Программистам часто приходится работать в консоли — например, чтобы запустить тестирование проекта, закоммитить новый код на Github или отредактировать документ в vim. Всё это происходит так часто, что все основные действия с файлами становится быстрее и привычнее выполнять в консоли. Рассказываем и показываем основные команды, которые помогут ускорить работу в терминале под OS Windows.
Для начала нужно установить терминал или запустить командную строку, встроенную в Windows — для этого нажмите Win+R и введите cmd. Терминал часто встречается и прямо в редакторах кода, например, в Visual Studio Code.
Чтобы ввести команду в консоль, нужно напечатать её и нажать клавишу Enter.
Содержимое текущей папки — dir
Выводит список файлов и папок в текущей папке.
C:\content-server>dir
Том в устройстве C имеет метку SYSTEM
Серийный номер тома: 2C89-ED9D
Содержимое папки C:\content-server
06.10.2020 00:41 <DIR> .
06.10.2020 00:37 <DIR> .circleci
16.07.2020 16:04 268 .editorconfig
16.07.2020 16:04 10 .eslintignore
16.07.2020 16:04 482 .eslintrc
06.10.2020 00:37 <DIR> .github
16.07.2020 16:04 77 .gitignore
06.10.2020 00:41 <DIR> assets
06.10.2020 00:41 <DIR> gulp
16.07.2020 16:10 379 gulpfile.js
16.07.2020 16:10 296 320 package-lock.json
16.07.2020 16:10 751 package.json
16.07.2020 16:04 509 README.md
Открыть файл
Чтобы открыть файл в текущей папке, введите его полное имя с расширением. Например, blog.txt или setup.exe.
Перейти в другую папку — cd
Команда cd без аргументов выводит название текущей папки.
Перейти в папку внутри текущего каталога:
C:\content-server>cd assets
C:\content-server\assets>
Перейти на одну папку вверх:
C:\content-server\assets>cd ..
C:\content-server>
Перейти в папку на другом диске:
c:\content-server>cd /d d:/
d:\>
Чтобы просто изменить диск, введите c: или d:.
Создать папку — mkdir или md
Создаём пустую папку code внутри папки html:
d:\html>mkdir coded:\html>dir
Содержимое папки d:\html
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> .
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> ..
03.11.2020 19:25 <DIR> code
0 файлов 0 байт
3 папок 253 389 438 976 байт свободно
Создаём несколько пустых вложенных папок — для этого записываем их через косую черту:
d:\html>mkdir css\js
d:\html>dir
Том в устройстве D имеет метку DATA
Серийный номер тома: 0000-0000
Содержимое папки d:\html
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> .
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> ..
03.11.2020 19:25 <DIR> code
03.11.2020 19:29 <DIR> css
Создаётся папка css, внутри которой находится папка js. Чтобы проверить это, используем команду tree. Она показывает дерево папок.
Удалить папку — rmdir или rd
Чтобы удалить конкретную папку в текущей, введите команду rmdir:
d:\html\css>rmdir js
При этом удалить можно только пустую папку. Если попытаться удалить папку, в которой что-то есть, увидим ошибку:
d:\html\css>d:\html>rmdir css
Папка не пуста.
Чтобы удалить дерево папок, используйте ключ /s. Тогда командная строка запросит подтверждение перед тем, как удалить всё.
d:\html>rmdir css /s
css, вы уверены [Y(да)/N(нет)]? y
Показать дерево папок — tree
В любом момент мы можем увидеть структуру папок. Для этого используется команда tree.
d:\html>tree
Структура папок тома DATA
Серийный номер тома: 0000-0000
D:.
├───code
└───css
└───js
Если вы хотите посмотреть содержимое всего диска, введите tree в корне нужного диска. Получится красивая анимация, а если файлов много, то ещё и немного медитативная.
Удаление файла — del или erase
Команда для удаления одного или нескольких файлов.
d:\html>del blog.txt
Переименование файла — ren или rename
Последовательно вводим ren, старое и новое имя файла.
d:\html>dir
Содержимое папки d:\html
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> .
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> ..
03.11.2020 19:59 0 blag.txt
d:\html>ren blag.txt blog.txt
d:\html>dir
Содержимое папки d:\html
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> .
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> ..
03.11.2020 19:59 0 blog.txt
Команды одной строкой
Очистить консоль — cls.
Информация о системе — systeminfo.
d:\html>systeminfo
Имя узла: DESKTOP-6MHURG5
Название ОС: Майкрософт Windows 10 Pro
Версия ОС: 10.0.20246 Н/Д построение 20246
Изготовитель ОС: Microsoft Corporation
Параметры ОС: Изолированная рабочая станция
Сборка ОС: Multiprocessor Free
Информация о сетевых настройках — ipconfig.
d:\html>ipconfig
Настройка протокола IP для Windows
Адаптер Ethernet Ethernet 2:
Состояние среды. . . . . . . . : Среда передачи недоступна.
DNS-суффикс подключения . . . . . :
Список запущенных процессов — tasklist.
c:\>tasklist
Имя образа PID Имя сессии № сеанса Память
========================= ======== ================ =========== ============
System Idle Process 0 Services 0 8 КБ
System 4 Services 0 2 688 КБ
Secure System 72 Services 0 23 332 КБ
…
Справка по командам — help
Команда help без аргументов выводит список всех возможных команд. help вместе с именем команды выведет справку по этой команде.
d:\html>help tree
Графическое представление структуры папок или пути.
TREE [диск:][путь] [/F] [/A]
/F Вывод имён файлов в каждой папке.
/A Использовать символы ASCII вместо символов национальных алфавитов.
В этой статье приведены не все команды и не все их возможности, но вы всегда можете воспользоваться командой help и узнать о том, что ещё может командная строка.
👉🏻 Больше статей о фронтенде и работе в айти в телеграм-канале.
Подписаться
Материалы по теме
- 10 горячих клавиш VS Code, которые ускорят вашу работу
- Полезные команды для работы с Git
- Полезные команды для работы с Node. js
«Доктайп» — журнал о фронтенде. Читайте, слушайте и учитесь с нами.
ТелеграмПодкастБесплатные учебники
