Во многих случаях для выхода из безопасного режима Windows достаточно простой перезагрузки компьютера или ноутбука, но не всегда. Если вы «застряли» в безопасном режиме, а перезагрузка не помогает, проблему обычно сравнительно просто решить.
В этой пошаговой инструкции о способах выйти из безопасного режима Windows 11 или Windows 10, все они предполагают изменение параметров загрузки таким образом, чтобы система загружалась в обычном режиме при последующем запуске.
Выход из безопасного режима путем изменения параметров загрузки в окне конфигурации системы
Самый простой способы выхода из безопасного режима — отключение соответствующего параметра в окне «Конфигурация системы». Шаги будут следующими:
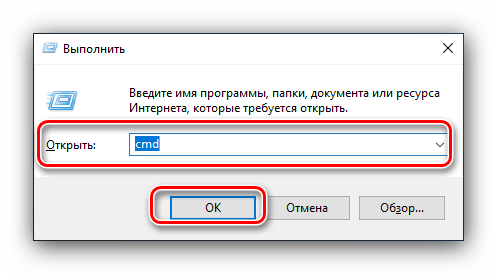
- Нажмите клавиши Win+R на клавиатуре, либо нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по кнопке «Пуск» и выберите пункт «Выполнить».
- Введите msconfig в окно «Выполнить» и нажмите Ок или Enter.
- В открывшемся окне «Конфигурация системы» перейдите на вкладку «Загрузка».
- Снимите отметку «Безопасный режим» для текущей операционной системы, нажмите «Ок» и подтвердите перезагрузку компьютера.
После перезагрузки Windows должна будет загрузиться в обычном режиме.
Как правило, этого способа оказывается достаточно для решения проблемы. Если по какой-то причине этот способ не сработал или требуются иные варианты решения проблемы, о них — далее.
Отключение безопасного режима в командной строке
Следующий способ — использование командной строки для удаления параметра, включающего загрузку в безопасном режиме. Необходимые шаги:
- Нажмите клавиши Win+R на клавиатуре, введите cmd (убедитесь, что в окне «Выполнить» указано, что это задание будет создано с правами администратора) и нажмите Enter.
- В открывшейся командной строке введите команду
bcdedit /deletevalue {current} safebootи нажмите Enter. Вы должны будете увидеть сообщение «Операция успешно завершена».
- Закройте командную строку и перезагрузите компьютер, либо можно использовать следующую команду для перезагрузки прямо из командной строки: shutdown /r
В результате после перезагрузки ваша Windows 11 или Windows 10 должна будет загрузиться в обычном, а не безопасном режиме работы.
Выключение загрузки в безопасном режиме в EasyBCD
На мой взгляд, использование сторонних программ для решения рассматриваемой проблемы и выхода из безопасного режима, будет излишним. Однако, с их помощью это тоже можно сделать. Для примера будем использовать бесплатную для домашнего использования EasyBCD:
- Скачайте (если Интернет в безопасном режиме не работает, можно скачать на телефон и скопировать на компьютер) утилиту EasyBCD.
- Перейдите в раздел программы «Дополнительные настройки».
- Убедитесь, что в поле «Выбор операционной системы» выбрана нужная ОС.
- На вкладке «Дополнительные» в пункте «Безопасный режим» выберите опцию «Обычный» и нажмите кнопку «Сохранить».
- Закройте программу и перезагрузите компьютер для загрузки в обычном режиме.
На этом всё. Если же проблемы остаются, опишите в комментариях детально, что именно происходит и что привело к текущей ситуации, возможно, решение найдётся.
Все способы:
- Выходим из «Безопасного режима»
- Способ 1: Консоль
- Способ 2: «Конфигурация системы»
- Заключение
- Вопросы и ответы: 14
«Безопасный режим» позволяет решать множество проблем с операционной системой, но однозначно не подходит для повседневного использования вследствие ограничений на загрузку некоторых служб и драйверов. После устранения сбоев его лучше отключить, и сегодня мы хотим ознакомить вас с тем, как выполнить эту операцию на компьютерах под управлением Windows 10.
