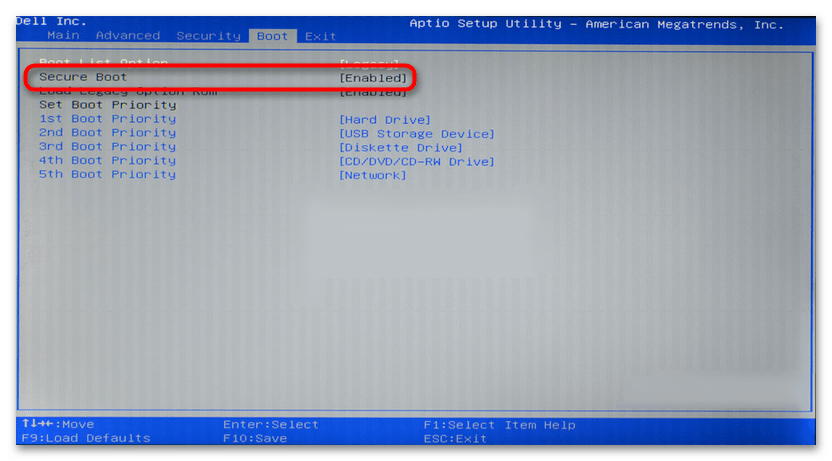
Secure Boot is an important security feature designed to prevent malicious software from loading when your PC starts up (boots). Most modern PCs are capable of Secure Boot, but in some instances, there may be settings that cause the PC to appear to not be capable of Secure Boot. These settings can be changed in the PC firmware. Firmware, often called BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), is the software that starts up before Windows when you first turn on your PC.
Note: This article is intended for users who are not able to upgrade to Windows 11 because their PC is not currently Secure Boot capable. If you are unfamiliar with this level of technical detail, we recommend that you consult your PC manufacturer’s support information for more instructions specific to your device.
How to enable Secure Boot on my PC
To access these settings, you can consult your PC manufacturer’s documentation or follow these instructions:
-
Go to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery and select Restart now under Advanced startup.
-
On the next screen, select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > UEFI Firmware Settings > Restart to make changes.
To change these settings, you will need to switch the PC boot mode from one enabled as “Legacy” BIOS (also known as “CSM” Mode) to UEFI/BIOS (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface). In some cases, there are options to enable both UEFI and Legacy/CSM. If so, you will need to choose for UEFI to be the first or only option. If you are unsure how to make any necessary changes to enable the UEFI/BIOS, we recommend that you check your PC manufacturer’s support information on their website. Here are a few links to information from some PC manufacturers to help get you started:
Dell | Lenovo | HP
While the requirement to upgrade a Windows 10 device to Windows 11 is only that the PC be Secure Boot capable by having UEFI/BIOS enabled, you may also consider enabling or turning Secure Boot on for better security.
Related articles
Windows 11 System Requirements
Ways to install Windows 11
Windows help & learning
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Если установщик Windows 11, а возможно и какая-то программа или игра (такое тоже возможно) сообщает о том, что его не устраивает состояние безопасной загрузки и её необходимо включить — сделать это сравнительно легко, но возможны нюансы.
В этой инструкции подробно о способах включить безопасную загрузку на вашем компьютере или ноутбуке, при условии, что это возможно. Обратите внимание, если задача — установка Windows 11, существуют возможности запуска установки и без включенной безопасной загрузки (Secure Boot), например — создание загрузочной флешки в Rufus с отключением проверки совместимости при чистой установке, или обновление с обходом требований для установки.
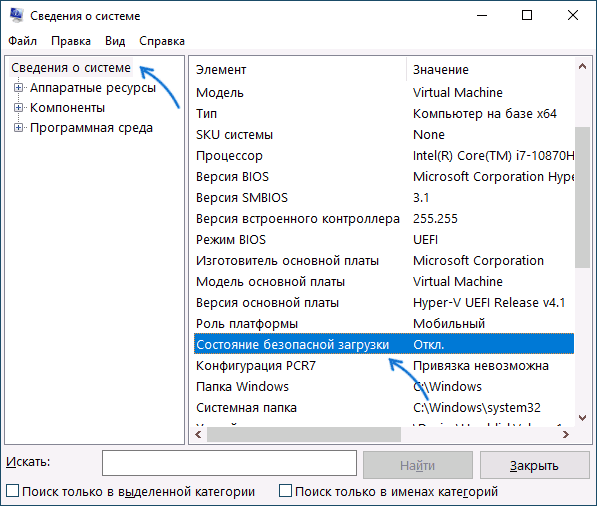
Проверка состояния безопасной загрузки, особенности работы после включения
Прежде чем начать, о том, где вы можете проверить текущее состояние безопасной загрузки в Windows 11 или Windows 10:
- Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по кнопке «Пуск», выберите пункт «Выполнить», введите msinfo32 и нажмите Enter. В разделе «Сведения о системе» вы увидите пункт «Состояние безопасной загрузки» с её текущим статусом.
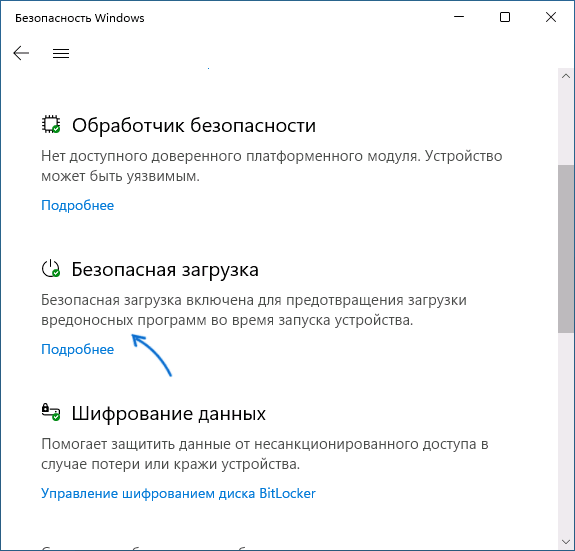
- Можно зайти в окно «Безопасность Windows», например, с помощью значка в области уведомлений и открыть раздел «Безопасность устройства». Если вы наблюдаете там пункт «Безопасная загрузка» с зеленой отметкой, она включена. Иначе — нет.
Ещё один важный момент: загрузка с включенной безопасной загрузкой возможна только для систем, установленных в UEFI-режиме на GPT диск.
Если, к примеру, у вас Windows 10 и установлена в Legacy-режиме на диск MBR, после включения Secure Boot она перестанет загружаться. Возможные варианты действий: конвертировать диск в GPT с помощью mbr2gpt.exe и включить UEFI-загрузку, либо использовать вариант с чистой установкой с флешки и обходом требований Windows 11, как было указано в начале статьи.
Включение безопасной загрузки Secure Boot в БИОС/UEFI
Само включение безопасной загрузки или Secure Boot выполняется не в Windows 11/10, а в БИОС/UEFI вашего компьютера или ноутбука. Для того, чтобы включить её, необходимо:
- Зайти в БИОС при включении/перезагрузке устройства. На ноутбуках для этого обычно используется клавиша F2 (или сочетание Fn+F2), которую необходимо ритмично нажимать сразу после появления заставки производителя (но бывают и другие варианты клавиши), на ПК как правило используется клавиша Delete. Более подробно: Как зайти в БИОС/UEFI на компьютере или ноутбуке.
- Найти раздел БИОС, на котором доступна опция включения (установка в Enabled) функции Secure Boot. Учитывайте, что на очень старых компьютерах такой настройки может и не быть. Как правило, она располагается где-то в разделе Security, Boot, System Configuration, иногда — Advanced Settings. Несколько примеров расположения будут приведены далее.
- Сменить состояние Secure Boot на Enabled (если ранее выполнялась очистка ключей Secure Boot, восстановить их), сохранить настройки БИОС/UEFI (обычно выполняется клавишей F10 или на вкладке Exit) и перезагрузиться обратно в систему.
Примеры расположения опции для включения безопасной загрузки (Secure Boot)
Ниже — несколько примеров, где можно найти опцию включения безопасной загрузки на разных материнских платах и ноутбуках. У вас может отличаться, но логика везде одна и та же.