The dir command is one of the most useful commands while navigating the command line, and is present in its different forms in several operating systems. In this article, we will look at the Dir command and learn several use cases for it.
What is the dir Command
dir command in Windows OS is a built-in function that allows the user to do the following task:
- View the contents of any directory
- Check file attributes (both hidden and read-only)
- Filter search results based on date or file type.
Basic Syntax
The general syntax of the dir command is:
dir [path] [options]
- Path: specifies the location
- Options: modifies to filter the output
1. List Files & Directories
This command is used to list all files and directories in the current one:
help dir
help dir command
Output :
Displays a list of files and subdirectories in a directory.
DIR [drive:][path][filename] [/A[[:]attributes]] [/B] [/C] [/D] [/L] [/N]
[/O[[:]sortorder]] [/P] [/Q] [/R] [/S] [/T[[:]timefield]] [/W] [/X] [/4]
[drive:][path][filename]
Specifies drive, directory, and/or files to list.
/A Displays files with specified attributes.
attributes D Directories R Read-only files
H Hidden files A Files ready for archiving
S System files I Not content indexed files
L Reparse Points O Offline files
- Prefix meaning not
/B Uses bare format (no heading information or summary).
/C Display the thousand separator in file sizes. This is the
.
.
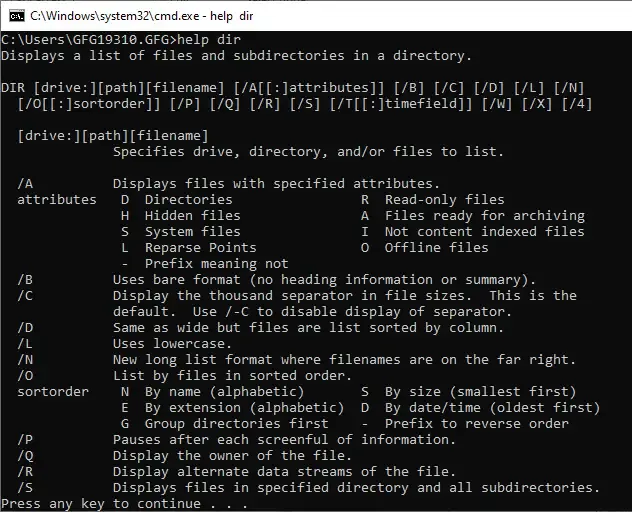
output
Usage explanation:
The command is mainly used for displaying the list of files and subdirectories in a directory. This could be done by executing the Dir command without any arguments.
Dir
dir
Which would produce an output similar to this.
Output
Directory of C:\Users
09/26/2020 11:34 AM <DIR> .
09/26/2020 11:34 AM <DIR> ..
09/02/2020 07:07 PM 1, 000 applese
09/24/2020 08:59 PM <DIR> Public
10/20/2020 06:39 PM <DIR> Soap
1 File(s) 1, 000 bytes
4 Dir(s) 13, 879, 459, 840 bytes free
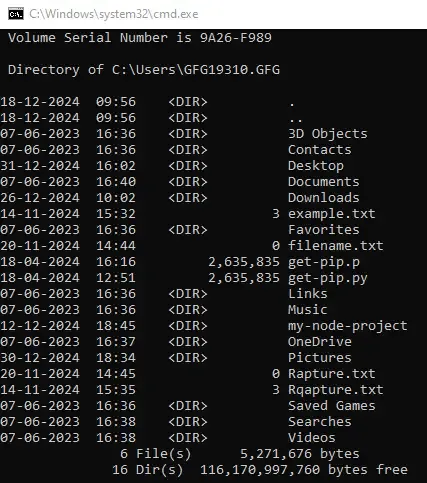
Output
2. List Content of a Specific Directory
The output of the dir command in this enable users to specify a directory to view its contents. The syntax for this command is as follows:
Input
dir C:\Users\gfg19310\Documents
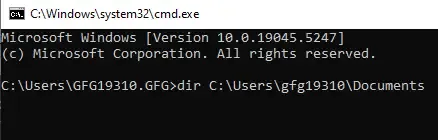
List all content – Input
Output
Directory of C:\Users\gfg19310\Documents
20-03-2023 13:02 <DIR> .
20-03-2023 13:02 <DIR> ..
20-03-2023 13:02 <DIR> Custom Office Templates
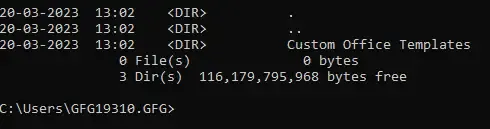
List all content – Output
3. Show Hidden Files
Here, we will use /A option with the H attribute to include hidden files along with it. Here’s the syntax:
Input
dir /A:H
show hidden file – Input
Output
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> AppData
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Application Data [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming]
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Cookies [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\INetCookies]
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Local Settings [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Local]
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> My Documents [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\Documents]
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> NetHood [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Network Shortcuts]
11-12-2024 05:46 3,670,016 NTUSER.DAT
07-06-2023 16:36 688,128 ntuser.dat.LOG1
07-06-2023 16:36 1,085,440 ntuser.dat.LOG2
02-01-2025 10:40 1,048,576 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e87-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TxR.0.regtrans-ms
18-12-2024 09:56 1,048,576 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e87-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TxR.1.regtrans-ms
18-12-2024 09:56 1,048,576 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e87-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TxR.2.regtrans-ms
18-12-2024 09:56 65,536 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e87-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TxR.blf
07-06-2023 16:36 65,536 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e88-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TM.blf
07-06-2023 16:36 524,288 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e88-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TMContainer00000000000000000001.regtrans-ms
07-06-2023 16:36 524,288 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e88-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TMContainer00000000000000000002.regtrans-ms
07-06-2023 16:36 20 ntuser.ini
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> PrintHood [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Printer Shortcuts]
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Recent [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Recent]
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> SendTo [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\SendTo]
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Start Menu [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu]
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Templates [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Templates]
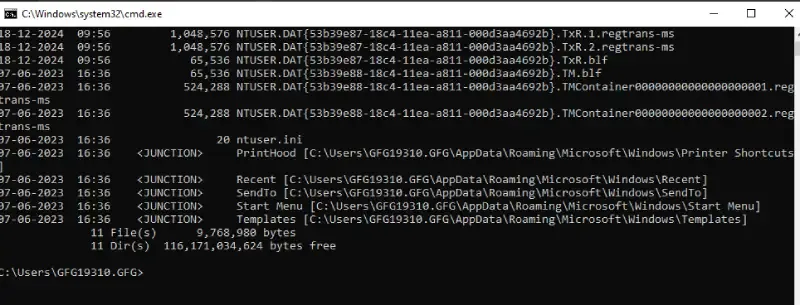
show hidden file – Output
4. List Files with Specific Extensions
To display files with a specific extension (e.g., .txt): Here’s a sample
Input
dir *.txt
Display Text -input
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG
14-11-2024 15:32 3 example.txt
20-11-2024 14:44 0 filename.txt
20-11-2024 14:45 0 Rapture.txt
14-11-2024 15:35 3 Rqapture.txt
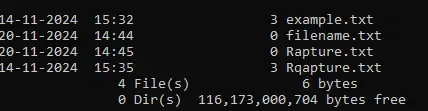
Display Text -Output