Выходим из «Безопасного режима»
В Виндовс 10, в отличие от более старых вариантов системы от Microsoft, обычной перезагрузки компьютера может быть недостаточно для выхода из «Safe Mode», поэтому следует задействовать более серьёзные варианты – например, «Командную строку» или «Конфигурацию системы». Начнём с первого.
Читайте также: Безопасный режим в Windows 10
Способ 1: Консоль
Интерфейс ввода команд Windows поможет в случае, когда запуск «Безопасного режима» осуществляется по умолчанию (как правило, вследствие невнимательности пользователя). Проделайте следующее:
- Используйте сочетание клавиш Win+R для вызова окошка «Выполнить», в котором введите cmd и нажмите «ОК».
Читайте также: Открываем «Командную строку» с полномочиями администратора в Windows 10
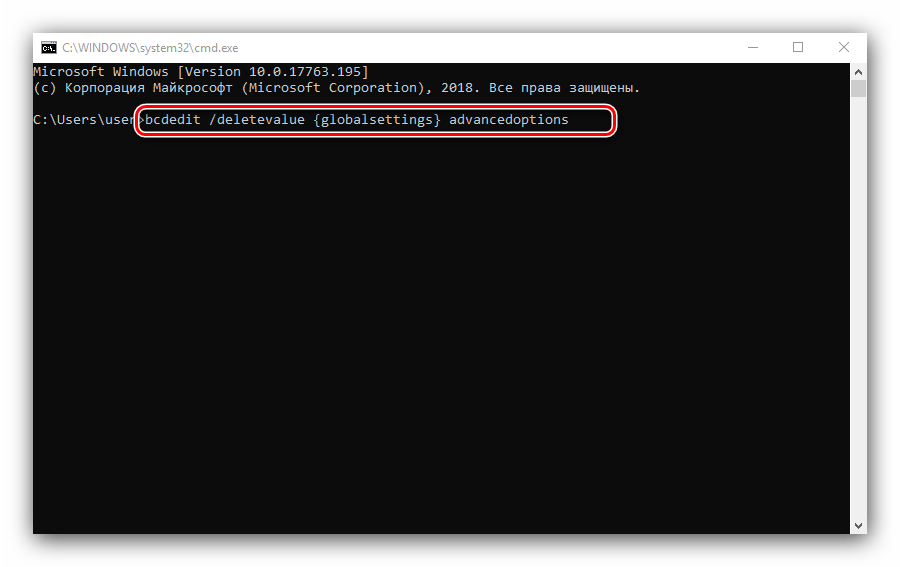
- Введите следующую команду:
bcdedit /deletevalue {globalsettings} advancedoptionsОператоры этой команды отключают запуск «Безопасного режима» по умолчанию. Нажмите Enter для подтверждения.
- Закрывайте окно ввода команд и перезагружайте компьютер.
Теперь система должна загрузиться как обычно. Этот способ можно также задействовать с помощью загрузочного диска Windows 10, если невозможно получить доступ к основной системе: в окне установки на моменте выбора языка нажмите Shift+F10 для вызова «Командной строки» и введите туда вышеуказанные операторы.
Способ 2: «Конфигурация системы»
Альтернативный вариант – отключение «Safe Mode» через компонент «Конфигурация системы», который пригодится в случае, если этот режим был запущен в уже работающей системе. Порядок действий следующий:
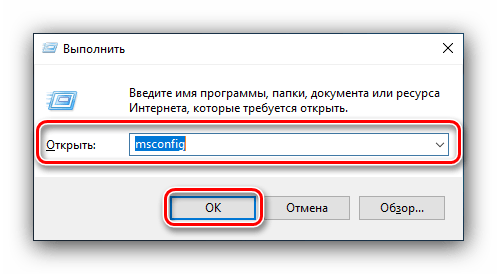
- Снова вызовите окошко «Выполнить» комбинацией Win+R, но на этот раз введите сочетание msconfig. Не забудьте нажать «ОК».