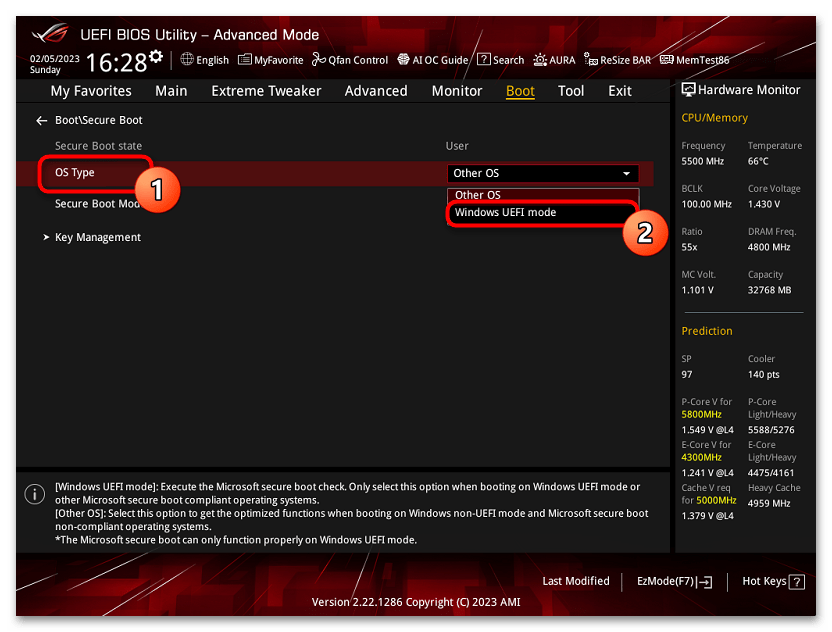
Ещё раз отмечу: включить безопасную загрузку можно только в случае, если у вас включен режим загрузки UEFI, а режим Legacy/CSM отключен, иначе опция будет недоступна. В некоторых вариантах БИОС переключение в режим загрузки UEFI выполняется путем выбора типа операционной системы (OS Type) между Windows 11/10/8 и «Other OS» (нужно выбрать Windows).
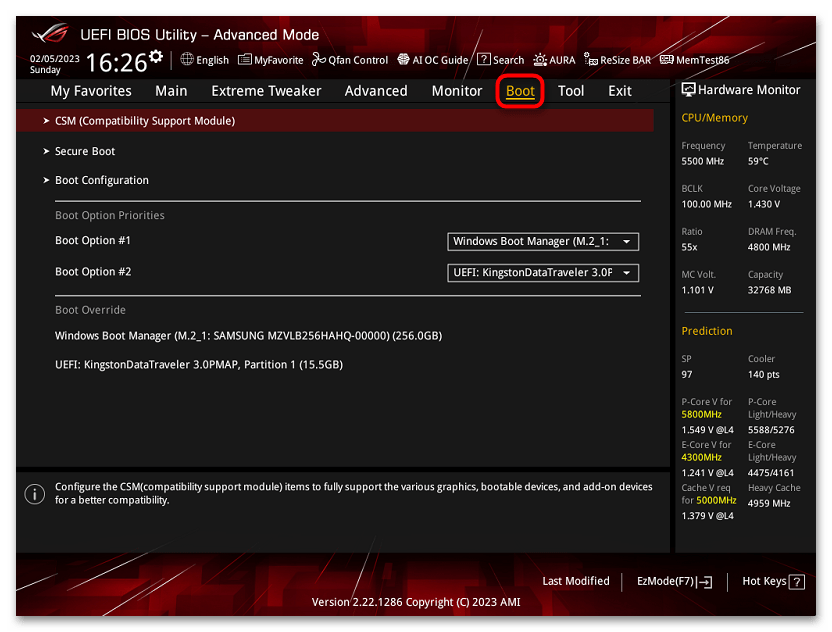
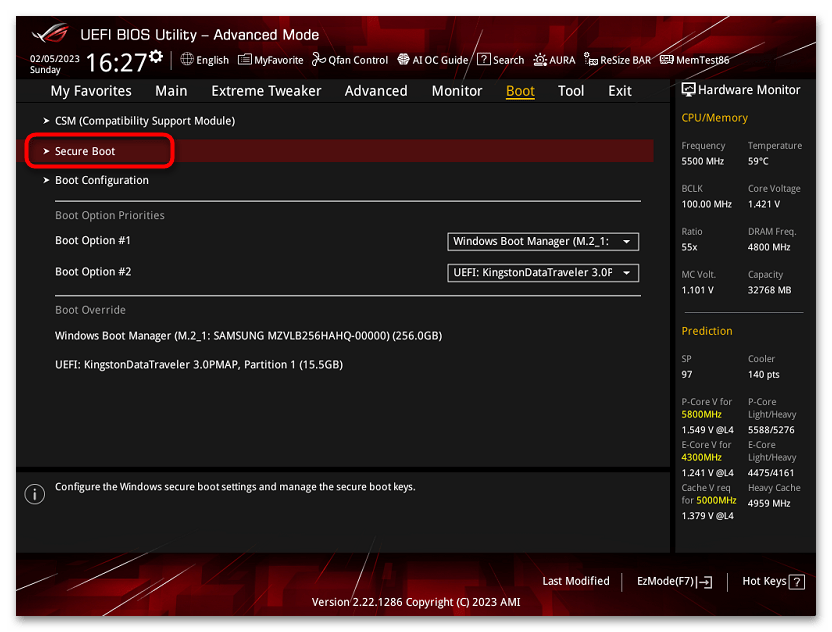
ASUS
На разных версиях материнских плат и ноутбуков включение Secure Boot реализовано слегка по-разному. Обычно пункт «Secure Boot» можно найти на вкладке «Boot» или «Security». При этом для OS Type может потребоваться выставить Windows UEFI Mode (параметр может и отсутствовать).
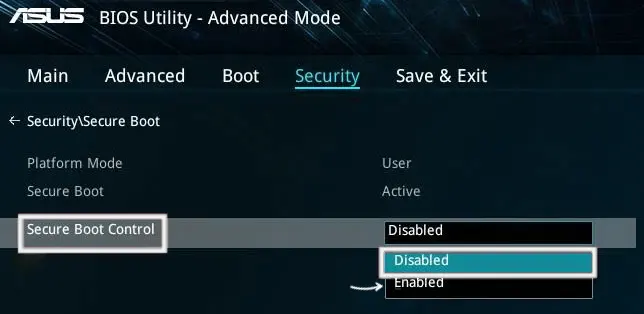
Также, для доступности пункта настройки безопасной загрузки в БИОС может потребоваться перейти в Advanced Mode, обычно — по клавише F7.
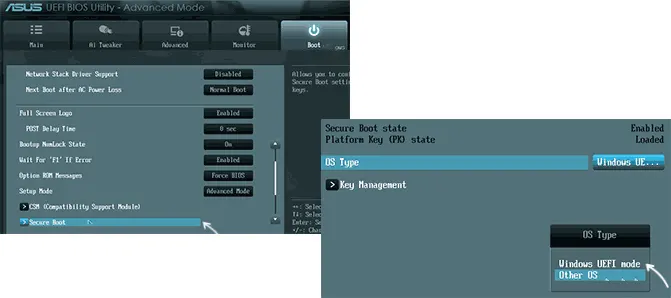
В некоторых случаях может потребоваться восстановление ключей безопасной загрузки, обычно выполняется следующим образом: в Advanced Mode в BIOS на вкладке Boot или в Secure Boot — Key Management выбираем Load Default PK и подтверждаем загрузку ключей по умолчанию.
AsRock
Настройка для включения безопасной загрузки на материнских платах AsRock обычно находится в разделе «Security».

Зайдя в раздел необходимо будет установить значение Secure Boot в Enabled, а если выбор недоступен, включить стандартный Secure Boot Mode и установить ключи по умолчанию (Install default Secure Boot keys).

Acer
Как правило, опция включения Secure Boot на ноутбуках Acer находится либо в разделе Advanced — System Configuration, либо в Boot или Authentication.
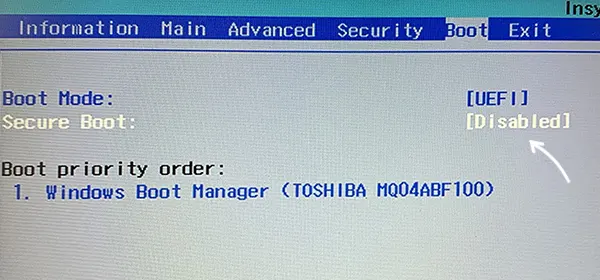
Также помните, о том, что должен быть включен режим загрузки UEFI, а не Legacy/CSM для возможности изменения состояния безопасной загрузки на Enabled.