5. View Subdirectories
To include all subdirectories and their contents, use the following command:
Input
dir /S
dir /S
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\Saved Games
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> .
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> ..
0 File(s) 0 bytes
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\Searches
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> .
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> ..
08-11-2022 16:52 855 winrt--{S-1-5-21-1623517014-2252875782-278851815-1404}-.searchconnector-ms
07-06-2023 16:37 859 winrt--{S-1-5-21-2245693176-3959787992-2909979321-1244}-.searchconnector-ms
2 File(s) 1,714 bytes
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\Videos
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> .
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> ..
26-12-2024 13:37 <DIR> Captures
0 File(s) 0 bytes
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\Videos\Captures
26-12-2024 13:37 <DIR> .
26-12-2024 13:37 <DIR> ..
26-12-2024 13:37 185,053 File Explorer 26-12-2024 13_37_47.png
11-10-2023 15:51 23,668 Network Connections .png
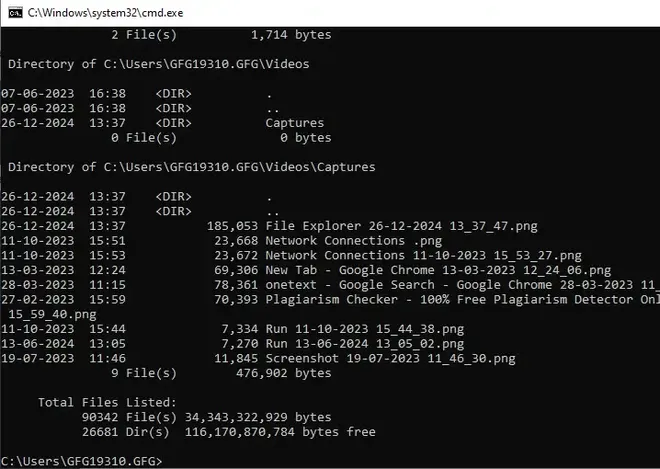
Fetching Directory
6. Sort by Date, Size, or Name
We can fetch data based on date, size or name. Let’s check them out:
By Date:
Input
dir /O:D
dir /O:D
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> 3D Objects
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Contacts
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Favorites
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Music
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Saved Games
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Links
07-06-2023 16:37 <DIR> OneDrive
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Searches
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Videos
07-06-2023 16:40 <DIR> Documents
18-04-2024 12:51 2,635,835 get-pip.py
18-04-2024 16:16 2,635,835 get-pip.p
14-11-2024 15:32 3 example.txt
14-11-2024 15:35 3 Rqapture.txt
20-11-2024 14:44 0 filename.txt
20-11-2024 14:45 0 Rapture.txt
12-12-2024 18:45 <DIR> my-node-project
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> .
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> ..
26-12-2024 10:02 <DIR> Downloads
30-12-2024 18:34 <DIR> Pictures
31-12-2024 16:02 <DIR> Desktop
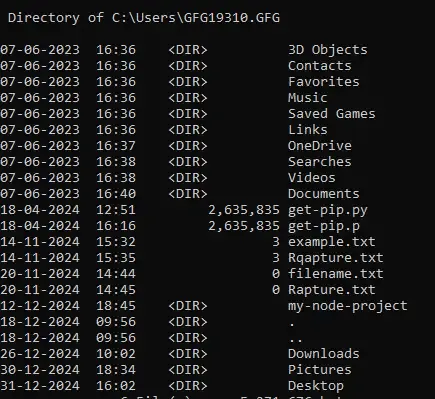
Output
By Size:
Input
dir /O:S
dir /O:S
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> .
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> ..
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> 3D Objects
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Contacts
31-12-2024 16:02 <DIR> Desktop
07-06-2023 16:40 <DIR> Documents
26-12-2024 10:02 <DIR> Downloads
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Searches
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Favorites
20-11-2024 14:44 0 filename.txt
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Saved Games
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Videos
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Links
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Music
12-12-2024 18:45 <DIR> my-node-project
07-06-2023 16:37 <DIR> OneDrive
30-12-2024 18:34 <DIR> Pictures
20-11-2024 14:45 0 Rapture.txt
14-11-2024 15:32 3 example.txt
14-11-2024 15:35 3 Rqapture.txt
18-04-2024 12:51 2,635,835 get-pip.py
18-04-2024 16:16 2,635,835 get-pip.p
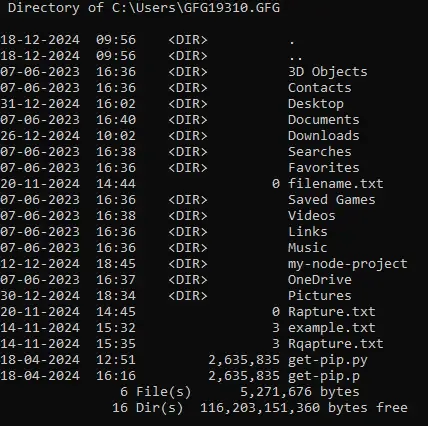
Output
By Name:
Input
dir /O:N
dir /O:N
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> .
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> ..
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> 3D Objects
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Contacts
31-12-2024 16:02 <DIR> Desktop
07-06-2023 16:40 <DIR> Documents
26-12-2024 10:02 <DIR> Downloads
14-11-2024 15:32 3 example.txt
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Favorites
20-11-2024 14:44 0 filename.txt
18-04-2024 16:16 2,635,835 get-pip.p
18-04-2024 12:51 2,635,835 get-pip.py
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Links
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Music
12-12-2024 18:45 <DIR> my-node-project
07-06-2023 16:37 <DIR> OneDrive
30-12-2024 18:34 <DIR> Pictures
20-11-2024 14:45 0 Rapture.txt
14-11-2024 15:35 3 Rqapture.txt
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Saved Games
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Searches
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Videos
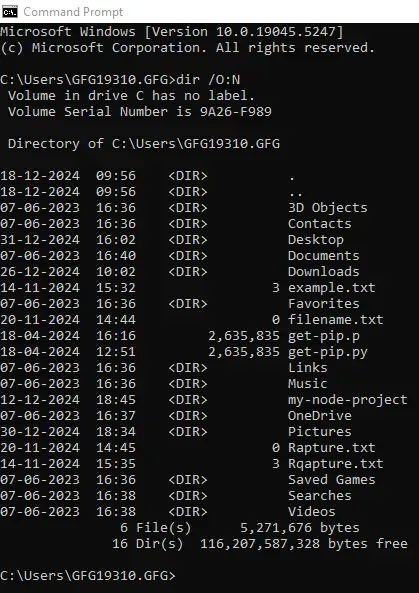
Output
7. View Results Page by Page
This command is used where too many files exists, we can use the /P option to get results one page at a time. Here’s the command:
Input
dir /P
dir /P
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> .
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> ..
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> 3D Objects
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Contacts
31-12-2024 16:02 <DIR> Desktop
07-06-2023 16:40 <DIR> Documents
26-12-2024 10:02 <DIR> Downloads
14-11-2024 15:32 3 example.txt
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Favorites
20-11-2024 14:44 0 filename.txt
18-04-2024 16:16 2,635,835 get-pip.p
18-04-2024 12:51 2,635,835 get-pip.py
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Links
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Music
12-12-2024 18:45 <DIR> my-node-project
07-06-2023 16:37 <DIR> OneDrive
30-12-2024 18:34 <DIR> Pictures
20-11-2024 14:45 0 Rapture.txt
14-11-2024 15:35 3 Rqapture.txt
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Saved Games
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Searches
