIC to coalesce multiple TCP/IP packets that arrive within a single interrupt into a single larger packet (up to 64KB) so that the network stack has to process fewer headers, resulting in 10% to 30% reduction in I/O overhead depending on the workload, thereby improving throughput. Receive Segment Coalescing (RCS) is able to collect packets that are received during the same interrupt cycle and put them together so that they can be more efficiently delivered to the network stack. While this reduces CPU utilization and improves thorughput, it can also have a negative impact on latency. That is why we recommend you disable it where latency is more important than throughput.
Possible states: enabled, disabled, default. Default state: disabled
Recommended: disabled for pure gaming latency, enabled for better throughput.
To enable using netsh:
netsh int tcp set global rsc=disabled
To change using PowerShell cmdlets:
Disable-NetAdapterRsc -Name * (use to disable RSC for all adapters)
Enable-NetAdapterRsc -Name * (use to enables RSC for all adapters that support it)
Get-NetAdapterRsc -Name * (use to view adapters that support RSC)
Notes: Only supported by some network adapters. May need «Checksum Offload» enabled as well to work.
Disable Large Send Offload (LSO)
(Editable with the TCP Optimizer) Windows 8/10/2012 Server, not available in earlier Windows versions
Large Send Offload lets the network adapter hardware to complete data segmentation, rather than the OS. Theoretically, this feature may improve transmission performance, and reduce CPU load. The problem with this setting is buggy implementation on many levels, including Network Adapter Drivers. Intel and Broadcom drivers are known to have this enabled by default, and may have many issues with it. In addition, in general any additional processing by the network adapter can introduce some latency which is exactly what we are trying to avoid when tweaking for gaming performance. We recommend disabling LSO at both the Network Adapter properties, and at the OS level with the setting below.
Default: adapter-dependent
Recommended: disable (both in network adapter properties and in the TCP/IP stack at the OS level)
Disable-NetAdapterLso -Name * (disable LSO for all visible network adapters)
Enable-NetAdapterLso -Name * (to enable LSO for both IPv4 and IPv6 on all network adapters, not recommended)
Get-NetAdapterLso -Name * (get a list of network adapters that support LSO)
Notes: Default state is network adapter dependent. Needs Checksum Offload to be enabled to work.
Receive-Side Scaling State (RSS)
(Editable with the TCP Optimizer)
It is sometimes useful to disable RSS if you need to reduce CPU load. This is useful on systems with older/slower CPUs where games tax the processor up to 100% at times. This could be checked with «Task Monitor». Disabling RSS will only have an effect if your network adapter is capable/using RSS, and the CPU is being used up to 100%. Otherwise, you can leave it enabled.
To disable:
netsh int tcp set global rss=disabled
Advanced Concepts
Disable Coalescing: Some network adapters support advanced settings, such as DMA Coalescing, DCA Coalescing, Receive Segment Coalescing (RSC). In general, any type of packet or memory coalescing can reduce CPU utilization (also power consumption) and increases throughput, as it allows the network adapter to combine multiple packets, however, coalescing can also have negative impact on latency, especially with more aggressive settings. That is why it should be either disabled, or used very conservatively for gaming. Any type of network adapter packet/memory coalescing allows the NIC to collect packets before it interacts with other hardware. This may increase network latency. For gaming, disable «DMA coalescing» and «Receive Side Coalescing State (RSC)», where applicable.
NetDMA: This setting needs to be supported by the NIC, BIOS, and CPU (Intel I/O Acceleration Technology — I/OAT). It allows the network adapter direct memory access (DMA), theoretically reducing CPU usage. It is ok to enable for OSes that support it (according to Microsoft it is no longer supported in Windows 8/10). Note that NetDMA is not compatible with TCP Chimney Offload (Chimney offload should be disabled for gaming anyway).
TCP Offloading: TCP Offloads can improve throughput in general, however, they’ve been plagued by driver issues in the past, and, they also put more strain on the network adapter. For pure gaming, disable any TCP Offloads, such as «Large Send Offload (LSO)», for example. For pure gaming and lowest possible latency, the only safe offload that should be left to the network adapter is «Checksum Offload».