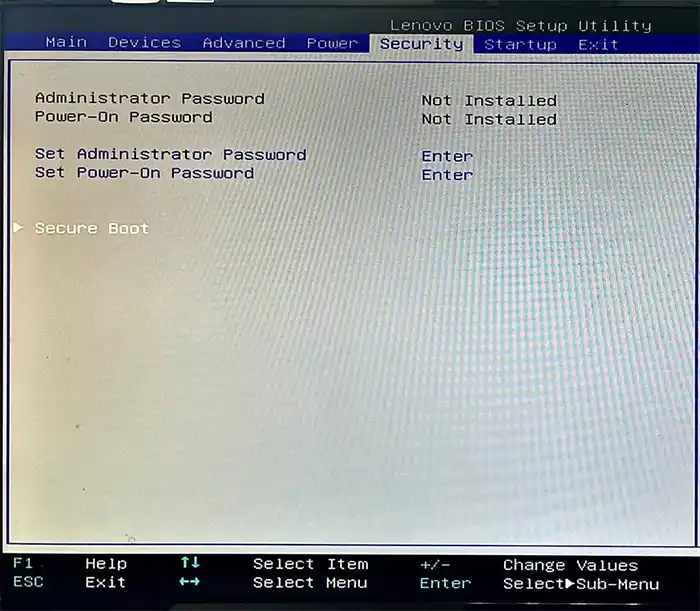
Lenovo
ПК и ноутбуки Lenovo имеют разные варианты интерфейса БИОС, но обычно нужная опция находится на вкладке Security, как на фото ниже:

Ещё один пример с ноутбука Lenovo:
Gigabyte
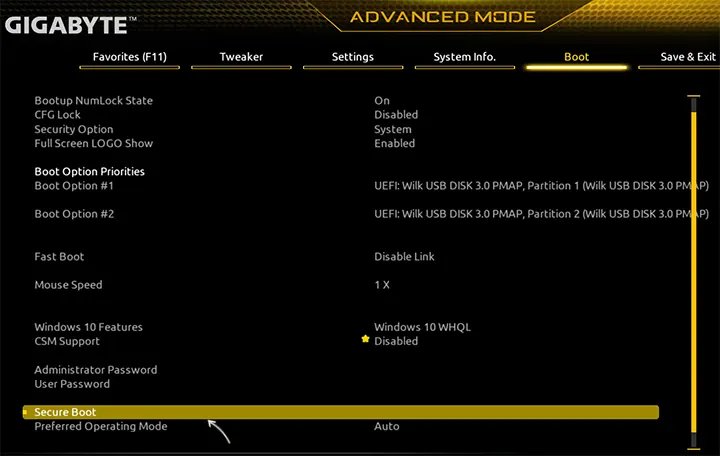
Варианты отключения Secure Boot на материнских платах и ноутбуках Gigabyte могут отличаться, обычно порядок действий следующий:
- На вкладке Boot или BIOS отключить CSM Support, и выбрать тип операционной системы или установить пункт Windows 8/10 Features в, соответственно, Windows 8/10, а не Other OS.
- После этого должен появиться пункт Secure Boot, в который необходимо зайти, чтобы включить безопасную загрузку.
Несколько дополнительных мест расположения опции включения Secure Boot (устанавливаем в Enabled) на старых Dell, Gigabyte, HP:

Также, если в вашем интерфейсе БИОС предусмотрен поиск, можно использовать его:

В случае, если вы не нашли способа включить безопасную загрузку на вашей материнской плате, либо её не удается перевести в Enabled, укажите её марку и модель в комментариях, я постараюсь подсказать, где именно требуется включать этот параметр. Кстати, часто достаточно просто сбросить настройки БИОС (Load Defaults на вкладке Exit), чтобы включить безопасную загрузку, так как на большинстве современных материнских плат она по умолчанию включена.
Having Secure Boot enabled on Windows 11 is a critical step for users wanting to run Microsoft’s latest operating system. Secure Boot is a security mechanism that ensures your computer boots in a protected environment, safeguarding against malicious software. It’s part of the hardware and software requirements introduced with Windows 11, along with the need for a compatible CPU, TPM 2.0, and sufficient RAM and storage.
Although most modern systems have Secure Boot enabled by default, some configurations may show it as inactive due to certain BIOS or firmware settings. While enabling Secure Boot strengthens the overall security posture of a machine, there are cases—such as working with specific Linux instances or older systems—where disabling it might be preferable.
Turning on Secure Boot for Windows 11
Secure Boot works by verifying the digital signatures of drivers, the operating system, and firmware each time your PC starts. Before going through the process of enabling Secure Boot, it’s a good idea to first check whether it’s already active on your system, as the setup can be somewhat involved.
How to check if Secure Boot is already enabled
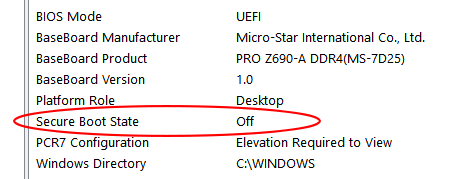
(Image: © Future)
To verify whether Secure Boot is active on your system:
- Click Start
- Type System Information into the search bar and press Enter
- Scroll through the system data list to locate the Secure Boot State
- If the label shows On, then Secure Boot is already enabled. If it shows Off, you’ll need to enable it manually
How to enable Secure Boot in Windows 11
If Secure Boot is not enabled, you can turn it on through the BIOS settings:
- Restart your PC and wait for the BIOS splash screen to appear
- As the splash screen appears, press the key to access the BIOS menu. This is typically Delete, F12, or another key specific to your manufacturer
- Navigate through the BIOS menu to find the Security or Boot section. This may vary depending on your motherboard
- Look for the Secure Boot option. It will typically appear as a toggle or dropdown menu
- Set Secure Boot to Enabled
- Exit the BIOS, save the changes, and restart your PC
Once enabled, your system will now use Secure Boot to help prevent unauthorized software from running during startup.
What is Secure Boot and why is it so important?
Secure Boot acts as a vital system safeguard by verifying the digital signatures of firmware, bootloaders, and drivers before allowing them to run. When your PC boots, Secure Boot verifies that the UEFI firmware is signed and trusted, checking every critical piece of software before it loads.
For instance, if a rootkit—a type of malware that runs deep within the kernel—is present, Secure Boot helps prevent it from being loaded. By ensuring only trusted software is allowed to run, Secure Boot protects against threats like bootkits, which can hijack the bootloader and gain full control over the operating system.
Introduced with Windows 8, Secure Boot is now a fundamental requirement for Windows 11. All certified x86-based Windows devices must have Secure Boot enabled by default, trust Microsoft’s certificates, and allow users to customize Secure Boot to trust non-Microsoft software or disable it entirely if needed.
Sign up today and you will receive a free copy of our Future Focus 2025 report — the leading guidance on AI, cybersecurity and other IT challenges as per 700+ senior executives
Why would you disable Secure Boot?
Although Secure Boot enhances security, there are certain scenarios where disabling it might be necessary. For example, if you’re running specific Linux distributions or legacy versions of Windows, Secure Boot may prevent those operating systems from loading. In such cases, disabling Secure Boot temporarily allows for the installation and use of non-signed software.
However, it’s important to remember that turning off Secure Boot reduces your system’s protection against malware and unauthorized software, so it’s recommended only for specific use cases where compatibility is a concern.
Troubleshooting common secure boot issues
In some cases, you may encounter issues when trying to enable Secure Boot. Here are a few common problems and their solutions:
- Secure Boot is grayed out in BIOS: This can happen if your system is set to Legacy Boot Mode instead of UEFI. To fix this, switch to UEFI Mode in the BIOS settings
- System won’t boot after enabling Secure Boot: Double-check that your operating system and bootloader are UEFI-compliant. If they aren’t, your system may fail to boot, and you’ll need to revert the Secure Boot setting in the BIOS
- Secure Boot is enabled, but Windows still reports it as off: Ensure your BIOS firmware is up to date, as outdated firmware can cause Windows to misreport Secure Boot status
Further reading on Windows 11 and security
To learn more about Windows 11 security features, check out our other guides. We cover everything from how to boot into Windows 11 Safe Mode to managing encryption tools like BitLocker, ensuring your PC meets the latest security standards. For those exploring Linux or other OS setups, see our articles on comparing Windows 11 with Linux, UEFI settings, and switching to Linux from Windows.