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Videos
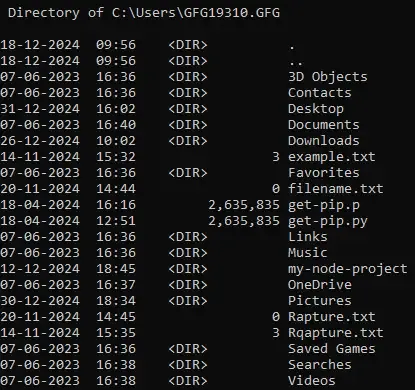
Output
8. List File Attributes
We can also include attributes such as read-only files and archives using the following command:
Input
dir /A
dir /A
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> .
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> ..
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> 3D Objects
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> AppData
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Application Data [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming]
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Contacts
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Cookies [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\INetCookies]
31-12-2024 16:02 <DIR> Desktop
07-06-2023 16:40 <DIR> Documents
26-12-2024 10:02 <DIR> Downloads
14-11-2024 15:32 3 example.txt
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Favorites
20-11-2024 14:44 0 filename.txt
18-04-2024 16:16 2,635,835 get-pip.p
18-04-2024 12:51 2,635,835 get-pip.py
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Links
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Local Settings [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Local]
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Music
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> My Documents [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\Documents]
12-12-2024 18:45 <DIR> my-node-project
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> NetHood [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Network Shortcuts]
11-12-2024 05:46 3,670,016 NTUSER.DAT
07-06-2023 16:36 696,320 ntuser.dat.LOG1
07-06-2023 16:36 1,003,520 ntuser.dat.LOG2
02-01-2025 10:40 1,048,576 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e87-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TxR.0.regtrans-ms
18-12-2024 09:56 1,048,576 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e87-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TxR.1.regtrans-ms
18-12-2024 09:56 1,048,57 ..
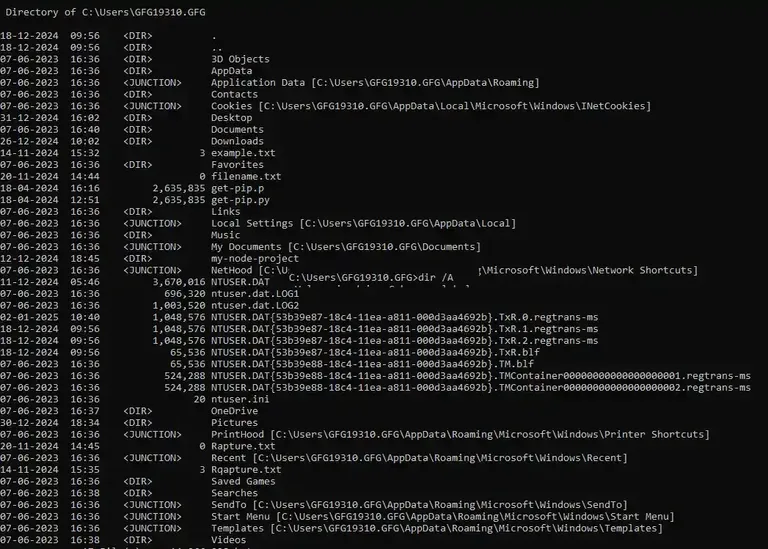
Output
9. Display File Size
You can also check the file size (in bytes) using the following command:
Input
dir /-C
dir /-C
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> .
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> ..
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> 3D Objects
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Contacts
31-12-2024 16:02 <DIR> Desktop
07-06-2023 16:40 <DIR> Documents
26-12-2024 10:02 <DIR> Downloads
14-11-2024 15:32 3 example.txt
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Favorites
20-11-2024 14:44 0 filename.txt
18-04-2024 16:16 2635835 get-pip.p
18-04-2024 12:51 2635835 get-pip.py
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Links
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Music
12-12-2024 18:45 <DIR> my-node-project
07-06-2023 16:37 <DIR> OneDrive
30-12-2024 18:34 <DIR> Pictures
20-11-2024 14:45 0 Rapture.txt
14-11-2024 15:35 3 Rqapture.txt
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Saved Games
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Searches
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Videos
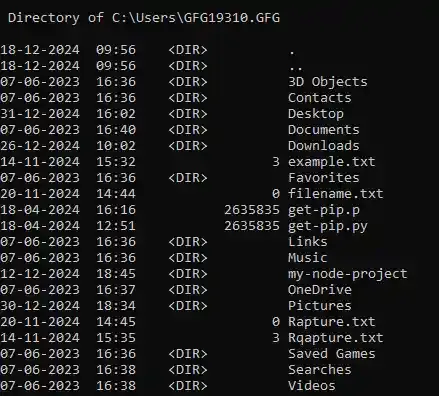
Output
Advanced Syntax
The above-mentioned syntaxes is for general usage. Now, let’s see some of the advanced usage syntax along with their examples.
10. Save Output to a File
We can redirect the output to a text file (dir command) using the syntax below:
Input (file name: rapture.txt)
dir /S > rapture.txt
dir /S > filename
Output
A file name with the provided name will be created containing the directory list.
Output
11. Search for any Specific File
You can search for any file by its name (or even partial name), following this syntax:
Input (file name: rapture – taken as a partial name “rapt”)
dir *rapt*
*filename*
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG
03-01-2025 11:03 7,854,908 Rapture.txt
1 File(s) 7,854,908 bytes
0 Dir(s) 116,168,089,600 bytes free
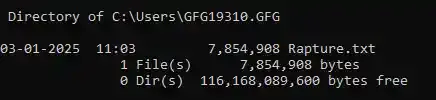
Output
12. Check the Total Number of Files
This syntax will summarise the total count of a file including directory:
Input
dir /W
dir /W
Output
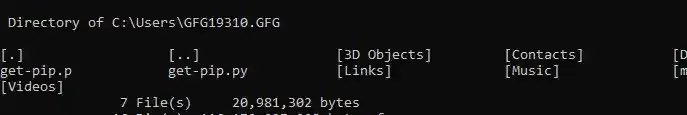
Output
Bonus: Useful cmd Options (Summarization)
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
/P |
Fetch results one page at a time |
/S |
Includes all files in subdirectories. |
/A |
Displays files with specified attributes (e.g., /A:H for hidden files). |
/O |
Sorts output (e.g., /O:D for date, /O:N for name). |
/B |
Displays output in bare format (file names only, without additional details). |
/L |
Displays names in lowercase. |
/T |
Displays time attributes (e.g., /T:C for creation time). |
/Q |
Displays file ownership information. |
The dir command is vastly used among users for managing and exploring directories through different ways and patterns in Windows OS. You can give it all a try and organize your work smoothly.
- Use the “DIR” command to list files and folders in the current directory, or “DIR /S” to list files and folders recursively, in subdirectories as well.
- To search for specific file types use the asterisk followed by the file extension type, in this syntax: DIR *.jpg
- Use attribute switches to filter the type of files and folders to list.
It can be tricky to keep tabs on all files and folders on a Windows computer, especially if there are too many. There can be many folders and subfolders inside a partition, and many different types of file extensions. It can be difficult to view all the files and folders, or even search for specific ones using File Explorer.