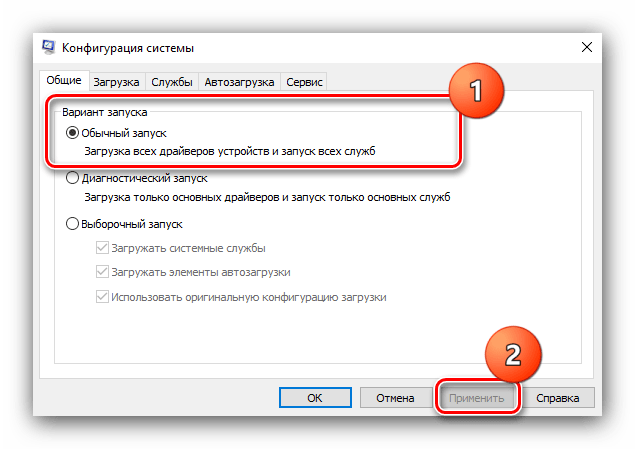
- Первым делом в разделе «Общие» установите переключатель в положение «Обычный запуск». Для сохранения выбора нажмите на кнопку «Применить».
- Далее перейдите на вкладку «Загрузка» и обратитесь к блоку настроек под названием «Параметры загрузки». Если установлена галочка напротив пункта «Безопасный режим», снимите её. Также лучше снять отметку с опции «Сделать эти параметры загрузки постоянными»: в противном случае для включения «Безопасного режима» вам снова потребуется открыть текущий компонент. Снова нажмите «Применить», затем «ОК» и перезагружайтесь.
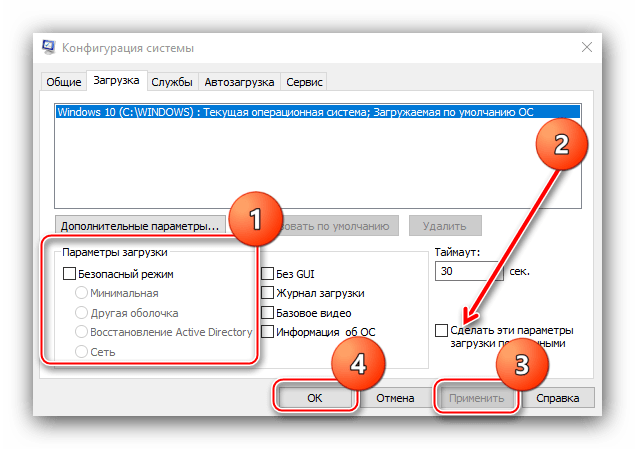
Данный вариант способен раз и навсегда решить проблему с постоянно включённым «Safe Mode».
Заключение
Мы ознакомились с двумя методами выхода из «Безопасного режима» в Windows 10. Как видите, покинуть его очень просто.
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
Exiting Safe Mode with Command Prompt can be a useful troubleshooting technique for Windows 7 users who encounter system issues. Safe Mode is a diagnostic mode in Windows that helps isolate problems with drivers, files, and other features. It loads only essential services and drivers, allowing users to identify and fix issues without any interference from non-essential software or drivers. However, sometimes exiting Safe Mode can be challenging, especially for those who are not familiar with advanced Windows commands. In this blog post, we will explore several methods to exit Safe Mode with Command Prompt in Windows 7 and provide step-by-step instructions to make the process easier for users.
Video Tutorial:
What’s Needed
To exit Safe Mode with Command Prompt in Windows 7, you will need a computer running Windows 7 and administrative access to the system. Additionally, basic knowledge of Windows commands and the ability to follow instructions is recommended.
What Requires Your Focus?