Включение безопасной загрузки («Secure Boot») для Windows 11
Вне зависимости от производителя материнской платы, параметр «Безопасная загрузка» («Secure Boot») для Windows включается через BIOS. Алгоритм действий в целом будет одинаковый, различается лишь внешний вид БИОС и расположение нужной опции внутри него.
- Первым делом вам следует зайти в BIOS. Для этого при включении компьютера сразу же несколько раз быстро нажимайте на кнопку, предназначенную для входа в данное меню. Узнать, какая кнопка отведена под вход в БИОС для вашего устройства, вы можете сразу же при отображении логотипа материнской платы/производителя ноутбука.
Или же воспользовавшись поиском в интернете, куда нужно ввести модель материнки либо ноутбука.
Читайте также: Как попасть в BIOS на компьютере / на ноутбуке
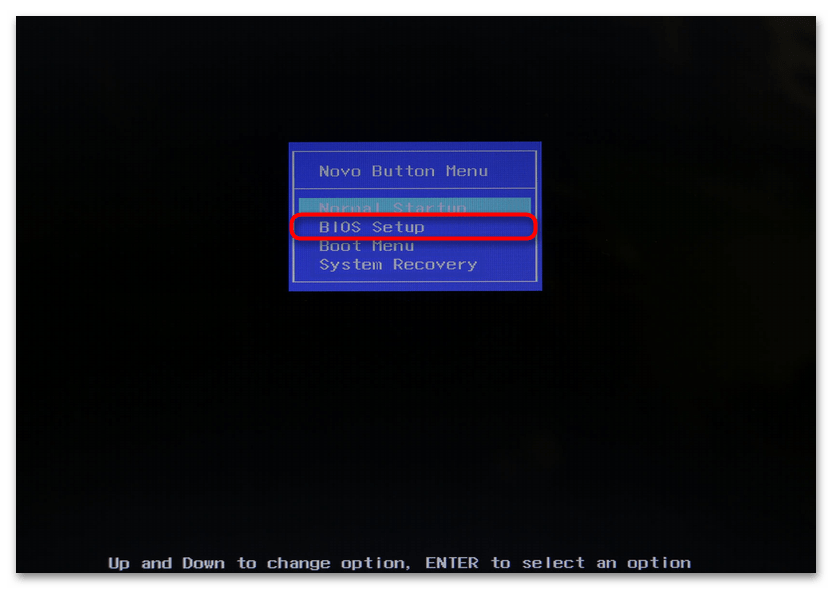
На некоторых ноутбуках, например на Lenovo, для входа в БИОС можно у выключенного устройства отыскать с левого или правого торца с падающей стрелкой, нажать на утопленную кнопку чем-то острым типа скрепки, в результате чего на экране появится окно «Novo Button Menu», из которого следует выбрать «BIOS Setup».
- Теперь все, что вам остается, это отыскать опцию среди доступных. Управление в BIOS происходит с клавиатуры, в UEFI — клавиатурой или мышью.
Обладателям UEFI BIOS (версии с графическим интерфейсом) предварительно следует перейти в расширенное меню, нажав на кнопку «Advanced Mode».
- В большинстве случаев нужная опция расположена на вкладке «Boot» / «Загрузка». Иногда — на вкладке «System Configuration» или «Security».
- Называется она «Secure Boot» / «Безопасная загрузка». Выделите ее и нажмите по ней ЛКМ либо клавишу Enter.
- В новых БИОС, как правило, «Secure Boot» — это подраздел, поэтому в результате вы попадете внутрь него. Тут в строке «OS Type» выберите режим «Windows UEFI mode» для включения опции. Вариант «Other OS» отключает опцию.
В старых БИОС при нажатии по «Secure Boot» появится небольшое окно с выбором значения. Для включения выставьте «Enabled». Где-то вместо этого значения понадобится выбрать «UEFI», что тоже будет соответствовать включению опции.
Если на указанной вкладке вы не найдете нужный параметр, воспользуйтесь одним из следующих вариантов:
- «More Settings» > «Security» (Lenovo)
- «Advanced» > «Secure Boot Configuration» > «Configure Legacy Support and Secure Boot» > «Legacy Support Disable and Secure Boot Enable» (HP с фирменным UEFI)
- «Secure Boot» (это отдельная вкладка) > «Secure Boot Enable» (некоторые Dell)
- Сохраните изменения, нажав клавишу F10 на клавиатуре, и в окне с вопросов подтвердив действие клавишей Y.
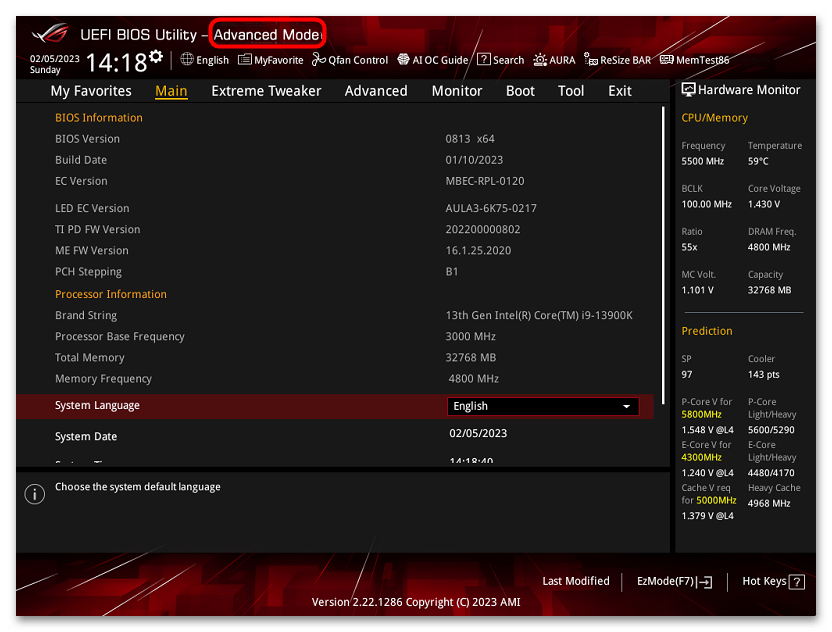
Если опция «Secure Boot» недоступна для изменения, попробуйте сбросить настройки BIOS к заводским. Однако учтите, что после этого в отдельных случаях может понадобиться его донастройка (если перед установкой текущей Windows производились какие-то специфические изменения в конфиг).
После изменения статуса этой опции некоторые компьютеры могут перестать загружаться. Тогда следует вернуть статус «Secure Boot» к изначальному.
Те пользователи, кто не может включить «Secure Boot», но пытается сделать это для установки Windows 11, могут воспользоваться другой нашей инструкцией для отключения ограничений при попытке инсталляции этого выпуска.