Using the Command Prompt, you can view and list all sorts of files and folders inside a directory, and even its subdirectories using recursive switches. Not only that, but you can also list all items with a specific file type, or exclude them. Moreover, you can also view hidden items as well directly from the Command Prompt.
In this article, we give you a bunch of different examples to list files and folders inside the Command Prompt using the DIR cmdlet.
Command to List Files and Folders in Command Prompt
The DIR command is used to list files and folders inside a directory in Command Prompt. This command can be used with a number of switches and attributes to filter the items to display, their order or displaying, to include and exclude, and so on.
However, the only switches we will be interested in are /a and /s.
Using the DIR command alone will display all the files and folders inside that particular directory. It will not show any hidden items, and it will now show any items inside the subdirectories. However, if you use DIR /a, it will show the hidden items as well.
To perform a recursive search, we must use the /s switch.
The table below summarises the commands to use to list files and folders and these switches:
| Command | Description |
| DIR | Display items inside the current directory |
| DIR /a | Display all items inside the current directory, including hidden ones. |
| DIR /s | List items inside the current directory as well as all subdirectories |
With that known, there is a list of attributes that you can use with the DIR /a cmdlet to filter the type of information you want to list. Here is a list of the attributes you can use with /a.
| Attribute Alphabet | Description | Syntax Example |
| d | Shows directories only | DIR /ad |
| h | Show hidden items only | DIR /ah |
| s | Show system files only | DIR /as |
| l | Show reparse points only | DIR /al |
| r | Show read-only files | DIR /ar |
| a | Show files that can be archived | DIR /aa |
| i | Show files whose content is not indexed | DIR /ai |
| – (hyphen) | Used before an attribute to exclude it from the list | DIR /a-s (hide system files) |
| : (colon) | To combine multiple attributes | DIR /a:h-s (Show hidden items but hide system files) |
Example Commands to List Files and Folders in Command Prompt
Let us now continue to see more extensive examples with images to better understand how you can list files and folders using the DIR cmdlet.
-
To list all files and folders in the current directory:
DIRList files and folders in the current directory using Command Prompt -
To list all files and folders in the current directory and subdirectories:
DIR /SList recursive files and folders in Command Prompt -
To list only folders in the current directory:
DIR /ADList only folders in the current directory in Command Prompt -
To list only folders in the current directory and subdirectories:
DIR /AD /SList only folders in the current directory and subdirectories in Command Prompt -
To list all files in the current directory and exclude all folders:
DIR /A-DList all files and exclude folders in the current directory in Command Prompt -
To list all hidden system files in the current directory:
DIR /ASHList all hidden system files in current directory in Command Prompt -
To list all system files and exclude read-only files in the current directory and subdirectories:
DIR /A:S-A /SList all system files and exclude read-only files in the current directory and subdirectories using Command Prompt -
To list all specific file type files in the current directory and subdirectories:
Note: You can change the file type extension to list the files you are looking for.
DIR *.txtList all files with a specific file type using Command Prompt -
To list multiple file types in the current directory and subdirectories:
DIR *.txt *.doc *.docx /SList multiple file types in the current directory and subdirectories from Command Prompt
There can be many different examples and syntaxes to list files and folders inside the Command Prompt. However, we hope that the examples above are sufficient so that you can combine and modify them as per your requirements.
Closing Words
The Windows command line offers much more control over the fetched data than its GUI. Using the Command Prompt, you can list different files and folders inside the current directory as well as its subdirectories. You can also filter out the type of files and folders to include, or exclude from the list.
При работе на компьютере иногда возникает необходимость получить полный список файлов и папок в каталоге или даже целом томе. Понадобиться он может для самых разных целей, например, для каталогизации, для сравнения, для использования в какой-то базе данных и так далее. В большинстве случаев приходится иметь дело с большим числом объектов, поэтому нечего и думать, чтобы составить такой список вручную.
Если создание списка файлов вручную представляется едва ли возможным, то какая есть тому альтернатива, какие программные инструменты лучше всего подойдут для этих целей? Решений существует несколько, все они очень просты и удобны. Получить список файлов и папок можно с помощью обычной командной строки, с помощью PowerShell, штатного Проводника, любого браузера, а также с помощью сторонних специализированных утилит.
Получаем список файлов и папок в командной строке
Для чтения содержимого каталогов в старой доброй командной строке предусмотрена команда dir, её то как раз мы и будем использовать. Итак, запускаем консоль CMD, командой cd Буква диска:/путь (если нужно перейти в другой диск, добавляем после cd ключ /d) переходим в нужное расположение и выполняем эти две команды:
chcp 1251 dir /b /s > D:\filelist.tхt