When attempting to exit Safe Mode with Command Prompt, there are a few crucial points to keep in mind. Firstly, it’s important to follow the steps carefully and pay attention to any errors or warnings that may appear during the process. Secondly, ensure that you have administrative access to the system to perform the necessary commands. Lastly, if you are uncomfortable using Command Prompt or are unsure about any step, it’s always a good idea to seek assistance from someone with more experience.
Method 1. Exiting Safe Mode via MSCONFIG Command
Using MSCONFIG command is a straightforward method to exit Safe Mode in Windows 7. Follow the steps below:
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type “msconfig” in the text field and press Enter to open the System Configuration window.
3. In the System Configuration window, navigate to the “Boot” tab.
4. Under the “Boot Options” section, uncheck the box next to “Safe boot.”
5. Click on the “Apply” button and then click “OK” to save the changes.
6. A prompt will appear asking to restart the computer. Select “Restart” to exit Safe Mode and boot into normal mode.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| 1. Easy and straightforward process to exit Safe Mode. | 1. Requires access to the Windows desktop to use MSCONFIG command. |
| 2. Can be done without any advanced knowledge of Command Prompt. | 2. If the system is not responding, this method may not be applicable. |
| 3. Changes made using MSCONFIG can be easily reverted if necessary. | 3. May not resolve underlying issues causing the system to boot into Safe Mode. |
Method 2. Exiting Safe Mode via Command Prompt
Using the Command Prompt directly to exit Safe Mode is another method that can be effective. Follow the steps below:
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type “cmd” in the text field and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to open an elevated Command Prompt.
3. In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter: “bcdedit /deletevalue {current} safeboot”
4. Once the command is executed successfully, restart the computer to exit Safe Mode and boot into normal mode.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| 1. Provides a direct and efficient method to exit Safe Mode. | 1. Requires administrative access to access Command Prompt. |
| 2. Can be done even if the system is not responding properly. | 2. Users need to be cautious when using Command Prompt as incorrect commands may cause system issues. |
| 3. Allows users to exit Safe Mode without the need to navigate through various windows or menus. | 3. May not address the underlying problem that caused the system to enter Safe Mode. |
Method 3. Exiting Safe Mode via System Configuration
The System Configuration utility provides an alternative method to exit Safe Mode in Windows 7. Follow the steps below:
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type “msconfig” in the text field and press Enter to open the System Configuration window.
3. In the System Configuration window, navigate to the “Boot” tab.
4. Under the “Boot Options” section, select the “Safe boot” checkbox to remove the checkmark.
5. Choose the desired boot option from the “Safe boot” options: “Minimal,” “Alternate shell,” or “Network.”
6. Click on the “Apply” button and then click “OK” to save the changes.
7. A prompt will appear asking to restart the computer. Select “Restart” to exit Safe Mode and boot into normal mode.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| 1. Uses a familiar and accessible utility for managing system boot configuration. | 1. Requires administrative access to access System Configuration. |
| 2. Allows users to customize boot options based on specific needs (e.g., network support). | 2. Not suitable for users who prefer using Command Prompt. |
| 3. Offers an intuitive interface for managing system startup settings. | 3. May not resolve underlying issues causing the system to boot into Safe Mode. |
Method 4. Exiting Safe Mode via Advanced Boot Options
The Advanced Boot Options menu can be accessed during system startup to exit Safe Mode in Windows 7. Follow the steps below:
1. Restart your computer.
2. During startup, repeatedly press the F8 key until the Advanced Boot Options menu appears.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the “Safe Mode with Command Prompt” option and press Enter.
4. Once the Command Prompt window appears, type “bcdedit /deletevalue {current} safeboot” and press Enter.
5. Restart the computer to exit Safe Mode and boot into normal mode.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| 1. Can be accessed even if the system is not responding or experiencing issues. | 1. Requires familiarity with the Advanced Boot Options menu and ability to navigate it. |
| 2. Provides an alternative method for exiting Safe Mode. | 2. Inexperienced users may find the Advanced Boot Options menu intimidating. |
| 3. Allows users to choose different boot options based on specific needs (e.g., safe mode, safe mode with networking). | 3. May not address the underlying problem that caused the system to enter Safe Mode. |
Why Can’t I Exit Safe Mode?