Подробнее: Как установить Windows 11 без TPM 2.0 и Secure Boot
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
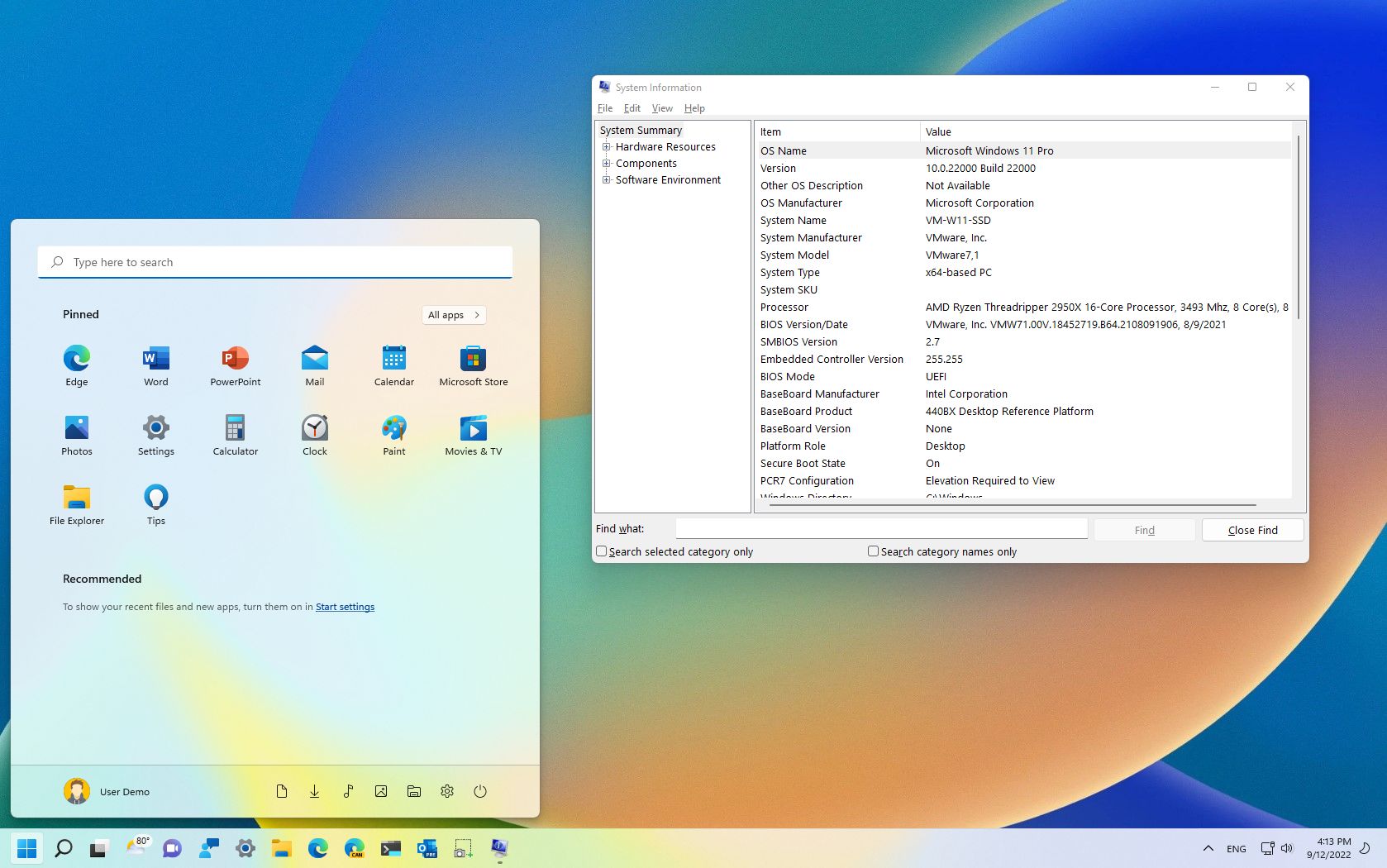
(Image credit: Future)
As part of the system requirements, alongside a Trusted Platform Module (TPM), a device must have «Secure Boot» enabled to install Windows 11.
Secure Boot is a security feature available on most modern hardware with UEFI firmware to provide a secure environment to start Windows and prevent malware from hijacking the system during the boot process. In other words, Secure Boot allows the computer to boot only with trusted software from the Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM).
The benefit of this feature is a more secure experience, which is one of the reasons Microsoft is making it a requirement to install Windows 11. The only problem is that enabling this feature will prevent running other operating systems like Linux.
This guide will walk you through the steps to check and enable Secure Boot to upgrade from Windows 10 to 11.
How to check Secure Boot state on Windows 10
To check the Secure Boot state on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for System Information and click the top result to open the app.
- Click on System Summary on the left pane.
- Check the «Secure Boot State» information:
- On — the feature is enabled.
- Off — the feature is disabled or not supported.
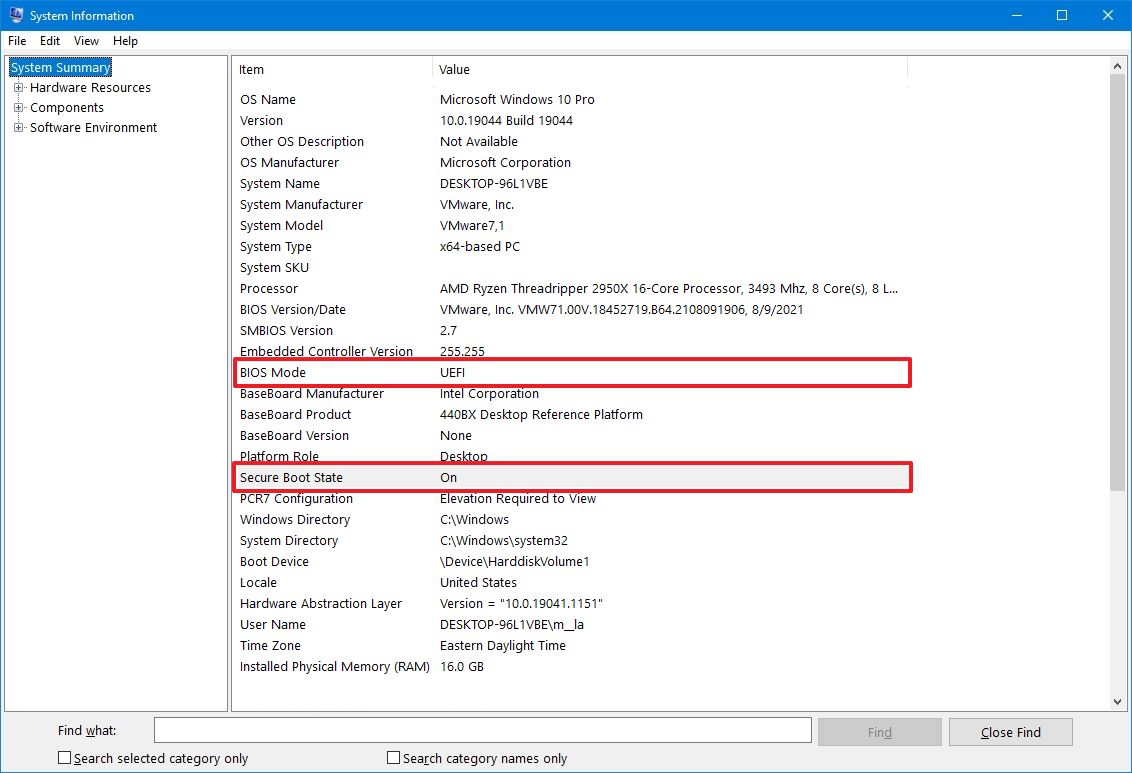
- Check the «BIOS Mode» information:
- UEFI — indicates you can enable Secure Boot.
- Legacy (BIOS) — indicates you can enable the feature, but it will require additional steps.
Once you complete the steps, if the «Secure Boot State» is Off and BIOS Mode is UEFI, you can use the steps outlined below to enable a more secure experience and comply with the Windows 11 requirements.
If the «Secure Boot State» is set to Off and «BIOS Mode» to Legacy, then you want to create a backup of your computer, use the following instructions to convert the installation from MBR to GPT, and then continue with the steps to enable Secure Boot.
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
How to convert MBR to GTP drive on Windows 10
If you plan to upgrade Windows 10 to Windows 11 on older hardware that supports UEFI, you must first convert the drive from the legacy MBR partition style to GPT in order to switch the system firmware type properly. Otherwise, the computer will no longer start correctly.
On Windows 10, you can use the MBR2GPT command-line tool to change the partition type from MBR to GTP without reinstalling Windows.
Check MBR or GPT partition style
To check the current drive partition style, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Disk Management and click the top result to open the experience.
- Right-click the Windows 10 disk (not the volume) and select the Properties option.