Первая команда устанавливает кириллическую кодировку, вторая сохраняет список всех файлов, папок и вложенных в них объектов в текстовый лог на диске D.

Если нужно получить список только файлов (без вложенных каталогов), достаточно использовать только ключ /b.
Примечание: в Windows 8.1 и 7 для быстрого перехода в папку в командной строке, зажмите Shift, кликните ПКМ по папке и выберите в контекстном меню опцию «Открыть окно команд».
Список файлов и папок в PowerShell
В Windows 10 командная строка заменена консолью PowerShell, для получения списка файлов можете использовать её. Для примера выведем в файл содержимое папки Тест с её подкаталогами:
Get-Childitem -Path D:\Тест -Recurse | Out-File D:\filelist.tхt

А можно и проще. Зажав Shift, кликаем по папке ПКМ, выбираем в меню «Открыть PowerShell здесь».

И выполняем в открывшемся окне консоли команду Get-Childitem -Recurse | Out-File D:\filelist.tхt.

Необходимость использования параметра -Path с указанием пути в данном случае отпадает.
Получение списка файлов или папок в Проводнике
Этот способ позволяет получить список либо файлов, либо папок в конкретном расположении. Заходим в целевую папку, выделяем в ней все файлы или папки, зажимаем Shift, кликаем правой кнопкой мыши и выбираем в меню опцию «Копировать как путь».