Encountering difficulties when exiting Safe Mode in Windows 7 is not uncommon. Here are a few common reasons why users might struggle to exit Safe Mode and the corresponding fixes:
1. Problematic Drivers: Certain drivers or software configurations can cause Windows to continuously boot into Safe Mode. To fix this issue, update or reinstall the problematic drivers or software.
2. Stuck Restart Loop: Occasionally, Windows may enter a restart loop and keep booting back into Safe Mode. To resolve this problem, try performing a startup repair or perform a system restore to a previous working state.
3. Corrupted System Files: If system files are corrupted, it can prevent Windows from exiting Safe Mode. Running the System File Checker utility (SFC) can help identify and repair any corrupted files.
Implications and Recommendations:
1. Regularly update drivers and software to ensure compatibility and minimize the chances of encountering issues that may result in Safe Mode boot.
2. Create system restore points before making any major changes to your system to provide a fallback option in case things go wrong.
3. Familiarize yourself with basic Command Prompt commands to troubleshoot and perform advanced system operations more efficiently.
5 FAQs about Exiting Safe Mode with Command Prompt Windows 7
Q1: Can I exit Safe Mode from the Windows Start menu?
A1: No, Safe Mode cannot be exited directly from the Windows Start menu. It requires using specific commands or accessing advanced boot options during system startup.
Q2: Will exiting Safe Mode erase my data or files?
A2: No, exiting Safe Mode will not erase your data or files. Safe Mode only loads essential services and drivers, but your files remain intact.
Q3: Can I permanently disable Safe Mode in Windows 7?
A3: No, you cannot permanently disable Safe Mode in Windows 7 as it serves as a diagnostic mode to troubleshoot system issues. However, you can prevent the system from automatically booting into Safe Mode by resolving the underlying problems causing it to enter Safe Mode repeatedly.
Q4: How can I identify the cause of Windows continuously booting into Safe Mode?
A4: To identify the cause, you can review recent changes to your system, such as driver updates or software installations. Additionally, using system event logs or running diagnostics can help pinpoint the underlying issue.
Q5: Is it safe to use Command Prompt to exit Safe Mode?
A5: Yes, using Command Prompt to exit Safe Mode is safe as long as you follow the correct commands and instructions. However, it is essential to exercise caution while using Command Prompt to avoid executing incorrect commands that may cause system issues.
Final Words
Exiting Safe Mode with Command Prompt in Windows 7 can be a useful solution for users experiencing system issues. By following the methods and steps provided in this blog post, users can easily exit Safe Mode and resume normal operation of their systems. Remember to pay attention to the instructions, ensure administrative access, and be cautious when using Command Prompt. Troubleshooting system issues can be challenging, but with the right knowledge and guidance, you can overcome them and enjoy a seamless Windows experience.{“@context”:”https://schema.org”,”@type”:”FAQPage”,”mainEntity”:null}
After you are done with the purpose of booting the computer in Safe Mode, you should be able to Exit Safe Mode by simply restarting your device.
However, if your computer is always switching back to Safe Mode after restart, you will be required to exit Safe Mode by going to the System Configuration screen on your computer.
In addition to this, you can exit Safe Mode on a Windows computer by using Command prompt and also from the Login screen by using “Shift Key Restart” method as provided below in this guide.
If you have booted your computer in Safe Mode or if it is repeatedly booting up in Safe Safe Mode, you can easily exit Safe Mode by using any of the following methods.
Advertisement
1. Exit Safe Mode By Using Restart
In most cases, you should be able to disable Safe Mode on your computer by restarting the device.