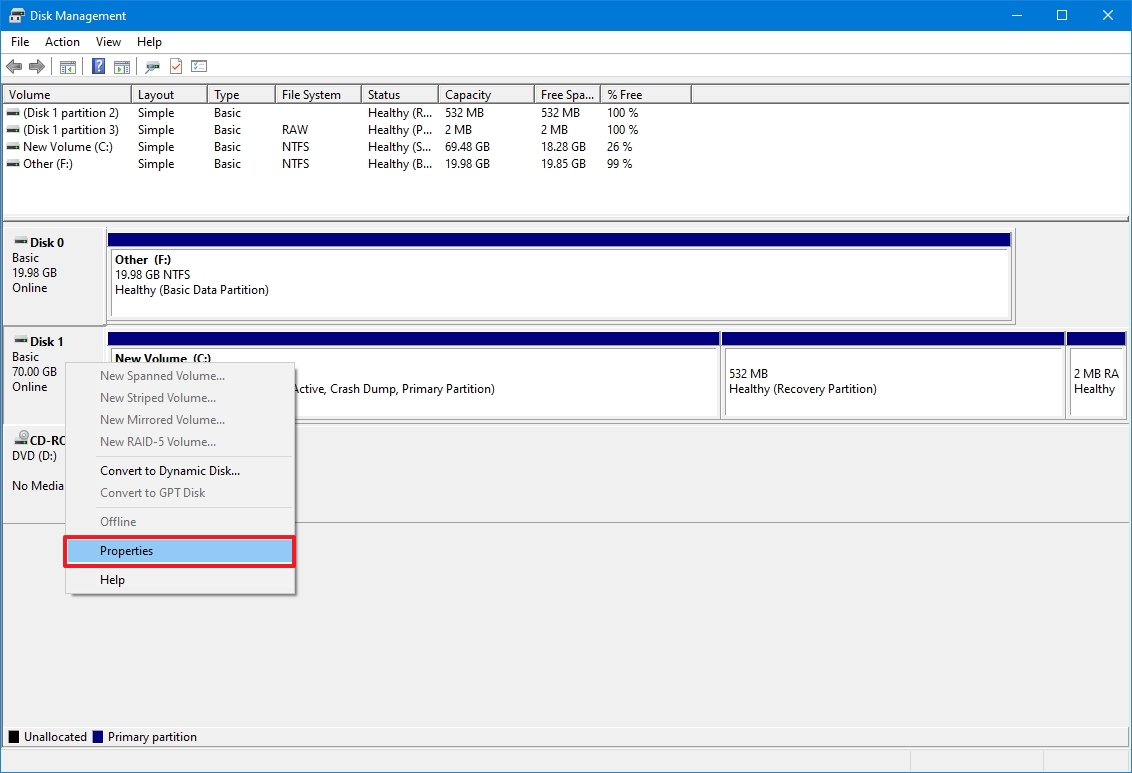
- Click on the Volumes tab.
- Under the «Partition style» field, if the field reads GUID Partition Table (GPT), the drive does not need conversion, but if you see the Master Boot Record (MBR) label, you can use the conversion tool to switch.
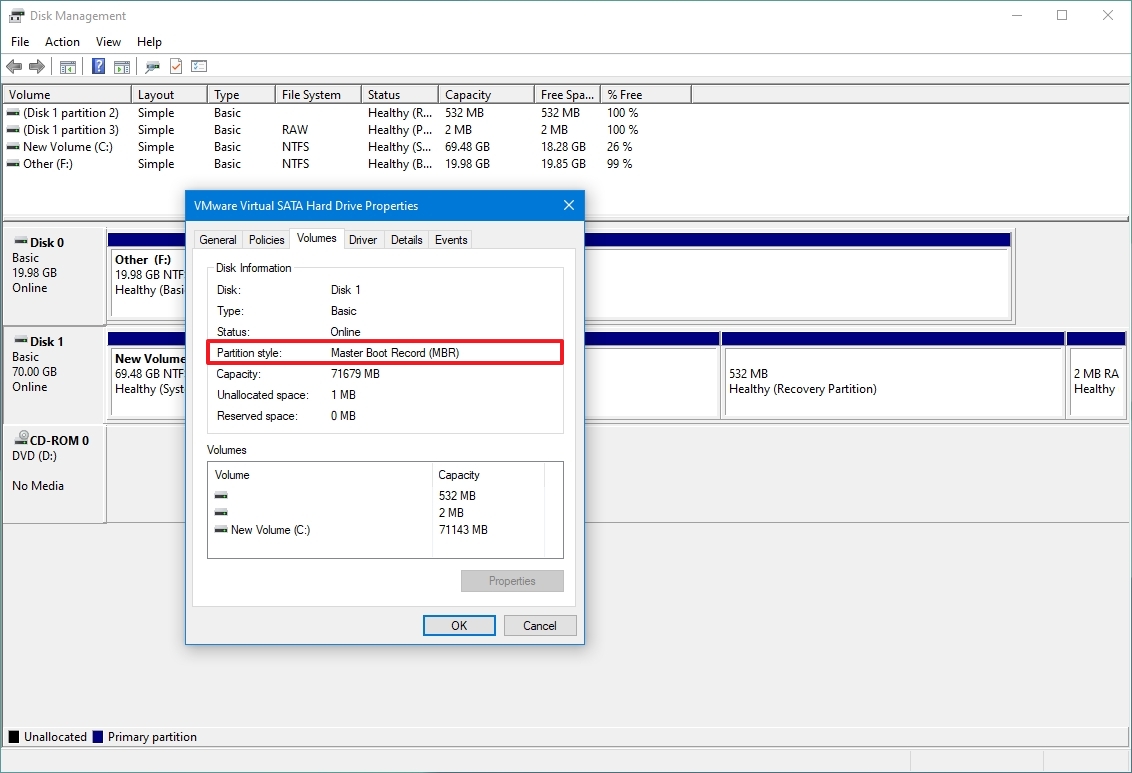
- Click the Cancel button.
Once you complete the steps, if the drive needs conversion, use the instructions outlined below.
Convert MBR to GPT partition style
To convert MBR to GPT partition style on Windows 10, use these steps:
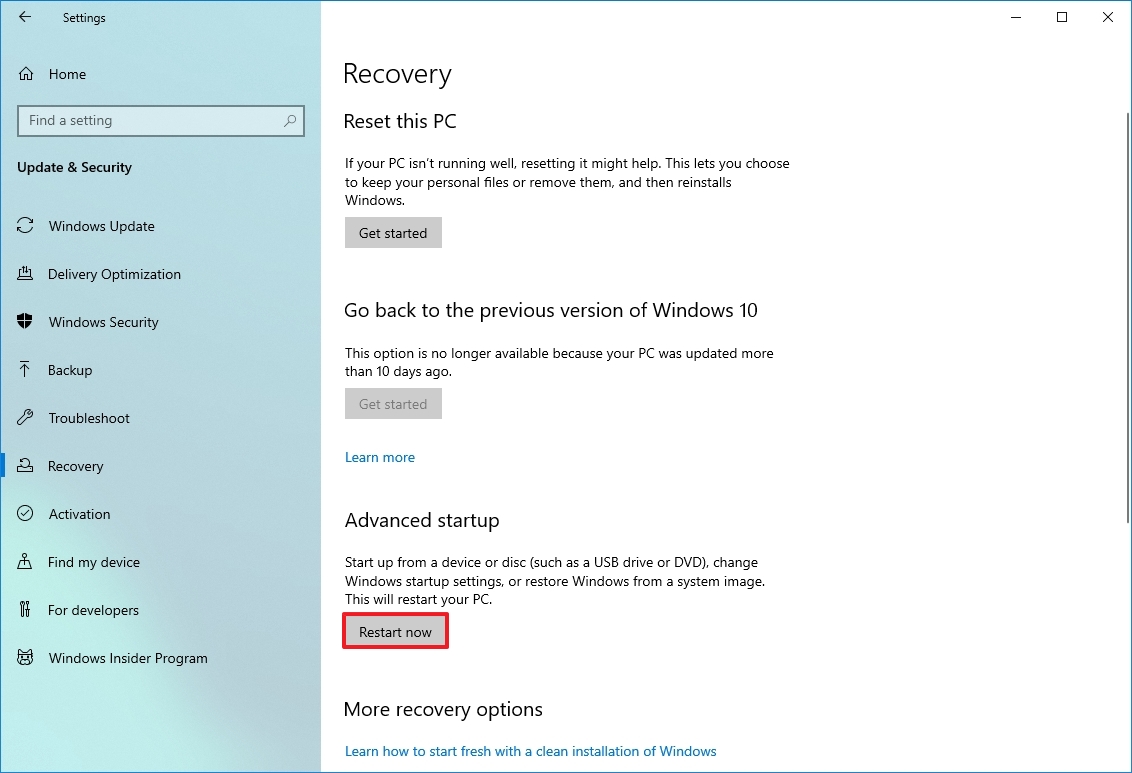
- Open Settings.
- Click on Update & Security.
- Click on Recovery.
- Under the «Advanced startup» section, click the Restart now button.
- Click the Troubleshoot option.