Пути и имена выделенных объектов будут переданы в буфер обмена, откуда вы уже сможете перенести их в текстовый файл.
Получение списка файлов с помощью DirLister
Для получения хорошо структурированного списка объектов файловой системы можно воспользоваться бесплатной портативной утилитой DirLister, скачав её с официального сайта:
www.barrysoft.it/blog/software/dirlister
Запустив утилиту, укажите в разделе «Directory To Scan» путь к сканируемому каталогу или диску, в разделе «Output File» выберите расположение для сохранения списка.

Здесь же можно задать параметры сканирования — выбрать формат, указать, нужно ли включать в список вложенные директории и скрытые объекты, задать поиск по маске. После нажатия кнопки «Make List» список будет сохранён в выбранном расположении.
Используем для получения списка файлов браузер
На худой конец для создания списка файлов и папок на диске можно воспользоваться любым браузером. Перетаскиваем папку или диск на новую вкладку браузера и получаем список имеющихся в ней файлов и каталогов.

Рекурсивно пройтись по всем вложенным каталогам, правда, не получится да и для копирования путей и имён файлов и переноса их в отдельный файл придется использовать Ctrl + C и Ctrl + V.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to list files, folders, and subfolders using Windows CMD commands and PowerShell.
I’ll also demonstrate using the NTFS Permissions Tool, which is a graphical program that displays the permissions on folders and subfolders.
In this article
- List Files and Folders using the DIR Command
- Display Folder Structure using TREE Command
- Powershell List Folders and Subfolders
- Get Folder and Subfolder NTFS Permissions
Check it out.
List Files and folders using the DIR Command
The dir command is built into all versions of Windows. It is an easy to use command to list files, folders, and subfolders from the Windows command prompt.
Let’s look at some examples.
Example 1. List files and folders in the current directory
To list the files and folders in the current directory, open the Windows command prompt, enter dir and press enter. The dir command by default does not display subfolders.
dirIn this example, my current location is c:\it, so when I run the dir command it will list everything in this folder.