1. Click on Start button > Power Icon and select the Restart option.
2. When your computer restarts, it should no longer be in Safe Mode. If it does not, use the next method.
2. Exit Safe Mode By Using System Configuration
In certain cases, you may find the computer switching back to Safe Mode, every time it is restarted. The reason for this behavior is due to your device being set to always Boot in Safe Mode.
1. Right click on the Start button and click on the Run.
2. On the Run Command window, type msconfig and click on OK.
3. On the next screen, switch to Boot tab and uncheck Safe Boot option and click on Apply and click on OK.
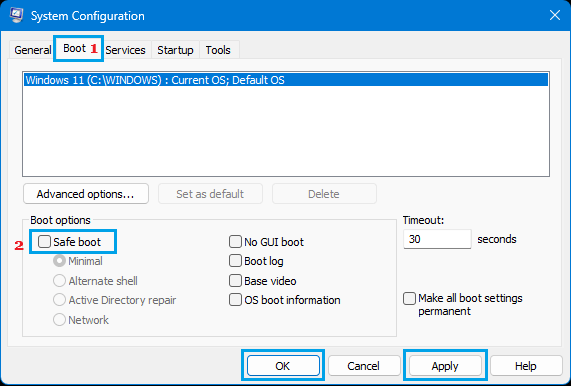
4. On the confirmation pop-up, click on Restart to start the process of starting the computer in Safe Mode.
Advertisement
You should now find your computer coming out of Safe Mode and starting normally.
3. Disable Safe Mode Using Command Prompt
As mentioned above, you can Exit Safe Mode by using Command Prompt.
1. Type Command Prompt in the search bar, right-click on Command Prompt and select Run As Administrator option.
2. On the Command prompt window, type bcdedit /deletevalue {current} safeboot and press the Enter key on the Keyboard of your computer.
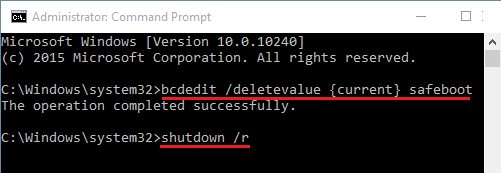
3. Restart the computer and it should now come out of Safe Mode.
Note: You can also type shutdown /r in the command prompt screen and press the Enter Key to restart the computer.
4. Exit Safe Mode from Login Screen
Another way to Exit Safe Mode is by restarting the computer, while holding down the Shift Key.
1. Click on Power Icon located at bottom-right corner of the screen > Press and Hold the Shift Key on the keyboard of your computer and select the Restart option.
2. After the computer restarts, navigate to Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > Startup Settings and click on the Restart button.
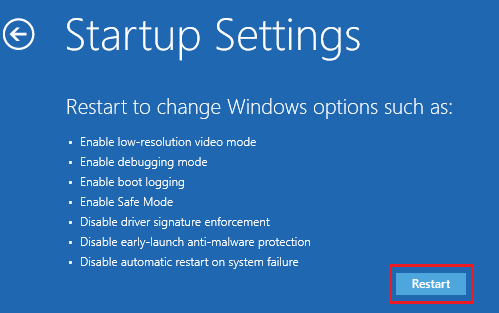
3. On the next screen, press the Enter Key on the Keyboard of your computer.
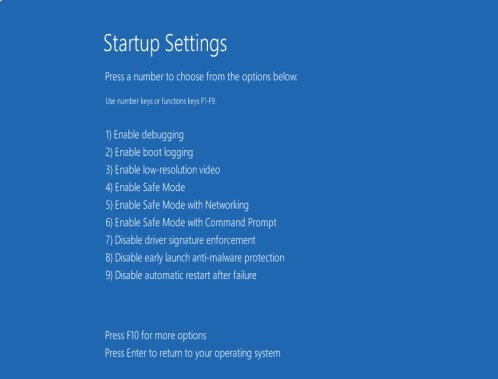
4. This time, you should find your computer coming out of Safe Mode and Restarting normally.