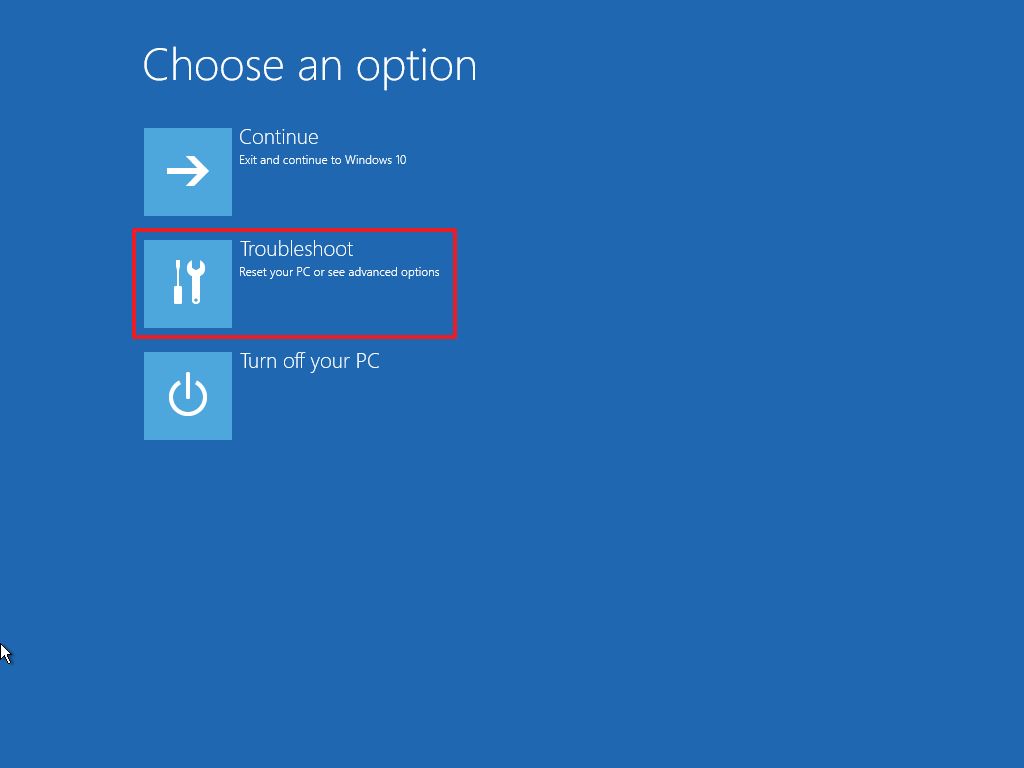
- Click on Advanced options.
- Click the Command Prompt option.
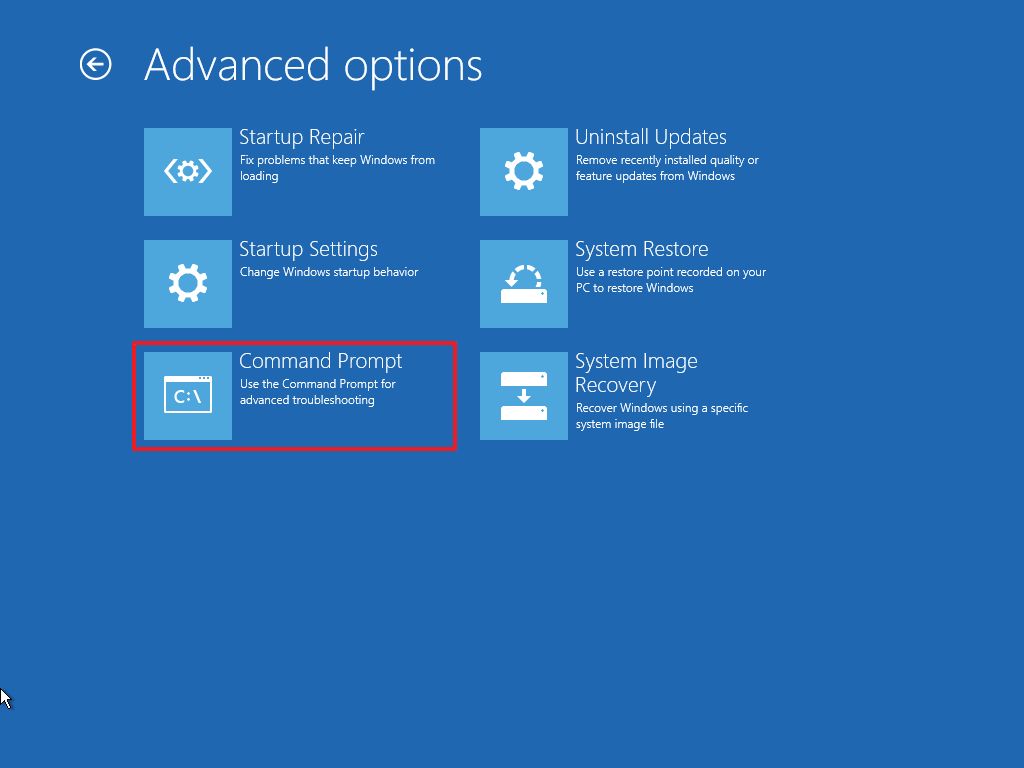
- Select your administrator account and sign in (if applicable).
- Type the following command to validate that the drive meets the requirements and press Enter: mbr2gpt /validate
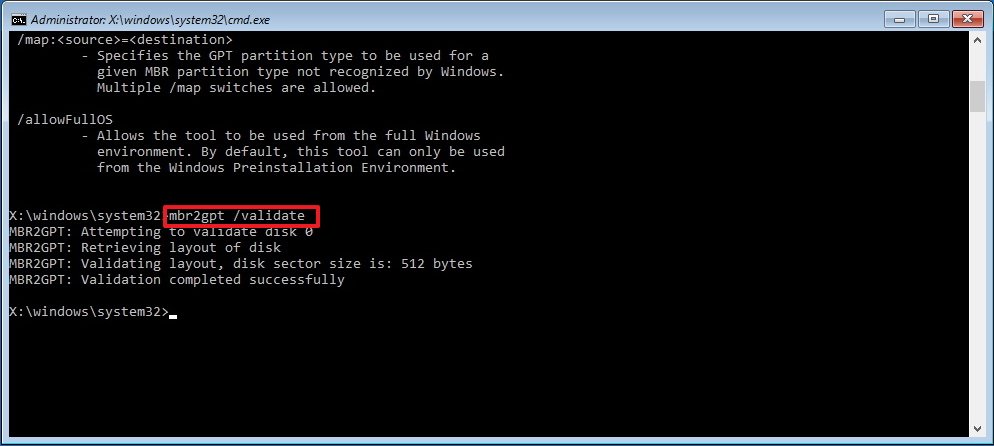
- Quick tip: The mbr2gpt.exe is located in the «System32» folder inside the «Windows» folder. If you want to see all the available options, use the mbr2gpt /? command.
- Type the following command to convert the drive from MBR to GPT and press Enter: mbr2gpt /convert
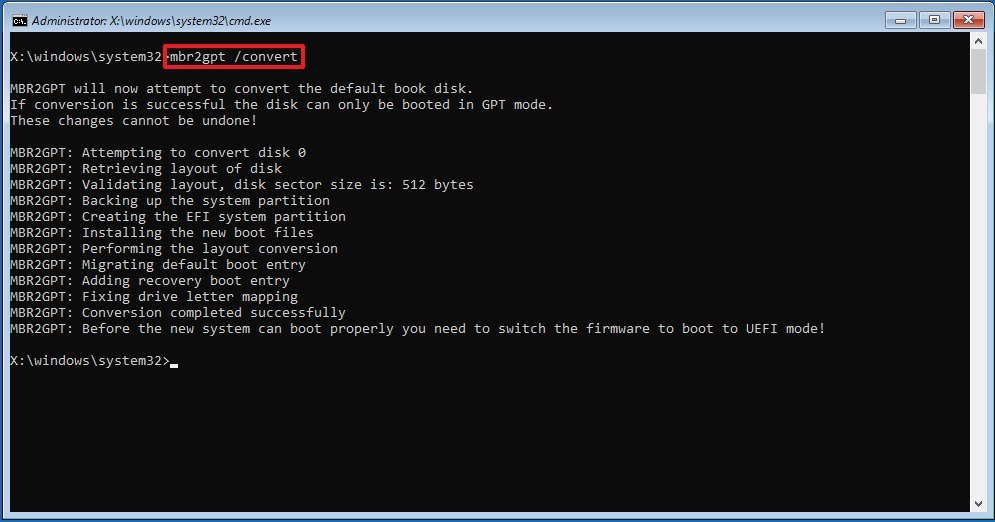
- Click the Close button.