I have put the command output into colored boxes to explain what each column means.
- Red = This column is the last modified date of the file or folder
- Green = Indicates if the item is a folder, folders are labeled with DIR
- Purple = The size of the file
- Yellow = Name of the file or folder.
Example 2. List subfolders
Use the /s option to include subfolders.
dir /sI ran the command from the c:\it location and it lists all subfolders and files from this directory. I’ve highlighted some of the subfolders in the screenshot below.

Example 3. Specify a directory path
To list files and folders from a specific directory enter the complete directory path.
dir /s c:\itFor example, if my current location is the root of c: and I type dir /s c:\it the command will display the items from the c:\it directory.

Example 4. Export list of files and folders
To export the screen output use the command below. You can name the file whatever you want, in this example, I named the file files2.txt
dir > files2.txtThe file will be saved to the current directory.

Pretty easy right?
I covered some of the most basic dir command options. To see a full list of options type dir /? and press enter.

To learn more about the dir command check out the Microsoft dir documentation page.
Display Folder Structure using TREE Command
The tree command is another built-in Windows command. This command will display the contents of a directory in a tree structure. This can be useful to give you an overview of the folder layout.
You must specify a path or this command will start at the root of c
Example 1. List all folders and subfolders using TREE
To list all folders and subfolders enter the tree command and the path.
tree c:\it\toolkit
Example 2. List all folders and files using TREE
To include files with the tree command use the /f option.
tree c:\it\toolkit /f
In my experience, I never use the tree command. I find it more useful when a command provides more details like modified dates, permissions, ownership, and so on. If you just need to see the files and folders with no other details then this is a great option.
Powershell List Folders and Subfolders
You can use the Get-Childitem PowerShell cmdlet to list files and folders. The Get-Childitem cmdlet is similar to dir but much more Powerful.
Let’s look at some examples
Example 1. List files and folders using Get-Childitem
This example gets the folder contents from a specific directory
Get-ChildItem -path c:\it\toolkit
By default, the Get-ChildItem cmdlet lists the mode, LastWriteTime, Length, and Name of the filer or folder.
The mode can be the following:
- l = Link
- d – directory
- a = archive
- r = read-only
- h = hidden
- s = system
Example 2. Get subfolders using Get-ChildItem
Use the -Recurse option to get subfolders and files.
Get-ChildItem -path c:\it\toolkit -Recurse
Example 3. Get items using the Depth parameter
You can use the -Depth parameter to control how many subfolders deep to include in the list.
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\it -Depth 2Example 4. PowerShell List only specific file types
In this example, I will list only files that end in a .msi file extension. This will search all subfolders in the directory path.
get-childitem -path c:\it -include *.msi -recurse
Example 5. PowerShell List only folder or files name
The -Name parameter will only return the file or folder name.
Get-ChildItem -path c:\it\toolkit -Name
Example 6. PowerShell List all Files and Folder Details
To display all details of a file or folder use the fl option.
Get-ChildItem -path c:\it\toolkit | FLYou can see below this command will display additional details, if there are any.

Example 7. PowerShell count files and folders
To get a count of the files and folders use the measure-object option.
Get-ChildItem -path c:\it\toolkit | Measure-Object
Example 8. Powershell Get Folder Size
You can also use the measure-object option to get the folder size.
Get-ChildItem -path c:\it\toolkit | Measure-Object -Property Length -sum
As you can see using PowerShell there are a lot of options when it comes to getting files and folders, you can create some really powerful reports.
Check out the Get-ChildItem documentation page to learn more.
Get Folder and Subfolder NTFS Permissions
If you need a report of folders and subfolders that includes who has permission to what, then check out the NTFS Permissions Reporting Tool below.
Example 1. List NTFS Permissions on Shared Folder
You can try this tool for FREE, click here to download it.
In this example, I’ll get the permissions on the shared folder \\srv-vm1\share

The NTFS Report will display the following:
- DirectoryName = Path of the folder
- Account = Account listed on the folder (this can be a user or group)
- DirectoryOwner = Owner listed on the folder
- DirectoryRights = Permissions the user or group has to the folder
- Type = Allow or Deny
- AppliesTo = What the permissions applies to
- IsInherited = Are the permissions inherited from a parent folder
Example 2. List Folder Permissions on Local Folder
If you want to check the permissions on a local folder click the browse button or enter the folder path.

Which Command Will You Use?
In this article, I showed you three different commands to get files, folders, and subfolders.
I use the dir command for basic stuff and use Get-Childitem for more advanced searches.
Which command did you find most useful? Let me know in the comments below.
Related Articles
- PowerShell get NTFS Permissions
- Windows list open files
- 10 Windows File Share Best Practices