Disable Interrupt Moderation: If your Network Adapter supports this setting, it should be disabled for the lowest possible latency (at the expense of a bit higher CPU utilization).
For some of those settings specific to your OS, see our tweaking articles. To disable at the network adapter, see our Network Adapter Optimization article.
Use adequate Send/Receive buffers: low send/receive buffers values conserve a bit of memory, however they can result in dropped packets and decreased performance if exhausted, so they shouldn’t be set to values less than 256 in general. Higher-end NICS/systems can increase the values a bit to 512, or up to 1024.
Router Settings
Most broadband users have some type of NAT router that sits between them and the internet. There are some settings that may help your router better prioritize gaming traffic and improve gaming experience.
Enable upstream QoS in your router. It may be useful to enable upstream QoS at the router, if available, to prioritize the different types of traffic. Upstream QoS is important, because typically residential connections have much lower upstream cap, and when upstream bandwidth is all utilized, it can introduce some delay in the downstream traffic as well. Note this is only recommended for newer routers, where the router has ample computing power to handle the QoS overhead.
Enable WMM if using Wi-Fi. If you must use Wi-Fi, enable WMM, and try to avoid USB Wi-Fi adapters.
Use Open Source Firmware. Many NAT router models support open source firmware, such as dd-wrt, Tomato, etc. If your router’s default firmware does not support advanced functionality that you may need (QoS, WMM, VLANs, etc.), you may be able to flash dd-wrt instead. It is not uncommon for open source firmware to make your connection more stable and reduce router overhead/delay.
Enable CTF (Cut Through Forwarding) — CTF is Broadcom proprietary NAT acceleration. It is a software module that allows routers based on their hardware/firmware to achieve near-gigabit performance and lower CPU utilization through various methods, including bypassing parts of the Linux stack. It is a great feature to use, however there is a catch — it is only available when not using certain other incompatible features that need the Linux functionality (like QoS). You’d have to pick which feature you prefer by testing. In our experience CTF performs better, as the lower CPU/memory utilization and minimal processing trumps QoS in both throughput and latency.
TCP/UDP Timeouts — tweaking the TCP/UDP timeouts can have a noticeable impact on your connection by freeing up resources for active connections. Some of the more advanced router firmwares (Tomato, ASUS Merlin, dd-wrt) have a number of tweakable timeout settings that we’ve already covered in our Wireless Network Speed Tweaks article linked below.
Note: If using dd-wrt, or on Wi-Fi, check our wireless network speed tweaks, some of the advanced router settings are applicable to wired connections as well.
General Online Gaming Recommendations
- Use brand-name, wired Ethernet cards when possible — avoid Wi-Fi, especially with USB client adapters.
- When tweaking TCP/IP (using our general tweaking articles), enable CTCP, enable DCA, and try disabling most «TCP Offloading» settings, with the exception of «Checksum Offload» in both the OS and the Network Adapter Properties.
- Disable «Flow Control» and «Interrupt Moderation» in your Network adapter properties
- Disable TCP/IPv6 in Network adapter properties if not using IPv6
- Reduce the number of background processes, enable QoS at your router and give priority to your traffic.
- Test your latency to game servers using «tracert» in Command Prompt (or PowerShell).
- Disable search indexing on your SSD/hard drive (right-click on drive in Explorer -> choose «Properties» -> untick «Allow files on this drive to have contents indexed…» and wait a few minutes, ignore errors for system-protected files)
- Close unnecessary programs running on your network, you can close the processes in task manager (ctrl+shift+escape). P2P applications such as utorrent and skype open many sockets purely for passive listening and eat up a lot of your available bandwidth. Programs that check for software updates, eg google updates, adobe update, etc. can cause ping spikes.