- Click the Turn off your PC option.
After you complete the steps, the command-line tool will change the partition type to GPT to comply with the system requirements to install Windows 11.
If the conversion is successful, the return code should be «0,» but if the process fails, you may see one of the 11 error codes.
How to enable Secure Boot on Windows 10
Changing the incorrect firmware settings can prevent a computer from starting correctly. You should access the motherboard settings only when you have a good reason. It’s assumed you know what you’re doing.
Also, these steps assume the device is already running with UEFI firmware. If the computer is still in the legacy BIOS, you may first need to convert the drive using MBR to GPT (see above steps). The conversion is unnecessary if you plan to perform a clean installation, but you must go through the conversion before an in-place upgrade. Converting the drive partition should not affect the installation, but creating a backup is always recommended before proceeding.
To enable the Secure Boot on a computer with UEFI firmware, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Update & Security.
- Click on Recovery.
- Under the «Advanced startup» section, click the Restart now button.

- Click on Troubleshoot.

- Click on Advanced options.
- Click the UEFI Firmware Settings option.
- Quick tip: If you have a legacy BIOS, the option will not be available.
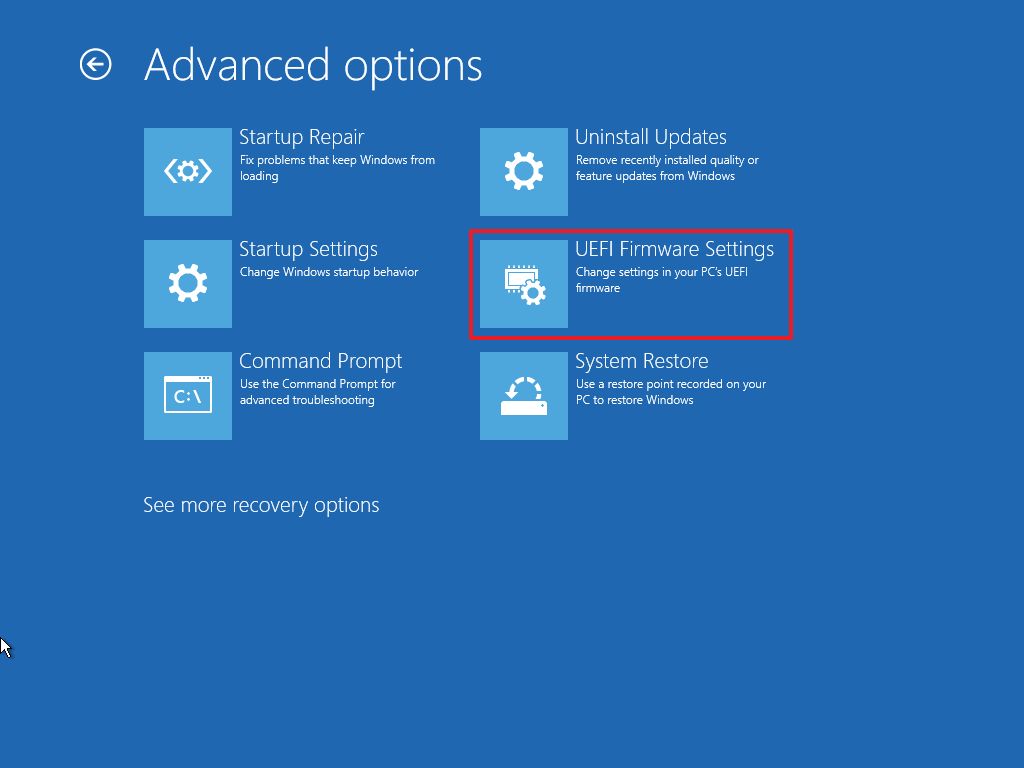
- Click the Restart button.

- Open the boot or security settings page.
- Quick note: The UEFI settings are different per manufacturer and even per computer model. You may need to check the manufacturer support website for more specific details to find the settings.
- Select the Secure Boot option and press Enter.
- Select the Enabled option and press Enter.
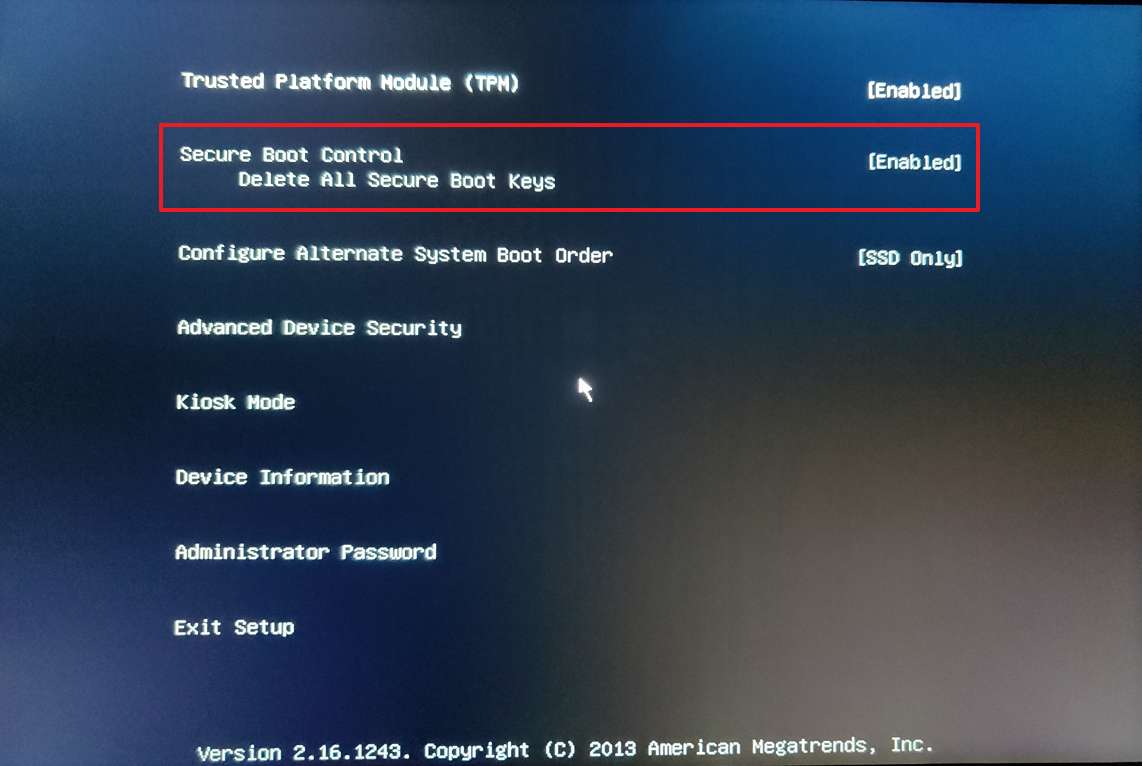
- Exit the UEFI settings.
- Confirm the changes to restart the device.
After you complete the steps, the computer will start using the Secure Boot feature to comply with the Windows 11 requirements.
How to enable Secure Boot during startup
You can also enable Secure Boot on the computer during startup instead of using the Settings app.
To access the device firmware during the boot process on Windows, use these steps:
- Press the Power button.
- See the screen splash to identify the key you must press to enter the firmware (if applicable).
- Press the required key repeatedly until you enter the setup mode. Usually, you need to press the Esc, Delete, or one of the Function keys (F1, F2, F10, etc.).
- Open the boot or security settings page (as needed).
- Select the Secure Boot option and press Enter.
- Select the Enabled option and press Enter.

- Exit the UEFI settings.
- Confirm the changes to restart the device.
Once you complete the steps, Secure Boot will enable you to support the installation of Windows 11.
If you cannot access the keyboard’s firmware, you may need to check the manufacturer documentation to find the keyboard key to use during boot. Here are some brands and their respective keys to access the motherboard’s firmware:
- Dell: F2 or F12.
- HP: Esc or F10.
- Acer: F2 or Delete.
- ASUS: F2 or Delete.
- Lenovo: F1 or F2.
- MSI: Delete.
- Toshiba: F2.
- Samsung: F2.
- Surface: Press and hold the volume up button.
More resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 and Windows 11, visit the following resources:
- Windows 11 on Windows Central — All you need to know
- Windows 10 on Windows Central — All you need to know
Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 15 years of experience writing comprehensive guides. He also has an IT background and has achieved different professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA. He has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.