Intel Recommended Network Adapter Settings
Optimized for quick response and low latency (Gaming):
- Minimize or disable Interrupt Moderation Rate
- Disable Offload TCP Segmentation
- Increase Transmit Descriptors
- Increase Receive Descriptors
- Increase RSS Queues
Optimized for throughput:
- Enable Jumbo Frames
- Increase Transmit Descriptors
- Increase Receive Descriptors
For low CPU utilization:
- Maximize Interrupt Moderation Rate
- Keep Receive Descriptors at default
- Avoid setting large Receive Descriptors
- Decrease RSS Queues
- Decrease the Max number of RSS CPUs in Hyper-V environments
Notes
In some situations, latency can even be reduced by using a VPN provider. Many ISPs provide fast/reliable internet locally between you and their servers, however lack in both speed in latency when it comes to their peering arrangements and backbones for longer distance connections. They could also be throttling certain traffic types. In such situations, a local to you quality VPN provider may allow you to avoid the ISP bottleneck by bypassing a lot of internal/cluttered routing and skip to a distant location faster, providing a lower latency connection.
Some of the tweaks in our general broadband tweaks articles can benefit gaming as well, like disabling «Windows Scaling Heuristics», disabling TCP 1323 Timestamps to reduce the TCP headers overhead, etc.
Most of the Registry tweaks above (with the exception of «More Gaming Tweaks») can be applied easily by using the TCP Optimizer
See Also
Wireless Network Speed Tweaks — some of the router recommendations apply to wired networks and gaming as well.
Network Adapter Optimization — tweaking your NIC settings can help improve your connection.
We appreciate any feedback and always listen to user suggestions.
The system allows changed pages to remain in physical memory until the number of available pages drops to approximately 250. This setting is recommended for most computers running Windows 2000 Server on large networks.
Should I enable large system cache?
Large System Cache allows windows to use more RAM for cache thus needing to page to the SSD less often. For older machines this caused issues when RAM was at a premium but for machines with 4GB+ RAM you will only notice performance improvements.
How do I enable large system cache?
following steps:
- Start a registry editor (e.g., regedit.exe).
- Navigate to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management registry subkey.
- Double-click LargeSystemCache, set it to 0 for desktop mode or 1 for server mode, then click OK.
- Close the registry editor.
How do I increase disk cache in Windows 10?
In Windows it is possible to increase the performance of a disk cache through a modification of the system registry. Take a backup of the registry before running REGEDIT. Change the values of the LargeSystemCache key in the registry from 0 to 1. This should increase the performance of a disk cache.
How do I turn off paging executive?
Disabling paging the executive
- From an elevated Windows Command Prompt, load the regedit.exe application.
- Navigate to HKLM | System | CurrentControlSet | Control | Session Manager | Memory Management.
- Update the Disable Paging Executive DWORD to a value of 1 (from 0 ) to disable …
How do I enable L3 cache?
To enable L3 cache in Windows: In a free area in the right window, right click and click on “New” >; “DWORD 32 bit value” Rename the new key by “ThirdLevelDataCache” (without the quotes) Right click on this new key renamed and click on ‘Edit’ Click “Decimal”
What is Clearpagefileatshutdown?
The pagefile is where virtual memory that the operating system is using is stored when the physical memory (RAM) is not enough to fit all the running apps and system demands. Windows 10 creates a special file pagefile. sys in the root of your system drive like all previous releases of the OS.
How do I increase RAM cache size?
Select Configure > Subsystems > Cache > General. In the Ram Cache Size field, enter the amount of space (in megabytes) you want to allocate to the RAM cache. Although the user interface will accept larger values, do not exceed 512 MB. The default size is 104857600 (100 MB).
How do I increase my cache memory?
With newer systems, the most effective way to increase cache memory is to replace the current CPU with one that has a higher capacity. This will automatically make it possible to increase the size of the cache memory, as well as enhance the processor speed and overall performance of the system.
What is paging executive Windows 10?
The paging executive setting in Windows is used to load system files such as the kernel and hardware drivers to the page file when needed. These sets of system files are called executive files. Disabling the paging executive will force the executive files to run in memory regardless of the current usage.
How much cache do I need?
The higher the demand from these factors, the larger the cache needs to be to maintain good performance. Disk caches smaller than 10 MB do not generally perform well. Machines serving multiple users usually perform better with a cache of at least 60 to 70 MB.
How do I increase L2 cache?
4 Answers. the L2 cache is built into the CPU itself. The only way to get more is to replace your CPU with one that has more L2 cache. The Celeron is more of a budget class processor compared to your C2D, so it makes sense that it has less cache.
Is the largesystemcache setting a good thing?
The LargeSystemCache setting upset the balance so as to favor the file cache, even to the point where applications ran short of memory. This is a good thing, but only in a computer used primarily as a server. I used the setting on a computer running Windows 2000 server.
How do I Turn on large system cache?
1. Right click My Computer 2. Select Properties 3. Click Advanced 4. Choose Performance 5. Click Advanced again 6. Select either Programs or System Cache under Memory Usage. On NT Server (in this case XP), the Large System Cache option is enabled, but disabled on Workstation.
Is the large system cache enabled on NT Server?
On NT Server, the Large System Cache option is enabled, but disabled on Workstation. The two different settings effect how the cache manager allocates free memory. If the Large Cache option is on, the manager marks all the free memory, which isn’t being used by the system and/or applications, as freely available for disk caching.
How does increasing the file system cache improve performance?
Increasing the size of the file system cache generally improves server performance, but it reduces the physical memory space available to applications and services. Similarly, writing system data less frequently minimizes use of the disk subsystem, but the changed pages occupy memory that might otherwise be used by applications.
Главная »
Инструкции по Windows » Максимальная производительность Windows 10: эффективная настройка Largesystemcache
Узнайте, как правильно настроить параметр Largesystemcache в операционной системе Windows 10, чтобы повысить производительность вашего компьютера и оптимизировать использование системных ресурсов.

Проверьте текущее значение параметра Largesystemcache и установите оптимальное значение в соответствии с характеристиками вашего компьютера.
КАК УСКОРИТЬ И ОСВОБОДИТЬ ОЗУ Windows 10 Pro? 100% лайфхак для оперативной памяти
Помните, что увеличение значения Largesystemcache может улучшить производительность при работе с крупными файлами и приложениями, требующими больших объемов памяти.
Как оптимизировать Windows 10? Увеличение файлов подкачки
Однако не стоит устанавливать слишком большое значение Largesystemcache, так как это может привести к неэффективному использованию оперативной памяти и замедлению работы системы.
Оптимизаторы Windows больше не нужны?
Регулярно следите за изменениями в работе системы после настройки параметра Largesystemcache и в случае необходимости корректируйте его значение для достижения оптимальной производительности.
Индекс производительности в Windows 10

Помните о резервировании достаточного объема оперативной памяти для других процессов и задач при установке значения Largesystemcache, чтобы избежать конфликтов и снижения общей производительности системы.
Удаляем из Windows все лишнее! Выпилим хлам, повысим стабильность и скорость загрузки.

Изучите рекомендации и советы от производителя вашего оборудования или программного обеспечения относительно оптимальной настройки параметра Largesystemcache для вашей конкретной конфигурации системы.
Индекс производительности windows равен — 1 или вовсе не удается его вычислить? ЗДЕСЬ РЕШЕНИЕ ☑

При внесении изменений в параметр Largesystemcache не забудьте создать резервную копию важных данных и системных файлов, чтобы в случае необходимости можно было быстро восстановить предыдущую конфигурацию.
Реставрирую старый Уаз!
Используйте профессиональные инструменты для анализа производительности системы и мониторинга использования ресурсов, чтобы более точно определить оптимальное значение параметра Largesystemcache для вашей системы.
fixicomp.ruные прерывания, процессор 100%, майнер вирус.
При возникновении проблем с производительностью после настройки параметра Largesystemcache обратитесь к специалистам или форумам сообщества пользователей Windows 10 для получения дополнительной помощи и советов.
how to enable largesystemcache (performance boost)
Не забывайте регулярно обновлять операционную систему и драйвера устройств для обеспечения совместимости и оптимальной работы системы с учетом внесенных изменений в параметр Largesystemcache.
Увеличение системного кеша
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Configure-dfacb15f9ff74809900622227b6a9073.jpg)